Multidrug-Resistant Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Strains and Association of Their Virulence Genes in Bangladesh
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
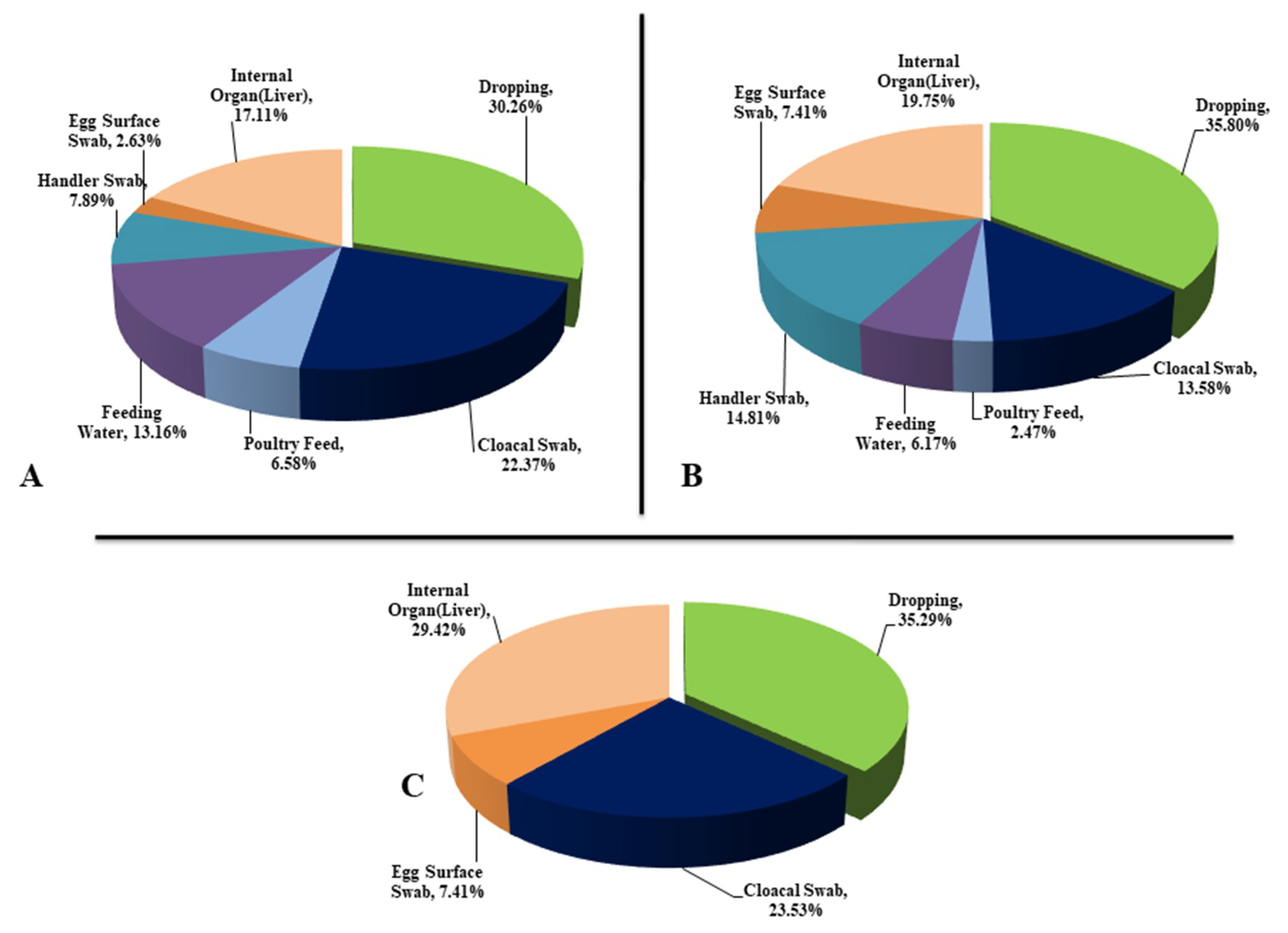
2.1. Sample Collection and Processing
2.2. Isolation and Identification of Pathogenic E. coli
2.3. Phenotypic Virulence Assays
2.3.1. Congo Red Binding Assay
2.3.2. Production of Hemolysins and Swimming Motility Assays
2.3.3. Biofilm Formation Assay
2.4. DNA Extraction
2.5. Molecular Typing Methods
2.6. Clermont’s Phylogenetic Typing
2.7. Ribosomal Gene (16S rRNA) Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.8. Antimicrobial Sensitivity Testing
2.9. Detection of Virulence Genes
2.10. Plasmid DNA Isolation
2.11. Discriminatory Index (D)
2.12. Correspondence Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Characterization of APEC: Isolation and Identification
3.2. Genetic Diversity of APEC by Molecular Fingerprinting
3.3. Phylogenetic Distribution of APEC in Poultry Isolates
3.4. Biofilm Formation (BF) Assay
3.5. Distribution of Virulence Genes of APEC in Poultry Isolates
3.6. Genetic Diversity of APEC Isolates Based on Ribosomal Gene (16S rRNA) Sequencing
3.7. Antibiogram Profiling of Circulating APEC Phylotypes
3.8. Existence of Plasmid
3.9. Associations between Sample Types, APEC Phylotypes, and Pathogenic Intensity
4. Discussion
4.1. Circulatory Molecular Phylotypes of the APEC in Bangladesh
4.2. Pathogenic Properties of the Circulating APEC
4.3. Correlations between Phylotypes and MDR of Circulating APEC
4.4. Correlations among Sample Types, Molecular Typing Methods, Pathogenic Intensity, and MDR Properties of Circulating APEC
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability
References
- Jang, J.; Hur, H.G.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Byappanahalli, M.N.; Yan, T.; Ishii, S. Environmental Escherichia coli: Ecology and public health implications—A review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 123, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solà-Ginés, M.; Cameron-Veas, K.; Badiola, I.; Dolz, R.; Majó, N.; Dahbi, G.; Viso, S.; Mora, A.; Blanco, J.; Piedra-Carrasco, N.; et al. Diversity of Multi-Drug Resistant Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) Causing Outbreaks of Colibacillosis in Broilers during 2012 in Spain. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kabiswa, W.; Nanteza, A.; Tumwine, G.; Majalija, S. Phylogenetic Groups and Antimicrobial Susceptibility Patterns of Escherichia coli from Healthy Chicken in Eastern and Central Uganda. J. Vet. Med. 2018, 2018, 9126467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, A.; Saralaya, V.; Adhikari, P.; Shenoy, S.; Baliga, S.; Hegde, A. Characterization of Escherichia coli Phylogenetic Groups Associated with Extraintestinal Infections in South Indian Population. Ann. Med. Health Sci. Res. 2015, 5, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tikoo, A.; Tripathi, A.K.; Verma, S.C.; Agrawal, N.; Nath, G. Application of PCR fingerprinting techniques for identification and discrimination of Salmonella isolates. Current Sci. 2001, 80, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, M.Y.; Min, K.B.; Lee, K.-M.; Yoon, Y.; Kim, Y.; Oh, Y.T.; Lee, K.; Chun, J.; Kim, B.-Y.; Yoon, S.-H.; et al. A single gene of a commensal microbe affects host susceptibility to enteric infection. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moulin-Schouleur, M.; Répérant, M.; Laurent, S.; Brée, A.; Mignon-Grasteau, S.; Germon, P.; Schouler, C. Extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli strains of avian and human origin: Link between phylogenetic relationships and common virulence patterns. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3366–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dombek, P.E.; Johnson, L.K.; Zimmerley, S.T.; Sadowsky, M.J. Use of repetitive DNA sequences and the PCR to differentiate Escherichia coli isolates from human and animal sources. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 2572–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clermont, O.; Christenson, J.K.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.M. The Clermont Escherichia coli phylo-typing method revisited: Improvement of specificity and detection of new phylo-groups. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daga, A.P.; Koga, V.L.; Soncini, J.G.M.; De Matos, C.M.; Perugini, M.R.E.; Pelisson, M.; Kobayashi, R.K.T.; Vespero, E.C. Escherichia coli Bloodstream Infections in Patients at a University Hospital: Virulence Factors and Clinical Characteristics. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Johnston, B.D.; Gordon, D.M. Rapid and Specific Detection of the Escherichia coli Sequence Type 648 Complex within Phylogroup F. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 1116–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pasquali, F.; Lucchi, A.; Braggio, S.; Giovanardi, D.; Franchini, A.; Stonfer, M.; Manfreda, G. Genetic diversity of Escherichia coli isolates of animal and environmental origins from an integrated poultry production chain. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 178, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, M.; Toufeer, M.; Bravo, C.N.; Lai, V.; Rempel, H.; Manges, A.; Diarra, M.S. Characterization of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from retail poultry meats from Alberta, Canada. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 177, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanbarpour, R.; Sami, M.; Salehi, M.; Ouromiei, M. Phylogenetic background and virulence genes of Escherichia coli isolates from colisepticemic and healthy broiler chickens in Iran. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2011, 43, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-M.; Liao, X.-P.; Zhang, W.-J.; Jiang, H.-X.; Sun, J.; Zhang, M.-J.; He, X.-F.; Lao, D.-X.; Liu, Y.-H. Prevalence of Serogroups, Virulence Genotypes, Antimicrobial Resistance, and Phylogenetic Background of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli in South of China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, D.R.A.; Wijewardana, T.G.; Gunawardena, G.A.; Poxton, I.R. Distribution of lipopolysaccharide core types among avian pathogenic Escherichia coli in relation to the major phylogenetic groups. Vet. Microbiol. 2008, 132, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müştak, H.K.; Gunaydin, E.; Kaya, İ.B.; Salar, M.Ö.; Babacan, O.; Onat, K.; Ata, Z.; Diker, K.S. Phylo-typing of clinical Escherichia coli isolates originating from bovine mastitis and canine pyometra and urinary tract infection by means of quadruplex PCR. Vet. Q. 2015, 35, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Carli, S.; Ikuta, N.; Lehmann, F.K.M.; da Silveira, V.P.; de MeloPredebon, G.; Fonseca, A.S.K.; Lunge, V.R. Virulence gene content in Escherichia coli isolates from poultry flocks with clinical signs of colibacillosis in Brazil. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 2635–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knöbl, T.; Saidenberg, A.; Moreno, A.M.; Gomes, T.A.T.; Vieira, M.A.; Leite, D.S.; Blanco, J.; Ferreira, A.J.P. Serogroups and virulence genes of Escherichia coli isolated from psittacine birds. Pesqui. Vet. Bras. 2011, 31, 916–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amer, M.M.; Bastamy, M.A.; Ibrahim, H.M.; Salim, M.M. Isolation and characterization of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli from broiler chickens in some Governorates of Egypt. Vet. Med. J. Giza 2015, 61, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zahid, A.A.; AL-Mossawei, M.T.; Mahmood, A.B. In vitro and In vivo Pathogenicity tests of Local Isolates APEC from Naturally Infected Broiler in Baghdad. Int. J. Adv. Res. Biol. Sci. 2016, 3, 89–100. [Google Scholar]
- Stebbins, M.B.; Berkhoff, H.A.; Corbett, W.T. Epidemiological studies of Congo Red E. coli in broiler chicken. Can. J. Vet. Res. 1992, 56, 202–205. [Google Scholar]
- Reichhardt, C.; Cegelski, L. The Congo red derivative FSB binds to curli amyloid fibers and specifically stains curliated E. coli. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.D.; Hashmi, A.; Anjum, A.A.; Hanif, A.; Ratyal, R.H. Drinking water quality by the use of Congo Red medium to differentiate between pathogenic and nonpathogenic E. coli at poultry farms. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2009, 19, 108–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ezz El Deen, A.N.; Mohamed, K.F.; Abd-El Hafez, N.M. Characterization of Surface Proteins of Escherichia coli Isolated from Different Egyptian Sources. Int. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 1, 147–161. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.M.; Shimamoto, T.; Shimamoto, T. Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant avian pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from septicemic broilers. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 303, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Doetkott, C.; Johnson, S.J.; Rosenberger, S.C.; Nolan, L.K. Identification of minimal predictors of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli virulence for use as a rapid diagnostic tool. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 3987–3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, J.R.; Kuskowski, M.A.; Owens, K.; Gajewski, A.; Winokur, P.L. Phylogenetic origin and virulence genotype in relation to resistance to fluoroquinolones and/or extended-spectrum cephalosporins and cephamycins among Escherichia coli isolates from animals and humans. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 759–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Saucedo, C.; Cerna, J.F.; Villegas-Sepulveda, N.; Thompson, R.; Velazquez, F.R.; Torres, J.; Estrada-Garcia, T. Single multiplex polymerase chain reaction to detect diverse loci associated with diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Campos, T.A.; Stehling, E.G.; Ferreira, A.; de Castro, A.F.P.; Brocchi, M.; da Silveira, W.D. Adhesion properties, fimbrial expression and PCR detection of adhesin-related genes of avian Escherichia coli strains. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 106, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amer, M.M.; Mekkym, H.M.; Amer, A.M.; Fedawy, H.S. Antimicrobial resistance genes in pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from diseased broiler chickens in Egypt and their relationship with the phenotypic resistance characteristics. Vet. World 2018, 11, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borzi, M.M.; Cardozo, M.V.; de Oliveira, E.S.; de Souza Pollo, A.; Guastalli, E.A.L.; dos Santos, L.F.; de Ávila, F.A. Characterization of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from free-range helmeted guineafowl. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kur, J.W. Biofilm formation as a virulence determinant of uropathogenic Escherichia coli Dr+ strains. Pol. Soc. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Römling, U.; Balsalobre, C. Biofilm infections, their resilience to therapy and innovative treatment strategies. J. Int. Med. 2012, 272, 541–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Bai, X.; Jin, Y.; Hu, B.; Wang, H.; Sun, H.; Fan, R.; Fu, S.; Xiong, Y. High prevalence of virulence genes in specific genotypes of atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramadan, H.; Awad, A.; Ateya, A. Detection of phenotypes, virulence genes and phylotypes of avian pathogenic and human diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in Egypt. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2016, 10, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Glass-Kaastra, S.K.; Pearl, D.L.; Reid-Smith, R.; McEwen, B.; Slavic, D.; Fairles, J.; McEwen, S.A. Multiple-class antimicrobial resistance surveillance in swine Escherichia coli F4, Pasteurella multocida and Streptococcus suis isolates from Ontario and the impact of the 2004–2006 Porcine Circovirus type-2 Associated Disease outbreak. Prev. Vet. Med. 2014, 113, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi-Aznaveh, A.; Bakhshi, B.; Najar-Peerayeh, S.; Kazemnejad, A.; Rafieepour, Z.; Rahbar, M.; Abbaspour, S. Commensal E. coli as an Important Reservoir of Resistance encoding Genetic elements. Int. J. Enteric. Pathog. 2013, 1, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello, A.; Austin, B.; Telfer, T.C. Selective pressure of antibiotic pollution on bacteria of importance to public health. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Azad, M.A.R.; Rahman, M.; Amin, R.; Begum, M.I.A.; Fries, R.; Husna, A.; Khairalla, A.S.; Badruzzaman, A.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Na Lampang, K.; et al. Susceptibility and Multidrug Resistance Patterns of Escherichia coli Isolated from Cloacal Swabs of Live Broiler Chickens in Bangladesh. Pathogens 2019, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarker, M.S.; Mannan, M.S.; Ali, M.Y.; Bayzid, M.; Ahad, A.; Bupasha, Z.B. Antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from broilers sold at live bird markets in Chattogram, Bangladesh. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2019, 6, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logue, C.M.; Wannemuehler, Y.; Nicholson, B.A.; Doetkott, C.; Barbieri, N.L.; Nolan, L.K. Comparative analysis of phylogenetic assignment of human and avian ExPEC and fecal commensal Escherichia coli using the (previous and revised) Clermont phylogenetic typing methods and its impact on avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) classification. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reza, S.; Akond, M.A.; Hassan, S.M.; Alam, S.; Shirin, M. Antibiotic Resistance of Escherichia coli Isolated from Poultry and Poultry Environment of Bangladesh. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 5, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Osman, K.M.; Kappell, A.D.; Elhadidy, M.; ElMougy, F.; El-Ghany, W.A.A.; Orabi, A.; Hessain, A.M. Poultry hatcheries as potential reservoirs for antimicrobial-resistant Escherichia coli: A risk to public health and food safety. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knöbl, T.; Moreno, A.M.; Paixão, R.; Gomes, T.A.; Vieira, M.A.; da Silva Leite, D.; Ferreira, A.J. Prevalence of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) clone harboring sfa gene in Brazil. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 437342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, P.; Weagant, S.D.; Grant, M.A.; Burkhardt, W. Bacteriological Analytical Manual Chapter 4 Enumeration of Escherichia coli and the Coliform Bacteria; MD 20993 1-888-INFO-FDA (1-888-463-6332); U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2015.
