Bile Acid Sequestration Attenuates Desulfovibrio-Induced Hepatic Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Culture Conditions
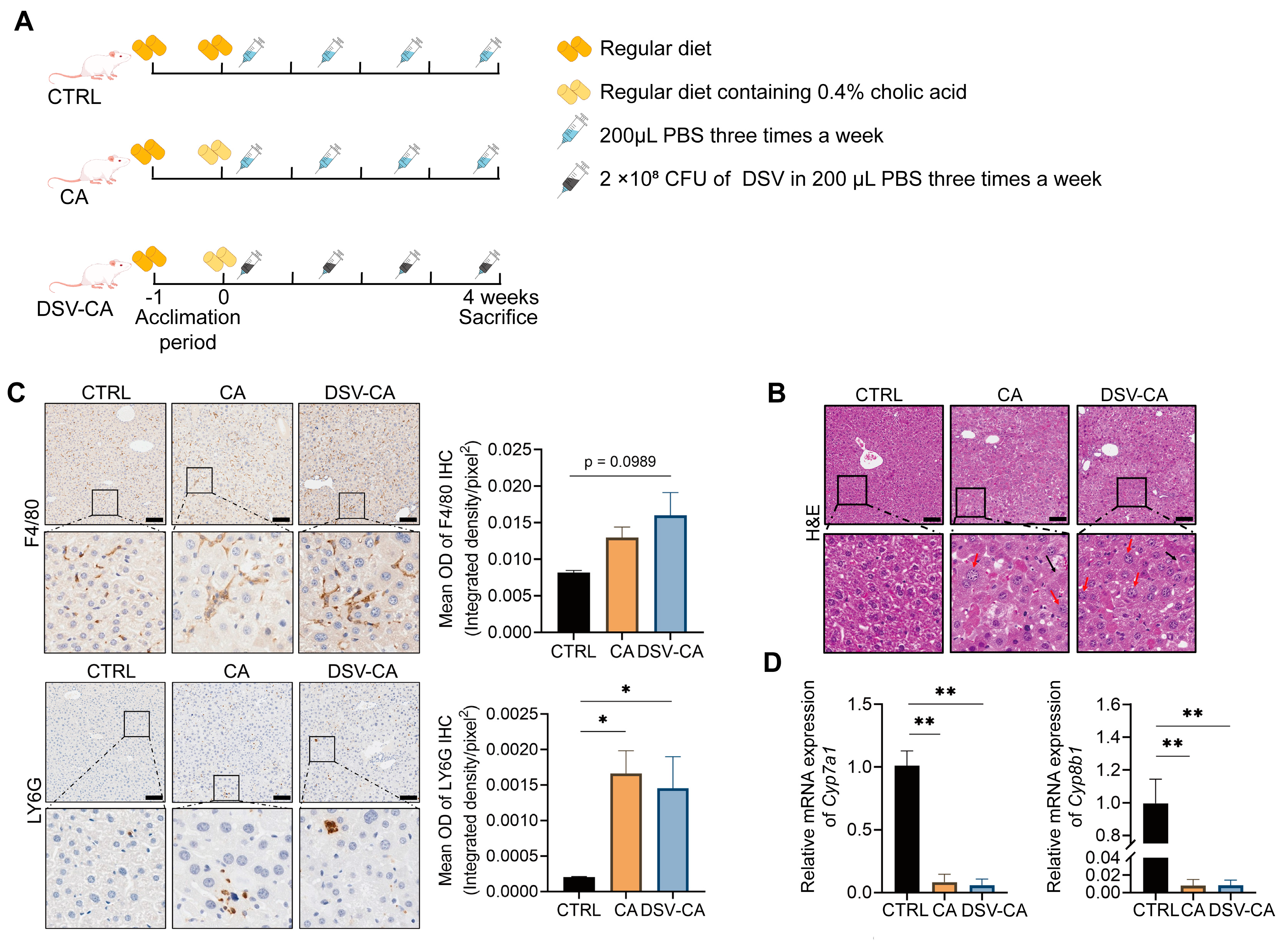
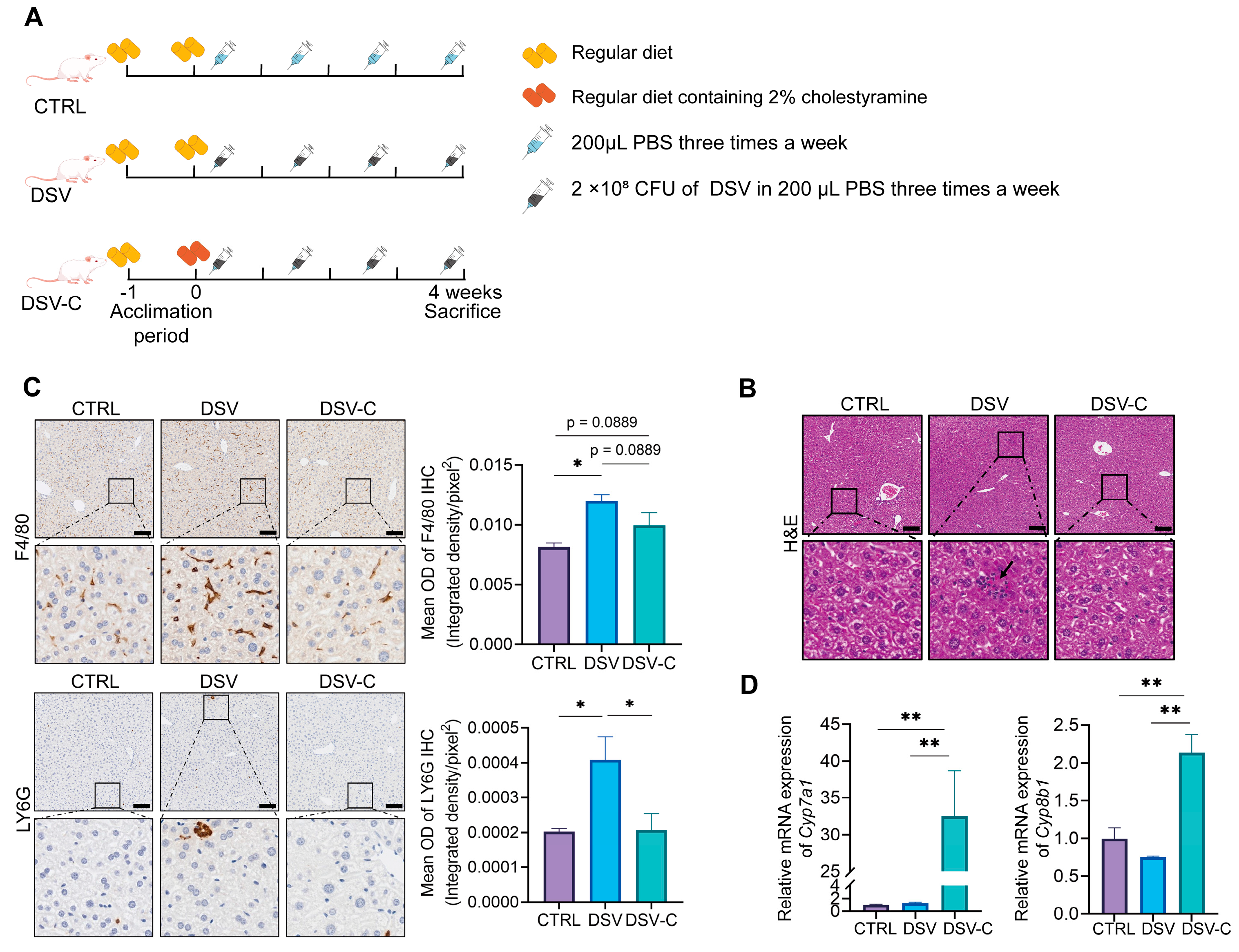
2.2. Animals and Experimental Designs
2.3. Pathology Analysis
2.4. qRT-PCR Analysis
2.5. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Effects of Cholic Acid and DSV on Liver Damage
3.2. The Effects of CA and DSV on the Gut Microbiota
3.3. The Effects of Cholestyramine on Liver Damage Induced by DSV
3.4. The Effects of Cholestyramine on the Gut Microbiota of Mice with Liver Damage Induced by DSV
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Long, S.L.; Gahan, C.G.M.; Joyce, S.A. Interactions between gut bacteria and bile in health and disease. Mol. Asp. Med. 2017, 56, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varanasi, S.K.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y.; Johnson, M.A.; Miller, C.M.; Ganguly, S.; Lande, K.; LaPorta, M.A.; Hoffmann, F.A.; Mann, T.H.; et al. Bile acid synthesis impedes tumor-specific T cell responses during liver cancer. Science 2025, 387, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simbrunner, B.; Trauner, M.; Reiberger, T. Review article: Therapeutic aspects of bile acid signalling in the gut-liver axis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 54, 1243–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, M.; Kuang, J.; Liang, D.; Wang, J.; Wei, M.; Rajani, C.; Ma, X.; et al. Gut microbiota-bile acid crosstalk contributes to the rebound weight gain after calorie restriction in mice. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.Y.L.; Ferrell, J.M. Bile acid receptors FXR and TGR5 signaling in fatty liver diseases and therapy. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 318, G554–G573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.Y. Recent advances in understanding bile acid homeostasis. F1000Research 2017, 6, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.L.; Li, C.X.; Ma, C.Y.; Chen, D.; Chen, J.H.; Xu, W.X.; Chen, C.A.; Cheng, F.F.; Wang, X.Q. Linking Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Brain Disease: Focusing on Bile Acid Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, L.; Xia, H.; Liao, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, N.; Xie, Q.; Liao, M.; Tan, Y.; et al. Runt-related transcription factor-1 ameliorates bile acid-induced hepatic inflammation in cholestasis through JAK/STAT3 signaling. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1866–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Li, Z.J.; Gou, H.Z.; Song, X.J.; Zhang, L. The gut microbiota-bile acid axis: A potential therapeutic target for liver fibrosis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 945368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Luo, Y.; Ranjit, S.; Xie, C.; Libby, A.E.; Orlicky, D.J.; Dvornikov, A.; Wang, X.X.; Myakala, K.; Jones, B.A.; et al. Bile acid sequestration reverses liver injury and prevents progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in Western diet-fed mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 4733–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, Z.; Bao, R.; Guo, X.; Gu, Y.; Yang, W.; Wei, J.; Chen, X.; Tong, L.; Meng, J.; et al. Loss of SIRT5 promotes bile acid-induced immunosuppressive microenvironment and hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2022, 77, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhao, J.; Yang, H.; Ouyang, Z.; Lv, C.; Geng, Z.; Zhao, J. The bile acid-gut microbiota axis: A central hub for physiological regulation and a novel therapeutic target for metabolic diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2025, 188, 118182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, M.; Chen, P.; Zhu, M.; Chen, L. A high-dose of ursodeoxycholic acid treatment alleviates liver inflammation by remodeling gut microbiota and bile acid profile in a mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 174, 116617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yuan, M.; Niu, K.; Yang, W.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, J. Involvement of Bile Acid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in the Amelioration of Experimental Metabolism-Associated Fatty Liver Disease by Nobiletin. Molecules 2024, 29, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Lau, H.C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J. Bile acids, gut microbiota, and therapeutic insights in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Med. 2023, 21, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Adolph, T.E.; Trauner, M. Gut-liver axis: Pathophysiological concepts and clinical implications. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1700–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, B.; Huang, G.; Li, J.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, H.; Lan, P.; Chen, Z. Gut microbiota-mediated bile acid metabolism aggravates biliary injury after liver transplantation through mitochondrial apoptosis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143, 113413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Huang, D.; Sun, Z.; Chen, X. Effects of intestinal Desulfovibrio bacteria on host health and its potential regulatory strategies: A review. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 284, 127725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Cao, F.; Huang, J.; Gao, X. Gut microbiota and metabolic health risks from chronic low-dose microplastic exposure with focus on Desulfovibrio spp. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 302, 118721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Qin, X.; Qiu, J.; Sun, T.; Qu, K.; Din, A.U.; Yan, W.