Soil Type Affects Organic Acid Production and Phosphorus Solubilization Efficiency Mediated by Several Native Fungal Strains from Mexico
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Area
2.2. Isolation of Fungal Strains
2.3. Analysis of Rock Phosphate Solubilization
2.4. Molecular and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.5. RP Solubilization in Liquid Medium
2.6. Organic Acid Analysis Using HPLC
2.7. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Selection of Fungal Strains
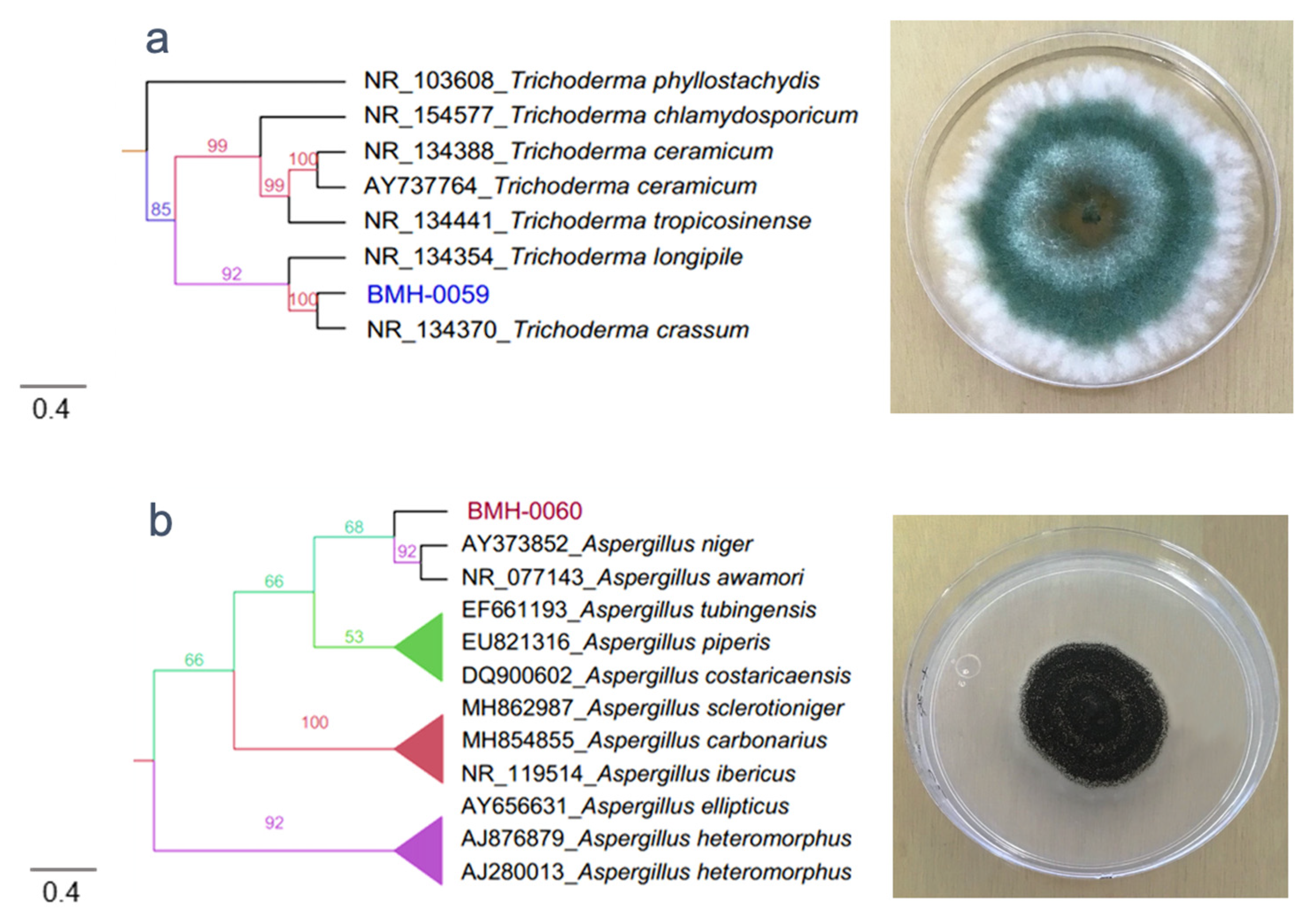
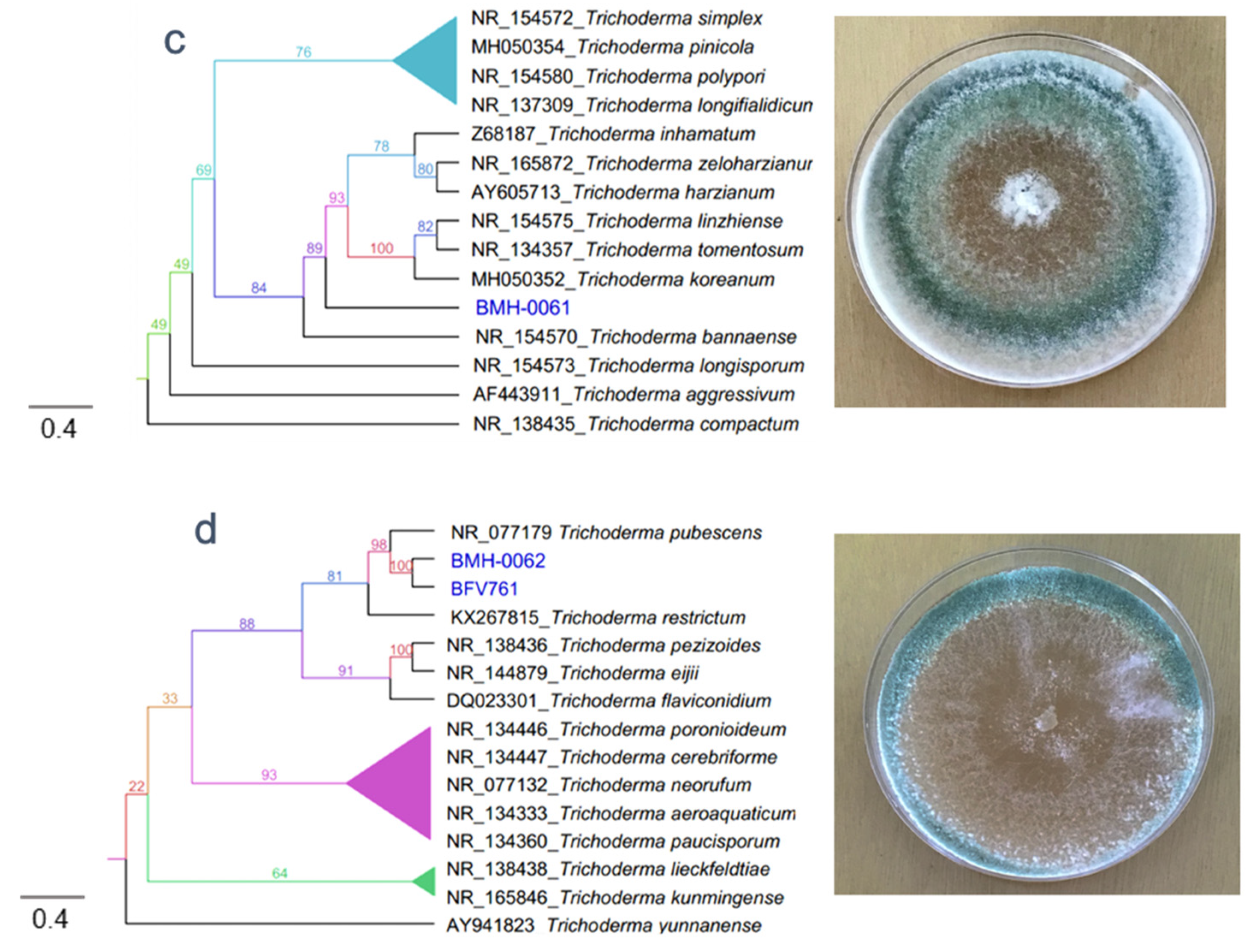
3.2. Molecular and Phylogenetic Analysis
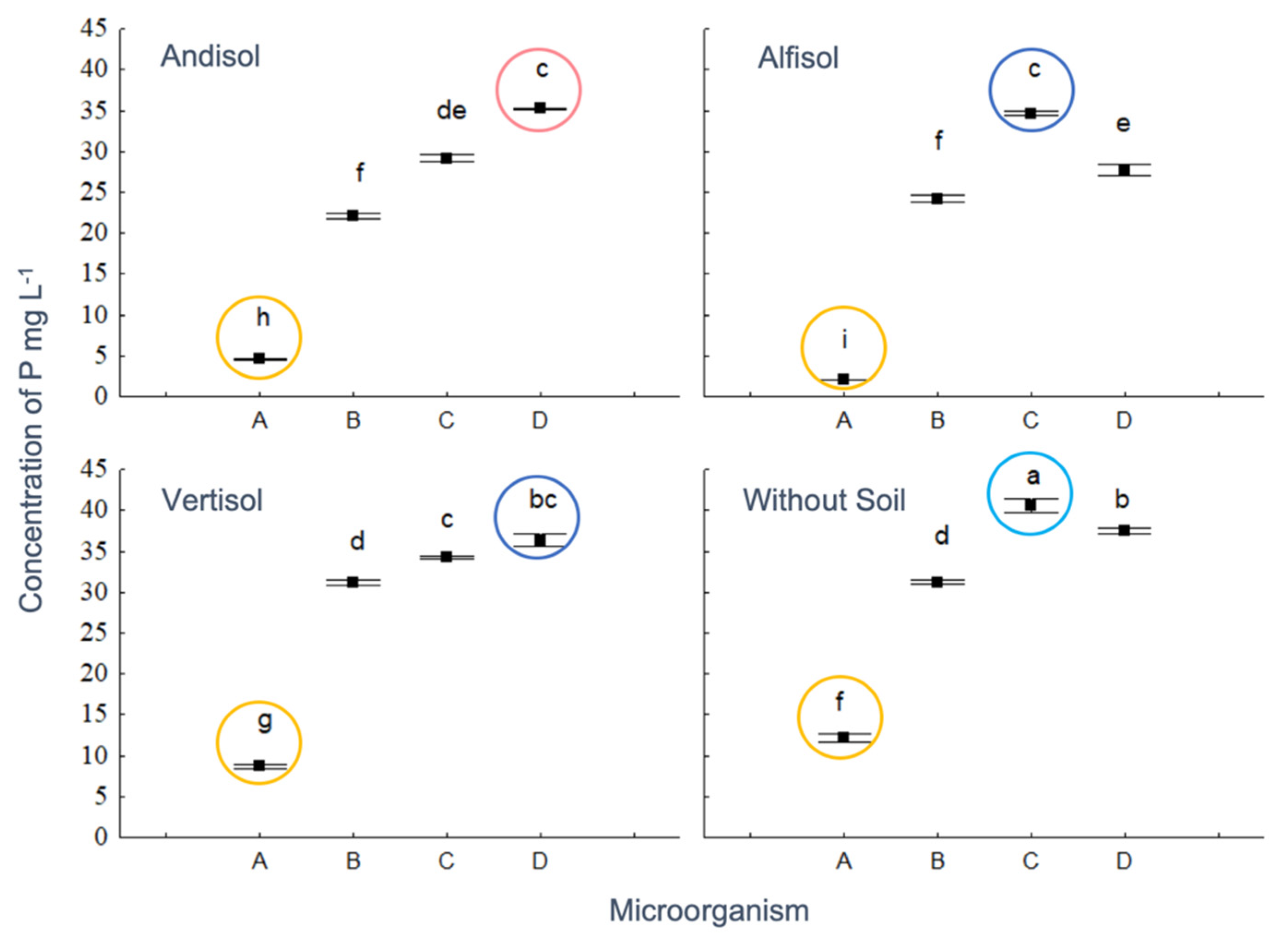
3.3. RP Solubilization in the Liquid Medium
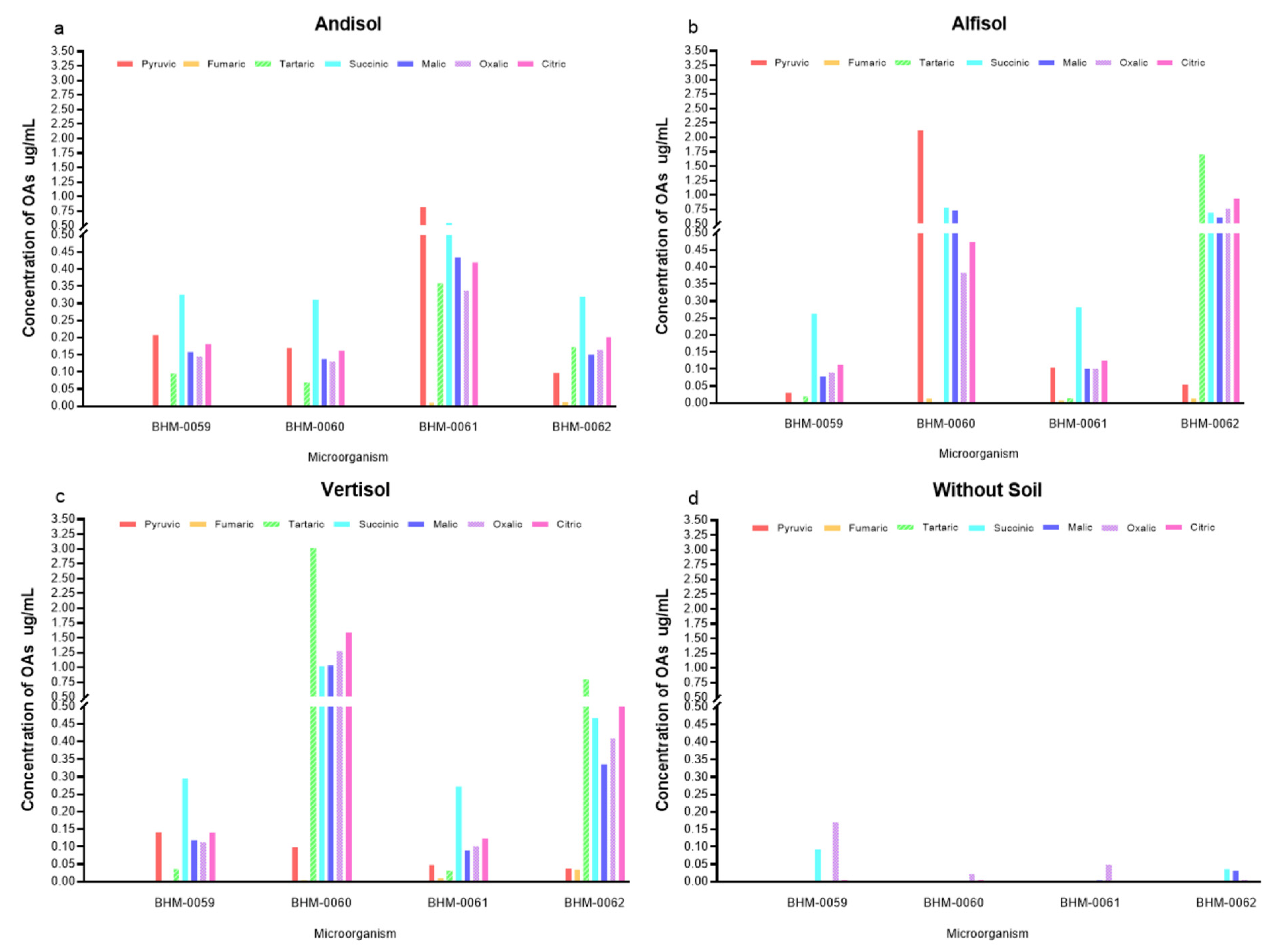
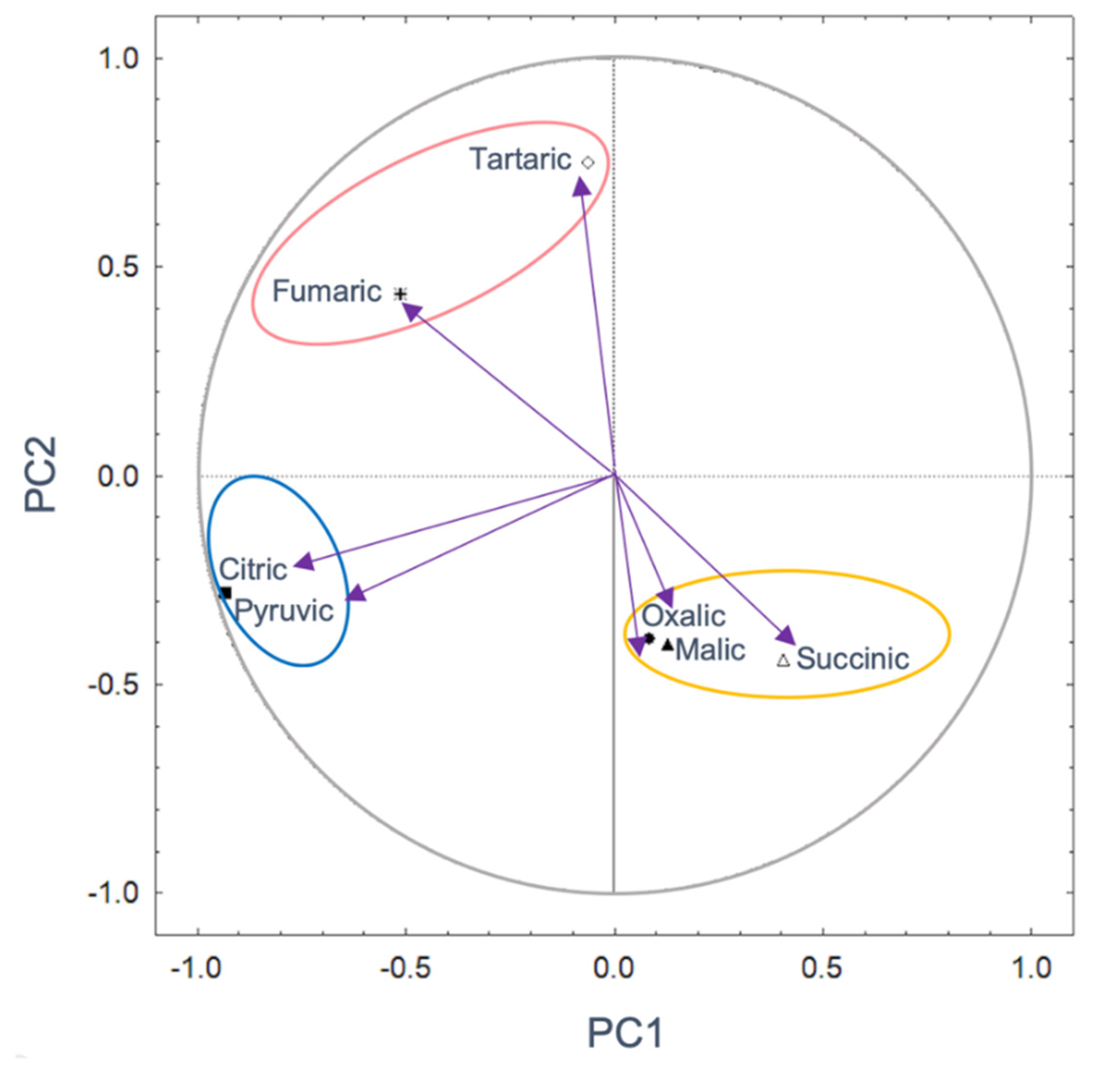
3.4. Profile of OAs and Its Correlation with the P Concentration in Different Soil Types
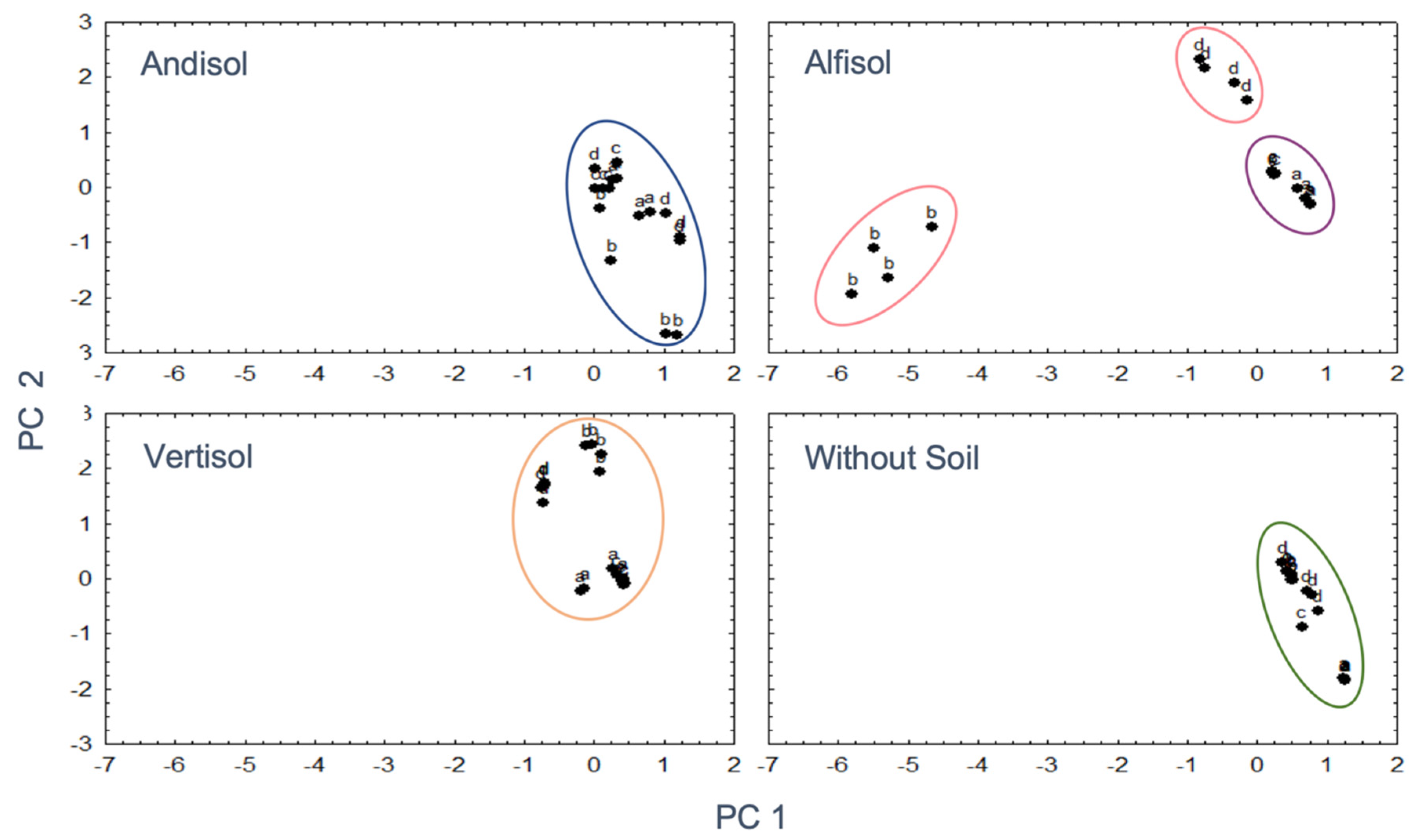
3.5. Interaction between Soil Mineralogy and OA
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Garland, G.; Bünemann, E.; Oberson, A.; Frossard, E.; Snapp, S.; Chikowo, R.; Sixa, J. Phosphorus cycling within soil aggregate fractions of a highly weathered tropical soil: A conceptual model. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Camberato, J.J. A Critical Review on Soil Chemical Processes that Control How Soil pH Affects Phosphorus Availability to Plants. Agriculture 2019, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, J.; León, J.; Osorio, W. Tree seedling growth promotion by dual inoculation with Rhizoglomus fasciculatum (Thaxt.) Sieverding, Silva & Oehl and Mortierella sp., rhizosphere fungi for reforestation purposes, to promote plant P uptake and growth at the nursery state. Acta Agron. 