Environmental Effects on Bacterial Community Assembly in Arid and Semi-Arid Grasslands
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
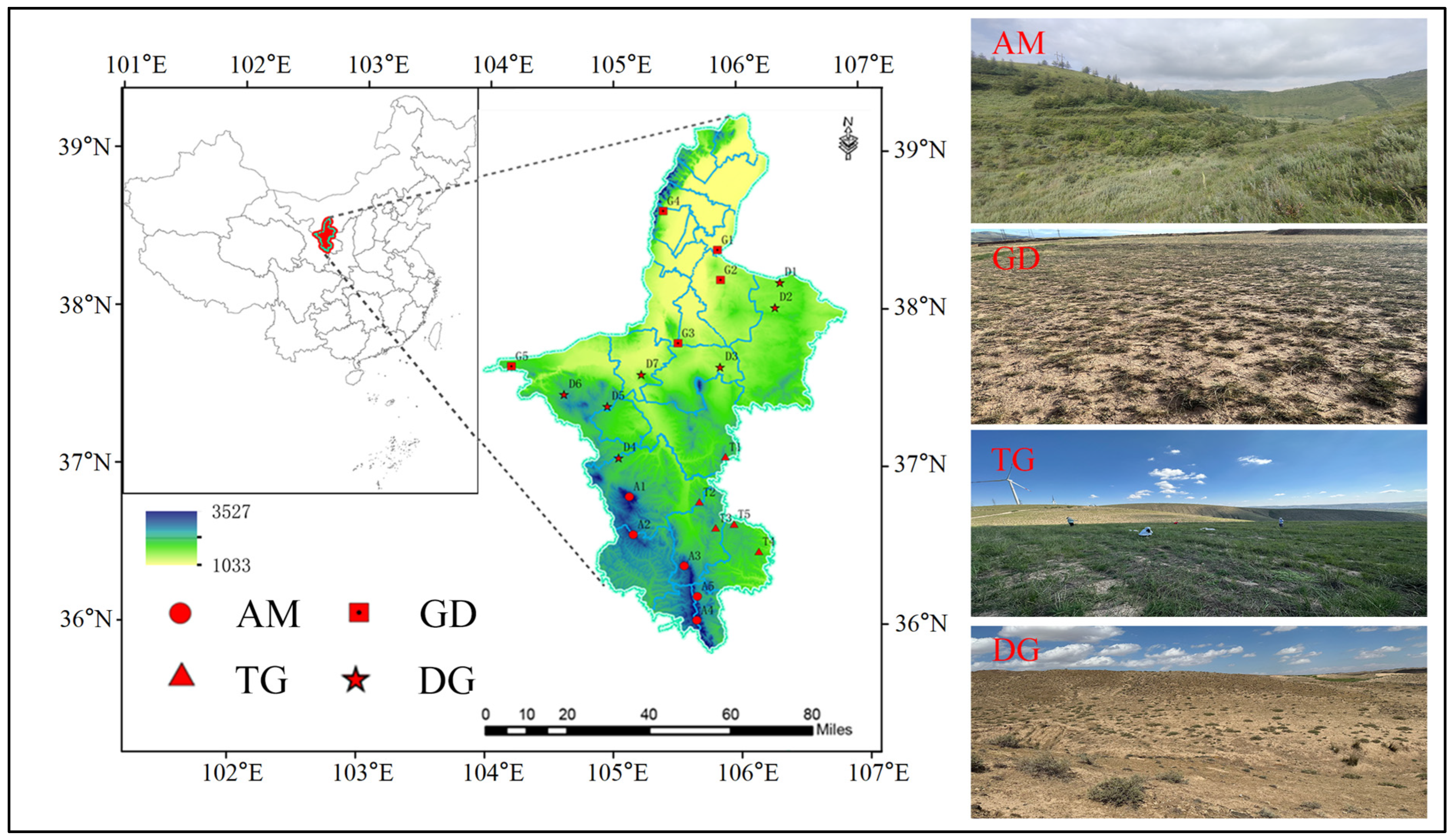
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Site Selection and Soil Sampling
2.3. Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.4. Illumina Sequencing Analysis of 16S rRNA Gene Amplicons
2.5. Cooccurrence Network Analysis
2.6. Estimation of Community Assembly Processes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Properties Depending on Depth
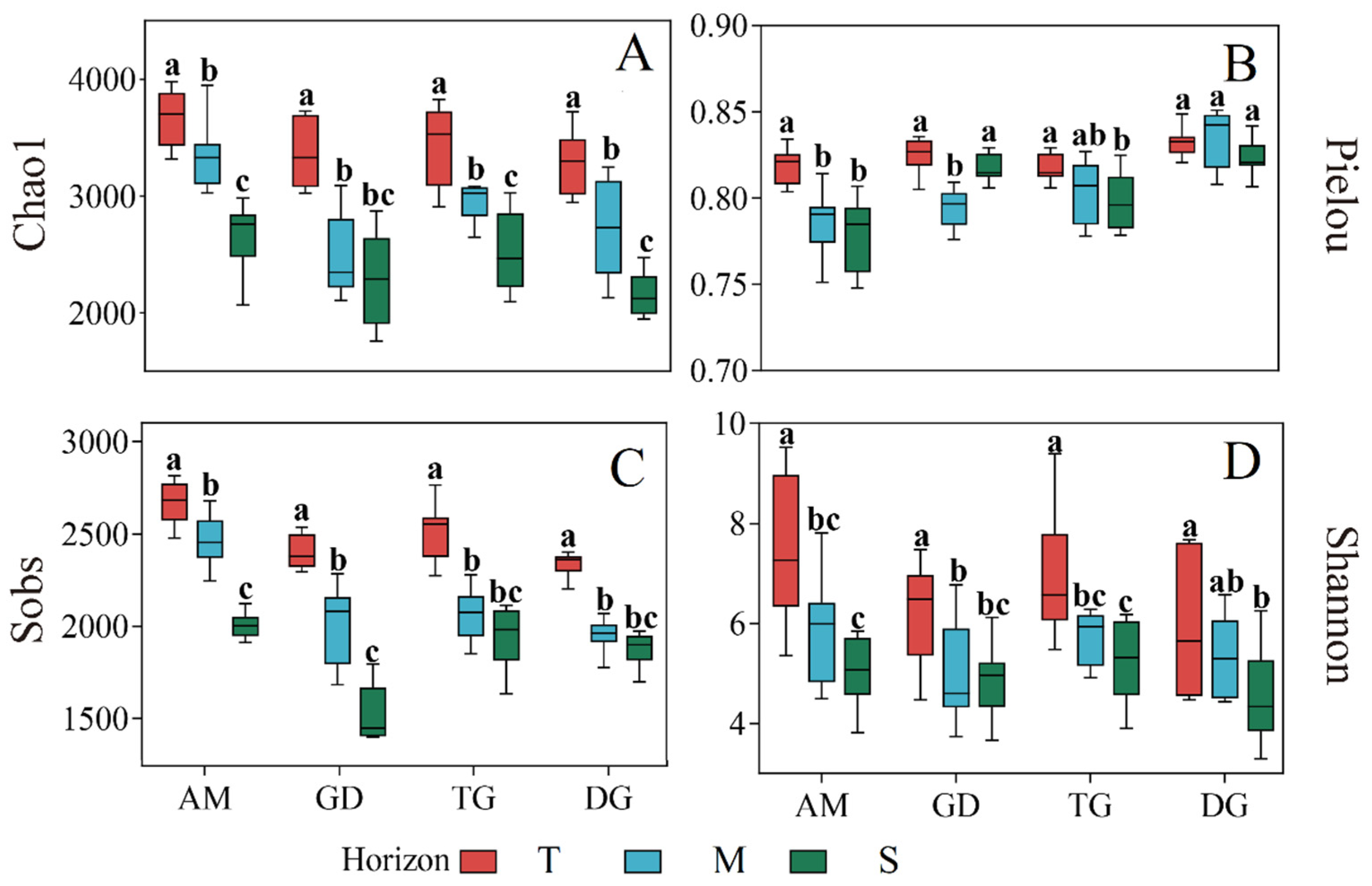
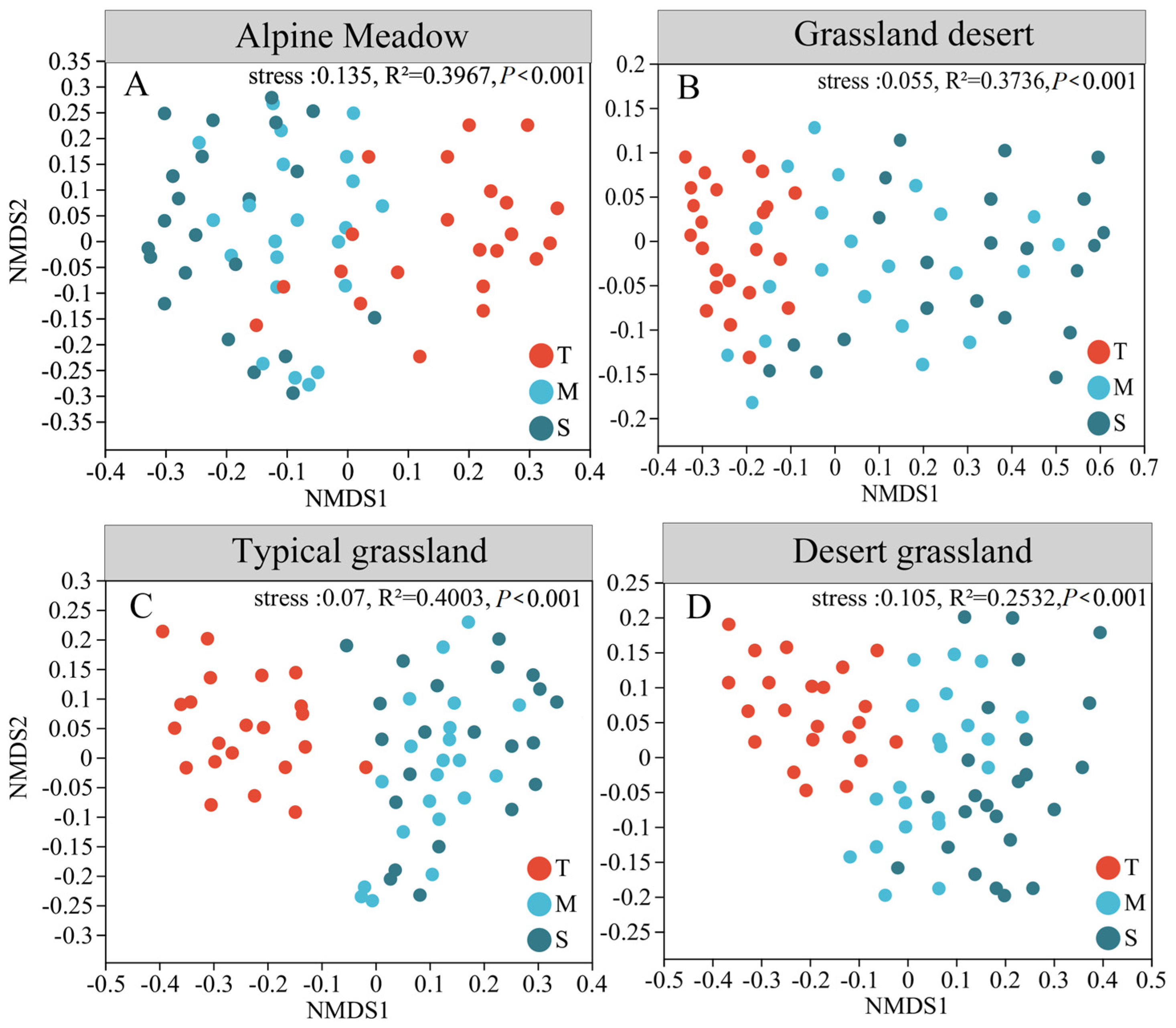
3.2. Dissimilarity of Bacterial Community Diversity Depending on Depth
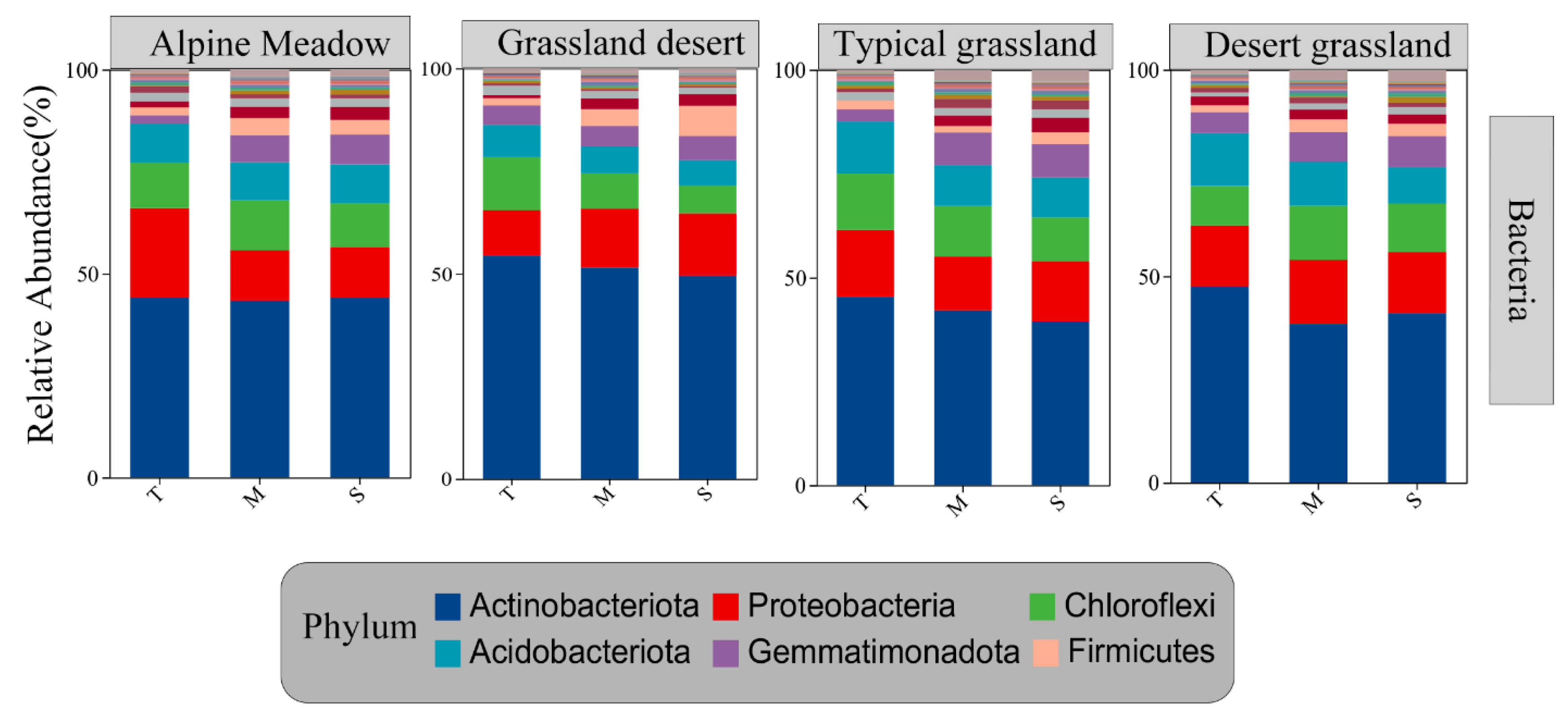
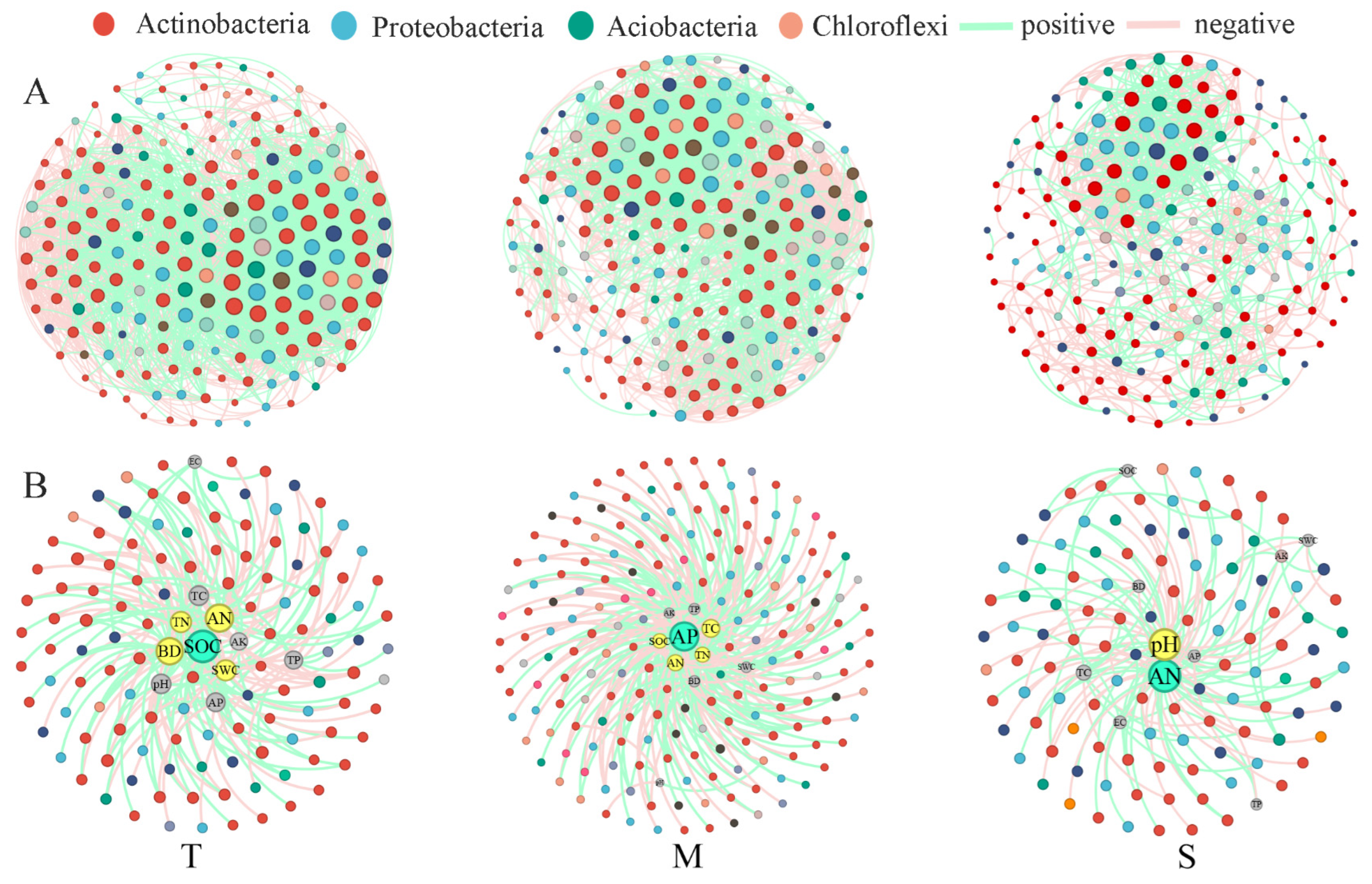
3.3. Trends in Taxon-Taxon and Taxon-Environment Networks with Soil Depth
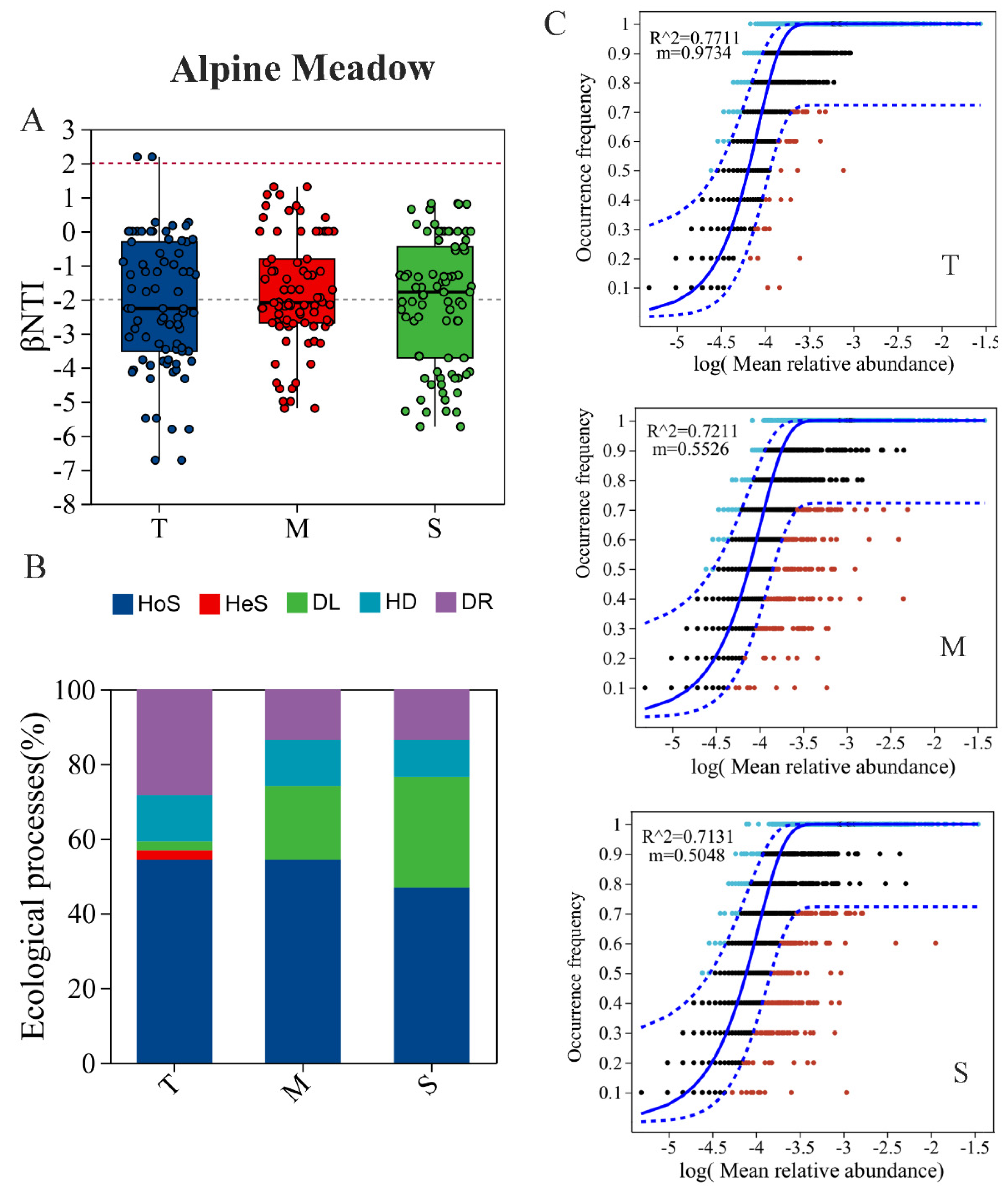
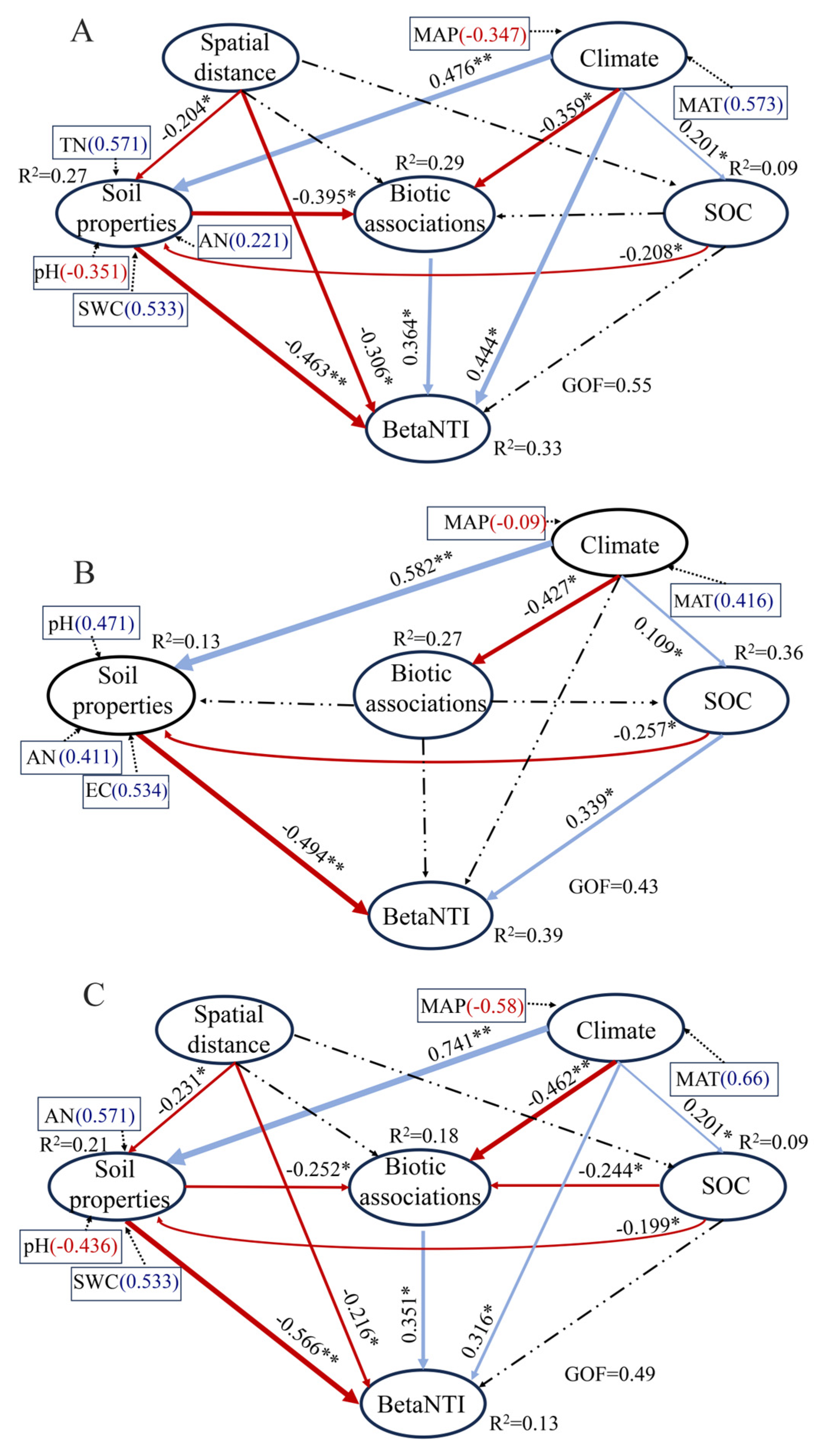
3.4. Bacterial Community Assembly Depending on Soil Depth
4. Discussion
4.1. Dissimilarity in Bacterial Community Within Soil Profiles
4.2. Changes in Taxa–Taxa and Taxa–Environment Associations with Soil Depth
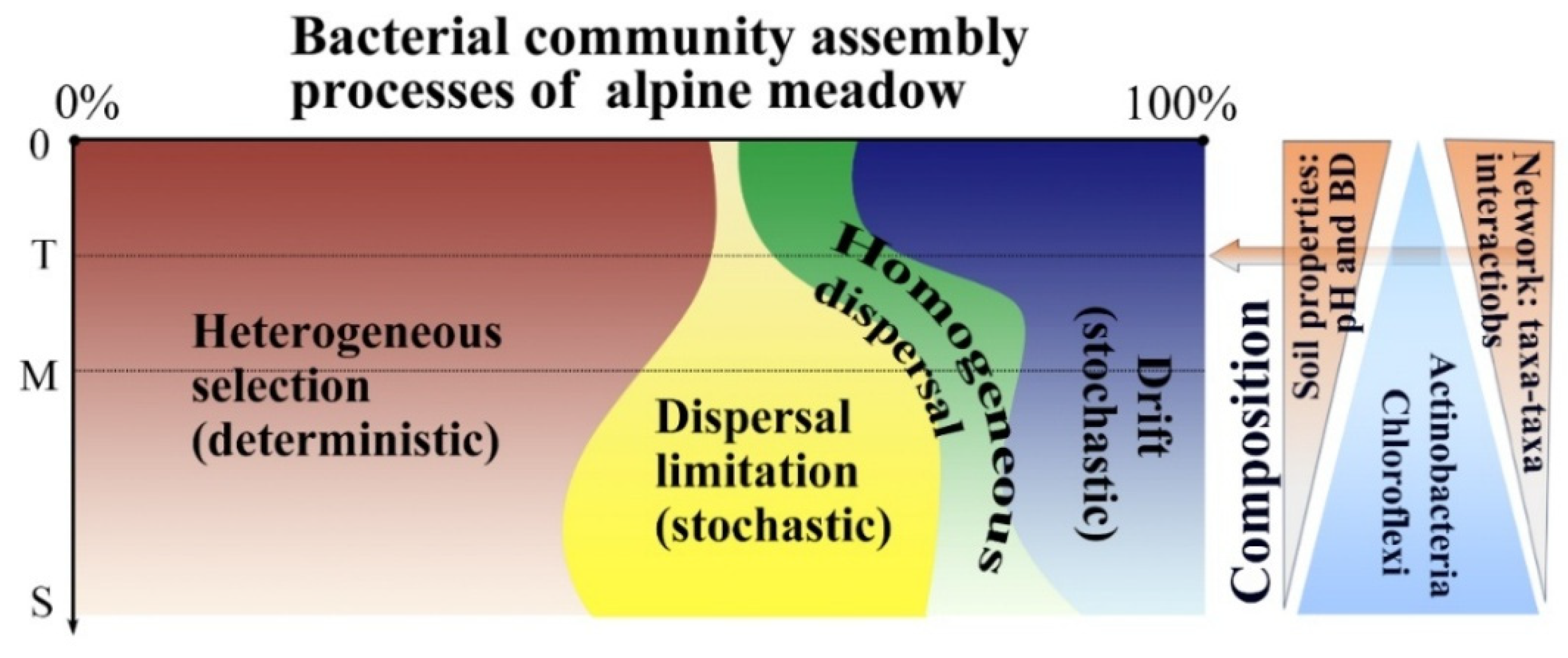
4.3. Effects of Soil Depth on Bacterial Community Assembly Processes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, X.M.; Hu, Y.J.; Peng, P.Q.; Zhu, Z.K.; Atere, C.T.; O’Donnell, A.G.; Wu, J.H.; Ge, T.D. Effect of P stoichiometry on the abundance of nitrogen-cycle genes in phosphorus-limited paddy soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 53, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahram, M.; Hildebrand, F.; Forslund, S.K.; Anderson, J.L.; Soudzilovskaia, N.A.; Bodegom, P.M.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Anslan, S.; Coelho, L.P.; Harend, H.; et al. Structure and function of the global topsoil microbiome. Nature 2018, 560, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Dai, Z.M.; Wang, H.Z.; Dsouza, M.; Liu, X.M.; He, Y.; Wu, J.J.; Rodrigues, J.L.M.; Gilbert, J.A.; Brookes, P.C.; et al. Distinct Biogeographic Patterns for Archaea, Bacteria, and Fungi along the Vegetation Gradient at the Continental Scale in Eastern China. Msystems 2017, 2, e00174-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, H.Y.; Sun, H.B.; Tripathi, B.M.; Adams, J.M.; Huang, R.; Zhang, Y.J.; Shi, Y. Bacterial community dissimilarity between the surface and subsurface soils equals horizontal differences over several kilometers in the western Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardy, V.; Mathieu, O.; Lévêque, J.; Terrat, S.; Chabbi, A.; Lemanceau, P.; Ranjard, L.; Maron, P.A. Stability of soil microbial structure and activity depends on microbial diversity. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.; Ghosh, D.; DeBruyn, J.M.; Dasgupta, T.; Wommack, K.E.; Liang, X.L.; Wagner, R.E.; Radosevich, M. Temporal Dynamics of Soil Virus and Bacterial Populations in Agricultural and Early Plant Successional Soils. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.M.; Chen, Y.C.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.W.; Lu, X.Y. Soil Bacterial Communities and Diversity in Alpine Grasslands on the Tibetan Plateau Based on 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Guo, T.Y.; Yao, Y.S.; Wang, R.H.; Chai, B.F. Seasonal Microbial Community Characteristic and Its Driving Factors in a Copper Tailings Dam in the Chinese Loess Plateau. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Wemheuer, B.; Korolkow, V.; Wemheuer, F.; Nacke, H.; Schöning, I.; Schrumpf, M.; Daniel, R. Driving forces of soil bacterial community structure, diversity, and function in temperate grasslands and forests. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantri, S.S.; Negri, T.; Sales-Ortells, H.; Angelov, A.; Peter, S.; Neidhardt, H.; Oelmann, Y.; Ziemert, N. Metagenomic Sequencing of Multiple Soil Horizons and Sites in Close Vicinity Revealed Novel Secondary Metabolite Diversity. Msystems 2021, 6, e0101821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elul, M.; Rubin-Blum, M.; Ronen, Z.; Bar-Or, I.; Eckert, W.; Sivan, O. Metagenomic insights into the metabolism of microbial communities that mediate iron and methane cycling in Lake Kinneret iron-rich methanic sediments. Biogeosciences 2021, 18, 2091–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.Y.; Chen, L.L.; Deng, Q.; Shi, X.R.; Lock, T.R.; Kallenbach, R.L.; Yuan, Z.Y. Vertical changes in bacterial community composition down to a depth of 20 m on the degraded Loess Plateau in China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1300–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kautz, T.; Amelung, W.; Ewert, F.; Gaiser, T.; Horn, R.; Jahn, R.; Javaux, M.; Kemna, A.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Munch, J.C.; et al. Nutrient acquisition from arable subsoils in temperate climates: A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 1003–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, R.; Qin, H.L.; O’Donnell, A.G.; Huang, S.; Wu, J.S.; Wei, W.X. Bacterial succession in paddy soils derived from different parent materials. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 982–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.F.; Wang, Y.Y.; Lu, S.E.; Xiang, Q.J.; Yu, X.M.; Zhao, K.; Zou, L.K.; Chen, Q.; Tu, S.H.; Zhang, X.P. Long-term Fertilization Structures Bacterial and Archaeal Communities along Soil Depth Gradient in a Paddy Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Bu, L.Y.; Tian, J.; Hu, Y.W.; Song, F.Q.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wei, G.H. Particular microbial clades rather than total microbial diversity best predict the vertical profile variation in soil multifunctionality in desert ecosystems. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2157–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upton, R.N.; Sielaff, A.C.; Hofmockel, K.S.; Xu, X.; Polley, H.W.; Wilsey, B.J. Soil depth and grassland origin cooperatively shape microbial community co-occurrence and function. Ecosphere 2020, 11, e02973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; He, N.P.; Kong, W.D.; Deng, Y.; Feng, K.; Green, S.M.; Wang, X.B.; Zhou, J.Z.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Ye, G.R. Deforestation decreases spatial turnover and alters the network interactions in soil bacterial communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 123, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Walder, F.; Büchi, L.; Meyer, M.; Held, A.Y.; Gattinger, A.; Keller, T.; Charles, R.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Agricultural intensification reduces microbial network complexity and the abundance of keystone taxa in roots. Isme J. 2019, 13, 1722–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toju, H.; Peay, K.G.; Yamamichi, M.; Narisawa, K.; Hiruma, K.; Naito, K.; Fukuda, S.; Ushio, M.; Nakaoka, S.; Onoda, Y.; et al. Core microbiomes for sustainable agroecosystems. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 247–257, Erratum in Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.S.; Peng, J.; Ni, S.M.; Zhang, C.Y.; Wang, J.G.; Cai, C.F. Erosion and deposition significantly affect the microbial diversity, co-occurrence network, and multifunctionality in agricultural soils of Northeast China. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herren, C.M.; McMahon, K.D. Keystone taxa predict compositional change in microbial communities. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 2207–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Jnana, A.; Murali, T.S. Modeling Microbial Community Networks: Methods and Tools for Studying Microbial Interactions. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 87, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, B.; Wang, Y.L.; Ye, S.D.; Liu, S.; Stirling, E.; Gilbert, J.A.; Faust, K.; Knight, R.; Jansson, J.K.; Cardona, C.; et al. Earth microbial co-occurrence network reveals interconnection pattern across microbiomes. Microbiome 2020, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.Y.; Yang, T.; Xia, S.G.; Yin, T.; Liu, X.; Li, S.P.; Sun, R.B.; Gao, H.J.; Chu, H.Y.; Ma, C. Soil depth exerts stronger impact on bacterial community than elevation in subtropical forests of Huangshan Mountain. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.M.; Xiao, E.Z.; Pu, Z.L.; Krumins, V.; Dong, Y.R.; Li, B.Q.; Hu, M. Paddy soil microbial communities driven by environment- and microbe-microbe interactions: A case study of elevation-resolved microbial communities in a rice terrace. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosetta, C.M.; Wolfe, B.E. Causes and consequences of biotic interactions within microbiomes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2019, 50, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.J.; Li, C.N.; Wang, J.M.; Li, J.B.; Li, X.Z. Elevation rather than season determines the assembly and co-occurrence patterns of soil bacterial communities in forest ecosystems of Mount Gongga. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 7589–7602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, X.Z.; Mansoldo, F.R.P.; An, J.X.; Kou, Y.P.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, J.X.; Vermelho, A.B.; Wang, J.M.; Yao, M.J. Microbial habitat specificity largely affects microbial co-occurrence patterns and functional profiles in wetland soils. Geoderma 2022, 418, 115866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.T.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Zheng, Y.L.; Li, P.F.; Li, G.L.; Liu, M.; Alharbi, H.A.; Li, Z.P. Depth effects on bacterial community assembly processes in paddy soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 165, 108517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.F.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.Z.; Escalas, A.; Feng, K.; He, Q.; Wang, Z.J.; Wu, Y.N.; Wang, D.R.; Peng, X.; et al. Steeper spatial scaling patterns of subsoil microbiota are shaped by deterministic assembly process. Mol. Ecol. 2021, 30, 1072–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.B.; Sun, X.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Zhou, W.Z.; Yu, J.T.; Zhao, G.Y.; Chen, Z.; Bai, X.T.; Zhang, J.S. Depth effects on bacterial community altitudinal patterns and assembly processes in the warm-temperate montane forests of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 914, 169905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Shen, F.Y.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.C.; Wang, J.; Purahong, W.; Yang, L.X. Contrasting altitudinal patterns and co-occurrence networks of soil bacterial and fungal communities along soil depths in the cold-temperate montane forests of China. Catena 2022, 209, 105844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.C.; Shi, Y.; Fan, K.K.; He, J.S.; Adams, J.M.; Ge, Y.; Chu, H.Y. Soil pH dominates elevational diversity pattern for bacteria in high elevation alkaline soils on the Tibetan Plateau. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2019, 95, fiz003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.L.; Wu, D.; Yan, Y.G.; Guo, W.; Li, K. Interpreting regional ecological security from perspective of ecological networks: A case study in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 65412–65426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cheng, C.X.; Wang, Z.H.; Hai, H.X.; Miao, L.L. Spatiotemporal Variation and Driving Factors of Carbon Sequestration Rate in Terrestrial Ecosystems of Ningxia, China. Land 2025, 14, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Wang, D.N.; Ma, K.X.; Sun, D.; Yang, F.L.; Lin, H.L. Spatiotemporal evolution of soil water erosion in Ningxia grassland based on the RUSLE-TLSD model. Environ. Res. 2023, 236, 116744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.C.; Wang, Z.Q.; Heinonsalo, J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Liu, G. Soil organic carbon stocks and dynamics in a mollisol region: A 1980s–2010s study. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 150910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.J.; Liu, J.; Chen, H.; Zheng, L.; Wang, K.L. Soil gross nitrogen transformations in responses to land use conversion in a subtropical karst region. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 212, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.; Bol, R.; Jones, D.L. Free amino sugar reactions in soil in relation to soil carbon and nitrogen cycling. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 3081–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhang, B.; Liang, C.; He, H.B.; Horwath, W.R. Warming increases microbial residue contribution to soil organic carbon in an alpine meadow. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Ling, Z.B.; Wang, Y.; Dong, R.; Zheng, Y.H.; Qi, J.T. A method for measuring soil water content based on principal component analysis. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2024, 95, 025104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Pan, Y.P.; Liu, Y.; Li, M. High-Level Diversity of Basal Fungal Lineages and the Control of Fungal Community Assembly by Stochastic Processes in Mangrove Sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, AEM0092821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S.P. Exact sequence variants should replace operational taxonomic units in marker-gene data analysis. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2639–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Kaehler, B.D.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.; Bolyen, E.; Knight, R.; Huttley, G.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2′s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 2018, 6, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.T.; Wang, J.C.; Dong, H.L.; Chen, J.M.; Ge, Y. Relative importance of soil properties and heavy metals/metalloids to modulate microbial community and activity at a smelting site. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. Fast R Functions for Robust Correlations and Hierarchical Clustering. J. Stat. Softw. 2012, 46, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Jing, Z.W.; Diao, Q.Y.; He, J.Z.; Liu, Y.J. Host Species and Geography Differentiate Honeybee Gut Bacterial Communities by Changing the Relative Contribution of Community Assembly Processes. Microb. Ecol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martiny, J.B.H.; Eisen, J.A.; Penn, K.; Allison, S.D.; Horner-Devine, M.C. Drivers of bacterial β-diversity depend on spatial scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7850–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, B.M.; Stegen, J.C.; Kim, M.; Dong, K.; Adams, J.M.; Lee, Y.K. Soil pH mediates the balance between stochastic and deterministic assembly of bacteria. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmandrier, L.; Pansu, J.; Zinger, L.; Boyer, F.; Coissac, E.; Génin, A.; Gielly, L.; Lavergne, S.; Legay, N.; Schilling, V.; et al. Environmental and biotic drivers of soil microbial β-diversity across spatial and phylogenetic scales. Ecography 2019, 42, 2144–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewin, G.R.; Carlos, C.; Chevrette, M.G.; Horn, H.A.; McDonald, B.R.; Stankey, R.J.; Fox, B.G.; Currie, C.R. Evolution and Ecology of Actinobacteria and Their Bioenergy Applications. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 70, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, P.; Wang, J.T.; Hu, H.W.; Zheng, Y.M.; Ge, Y.; Shen, J.P.; He, J.Z. Environmental Filtering Process Has More Important Roles than Dispersal Limitation in Shaping Large-Scale Prokaryotic Beta Diversity Patterns of Grassland Soils. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 72, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Bai, X.X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cui, Y.X.; Hu, S.L.; Jonathan, M.A.; Dong, L.G.; Yu, X. Soil microbial trait-based strategies drive the storage and stability of the soil carbon pool in Robinia pseudoacacia plantations. Catena 2023, 222, 106894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Morrissey, E.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.F.; Qu, L.R.; Sang, C.P.; Zhang, H.; Li, G.C.; et al. Integrating microbial community properties, biomass and necromass to predict cropland soil organic carbon. ISME Commun. 