Abstract
Despite Aspergillus being the leading cause of exogenous fungal endophthalmitis following traumatic injury to the eye, its pathogenesis is not fully understood. In the current study, we developed a murine model of Aspergillus fumigatus (AF) endophthalmitis and investigated the disease pathobiology. Endophthalmitis was induced by intravitreal injection of Aspergillus spores in immunocompetent and immunocompromised (neutropenic) C57BL/6 mice, and disease severity was assessed by eye exam, fungal burden estimation, and histological examination. Our data showed that AF infection caused a time-dependent increase in corneal haze, opacity, and hypopyon beginning at two days post-infection (DPI). The fungal burden in infected eyes of immunocompetent mice peaked at 2 DPI and declined over 9 DPI. AF-infected neuroretina exhibited induction of innate immune response via upregulation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) and inflammatory mediators (TNFα, IL-1β, and IL6), and increased polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) infiltration. Histological analysis revealed heavy cellular infiltrates in the vitreous cavity as well as disruption of normal retinal architecture and increased retinal cell death. Neutropenic mice exhibited severe disease pathology with the prolonged fungal burden and increased inflammatory mediators. Our study described the first immunocompetent murine model of exogenous AF endophthalmitis and demonstrated an important role of neutrophils in innate defense against fungal endophthalmitis.
1. Introduction
Endophthalmitis is a detrimental ocular infection leaving one-third of those infected nearly blind [1]. Severe vision loss is a result of retinal damage caused by both pathogen virulence factors and an uncontrolled host inflammatory response [2,3,4]. After bacterial pathogens [5], fungi are the leading cause of both exogenous and endogenous endophthalmitis [6]. The exogenous fungal endophthalmitis is more common following penetrating ocular trauma, whereas endogenous fungal endophthalmitis results from hematogenous spread of organisms to the eye mainly in immunocompromised individuals [7,8,9]. Fungal endophthalmitis accounts for 8.6 to 18.6% of culture-positive endophthalmitis where Candida and Aspergillus spp. are the most common causative agents [10,11]. The prognosis of fungal endophthalmitis is poor, depending on the virulence of the pathogen, timing, and mode of intervention.
Aspergillus species are ubiquitous saprophytic molds, often affecting immunocompromised patients. However, infection in an immunocompetent individual has been also reported [12]. Aspergillus has been reported to cause both exogenous [13] and endogenous [14,15,16] endophthalmitis. In the eye, Aspergillus grows preferentially along retinal pigment epithelium and subretinal space resulting in a poor visual prognosis [17]. Aspergillus endophthalmitis results in the rapid onset of pain, along with confluent yellowish infiltrate in the macula, choroid and subretinal space, hypopyon in subretinal and subhyaloidal space, retinal hemorrhage, and visual loss [18].
Since most data on Aspergillus endophthalmitis are limited to clinical and epidemiological studies [19,20], the molecular pathogenesis of this disease is not well understood. This, in part, could be due to limited or unavailability of appropriate fungal endophthalmitis animal models. However, few earlier studies have utilized guinea pig [21] and rabbit [22,23] models to test the therapeutic efficacy of antifungal agents in Aspergillus fumigatus (AF) endophthalmitis. Similarly, we evaluated isavuconazole for the treatment of AF endophthalmitis in a mouse model [11]. Thus the development of animal models for Aspergillus endophthalmitis can help to address the pathophysiologic process of this disease and the determination of therapeutic efficacy of antifungal drugs.
In the current study, we describe a murine model of exogenous A. fumigatus endophthalmitis and characterize the disease pathogenesis and retinal innate immune response. Better understanding of the protective immune mechanisms evoked in A. fumigatus endophthalmitis is likely to lead to newer immunomodulatory approaches to mitigate vision loss.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice and Ethics Statement
C57BL/6 mice (both male and female mice, 8–12 weeks of age) were purchased from the Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME, USA) and housed at the Kresge Eye Institute (Detroit, MI, USA). Animals were maintained in a 12:12 light/dark cycle, and fed LabDiet rodent chow (Labdiet; Pico Laboratory, St. Louis, MO, USA) and water ad libitum. Mice were treated in compliance with the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) Statement for the Use of Animals in Ophthalmic and Vision Research, and all procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Wayne State University under protocol 16-06-104.
2.2. Preparation of Fungal Spores
A clinical isolate of A. fumigatus was obtained from the Division of Infectious Diseases [11], Department of Internal Medicine, at Wayne State University School of Medicine. For sporulation, A. fumigatus was grown on Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SDA) plates for six days at room temperature. Following sporulation, the spores were harvested, and the count was adjusted to the desired colony forming units (CFU) by diluting the spores in sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS).
2.3. Induction of Aspergillus Endophthalmitis
Endophthalmitis was induced in C57BL/6 mice by intravitreal injection of A. fumigatus spores (15,000 CFU/µL/eye). The PBS injected eye served as control. At the desired time points post-infection (up to 9 days post-infection (DPI)) clinical examinations were performed using a slit lamp. The ocular disease was graded on a four-point scale, as described previously [24,25]. The enucleated eyes of the infected mouse were subjected to fungal burden estimation, inflammatory cytokine/chemokine assays, polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) infiltration, and histological analysis as described in the following sections.
