A First Insight into the Structural and Functional Comparison of Environmental Microbiota in Freshwater Turtle Chinemys reevesii at Different Growth Stages under Pond and Greenhouse Cultivation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Detection of Water Quality Indices
2.2. DNA Extraction, Amplicon Generation, Library Preparation and Sequencing
2.3. 16S rRNA Gene Sequence Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Environmental Factors Analyese
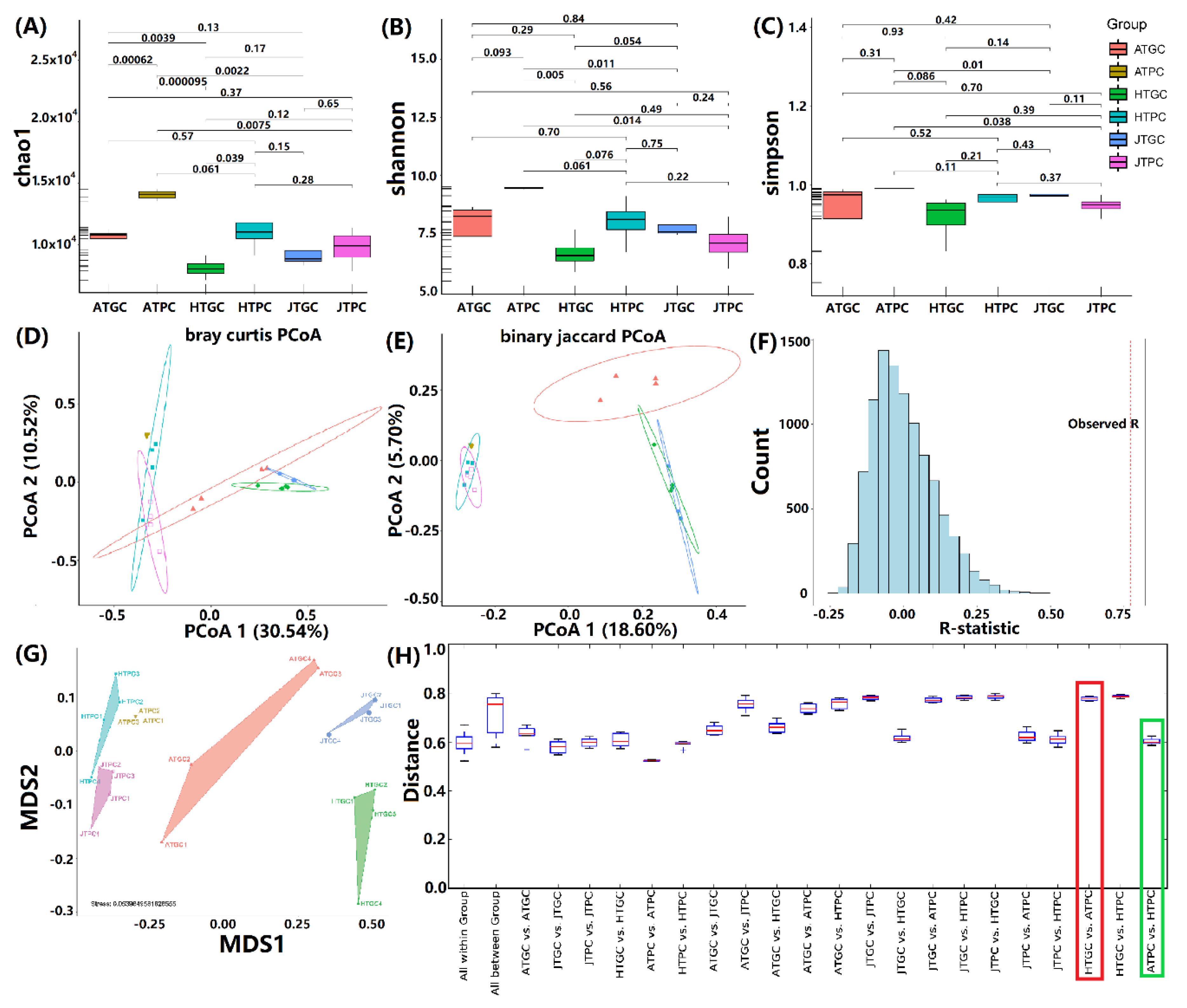
3.2. Analyses of Bacterial Diversity
3.3. Analysis of Microbiota Structure
3.4. Annotation Analysis of the Microbiota
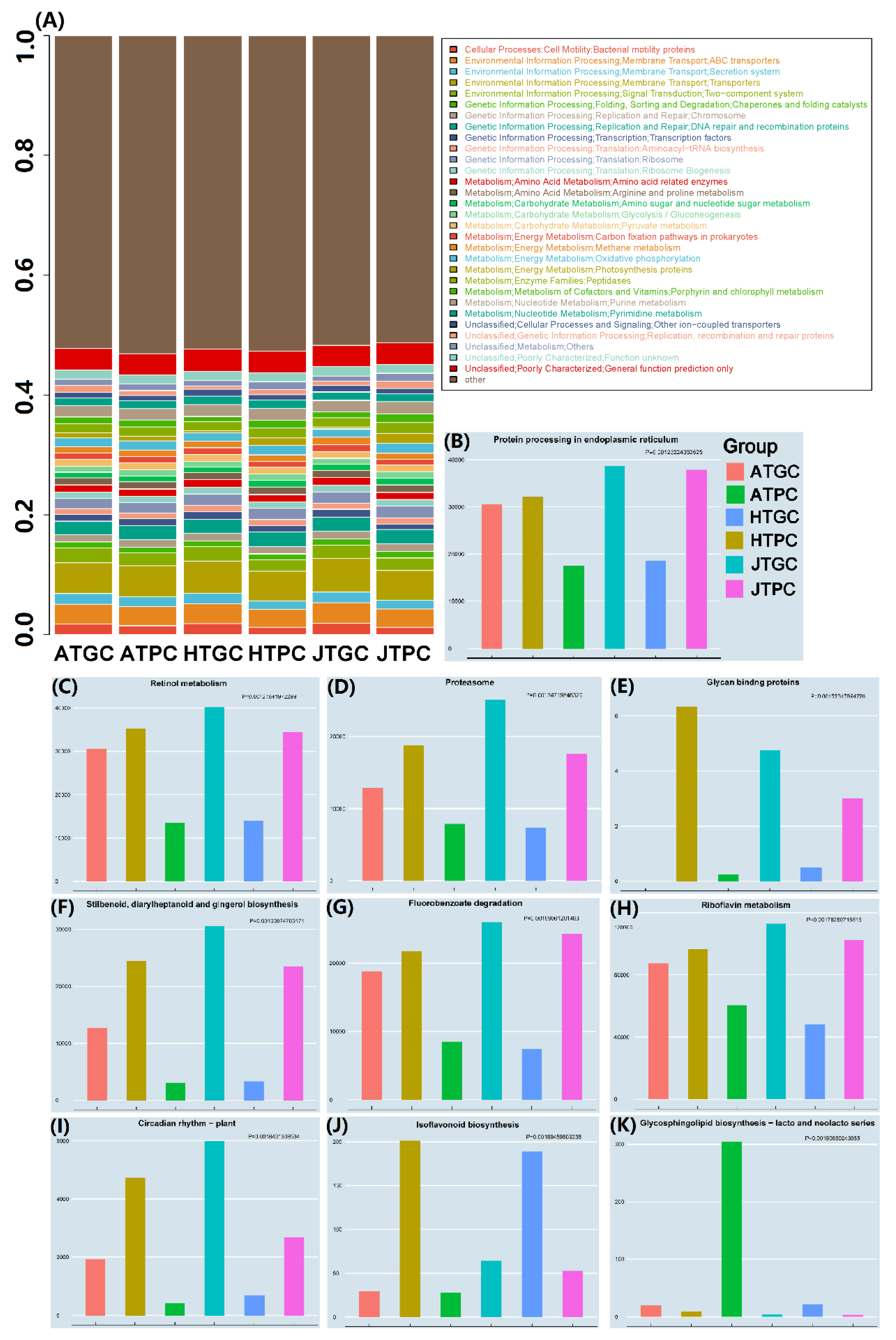
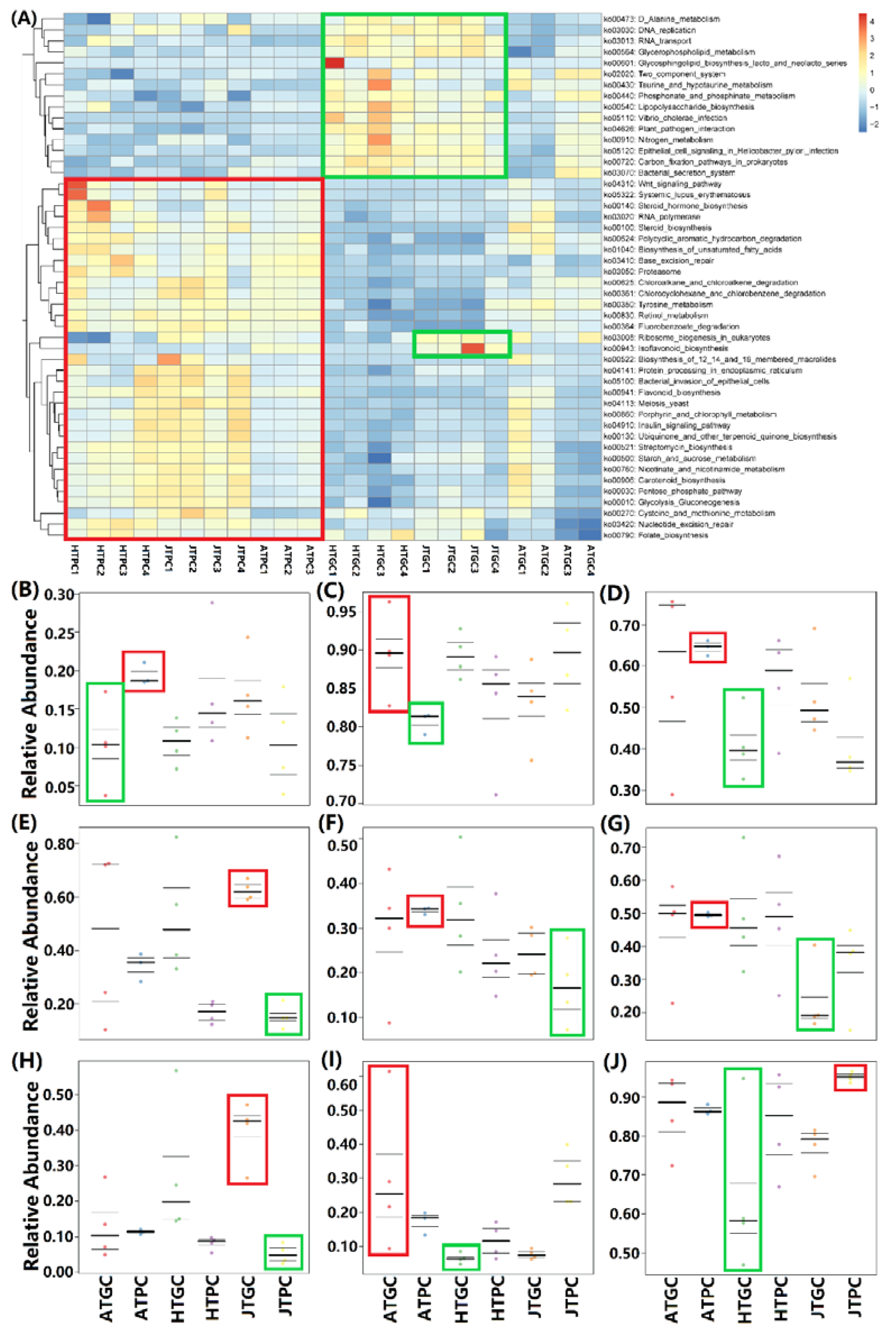
3.5. Functional Prediction of the Microbiota
3.5.1. Analyses of Picrust Gene Function Prediction Expression
3.5.2. KEGG Pathway Annotation and Bacterial Phenotype Prediction
3.6. Correlation Analyses of Environmental Factors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chakroff, M. Freshwater Fish Pond Culture and Management; VITA. Publications: Arlington, VA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, B.; Tiwari, G.N. Thermal modeling of a greenhouse fish pond system. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2005, 7, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Borowitzka, M.A.; Moheimani, N.R. Open Pond Culture Systems. In Algae for Biofuels and Energy; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 133–152. [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland, R.; Norris, R.D.; Mace, I. Global Fish Production in the Cenozoic Greenhouse and Icehouse Oceans. In Proceedings of the AGU Fall Meeting 2019; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.R. The development history and training algorithm of artificial neuralnetwork. Public Commun. Sci. Technol. 2018, 10, 129–130. [Google Scholar]
- Dagoon, N.J. Malaysian school engages in bullfrog and turtle farming. SEAFDEC Asian Aquac. 2000, 22, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- China Fishery Statistical Yearbook; China Argriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2019. (In Chinese)
- Huo, J.; Dong, A.; Yan, J.; Wang, L.; Ma, C.; Lee, S. Cadmium toxicokinetics in the freshwater turtle, Chinemys reevesii. Chemosphere 2017, 182, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, J.; Dong, A.; Yan, J.; Dong, A. Effects of cadmium on the gene transcription of the liver in the freshwater turtle (Chinemys reevesii). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 8431–8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, T.; Jian-Ye, Y.; Jie, R.; Shun-Xiang, L. Differentiating Trachemys scripta elegans Shell Glue from Chinemys reevesii Shell Glue by UPLC-QTOF/MS Coupled with Binary Compare Tool of UNIFI. Digit. Chin. Med. 2019, 2, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Han, X.K.; Chen, W.; Zhou, H.B.; Zhang, Y.P. Phenotypic Consequences of Embryonic Responses to Developmental Temperatures in Two Latitudinally Separated Populations of Asian Yellow Pond Turtles. J. Herpetol. 2018, 52, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.S. Experiment of Industrial Culture of Chinemys reevesii. Shandong Fish. 2000, 4, 6. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- He, R.; Xie, J.; Huang, S.L.; Shi, J.B.; Gao, Z.L.; Xiong, Q. Comparison of nutritional composition of Chinese soft-shelled turtles (Pelodiscus sinensis) grown in greenhouse and imitative ecological farming conditions. Food Sci. 2013, 34, 234–238. [Google Scholar]
