Three Antibiotics Exert Differential Effects on the Larval Microbiome and Fitness of Hyphantria cunea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Insect Rearing and Sample Collection
2.2. Insect Fitness Determination
2.3. Microbiome Sequencing and Data Assembly
2.4. Microbial Diversity and Community Structure Analysis
2.5. Microbial Community Difference Analysis
2.6. Microbial Function Prediction
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Antibiotics on Fitness
3.2. Overview of Larval Microbiome
3.3. Effects of Antibiotics on Microbial Diversity
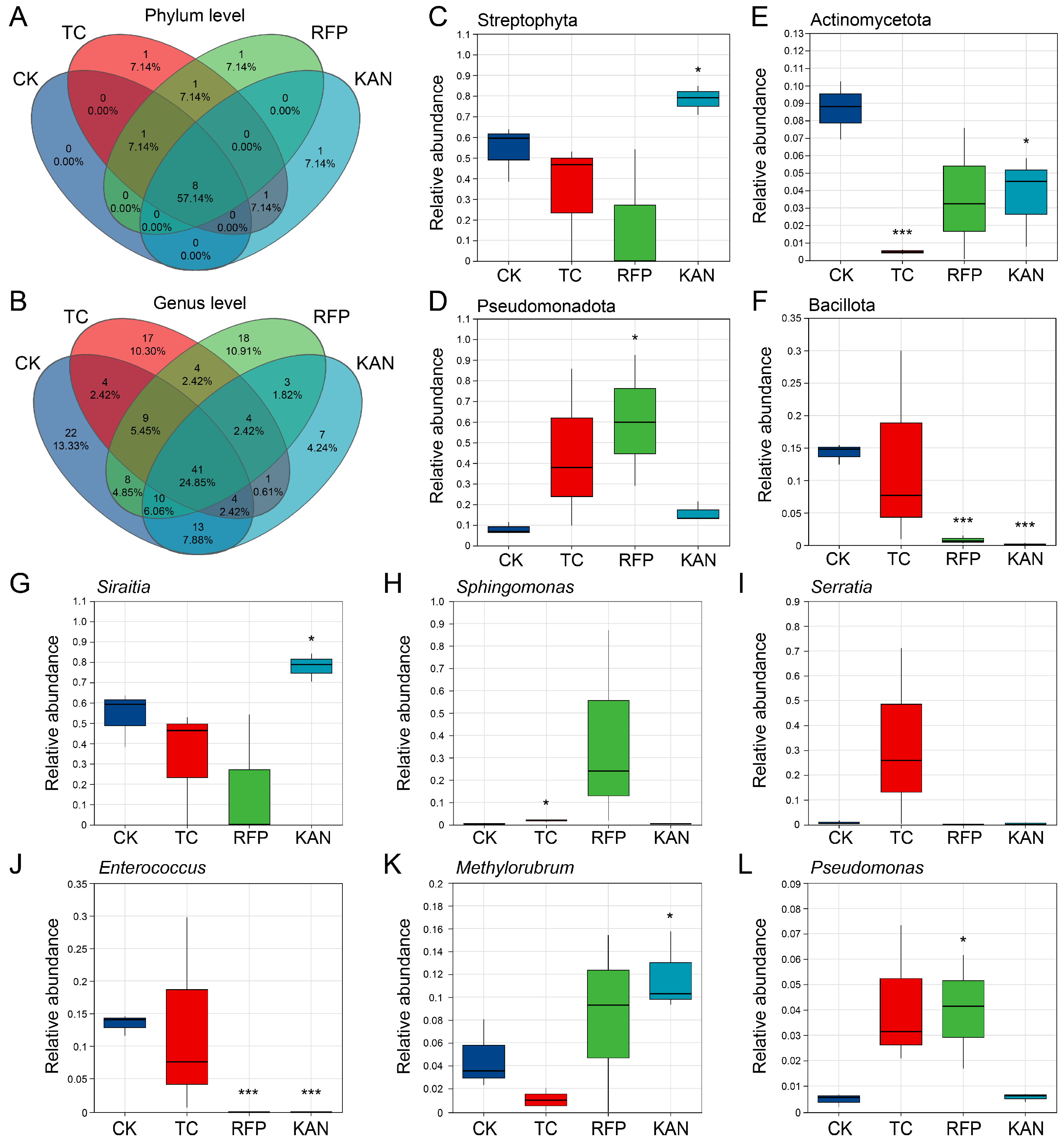
3.4. Effects of Antibiotics on Microbial Community Structure
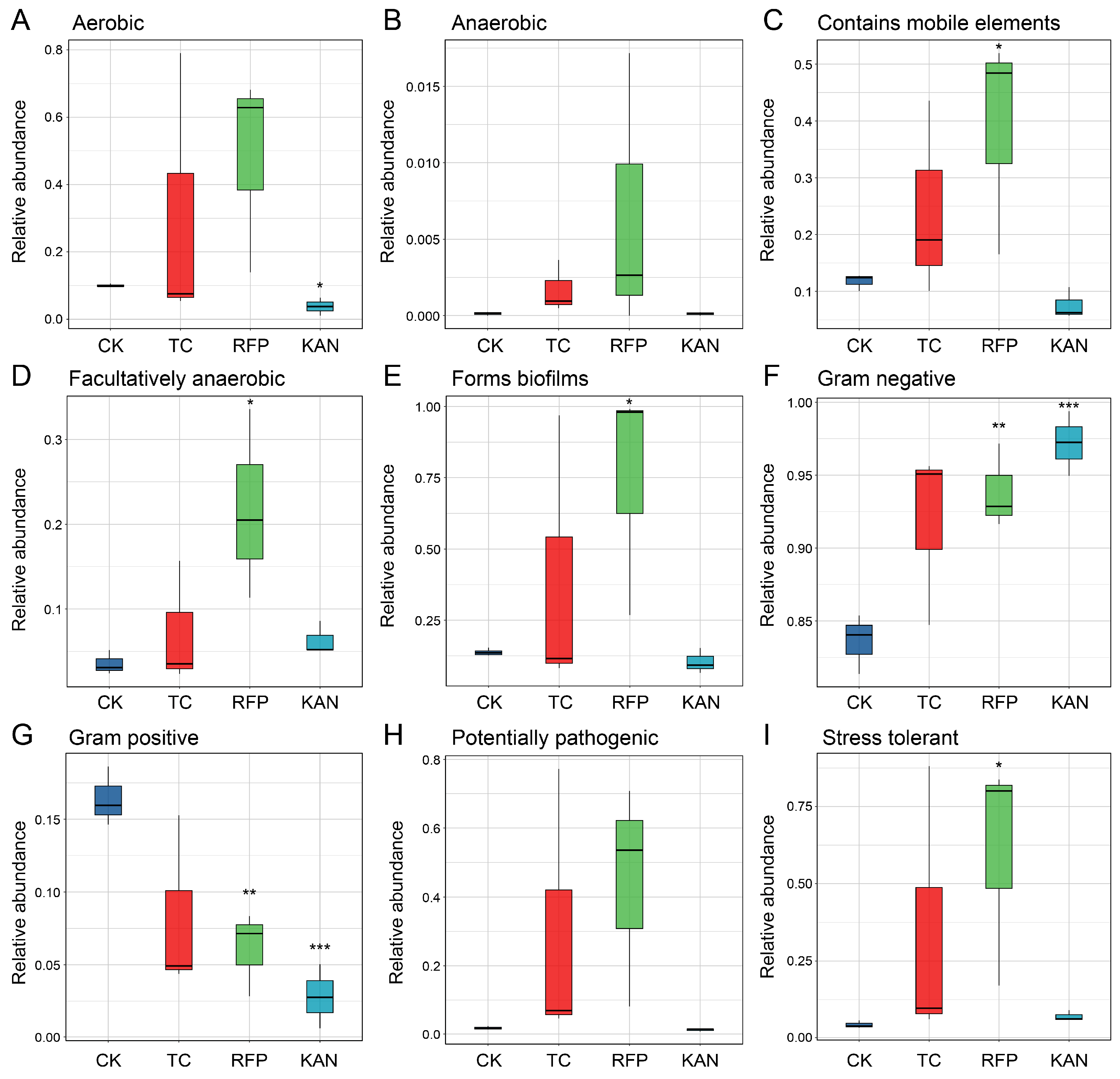
3.5. Effects of Antibiotics on Microbial Functions
4. Discussion
4.1. The Differential Effects of Antibiotics on the Fitness of H. cunea
4.2. Antibiotics Remodel Microbial Diversity and Community Structure
4.3. Effects of Antibiotics on Microbiome Function
4.4. Advantages of Microbial Regulation-Based Pest Control Strategies and Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akman, G.E.; Douglas, A.E. Symbiotic bacteria enable insect to use a nutritionally inadequate diet. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 987–991. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wu, J.; Li, K.; Sadd, B.M.; Guo, Y.; Zhuang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Evans, J.D.; Guo, J. Dynamic changes of gut microbial communities of bumble bee queens through important life stages. mSystems 2019, 4, e00631–e00719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Benavent, M.; Pérez-Cobas, A.E.; García-Ferris, C.; Moya, A.; Latorre, A. Insects’ potential: Understanding the functional role of their gut microbiome. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. 2021, 194, 113787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W. Intestinal microbiota in various animals. Integr. Zool. 2022, 17, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.T.; Li, T.P.; Wang, M.K.; Hong, X.Y. Wolbachia-based strategies for control of agricultural pests. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2023, 57, 101039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, A.E. The microbial dimension in insect nutritional ecology. Funct. Ecol. 2009, 23, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Start, C.C.; Anderson, C.M.H.; Gatehouse, A.M.R.; Edwards, M.G. Dynamic response of essential amino acid biosynthesis in Buchnera aphidicola to supplement sub-optimal host nutrition. J. Insect Physiol. 2024, 158, 104683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P.A.; Yeatman, E.; Berran, M.S.; Gu, X.; Hoffmann, A.A.; van Heerwaarden, B. Wolbachia strain wMelM disrupts egg retention by Aedes aegypti females prevented from ovipositing. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2025, 91, e0149124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Amin, H.M.; Gyawali, N.; Graham, M.; Alam, M.S.; Lenhart, A.; Xi, Z.; Rašić, G.; Beebe, N.W.; Hugo, L.E.; Devine, G.J. Fitness compatibility and dengue virus Inhibition in a Bangladeshi strain of Aedes aegypti infected with the Wolbachia strain wAlbB. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Qian, Z.; He, J.; Shen, X.; Lei, X.; Sun, C.; Fan, J.; Felton, G.W.; Shao, Y. Gut bacteria of lepidopteran herbivores facilitate digestion of plant toxins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2412165121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, A.L.; Zhang, V.; Lamberti, L.; Jones, E.W.; Obadia, B.; Korasidis, N.; Gavryushkin, A.; Carlson, J.M.; Beerenwinkel, N.; Ludington, W.B. Microbiome interactions shape host fitness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E11951–E11960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.C.; Kim, S.H.; You, H.; Kim, B.; Kim, A.C.; Lee, K.A.; Yoon, J.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, W.J. Drosophila microbiome modulates host developmental and metabolic homeostasis via insulin signaling. Science 2011, 334, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymann, K.; Shaffer, Z.; Moran, N.A. Antibiotic exposure perturbs the gut microbiota and elevates mortality in honeybees. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2001861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, E.V.S.; Moran, N.A. The honeybee microbiota and its impact on health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.P.; Wang, C.H.; Xie, J.C.; Wang, M.K.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.X.; Hao, D.J.; Hong, X.Y. Microbial changes and associated metabolic responses modify host plant adaptation in Stephanitis nashi. Insect Sci. 2024, 31, 1789–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chee-Sanford, J.C.; Mackie, R.I.; Koike, S.; Krapac, I.G.; Lin, Y.F.; Yannarell, A.C.; Maxwell, S.; Aminov, R.I. Fate and transport of antibiotic residues and antibiotic resistance genes following land application of manure waste. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 38, 1086–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Zheng, L.; Zhai, Y.; Zheng, H. The honeybee gut resistome and its role in antibiotic resistance dissemination. Integr. Zool. 2023, 18, 1014–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Yin, Y.; Du, Y.Z. Wolbachia modify host cell metabolite profiles in response to short-term temperature stress. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2024, 16, e70013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.X.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, X.; Hong, X.Y. Antibiotics and temperature alter microbiome assembly and host fecundity in spider mites. Syst. Appl. Acarol. 2023, 28, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Gu, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Lyu, K.; Yang, Z. Elevated temperature and toxic Microcystis reduce Daphnia fitness and modulate gut microbiota. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghrir, R.; Drogui, P. Tetracycline antibiotics in the environment: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2013, 11, 209–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jia, S.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, N.; Xie, Y.; Wei, R.; Huang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hu, F.; Zheng, H. Tetracycline-induced gut community dysbiosis and Israeli Acute Paralysis Virus infection synergistically negatively affect honeybees. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 282, 116706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosca, M.; Gyorffy, A.; Milito, M.; Di Ruggiero, C.; De Carolis, A.; Pietropaoli, M.; Giannetti, L.; Necci, F.; Marini, F.; Smedile, D. Antibiotic use in beekeeping: Implications for health and environment from a one-health Perspective. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, G.; Wang, S.; Hu, F.; Zheng, H. The Pass-on effect of tetracycline-induced honey bee (Apis mellifera) gut community dysbiosis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 781746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, W.; Mu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, W.; Shi, X.; He, Y. Rifampicin synergizes the toxicity of insecticides against the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 276, 116291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Chronic sublethal effects of cantharidin on the diamondback moth Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Toxins 2015, 7, 1962–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goane, L.; Salgueiro, J.; Medina Pereyra, P.; Arce, O.E.A.; Ruiz, M.J.; Nussenbaum, A.L.; Segura, D.F.; Vera, M.T. Antibiotic treatment reduces fecundity and nutrient content in females of Anastrepha fraterculus (Diptera: Tephritidae) in a diet dependent way. J. Insect Physiol. 2022, 139, 104396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, H.; Wen, M.; Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Du, L.; Kang, H.; et al. Genome of the webworm Hyphantria cunea unveils genetic adaptations supporting its rapid invasion and spread. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, P.; Yang, R.; Cao, R.; Hu, X.; Feng, J. Niche and range shifts of the fall webworm (Hyphantria cunea Dury) in europe imply its huge invasion potential in the future. Insects 2023, 14, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Gong, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y. Analysis of the spatiotemporal trends and influencing factors of Hyphantria cunea in China. J. For. Res. 2024, 35, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Wu, S.; Tan, M.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, L.; Yan, S.C. The high adaptability of Hyphantria cunea larvae to cinnamic acid involves in detoxification, antioxidation and gut microbiota response. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 174, 104805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Song, F.