2.4. Fungal Burden Estimation
Fungal burden was estimated using serial dilution and plate count method as described previously [11,26]. Briefly, at each respective time point, the eyes were enucleated and homogenized in sterile PBS by using a Dounce homogenizer. The homogenate was serially diluted in sterile PBS and plated on SDA plates and incubated at 37 °C. Following growth, the fungal colonies were counted and the results were expressed as mean number of CFU/eye ± Standard deviation (SD).
2.5. Cytokine/Chemokine ELISA
At desired time points post-infection, eyes were enucleated, and lysates were prepared using TissueLyser II (Qiagen, Valencia, CA, USA). The total protein was estimated using a bicinchoninic acid (BCA) protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA), and 15–20 μg total protein was used for cytokine measurements. The ELISA was performed using commercially available ELISA kits for TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) per the manufacturer’s instructions. The data are presented as the mean pg/mg of the tissue lysates ± standard deviation (SD).
2.6. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from Aspergillus infected and control mice retina using Trizol as per the manufacturer’s recommendation (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA). cDNA was synthesized using 1 µg of total RNA by Maxima first-strand cDNA synthesis kit, as per the manufacturer’s instructions (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA). The cDNA was amplified using gene-specific PCR primers using StepOnePlus™ Real-Time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Grand Island, NY, USA). All primers and TaqMan probes (Prime Time Mini qPCR Assay) were purchased from Integrated DNA Technologies (Coralville, IA, USA). The quantification of gene expression was determined via the comparative ΔΔCT method. Gene expression in the test samples was normalized to the endogenous control, GAPDH, and was reported as fold change relative to GAPDH gene expression.
2.7. Immunofluorescence and TUNEL Staining
Immunostaining was performed on retinal cryosections following Aspergillus infection as described in our recent publications [27,28]. Briefly, infected and control mice eyes were enucleated and fixed in 4% PFA, dehydrated, and embedded in paraffin. Thin (10–12 µm) sections were made using a cryostat and mounted onto lysine coated microscope slides. For immunostaining, retinal sections were fixed in 4% PFA for 20 min followed by four washes with PBS (10 min each wash). Retinal sections were permeabilized and blocked with 10% normal goat serum with 0.5% Triton X100 for 2 h at room temperature (RT) and incubated overnight with primary antibody (1:100). The next day, sections were washed four times with PBS (10 min each) and incubated with anti-mouse/rabbit Alexa Fluor 485/594-conjugated secondary antibody (1:200) for 2 h at RT. The retinal sections were washed with PBS (four washes, 10 min each), and the slides were mounted in Vectashield anti-fade mounting medium (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA) and visualized using Eclipse 90i fluorescence microscope (Nikon, Melville, NY, USA).
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) was performed on retinal cryosections using an ApopTag® Fluorescein In situ Apoptosis Detection Kit (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) as per the manufacturer’s instructions. The TUNEL-stained cells were imaged using an Eclipse 90i fluorescence microscope (Nikon).
2.8. Histological Assay
Eyes from the Aspergillus infected, and control mice were enucleated at desired time points post-infection for histopathological examination and fixed in 4% formalin. The embedding, sectioning, and hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining were performed by Excalibur Pathology, Inc. (Oklahoma City, OK, USA). Histological sections were scanned using a PathScan Enabler IV scanner (Mayer Instruments, Houston, TX, USA).
2.9. PMN Infiltration
Flow cytometry was used to determine the infiltration of PMNs in Aspergillus infected retina, as described previously [26,29]. Briefly, at each desired time point post-infection, the retinas were isolated from the eyes and digested with Accumax (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) for 10 min at 37 °C. Following digestion, the retinal tissue was triturated by passing through a 23-gauge needle and syringe and filtered through a 40 µm cell strainer (BD Falcon, San Jose, CA, USA). The cells were blocked using Fc Block (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) for 30 min, followed by washing with PBS containing 0.5% bovine serum albumin (BSA). Cells were then incubated with CD45-PE-Cy5 and Ly6G-FITC antibodies (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) for 30 min in the dark. After subsequent washing steps, the cells were acquired by a BD AccuriC6 flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, Ann Arbor, MI, USA). At least 50,000 cells were analyzed in each treatment. The data were analyzed using AccuriC6 software (BD Biosciences, Ann Arbor, MI, USA).
2.10. Neutrophil Depletion
To make mice neutropenic, Anti-Ly6G-1A8 antibody (200 µg/100 µL/mice) (R&D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) were administered systemically by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection 24 h before Aspergillus infection [30]. Control mice received PBS by i.p. injections.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
All data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) unless indicated otherwise. Statistical differences between experimental groups were determined using unpaired Student’s t-test and one-way ANOVA. All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 8 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA). A value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All experiments were performed at least three times unless indicated otherwise.
3. Results
3.1. Intravitreal Inoculation of AF Spores Causes Endophthalmitis in C57BL/6 Murine Eyes
In healthy individuals, AF mainly causes exogenous endophthalmitis. To mimic this situation, we performed a dose-response study by injecting AF spores in the eyes of immunocompetent, C57BL/6 (B6) mice. We found that intravitreal injections of 15,000 spores/eye resulted in reproducible fungal endophthalmitis in B6 mice as evidenced by a time-dependent increase in corneal opacity, hypopyon, angiogenesis, and intraocular inflammation (Figure 1A). In contrast, control animals exhibited comparatively clear cornea and anterior chamber with no visible signs of inflammation. To further assess the disease severity, histological analysis was performed which demonstrated a time-dependent increase in cellular infiltration, retinal folding as well as disorganization of the retinal architecture; 5 DPI onwards the AF-infected retina was totally disintegrated (Figure 1B). These findings coincided with increased retinal cell death, as indicated by a greater number of TUNEL positive cells in the infected eyes (Figure 1C). Together, these results indicate that AF causes endophthalmitis and results in severe retinal tissue damage in mouse eyes.
