Characterization and Transcriptional Regulation of n-Alkane Hydroxylase Gene Cluster of Rhodococcus jostii RHA1
Abstract
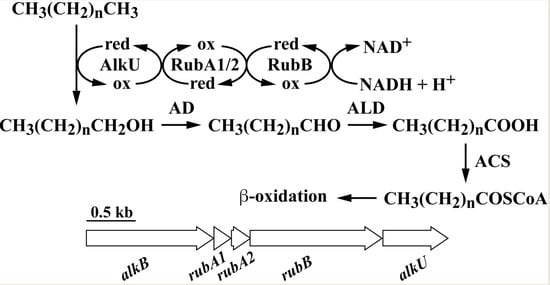
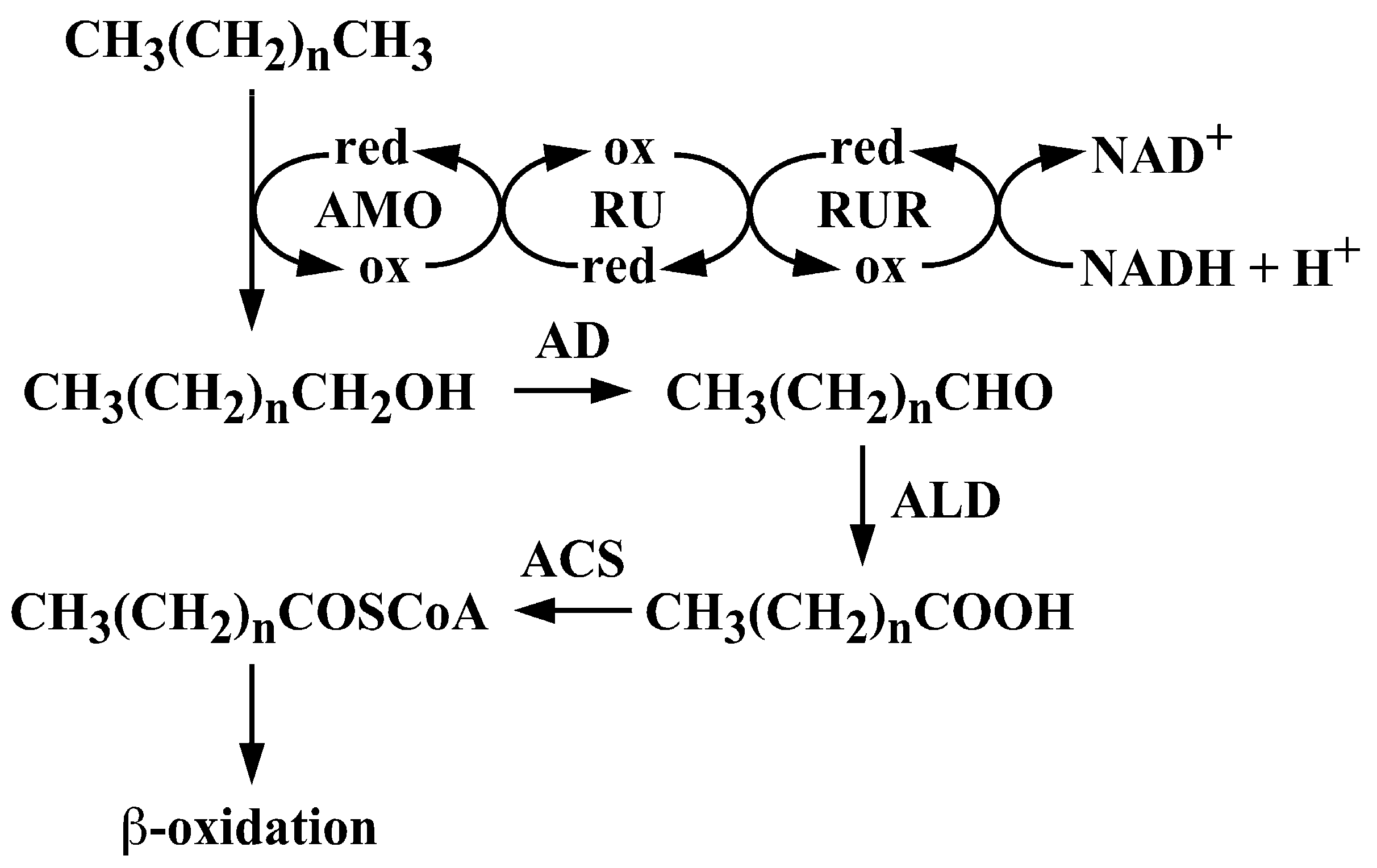
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids, and Culture Conditions
2.2. DNA Manipulations, Nucleotide Sequencing, and Sequence Analysis
2.3. Construction of Disruption Mutants
2.4. Growth Curves on n-Alkanes
2.5. Resting Cell Assay
2.6. RNA Isolation
2.7. Reverse Transcription (RT)-PCR and Quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR)
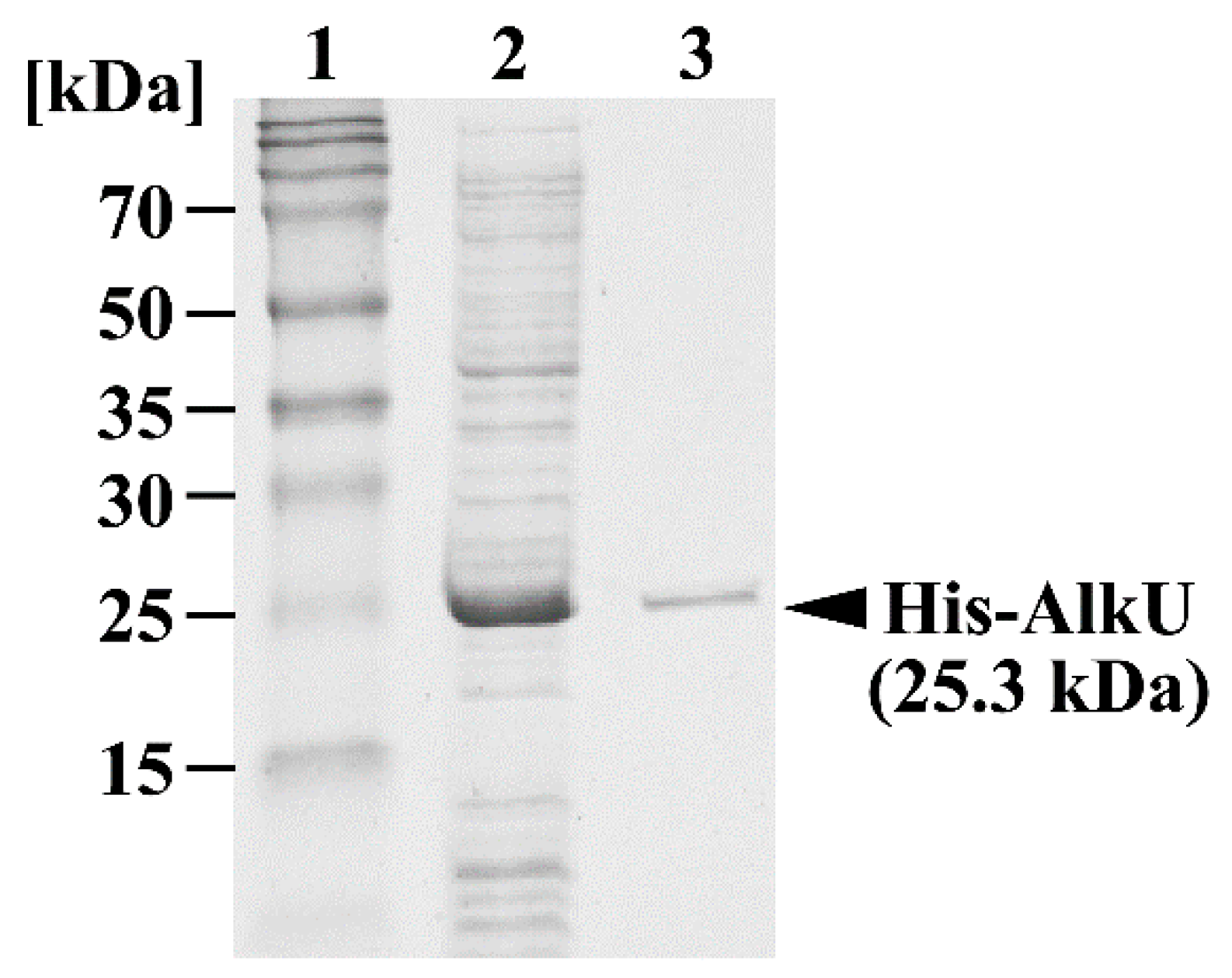
2.8. Purification of His-Tagged alkU
2.9. Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assays (EMSAs)
3. Results
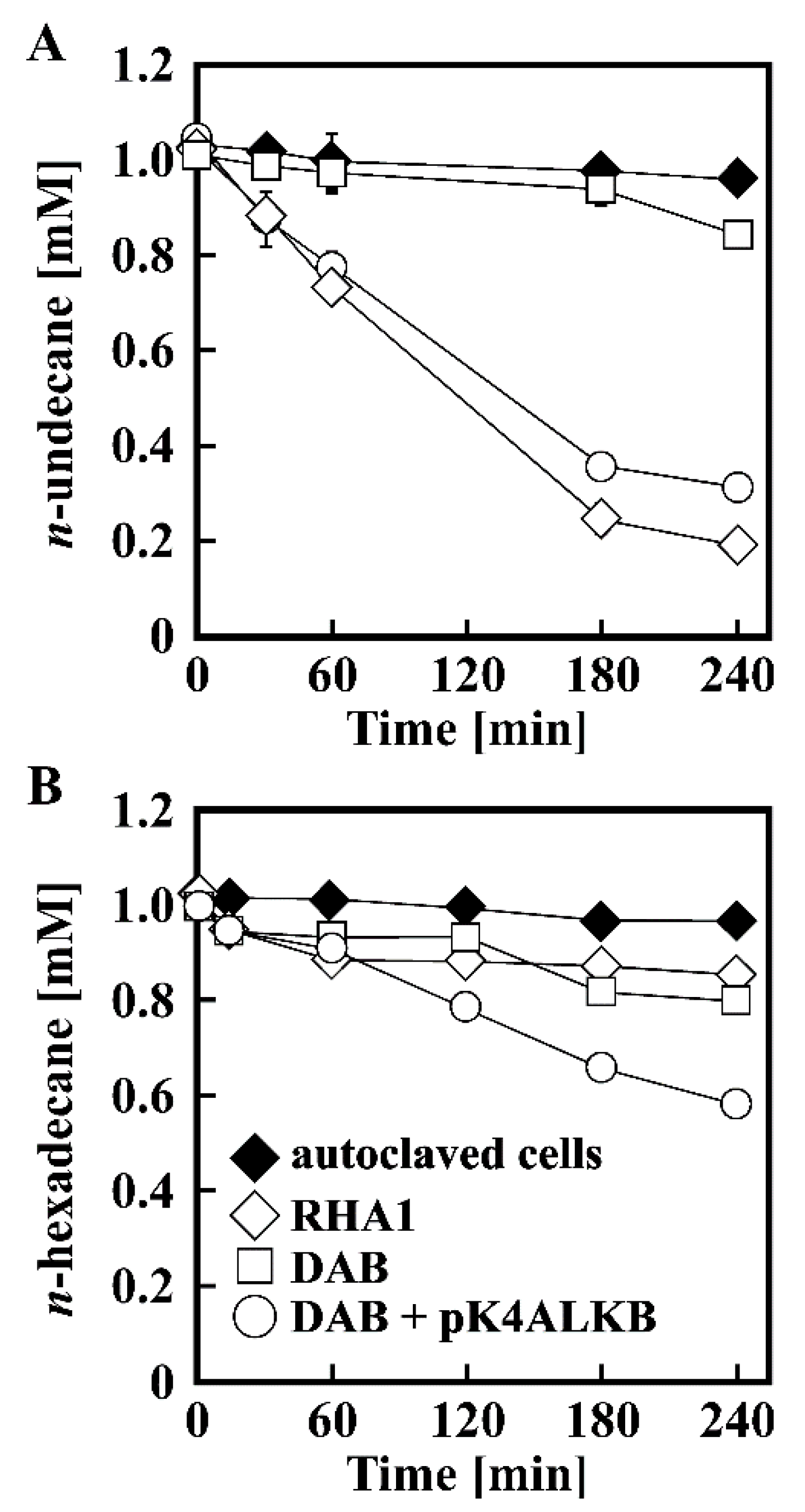
3.1. Growth of RHA1 on n-Alkanes
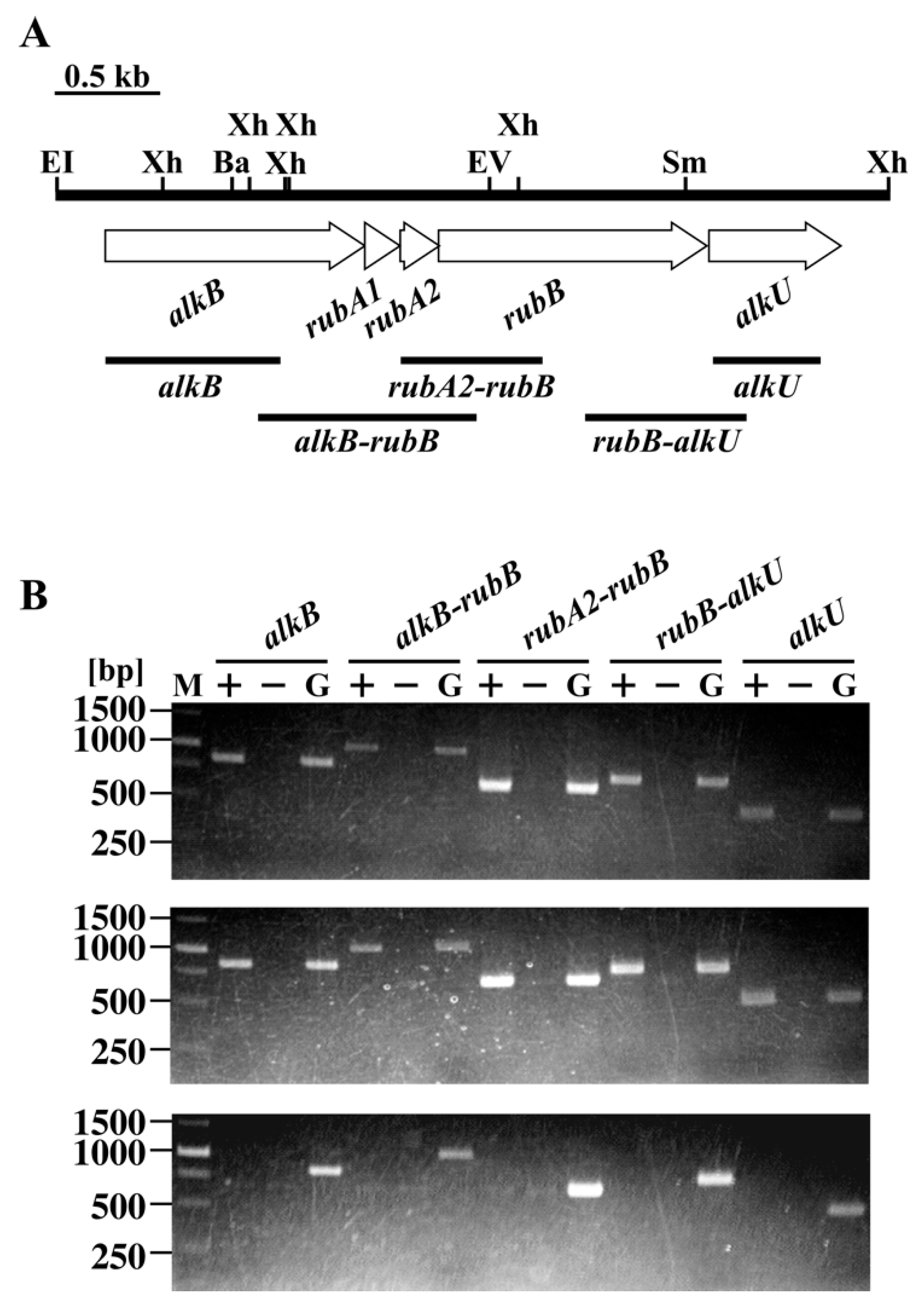
3.2. The alk Gene Cluster of Strain RHA1
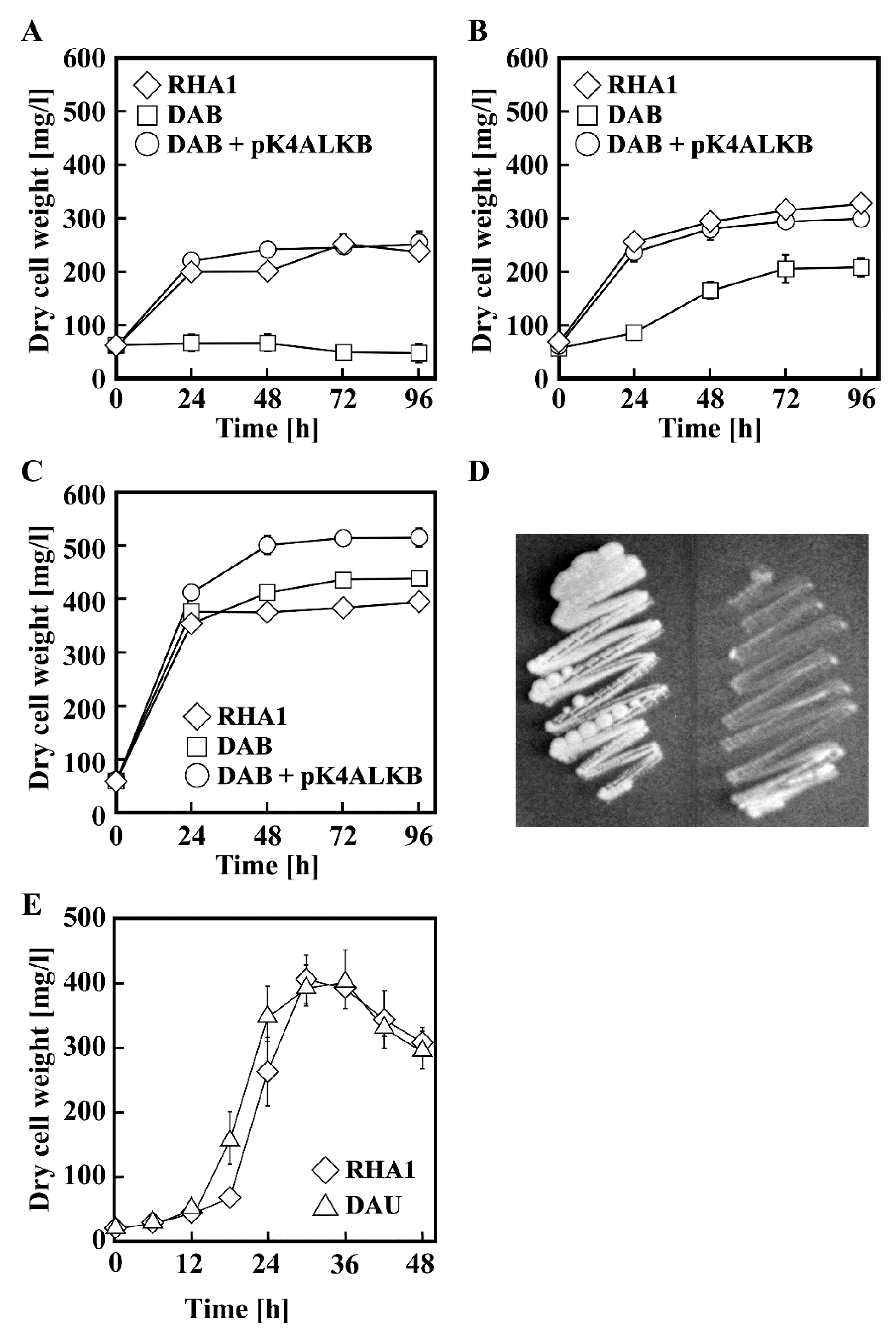
3.3. Disruption of alkB in RHA1
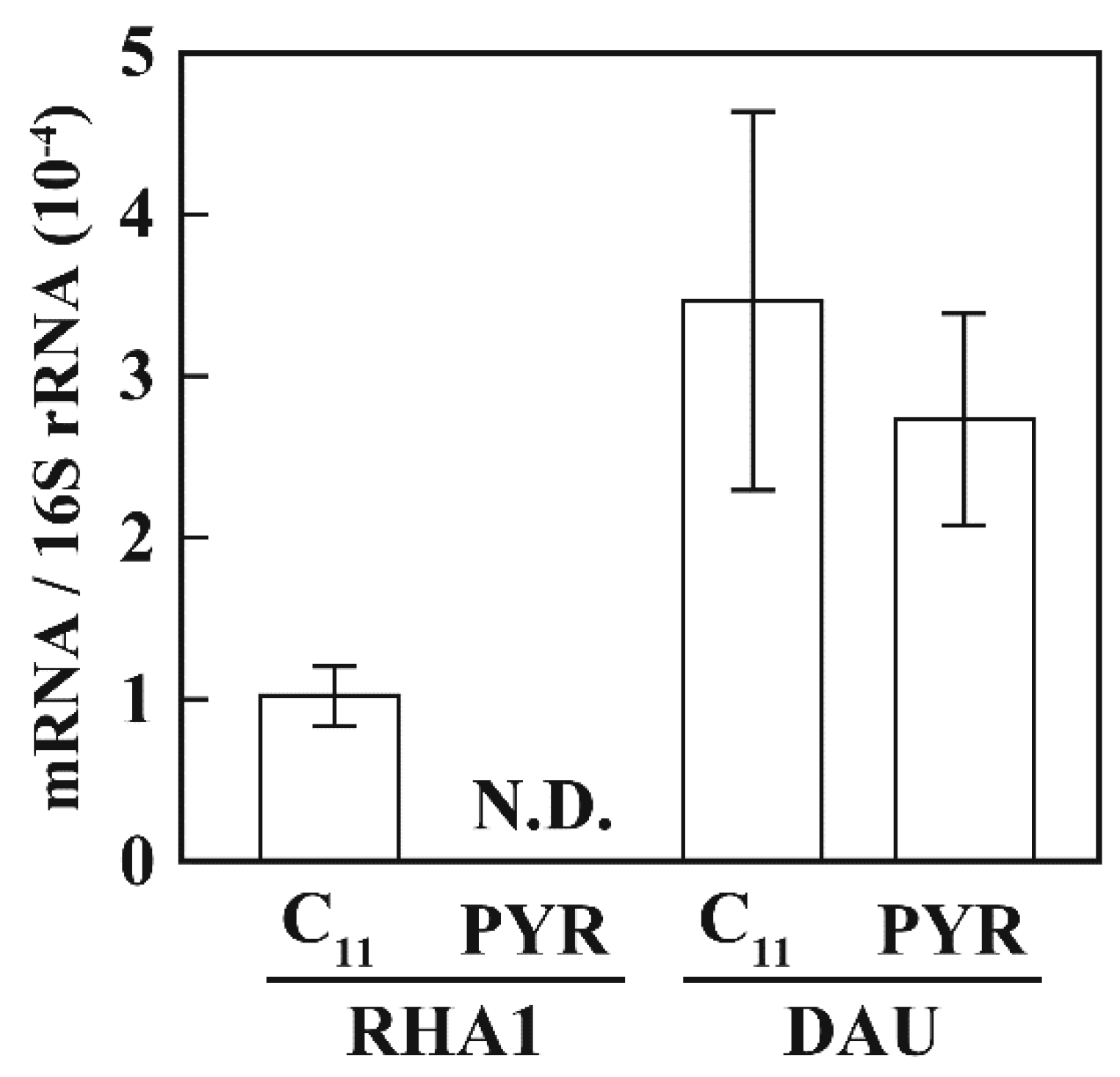
3.4. Transcriptional Regulation of alk Operon
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leahy, J.G.; Colwell, R.R. Microbial degradation of hydrocarbons in the environment. Microbiol. Rev. 1990, 54, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rojo, F. Degradation of alkanes by bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2477–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wentzel, A.; Ellingsen, T.E.; Kotlar, H.K.; Zotchev, S.B.; Throne-Holst, M. Bacterial metabolism of long-chain n-alkanes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 76, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamura, N.; Yeager, C.M.; Arp, D.J. Two distinct monooxygenases for alkane oxidation in Nocardioides sp. strain CF8. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 4992–4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, T.; Forster, H.H.; Asperger, O.; Hahn, U. Molecular characterization of the 56-kDa CYP153 from Acinetobacter sp. EB104. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 286, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeng, J.H.; Sakai, Y.; Tani, Y.; Kato, N. Isolation and characterization of a novel oxygenase that catalyzes the first step of n-alkane oxidation in Acinetobacter sp. strain M-1. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 3695–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkinson, R.J.; Morgan, P. Physiology of aliphatic hydrocarbon-degrading microorganisms. Biodegradation 1990, 1, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beilen, J.B.; Panke, S.; Lucchini, S.; Franchini, A.G.; Rothlisberger, M.; Witholt, B. Analysis of Pseudomonas putida alkane-degradation gene clusters and flanking insertion sequences: Evolution and regulation of the alk genes. Microbiology 2001, 147, 1621–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissdörfer, W.; Kok, R.G.; Ratajczak, A.; Hellingwerf, K.J.; Hillen, W. The genes rubA and rubB for alkane degradation in Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1 are in an operon with estB, encoding an esterase, and oxyR. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 4292–4298. [Google Scholar]
- Ratajczak, A.; Geissdörfer, W.; Hillen, W. Alkane hydroxylase from Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1 is encoded by alkM and belongs to a new family of bacterial integral-membrane hydrocarbon hydroxylases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 1175–1179. [Google Scholar]
- Ratajczak, A.; Geissdörfer, W.; Hillen, W. Expression of alkane hydroxylase from Acinetobacter sp. strain ADP1 is induced by a broad range of n-alkanes and requires the transcriptional activator AlkR. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 5822–5827. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Throne-Holst, M.; Wentzel, A.; Ellingsen, T.E.; Kotlar, H.K.; Zotchev, S.B. Identification of novel genes involved in long-chain n-alkane degradation by Acinetobacter sp. strain DSM 17874. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3327–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Wang, W.; Cheng, J.; Ren, Y.; Zhao, G.; Gao, C.; Tang, Y.; Liu, X.; Han, W.; Peng, X.; et al. Genome and proteome of long-chain alkane degrading Geobacillus thermodenitrificans NG80-2 isolated from a deep-subsurface oil reservoir. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 5602–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Lai, Q.; Shao, Z. Multiple alkane hydroxylase systems in a marine alkane degrader, Alcanivorax dieselolei B-5. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funhoff, E.G.; Bauer, U.; Garcia-Rubio, I.; Witholt, B.; van Beilen, J.B. CYP153A6, a soluble P450 oxygenase catalyzing terminal-alkane hydroxylation. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 5220–5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínková, L.; Uhnáková, B.; Pátek, M.; Nešvera, J.; Křen, V. Biodegradation potential of the genus Rhodococcus. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameshima, Y.; Honda, K.; Kato, J.; Omasa, T.; Ohtake, H. Expression of Rhodococcus opacus alkB genes in anhydrous organic solvents. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2008, 106, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amouric, A.; Quemeneur, M.; Grossi, V.; Liebgott, P.P.; Auria, R.; Casalot, L. Identification of different alkane hydroxylase systems in Rhodococcus ruber strain SP2B, an hexane-degrading actinomycete. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 1903–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti, M.; Fedi, S.; Frascari, D.; Ohtake, H.; Turner, R.J.; Zannoni, D. Analyses of both the alkB gene transcriptional start site and alkB promoter-inducing properties of Rhodococcus sp. strain BCP1 grown on n-alkanes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 1619–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, D.; Washio, K.; Morikawa, M. Identification of alkane hydroxylase genes in Rhodococcus sp. strain TMP2 that degrades a branched alkane. Biotechnol. Lett. 2008, 30, 1447–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, L.G.; Smits, T.H.; Labbe, D.; Witholt, B.; Greer, C.W.; van Beilen, J.B. Gene cloning and characterization of multiple alkane hydroxylase systems in Rhodococcus strains Q15 and NRRL B-16531. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5933–5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo Piccolo, L.; De Pasquale, C.; Fodale, R.; Puglia, A.M.; Quatrini, P. Involvement of an alkane hydroxylase system of Gordonia sp. strain SoCg in degradation of solid n-alkanes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quatrini, P.; Scaglione, G.; De Pasquale, C.; Riela, S.; Puglia, A.M. Isolation of Gram-positive n-alkane degraders from a hydrocarbon-contaminated Mediterranean shoreline. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seto, M.; Masai, E.; Ida, M.; Hatta, T.; Kimbara, K.; Fukuda, M.; Yano, K. Multiple polychlorinated biphenyl transformation systems in the gram-positive bacterium Rhodococcus sp. strain RHA1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 4510–4513. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Seto, M.; Kimbara, K.; Shimura, M.; Hatta, T.; Fukuda, M.; Yano, K. A novel transformation of polychlorinated biphenyls by Rhodococcus sp. strain RHA1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 3353–3358. [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki, T.; Miyauchi, K.; Masai, E.; Fukuda, M. Multiple-subunit