2016, 65, 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo-Llanos, M.; Osorio- Vega, N.; León-Pelaéz, J. Plant growth response of Pinus patula and P. maximinoi seedlings at nursery to three types of ectomycorrhizal inocula. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, P.; Pandey, A. Phosphate solubilization potential of endophytic fungi isolated from Taxus wallichiana Zucc. Roots. Rhizosphere 2019, 9, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Lou, H.Q.; Yang, J.L.; Zheng, S.J. The roles of STOP1-like transcription factors in aluminum and proton tolerance. Plant Signal. Behav. 2016, 11, 1113–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira-Mendes, G.; Moreira de Freitas, A.; Liparini-Pereira, O.; Ribeiro da Silva, I.; Bojkov-Vassilev, N.; Dutra-Costa, M. Mechanisms of phosphate solubilization by fungal isolates when exposed to different P sources. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiruma, K.; Gerlach, N.; Sacristan, S.; Nakano, R.; Hacquard, S.; Kracher, B.; Neumann, U.; Ramírez, D.; Bucher, M.; O’Connell, R.; et al. Root endophyte Colletotrichum tofieldiae confers plant fitness benefits that are phosphate status dependent. Cell 2016, 165, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, W.; Osorno, L.; León, J.; Alvarez, C. Plant-Microbe interactions for phosphate management in tropical soils. In Essential Plant