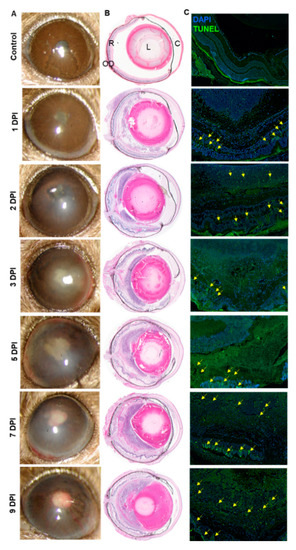
Figure 1.
Wild type (WT) C57BL/6 (B6) mice eyes (n = 12 each time point) were infected with Aspergillus fumigatus spores (15,000 colony forming units (CFU)/eye) by intravitreal injections. Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) injected eyes were used as control. (A) Slit-lamp examination was performed at indicated time points and photomicrographs were taken from representative eyes. (B) For histological analysis, eyes were enucleated at indicated time points and subjected to hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining. (C) To evaluate retinal cell death, retinal cryosections were subjected to TUNEL staining (TUNEL positive cells shown by the yellow arrow) at indicated time points. R: retina, OD: optic disc, L: lens, C: cornea.
3.2. AF Infected Eyes Exhibited a Temporal Decrease in Fungal Burden and Neutrophil Infiltration
To determine the fungal growth, serial dilution and plate counting were performed on enucleated eyes at various days post-infection (DPI), and our data showed that fungal burden modestly increased at 2 DPI followed by a gradual decline (Figure 2A). Since neutrophils are the main innate immune cells recruited in response to microbial infection, the flowcytometry analysis was performed to assess neutrophil infiltration (Figure 2B). Similar to the fungal burden, our data showed that neutrophil infiltration peaked at 2 DPI and declined at later time points (3–7 DPI), but remains significantly higher as compared to uninfected control eyes (Figure 2C). Immunostaining also confirmed the presence of PMNs in infected mouse retinal tissue, as evidenced by increased staining of Ly6G positive cells (Figure 2D). These results indicate a direct correlation between fungal load and increased neutrophil infiltration in AF endophthalmitis.
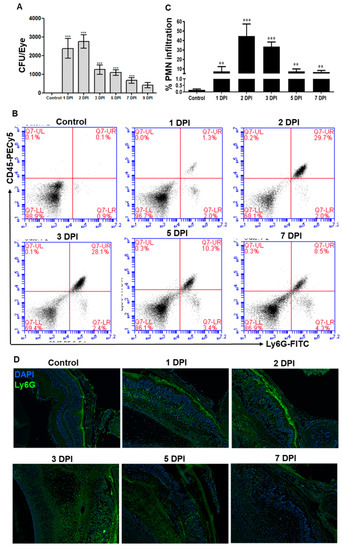
Figure 2.
WT B6 mice eyes (n = 10 each time point) were infected with A. fumigatus spores (15,000 CFU/eye) by intravitreal injections. (A) At indicated days post-infection (DPI), eyes were enucleated, homogenized, and the bacterial burden was estimated via serial dilution plating. (B) Two retinas were pooled to make single-cell suspensions and the cells were stained with anti-CD45-PE-Cy5 and anti-Ly6G-FITC antibodies for polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) staining. Dot plot showing CD45-Ly6G positive (upper-right quadrant) PMNs. (C) Bar graph representing the percent PMN infiltration in the retina using flow-cytometry. (D) Retinal cryosections were subjected to anti-Ly6G staining for PMNs. **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.0005; One-way ANOVA.
3.3. AF Infected Retina Exhibited Increased Inflammatory Mediators and Induced Expression of Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs)
The recruitment of neutrophils is a dynamic process regulated by the production of inflammatory chemokine and cytokines. Therefore, we assessed the expression of various inflammatory mediators at transcripts as well as protein levels. The qRT-PCR analysis revealed significantly increased mRNA levels of several inflammatory cytokines and chemokines e.g., Tnf α, Il-6, and Cxcl2 in AF-infected retina (Figure 3A). Tnf α transcripts showed time-dependent increased expression while the transcripts of Il-6 and Cxcl2 peaked at 2 and 1 DPI respectively and slightly declined thereafter.
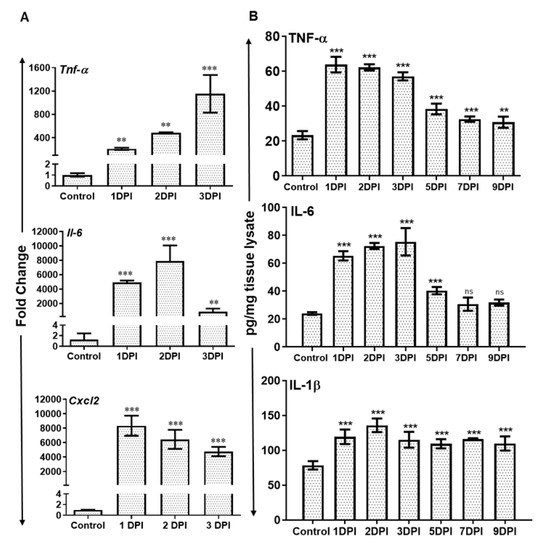
Figure 3.