genes of the aromatic-ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase play an active role in biphenyl and polychlorinated biphenyl degradation in Rhodococcus sp. strain RHA1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5396–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, J.M.; Mohn, W.W.; Eltis, L.D.; LeBlanc, J.C.; Stewart, G.R.; Dresen, C.; Okamoto, K.; Alvarez, P.J. 7-ketocholesterol catabolism by Rhodococcus jostii RHA1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrauchan, M.A.; Florizone, C.; Eapen, S.; Gómez-Gil, L.; Sethuraman, B.; Fukuda, M.; Davies, J.; Mohn, W.W.; Eltis, L.D. Roles of ring-hydroxylating dioxygenases in styrene and benzene catabolism in Rhodococcus jostii RHA1. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, J.O.; Sales, C.M.; LeBlanc, J.C.; Liu, J.; Wood, T.K.; Eltis, L.D.; Mohn, W.W.; Alvarez-Cohen, L. An inducible propane monooxygenase is responsible for N-nitrosodimethylamine degradation by Rhodococcus sp. strain RHA1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 6930–6938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araki, N.; Niikura, Y.; Miyauchi, K.; Kasai, D.; Masai, E.; Fukuda, M. Glucose-mediated transcriptional repression of PCB/biphenyl catabolic genes in Rhodococcus jostii RHA1. J. Mol. Microb. Biotech. 2011, 20, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanisch-Perron, C.; Vieira, J.; Messing, J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: Nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 1985, 33, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, R.; Priefer, U.; Pühler, A. A broad host range mobilization system for in vivo genetic engineering: Transposon mutagenesis in gram negative bacteria. Nat. Biotechnol. 1983, 1, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studier, F.W.; Moffatt, B.A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J. Mol. Biol. 1986, 189, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, J.M.; Fernandez, J.M.; Sorge, J.A.; Huse, W.D. λ ZAP: A bacteriophage λ expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 7583–7600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, A.; Tauch, A.; Jäger, W.; Kalinowski, J.; Thierbach, G.; Pühler, A. Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: Selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Gene 1994, 145, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Nishiyama, M.; Yu, F.; Watanabe, I.; Horinouchi, S.; Beppu, T. Development of a host-vector system in a Rhodococcus strain and its use for expression of the cloned nitrile hydratase gene cluster. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1992, 138, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masai, E.; Yamada, A.; Healy, J.M.; Hatta, T.; Kimbara, K.; Fukuda, M.; Yano, K. Characterization of biphenyl catabolic genes of gram-positive polychlorinated biphenyl degrader Rhodococcus sp. strain RHA1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1995, 61, 2079–2085. [Google Scholar]
- Kasai, D.; Fujinami, T.; Abe, T.; Mase, K.; Katayama, Y.; Fukuda, M.; Masai, E. Uncovering the protocatechuate 2,3-cleavage pathway genes. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 6758–6768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Geize, R.; Hessels, G.I.; van Gerwen, R.; van der Meijden, P.; Dijkhuizen, L. Unmarked gene deletion mutagenesis of kstD, encoding 3-ketosteroid Δ1-dehydrogenase, in Rhodococcus erythropolis SQ1 using sacB as counter-selectable marker. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2001, 205, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, E.R.; Hara, H.; Miyazawa, D.; Davies, J.E.; Eltis, L.D.; Mohn, W.W. Transcriptomic assessment of isozymes in the biphenyl pathway of Rhodococcus sp. strain RHA1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 6183–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleight, S.C.; Bartley, B.A.; Lieviant, J.A.; Sauro, H.M. In-Fusion BioBrick assembly and re-engineering. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 2624–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamimura, N.; Takamura, K.; Hara, H.; Kasai, D.; Natsume, R.; Senda, T.; Katayama, Y.; Fukuda, M.; Masai, E. Regulatory system of the protocatechuate 4,5-cleavage pathway genes essential for lignin downstream catabolism. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 3394–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Beilen, J.B.; Neuenschwander, M.; Smits, T.H.; Roth, C.; Balada, S.B.; Witholt, B. Rubredoxins involved in alkane oxidation. J. Bacteriol 2002, 184, 1722–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanklin, J.; Achim, C.; Schmidt, H.; Fox, B.G.; Münck, E. Mössbauer studies of alkane omega-hydroxylase: Evidence for a diiron cluster in an integral-membrane enzyme. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 2981–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanklin, J.; Whittle, E.; Fox, B.G. Eight histidine residues are catalytically essential in a membrane-associated iron enzyme, stearoyl-CoA desaturase, and are conserved in alkane hydroxylase and xylene monooxygenase. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 12787–12794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Beilen, J.B.; Penninga, D.; Witholt, B. Topology of the membrane-bound alkane hydroxylase of Pseudomonas oleovorans. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 9194–9201. [Google Scholar]
- van Beilen, J.B.; Smits, T.H.; Roos, F.F.; Brunner, T.; Balada, S.B.; Rothlisberger, M.; Witholt, B. Identification of an amino acid position that determines the substrate range of integral membrane alkane hydroxylases. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, A.; Ishige, T.; Sakai, Y.; Kato, N. Gene structures and regulation of the alkane hydroxylase complex in Acinetobacter sp. strain M-1. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 1819–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canosa, I.; Yuste, L.; Rojo, F. Role of the alternative sigma factor σS in expression of the AlkS regulator of the Pseudomonas oleovorans alkane degradation pathway. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 1748–1754. [Google Scholar]
- Canosa, I.; Sanchez-Romero, J.M.; Yuste, L.; Rojo, F. A positive feedback mechanism controls expression of AlkS, the transcriptional regulator of the Pseudomonas oleovorans alkane degradation pathway. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 35, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.L.; Martínez-Bueno, M.; Molina-Henares, A.J.; Terán, W.; Watanabe, K.; Zhang, X.; Gallegos, M.T.; Brennan, R.; Tobes, R. The TetR family of transcriptional repressors. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2005, 69, 326–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompeani, A.J.; Irgon, J.J.; Berger, M.F.; Bulyk, M.L.; Wingreen, N.S.; Bassler, B.L. The Vibrio harveyi master quorum-sensing regulator, LuxR, a TetR-type protein is both an activator and a repressor: DNA recognition and binding specificity at target promoters. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 70, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, A.M.; Levy, S.B. Gene in the major cotransduction gap of the Escherichia coli K-12 linkage map required for the expression of chromosomal resistance to tetracycline and other antibiotics. J. Bacteriol. 1983, 155, 541–548. [Google Scholar]