Nutrients; Naeem, M., Ansari, A., Gill, S., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Swizerland, 2017; pp. 491–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, K.D.; van Straaten, P.; de Orduña, R.M.; Glasauer, S.; Trevors, J.; Fallow, D.; Smith, P.S. Comparing phosphorus mobilization strategies using Aspergillus niger for the mineral dissolution of three phosphate rocks. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 1364–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, G.; Bünemann, E.K.; Oberson, A.; Frossard, E.; Six, J. Plant-mediated rhizosphere interactions in maize-pigeon pea intercropping enhance soil aggregation and organic phosphorus storage. Plant Soil 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.; Cocq, K.; Paszkiewicz, K.; Moore, K.; Winsbury, R.; De Torres, M.; Studholme, D.; Salmon, D.; Thornton, C.; Grant, M. Transcriptional reprogramming underpins enhanced plant growth promotion by the biocontrol fungus Trichoderma hamatum GD12 during antagonistic interactions with Sclerotinia sclerotiorumin soil. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 1425–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zúñiga-Silgado, D.; Vélez-Vargas, L. Evaluation of phosphodissolvent IAA producing strains of Trichoderma spp. through biometric response of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Int. J. Biosci. 2016, 8, 103–118. [Google Scholar]
- Louw-Gaume, A.E.; Schweizer, N.; Rao, I.M.; Gaume, A.J.; Frossard, E. Temporal differences in plant growth and root exudation of two Brachiaria grasses in response to low phosphorus supply. Trop Grassl-Forrajes Trop 2017, 5, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Law, A.D.; Sahib, M.R.; Pervaiz, Z.H.; Zhang, Q. Impact of root system architecture on rhizosphere and root microbiome. Rhizosphere 2018, 6, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Yap, M.; Behringer, G.; Hung, R.; Bennett, J.W. Volatile organic compounds emitted by Trichoderma species mediate plant growth. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2016, 3, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Giles, C.; Darch, T.; George, T.S.; Blackwell, M.; Stutter, M.; Shand, C.; Lumsdon, D.; Cooper, P.; Wendler, R.; et al. Opportunities for mobilizing recalcitrant phosphorus from agricultural soils: A review. Plant Soil 2017, 427, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margenot, A.J.; Sommer, R.; Mukalama, J.; Parikh, S.J. Biological P cycling is influenced by the form of P fertilizer in an Oxisol. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zou, H. Plant growth and their root development after inoculation of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in coal mine subsided areas. Int. J. Coal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 5, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, A.L.; Rossmann, M.; Brearley, C.; Akkari, E.; Guyomar, C.; Clark, I.M.; Allen, E.; Hirsch, P.R. Land-use influences phosphatase gene microdiversity in soils. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 2740–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.C.; Yadav, H.; Singh, S.K.; Mishra, R.R.; Sethi, B.K.; Dutta, S.K.; Thatoi, H.N. Phosphate solubilization and acid phosphatase activity of Serratia sp. Isolated from mangrove soil of Mahanadi river delta, Odisha, India. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2017, 15, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haygarth, P.M.; Harrison, A.F.; Turner, B.L. On the history and future of soil organic phosphorus research: A critique across three generations. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahas, E. Phosphate solubilizing microorganism: Effect of carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus sources. In First International Meeting on Microbial Phosphate Solubilization. Developments in Plant and Soil Sciences 102; Velázquez, E., Rodríguez-Barruco, C., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Nertherland, 2007; pp. 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Moran-Diez, M.; Trushina, N.; Lamdan, N.; Rosenfelder, L.; Mukherjee, P.; Kenerley, C.; Horwitz, B. Host-specific transcriptomic pattern of Trichoderma virens during interaction with maize or tomato roots. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto-Jacobo, M.F.; Steyaert, J.M.; Salazar-Badillo, F.B.; Nguyen, D.V.; Rostás, M.; Braithwaite, M.; De Souza, J.T.; Jimenez-Bremont, J.F.; Ohkura, M.; Stewart, A.; et al. Environmental growth conditions of Trichoderma spp. affects indole acetic acid derivatives, volatile organic compounds and plant growth promotion. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Bai, T.; Dai, L.; Wang, F.; Tao, J.; Meng, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, S.; Hu, S. A study of organic acid production in contrasts between two phosphate solubilizing fungi: Penicillium oxalicum and Aspergillus niger. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, D.S.; Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Turner, B.L.; Wearing, C.; Haygarth, P.M.; Rosolem, C.A. Urochloa ruziziensis cover crop increases the cycling of soil inositol phosphates. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 54, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagos, L.M.; Acuña, J.J.; Maruyama, F.; Ogram, A.; de la Luz Mora, M.; Jorquera, M.A. Effect of phosphorus addition on total and alkaline phosphomonoesterase-harboring bacterial populations in ryegrass rhizosphere microsites. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2016, 52, 1007–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Paredes, C.; Zhang, H.; Giles, C.D.; Darch, T.; Stutter, M.; George, T.S.; Shand, C.; Lumsdon, D.; Cooper, P.; et al. Organic acids regulation of chemical–microbial phosphorus transformations in soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 11521–11531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorno, L.; Osorio, N. Effect of Carbon and nitrogen source and concentration on rock phosphate dissolution induced by fungi. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Rep. 2014, 2, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade-Menun, B. Characterizing phosphorus forms in cropland soils with solution 31P-NMR: Past studies and future research needs. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2017, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, D. Filamentous Fungi. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Sparks, D.L., Page, A.L., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Olutiola, P.O.; Famurewa, O.; Sonntag, H.G. An Introduction to General Microbiology: A Practical Approach, Reprinted ed.; Hygiene-Institute Der Universitat Heiderberg: Heidelberg, Germany, 2000; pp. 50, 196, 223. ISBN 3-89426-042-4. [Google Scholar]
- Otto, J.C.G. Rose Bengal as a Selective Aid in the Isolation of Fungi and Actinomycetes from Natural Sources. Mycologia 1972, 64, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuchat, L.R.; Cousin, M.A. Yeasts and molds. In Compendium of Methods for the Microbiological Examination of Foods, Fourth ed.; Downes, F.P., Ito, K., Eds.; American Public Health Association: Washington DC, USA, 2001; Chapter 20; pp. 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Osorio, N.W.; Habte, M. Soil phosphate desorption induced by a phosphate-solubilizing fungus. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 2014, 45, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Niu, B.; Gao, Y.; Fu, L.; Li, W. CD-HIT Suite: A web server for clustering and comparing biological sequences. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 680–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castresana, J.; Gblocks, v. 0.91 b. 2002. Available online: http://molevol.cmima.csic.es/castresana/Gblocks_server.html (accessed on 2 May 2020).
