Host Starvation and Female Sex Influence Enterobacterial ClpB Production: A Possible Link to the Etiology of Eating Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model of Food Restriction
2.2. Fecal and Tissue Sampling
2.3. Identification of Bacteria by MALDI-TOF MS Biotyper
2.4. ClpB DNA Analysis
2.5. Protein Extraction
2.6. ClpB ELISA
2.7. ClpB- and α-MSH-Reactive Antibody Assay
2.8. Bacterial Culture
2.9. Immunocytochemistry
2.10. Total RNA Extraction
2.11. Data and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
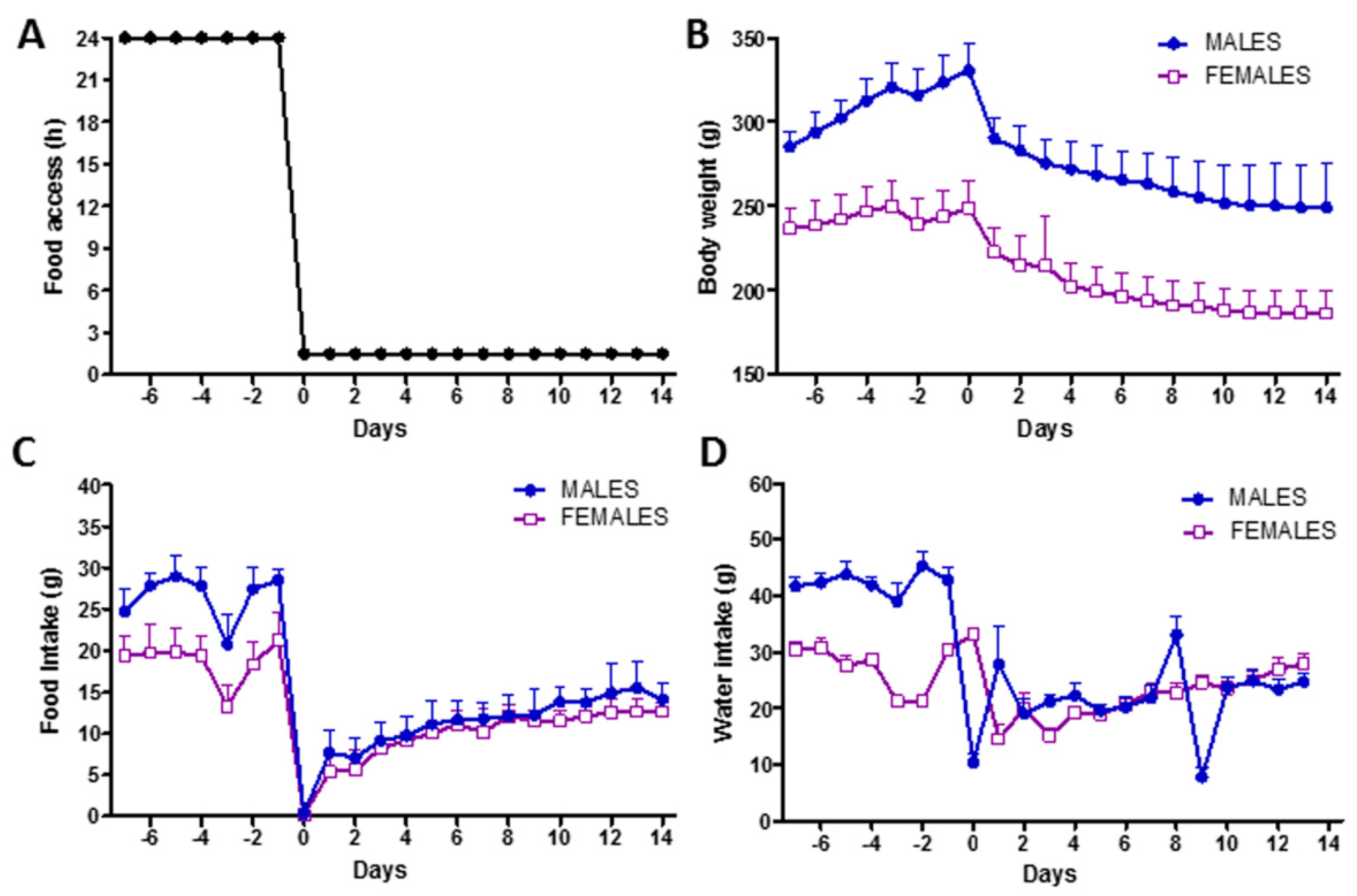
3.1. Rat Model of Food Restriction
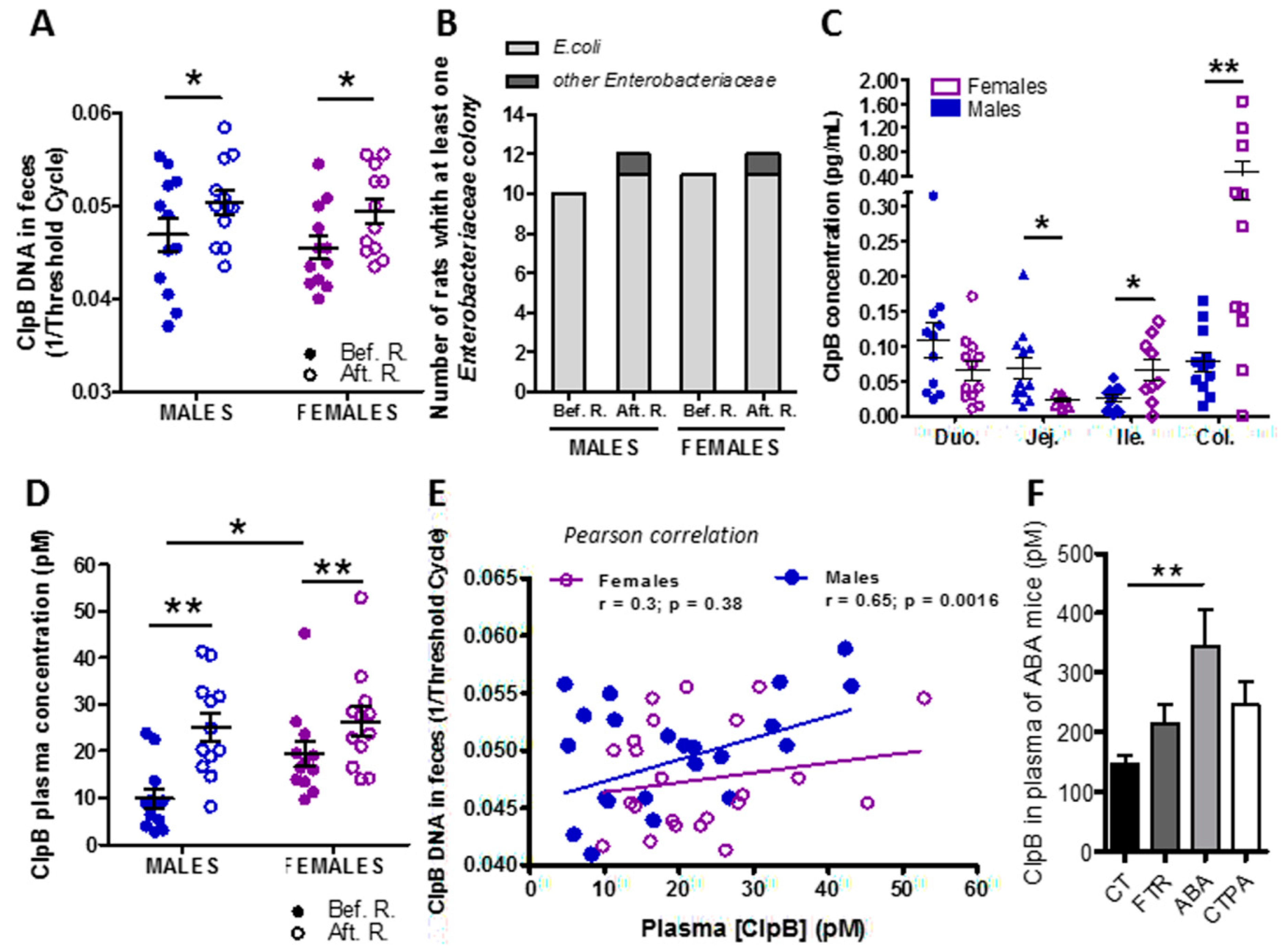
3.2. Effects of Food Restriction on ClpB Production
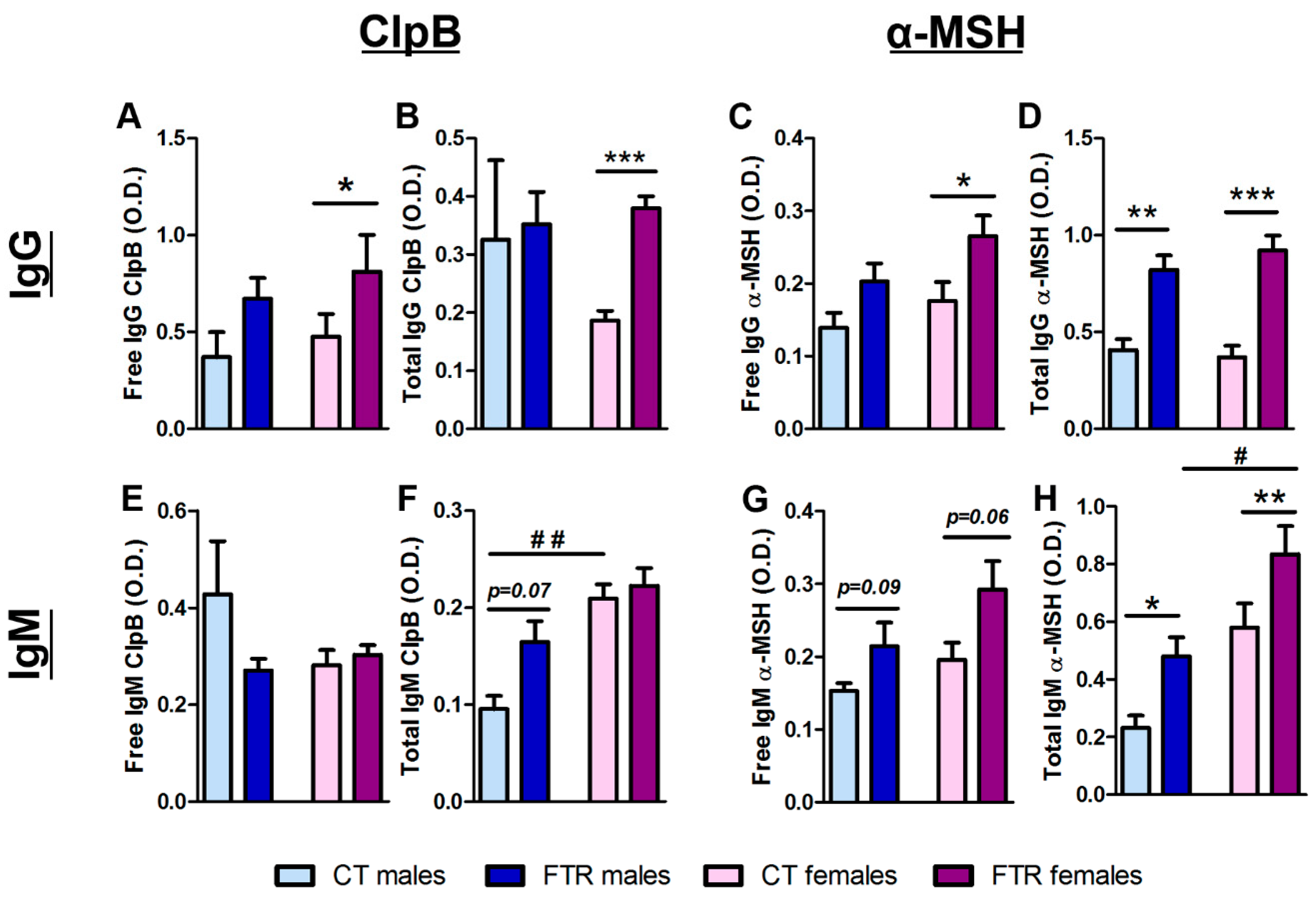
3.3. Effects of Food Restriction on ClpB- and α-MSH-Reactive Immunoglobulin Production
3.4. Effects of Sex Hormones on In Vitro ClpB Production
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Himmerich, H.; Bentley, J.; Kan, C.; Treasure, J. Genetic risk factors for eating disorders: An update and insights into pathophysiology. Adv. Psychopharmacol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedman, A.; Breithaupt, L.; Hübel, C.; Thornton, L.M.; Tillander, A.; Norring, C.; Birgegård, A.; Larsson, H.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; Sävendahl, L.; et al. Bidirectional relationship between eating disorders and autoimmune diseases. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerwas, S.; Larsen, J.T.; Petersen, L.; Thornton, L.M.; Quaranta, M.; Koch, S.V.; Pisetsky, D.; Mortensen, P.B.; Bulik, C.M. Eating disorders, autoimmune, and autoinflammatory disease. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20162089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, L.; Yilmaz, Z.; Gaspar, H.; Walters, R.; Goldstein, J.; Anttila, V.; Bulik-Sullivan, B.; Ripke, S.; Thornton, L.; Hinney, A.; et al. Significant locus and metabolic genetic correlations revealed in genome-wide association study of anorexia nervosa. Am. J. Psychiatry 2017, 174, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennoune, N.; Chan, P.; Breton, J.; Legrand, R.; Chabane, Y.N.; Akkermann, K.; Jarv, A.; Ouelaa, W.; Takagi, K.; Ghouzali, I.; et al. Bacterial clpb heat-shock protein, an antigen-mimetic of the anorexigenic peptide [alpha]-msh, at the origin of eating disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2014, 4, e458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetissov, S.O.; Hökfelt, T. On the origin of eating disorders: Altered signaling between gut microbiota, adaptive immunity and the brain melanocortin system regulating feeding behavior. Curr. Opin. Pharm. 