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Xu, L. Gut microbiota facilitate adaptation of invasive moths to new host plants. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, L. Horizontal gene transfer-mediated enhancement of gut antifungal defense facilitates host plant adaptation in an invasive pest. Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 115970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, J.A.; Khan, M.M.; Bamisile, B.S.; Hafeez, M.; Qasim, M.; Rasheed, M.T.; Rasheed, M.A.; Ahmad, S.; Shahid, M.I.; Xu, Y. Role of insect gut microbiota in pesticide degradation: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 870462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.P.; Xie, J.C.; Wang, C.H.; Zhao, L.Q.; Hao, D.J. Diffusive phyllosphere microbiome potentially regulates harm and defence interactions between Stephanitis nashi and its crabapple host. Plant Cell Environ. 2025, 48, 1311–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Lozupone, C.A.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Fierer, N.; Knight, R. Global patterns of 16S rRNA diversity at a depth of millions of sequences per sample. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108 (Suppl. S1), 4516–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.; Kikuchi, Y. Impact of the insect gut microbiota on ecology, evolution, and industry. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2020, 41, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xia, X.; Zhao, S.; Shi, M.; Liu, F.; Zhu, Y. The physiological and toxicological effects of antibiotics on an interspecies insect model. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 126019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Schal, C.; Pan, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, F. Effects of antibiotics on the dynamic balance of bacteria and fungi in the gut of the German cockroach. J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 2666–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabanol, E.; Gendrin, M. Insects and microbes: Best friends from the nursery. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2024, 66, 101270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Liu, B.Q.; Yu, P.H.; Yu, Z.P.; Zhang, R.; Luo, G.H.; Fang, J.C. Antibiotic feeding changes the bacterial community of Chilo suppressalis and thereby affects its pesticide tolerance. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Guo, Z.; Liu, X.; Wang, P.; Yuan, X.; Li, Y. Antibiotic treatment reduced the gut microbiota diversity, prolonged the larval development period and lessened adult fecundity of Grapholita molesta (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae). Insects 2022, 13, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.P.; Wang, C.H.; Wang, Z.H.; Hao, B.R.; Xie, J.C.; Li, H.X.; Cai, D.J.; Ye, S.C.; Zhao, L.Q. Tetracycline changes the microbial assembly of Hyphantria cunea and reduces its fitness. Environ. Entomol. 