- Orth, P.; Schnappinger, D.; Hillen, W.; Saenger, W.; Hinrichs, W. Structural basis of gene regulation by the tetracycline inducible Tet repressor-operator system. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2000, 7, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthbertson, L.; Nodwell, J.R. The TetR family of regulators. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2013, 77, 440–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
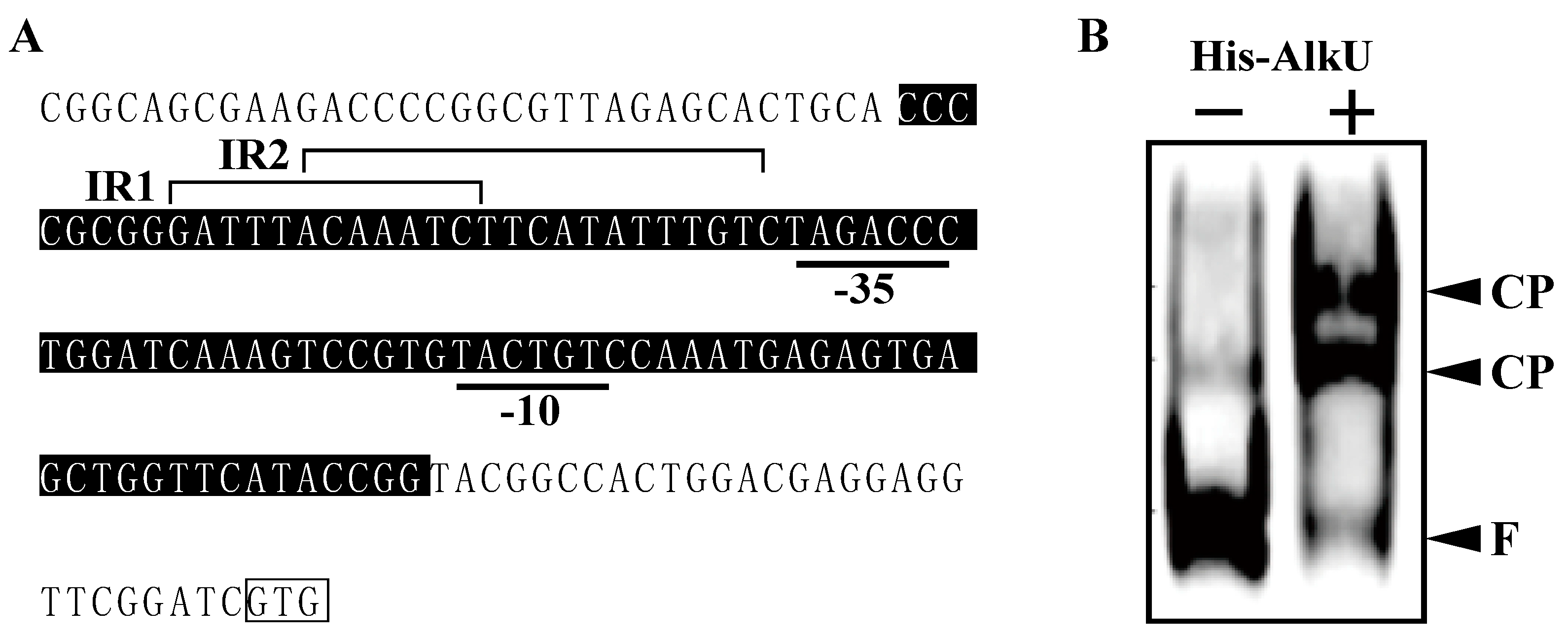
| Strain or Plasmid | Relevant Characteristic(s) a | Source or Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Strains | ||
| R. jostii | ||
| RHA1 | Wild type | [25] |
| DAB | RHA1 derivative; ΔalkB | This study |
| DAU | RHA1 derivative; ΔalkU | This study |
| E. coli | ||
| JM109 | endA1 recA1 gyrA96 thi hsdR17 relA1 supE44 Δ(lac-proAB) mcrA [F’, traD36 proAB+ laclq ΔZM15] | [31] |
| S17-1 | RK2 tra regulon, λ pir, host for pir-dependent plasmids | [32] |
| BL21(DE3) | F− ompT hsdSB(rB-mB-) gal dcm (DE3); T7 RNA polymerase gene under the control of the lacUV5 promoter | [33] |
| Plasmids | ||
| pT7Blue | Cloning vector; T7 promoter, Ap r | Novagen |
| pBluescript II KS(+) | Cloning vector; Ap r | [34] |
| pK19mobsacB | oriT sacB Km r | [35] |
| pK4 | Rhodococcus-E. coli shuttle vector, Km r | [36] |
| pET16b | Expression vector, N-terminal His10 tag, Ap r T7 promoter | Novagen |
| pTALKBL | pT7Blue with a 917-bp PCR fragment generated by alkBL_F/R primer pair | This study |
| pTALKBR | pT7Blue with a 723-bp PCR fragment generated by alkBR_F/R primer pair | This study |
| pTALKBLR | pTALKBR with a 733-bp EcoRI-SacI fragment of pTALKBL | This study |
| pABSmobsacB | pK19mobsacB with a 1.5-kb EcoRI-HindIII fragment of pTALKBLR | This study |
| pTALKBD | pT7Blue with a 967-bp PCR fragment generated by alkBD_F/R primer pair | This study |
| pT7BL | pT7Blue with a 0.8-kb EcoRI-BamHI fragment of pTALKBL | This study |
| pT7B | pT7BL with a 0.7-kb BamHI-HindIII fragment of pTALKBD | This study |
| pK4ALKB | pK4 with a 1.5-kb EcoRI fragment of pT7B | This study |
| pTUPU | pT7Blue with a 761-bp PCR fragment generated by UPalkU_F/R primer pair | This study |
| pTDWU | pT7Blue with a 792-bp PCR fragment generated by DWalkU_F/R primer pair | This study |
| pKU | pK19mobsacB with a 1.6-kb HindIII fragment carrying part of alkU | This study |
| pETALKU | pET16b with a 0.7-kb PCR amplified fragment carrying of alkU | This study |
| Primer | Sequence (5′ to 3′) a |
|---|---|
| alkB_F | TGACGACGTCGAATATCAGC |
| alkB_R | CCTGAATGATCAGGAACGG |
