Effects of Vitamin B2 Supplementation in Broilers Microbiota and Metabolome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals, Housing and Experimental Diets
2.2. Sampling
2.3. DNA Extraction from Caeca, Ileum and Litter Samples
2.4. 16S rRNA Gene PCR Amplification and Sequencing
2.5. Bioinformatics and Statistics in Microbiota Analysis
2.6. Sample Preparation for NMR Analysis
2.7. NMR Spectra Acquisition
2.8. H-NMR Spectra Pre-Processing
2.9. Bioinformatics and Statistics for Metabolomics
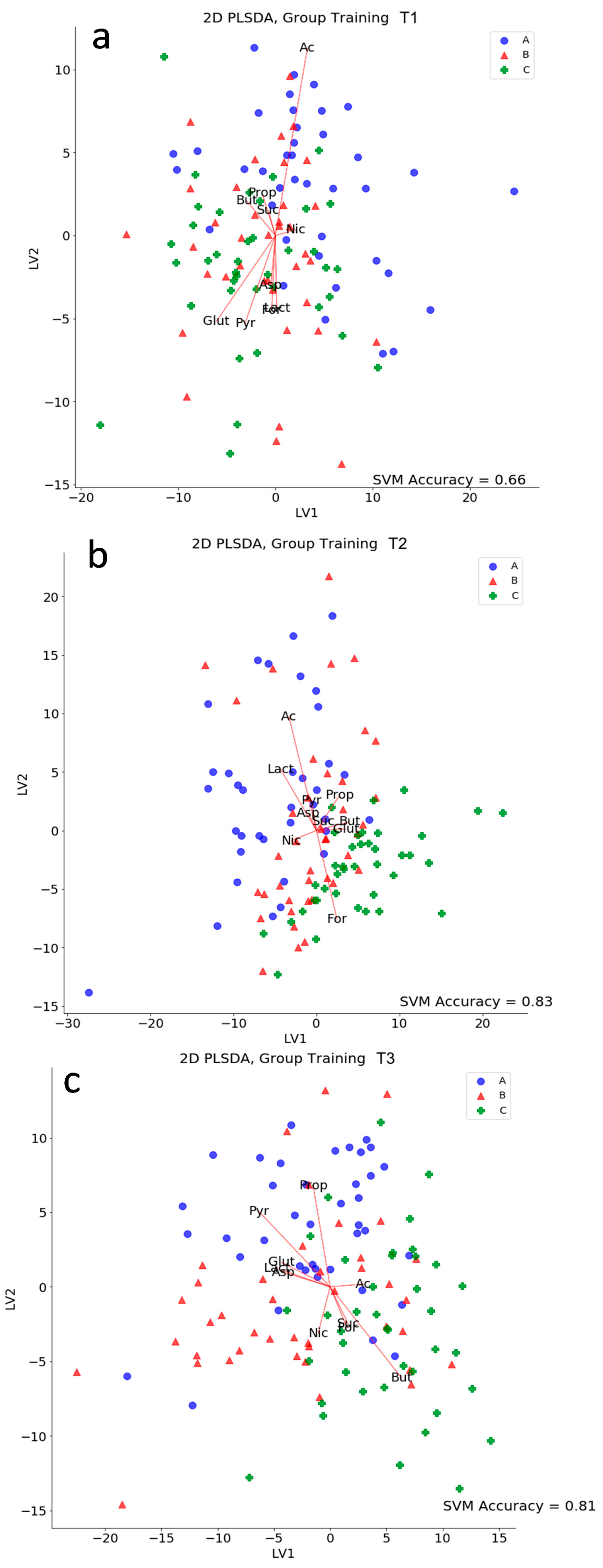
2.10. Partial Least Square Discriminant Analysis (PLS-DA)
2.11. Classification
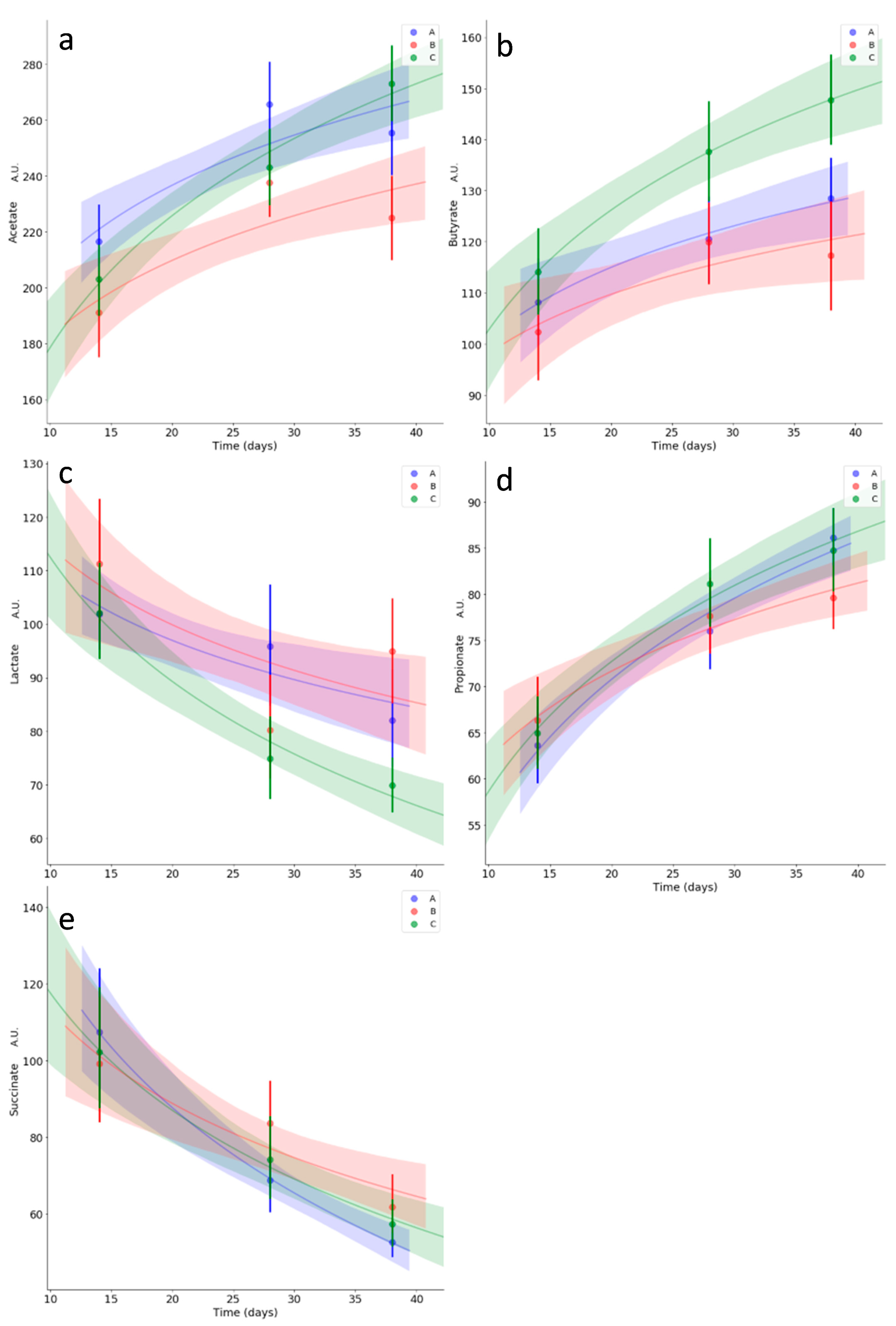
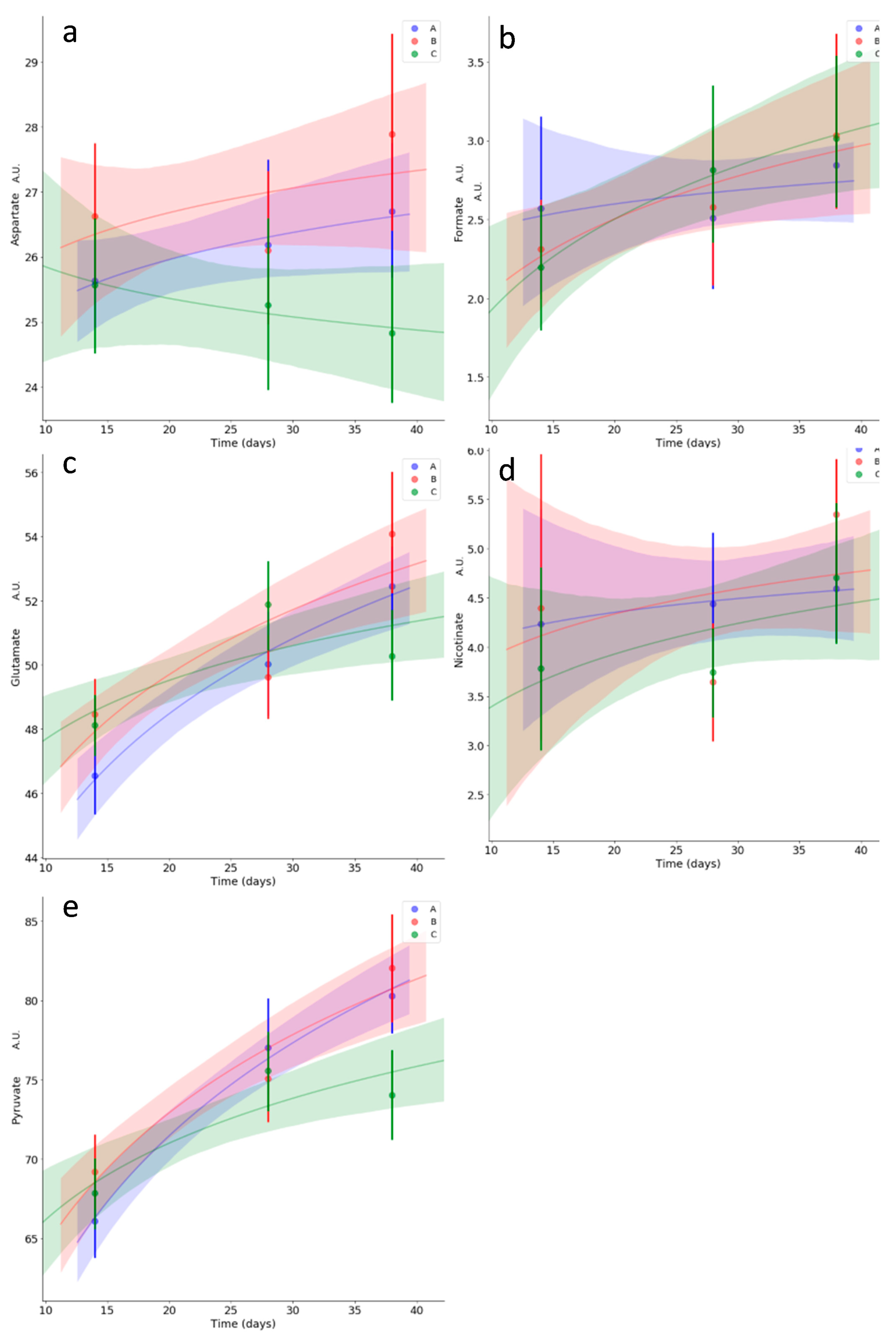
2.12. Kinetics Fitting
3. Results
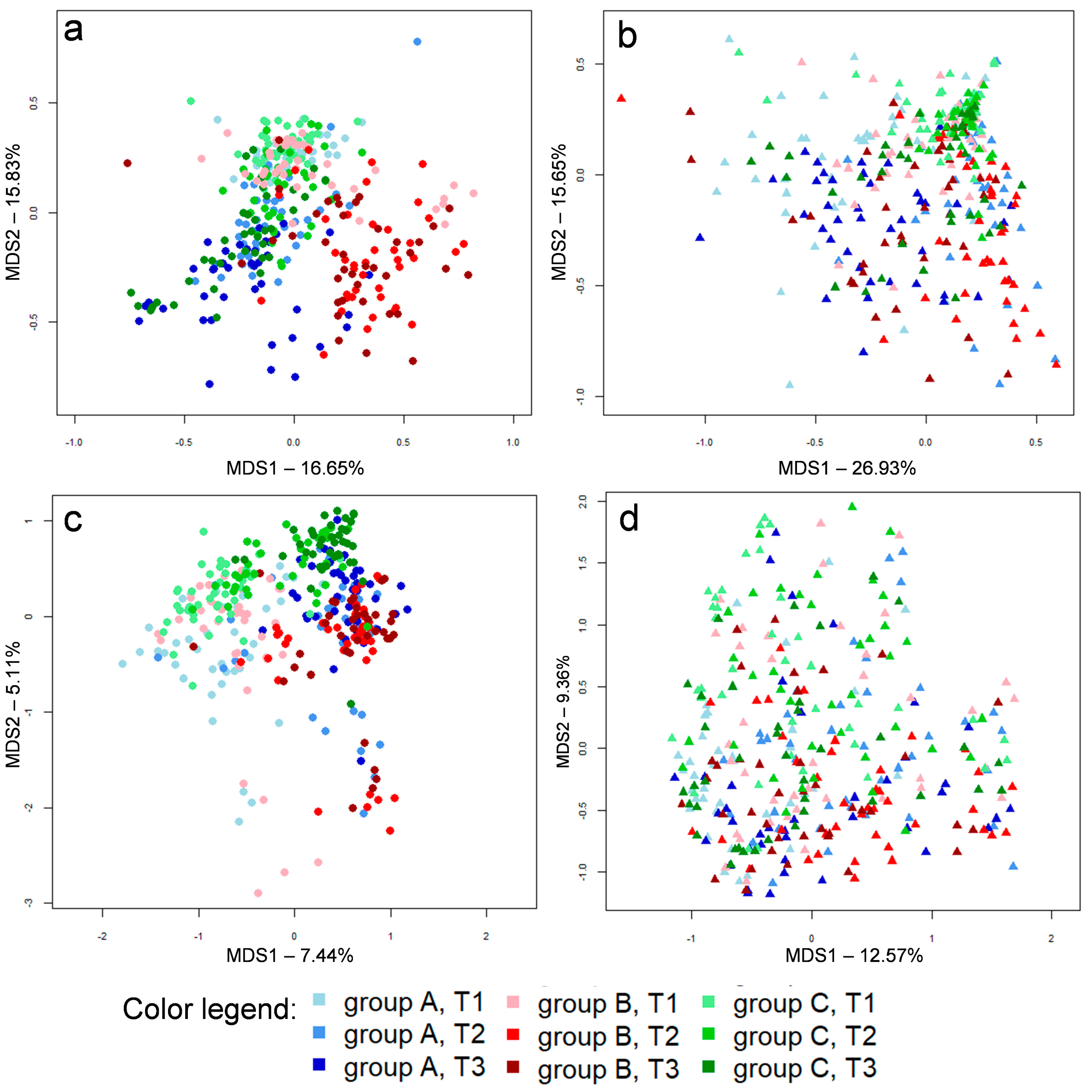
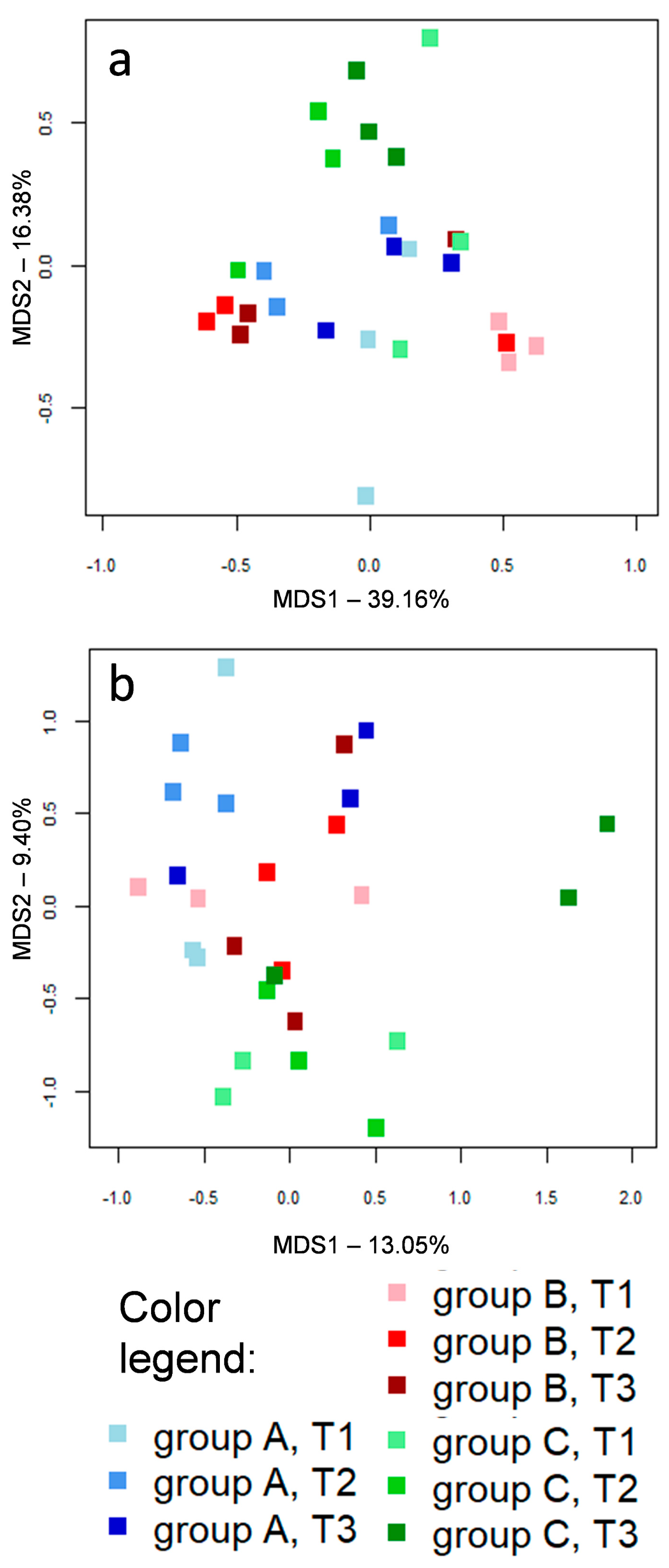
3.1. Microbial Communities
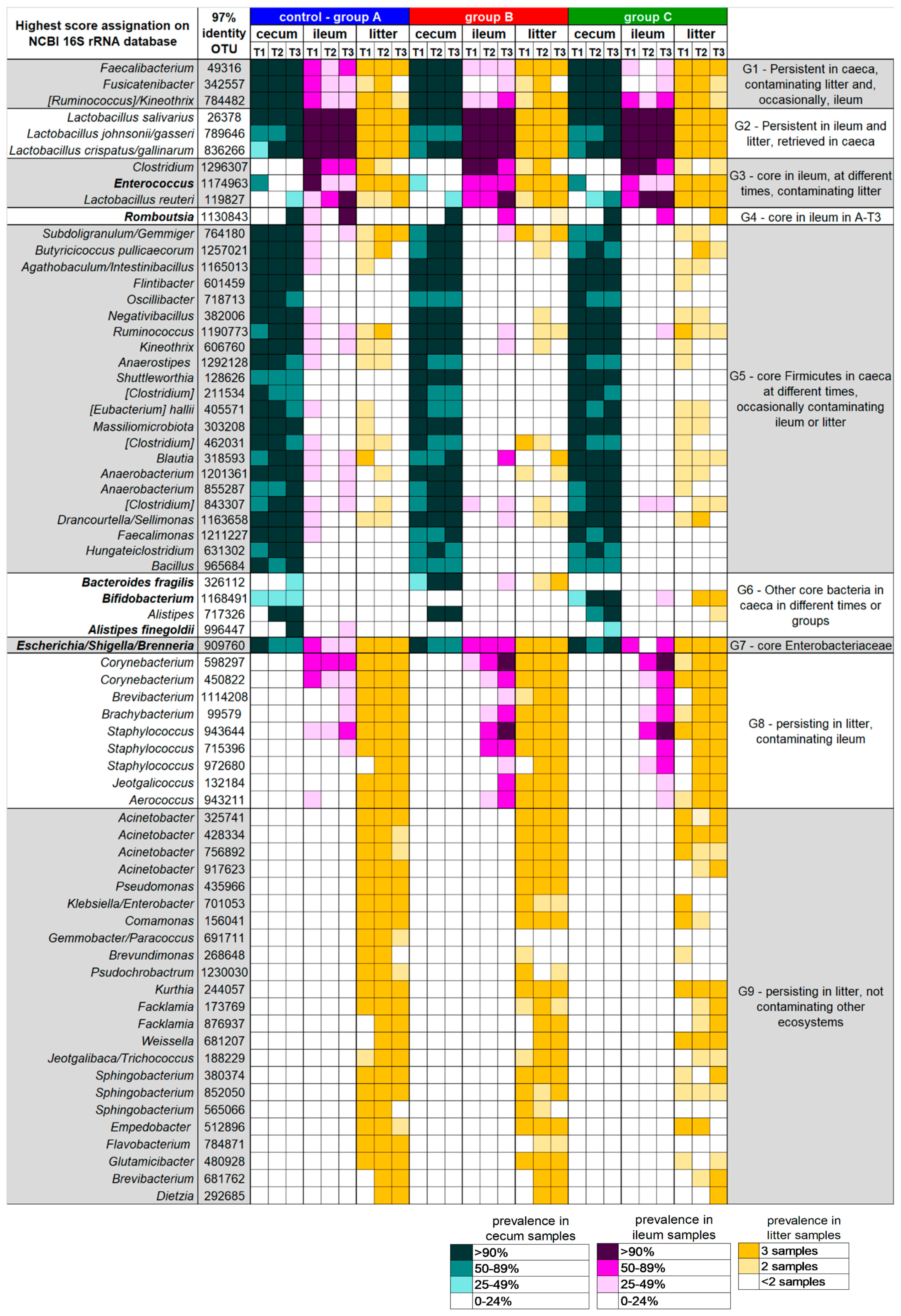
3.2. Caeca, Ileum and Litter Microbiota Composition
3.3. Ecological Perspective of Broiler Caeca, Ileum and Litter Microbiota
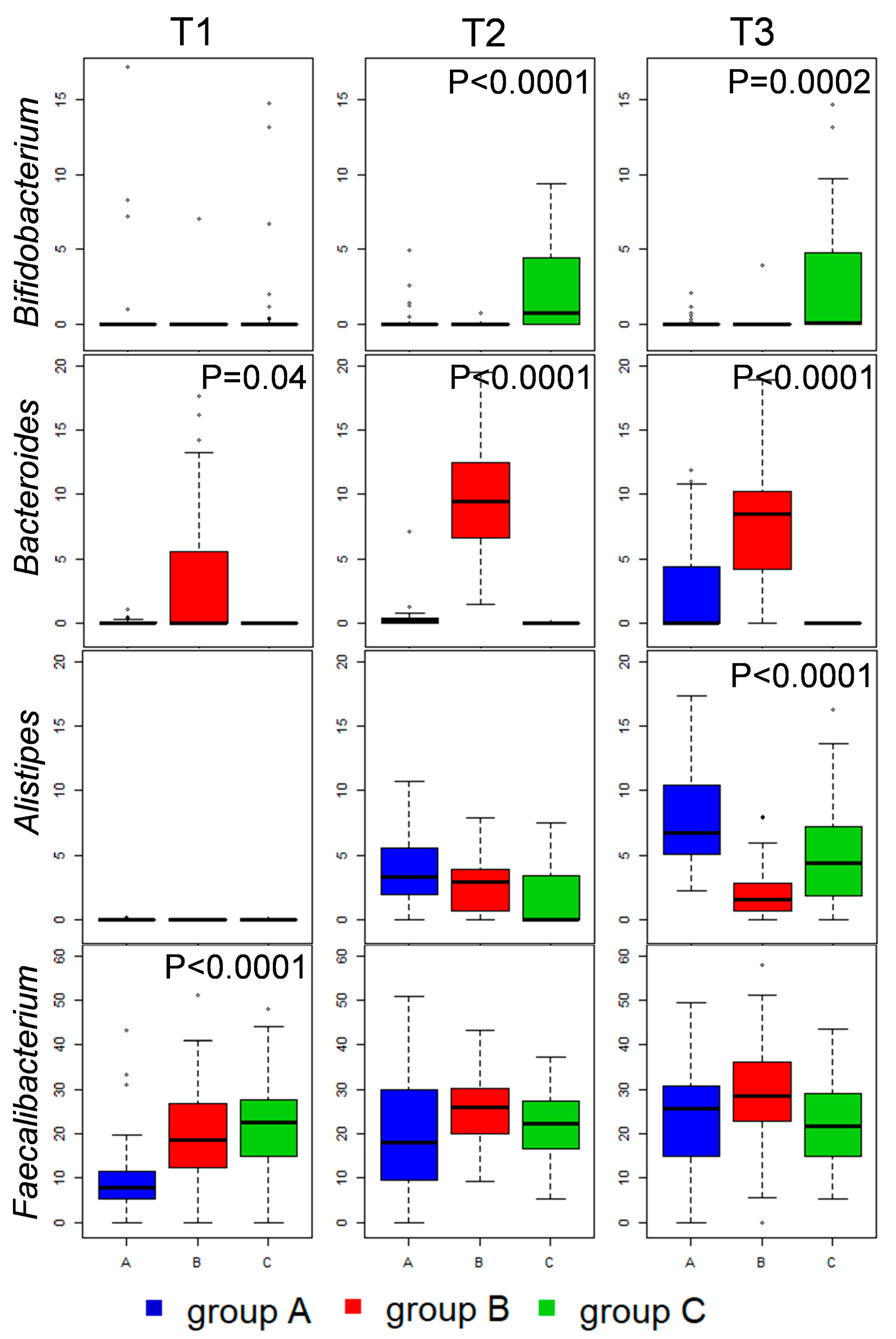
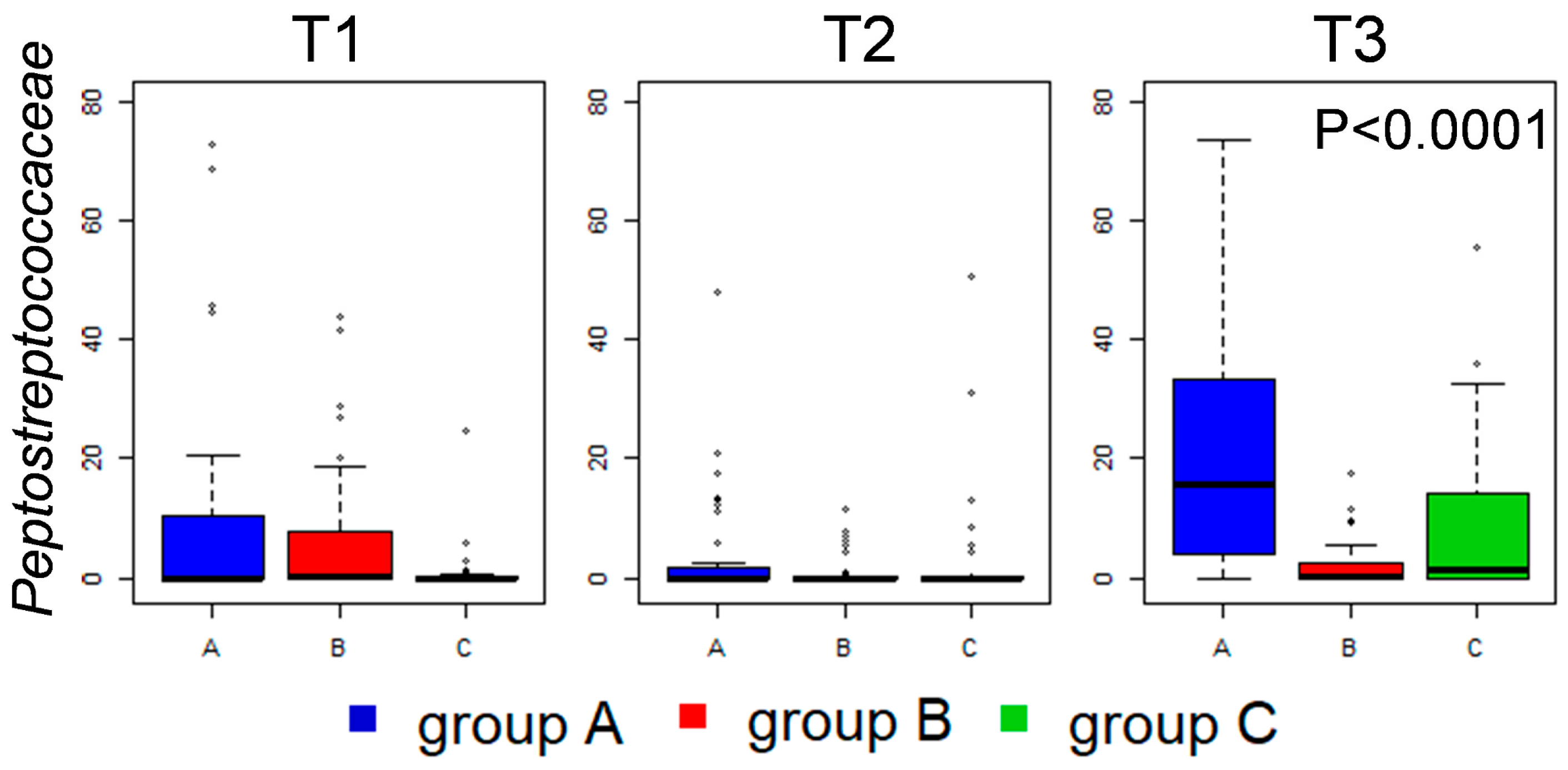
3.4. Caeca Metabolome Analysis
3.5. Kinetics of Relevant Metabolites
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borda-Molina, D.; Seifert, J.; Camarinha-Silva, A. Current Perspectives of the Chicken Gastrointestinal Tract and Its Microbiome. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz Carrasco, J.M.; Casanova, N.A.; Fernández Miyakawa, M.E. Microbiota, Gut Health and Chicken Productivity: What Is the Connection? Microorganisms 2019, 7, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conway, A. Top poultry countries to add 15 million metric tons by 2027. Poult. Trends 2018, 22–31. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/237597/leading-10-countries-worldwide-in-poultry-meat-production-in-2007/ (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Yadav, S.; Jha, R. Strategies to modulate the intestinal microbiota and their effects on nutrient utilization, performance, and health of poultry. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2019, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celi, P.; Cowieson, A.J.; Fru-Nji, F.; Steinert, R.E.; Kluenter, A.