- Maragkoudakis, P.A.; Zoumpopoulou, G.; Miaris, C.; Kalantzopoulos, G.; Pot, B.; Tsakalidou, E. Probiotic potential of Lactobacillus strains isolated from dairy products. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Yang, D.; Wang, D.; Han, X.; Yu, S. Escherichia coli Type III Secretion System 2 ATPase EivC Is Involved in the Motility and Virulence of Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoque, M.N.; Istiaq, A.; Clement, R.A.; Gibson, K.M.; Saha, O.; Islam, O.K.; Abir, R.A.; Sultana, M.; Siddiki, A.Z.; Crandall, K.A.; et al. Insights into the Resistome of Bovine Clinical Mastitis Microbiome, a Key Factor in Disease Complication. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, A.; Saha, O.; Siddiqui, A.R.; Saha, A.; Hussain, M.S.; Islam, T. Molecular Detection of Multidrug Resistance Pathogenic Bacteria from Protective Materials Used By Healthcare Workers (HCW); Bangladesh Scenario. J. Appl. Sci. 2018, 18, 48–55. [Google Scholar]
- Momtaz, S.; Hossain, M.A. Occurrence of Pathogenic and Multidrug Resistant Salmonella spp. Biores. Commun. 2018, 4, 506–515. [Google Scholar]
- Iranpour, D.; Hassanpour, M.; Ansari, H.; Tajbakhsh, S.; Khamisipour, G.; Najafi, A. Phylogenetic groups of Escherichia coli strains from patients with urinary tract infection in Iran based on the new Clermont phylotyping method. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 846219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abbey, T.C.; Deak, E. What’s New from the CLSI Subcommittee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing M100. Clin. Microbiol. Newsl. 2019, 41, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, B.A.; Donaldson, S.C.; Padte, R.; Sawant, A.A.; DebRoy, C.; Jayarao, B.M. Assessment of phenotypic and genotypic diversity of Escherichia coli shed by healthy lactating dairy cattle. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2008, 5, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toma, C.; Lu, Y.; Higa, N.; Nakasone, N.; Chinen, I.; Baschkier, A.; Iwanaga, M. Multiplex PCR assay for identification of human diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 2669–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rakhi, N.N.; Alam, A.R.U.; Sultana, M.; Rahaman, M.M.; Hossain, M.A. Diversity of carbapenemases in clinical isolates: The emergence of blaVIM-5 in Bangladesh. J. Infect. Chem. 2019, 25, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrina, F.L.; Kopecko, D.J.; Jones, K.R.; Ayers, D.J.; McCowen, S.M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: Convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid 1978, 1, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikandi, J.; Millán, R.S.; Rementeria, A.; Garaizar, J. In silico analysis of complete bacterial genomes: PCR, AFLP–PCR and endonuclease restriction. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 798–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coura, F.M.; Diniz, S.A.; Silva, M.X.; Arcebismo, T.L.; Minharro, S.; Feitosa, A.C.; Heinemann, M.B. Phylogenetic group of Escherichia coli isolates from broilers in Brazilian Poultry Slaughterhouse. Sci. World J. 2017, 2017, 2898701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, T.; Otun Saha, S.S.; Hridoy, M.; Hasan, M.; Marzan, S.; Rahman, M.M. Comparison between reduced susceptibility to disinfectants and multidrug resistance among hospital isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus in Bangladesh. Bagcilar Med. Bull. 2017, 2, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, R.A.; Cryer, T.L.; Lafi, S.Q.; Basha, E.A.; Good, L.; Tarazi, Y.H. Identification of Escherichia coli from broiler chickens in Jordan, their antimicrobial resistance, gene characterization and the associated risk factors. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi-Nik, H.; Bassami, M.R.; Mohri, M.; Rad, M.; Khan, M.I. Bacterial ghost of avian pathogenic E. coli (APEC) serotype O78:K80 as a homologous vaccine against avian colibacillosis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fakhruzzaman, M.; Islam, M.M.; Sharifuzzaman, F.M.; Rahman, M.A.; Sharifuzzaman, J.U.; Sarker, E.H.; Shahiduzzaman, M.; Mostofa, M.; Sharifuzzaman, M.M. Isolation and identification of Escherichia coli and Salmonella from poultry litter and feed. Int. J. Nat. Soc. Sci. 2014, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sarba, E.J.; Kelbesa, K.A.; Bayu, M.D.; Gebremedhin, E.Z.; Borena, B.M.; Teshale, A. Identification and antimicrobial susceptibility profile of Escherichia coli isolated from backyard chicken in and around ambo, Central Ethiopia. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saud, B.; Paudel, G.; Khichaju, S.; Bajracharya, D.; Dhungana, G.; Awasthi, M.S.; Shrestha, V. Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria from Raw Meat of Buffalo and Chicken, Nepal. Vet. Med. Int. 2019, 2019, 7960268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Younis, G.; Awad, A.; Mohamed, N. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of antimicrobial susceptibility of avian pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from broiler chickens. Vet. World 2017, 10, 1167–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, J.L.; Fratamico, P.M.; Gunther, N.W. Extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2007, 4, 134–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asadi, A.; ZahraeiSalehi, T.; Jamshidian, M.; Ghanbarpour, R. ECOR phylotyping and determination of virulence genes in Escherichia coli isolates from pathological conditions of broiler chickens in poultry slaughter-houses of southeast of Iran. Vet. Res. Forum Int. Q. J. 2018, 9, 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X.; Yang, W.; Dong, L.; Xu, X.; Gao, S.; Liu, X. Prevalence of virulence factors and antimicrobial resistance of uropathogenic Escherichia coli in Jiangsu province (China). Urology 2009, 74, 702–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.N.; Istiaq, A.; Clement, R.A.; Sultana, M.; Crandall, K.A.; Siddiki, A.Z.; Hossain, M.A. Metagenomic deep sequencing reveals association of microbiome signature with functional biases in bovine mastitis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Subedi, M.; Luitel, H.; Devkota, B.; Bhattarai, R.K.; Phuyal, S.; Panthi, P.; Shrestha, A.; Chaudhary, D.K. Antibiotic resistance pattern and virulence genes content in avian pathogenic Escherichia coli (APEC) from broiler chickens in Chitwan, Nepal. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, E.; Prats, G.; Sabaté, M.; Pérez, T.; Johnson, J.R.; Andreu, A. Quinolone, fluoroquinolone and trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole resistance in relation to virulence determinants and phylogenetic background among uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2006, 57, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Etebarzadeh, Z.; Oshaghi, M.; Mozafari, N.A. Evaluation of relationship between phylogenetic typing and antibiotic resistance of uropathogenic Escherichia coli. J. Microbiol. World 2012, 3–4, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Wu, X.; Huo, S. Molecular characterization of multidrug-resistant avian pathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from septicemic broilers. Poult. Sci. 2015, 94, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, J.F.; Baggot, J.D. Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary Medicine; Blackwell scientific publications, Iowa State Press: Ames, IA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Carlos, C.; Pires, M.M.; Stoppe Johnson, N.C.; Hachich, E.M.; Sato, M.I.; Gomes, T.A.; Ottoboni, L.M. Escherichia coli phylogenetic group determination and its application in the identification of the major animal source of fecal contamination. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Resistance % (Strains) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotics | % (Total) | A1 (n = 40) | D2 (n = 11) | B23 (n = 43) | B22 (n = 11) | B1 (n = 9) |
| Ampicillin (AMP) | 74.56 (84) | 70 (28) | 63.64 (7) | 74.42 (31) | 90.91 (10) | 88.89 (8) |
| Doxycycline (Do) | 78.95 (90) | 77.5 (31) | 72.73 (8) | 79.07 (34) | 72.72 (8) | 100 (9) |
| Tetracycline (Te) | 75.44 (86) | 85 (34) | 90.91 (10) | 83.72 (36) | 81.82 (9) | 77.78 (7) |
| Nitrofurantoin (F) | 63.16 (72) | 60 (24) | 63.64 (7) | 65.12 (28) | 72.72 (8) | 55.56 (5) |
| Ciprofloxacin (CIP) | 44.74 (51) | 35 (14) | 45.46 (5) | 51.16 (22) | 45.45 (5) | 44.45 (4) |
| Nalidixic acid (NA) | 76.32 (87) | 65 (26) | 90.91 (10) | 76.74 (33) | 90.11 (10) | 88.89 (8) |
| Cefoxitin(Fox) | 41.23 (47) | 45 (18) | 9.01 (1) | 50 (21) | 27.27 (3) | 44.45 (4) |
| Imipenem (IMP) | 22.81 (26) | 17.5 (7) | 18.18 (2) | 16.28 (7) | 36.36 (4) | 66.65 (6) |
| Gentamycin (GN) | 26.32 (30) | 17.5 (7) | 27.27 (3) | 23.26 (10) | 45.45 (5) | 44.46 (4) |
| Chloramphenicol (C) | 51.75 (59) | 42.5 (17) | 54.55 (6) | 60.47 (26) | 45.45 (5) | 66.65 (6) |
| Sulfonamide (S) | 44.74 (51) | 45 (17) | 45.46 (5) | 48.84 (21) | 27.27 (4) | 55.56 (5) |
| Azithromycin (ATM) | 31.58 (36) | 27.5 (11) | 30.23 (13) | 30.23 (13) | 54.55 (6) | 33.36 (3) |
| Polymexin B (Pb) | 7.89 (9) | 7.5 (3) | 18.18 (2) | 9.30 (4) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saha, O.; Hoque, M.N.; Islam, O.K.; Rahaman, M.M.; Sultana, M.; Hossain, M.A. Multidrug-Resistant Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Strains and Association of Their Virulence Genes in Bangladesh. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081135
Saha O, Hoque MN, Islam OK, Rahaman MM, Sultana M, Hossain MA. Multidrug-Resistant Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Strains and Association of Their Virulence Genes in Bangladesh. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(8):1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081135
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaha, Otun, M. Nazmul Hoque, Ovinu Kibria Islam, Md. Mizanur Rahaman, Munawar Sultana, and M. Anwar Hossain. 2020. "Multidrug-Resistant Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Strains and Association of Their Virulence Genes in Bangladesh" Microorganisms 8, no. 8: 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081135
APA StyleSaha, O., Hoque, M. N., Islam, O. K., Rahaman, M. M., Sultana, M., & Hossain, M. A. (2020). Multidrug-Resistant Avian Pathogenic Escherichia coli Strains and Association of Their Virulence Genes in Bangladesh. Microorganisms, 8(8), 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8081135