- Janda, J.M.; Abbott, S.L. 16S rRNA gene sequencing for bacterial identification in the diagnostic laboratory: Pluses, perils, and pitfalls. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2761–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Muinck, E.J.; Trosvik, P.; Gilfillan, G.D.; Hov, J.R.; Sundaram, A.Y. A novel ultra high-throughput 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing library preparation method for the Illumina HiSeq platform. Microbiome 2017, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagkouvardos, I.; Fischer, S.; Kumar, N.; Clavel, T. Rhea: A transparent and modular R pipeline for microbial profiling based on 16S rRNA gene amplicons. PeerJ 2017, 5, e2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawley, B.; Tannock, G.W. Analysis of 16S rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequences Using the QIIME Software Package. In Oral Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 153–163. [Google Scholar]
- Tourlousse, D.M.; Yoshiike, S.; Ohashi, A.; Matsukura, S.; Noda, N.; Sekiguchi, Y. Synthetic spike-in standards for high-throughput 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syromyatnikov, M.Y.; Kokina, A.V.; Solodskikh, S.A.; Panevina, A.V.; Popov, E.S.; Popov, V.N. High-Throughput 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing of Butter Microbiota Reveals a Variety of Opportunistic Pathogens. Foods 2020, 9, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Estrada, Á.M.; Gollas-Galván, T.; Martínez-Córdova, L.R.; Martínez-Porchas, M. Predictive functional profiles using metagenomic 16S rRNA data: A novel approach to understanding the microbial ecology of aquaculture systems. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.T.; Taylor, N.G. Models suggest pathogen risks to wild fish can be mitigated by acquired immunity in freshwater aquaculture systems. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Chang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Qiao, L.; Song, X.; Li, J. Effects of carbon source addition on microbial community and water quality in recirculating aquaculture systems for Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish. Sci. 2020, 86, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suurnäkki, S.; Pulkkinen, J.T.; Lindholm-Lehto, P.C.; Tiirola, M.; Aalto, S.L. The effect of peracetic acid on microbial community, water quality, nitrification and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) performance in recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 2020, 516, 734534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Liu, B.; Xuan, Y.; Jiang, M.