WT B6 mice eyes (n = 10 each time point) were infected with A. fumigatus spores (15,000 CFU/eye) by intravitreal injections. (A) The neural retina was used for RNA isolation and qRT-PCR for inflammatory cytokines/chemokines Tnfα, Il-6, and Cxcl2. (B) The eye lysates from infected and control eyes were subjected to ELISA to quantify the protein level of indicated inflammatory cytokines. ns, not significant, **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.0005; One-way ANOVA.
We confirmed the translation of these mRNA transcripts by measuring the protein levels of inflammatory cytokines by ELISA. Our results show that Aspergillus infection resulted in the induction of inflammatory mediators TNFα, IL-1β, and IL-6 at protein level as well (Figure 3B). The expression of these cytokines peaked at 1 or 2 DPI and remained elevated until 3 DPI, followed by a slight decline thereafter.
Activation of Toll-like receptors (TLRs) following pathogen challenge plays an important role in the initiation of the early innate immune response against microbial infections. Since we observed PMN infiltration and induction of inflammatory mediators in AF-infected eyes, we assessed the expression of TLRs using qRT-PCR. To this end, our results show that AF infection resulted in a significant and time-dependent induced expression of mRNA transcripts of several TLRs including TLR1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, and 9 in infected mouse retina (Figure 4).
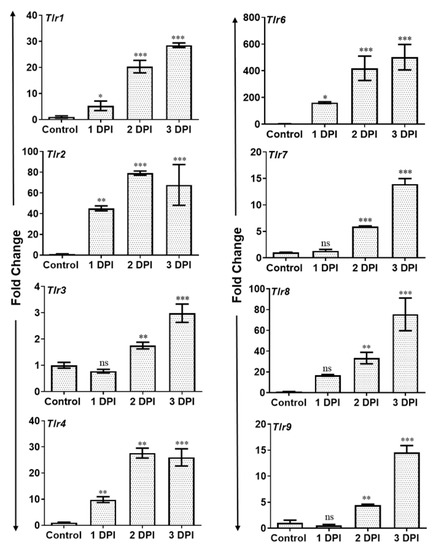
Figure 4.
WT B6 mice eyes (n = 10 each time point) were infected with A. fumigatus spores (15,000 CFU/eye) by intravitreal injections and the vitreous/retina were isolated at the indicated time points. Infected and control neural retina were used for RNA isolation and subjected to qRT-PCR for various Toll-like receptors (Tlr1–9) at indicated DPI. The data are presented as fold changes in comparison with uninfected controls. ns = not significant, *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005, ***, p < 0.0005; One-way ANOVA.
3.4. Neutropenic Mice Are More Susceptible to AF Endophthalmitis
Since we observed increased PMN infiltration correlating with the fungal burden in AF-infected eyes, we sought to determine the specific role of PMNs in this model. As we reported earlier, mice were made neutropenic using systemic injections of an anti-Ly6G-1A8 antibody to specifically deplete PMNs [30]. Our results show that neutropenic C57BL/6 mice sustained more severe AF endophthalmitis as revealed by increased hypopyon, anterior chamber haze, corneal opacity, as well as angiogenesis in infected eyes (Figure 5A). Histological analysis also corroborated with increased retinal tissue damage in neutropenia versus immunocompetent mice (Figure 5B). Fungal burden estimation revealed that immunocompetent mice had a slight increased fungal burden at 2 DPI followed by decline up to 9 DPI. In contrast, the fungal burden remained elevated up to 5 DPI in neutropenic mice, but no significant difference was observed at 7 and 9 DPI time points (Figure 5C). Interestingly, the levels of inflammatory mediators (e.g., IL-1β) remained higher at all time points in neutropenic versus immunocompetent mice (Figure 5D). These results indicate an essential role of PMNs in protection against fungal endophthalmitis.
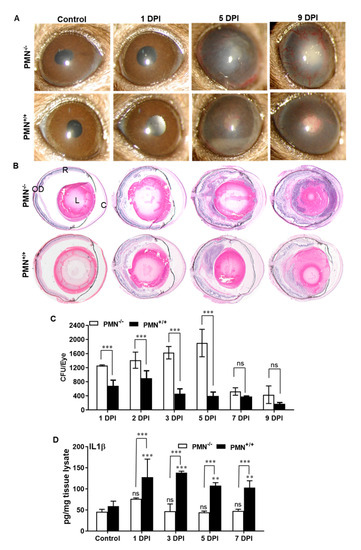
Figure 5.
WT B6 mice were made neutropenic (PMN−/−) by intraperitoneal injection of Anti-Ly6G-1A8 antibody. Immunocompetent B6 mice (without PMN depletion, PMN+/+) were used as control. Then, 24 h following neutropenia eyes (n = 10 each time point) were infected with A. fumigatus spores (15,000 CFU/eye) by intravitreal injections. (A) Slit-lamp examination was performed at indicated time points and photomicrographs were taken from representative eyes. (B) For histological analysis, eyes were enucleated at indicated DPI and subjected to H&E staining. (C) Fungal burden was estimated from eye lysates via serial dilution plating. (D) The eye lysate was subjected to ELISA for representative inflammatory cytokine e.g., IL-1β. ns, not significant; **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.0005; One-way ANOVA. R: retina, OD: optic disc, L: lens, C: cornea.
