A Cross-Sectional Study of the Gut Microbiota Composition in Moscow Long-Livers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Recruitment of Study Participants
2.2. Sample Collection and Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.3. Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of the Microbiota Composition in Long-Livers and Conditionally Healthy Elderly
3.2. Comparison of the Gut Microbiota of Long-Livers from Russia, Japan and Italy
3.3. Correlation between Gut Microbiota and Health Status
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seidel, J.; Valenzano, D.R. The role of the gut microbiome during host ageing. F1000Res 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, R.C.; Manges, A.R.; Finlay, B.B.; Prendergast, A.J. The human microbiome and child growth—First 1000 days and beyond. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ticinesi, A.; Nouvenne, A.; Cerundolo, N.; Catania, P.; Prati, B.; Tana, C.; Meschi, T. Gut microbiota, muscle mass and function in aging: A focus on physical frailty and sarcopenia. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrucci, L.; Fabbri, E. Inflammageing: Chronic inflammation in ageing, cardiovascular disease, and frailty. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevaranjan, N.; Puchta, A.; Schulz, C.; Naidoo, A.; Szamosi, J.C.; Verschoor, C.P.; Loukov, D.; Schenck, L.P.; Jury, J.; Foley, K.P.; et al. Age-associated microbial dysbiosis promotes intestinal permeability, systemic inflammation, and macrophage dysfunction. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 21, 455–466.e454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruno, G.; Gagliardi, A.; Oliva, A.; Trancassini, M.; Macone, A.; Cicerone, C.; D’Abramo, A.; Iebba, V.; Auria, S.; Bonfiglio, G.; et al. Fecal microbial transplantation impact on gut microbiota composition and metabolome, microbial translocation and t-lymphocyte immune activation in recurrent clostridium difficile infection patients. New Microbiol. 2019, 42, 221–224. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Zeng, T.; Zinellu, A.; Rubino, S.; Kelvin, D.J.; Carru, C. A cross-sectional study of compositional and functional profiles of gut microbiota in sardinian centenarians. mSystems 2019, 4, e00325-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.S.; Choi, C.W.; Shin, H.; Jin, S.P.; Bae, J.S.; Han, M.; Seo, E.Y.; Chun, J.; Chung, J.H. Comparison of the gut microbiota of centenarians in longevity villages of south korea with those of other age groups. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 29, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashtanova, D.A.; Tkacheva, O.N.; Doudinskaya, E.N.; Strazhesko, I.D.; Kotovskaya, Y.V.; Popenko, A.S.; Tyakht, A.V.; Alexeev, D.G. Gut microbiota in patients with different metabolic statuses: Moscow study. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efimova, D.; Tyakht, A.; Popenko, A.; Vasilyev, A.; Altukhov, I.; Dovidchenko, N.; Odintsova, V.; Klimenko, N.; Loshkarev, R.; Pashkova, M.; et al. Knomics-biota—a system for exploratory analysis of human gut microbiota data. BioData Min. 2018, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Pena, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. Qiime allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeSantis, T.Z.; Hugenholtz, P.; Larsen, N.; Rojas, M.; Brodie, E.L.; Keller, K.; Huber, T.; Dalevi, D.; Hu, P.; Andersen, G.L. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16s rrna gene database and workbench compatible with arb. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5069–5072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, R.; Vrbanac, A.; Taylor, B.C.; Aksenov, A.; Callewaert, C.; Debelius, J.; Gonzalez, A.; Kosciolek, T.; McCall, L.I.; McDonald, D.; et al. Best practices for analysing microbiomes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 410–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. Dada2: High-resolution sample inference from illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods. 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Chase, J.; Pitman, T.A.; Shiffer, A.; Mercurio, W.; Dillon, M.R.; Caporaso, J.G. An introduction to applied bioinformatics: A free, open, and interactive text. J. Open Source Educ. 2018, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagi, E.; Franceschi, C.; Rampelli, S.; Severgnini, M.; Ostan, R.; Turroni, S.; Consolandi, C.; Quercia, S.; Scurti, M.; Monti, D.; et al. Gut microbiota and extreme longevity. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 1480–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odamaki, T.; Kato, K.; Sugahara, H.; Hashikura, N.; Takahashi, S.; Xiao, J.Z.; Abe, F.; Osawa, R. Age-related changes in gut microbiota composition from newborn to centenarian: A cross-sectional study. BMC Microbiol. 2016, 16, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Pinto, J.; Egozcue, J.J.; Pawlowsky-Glahn, V.; Paredes, R.; Noguera-Julian, M.; Calle, M.L. Balances: A new perspective for microbiome analysis. mSystems 2018, 3, e00053-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, R.; Mainali, R.; Ahmadi, S.; Wang, S.; Singh, R.; Kavanagh, K.; Kitzman, D.W.; Kushugulova, A.; Marotta, F.; Yadav, H. Gut microbiome and aging: Physiological and mechanistic insights. Nutr. Healthy Aging 2018, 4, 267–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelakkot, C.; Choi, Y.; Kim, D.K.; Park, H.T.; Ghim, J.; Kwon, Y.; Jeon, J.; Kim, M.S.; Jee, Y.K.; Gho, Y.S.; et al. Akkermansia muciniphila-derived extracellular vesicles influence gut permeability through the regulation of tight junctions. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, e450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, T.; Hamai, T.; Hori, T.; Sato, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Sato, Y.; Inaba, T.; Ogata, A.; Habe, H.; Sakata, T. Hydraulic retention time and ph affect the performance and microbial communities of passive bioreactors for treatment of acid mine drainage. AMB Express 2017, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, I.; Lattimer, J.M.; Hubach, K.L.; Case, J.A.; Yang, J.; Weber, C.G.; Louk, J.A.; Rose, D.J.; Kyureghian, G.; Peterson, D.A.; et al. Gut microbiome composition is linked to whole grain-induced immunological improvements. ISME J. 2013, 7, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Aimmo, M.R.; Mattarelli, P.; Biavati, B.; Carlsson, N.G.; Andlid, T. The potential of bifidobacteria as a source of natural folate. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudeja, P.K.; Kode, A.; Alnounou, M.; Tyagi, S.; Torania, S.; Subramanian, V.S.; Said, H.M. Mechanism of folate transport across the human colonic basolateral membrane. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001, 281, G54–G60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoog, S.; Taneri, P.E.; Roa Diaz, Z.M.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Troup, J.P.; Bally, L.; Franco, O.H.; Glisic, M.; Muka, T. Dietary factors and modulation of bacteria strains of akkermansia muciniphila and faecalibacterium prausnitzii: A systematic review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, T.; Liang, S.; Duan, Y.; Jin, F.; Qin, B. Structural changes of gut microbiota in parkinson’s disease and its correlation with clinical features. Sci. China Life Sci. 2017, 60, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Zheng, W.; He, Y.; Tang, W.; Wei, X.; He, R.; Huang, W.; Su, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, H.; et al. Gut microbiota in patients with parkinson’s disease in southern china. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2018, 53, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Taxon | Taxa Level | LDA Score | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value | Group with Higher Abundance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| f__Ruminococcaceae | family | 4.6572 | 0.001 | 0.006 | LL |
| f__Christensenellaceae | family | 4.2216 | 0.001 | 0.006 | LL |
| f__Lactobacillaceae | family | 3.7116 | 0.001 | 0.006 | LL |
| g__u(f__Ruminococcaceae) | genus | 4.3331 | 0.006 | 0.030 | LL |
| g__u(f__Christensenellaceae) | genus | 4.2426 | 0.001 | 0.007 | LL |
| g__Roseburia | genus | 4.0216 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | LL |
| g__Lactobacillus | genus | 3.9426 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | LL |
| c__Betaproteobacteria | class | 3.5691 | <0.0001 | 0.003 | HE |
| o__Burkholderiales | order | 3.5490 | <0.0001 | 0.003 | HE |
| f__u(o__Clostridiales) | family | 4.5760 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | HE |
| f__Veillonellaceae | family | 3.7684 | 0.002 | 0.008 | HE |