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Lu, X.; Yu, D.; et al. Dynamic changes of microbial communities in Litopenaeus vannamei cultures and the effects of environmental factors. Aquaculture 2016, 455, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, A.; Song, L.Y.; Xiong, Y.H.; Lu, C.J.; Junaid, M.; Pei, D.S. Impact of water quality on the microbial diversity in the surface water along the Three Gorge Reservoir (TGR), China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 181, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.S.; Tu, Q.Y. The Investigation Standard of Lake Eutrophication; Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sartory, D.P.; Grobbelaar, J.U. Extraction of chlorophyll a from freshwater phytoplankton for spectrophotometric analysis. Hydrobiologia 1984, 114, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rDNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Bai, Y. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, T.M.; Golding, G.B.; King, C.; Froese, D.; Zazula, G.; Poinar, H.N. Amplicon pyrosequencing late Pleistocene permafrost: The removal of putative contaminant sequences and small-scale reproducibility. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 798–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvado, A.; Coelho, F.J.R.C.; Oliveira, V.; Gomes, H.; Cleary, D.F.R.; Simões, M.M.Q.; Cunha, A.; Gomes, N.C.M. Microcosm evaluation of the impact of oil contamination and chemical dispersant addition on bacterial communities and sediment remediation of an estuarine port environment. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 134–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Development Core Team, R. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Chapman, M.G.; Underwood, A.J. Ecological patterns in multivariate assemblages: Information and interpretation of negative values in ANOSIM tests. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1999, 180, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, G.B. An introduction to nonmetric multidimensional scaling. Am. J. Political Sci. 1975, 19, 343–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Programming with ggplot2. In ggplot2; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 241–253. [Google Scholar]
- Langille, M.G.; Zaneveld, J.; Caporaso, J.G.; McDonald, D.; Knights, D.; Reyes, J.A.; Clemente, J.C.; Burkepile, D.E.; Vega Thurber, R.L.; Knight, R.; et al. Predictive functional profiling of microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.; Yen, J.Y.; Guan, Y.; Ke, D.; Liu, C. Differential responses of stream water and bed sediment microbial communities to watershed degradation. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Person-Le Ruyet, J.; Labbé, L.; Le Bayon, N.; Sévère, A.; Le Roux, A.; Le Delliou, H.; Quéméner, L. Combined effects of water quality and SD on welfare and growth of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquat. Living Resour. 