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Gu, W.; et al. Desulfovibrio desulfuricans aggravates atherosclerosis by enhancing intestinal permeability and endothelial TLR4/NF-κB pathway in Apoe−/− mice. Genes. Dis. 2023, 10, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, X.; Sun-Waterhouse, D.; Zhu, B.; You, L.; Hileuskaya, K. Polysaccharides from Sargassum fusiforme after UV/H2O2 degradation effectively ameliorate dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 11747–11759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Shao, W.; Liu, Q.; Liu, N.; Wang, Q.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Weng, Z.; Lu, Q.; Jiao, L.; et al. Gut microbiota promotes cholesterol gallstone formation by modulating bile acid composition and biliary cholesterol secretion. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Lu, G.; Nie, Y.; Ren, Y.; Shi, J.S.; Xue, Y.; Xu, Z.H.; Geng, Y. Restricted intake of sulfur-containing amino acids reversed the hepatic injury induced by excess Desulfovibrio through gut-liver axis. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2370634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, J.P.; Karpen, S.J.; Dawson, P.A.; Arrese, M.; Trauner, M. Bile acids and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Molecular insights and therapeutic perspectives. Hepatology 2017, 65, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joyce, S.A.; Gahan, C.G. Bile Acid Modifications at the Microbe-Host Interface: Potential for Nutraceutical and Pharmaceutical Interventions in Host Health. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y. New insights into the bile acid-based regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives in alcohol-related liver disease. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cai, S.Y.; Boyer, J.L. Mechanisms of bile acid mediated inflammation in the liver. Mol. Asp. Med. 2017, 56, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, A.; Fiorotto, R.; Strazzabosco, M. Bile acids and their receptors: Modulators and therapeutic targets in liver inflammation. Semin. Immunopathol. 2022, 44, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Jin, L.; Huang, W. Bile Acids, Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction, and Related Diseases. Cells 2023, 12, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.B.; Carroll-Portillo, A.; Lin, H.C. Desulfovibrio in the Gut: The Enemy within? Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.B.; Coffman, C.N.; Varga, M.G.; Carroll-Portillo, A.; Braun, C.A.; Lin, H.C. Intestinal Alkaline Phosphatase Prevents Sulfate Reducing Bacteria-Induced Increased Tight Junction Permeability by Inhibiting Snail Pathway. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 882498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Meng, F.; Wang, J.; Wei, J.; Zhang, K.; Qin, S.; Li, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, B.; Liu, T.; et al. Desulfovibrio vulgaris flagellin exacerbates colorectal cancer through activating LRRC19/TRAF6/TAK1 pathway. Gut Microbes 2025, 17, 2446376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, G.; Tian, F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Quantity of Desulfovibrios and analysis of intestinal microbiota diversity in health and intestinal disease people in Wuxi, Jiangsu province. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 2012, 52, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Coker, O.O.; Chu, E.S.; Fu, K.; Lau, H.C.H.; Wang, Y.X.; Chan, A.W.H.; Wei, H.; Yang, X.; Sung, J.J.Y.; et al. Dietary cholesterol drives fatty liver-associated liver cancer by modulating gut microbiota and metabolites. Gut 2021, 70, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Pérez, A.M.; Ruiz-Limón, P.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Vioque, J.; Corella, D.; Fitó, M.; Vidal, J.; Atzeni, A.; Torres-Collado, L.; Álvarez-Sala, A.; et al. Gut microbiota in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A PREDIMED-Plus trial sub analysis. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2223339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wei, W.; Li, Y.; Ge, S.; Shen, J.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Sun, X.; Cheng, D.; et al. Cholestyramine alleviates bone and muscle loss in irritable bowel syndrome via regulating bile acid metabolism. Cell Prolif. 2024, 57, e13638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Luo, Q.; Tao, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, C. Pharmacotherapies for Drug-Induced Liver Injury: A Current Literature Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 806249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuers, U.; Wolters, F.; Oude Elferink, R.P.J. Mechanisms of pruritus in cholestasis: Understanding and treating the itch. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaldaferri, F.; Pizzoferrato, M.; Ponziani, F.R.; Gasbarrini, G.; Gasbarrini, A. Use and indications of cholestyramine and bile acid sequestrants. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2013, 8, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlström, A.; Sayin, S.I.; Marschall, H.U.; Bäckhed, F. Intestinal Crosstalk between Bile Acids and Microbiota and Its Impact on Host Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stellaard, F.; Lütjohann, D. Dynamics of the enterohepatic circulation of bile acids in healthy humans. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 321, G55–G66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staley, C.; Weingarden, A.R.; Khoruts, A.; Sadowsky, M.J. Interaction of gut microbiota with bile acid metabolism and its influence on disease states. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.V.; Begley, M.; Hill, C.; Gahan, C.G.M.; Marchesi, J.R. Functional and comparative metagenomic analysis of bile salt hydrolase activity in the human gut microbiome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13580–13585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Han, D.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J. Exploring the role of a novel postbiotic bile acid: Interplay with gut microbiota, modulation of the farnesoid X receptor, and prospects for clinical translation. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 287, 127865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, A.; Fukiya, S.; Islam, K.B.; Ooka, T.; Ogura, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Hagio, M.; Ishizuka, S. Is bile acid a determinant of the gut microbiota on a high-fat diet? Gut Microbes 2012, 3, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustos, A.Y.; Font de Valdez, G.; Fadda, S.; Taranto, M.P. New insights into bacterial bile resistance mechanisms: The role of bile salt hydrolase and its impact on human health. Food Res. Int. 2018, 112, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, K.B.; Fukiya, S.; Hagio, M.; Fujii, N.; Ishizuka, S.; Ooka, T.; Ogura, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Yokota, A. Bile acid is a host factor that regulates the composition of the cecal microbiota in rats. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Franklund, C.V.; Coleman, J.P.; Hylemon, P.B. Evidence for a multigene family involved in bile acid 7-dehydroxylation in Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708. J. Bacteriol. 1988, 170, 4555–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Lordan, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Gut microbes from the phylogenetically diverse genus Eubacterium and their various contributions to gut health. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1802866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shen, Y.; Xin, J.; Xu, X.; Ding, Q.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Lv, Y.; Wei, X.; Wei, Y.; et al. Cryptotanshinone alleviates radiation-induced lung fibrosis via modulation of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism. Phytother. Res. 2023, 37, 4557–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Shen, S.; Zhuang, Q.; Ye, X.; Qian, Y.; Dong, Z.; Wan, X. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide ameliorates cholesterol gallstone formation by modulating cholesterol and bile acid metabolism in an FXR-dependent manner. Chin. Med. 2024, 19, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Yang, S.; Zhou, L.; Dong, J.; Wang, S.; Xue, Y.; Ren, Y.; Geng, Y. Bile Acid Sequestration Attenuates Desulfovibrio-Induced Hepatic Injury. Microorganisms 2026, 14, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms14010079
Yang S, Zhou L, Dong J, Wang S, Xue Y, Ren Y, Geng Y. Bile Acid Sequestration Attenuates Desulfovibrio-Induced Hepatic Injury. Microorganisms. 2026; 14(1):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms14010079
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Songfan, Lingxi Zhou, Jie Dong, Sifan Wang, Yuzheng Xue, Yilin Ren, and Yan Geng. 2026. "Bile Acid Sequestration Attenuates Desulfovibrio-Induced Hepatic Injury" Microorganisms 14, no. 1: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms14010079
APA StyleYang, S., Zhou, L., Dong, J., Wang, S., Xue, Y., Ren, Y., & Geng, Y. (2026). Bile Acid Sequestration Attenuates Desulfovibrio-Induced Hepatic Injury. Microorganisms, 14(1), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms14010079