| alkBrubB_F | GAGCATTCACAACGATGTGC |
| alkBrubB_R | ACAGGAAGTCCTTCGACACC |
| rubA2B_F | GTACCGATTTCAAGCTCTACC |
| rubA2B_R | CACATCCGATGAGACCTCC |
| rubBalkU_F | ACGGTCGAAGTTGGAGTGC |
| rubBalkU_R | CTTTGTAGATCGTCTGCCTGC |
| alkU_F | CGAGCGACAGAGTCGATACC |
| alkU_R | ATGAAACTCAAGGCGAGCC |
| alkBL_F | ACAGGTGAAGCTACCAGCG |
| alkBL_R | GTGAGAGCTTCTGGACTTTCC |
| alkBR_F | CTTCGGTGAGAGCTTCTGG |
| alkBR_R | AAGCTTGTCGTCGGGCACATCG (HindIII) |
| alkBD_F | AACAGCTCGAGAACGACAGG |
| alkBD_R | GAATTCCATCACCGAACTCCGC (EcoRI) |
| UPalkU_F | AAGCTTTGTCCTCGCTCGACGTGAGC (HindIII) |
| UPalkU_R | GGATCCATTGTCGGCCAGGGACGTTCG (BamHI) |
| DWalkU_F | GGATCCAACGGTCGTGGGTGAACTCG (BamHI) |
| DWalkU_R | AAGCTTAGGAACTGATCTACGCCAACC (HindIII) |
| HISalkU_F | TCGAAGGTCGTCATAGCAGACGACCGCACCGCAGACGACCGCACC |
| HISalkU_R | GGATCCTCGAGCATAAAGTACTCACGGGTGAAGTACTCACGGGTG |
| Media | Strains | n-Alkanes a | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | C11 | C12 | C13 | C14 | C15 | C16 | C17 | C18 | C19 | C20 | C30 | ||
| Liquid | RHA1 | ND | ND | ND | ND | − | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | − |
| DAB | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | − | − | ± | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | |
| Solid | RHA1 | − | − | − | − | − | + | + | + | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND |
| DAB | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ± | − | ± | + | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gibu, N.; Kasai, D.; Ikawa, T.; Akiyama, E.; Fukuda, M. Characterization and Transcriptional Regulation of n-Alkane Hydroxylase Gene Cluster of Rhodococcus jostii RHA1. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110479
Gibu N, Kasai D, Ikawa T, Akiyama E, Fukuda M. Characterization and Transcriptional Regulation of n-Alkane Hydroxylase Gene Cluster of Rhodococcus jostii RHA1. Microorganisms. 2019; 7(11):479. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110479
Chicago/Turabian StyleGibu, Namiko, Daisuke Kasai, Takumi Ikawa, Emiko Akiyama, and Masao Fukuda. 2019. "Characterization and Transcriptional Regulation of n-Alkane Hydroxylase Gene Cluster of Rhodococcus jostii RHA1" Microorganisms 7, no. 11: 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110479
APA StyleGibu, N., Kasai, D., Ikawa, T., Akiyama, E., & Fukuda, M. (2019). Characterization and Transcriptional Regulation of n-Alkane Hydroxylase Gene Cluster of Rhodococcus jostii RHA1. Microorganisms, 7(11), 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7110479