2025, 54, 790–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Li, S.S.; Yang, C.; Zhang, Y.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, J.Z. Tetracycline inhibits tick host reproduction by modulating bacterial microbiota, gene expression and metabolism levels. Pest Manag. Sci. 2024, 80, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausi, M.; Leone, D.; Strano, A.; Lizio, A.; Rappazzo, G.; Mulder, C.; Conti, E. Effects of tetracycline on entomopathogenic nematodes and their bacterial symbionts. Ecotoxicology 2021, 30, 705–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowen, W.H.; Burne, R.A.; Wu, H.; Koo, H. Oral biofilms: Pathogens, matrix, and polymicrobial interactions in microenvironments. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yao, H.; Chapman, S.J.; Su, J.; Wang, C. Changes in gut bacterial communities and the incidence of antibiotic resistance genes during degradation of antibiotics by black soldier fly larvae. Environ. Int. 2020, 142, 105834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, K.O.; Oliveira, C.J.B.D.; Rodrigues, A.E.; Vasconcelos, P.C.; Silva, N.M.V.D.; Cunha Filho, O.G.D.; Madden, C.; Hale, V.L. Tetracycline exposure alters key gut microbiota in Africanized honey bees (Apis mellifera scutellata x spp.). Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 716660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ourry, M.; Lopez, V.; Hervé, M.; Lebreton, L.; Mougel, C.; Outreman, Y.; Poinsot, D.; Cortesero, A.M. Long-lasting effects of antibiotics on bacterial communities of adult flies. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramond, P.; Galand, P.E.; Logares, R. Microbial functional diversity and redundancy: Moving forward. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2025, 49, fuae031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adair, K.L.; Wilson, M.; Bost, A.; Douglas, A.E. Microbial community assembly in wild populations of the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. ISME J. 2018, 12, 959–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spragge, F.; Bakkeren, E.; Jahn, M.T.; B N Araujo, E.; Pearson, C.F.; Wang, X.; Pankhurst, L.; Cunrath, O.; Foster, K.R. Microbiome diversity protects against pathogens by nutrient blocking. Science 2023, 382, eadj3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillings, M.R.; Gaze, W.H.; Pruden, A.; Smalla, K.; Tiedje, J.M.; Zhu, Y.G. Using the class 1 integron-integrase gene as a proxy for anthropogenic pollution. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerminiaux, N.A.; Cameron, A.D.S. Horizontal transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in clinical environments. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelis, C.; Grohmann, E. Horizontal gene transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in biofilms. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joannard, B.; Sanchez-Cid, C. Bacterial dynamics of the plastisphere microbiome exposed to sub-lethal antibiotic pollution. Microbiome 2024, 12, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Lin, J. Factors influencing horizontal gene transfer in the intestine. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2017, 18, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, O.; Joshi, N.K. Microbial symbiont-based detoxification of different phytotoxins and synthetic toxic chemicals in insect pests and pollinators. J. Xenobiotics 2024, 14, 753–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaili, S.J.; Kabiraj, U.K.; Mahedi, M. Fungal biocontrol in agriculture: A Sustainable alternative to chemical pesticides–a Comprehensive review. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2025, 26, 2305–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

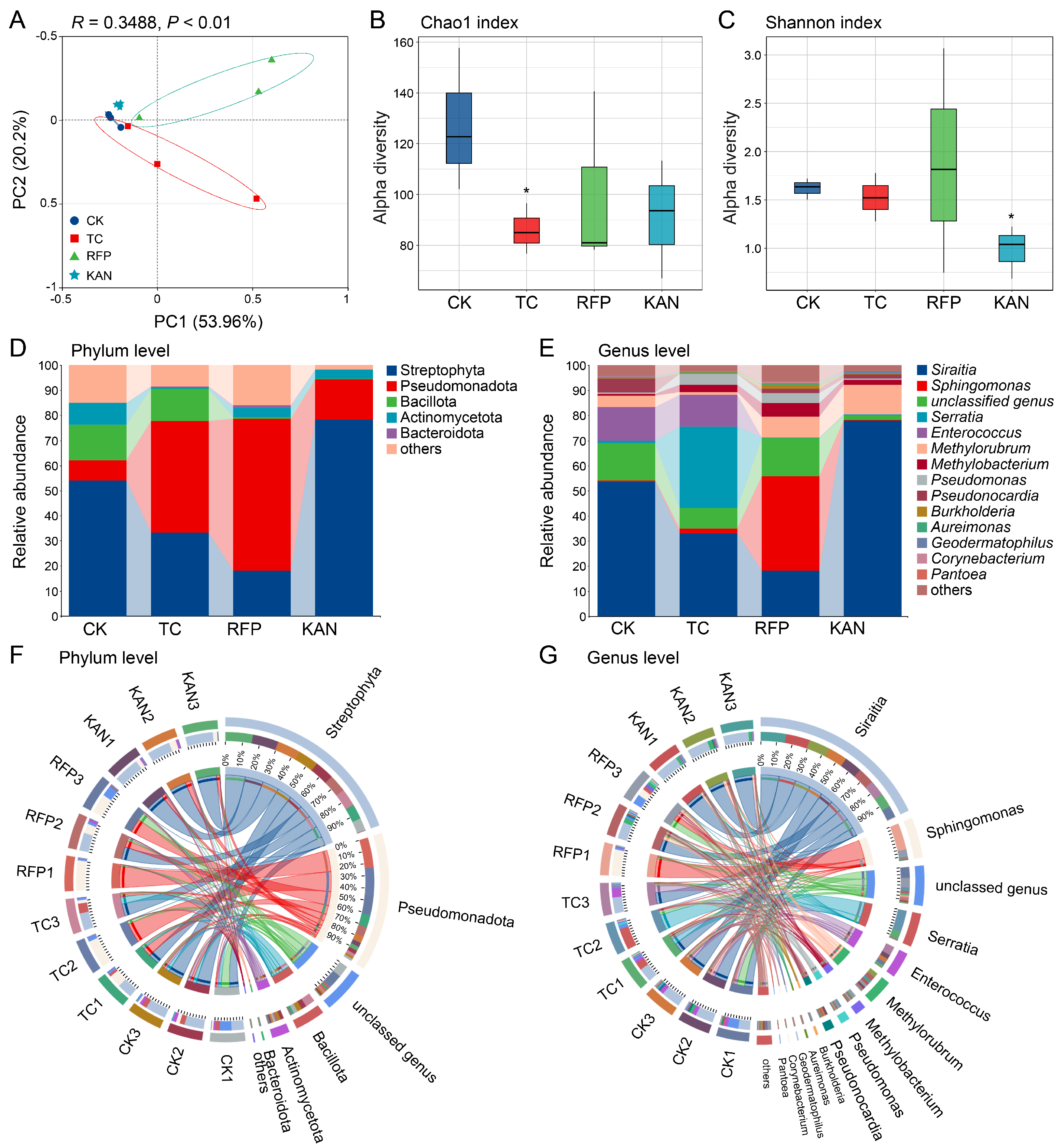
| Sample Types | Read Counts | Observed Species Number | ACE Richness Index | Chao1 Richness Index | Shannon Diversity Index | Simpson Diversity Index | Sequencing Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 64,469 ± 3551.232 | 124.333 ± 30.139 | 128.15 ± 28.831 | 127.503 ± 28.071 | 1.62 ± 0.11 | 0.367 ± 0.074 | 0.9998 ± 0 |
| TC | 52,413.333 ± 14,571.579 | 85.333 ± 9.504 | 86.572 ± 10.323 | 86.083 ± 9.919 | 1.526 ± 0.249 | 0.395 ± 0.116 | 0.9999 ± 0.0001 |
| RFP | 89,808.333 ± 23,278.021 | 97 ± 37.269 | 100.173 ± 36.076 | 99.95 ± 35.231 | 1.877 ± 1.163 | 0.399 ± 0.33 | 0.9999 ± 0 |
| KAN | 64,490 ± 61.879 | 84.667 ± 21.595 | 92.714 ± 22.642 | 91.291 ± 23.223 | 0.982 ± 0.274 | 0.625 ± 0.099 | 0.9997 ± 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.-P.; Wang, Z.-H.; Wang, C.-H.; Hao, B.-R.; Song, S.-Y.; Dawa, Z.; Lei, H.; Zhao, L.-Q. Three Antibiotics Exert Differential Effects on the Larval Microbiome and Fitness of Hyphantria cunea. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2078. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092078
Li T-P, Wang Z-H, Wang C-H, Hao B-R, Song S-Y, Dawa Z, Lei H, Zhao L-Q. Three Antibiotics Exert Differential Effects on the Larval Microbiome and Fitness of Hyphantria cunea. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(9):2078. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092078
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tong-Pu, Zhi-Heng Wang, Chen-Hao Wang, Bing-Ren Hao, Si-Ying Song, Zhuoma Dawa, Han Lei, and Lv-Quan Zhao. 2025. "Three Antibiotics Exert Differential Effects on the Larval Microbiome and Fitness of Hyphantria cunea" Microorganisms 13, no. 9: 2078. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092078
APA StyleLi, T.-P., Wang, Z.-H., Wang, C.-H., Hao, B.-R., Song, S.-Y., Dawa, Z., Lei, H., & Zhao, L.-Q. (2025). Three Antibiotics Exert Differential Effects on the Larval Microbiome and Fitness of Hyphantria cunea. Microorganisms, 13(9), 2078. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13092078