| f__(Mogibacteriaceae) | family | 3.5914 | 0.001 | 0.006 | HE |
| f__Alcaligenaceae | family | 3.5608 | 0.001 | 0.006 | HE |
| f__Peptococcaceae | family | 3.3366 | 0.004 | 0.015 | HE |
| f__Peptostreptococcaceae | family | 3.1999 | 0.011 | 0.037 | HE |
| g__u(o__Clostridiales) | genus | 4.5985 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | HE |
| g__Dorea | genus | 4.2574 | <0.0001 | 0.001 | HE |
| g__Sutterella | genus | 4.0443 | 0.001 | 0.007 | HE |
| g__u(f__Peptostreptococcaceae) | genus | 4.0241 | 0.004 | 0.021 | HE |
| g__(Ruminococcus) (Lachnospiraceae) | genus | 3.9725 | 0.001 | 0.008 | HE |
| g__Dialister | genus | 3.7867 | <0.0001 | 0.004 | HE |
| Taxon | More Presented in | p-Value | Adj. p-Value | LDA Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| g__u(f__Enterobacteriaceae) | Japanese LL | 0.004 | 0.018 | 4.461 |
| g__Enterococcus | Japanese LL | <0.0001 | 0.004 | 4.321 |
| g__Parabacteroides | Japanese LL | 0.003 | 0.013 | 4.128 |
| g__u(f__Rikenellaceae) | Japanese LL | 0.006 | 0.023 | 3.913 |
| g__Butyricimonas | Japanese LL | 0.017 | 0.047 | 3.887 |
| g__Granulicatella | Japanese LL | 0.005 | 0.021 | 3.835 |
| g__Fusobacterium | Japanese LL | <0.0001 | 0.001 | 3.827 |
| g__u(f__Peptostreptococcaceae) | Japanese LL | 0.001 | 0.004 | 3.747 |
| g__Desulfovibrio | Japanese LL | <0.0001 | 0.001 | 3.744 |
| g__Sutterella | Japanese LL | 0.009 | 0.031 | 3.670 |
| g__u(f__Ruminococcaceae) | Russian LL | <0.0001 | 0.001 | 4.591 |
| g__u(f__Lachnospiraceae) | Russian LL | 0.006 | 0.023 | 4.508 |
| g__Akkermansia | Russian LL | 0.011 | 0.033 | 4.291 |
| g__Coprococcus | Russian LL | 0.001 | 0.006 | 4.274 |
| g__Dorea | Russian LL | <0.0001 | 0.001 | 4.033 |
| g__Methanobrevibacter | Russian LL | <0.0001 | 0.000 | 3.863 |
| g__Roseburia | Russian LL | <0.0001 | 0.003 | 3.787 |
| g__u(f__Coriobacteriaceae) | Russian LL | 0.011 | 0.033 | 3.536 |
| Table. | More Presented in | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value | LDA Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| g__Coprococcus | Russian LL | 0.006 | 0.042 | 4.195 |
| g__Dorea | Russian LL | 0.000 | 0.000 | 4.003 |
| g__Roseburia | Russian LL | 0.004 | 0.033 | 3.467 |
| g__Eggerthella | Italian LL | 0.000 | 0.000 | 3.446 |
| g__u(f__Coriobacteriaceae) | Italian LL | 0.007 | 0.044 | 3.415 |
| g__Coprobacillus | Italian LL | 0.000 | 0.000 | 3.362 |
| g__u(c__Gemm-1) | Italian LL | 0.000 | 0.000 | 3.251 |
| g__Desulfovibrio | Italian LL | 0.008 | 0.046 | 3.218 |
| g__Nesterenkonia | Italian LL | 0.000 | 0.000 | 3.215 |
| g__Actinomyces | Italian LL | 0.002 | 0.017 | 3.192 |
| Factor | Median | IQR |
|---|---|---|
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 25.10 | 5.66 |
| Local frailty scale (0–7) | 3.00 | 1.25 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | 155.00 | 32.50 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg | 78.00 | 9.00 |
| Heart rate, per minute | 69.00 | 9.00 |