2019, 48, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, E.J.P.; Çakir, I.; Carrington, S.J.; Cone, R.D.; Ghamari-Langroudi, M.; Gillyard, T.; Gimenez, L.E.; Litt, M.J. 60 years of pomc: Regulation of feeding and energy homeostasis by α-msh. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2016, 56, T157–T174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetissov, S.O.; Harro, J.; Jaanisk, M.; Järv, A.; Podar, I.; Allik, J.; Nilsson, I.; Sakthivel, P.; Lefvert, A.K.; Hökfelt, T. Autoantibodies against neuropeptides are associated with psychological traits in eating disorders. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 14865–14870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, N.; Legrand, R.; Bôle-Feysot, C.; Breton, J.; Coëffier, M.; Akkermann, K.; Järv, A.; Harro, J.; Déchelotte, P.; Fetissov, S.O. Immunoglobulin g modulation of the melanocortin 4 receptor signaling in obesity and eating disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fairburn, C.G.; Harrison, P.J. Eating disorders. Lancet 2003, 361, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queipo-Ortuno, M.I.; Seoane, L.M.; Murri, M.; Pardo, M.; Gomez-Zumaquero, J.M.; Cardona, F.; Casanueva, F.; Tinahones, F.J. Gut microbiota composition in male rat models under different nutritional status and physical activity and its association with serum leptin and ghrelin levels. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillion, M.; Mijouin, L.; Jaouen, T.; Barreau, M.; Meunier, P.; Lefeuvre, L.; Lati, E.; Chevalier, S.; Feuilloley, M.G.J. Comparative study of normal and sensitive skin aerobic bacterial populations. MicrobiologyOpen 2013, 2, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zommiti, M.; Cambronel, M.; Maillot, O.; Barreau, M.; Sebei, K.; Feuilloley, M.G.J.; Ferchichi, M.; Connil, N. Evaluation of probiotic properties and safety of enterococcus faecium isolated from artisanal tunisian meat ‘dried ossban’. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haigh, J.; Degun, A.; Eydmann, M.; Millar, M.; Wilks, M. Improved performance of bacterium and yeast identification by a commercial matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry system in the clinical microbiology laboratory. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogawa, K.; Watanabe, M.; Sato, K.; Segawa, S.; Ishii, C.; Miyabe, A. Use of the maldi biotyper system with maldi-tof mass spectrometry for rapid identification of microorganisms. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 1905–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, J.; Tennoune, N.; Lucas, N.; François, M.; Legrand, R.; Jacquemot, J.; Goichon, A.; Guérin, C.; Peltier, J.; Pestel-Caron, M.; et al. Gut commensal e.Coli proteins activate host satiety pathways following nutrient-induced bacterial growth. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetissov, S.O. Neuropeptide autoantibodies assay. Methods Mol Biol 2011, 789, 295–302. [Google Scholar]
- Breton, J.; Legrand, R.; Achamrah, N.; Chan, P.; do Rego, J.L.; do Rego, J.C.; Coëffier, M.; Déchelotte, P.; Fetissov, S.O. Proteome modifications of gut microbiota in mice with activity-based anorexia and starvation: Role in atp production. Nutrition 2019, 67–68, 110557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, J.; Trinh, S.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B. The microbiome and eating disorders. Psychiatr. Clin. North Am. 2019, 42, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tlaskalová-Hogenová, H.; Stepánková, R.; Hudcovic, T.; Tucková, L.; Cukrowska, B.; Lodinová-Zádníková, R.; Kozáková, H.; Rossmann, P.; Bártová, J.; Sokol, D.; et al. Commensal bacteria (normal microflora), mucosal immunity and chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Immunol. Lett. 2004, 93, 97–108. [Google Scholar]
- Sharon, G.; Sampson, T.R.; Geschwind, D.H.; Mazmanian, S.K. The central nervous system and the gut microbiome. Cell 2016, 167, 915–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, C.; Tsuji, H.; Hata, T.; Gondo, M.; Takakura, S.; Kawai, K.; Yoshihara, K.; Ogata, K.; Nomoto, K.; Miyazaki, K.; et al. Gut dysbiosis in patients with anorexia nervosa. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiman, S.C.; Watson, H.J.; Bulik-Sullivan, E.C.; Huh, E.Y.; Tarantino, L.M.; Bulik, C.M.; Carroll, I.M. The intestinal microbiota in acute anorexia nervosa and during renourishment: Relationship to depression, anxiety, and eating disorder psychopathology. Psychosom. Med. 2015, 77, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, I.; Cuntz, U.; Grämer, C.; Niedermaier, S.; Pohl, C.; Schwiertz, A.; Zimmermann, K.; Zipfel, S.; Enck, P.; Penders, J. Weight gain in anorexia nervosa does not ameliorate the faecal microbiota, branched chain fatty acid profiles, and gastrointestinal complaints. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hata, T.; Miyata, N.; Takakura, S.; Yoshihara, K.; Asano, Y.; Kimura-Todani, T.; Yamashita, M.; Zhang, X.-T.; Watanabe, N.; Mikami, K.; et al. The gut microbiome derived from anorexia nervosa patients impairs weight gain and behavioral performance in female mice. Endocrinology 2019, 160, 2441–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetissov, S.O. Role of the gut microbiota in host appetite control: Bacterial growth to animal feeding behaviour. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, J.; Legrand, R.; Akkermann, K.; Järv, A.; Harro, J.; Déchelotte, P.; Fetissov, S.O. Elevated plasma concentrations of bacterial clpb protein in patients with eating disorders. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2016, 49, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Million, M.; Angelakis, E.; Maraninchi, M.; Henry, M.; Giorgi, R.; Valero, R.; Vialettes, B.; Raoult, D. Correlation between body mass index and gut concentrations of lactobacillus reuteri, bifidobacterium animalis, methanobrevibacter smithii and escherichia coli. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37, 1460–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgo, F.; Riva, A.; Benetti, A.; Casiraghi, M.C.; Bertelli, S.; Garbossa, S.; Anselmetti, S.; Scarone, S.; Pontiroli, A.E.; Morace, G.; et al. Microbiota in anorexia nervosa: The triangle between bacterial species, metabolites and psychological tests. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanachi, M.; Manichanh, C.; Schoenenberger, A.; Pascal, V.; Levenez, F.; Cournède, N.; Doré, J.; Melchior, J.-C. Altered host-gut microbes symbiosis in severely malnourished anorexia nervosa (an) patients undergoing enteral nutrition: An explicative factor of functional intestinal disorders? Clin. Nutr. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattison, J.A.; Colman, R.J.; Beasley, T.M.; Allison, D.B.; Kemnitz, J.W.; Roth, G.S. Caloric restriction improves health and survival of rhesus monkeys. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mack, I.; Penders, J.; Cook, J.; Dugmore, J.; Mazurak, N.; Enck, P. Is the impact of starvation on the gut microbiota specific or unspecific to anorexia nervosa? A narrative review based on a systematic literature search. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 1131–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breton, J.; Giallourou, N.; Nobis, S.; Morin, A.; Achamrah, N.; Goichon, A.; Belmonte, L.; Dechelotte, P.; Rego, J.-L.d.; Coëffier, M.; et al. Characterizing the metabolic perturbations induced by activity-based anorexia in the c57bl/6 mouse using (1)h nmr spectroscopy. Clin. Nutr. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogk, A.; Deuerling, E.; Vorderwulbecke, S.; Vierling, E.; Bukau, B. Small heat shock proteins, clpb and the dnak system form a functional triade in reversing protein aggregation. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, N.; Legrand, R.; Deroissart, C.; Dominique, M.; Azhar, S.; Le Solliec, M.-A.; Léon, F.; do Rego, J.-C.; Déchelotte, P.; Fetissov, S.O.; et al. Hafnia alvei ha4597 strain reduces food intake and body weight gain and improves body composition, glucose, and lipid metabolism in a mouse model of hyperphagic obesity. Microorganisms 2019, 8, E35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, R.; Lucas, N.; Dominique, M.; Azhar, S.; Deroissart, C.; Le Solliec, M.-A.; Rondeaux, J.; Nobis, S.; Guérin, C.; Léon, F.; et al. Commensal hafnia alvei strain reduces food intake and fat mass in obese mice-a new potential probiotic for appetite and body weight management. Int. J. Obes. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeo, F.; Carmona-Gutierrez, D.; Hofer, S.J.; Kroemer, G. Caloric restriction mimetics against age-associated disease: Targets, mechanisms, and therapeutic potential. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 592–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, J.; Smith, G.P. Cholecystokinin and satiety in rats and rhesus monkeys. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1977, 30, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batterham, R.L.; Cowley, M.A.; Small, C.J.; Herzog, H.; Cohen, M.A.; Dakin, C.L.; Wren, A.M.; Brynes, A.E.; Low, M.J.; Ghatei, M.A.; et al. Gut hormone pyy(3-36) physiologically inhibits food intake. Nature 2002, 418, 650–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominique, M.; Breton, J.; Guérin, C.; Bole-Feysot, C.; Lambert, G.; Déchelotte, P.; Fetissov, S.O. Effects of macronutrients on the in vitro production of clpb, a bacterial mimetic protein of α-msh and its possible role in the satiety signaling. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, M.; Miller, K.K.; Tsai, P.; Gallagher, K.; Lin, A.; Lee, N.; Herzog, D.B.; Klibanski, A. Elevated peptide yy levels in adolescent girls with anorexia nervosa. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennoune, N.; Legrand, R.; Ouelaa, W.; Breton, J.; Lucas, N.; Bole-Feysot, C.; Rego, J.-C.d.; Déchelotte, P.; Fetissov, S.O. Sex-related effects of nutritional supplementation of escherichia coli: Relevance to eating disorders. Nutrition 2015, 31, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macpherson, A.J.; Gatto, D.; Sainsbury, E.; Harriman, G.R.; Hengartner, H.; Zinkernagel, R.M. A primitive t cell-independent mechanism of intestinal mucosal iga responses to commensal bacteria. Science 2000, 288, 2222–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardelli-Haefliger, D.; Roden, R.; Balmelli, C.; Potts, A.; Schiller, J.; De Grandi, P. Mucosal but not parenteral immunization with purified human papillomavirus type 16 virus-like particles induces neutralizing titers of antibodies throughout the estrous cycle of mice. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 9609–9613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachman, F.; Casimiri, V.; Psychoyos, A.; Bernard, O. Immunoglobulins in the mouse uterus during the ostrous cycle. Reproduction 1983, 69, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.M.; Al-Nakkash, L.; Herbst-Kralovetz, M.M. Estrogen-gut microbiome axis: Physiological and clinical implications. Maturitas 2017, 103, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Dahlman-Wright, K.; Gustafsson, J.