Exploring the Ambiguous Status of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in the Biosafety of Fermented Meats: The Case of Antibacterial Activity Versus Biogenic Amine Formation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Staphylococcal Strains
2.2. Screening for Antibacterial Activity
2.3. Screening for Anticlostridial Activity
2.4. Assessment of Temperature and Proteinase K on the Stability of Antibacterial Activity in Broth from Staphylococcus sciuri IMDO-S72 and its Spectrum of Activity
2.5. Analysis of Biogenic Amines
2.5.1. Growth Conditions and Sampling
2.5.2. Determination of Biogenic Amines by Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS)
2.6. Graphical Representation
3. Results
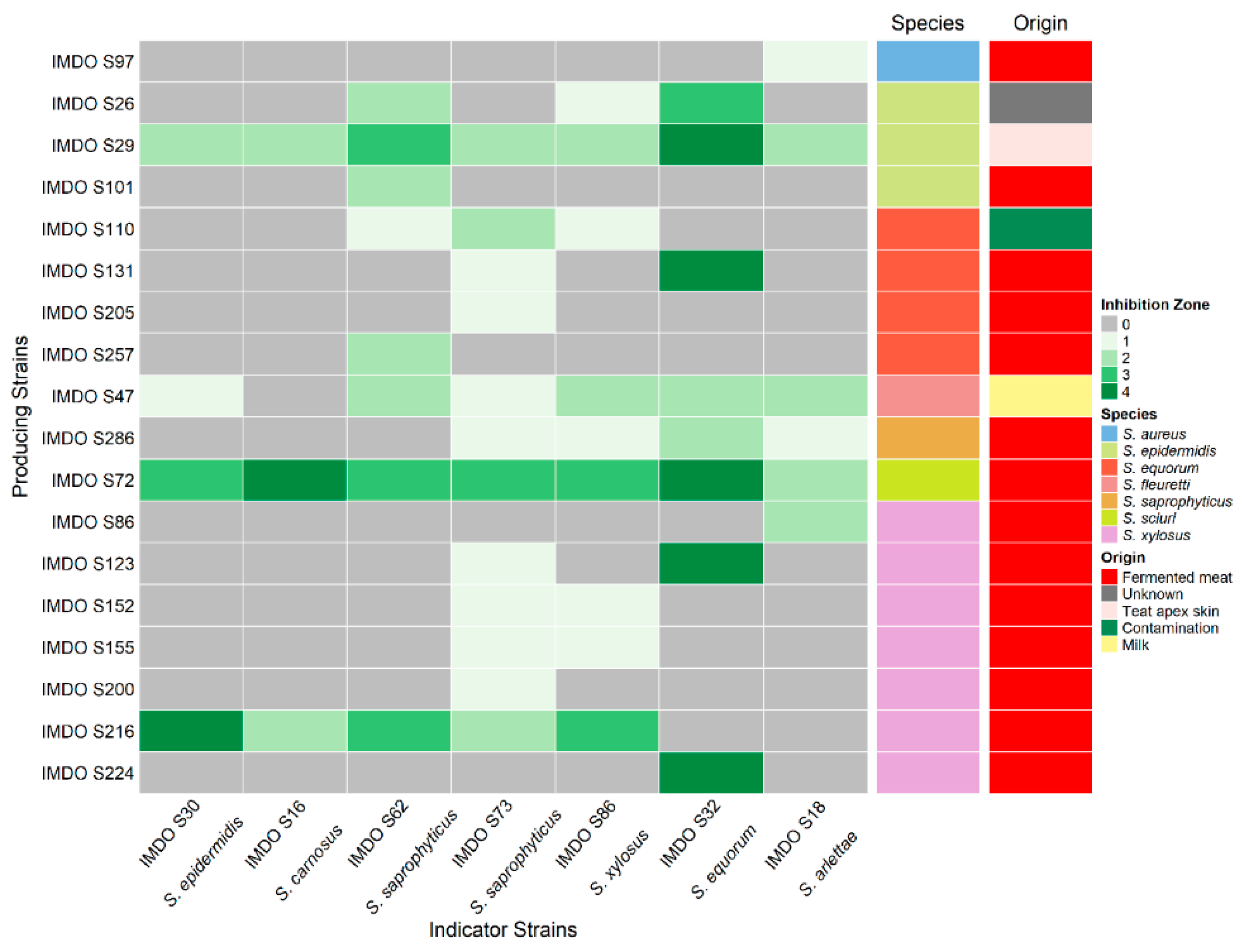
3.1. Prevalence of Antibacterial Activity in Staphylococci
3.2. Antibacterial Activity by Staphylococcus sciuri IMDO-S72
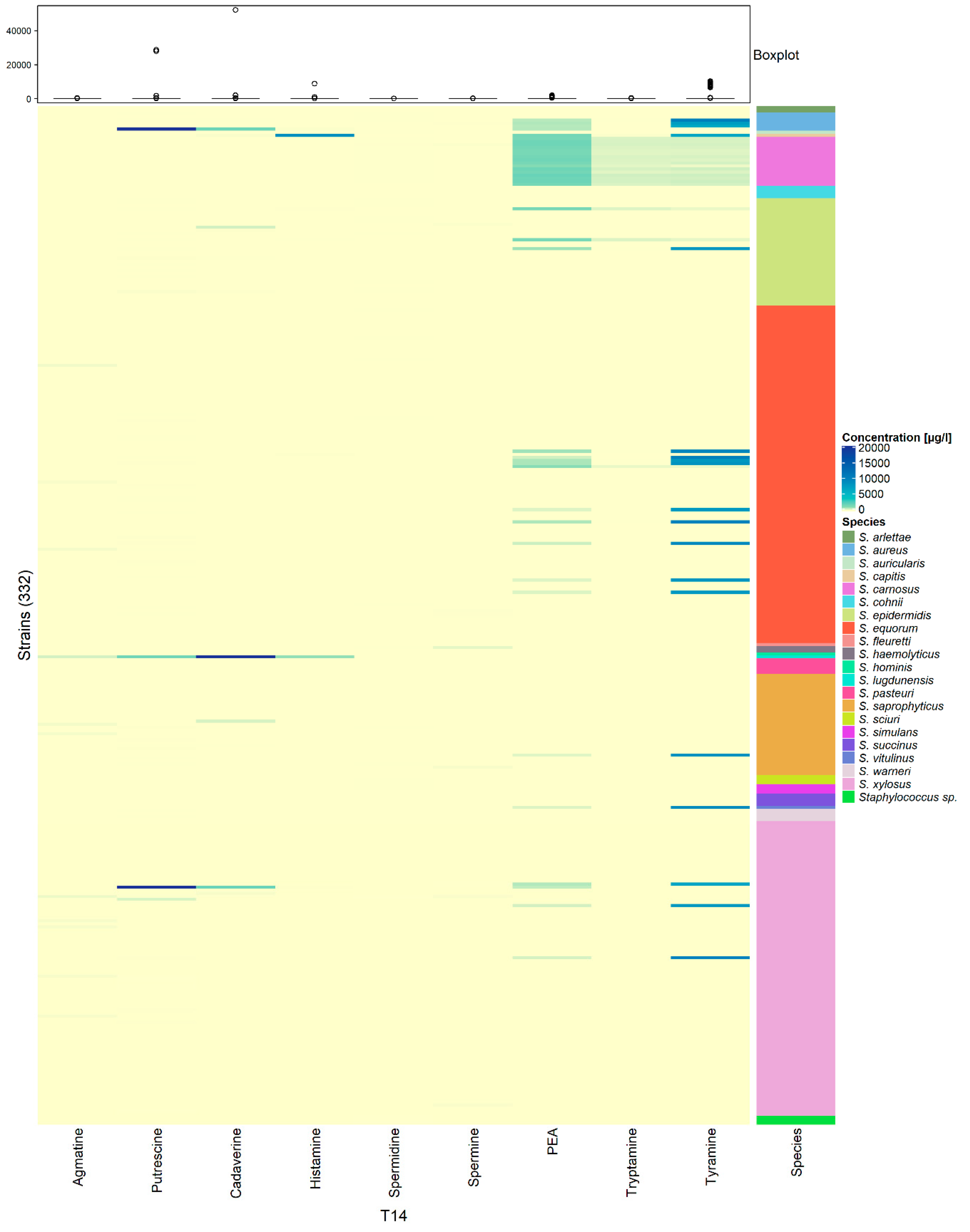
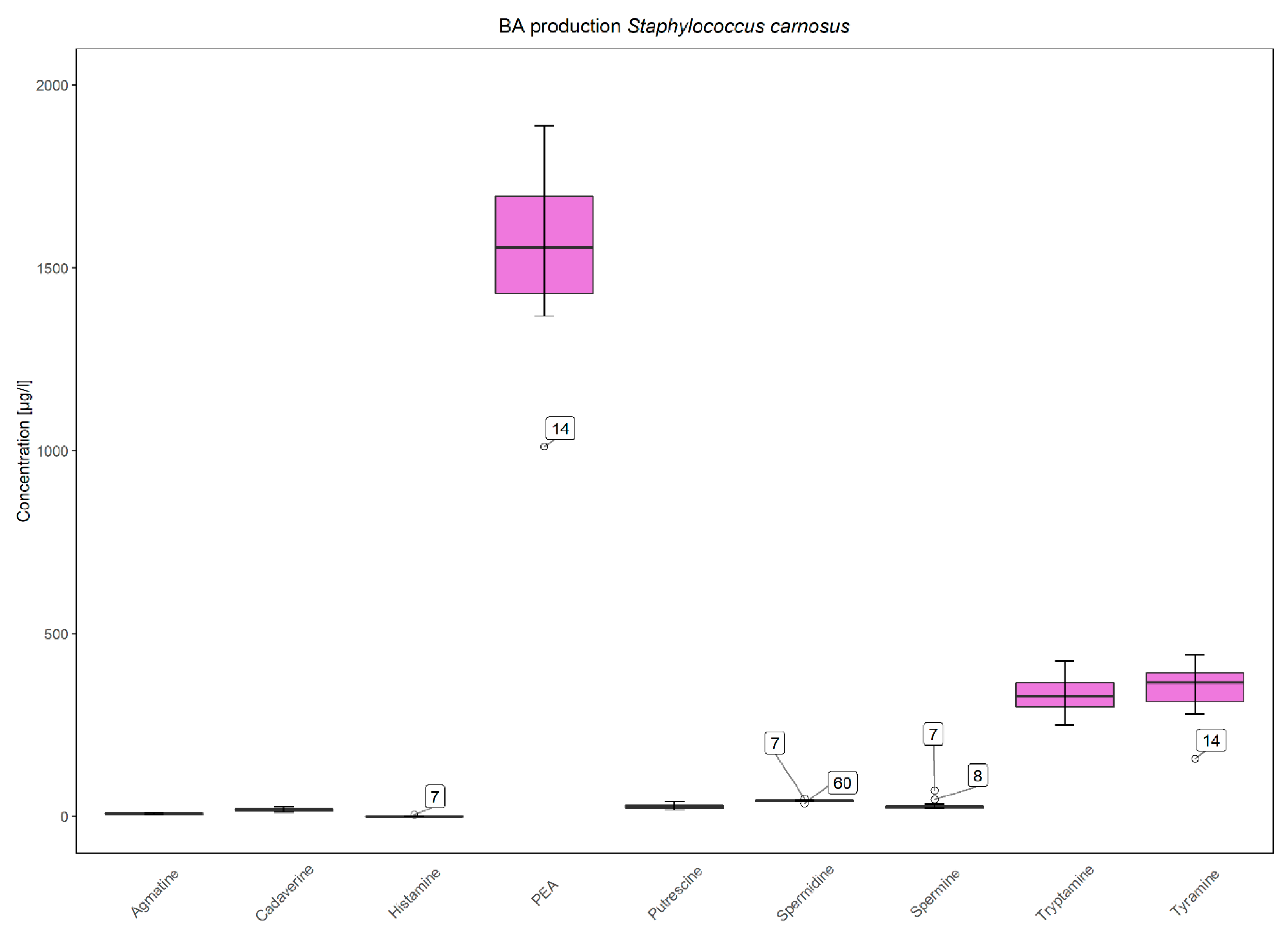
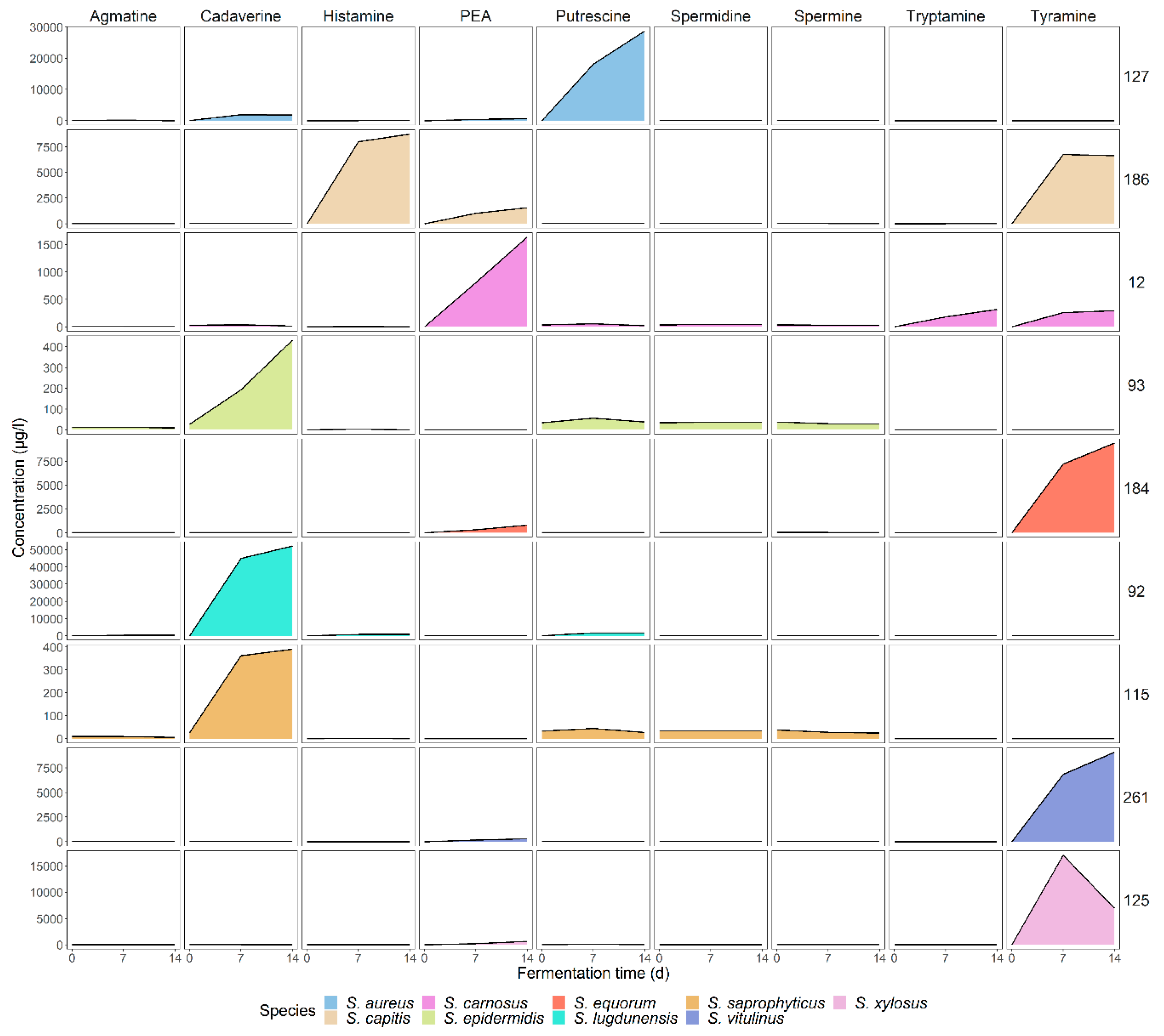
3.3. Low and Strain-Dependent Biogenic Amine Production in Staphylococci, Marked by Simultaneous Production of Tyramine and β-Phenylethylamine
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leroy, F.; Geyzen, A.; Janssens, M.; De Vuyst, L.; Scholliers, P. Meat fermentation at the crossroads of innovation and tradition: A historical outlook. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mey, E.; De Klerck, K.; De Maere, H.; Dewulf, L.; Derdelinckx, G.; Peeters, M.-C.; Fraeye, I.; Vander Heyden, Y.; Paelinck, H. The occurrence of N-nitrosamines, residual nitrite and biogenic amines in commercial dry fermented sausages and evaluation of their occasional relation. Meat Sci. 2014, 96, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majou, D.; Christieans, S. Mechanisms of the bactericidal effects of nitrate and nitrite in cured meats. Meat Sci. 2018, 145, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebranek, J.G.; Bacus, J.N. Cured meat products without direct addition of nitrate or nitrite: What are the issues? Meat Sci. 2007, 77, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honikel, K.-O. The use and control of nitrate and nitrite for the processing of meat products. Meat Sci. 2008, 78, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hospital, X.F.; Hierro, E.; Stringer, S.; Fernández, M. A study on the toxigenesis by Clostridium botulinum in nitrate and nitrite-reduced dry fermented sausages. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 218, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, B.M.; Peck, M.W. Clostridium botulinum. In Guide to Foodborne Pathogens, 2nd ed.; Labbé, R.G., Garcia, S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravyts, F.; Barbuti, S.; Frustoli, M.A.; Parolari, G.; Saccani, G.; De Vuyst, L.; Leroy, F. Competitiveness and antibacterial potential of bacteriocin-producing starter cultures in different types of fermented sausages. J. Food Protect. 2008, 71, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gioia, D.; Mazzola, G.; Nikodinoska, I.; Aloisio, I.; Langerholc, T.; Rossi, M.; Raimondi, S.; Melero, B.; Rovira, J. Lactic acid bacteria as protective cultures in fermented pork meat to prevent Clostridium spp. growth. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 235, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Mainar, M.; Xhaferi, R.; Samapundo, S.; Devlieghere, F.; Leroy, F. Opportunities and limitations for the production of safe fermented meats without nitrate and nitrite using an antibacterial Staphylococcus sciuri starter culture. Food Control 2016, 69, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, P.D.