4. Discussion
Over the past decades, the incidence of ocular fungal infections has increased due to extended use of cancer chemotherapy, immunosuppressive agents, long-term broad-spectrum antibiotics, and increasing number of immunocompromised patients with increased incidence of diabetes, cancer, and HIV infection [31,32]. Among ocular mycoses, corneal infection (keratitis) remains the most frequent presentation. Therefore, extensive studies, including the pathobiology are available for fungal keratitis. However, fungi have the ability to infect multiple ocular structures such as conjunctiva, eyelid, lacrimal gland, orbit, eyelid, sclera, and intraocular structures such as uvea and the retina. The delicate nature of intraocular tissues such as the retina, lends itself to significant visual disability, blindness, and even enucleation when challenged by fungal infections, like endophthalmitis. Considering the importance of understanding the molecular pathogenesis of fungal endophthalmitis, in this study, we demonstrated the pathological changes in Aspergillus infected murine eyes and the induction of retinal innate responses. Moreover, using neutropenic mice, our study elucidated the protective role of neutrophils in fungal endophthalmitis.
Aspergillus has the ability to cause both exogenous and endogenous endophthalmitis, in immunocompetent and immunocompromised individuals respectively [14,33,34,35,36,37,38]. Here, we mimicked exogenous fungal endophthalmitis by directly inoculating Aspergillus fumigatus (AF) spores in the eyes of immunocompetent C57BL/6 wild type mice. We observed that AF-infected eyes show the characteristics of endophthalmitis including the development of corneal haze, opacity, hypopyon, and corneal neovascularization. Furthermore, heavy cellular infiltrates, fibrin deposits and retinal tissue damage were evident in infected eyes. The retinal tissue integrity began to deteriorate 2 days post-infection (DPI) and by day 5 retinal architecture was completely disintegrated with increased retinal cell death. Similar disease pathology has been reported in severe cases of bacterial endophthalmitis including Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, and Acinetobacter baumannii [26,30,39,40,41]. Heavy corneal angiogenesis has also been reported in Candida albicans model of keratitis [42]. When we measured the fungal burden in infected eyes, we found the fungal burden peaked at 2 DPI and reduced thereafter. Despite the reduction in the fungal burden, we observed a time-dependent increase in angiogenesis and severe histological damage in the eye indicating that host-mediated inflammatory signals lead to the destruction of retinal tissue and vision in fungal infection. This trend correlated with A. baumannii endophthalmitis, where the bacterial growth has been reported to decrease by 3 DPI, but ocular damage increases in a time-dependent manner [43].
TLRs have been shown to play a key role in the initiation of innate immune defense in the retina following bacterial and viral infection and TLR deficiency makes mice more susceptible to disease [26,27,28,40,44,45,46,47,48]. Several fungal ligands have been shown to interact with various TLRs, e.g., fungal chitin directly binds to TLR2 and induce an inflammatory response [49]. Similarly, fungal-β-glucans, phospholipo-mannans and linear beat-1,2-oligomannoside are also recognized by TLR2 [50]. TLR4 has been reported to be activated by Candida albicans O-linked mannans as well as Cryptococcus neoformans glucuronoxylomannan [50]. TLR2 has been shown to be activated by unidentified ligands present on both conidia and hyphae forms of A. fumigatus whereas ligands for TLR4 have been reported only on conidial forms [50,51,52]. To investigate the potential involvement in Aspergillus induced host innate immune response we measured the expression of various TLRs in the retina. We showed that Aspergillus infection induced the innate immune response via activation of several TLRs including TLR1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8, and 9 in the retina. Our findings corroborated with studies showing initiation of immune response via TLR2 and TLR4 in murine macrophages [53] and Human PBMC [54] in vitro following Aspergillus challenge, as well as in experimental invasive pulmonary aspergillosis [55]. Further studies involving the knockdown of specific TLRs are needed to delineate their role.
TLR activation leads to the production of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines which recruit PMNs and control the growth of the pathogen. We observed that Aspergillus infection induced the production of several inflammatory cytokines and chemokines including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL6, and CXCL2 in the eyes. This observation corroborated with the findings in bacterial endophthalmitis and keratitis models [26,29,30,40,44,56]. Inflammatory cytokine TNFα is an early responder compared to other cytokine/chemokines, and its upregulation is in parallel with the influx of PMNs [57]. We observed an increase in CXCL2 chemokine expression which is also known to be regulated by TNFα upregulation and another contributor to the rise in PMNs [58]. Experimental models have identified PMNs as the primary infiltrating cell type during bacterial ocular infections [57,59] as well as Aspergillus keratitis [60,61], and our current data support these studies by showing heavy PMN infiltration in the case of Aspergillus endophthalmitis as well. We observed that in the Aspergillus infected retina, PMN recruitment began at 1 DPI, peaked at 2 DPI, and slightly declined thereafter. Yet, the recruitment and activation of neutrophils within an infected eye is a biological dilemma. PMN infiltration is the immediate response for acute intraocular infection, but the generation of toxic reactive oxygen intermediates and other inflammatory mediators by PMNs may results in bystander damage to delicate tissues of the retina [57,58]. It was also found that the injection of TNFα into the vitreous of rabbits and rats have induced vascular permeability, stimulates mononuclear phagocytes and activates proinflammatory signaling cascades [57,62,63]. Ramadan et al. reported TNFα- knockout mice infected with B. cereus faced a more rapid decline in retinal function, increased the bacterial burden, and lowered PMN count [57]. Hence, with the combination of PMN infiltration and inflammatory cytokine release, retina are more prone to damage. In the current study, we found the peak of inflammatory mediators and PMNs at day 2 or 3 following which there is the most retinal damage despite the reduction in fungal burden, as seen with the increased retinal folds, tissue destruction, and heavy angiogenesis.