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2–approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calich, V.L.; Purchio, A.; Paula, C.R. A new fluorescent viability test for fungi cells. Mycopathologia 1979, 66, 175–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Ramírez, G.; Flores-Vallejo, R.C.; Rivera-Leyva, J.C.; Tovar-Sánchez, E.; Sánchez-Reyes, A.; Mena-Portales, J.; Sánchez-Carbente, M.R.; Gaitán-Rodríguez, M.F.; Batista-García, R.A.; Villarreal, M.L.; et al. Characterization of fungal endophytes isolated from the metal hyperaccumulator plant Vachellia farnesiana growing in mine Tailings. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shi, M.; Cao, Z.; Lu, Q.; Yang, T.; Fan, Y.; Wei, Z. Effect of organic acids production and bacterial community on the possible mechanism of phosphorus solubilization during composting with enriched phosphate-solubilizing bacteria inoculation. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, M.J. GLIM for Ecologist; Blackwell Scientific Publication: Boston, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, R.A.; Wichern, D.W. Applied Multivariate Statistical Analysis, 6th ed.; Pearson Education. Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Perea Rojas, Y.C.; Arias, R.M.; Medel Ortiz, R.; Trejo, D.; Heredia, G.; Rodríguez, Y. Effects of native arbuscular mycorrhizal and phosphate-solubilizing fungi on coffee plants. Agroforest Syst. 2018, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaverri, P.; Branco-Rocha, F.; Jaklitsch, W.; Gazis, R.; Degenkolb, T.; Samuels, G. Systematics of the Trichoderma harzianum species complex and the re-identification of commercial biocontrol strains. Mycologia 2015, 107, 558–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Saxena, J.; Sharma, V. Solubilization of inorganic phosphates by Aspergillus awamori S19 isolated from rhizosphere soil of a semi-arid region. Ann. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendran, R.; Kathiresan, K.; Sathishkumar, R.S.; Kayalvizhi, K.; Sundaramanickam, A. Bioremoval of toxic substances in synthetic wastewater using Trichoderma pubescens (NPK2), isolated from mangrove soil. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2019, 19, 101100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Melchor, D.J.; Ferrera-Cerrato, R.; Alarcón, A. Trichoderma: Agricultural and biotechnological importance and fermentation systems for producing biomass and enzymes of industrial interest. Chil. J. Agric. Anim. Sci. 2019, 35, 98–112. [Google Scholar]
- Magallon-Servin, P.; Antoun, H.; Taktek, S.; de-Bashan, L.E. Designing a multi-species inoculant of phosphate rock-solubilizing bacteria compatible with arbuscular mycorrhizae for plant growth promotion in low P soil amended with PR. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 521–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Khalil, S.; Ayub, N.; Rashid, M. In vitro solubilization of inorganic phosphate by phosphate solubilizing microorganism (PSM) from maize rhizosphere. Intl. J. Agric. Biol. 2002, 4, 454–458. [Google Scholar]
- Akintokun, A.K.; Akande, G.A.; Akintokun, P.O.; Popoola, T.O.S.; Babalola, A.O. Solubilization of insoluble phosphorus by organic acid-producing fungi isolated from the Nigerian soil. Int. J. Soil Sci. 2007, 2, 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Mardad, I.; Serrano, A.; Soukri, A. Solubilization of inorganic phosphate and production of organic acids by bacteria isolated from a Moroccan mineral phosphate deposit. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 7, 626–635. [Google Scholar]
- Karaffa, L.; Kubicek, C.P. Aspergillus niger citric acid accumulation: Do we understand this well working black box? Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2003, 61, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makela, M.; Galkin, S.; Hatakka, A.; Lundell, T. Production of organic acids and oxalate decarboxylase in lignin-degrading white rot fungi. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2002, 30, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zúñiga-Silgado, D.; Rivera-Leyva, J.C.; Coleman, J.J.; Sánchez-Reyez, A.; Valencia-Díaz, S.; Serrano, M.; de-Bashan, L.E.; Folch-Mallol, J.L. Soil Type Affects Organic Acid Production and Phosphorus Solubilization Efficiency Mediated by Several Native Fungal Strains from Mexico. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091337
Zúñiga-Silgado D, Rivera-Leyva JC, Coleman JJ, Sánchez-Reyez A, Valencia-Díaz S, Serrano M, de-Bashan LE, Folch-Mallol JL. Soil Type Affects Organic Acid Production and Phosphorus Solubilization Efficiency Mediated by Several Native Fungal Strains from Mexico. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(9):1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091337
Chicago/Turabian StyleZúñiga-Silgado, Dorcas, Julio C. Rivera-Leyva, Jeffrey J. Coleman, Ayixon Sánchez-Reyez, Susana Valencia-Díaz, Mario Serrano, Luz E. de-Bashan, and Jorge L. Folch-Mallol. 2020. "Soil Type Affects Organic Acid Production and Phosphorus Solubilization Efficiency Mediated by Several Native Fungal Strains from Mexico" Microorganisms 8, no. 9: 1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091337
APA StyleZúñiga-Silgado, D., Rivera-Leyva, J. C., Coleman, J. J., Sánchez-Reyez, A., Valencia-Díaz, S., Serrano, M., de-Bashan, L. E., & Folch-Mallol, J. L. (2020). Soil Type Affects Organic Acid Production and Phosphorus Solubilization Efficiency Mediated by Several Native Fungal Strains from Mexico. Microorganisms, 8(9), 1337. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091337