-M.; Verlhac, V. Gastrointestinal functionality in animal nutrition and health: New opportunities for sustainable animal production. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2017, 234, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kers, J.G.; Velkers, F.C.; Fischer, E.A.J.; Hermes, G.D.A.; Stegeman, J.A.; Smidt, H. Host and Environmental Factors Affecting the Intestinal Microbiota in Chickens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waite, D.W.; Taylor, M.W. Exploring the avian gut microbiota: Current trends and future directions. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Cesare, A.; Faria do Valle, Ì.; Sala, C.; Sirri, F.; Astolfi, A.; Castellani, G.; Manfreda, G. Effect of a low protein diet on chicken ceca microbiome and productive performances. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 3963–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, B.B.; Lillehoj, H.S.; Kogut, M.H.; Kim, W.K.; Maurer, J.J.; Pedroso, A.; Lee, M.D.; Collett, S.R.; Johnson, T.J.; Cox, N.A. The chicken gastrointestinal microbiome. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2014, 360, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eeckhaut, V.; Van Immerseel, F.; Croubels, S.; De Baere, S.; Haesebrouck, F.; Ducatelle, R.; Louis, P.; Vandamme, P. Butyrate production in phylogenetically diverse Firmicutes isolated from the chicken caecum. Microb. Biotechnol. 2011, 4, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oakley, B.B.; Kogut, M.H. Spatial and Temporal Changes in the Broiler Chicken Caecal and Fecal Microbiomes and Correlations of Bacterial Taxa with Cytokine Gene Expression. Front. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ranjitkar, S.; Lawley, B.; Tannock, G.; Engberg, R.M. Bacterial Succession in the Broiler Gastrointestinal Tract. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 2399–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, T.J.; Youmans, B.P.; Noll, S.; Cardona, C.; Evans, N.P.; Karnezos, T.P.; Ngunjiri, J.M.; Abundo, M.C.; Lee, C.W. A Consistent and Predictable Commercial Broiler Chicken Bacterial Microbiota in Antibiotic-Free Production Displays Strong Correlations with Performance. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00362-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clavijo, V.; Flórez, M.J.V. The gastrointestinal microbiome and its association with the control of pathogens in broiler chicken production: A review. Poult. Sci. 2018, 97, 1006–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Martels, J.Z.H.; Bourgonje, A.R.; Klaassen, M.A.Y.; Alkhalifah, H.A.A.; Sadaghian Sadabad, M.; Vich Vila, A.; Gacesa, R.; Gabriëls, R.Y.; Steinert, R.E.; Jansen, B.H.; et al. Riboflavin supplementation in patients with Crohn’s disease (RISE-UP study). J. Crohns Colitis. 2019, 14, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, S.; Ashraf, M.A.; Sajid, M.; Shahzad, A.; Rafique, A.; Mahmood, M.S. Evaluation of synergistic antimicrobial effect of vitamins (A, B1, B2, B6, B12, C, D, E and K) with antibiotics against resistant bacterial strains. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2018, 13, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ma, L.; Zeng, Q.; Jiang, X.; Li, A.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, T. Antibiotic-mediated changes in the fecal microbiome of broiler chickens define the incidence of antibiotic resistance genes. Microbiome 2018, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biagi, E.; D’Amico, F.; Soverini, M.; Angelini, V.; Barone, M.; Turroni, S.; Rampelli, S.; Pari, S.; Brigidi, P.; Candela, M. Faecal bacterial communities from Mediterranean loggerhead sea turtles (Caretta caretta). Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2018, 11, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masella, A.P.; Bartram, A.K.; Truszkowski, J.M.; Brown, D.G.; Neufeld, J.D. PANDAseq: Paried-end assembler for illumine sequences. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulaszewska, M.M.; Weinert, C.H.; Trimigno, A.; Portmann, R.; Andres Lacueva, C.; Badertscher, R.; Brennan, L.; Brunius, C.; Bub, A.; Capozzi, F.; et al. Nutrimetabolomics: An Integrative Action for Metabolomic Analyses in Human Nutritional Studies. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 63, 1800384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassarre, M.E.; Di Mauro, A.; Tafuri, S.; Rizzo, V.; Gallone, M.S.; Mastromarino, P.; Capobianco, D.; Laghi, L.; Zhu, C.; Capozza, M.; et al. Effectiveness and safety of a probiotic-mixture for the treatment of infantile colic: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial with fecal real-time PCR and NMR-based metabolomics analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dieterle, F.; Ross, A.; Schlotterbeck, G.; Senn, H. Probabilistic Quotient Normalization as Robust Method to Account for Dilution of Complex Biological Mixtures. Application in 1 H NMR Metabonomics. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4281–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wold, H. Path models with latent variables: The NIPALS approach. In Quantitative Sociology: International Perspectives on Mathematical and Statistical Model Building; Blalock, H.M., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1975; pp. 307–357. [Google Scholar]
- Savitzky, A.; Golay, M.J.E. Smoothing and Differentiation of Data by Simplified Least Squares Procedures. Anal. Chem. 1964, 36, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Peng, S.; Jiang, A.; Wei, J.; Li, C.; Tan, J. Asymmetric least squares for multiple spectra baseline correction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 683, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-J. Libsvm: A Library for Sup- Port Vector Machines. 2013. Available online: http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/~cjlin/papers/libsvm.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Efron, B. Bootstrap Methods: Another Look at the Jackknife. Ann. Statist. 1979, 7, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, U.Z.; Sivaloganathan, L.; McKenna, A.; Richmond, A.; Kelly, C.; Linton, M.; Stratakos, A.C.; Lavery, U.; Elmi, A.; Wren, B.W.; et al. Comprehensive Longitudinal Microbiome Analysis of the Chicken Caeca Reveals a Shift From Competitive to Environmental Drivers and a Window of Opportunity for Campylobacter. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.; Jin, T.E.; Chang, D.H.; Rhee, M.S.