-Å. Estrogen receptor alpha and beta in health and disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beury-Cirou, A.; Tannières, M.; Minard, C.; Soulère, L.; Rasamiravaka, T.; Dodd, R.H.; Queneau, Y.; Dessaux, Y.; Guillou, C.; Vandeputte, O.M.; et al. At a supra-physiological concentration, human sexual hormones act as quorum-sensing inhibitors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Hillman, J.D.; Progulske-Fox, A. Microarray analysis of quorum-sensing-regulated genes in Porphyromonas gingivalis. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 4146–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shomaker, L.B.; Tanofsky-Kraff, M.; Savastano, D.M.; Kozlosky, M.; Columbo, K.M.; Wolkoff, L.E.; Zocca, J.M.; Brady, S.M.; Yanovski, S.Z.; Crocker, M.K.; et al. Puberty and observed energy intake: Boy, can they eat! Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timko, C.A.; DeFilipp, L.; Dakanalis, A. Sex differences in adolescent anorexia and bulimia nervosa: Beyond the signs and symptoms. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Breton, J.; Jacquemot, J.; Yaker, L.; Leclerc, C.; Connil, N.; Feuilloley, M.; Déchelotte, P.; Fetissov, S.O. Host Starvation and Female Sex Influence Enterobacterial ClpB Production: A Possible Link to the Etiology of Eating Disorders. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040530
Breton J, Jacquemot J, Yaker L, Leclerc C, Connil N, Feuilloley M, Déchelotte P, Fetissov SO. Host Starvation and Female Sex Influence Enterobacterial ClpB Production: A Possible Link to the Etiology of Eating Disorders. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(4):530. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040530
Chicago/Turabian StyleBreton, Jonathan, Justine Jacquemot, Linda Yaker, Camille Leclerc, Nathalie Connil, Marc Feuilloley, Pierre Déchelotte, and Sergueï O. Fetissov. 2020. "Host Starvation and Female Sex Influence Enterobacterial ClpB Production: A Possible Link to the Etiology of Eating Disorders" Microorganisms 8, no. 4: 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040530
APA StyleBreton, J., Jacquemot, J., Yaker, L., Leclerc, C., Connil, N., Feuilloley, M., Déchelotte, P., & Fetissov, S. O. (2020). Host Starvation and Female Sex Influence Enterobacterial ClpB Production: A Possible Link to the Etiology of Eating Disorders. Microorganisms, 8(4), 530. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8040530