Fungal ocular infection has been reported more frequently in immunocompromised individuals and, in general, neutropenic patients are at particularly high risk for A. fumigatus infection [12]. Here, we investigated the role of immunocompromisation by PMN depletion in A. fumigatus endophthalmitis. Our study reveals that neutropenia (PMN−/−) led to increased severity of Aspergillus endophthalmitis as revealed by increased corneal haze, neovascularization with angiogenesis, and destruction of retinal architecture as compared to immunocompetent (PMN+/+) mice. PMN−/− mice also exhibited increased fungal burden in the eyes as compared to PMN+/+ mice, indicating that limited PMN infiltration is required for fungal clearance. We also showed that neutropenic mice exhibited reduced cytokine response which initially may be required for pathogen clearance, and this might have led to increased severity of disease.
In conclusion, our study demonstrated Aspergillus endophthalmitis acquired by exogenous route initiated host innate immune response by activation of several TLRs, followed by induction of inflammatory cytokines and PMN recruitment. Neutropenia makes the mouse more susceptible towards the disease. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first murine model of Aspergillus-induced endophthalmitis in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised (neutropenic) mice. Further detailed studies are required to investigate the role of individual TLRs in this disease pathogenesis, and to understand the innate immune response can contribute to better management of patients affected by Aspergillus endophthalmitis.
Author Contributions
N.G. and P.K.S. performed experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote initial manuscript drafts. S.G.R. and P.H.C. participated in study design, data collection and analysis. A.K. conceived the idea and designed the study, interpreted the data, and provided important intellectual contents and obtained the final approval of the submitted manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in parts by NIH grants R01EY02738, R01EY026964, & R21AI140033, and an unrestricted grant to the Kresge Eye Institute from Research to Prevent Blindness Inc. The immunology resource core is supported by an NIH center grant P30EY004068.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the other members of the lab for their helpful discussion, critical reading, and reviewing the final manuscript. The funders had no role in study design, data collection, and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Disclaimer
Authors made significant efforts to ensure that appropriate and justified references being cited to the best of their knowledge. The authors would like to apologize to the groups whose references might have been overlooked while citing the literature.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sadaka, A.; Durand, M.L.; Gilmore, M.S. Bacterial endophthalmitis in the age of outpatient intravitreal therapies and cataract surgeries: Host-microbe interactions in intraocular infection. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2012, 31, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, F.C.; Coburn, P.S.; Huzzatul, M.M.; LaGrow, A.L.; Livingston, E.; Callegan, M.C. Targets of immunomodulation in bacterial endophthalmitis. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Pandey, R.K.; Miller, L.J.; Singh, P.K.; Kanwar, M. Muller glia in retinal innate immunity: A perspective on their roles in endophthalmitis. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 33, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, D.; Chakrabarti, M.; Jayasudha, R.; Hasnat Ali, M.; Tyagi, M.; Sharma, S.; Joseph, J. Elevated cytokine levels in vitreous as biomarkers of disease severity in infectious endophthalmitis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brockhaus, L.; Goldblum, D.; Eggenschwiler, L.; Zimmerli, S.; Marzolini, C. Revisiting systemic treatment of bacterial endophthalmitis: A review of intravitreal penetration of systemic antibiotics. Clin. Microbiol. Infec. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, T.V.; Dave, V.P.; Sharma, S.; Karolia, R.; Joseph, J.; Pathengay, A.; Pappuru, R.R.; Das, T. Infectious endophthalmitis leading to evisceration: Spectrum of bacterial and fungal pathogens and antibacterial susceptibility profile. J. Ophthalmic Inflamm. Infect. 2019, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durand, M.L. Bacterial and Fungal Endophthalmitis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 597–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, J.; Flynn, H.W., Jr.; Kuriyan, A.E.; Miller, D.; Albini, T. Endogenous fungal endophthalmitis: Risk factors, clinical features, and treatment outcomes in mold and yeast infections. J. Ophthalmic Inflamm. Infect. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangon, F.B.; Miller, D.; Giaconi, J.A.; Alfonso, E.C. In vitro investigation of voriconazole susceptibility for keratitis and endophthalmitis fungal pathogens. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 137, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, S.; Ertugrul, B.; Gultekin, B.; Uyar, G.; Kir, E. Treatment of two postoperative endophthalmitis cases due to Aspergillus flavus and Scopulariopsis spp. with local and systemic antifungal therapy. BMC Infect. Dis. 2007, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guest, J.M.; Singh, P.K.; Revankar, S.G.; Chandrasekar, P.H.; Kumar, A. Isavuconazole for Treatment of Experimental Fungal Endophthalmitis Caused by Aspergillus fumigatus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latgé, J.-P. Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 310–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruener, A.M.; Allen, F.; Stanford, M.R.; Graham, E.M. Aspergillus fumigatus Endophthalmitis with Necrotizing Scleritis following Pars Plana Vitrectomy. Case Rep. Ophthalmol. Med. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, J.; Ho, S.; Krishnan, P.; Teoh, S.C. Aspergillus terreus endogenous endophthalmitis in a nonimmunocompromised patient with a history of bronchiectasis. Ocul. Immunol. Inflamm. 