2008, 21, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, L.; Peng, G.; Li, J.; Yan, W.; Tang, J. Effects of SD on growth of Procambarus clarkii and aquaculture water quality. Acta Agric. Jiangxi 2014, 26, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Pitacco, V.; Mistri, M.; Aleffi, I.F.; Lardicci, C.; Prato, S.; Tagliapietra, D.; Munari, C. Spatial patterns of macrobenthic alpha and beta diversity at different scales in Italian transitional waters (central Mediterranean). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2019, 222, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzari, N.; Martín-López, B.; Sanabria-Fernandez, J.A.; Becerro, M.A. Alpha and beta diversity across coastal marine social-ecological systems: Implications for conservation. Ecol. Ind. 2020, 109, 105786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Song, C.; Zhang, C.; Hu, G.; Meng, S.; Qiu, L.; Fan, l.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Effects of multiple environmental factors on elimination of fenvalerate and its cis-trans isomers in aquaculture water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 3795–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbib, Z.; De Godos Crespo, I.; Corona, E.L.; Rogalla, F. Understanding the biological activity of high rate algae ponds through the calculation of oxygen balances. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 5189–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippen, T.L.; Sheffield, C.L.; Singh, B.; Byrd, J.A.; Beier, R.C. How Management Practices Within a Poultry House During Successive Flock Rotations Change the Structure of the Soil Microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Irving, B.; Fitzsimmons, C.; Plastow, G.; Plastow, G. Host genetics influence the rumen microbiota and heritable rumen microbial features associate with feed efficiency in cattle. Microbiome 2019, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, S.J.; Olijhoek, D.W.; Mclean, F.; Løvendahl, P.; Lund, P.; Højberg, O. Rumen and Fecal Microbial Community Structure of Holstein and Jersey Dairy Cows as Affected by Breed, Diet, and Residual Feed Intake. Animals 2019, 9, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañeda-Monsalve, V.A.; Junca, H.; García-Bonilla, E.; Montoya-Campuzano, O.I.; Moreno-Herrera, C.X. Characterization of the gastrointestinal bacterial microbiome of farmed juvenile and adult white Cachama (Piaractus brachypomus). Aquaculture 2019, 512, 734325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, Q.; Gao, J.; Zhai, S.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, Y. Long-term and inter-monthly dynamics of aquatic vegetation and its relation with environmental factors in Taihu Lake, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, W.; Bian, B.; Gao, N.; Min, J.; Shi, W.; Lin, X.; Shen, W. Nitrogen fertilization induced changes in ammonia oxidation are attributable mostly to bacteria rather than archaea in greenhouse-based high N input vegetable soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 93, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Liu, X.; Ma, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Zeng, X.; Xu, S.; Gu, Z. Vertical segregation and phylogenetic characterization of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in the sediment of a freshwater aquaculture pond. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Cheng, G. Review of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea in freshwater ponds. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio Technol. 2019, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.J.; De Anda, V.; Seitz, K.W.; Dombrowski, N.; Santoro, A.E.; Lloyd, K.G. Diversity, ecology and evolution of Archaea. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iverson, L.R.; Prasad, A.M.; Matthews, S.N.; Peters, M. Estimating potential habitat for 134 eastern US tree species under six climate scenarios. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 254, 390–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukassen, M.B.; Saunders, A.M.; Sindilariu, P.D.; Nielsen, J.L. Quantification of novel geosmin-producing bacteria in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 2017, 479, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhao, D.; Huang, R.; Xu, H.; Jiao, C. Seasonality overwhelms aquacultural activity in determining the composition and assembly of the bacterial community in Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 683, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Hu, G.; Qiu, L.; Meng, S.; Wu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Song, C.; Li, D.; Chen, J. Variations in bacterioplankton communities in aquaculture ponds and the influencing factors during the peak period of culture. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 258, 113656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Dai, W.; Qiu, Q.; Dong, C.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, J. Contrasting ecological processes and functional compositions between intestinal bacterial community in healthy and diseased shrimp. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mao, G.; Gao, G.; Wang, Y. Impact of planktonic low nucleic acid-content bacteria to bacterial community structure and associated ecological functions in a shallow lake. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibbs, S.P. The chloroplast endoplasmic reticulum: Structure, function, and evolutionary significance. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1981, 72, 49–99. [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz, D.S.; Blower, M.D. The endoplasmic reticulum: Structure, function and response to cellular signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowakiewicz, A.; Ziółkowska, G.; Zięba, P.; Dziedzic, B.M.; Gnat, S.; Wójcik, M.; Dziedzic, R.; Kostruba, A. Aerobic bacterial microbiota isolated from the cloaca of the European pond turtle (Emys orbicularis) in Poland. J. Wildl. Dis. 2015, 51, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, M.P.; Amini, A.; Dojka, M.A.; Pickering, I.J.; Dawson, S.C.; Pace, N.R.; Terry, N. Identification and characterization of bacteria in a selenium-contaminated hypersaline evaporation pond. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3785–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brönmark, C.; Hansson, L.A. The Biology of Lakes and Ponds; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, M.N.; Nguyen, P.N.; Le, D.V.; Nguyen, D.V.; Bossier, P. Effects of SD of gray mullet Mugil cephalus on water quality, growth performance, nutrient conversion rate, and microbial community structure in the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei integrated system. Aquaculture 2018, 496, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Xu, X.; Yin, X.; Lu, H.; Chen, G.; Yu, J.; Ruan, Y. Effect of stock density on the microbial community in biofloc water and Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) gut microbiota. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 4241–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimer, L.C.; Vetcininova, A.; Carbasse, J.S.; Söhngen, C.; Gleim, D.; Ebeling, C.; Overmann, J. Bac Dive in 2019: Bacterial phenotypic data for High-throughput biodiversity analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D631–D636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambino, M.; Cappitelli, F. Mini-review: Biofilm responses to oxidative stress. Biofouling 2016, 32, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Jiao, L.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, Q.; Zhang, H.; Gao, X.; Ma, Y.; Shi, H.N. The effect of exposure to high altitude and low oxygen on intestinal microbial communities in mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobeen, F.; Sharma, V.; Prakash, T. Functional signature analysis of extreme Prakriti endophenotypes in gut microbiome of western Indian rural population. Bioinformation 2019, 15, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, D.; Ge, Y.; Li, H.; You, Y. Change in the intestinal bacterial community structure associated with environmental microorganisms during the growth of Eriocheir sinensis. MicrobiologyOpen 2019, 8, e00727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, J.; Qi, D.; Huang, Z.; Yang, H. Correlation study of Submerged Macrophytes Growth and Environmental Factors in Lake Qionghai Wetland. E&ES 2020, 440, 052005. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Jin, J.; Liang, S.; Zhang, J. Characteristics of water quality and bacterial communities in three water supply pipelines. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 4035–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, F.P. Aquaculture disease and health management. J. Anim. Sci. 1991, 69, 4201–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.N.; Al-Harbi, A.H. Seasonal variation of bacterial flora in ponds in Saudi Arabia used for tilapia aquaculture. J. Appl. Aquac. 2004, 16, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahiri, S.; Ghosh, D.; Sarkar, D. Biogeochemical Cycling Bacteria and Nutrient Dynamics in Waste Stabilization Pond System. In Wastewater Management Through Aquaculture; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 29–52. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, U.L.; Falcon, D.R.; PESSÔA, M.N.D.C.; Correia, E.D.S. Carbon sources and C: N ratios on water quality for Nile tilapia farming in biofloc system. Rev. Caatinga 2017, 30, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Xiao, K.; Chen, M. An intelligent IoT-based control and traceability system to forecast and maintain water quality in freshwater fish farms. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2019, 166, 105013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, L.; Zhu, R.; Li, M.; Wu, L.F. Effects of bioflocs with different C/N ratios on growth, immunological parameters, antioxidants and culture water quality in Opsariichthys kaopingensis Dybowski. Aquac. Res. 2020, 51, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Samples | HTPC | JTPC | ATPC | HTGC | JTGC | ATGC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temp (°C) | 33.92 ABd ± 0.10 | 33.85 Ad ± 0.06 | 34 Bd ± 0.0 | 31.65 Bc ± 0.44 | 30.78 Ab ± 0.5 | 30.08 Aa ± 0.1 |
| pH | 9.08 ABcd ± 0.17 | 9.48 Bd ± 0.47 | 8.57 Abc ± 0.06 | 8.12 Bb ± 0.08 | 8.1 Bb ± 0.16 | 7.28 Aa ± 0.17 |
| Transparency (cm) | 21 Ce ± 1.41 | 4.75 Ab ± 0.29 | 14.67 Bc ± 0.58 | 2.5 Aa ± 0.58 | 2.5 Aa ± 0.56 | 18 Bd ± 0.82 |
| DO (mg/L) | 4.28 Bc ± 0.17 | 1.98 Aa ± 0.39 | 2.5 Ab ± 0.1 | 7.34 Be ± 0.06 | 7.48 Be ± 0.05 | 6.43 Ad ± 0.26 |
| NH4-N (mg/L) | 0.25 Aa ± 0.12 | 0.75 Ba ± 0.26 | 0.46 ABa ± 0.25 | 23.14 ABab ± 20.5 | 40.06 b ± 19.9 | 4.08 Aa ± 0.26 |
| NO2-N (mg/L) | 0.03 Aa ± 0.03 | 0.11 Aa ± 0.09 | 0.7 Bb ± 0.05 | 0.08 Aa ± 0.04 | 0.19 Ba ± 0.04 | 0.13 Aa ± 0.01 |
| PO4-P (mg/L) | 0.04 Aa ± 0.03 | 0.09 Aa ± 0.09 | 0.04 Aa ± 0.03 | 22.29 Bb ± 8.78 | 22.13 Bb ± 6.18 | 0.4 Aa ± 0.1 |
| Chlorophyll a(μg/L) | 81.96 Aa ± 110.08 | 576.09 Bb ± 687.06 | 175.86 Aa ± 77.54 | 120.65 Ba ± 61.35 | 21.94 Aa ± 15.78 | 45.3 ABa ± 30.19 |
| Stocking density(ea/m2) | 8.5 Cab ± 0.58 | 6.5 Bab ± 0.58 | 4.0 Aa ± 0.00 | 300 Cd ± 4.2 | 59.7 Bc ± 1.71 | 9.5 Ab ± 0.58 |
| Body weight (g/ea) | 12.2 Aa ± 0.21 | 368.5 Bb ± 19.87 | 1695.7 Cc ± 50.33 | 7.6 Aa ± 0.19 | 208.6 Bb ± 12.08 | 1357.1 Cc ± 37.69 |
| Sample ID | Counts | Alpha Diversity | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed OTUs | Chao1 | Equitability | Shannon | Simpson | Goods Coverage | PD Whole Tree | ||
| HTPC1 | 64,997 | 4825 | 11,095.6503 | 0.65086124 | 7.964142 | 0.9648892 | 0.92931319 | 398.22413 |
| HTPC2 | 68,075 | 5884 | 13,892.7109 | 0.72650334 | 9.09769732 | 0.98811813 | 0.91357092 | 458.74608 |
| HTPC3 | 61,492 | 5094 | 10,946.0206 | 0.66704508 | 8.21438221 | 0.97094908 | 0.92669342 | 418.07747 |
| HTPC4 | 91,084 | 3779 | 9148.1476 | 0.56251041 | 6.6847549 | 0.93072839 | 0.94304933 | 338.30432 |
| JTPC1 | 88,505 | 4507 | 10,507.5396 | 0.59343605 | 7.20309818 | 0.95088012 | 0.93311305 | 393.27832 |
| JTPC2 | 75,770 | 3969 | 9333.80887 | 0.5790958 | 6.92283544 | 0.9482456 | 0.94080717 | 354.25884 |
| JTPC3 | 74,256 | 5068 | 11,394.1533 | 0.6663094 | 8.20040355 | 0.97460536 | 0.92570215 | 417.67826 |
| JTPC4 | 81,081 | 3264 | 7848.80331 | 0.50961591 | 5.94845363 | 0.91409333 | 0.95031862 | 310.18648 |