2023, 3, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, G.B.; Xue, S.; Wang, G.L. Soil bacterial community dynamics reflect changes in plant community and soil properties during the secondary succession of abandoned farmland in the Loess Plateau. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhya, I.; Hansen, R.; El-Omar, E.M.; Hold, G.L. IBD-what role do Proteobacteria play? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.J.; Shen, C.C.; Wu, H.Y.; Zhang, L.M.; Wang, J.C.; Liu, S.Y.; Jing, Z.W.; Ge, Y. Environmental selection dominates over dispersal limitation in shaping bacterial biogeographical patterns across different soil horizons of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cline, L.C.; Hobbie, S.E.; Madritch, M.D.; Buyarski, C.R.; Tilman, D.; Cavender-Bares, J.M. Resource availability underlies the plant-fungal diversity relationship in a grassland ecosystem. Ecology 2018, 99, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, B.M.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.; Byun, E.; Yang, J.W.; Ahn, J.; Lee, Y.K. Variations in bacterial and archaeal communities along depth profiles of Alaskan soil cores. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, E.Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.D.; Yan, Z.Q.; Wu, H.D.; Li, M.; Yan, L.; Zhang, K.R.; Wang, J.Z.; Kang, X.M. Soil pH and nutrients shape the vertical distribution of microbial communities in an alpine wetland. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.H.; Jiao, C.C.; Wang, S.R.; Zhao, D.Y.; Jiang, C.L.; Zeng, J.; Wu, Q.L. Contrasting assembly mechanisms explain the biogeographic patterns of benthic bacterial and fungal communities on the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Adams, J.M.; Shi, Y.; Sun, H.B.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Chu, H.Y. Fungal community assemblages in a high elevation desert environment: Absence of dispersal limitation and edaphic effects in surface soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.B.; Sun, X.Y.; Li, S.Y.; Zhou, W.Z.; Chen, Z.; Bai, X.T. The vertical distribution and control factor of microbial biomass and bacterial community at macroecological scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 869, 161754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.Y.; Adams, J.M.; Shi, Y.; Li, Y.T.; Song, X.D.; Zhao, X.R.; Chu, H.Y.; Zhang, G.L. Depth-Dependent Patterns of Bacterial Communities and Assembly Processes in a Typical Red Soil Critical Zone. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Chen, W.M.; Wang, J.L.; Du, N.N.; Li, Q.P.; Wei, G.H. Soil microbiomes with distinct assemblies through vertical soil profiles drive the cycling of multiple nutrients in reforested ecosystems. Microbiome 2018, 6, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.J.; Chai, Y.N.; Lopes, L.D.; Ordoñez, R.A.; Wright, E.E.; Archontoulis, S.; Schachtman, D.P. The Effects of Soil Depth on the Structure of Microbial Communities in Agricultural Soils in Iowa (United States). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e02673-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.H.; Li, X.; Li, X.Y.; Zhang, H.W. Shifts in bacterial community composition increase with depth in three soil types from paddy fields in China. Pedobiologia 2019, 77, 150589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Q.; Luo, Y.H.; Chen, F.M.; Qi, M.D.; Luo, R.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, Y. Exploring the Co-Occurrence of Depressive Symptoms and Aggression among Chinese Adolescents: Patterns and Stability. J. Youth Adolesc. 2024, 54, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiana, N.; Arnoldi, J.F.; Mestre, F.; Rozenfeld, A.; Araújo, M.B. Power laws in species’ biotic interaction networks can be inferred from co-occurrence data. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 8, 209–217, Erratum in Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2024, 8, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveau, A.; Bonito, G.; Uehling, J.; Paoletti, M.; Becker, M.; Bindschedler, S.; Hacquard, S.; Hervé, V.; Labbé, J.; Lastovetsky, O.A.; et al. Bacterial-fungal interactions: Ecology, mechanisms and challenges. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 42, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, H.Z.; Dsouza, M.; Lou, J.; He, Y.; Dai, Z.M.; Brookes, P.C.; Xu, J.M.; Gilbert, J.A. Geographic patterns of co-occurrence network topological features for soil microbiota at continental scale in eastern China. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.Y.; Ren, C.J.; Wang, D.X.; Wu, R.Q.; Wang, Y.S.; Li, Z.F.; Huang, D.C.; Qi, H.Y. Microbial community assembly and its influencing factors of secondary forests in Qinling Mountains. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 184, 109075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Kerfahi, D.; Ogwu, M.C.; Wang, J.J.; Dong, K.; Takahashi, K.; Moroenyane, I.; Adams, J.M. Elevation-related climate trends dominate fungal co-occurrence network structure and the abundance of keystone taxa on Mt. Norikura, Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 799, 149368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; You, Q.; Wang, S.Y.; Zou, Y.Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.M.; Wang, H.Z. Depth-dependent patterns of soil microbial community in the E-waste dismantling area. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 444, 130379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, J.Y.; Liu, J.; He, H.P.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, Y.Y.; Wang, J.; Yin, M.L.; Wang, L.L.; Wei, X.D.; Huang, Y.L.; et al. Microbial response and adaption to thallium contamination in soil profiles. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 127080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liao, L.R.; Wang, G.L.; Liu, H.F.; Wu, Y.; Liu, G.B.; Zhang, C. N-induced root exudates mediate the rhizosphere fungal assembly and affect species coexistence. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 804, 150148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhalnina, K.; Louie, K.B.; Hao, Z.; Mansoori, N.; da Rocha, U.N.; Shi, S.J.; Cho, H.J.; Karaoz, U.; Loqué, D.; Bowen, B.P.; et al. Dynamic root exudate chemistry and microbial substrate preferences drive patterns in rhizosphere microbial community assembly. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faust, K.; Raes, J. Microbial interactions: From networks to models. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyte, K.Z.; Schluter, J.; Foster, K.R. The ecology of the microbiome: Networks, competition, and stability. Science 2015, 350, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Huang, M.B.; Li, C.H.; Wu, X.F.; Fang, L.C. Vegetation restoration increases the diversity of bacterial communities in deep soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 180, 104631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Shu, H.Y.; Lin, X.R.; Zhou, Q.X.; Bramryd, T.; Shu, W.S.; Huang, L.N. Microbial community structure and function in sediments from e-waste contaminated rivers at Guiyu area of China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini-Andreote, F.; Silva, M.; Triadó-Margarit, X.; Casamayor, E.O.; van Elsas, J.D.; Salles, J.F. Dynamics of bacterial community succession in a salt marsh chronosequence: Evidences for temporal niche partitioning. ISME J. 2014, 8, 1989–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.W.; Guo, Q.Q.; Li, H.E.; Luo, S.Q.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Yao, S.; Fan, X.; Sun, X.G.; Qi, Y.J. Dynamics of Soil Nutrients, Microbial Community Structure, Enzymatic Activity, and Their Relationships along a Chronosequence of Pinus massoniana Plantations. Forests 2021, 12, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, B.; Xiao, R.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Z.Q.; Bai, J.H.; Zhang, K.G.; Campos, M.; Jorquera, M.A. Bacterial community assembly in surface sediments of a eutrophic shallow lake in northern China. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2024, 24, 828–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, S.; Hou, W.G.; Feng, K.; Li, F.R.; Hai, W.M.; Zhang, Y.D.; Sun, Y.X.; Deng, Y. Temperature and microbial interactions drive the deterministic assembly processes in sediments of hot springs. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Maestre, F.T.; Reich, P.B.; Trivedi, P.; Osanai, Y.; Liu, Y.R.; Hamonts, K.; Jeffries, T.C.; Singh, B.K. Carbon content and climate variability drive global soil bacterial diversity patterns. Ecol. Monogr. 2016, 86, 373–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieder, W.R.; Boehnert, J.; Bonan, G.B. Evaluating soil biogeochemistry parameterizations in Earth system models with observations. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2014, 28, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Ning, D.L. Stochastic Community Assembly: Does It Matter in Microbial Ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00002-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Rufty, T.; Shi, W. Soil microbial diversity and composition: Links to soil texture and associated properties. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 149, 107953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, B.; Villerd, J.; Dequiedt, S.; Terrat, S.; Bouré, N.C.P.; Djemiel, C.; Lelièvre, M.; Tripied, J.; Nowak, V.; Saby, N.P.A.; et al. Biogeography of soil microbial habitats across France. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2020, 29, 1399–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.S.; Gao, W.; Zhao, B.Z.; Chen, M.Q.; Ma, L.; Jia, Z.J.; Zhang, J.B. Bacterial community composition and assembly along a natural sodicity/salinity gradient in surface and subsurface soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 157, 103731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.J.; Konopka, A.E.; Fredrickson, J.K. Stochastic and deterministic assembly processes in subsurface microbial communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putman, L.I.; Sabuda, M.C.; Brazelton, W.J.; Kubo, M.D.; Hoehler, T.M.; McCollom, T.M.; Cardace, D.; Schrenk, M.O. Microbial Communities in a Serpentinizing Aquifer Are Assembled through Strong Concurrent Dispersal Limitation and Selection. Msystems 2021, 6, e0030021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.J.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.Y.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Nan, J.; Xu, D.L.; Mo, L.; Zheng, Y.X.; Chao, L.M.; Qu, H.T.; Guo, Y.Q.; Li, F.S.; Bao, Y.Y. Response differences between soil fungal and bacterial communities under opencast coal mining disturbance conditions. Catena 2020, 194, 104779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bay, S.K.; McGeoch, M.A.; Gillor, O.; Wieler, N.; Palmer, D.J.; Baker, D.J.; Chown, S.L.; Greening, C. Soil Bacterial Communities Exhibit Strong Biogeographic Patterns at Fine Taxonomic Resolution. Msystems 2020, 5, e00540-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, P.F.; Huang, S.H.; Li, Z.Y.; Gong, H.Z.; Huang, W.J.; Zhao, Z.L.; Yu, Z.H. Environmental filtering dominates bacterioplankton community assembly in a highly urbanized estuarine ecosystem. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Xu, Y.Q.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.H. Environmental filtering drives distinct continental atlases of soil archaea between dryland and wetland agricultural ecosystems. Microbiome 2019, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.D.; Li, S.P.; Yang, X.; Zhou, J.Z.; Shu, W.S.; Jiang, L. Mechanisms of soil bacterial and fungal community assembly differ among and within islands. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1559–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.H.; Fang, J.; Song, B.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Hu, J.L.; Dong, K.; Takahashi, K.; Adams, J.M. Stochastic processes dominate soil arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal community assembly along an elevation gradient in central Japan. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, L.; Liang, C.; Chen, L.J.; Wang, H.T.; Xu, Q.S.; Jiang, Y.J.; Sun, B. Coupling Bacterial Community Assembly to Microbial Metabolism across Soil Profiles. Msystems 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.Y.; Chen, L.Y.; Zhang, D.Y.; Peng, Y.F.; Song, Y.T.; Kou, D.; Deng, Y.; Yang, Y.H. Stochastic processes regulate belowground community assembly in alpine grasslands on the Tibetan Plateau. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Guan, P.T.; Hao, C.; Yang, J.J.; Xie, Z.J.; Wu, D.H. Changes in assembly processes of soil microbial communities in forest-to-cropland conversion in Changbai Mountains, northeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.W.; Zhu, S.Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Yao, P.; Ge, T.T.; Zhang, X.H. Spatiotemporal dynamics of the archaeal community in coastal sediments: Assembly process and co-occurrence relationship. ISME J. 2020, 14, 1463–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, R.J.; Zeng, J.; Zhao, D.Y.; Wang, S.R.; Wu, Q.L.L. Decreased spatial variation and deterministic processes of bacterial community assembly in the rhizosphere of Phragmites australis across the Middle-Lower Yangtze plain. Mol. Ecol. 2022, 31, 1180–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.L.; Karwautz, C.; Andrei, S.; Klingl, A.; Pernthaler, J.; Lueders, T. A novel Methylomirabilota methanotroph potentially couples methane oxidation to iodate reduction. Mlife 2022, 1, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Goberna, M.; Liu, Y.G.; Cui, M.; Yang, H.S.; Sun, Q.X.; Insam, H.; Zhou, J.X. Competition and habitat filtering jointly explain phylogenetic structure of soil bacterial communities across elevational gradients. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 2386–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, T.; Chan, Y.K.; Lacap, D.C.; Lau, M.C.Y.; McKay, C.P.; Pointing, S.B. Stochastic and deterministic processes interact in the assembly of desert microbial communities on a global scale. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1406–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.Q.; Qi, Y.J.; Chen, D.; Liu, J.G.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.J.; Liu, X.L.; Li, W.W.; Mao, Z.C. Land use types and soil pH co-mediate bacterial community assembly processes: Application of the neutral community model and null model to determine stochastic and deterministic processes in a subtropical basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 175, 113561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.B.; Lü, X.T.; Yao, J.; Wang, Z.W.; Deng, Y.; Cheng, W.X.; Zhou, J.Z.; Han, X.G. Habitat-specific patterns and drivers of bacterial β-diversity in China’s drylands. ISME J. 2017, 11, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Bai, M.; Chen, Y.; Guo, J.; Chen, L. Environmental Effects on Bacterial Community Assembly in Arid and Semi-Arid Grasslands. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1934. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081934
Chen S, Zhang Y, Ma J, Bai M, Chen Y, Guo J, Chen L. Environmental Effects on Bacterial Community Assembly in Arid and Semi-Arid Grasslands. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1934. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081934
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shenggang, Yaqi Zhang, Jun Ma, Mingyue Bai, Yinglong Chen, Jianbin Guo, and Lin Chen. 2025. "Environmental Effects on Bacterial Community Assembly in Arid and Semi-Arid Grasslands" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1934. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081934
APA StyleChen, S., Zhang, Y., Ma, J., Bai, M., Chen, Y., Guo, J., & Chen, L. (2025). Environmental Effects on Bacterial Community Assembly in Arid and Semi-Arid Grasslands. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1934. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081934