2013, 21, 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, P.K.; Roy, R.; Pal, S.S.; Mukherjee, A.; Lobo, A. Aspergillus terreus endogenous endophthalmitis: Report of a case and review of literature. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 62, 887–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dogra, M.; Akella, M.; Dogra, M.R.; Gupta, A. Presumably contaminated intravenous infusion-induced Aspergillus terreus endogenous endophthalmitis presenting with posterior hypopyon. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 66, 593–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, T.B.; Vaz, F.; Rodrigues, A.; Donato, S. Intravitreal voriconazole as primary treatment for endogenous Aspergillus endophthalmitis. BMJ Case Rep. 2009, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalkanci, A.; Ozdek, S. Ocular fungal infections. Curr. Eye Res. 2011, 36, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, J.; Sontam, B.; Guda, S.J.M.; Gandhi, J.; Sharma, S.; Tyagi, M.; Dave, V.P.; Das, T. Trends in microbiological spectrum of endophthalmitis at a single tertiary care ophthalmic hospital in India: A review of 25 years. Eye (Lond) 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wykoff, C.C.; Flynn, H.W., Jr.; Miller, D.; Scott, I.U.; Alfonso, E.C. Exogenous Fungal Endophthalmitis: Microbiology and Clinical Outcomes. Ophthalmology 2008, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Song, X.; Wang, C.; Su, G.; Liu, Z. A Comparative Treatment Study of Intravitreal Voriconazole and Liposomal Amphotericin B in an Aspergillus fumigatus Endophthalmitis ModelComparison of Effects of VCZ and Liposomal Amp-B. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 7369–7376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Dong, X.; Wu, X.; Xie, L.; Min, X. Intravitreally implantable voriconazole delivery system for experimental fungal endophthalmitis. Retina 2011, 31, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, J.M.; Glickman, R.D.; Ballentine, C.S.; Trigo, Y.; Pena, M.A.; Kurian, P.; Najvar, L.K.; Kumar, N.; Patel, A.H.; Sponsel, W.E.; et al. Retinal function assessed by ERG before and after induction of ocular aspergillosis and treatment by the anti-fungal, micafungin, in rabbits. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2005, 110, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiston, E.A.; Sugi, N.; Kamradt, M.C.; Sack, C.; Heimer, S.R.; Engelbert, M.; Wawrousek, E.F.; Gilmore, M.S.; Ksander, B.R.; Gregory, M.S. αB-crystallin protects retinal tissue during Staphylococcus aureus-induced endophthalmitis. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 1781–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadan, R.T.; Ramirez, R.; Novosad, B.D.; Callegan, M.C. Acute inflammation and loss of retinal architecture and function during experimental Bacillus endophthalmitis. Curr. Eye Res. 2006, 31, 955–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talreja, D.; Singh, P.K.; Kumar, A. In Vivo Role of TLR2 and MyD88 Signaling in Eliciting Innate Immune Responses in Staphylococcal Endophthalmitis. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 1719–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.K.; Kasetti, R.B.; Zode, G.S.; Goyal, A.; Juzych, M.S.; Kumar, A. Zika Virus Infects Trabecular Meshwork and Causes Trabeculitis and Glaucomatous Pathology in Mouse Eyes. mSphere 2019, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Kumar, A. Retinal Photoreceptor Expresses Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) and Elicits Innate Responses Following TLR Ligand and Bacterial Challenge. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Donovan, D.M.; Kumar, A. Intravitreal Injection of the Chimeric Phage Endolysin Ply187 Protects Mice from Staphylococcus aureus Endophthalmitis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 4621–4629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talreja, D.; Kaye, K.S.; Yu, F.S.; Walia, S.K.; Kumar, A. Pathogenicity of ocular isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii in a mouse model of bacterial endophthalmitis. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 2392–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P.A. Current Perspectives on Ophthalmic Mycoses. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 730–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, S.A.; Penn, C.C.; Negvesky, G.J.; Butrus, S.I. Fungal and Parasitic Infections of the Eye. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 662–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dave, V.P.; Majji, A.B.; Suma, N.; Pappuru, R.R. A rare case of Aspergillus terreus endogenous endophthalmitis in a patient of acute lymphoid leukemia with good clinical outcome. Eye (Lond) 2011, 25, 1094–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kalina, P.H.; Campbell, R.J. Aspergillus terreus endophthalmitis in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1991, 109, 102–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, J.G. Endogenous Aspergillus-induced endophthalmitis. Successful treatment without systemic antifungal medication. Retina 1992, 12, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, M.; Kramer, M.R.; Blau, H.; Bishara, J.; Axer-Siegel, R.; Weinberger, D. Intravitreal voriconazole for the treatment of endogenous Aspergillus endophthalmitis. Ophthalmology 2006, 113, 1184–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riddell Iv, J.; McNeil, S.A.; Johnson, T.M.; Bradley, S.F.; Kazanjian, P.H.; Kauffman, C.A. Endogenous Aspergillus endophthalmitis: Report of 3 cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 2002, 81, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, B.; Vohra, R.; Kaur, R.; Singh, S.; Ashapritpal; Vartika. Excellent outcome of Aspergillous endophthalmitis in a case of allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 62, 352–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegan, M.C.; Kane, S.T.; Cochran, D.C.; Novosad, B.; Gilmore, M.S.; Gominet, M.; Lereclus, D. Bacillus endophthalmitis: Roles of bacterial toxins and motility during infection. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 3233–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegan, M.C.; Gilmore, M.S.; Gregory, M.; Ramadan, R.T.; Wiskur, B.J.; Moyer, A.L.; Hunt, J.J.; Novosad, B.D. Bacterial endophthalmitis: Therapeutic challenges and host-pathogen interactions. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2007, 26, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyer, A.L.; Ramadan, R.T.; Novosad, B.D.; Astley, R.; Callegan, M.C. Bacillus cereus-induced permeability of the blood-ocular barrier during experimental endophthalmitis. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 3783–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, X.; Wilhelmus, K.R. Corneal neovascularization during experimental fungal keratitis. Mol. Vis. 2009, 15, 1988–1996. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Callegan, M.C.; Jett, B.D.; Hancock, L.E.; Gilmore, M.S. Role of hemolysin BL in the pathogenesis of extraintestinal Bacillus cereus infection assessed in an endophthalmitis model. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 3357–3366. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Callegan, M.C.; Booth, M.C.; Jett, B.D.; Gilmore, M.S. Pathogenesis of gram-positive bacterial endophthalmitis. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 3348–3356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shamsuddin, N.; Kumar, A. TLR2 mediates the innate response of retinal Muller glia to Staphylococcus aureus. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 7089–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.K.; Guest, J.M.; Kanwar, M.; Boss, J.; Gao, N.; Juzych, M.S.; Abrams, G.W.; Yu, F.S.; Kumar, A. Zika virus infects cells lining the blood-retinal barrier and causes chorioretinal atrophy in mouse eyes. JCI Insight 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnardt, S. Innate immunity and neuroinflammation in the CNS: The role of microglia in Toll-like receptor-mediated neuronal injury. Glia 2010, 58, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, C.N.; Glybina, I.V.; Mahmoud, T.H.; Yu, F.S. Toll-like receptor 2 ligand-induced protection against bacterial endophthalmitis. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 201, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, K.; Cardona Gloria, Y.; Wolz, O.O.; Herster, F.; Sharma, L.; Dillen, C.A.; Taumer, C.; Dickhofer, S.; Bittner, Z.; Dang, T.M.; et al. The fungal ligand chitin directly binds TLR2 and triggers inflammation dependent on oligomer size. Embo Rep. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, C.; Kuchler, K. Fungal pathogens-a sweet and sour treat for toll-like receptors. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netea, M.G.; Warris, A.; Van der Meer, J.W.; Fenton, M.J.; Verver-Janssen, T.J.; Jacobs, L.E.; Andresen, T.; Verweij, P.E.; Kullberg, B.J. Aspergillus fumigatus evades immune recognition during germination through loss of toll-like receptor-4-mediated signal transduction. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netea, M.G.; Gow, N.A.; Munro, C.A.; Bates, S.; Collins, C.; Ferwerda, G.; Hobson, R.P.; Bertram, G.; Hughes, H.B.; Jansen, T.; et al. Immune sensing of Candida albicans requires cooperative recognition of mannans and glucans by lectin and Toll-like receptors. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1642–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, A.; Kirschning, C.J.; Nikolaus, T.; Wagner, H.; Heesemann, J.; Ebel, F. Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 and TLR4 are essential for Aspergillus-induced activation of murine macrophages. Cell. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, L.Y.; Kullberg, B.J.; Vonk, A.G.; Warris, A.; Cambi, A.; Latge, J.P.; Joosten, L.A.; van der Meer, J.W.; Netea, M.G. Modulation of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and TLR4 responses by Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 2184–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balloy, V.; Si-Tahar, M.; Takeuchi, O.; Philippe, B.; Nahori, M.A.; Tanguy, M.; Huerre, M.; Akira, S.; Latge, J.P.; Chignard, M. Involvement of toll-like receptor 2 in experimental invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 5420–5425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquart, M.E. Animal models of bacterial keratitis. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadan, R.T.; Moyer, A.L.; Callegan, M.C. A role for tumor necrosis factor-alpha in experimental Bacillus cereus endophthalmitis pathogenesis. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 4482–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Astley, R.A.; Coburn, P.S.; Parkunan, S.M.; Callegan, M.C. Modeling intraocular bacterial infections. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2016, 54, 30–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, A. Role of Staphylococcus aureus Virulence Factors in Inducing Inflammation and Vascular Permeability in a Mouse Model of Bacterial Endophthalmitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, H.L.; Abbondante, S.; Minns, M.S.; Greenberg, E.N.; Sun, Y.; Pearlman, E. Protein Deiminase 4 and CR3 Regulate Aspergillus fumigatus and beta-Glucan-Induced Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation, but Hyphal Killing Is Dependent Only on CR3. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, S.M., Jr.; Cowden, S.; Hsia, Y.C.; Ghannoum, M.A.; Momany, M.; Pearlman, E. Distinct roles for Dectin-1 and TLR4 in the pathogenesis of Aspergillus fumigatus keratitis. Plos Pathog. 2010, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luna, J.D.; Chan, C.C.; Derevjanik, N.L.; Mahlow, J.; Chiu, C.; Peng, B.; Tobe, T.; Campochiaro, P.A.; Vinores, S.A. Blood-retinal barrier (BRB) breakdown in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis: Comparison with vascular endothelial growth factor, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and interleukin-1beta-mediated breakdown. J. Neurosci. Res. 1997, 49, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, A.F.; van Haren, M.A.; Verhagen, C.; Hoekzema, R.; Kijlstra, A. Tumour necrosis factor-induced uveitis in the Lewis rat is associated with intraocular interleukin 6 production. Exp. Eye Res. 1995, 60, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).