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. Bacteriocins: Developing innate immunity for food. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2005, 3, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, P.D.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. Bacteriocins—A viable alternative to antibiotics? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugas, M. Bacteriocinogenic lactic acid bacteria for the biopreservation of meat and meat products. Meat Sci. 1998, 49, S139–S150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammor, S.; Tauveron, G.; Dufour, E.; Chevallier, I. Antibacterial activity of lactic acid bacteria against spoilage and pathogenic bacteria isolated from the same meat small-scale facility: 1—Screening and characterization of the antibacterial compounds. Food Control 2006, 17, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanlin, M.B.; Kalchayanand, N.; Ray, P.; Ray, B. Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria in combination have greater antibacterial activity. J. Food Protect. 1993, 56, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsetti, A.; Gobbetti, M.; Smacchi, E. Antibacterial activity of sourdough lactic acid bacteria: Isolation of a bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance from Lactobacillus sanfrancisco C57. Food Microbiol. 1996, 13, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghrairi, T.; Manai, M.; Berjeaud, J.M.; Frère, J. Antilisterial activity of lactic acid bacteria isolated from rigouta, a traditional Tunisian cheese. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 97, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, V.F.; Martinez, R.C.R.; Lavrador, M.A.S.; De Martinis, E.C.P. Antilisterial activity of lactic acid bacteria inoculated on cooked ham. Meat Sci. 2006, 74, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albano, H.; Oliveira, M.; Aroso, R.; Cubero, N.; Hogg, T.; Teixeira, P. Antilisterial activity of lactic acid bacteria isolated from “Alheiras” (traditional Portuguese fermented sausages): In situ assays. Meat Sci. 2007, 76, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, C.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Vignolo, G.; Saavedra, L. Occurrence of antilisterial structural bacteriocins genes in meat borne lactic acid bacteria. Food Control 2015, 47, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Mainar, M.; Stavropoulou, D.A.; Leroy, F. Exploring the metabolic heterogeneity of coagulase-negative staphylococci to improve the quality and safety of fermented meats: A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 247, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Even, S.; Leroy, S.; Charlier, C.; Ben Zakour, N.; Chacornac, J.-P.; Lebert, I.; Jamet, E.; Desmonts, M.-H.; Coton, E.; Pochet, S.; et al. Low occurrence of safety hazards in coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from fermented foodstuffs. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruaro, A.; Andrighetto, C.; Torriani, S.; Lombardi, A. Biodiversity and characterization of indigenous coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from raw milk and cheese of North Italy. Food Microbiol. 2013, 34, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcobal, A.; de las Rivas, B.; Landete, J.M.; Tabera, L.; Munoz, R. Tyramine and phenylethylamine biosynthesis by food bacteria. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 448–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jairath, G.; Singh, P.K.; Dabur, R.S.; Rani, M.; Chaudhari, M. Biogenic amines in meat and meat products and its public health significance: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 6835–6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pircher, A.; Bauer, F.; Paulsen, P. Formation of cadaverine, histamine, putrescine and tyramine by bacteria isolated from meat, fermented sausages and cheeses. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2007, 226, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzzi, G.; Gardini, F. Biogenic amines in dry fermented sausages: A review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 88, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Rio, B.; Redruello, B.; Linares, D.M.; Ladero, V.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Fernandez, M.; Martin, M.C.; Alvarez, M.A. The biogenic amines putrescine and cadaverine show in vitro cytotoxicity at concentrations that can be found in foods. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bover-Cid, S.; Hugas, M.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M.; Vidal-Carou, M.C. Amino acid-decarboxylase activity of bacteria isolated from fermented pork sausages. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 66, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bover-Cid, S.; Torriani, S.; Gatto, V.; Tofalo, R.; Suzzi, G.; Belletti, N.; Gardini, F. Relationships between microbial population dynamics and putrescine and cadaverine accumulation during dry fermented sausage ripening. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curiel, J.A.; Ruiz-Capillas, C.; de las Rivas, B.; Carrascosa, A.V.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Muñoz, R. Production of biogenic amines by lactic acid bacteria and enterobacteria isolated from fresh pork sausages packaged in different atmospheres and kept under refrigeration. Meat Sci. 2011, 88, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de las Rivas, B.; Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Carrascosa, A.V.; Curiel, J.A.; Jimenez-Colmenero, F.; Munoz, R. Biogenic amine production by Gram-positive bacteria isolated from Spanish dry-cured “chorizo” sausage treated with high pressure and kept in chilled storage. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komprda, T.; Sladkova, P.; Petirova, E.; Dohnal, V.; Burdychova, R. Tyrosine- and histidine-decarboxylase positive lactic acid bacteria and enterococci in dry fermented sausages. Meat Sci. 2010, 86, 870–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durlu-Ozkaya, F.; Ayhan, K.; Vural, N. Biogenic amines produced by Enterobacteriaceae isolated from meat products. Meat Sci. 2001, 58, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro, C.A.; Conte-Junior, C.A.; Canto, A.C.; Guerra Monteiro, M.L.; Costa-Lima, B.; da Cruz, A.G.; Marsico, E.T.; Franco, R.M. Biogenic amines as bacterial quality indicators in different poultry meat species. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wen, X.; Wen, Z.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Wei, X. Evaluation of the biogenic amines formation and degradation abilities of Lactobacillus curvatus from Chinese bacon. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, F.; Talon, R.; Montel, M.C. Histamine and tyramine production by bacteria from meat products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1996, 32, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landeta, G.; Curiel, J.A.; Carrascosa, A.V.; Munoz, R.; de las Rivas, B. Characterization of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from Spanish dry cured meat products. Meat Sci. 2013, 93, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landeta, G.; de las Rivas, B.; Carrascosa, A.V.; Muñoz, R. Screening of biogenic amine production by coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated during industrial Spanish dry-cured ham processes. Meat Sci. 2007, 77, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Marty, E.; Bodenmann, C.; Buchs, J.; Hadorn, R.; Eugster-Meier, E.; Lacroix, C.; Meile, L. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance in coagulase-negative staphylococci from spontaneously fermented meat products and safety assessment for new starters. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 159, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitter, M.; Geng, B.; Hertel, C. Binding to extracellular matrix proteins and formation of biogenic amines by food-associated coagulase-negative staphylococci. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 145, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonova, M.; Strompfova, V.; Marcinakova, M.; Laukovda, A.; Vesterlund, S.; Moratalla, M.L.; Bover-Cid, S.; Vidal-Carou, C. Characterization of Staphylococcus xylosus and Staphylococcus carnosus isolated from Slovak meat products. Meat Sci. 2006, 73, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavropoulou, D.A.; Borremans, W.; De Vuyst, L.; De Smet, S.; Leroy, F. Amino acid conversions by coagulase-negative staphylococci in a rich medium: Assessment of inter- and intraspecies heterogeneity. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 212, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coton, E.; Mulder, N.; Coton, M.; Pochet, S.; Trip, H.; Lolkema, J.S. Origin of the putrescine-producing ability of the coagulase-negative bacterium Staphylococcus epidermidis 2015B. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 5570–5576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braem, G.; De Vliegher, S.; Supré, K.; Haesebrouck, F.; Leroy, F.; De Vuyst, L. (GTG)5-PCR fingerprinting for the classification and identification of coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species from bovine milk and teat apices: A comparison of type strains and field isolates. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 147, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagg, J.R.; Bannister, L.V. “Fingerprinting” β-haemolytic streptococci by their production of and sensitivity to bacteriocine-like inhibitors. J. Med. Microbiol. 1979, 12, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.-K.; Jun, S.-A.; Ha, J.-U.; Paik, H.-D. Screening and characterization of bacteriocinogenic lactic acid bacteria from Jeot-Gal, a Korean fermented fish food. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2000, 10, 423–428. [Google Scholar]
- Clauwers, C.; Vanoirbeek, K.; Delbrassinne, L.; Michiels, C.W. Construction of nontoxigenic mutants of nonproteolytic Clostridium botulinum NCTC 11219 by insertional mutagenesis and gene replacement. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2016; p. 260. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team: Vienna, Austria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Stavropoulou, D.A.; De Maere, H.; Berardo, A.; Janssens, B.; Filippou, P.; De Vuyst, L.; De Smet, S.; Leroy, F. Species pervasiveness within the group of coagulase-negative staphylococci associated with meat fermentation is modulated by pH. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulou, D.A.; Van Reckem, E.; De Smet, S.; De Vuyst, L.; Leroy, F. The narrowing down of inoculated communities of coagulase-negative staphylococci in fermented meat models is modulated by temperature and pH. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 274, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, S.; Mauriello, G.; Aponte, M.; Moschetti, G.; Villani, F. Microbial succession during ripening of Naples-type salami, a southern Italian fermented sausage. Meat Sci. 2000, 56, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavropoulou, D.A.; De Maere, H.; Berardo, A.; Janssens, B.; Filippou, P.; De Vuyst, L.; De Smet, S.; Leroy, F. Pervasiveness of Staphylococcus carnosus over Staphylococcus xylosus is affected by the level of acidification within a conventional meat starter culture set-up. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 274, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otto, M. Staphylococcus epidermidis—The “accidental” pathogen. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 7, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raz, R.; Colodner, R.; Kunin, C.M. Who Are You—Staphylococcus saprophyticus? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 896–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janek, D.; Zipperer, A.; Kulik, A.; Krismer, B.; Peschel, A. High frequency and diversity of antimicrobial activities produced by nasal Staphylococcus strains against bacterial competitors. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandiford, S.; Upton, M. Identification, characterization, and recombinant expression of epidermicin NI01, a novel unmodified bacteriocin produced by Staphylococcus epidermidis that displays potent activity against staphylococci. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 1539–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, J.D.S.; Coelho, M.L.V.; Ceotto, H.; Potter, A.; Fleming, L.R.; Salehian, Z.; Nes, I.F.; Bastos, M.C.F. Genes involved in immunity to and secretion of aureocin A53, an atypical class II bacteriocin produced by Staphylococcus aureus A53. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navaratna, M.A.D.B.; Sahl, H.-G.; Tagg, J.R. Identification of genes encoding two-component lantibiotic production in Staphylococcus aureus C55 and other phage group II S. aureus strains and demonstration of an association with the exfoliative toxin B gene. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 4268–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennallack, P.R.; Burt, S.R.; Heder, M.J.; Robison, R.A.; Griffitts, J.S. Characterization of a novel plasmid-borne thiopeptide gene cluster in Staphylococcus epidermidis strain 115. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 4344–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, M.A.V.P.; Somkuti, G.A.; Renye, J.A. Production of antilisterial bacteriocins by staphylococci isolated from bovine milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmdel, S.; Shekarforoush, S.S.; Hosseinzadeh, S.; Torriani, S.; Gatto, V. Antimicrobial spectrum activity of bacteriocinogenic Staphylococcus strains isolated from goat and sheep milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 2928–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, D.A.; Barkema, H.W.; Naushad, S.; De Buck, J. Bacteriocins of non-aureus staphylococci isolated from bovine milk. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e01015-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, M.A.; Somkuti, G.A.; Renye, J.A. Isolation of bacteriocin-producing staphylococci from Brazilian cheese. J. Food Saf. 2011, 31, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Quan, L.-H.; Heu, S.; Jung, K.S.; Han, S.-W.; Moon, E.; Roh, E. A new antimicrobial substance produced by Staphylococcus pasteuri isolated from vegetables. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 983–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braem, G.; Stijlemans, B.; Van Haken, W.; De Vliegher, S.; De Vuyst, L.; Leroy, F. Antibacterial activities of coagulase-negative staphylococci from bovine teat apex skin and their inhibitory effect on mastitis-related pathogens. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 1084–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, J.D.S.; Fagundes, P.C.; Brito, M.A.V.P.; dos Santos, K.R.N.; Bastos, M.C.F. Production of bacteriocins by coagulase-negative staphylococci involved in bovine mastitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 106, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatsuji, T.; Chen, T.H.; Narala, S.; Chun, K.A.; Two, A.M.; Yun, T.; Shafiq, F.; Kotol, P.F.; Bouslimani, A.; Melnik, A.V.; et al. Antimicrobials from human skin commensal bacteria protect against Staphylococcus aureus and are deficient in atopic dermatitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaah4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleerebezem, M. Quorum sensing control of lantibiotic production; nisin and subtilin autoregulate their own biosynthesis. Peptides 2004, 25, 1405–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleerebezem, M.; Quadri, L.E. Peptide pheromone-dependent regulation of antimicrobial peptide production in Gram-positive bacteria: A case of multicellular behavior. Peptides 2001, 22, 1579–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleerebezem, M.; Kuipers, O.P.; de Vos, W.M.; Stiles, M.E.; Quadri, L.E.N. A two-component signal-transduction cascade in Carnobacterium piscicola LV17B: Two signaling peptides and one sensor-transmitter. Peptides 2001, 22, 1597–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leroy, F.; de Vuyst, L. Temperature and pH conditions that prevail during fermentation of sausages are optimal for production of the antilisterial bacteriocin sakacin K. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 974–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sarrau, B.; Clavel, T.; Clerté, C.; Carlin, F.; Giniès, C.; Nguyen-The, C. Influence of anaerobiosis and low temperature on Bacillus cereus growth, metabolism, and membrane properties. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kröckel, L. The role of lactic acid bacteria in safety and flavour development of meat and meat products. In Lactic Acid Bacteria—R & D for Food, Health and Livestock Purposes; Kongo, J.M., Ed.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peypoux, F.; Bonmatin, J.M.; Wallach, J. Recent trends in the biochemistry of surfactin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 51, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, G.I.; Correa, O.S.; Montecchia, M.S.; Kerber, N.L.; Pucheu, N.L.; Bachur, M.; García, A.F. Genetic and functional characterization of a Bacillus sp. strain excreting surfactin and antifungal metabolites partially identified as iturin-like compounds. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 97, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.T.; Munita, J.M.; Arias, C.A. Mechanisms of drug resistance: Daptomycin resistance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1354, 32–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fair, R.J.; Tor, Y. Antibiotics and bacterial resistance in the 21st century. Perspect. Med. Chem. 2014, 6, 25–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeghaire, S.; Argudín, M.A.; Feßler, A.T.; Hauschild, T.; Schwarz, S.; Butaye, P. The ecological importance of the Staphylococcus sciuri species group as a reservoir for resistance and virulence genes. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeman, M.; Mašlaňová, I.; Indráková, A.; Šiborová, M.; Mikulášek, K.; Bendíčková, K.; Plevka, P.; Vrbovská, V.; Zdráhal, Z.; Doškař, J.; et al. Staphylococcus sciuri bacteriophages double-convert for staphylokinase and phospholipase, mediate interspecies plasmid transduction, and package mecA gene. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, P.M.; Wolken, W.A.M.; Claisse, O.; Lolkema, J.S.; Lonvaud-Funel, A. Histamine-producing pathway encoded on an unstable plasmid in Lactobacillus hilgardii 0006. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spano, G.; Russo, P.; Lonvaud-Funel, A.; Lucas, P.; Alexandre, H.; Grandvalet, C.; Coton, E.; Coton, M.; Barnavon, L.; Bach, B.; et al. Biogenic amines in fermented foods. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, S95–S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Mainar, M.; Weckx, S.; Leroy, F. Coagulase-negative staphylococci favor conversion of arginine into ornithine despite a widespread genetic potential for nitric oxide synthase activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7741–7751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcobal, Á.; de las Rivas, B.; García-Moruno, E.; Muñoz, R. The tyrosine decarboxylation test does not differentiate Enterococcus faecalis from Enterococcus faecium. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 27, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aymerich, T.; Martín, B.; Garriga, M.; Vidal-Carou, M.C.; Bover-Cid, S.; Hugas, M. Safety properties and molecular strain typing of lactic acid bacteria from slightly fermented sausages. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landete, J.M.; Pardo, I.; Ferrer, S. Tyramine and phenylethylamine production among lactic acid bacteria isolated from wine. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 115, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardini, F.; Bover-Cid, S.; Tofalo, R.; Belletti, N.; Gatto, V.; Suzzi, G.; Torriani, S. Modeling the aminogenic potential of Enterococcus faecalis EF37 in dry fermented sausages through chemical and molecular approaches. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2740–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Capillas, C.; Herrero, A.M. Impact of biogenic amines on food quality and safety. Foods 2019, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de las Rivas, B.; Rodríguez, H.; Carrascosa, A.V.; Muñoz, R. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a histidine decarboxylase from Staphylococcus capitis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosinos, E.H.; Paramithiotis, S.; Kolovos, G.; Tsikouras, I.; Metaxopoulos, I. Phenotypic and technological diversity of lactic acid bacteria and staphylococci isolated from traditionally fermented sausages in Southern Greece. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitter, M.; Nerz, C.; Rosenstein, R.; Goetz, F.; Hertel, C. DNA microarray-based detection of genes involved in safety and technologically relevant properties of food associated coagulase-negative staphylococci. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 145, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.; Garriga, M.; Hugas, M.; Bover-Cid, S.; Veciana-Nogues, M.T.; Aymerich, T. Molecular, technological and safety characterization of Gram-positive catalase-positive cocci from slightly fermented sausages. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 107, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parente, E.; Martuscelli, M.; Gardini, F.; Grieco, S.; Crudele, M.A.; Suzzi, G. Evolution of microbial populations and biogenic amine production in dry sausages produced in Southern Italy. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2001, 90, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bover-Cid, S.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M.; Vidal-Carou, M.C. Effect of the interaction between a low tyramine-producing Lactobacillus and proteolytic staphylococci on biogenic amine production during ripening and storage of dry sausages. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 65, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Organic Compound | Ionisation Mode | SRM | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transition (m/z) | CV (V)/CE (eV) | ||
| Agmatine | ES + | 131.00 > 72.02 | 15/15 |
| Cadaverine | ES + | 103.08 > 86.04 | 15/12 |
| Histamine | ES + | 112.06 > 95.02 | 18/15 |
| β-Phenylethylamine | ES + | 122.08 > 105.02 | 23/12 |
| Putrescine | ES + | 89.05 > 72.02 | 11/11 |
| Tryptamine | ES + | 161.13 > 144.03 | 10/11 |
| Tyramine | ES + | 138.09 > 121.04 | 10/12 |
| Spermidine | ES + | 146.00 > 72.05 | 20/12 |
| Spermine | ES + | 203.22 > 129.12 | 22/12 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Van der Veken, D.; Benhachemi, R.; Charmpi, C.; Ockerman, L.; Poortmans, M.; Van Reckem, E.; Michiels, C.; Leroy, F. Exploring the Ambiguous Status of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in the Biosafety of Fermented Meats: The Case of Antibacterial Activity Versus Biogenic Amine Formation. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020167
Van der Veken D, Benhachemi R, Charmpi C, Ockerman L, Poortmans M, Van Reckem E, Michiels C, Leroy F. Exploring the Ambiguous Status of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in the Biosafety of Fermented Meats: The Case of Antibacterial Activity Versus Biogenic Amine Formation. Microorganisms. 2020; 8(2):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020167
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan der Veken, David, Rafik Benhachemi, Christina Charmpi, Lore Ockerman, Marijke Poortmans, Emiel Van Reckem, Chris Michiels, and Frédéric Leroy. 2020. "Exploring the Ambiguous Status of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in the Biosafety of Fermented Meats: The Case of Antibacterial Activity Versus Biogenic Amine Formation" Microorganisms 8, no. 2: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020167
APA StyleVan der Veken, D., Benhachemi, R., Charmpi, C., Ockerman, L., Poortmans, M., Van Reckem, E., Michiels, C., & Leroy, F. (2020). Exploring the Ambiguous Status of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in the Biosafety of Fermented Meats: The Case of Antibacterial Activity Versus Biogenic Amine Formation. Microorganisms, 8(2), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8020167