| Geriatric depression scale | 6.00 | 7.25 |
| IADL | 16.00 | 9.25 |
| MNA | 22.75 | 7.00 |
| Maximum carotid stenosis, % | 50.00 | 7.50 |
| Carotid IMT, mm | 1.31 | 0.25 |
| Femoral IMT, mm | 2.09 | 0.85 |
| Glycated hemoglobin, % | 5.79 | 0.50 |
| Protein, g/L | 67.40 | 2.85 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 89.40 | 22.23 |
| Mg, mmol/L | 0.88 | 0.11 |
| Fe, μmol/L | 12.90 | 5.40 |
| C-reactive protein, mg/L | 2.06 | 3.91 |
| Folic acid, nmol/L | 3.50 | 1.91 |
| Ionized calcium, mmol/L | 1.05 | 0.05 |
| Vitamin B12, pg/mL | 261.00 | 125.00 |
| NT-proBNP (n terminal fragment in the prohormone of brain natriuretic peptide), pg/mL | 976.30 | 1793.88 |
| Triglycerides, mmol/L | 1.04 | 0.34 |
| High density lipoproteins, mmol/L | 1.43 | 0.48 |
| Low density lipoproteins, mmol/L | 3.55 | 1.18 |
| Atherogenic index | 2.89 | 1.31 |
| Grip strength, kg | 17.00 | 6.38 |
| Montreal Cognitive Assessment | 11.50 | 18.00 |
| MMSE | 23.00 | 25.00 |
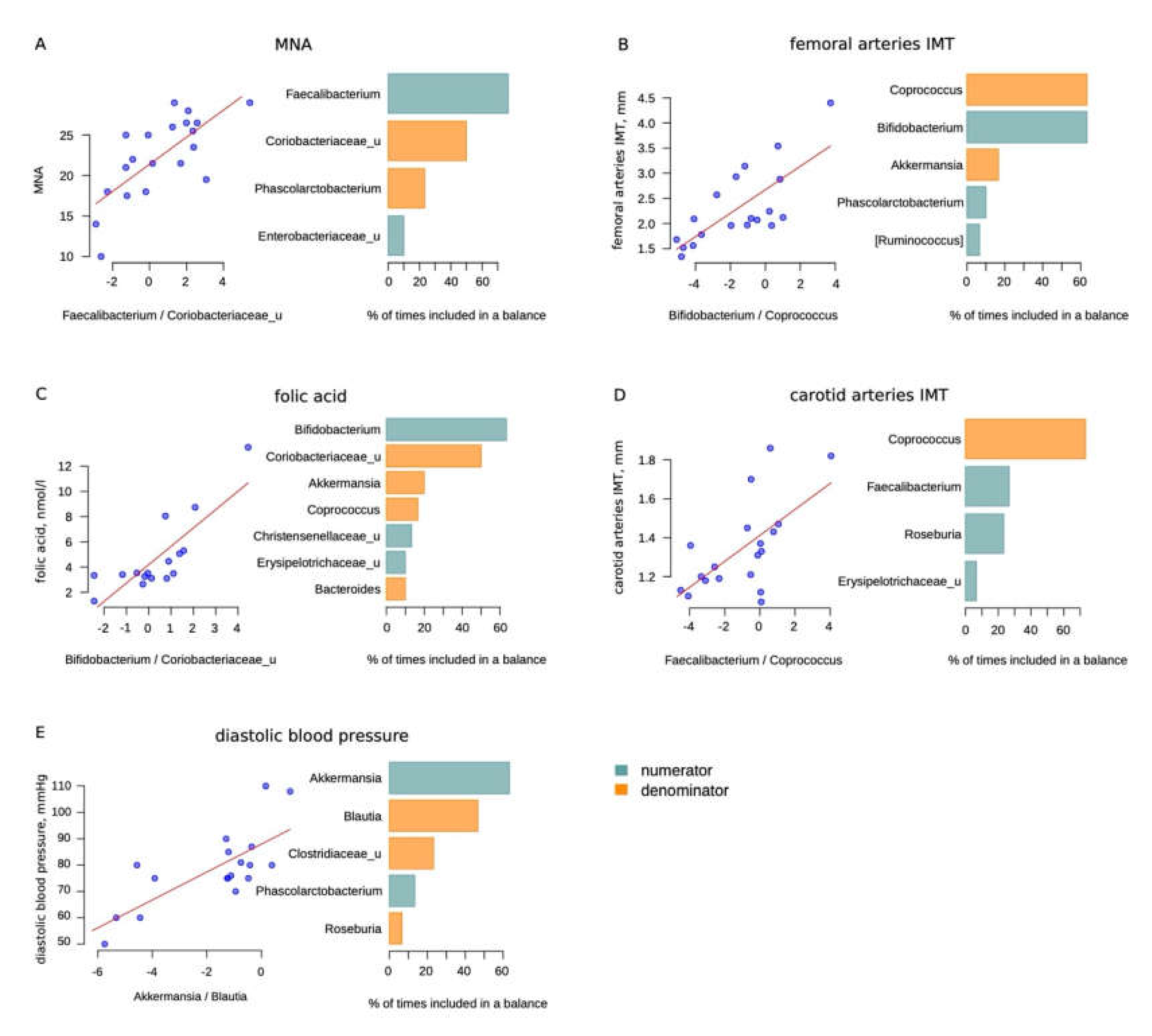
| Factor | Association Direction | Bacteria | R2 | p-Value for the Appropriate Balance | Adjusted p-Value for the Appropriate Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Femoral arteries IMT | + | Bifidobacterium | 0.5425 | 0.0003 | 0.0086 |
| - | Coprococcus | ||||
| Carotid arteries IMT | + | Faecalibacterium | 0.3868 | 0.0044 | 0.0876 |
| - | Coprococcus | ||||
| Folic acid | + | Bifidobacterium | 0.6486 | 0.0001 | 0.0028 |
| - | Coriobacteriaceae | ||||
| MNA | + | Faecalibacterium | 0.4941 | 0.0003 | 0.0086 |
| - | Coriobacteriaceae_u | ||||
| Diastolic blood pressure | + | Akkermansia | 0.5218 | 0.0004 | 0.0108 |
| - | Blautia * |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kashtanova, D.A.; Klimenko, N.S.; Strazhesko, I.D.; Starikova, E.V.; Glushchenko, O.E.; Gudkov, D.A.; Tkacheva, O.N. A Cross-Sectional Study of the Gut Microbiota Composition in Moscow Long-Livers. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081162
Kashtanova DA, Klimenko NS, Strazhesko ID, Starikova EV, Glushchenko OE, Gudkov DA, Tkacheva ON. A Cross-Sectional Study of the Gut Microbiota Composition in Moscow Long-Livers. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(8):1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081162
Chicago/Turabian StyleKashtanova, Daria A., Nataliya S. Klimenko, Irina D. Strazhesko, Elizaveta V. Starikova, Oksana E. Glushchenko, Denis A. Gudkov, and Olga N. Tkacheva. 2020. "A Cross-Sectional Study of the Gut Microbiota Composition in Moscow Long-Livers" Microorganisms 8, no. 8: 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081162
APA StyleKashtanova, D. A., Klimenko, N. S., Strazhesko, I. D., Starikova, E. V., Glushchenko, O. E., Gudkov, D. A., & Tkacheva, O. N. (2020). A Cross-Sectional Study of the Gut Microbiota Composition in Moscow Long-Livers. Microorganisms, 8(8), 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081162