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; Park, D.S.; Kim, B.C. Agathobaculum butyriciproducens gen. nov. sp. nov., a strict anaerobic, butyrate-producing gut bacterium isolated from human faeces and reclassification of Eubacterium desmolans as Agathobaculum desmolans comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3656–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, K.N.; Blanchard, J.L. Kineothrix alysoides, gen. nov., sp. nov., a saccharolytic butyrate-producer within the family Lachnospiraceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, M.; Ikeyama, N.; Yuki, M.; Ohkuma, M. Draft Genome Sequence of Faecalimonas umbilicata JCM 30896T, an Acetate-Producing Bacterium Isolated from Human Feces. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2018, 7, e01091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Blaser, M.J. Do you have a probiotic in your future? Microbes Infect. 2008, 10, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- EC Regulation 1831/2003. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/en/index.htm (accessed on 10 February 2020).
- Van Immerseel, F.; Eeckhaut, V.; Moore, R.J.; Choct, M.; Ducatelle, R. Beneficial microbial signals from alternative feed ingredients: A way to improve sustainability of broiler production? Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubio, L.A. Possibilities of early life programming in broiler chickens via intestinal microbiota modulation. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinert, R.; Lee, Y.K.; Sybesma, W. Vitamins for the gut microbiome. Trend. Mol. Med. 2020, 26, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.H.; Peng, H.W.; Wright, A.D.; Bai, S.P.; Ding, X.M.; Zeng, Q.F.; Li, H.; Zheng, P.; Su, Z.W.; Cui, R.Y.; et al. Broilers fed dietary vitamins harbor higher diversity of caecal bacteria and higher ratio of Clostridium, Faecalibacterium, and Lactobacillus than broilers with no dietary vitamins revealed by 16S rRNA gene clone libraries. Poult. Sci. 2013, 92, 2358–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torok, V.A.; Hughes, R.J.; Mikkelsen, L.L.; Perez-Maldonado, R.; Balding, K.; MacAlpine, R.; Percy, N.J.; Ophel-Keller, K. Identification and characterization of potential performance-related gut microbiotas in broiler chickens across various feeding trials. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 5868–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stanley, D.; Hughes, R.J.; Geier, M.S.; Moore, R.J. Bacteria within the Gastrointestinal Tract Microbiota Correlated with Improved Growth and Feed Conversion: Challenges Presented for the Identification of Performance Enhancing Probiotic Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ventura, M.; Canchaya, C.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Gupta, R.S.; van Sinderen, D. Genomics as a means to understand bacterial phylogeny and ecological adaptation: The case of bifidobacteria. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2007, 91, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz Carrasco, J.M.; Redondo, E.A.; Pin Viso, N.D.; Redondo, L.M.; Farber, M.D.; Fernández Miyakawa, M.E. Tannins and Bacitracin Differentially Modulate Gut Microbiota of Broiler Chickens. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 1879168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasato, I.; Ferrocino, I.; Biasibetti, E.; Grego, E.; Dabbou, S.; Sereno, A.; Gai, F.; Gasco, L.; Schiavone, A.; Cocolin, L.; et al. Modulation of intestinal microbiota, morphology and mucin composition by dietary insect meal inclusion in free-range chickens. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.Y.; Hou, R.; Yang, G.Q.; Zhao, F.; Dong, W.G. In vitro effects of inulin and soya bean oligosaccharide on skatole production and the intestinal microbiota in broilers. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ni, J.; Li, H. Effect of green tea and mulberry leaf powders on the gut microbiota of chicken. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.R.; Lepp, D.; Godfrey, D.V.; Orban, S.; Ross, K.; Delaquis, P.; Diarra, M.S. Effects of wild blueberry (Vaccinium angustifolium) pomace feeding on gut microbiota and blood metabolites in free-range pastured broiler chickens. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 3739–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Mao, P.; Tian, X.; Guo, Q.; Meng, L. Effects of dietary supplementation of alfalfa meal on growth performance, carcass characteristics, meat and egg quality, and intestinal microbiota in Beijing-you chicken. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 2250–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda-Quiroga, C.; Camarinha-Silva, A.; Borda-Molina, D.; Atxaerandio, R.; Ruiz, R.; García-Rodríguez, A. Feeding broilers with dry whey powder and whey protein concentrate affected productive performance, ileal digestibility of nutrients and caecal microbiota community. Animal 2018, 12, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, D.; Denman, S.E.; Hughes, R.J.; Geier, M.S.; Crowley, T.M.; Chen, H.; Haring, V.R.; Moore, R.J. Intestinal microbiota associated with differential feed conversion efficiency in chickens. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Hanson, R.W.; Berger, N.A.; Trubitsyn, A. Reprogramming of energy metabolism as a driver of aging. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 15410–15420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Louis, P.; Hold, G.L.; Flint, H.J. The gut microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurburg, S.D.; Brouwer, M.S.M.; Ceccarelli, D.; van der Goot, J.; Jansman, A.J.M.; Bossers, A. Patterns of community assembly in the developing chicken microbiome reveal rapid primary succession. Microbiologyopen 2019, 8, e00821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards-Rios, P.; Fothergill, J.; Bernardeau, M.; Wigley, P. Development of the Ileal Microbiota in Three Broiler Breeds. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mancabelli, L.; Ferrario, C.; Milani, C.; Mangifesta, M.; Turroni, F.; Duranti, S.; Lugli, G.A.; Viappiani, A.; Ossiprandi, M.C.; van Sinderen, D.; et al. Insights into the biodiversity of the gut microbiota of broiler chickens. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 4727–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crippen, T.L.; Sheffield, C.L.; Singh, B.; Byrd, J.A.; Beier, R.C. How Management Practices Within a Poultry House During Successive Flock Rotations Change the Structure of the Soil Microbiome. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dumas, M.D.; Polson, S.W.; Ritter, D.; Ravel, J.; Gelb, J., Jr.; Morgan, R.; Wommack, K.E. Impacts of poultry house environment on poultry litter bacterial community composition. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández-Rubio, C.; Ordóñez, C.; Abad-González, J.; Garcia-Gallego, A.; Honrubia, M.P.; Mallo, J.J.; Balaña-Fouce, R. Butyric acid-based feed additives help protect broiler chickens from Salmonella Enteritidis infection. Poult. Sci. 2009, 88, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmasso, G.; Nguyen, H.T.; Yan, Y.; Charrier-Hisamuddin, L.; Sitaraman, S.V.; Merlin, D. Butyrate transcriptionally enhances peptide transporter PepT1 expression and activity. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Group | n. of Chickens | Chicken Weight (g) (Mean ± SD) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 days | 28 days | 42 days | ||
| Group A—control 5 mg/kg VitB2 | 120 | 528.78 ± 8.48 | 1431.95 ± 15.56 | 2619.85 ± 22.10 |
| Group B—50 mg/kg VitB2 | 119 | 532.97 ± 9.36 | 1433.43 ± 12.63 | 2622.33 ± 20.51 |
| Group C—100mg/kg VitB2 | 118 | 534.46 ± 9.36 | 1433.15 ± 13.66 | 2618.92 ± 19.27 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Biagi, E.; Mengucci, C.; Barone, M.; Picone, G.; Lucchi, A.; Celi, P.; Litta, G.; Candela, M.; Manfreda, G.; Brigidi, P.; et al. Effects of Vitamin B2 Supplementation in Broilers Microbiota and Metabolome. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081134
Biagi E, Mengucci C, Barone M, Picone G, Lucchi A, Celi P, Litta G, Candela M, Manfreda G, Brigidi P, et al. Effects of Vitamin B2 Supplementation in Broilers Microbiota and Metabolome. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(8):1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081134
Chicago/Turabian StyleBiagi, Elena, Carlo Mengucci, Monica Barone, Gianfranco Picone, Alex Lucchi, Pietro Celi, Gilberto Litta, Marco Candela, Gerardo Manfreda, Patrizia Brigidi, and et al. 2020. "Effects of Vitamin B2 Supplementation in Broilers Microbiota and Metabolome" Microorganisms 8, no. 8: 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081134
APA StyleBiagi, E., Mengucci, C., Barone, M., Picone, G., Lucchi, A., Celi, P., Litta, G., Candela, M., Manfreda, G., Brigidi, P., Capozzi, F., & De Cesare, A. (2020). Effects of Vitamin B2 Supplementation in Broilers Microbiota and Metabolome. Microorganisms, 8(8), 1134. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081134