| ATPC1 | 57,370 | 6351 | 14,113.0676 | 0.74705529 | 9.4373762 | 0.99139504 | 0.90811895 | 487.5006 |
| ATPC2 | 67,386 | 6411 | 14,508.5938 | 0.7503018 | 9.48856696 | 0.99136054 | 0.90644324 | 512.41029 |
| ATPC3 | 68,135 | 6240 | 13,547.0426 | 0.74615905 | 9.40707362 | 0.99027745 | 0.91149398 | 496.93705 |
| HTGC1 | 11,5451 | 4327 | 9133.16981 | 0.6327939 | 7.64361337 | 0.96224922 | 0.93924947 | 373.40055 |
| HTGC2 | 89,853 | 3496 | 7863.80534 | 0.56062139 | 6.59934881 | 0.92033243 | 0.94949257 | 327.23926 |
| HTGC3 | 88,092 | 3601 | 8226.01093 | 0.49108532 | 5.80177125 | 0.83141427 | 0.94680198 | 329.16926 |
| HTGC4 | 10,7919 | 3193 | 7111 | 0.55434821 | 6.45299941 | 0.95083458 | 0.95374085 | 281.35905 |
| JTGC1 | 83,718 | 3699 | 8325.71587 | 0.62528623 | 7.41146738 | 0.97184881 | 0.94713241 | 323.67024 |
| JTGC2 | 108,954 | 3940 | 8986.31754 | 0.62914851 | 7.51453719 | 0.96952937 | 0.94337975 | 354.61208 |
| JTGC3 | 99,788 | 3933 | 8727.00998 | 0.6344613 | 7.5763653 | 0.97553313 | 0.94333255 | 344.44308 |
| JTGC4 | 93,833 | 5140 | 11,155.2791 | 0.70375189 | 8.67553846 | 0.98252414 | 0.9279679 | 406.05474 |
| ATGC1 | 115,298 | 3657 | 9607.0592 | 0.45725022 | 5.41221709 | 0.75224964 | 0.94399339 | 364.64287 |
| ATGC2 | 99,145 | 4728 | 10,791.9607 | 0.65504928 | 7.99619596 | 0.96793801 | 0.93186217 | 421.06455 |
| ATGC3 | 82,261 | 4925 | 10,803.0905 | 0.70347102 | 8.62871079 | 0.98902736 | 0.9308945 | 405.30658 |
| ATGC4 | 110,627 | 5128 | 11,262.0013 | 0.68522241 | 8.44480472 | 0.98016172 | 0.92763748 | 407.46934 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, A.; Xie, S.; Sun, D.; Zhang, P.; Dong, H.; Zuo, Z.; Li, X.; Zou, J. A First Insight into the Structural and Functional Comparison of Environmental Microbiota in Freshwater Turtle Chinemys reevesii at Different Growth Stages under Pond and Greenhouse Cultivation. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091277
Zhou A, Xie S, Sun D, Zhang P, Dong H, Zuo Z, Li X, Zou J. A First Insight into the Structural and Functional Comparison of Environmental Microbiota in Freshwater Turtle Chinemys reevesii at Different Growth Stages under Pond and Greenhouse Cultivation. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(9):1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091277
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Aiguo, Shaolin Xie, Di Sun, Pan Zhang, Han Dong, Zhiheng Zuo, Xiang Li, and Jixing Zou. 2020. "A First Insight into the Structural and Functional Comparison of Environmental Microbiota in Freshwater Turtle Chinemys reevesii at Different Growth Stages under Pond and Greenhouse Cultivation" Microorganisms 8, no. 9: 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091277
APA StyleZhou, A., Xie, S., Sun, D., Zhang, P., Dong, H., Zuo, Z., Li, X., & Zou, J. (2020). A First Insight into the Structural and Functional Comparison of Environmental Microbiota in Freshwater Turtle Chinemys reevesii at Different Growth Stages under Pond and Greenhouse Cultivation. Microorganisms, 8(9), 1277. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091277





