Blood Microbiome Analysis Reveals Biomarkers of Treatment Response in Drug-Naïve Patients with First-Episode Psychosis: A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Sample and Treatment
2.2. Clinical Measurements
| Patient Number | AGE | PANSS | BMI c | Antipsychotics Treatment | Hospitalization | Remission f | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (t0) a | (t1) b | (t0) | (t1) | At t0 (days e) | t0 to t1 | ||||
| 1 | 31 | 68 | 46 | 29.36 | 28.73 | risperidone | YES | YES | |
| 2 | 28 | 116 | 76 | 24.48 | 28.40 | risperidone | YES | NO | |
| 3 | 34 | 114 | 73 | 18.42 | 18.77 | olanzapine, haloperidol | YES | NO | |
| 4 | 21 | 93 | 67 | 21.20 | 23.60 | risperidone (2) | risperidone | YES | NO |
| 5 | 23 | 76 | 54 | 20.70 | 22.00 | risperidone | YES | NO | |
| 6 | 24 | 74 | 38 | 25.50 | 27.50 | olanzapine, amisulpride | YES | YES | |
| 7 | 28 | 75 | 41 | 25.30 | 26.50 | aripiprazole | YES | YES | |
| 8 | 20 | 87 | 59 | 23.12 | 25.76 | olanzapine (3) | olanzapine | YES | NO |
| 9 | 28 | 81 | 52 | 24.81 | 25.46 | olanzapine (10) | olanzapine | YES | NO |
| 10 | 20 | 79 | 45 | 28.40 | NA d | olanzapine, amisulpride, aripiprazole | YES | NO | |
| 11 | 31 | 136 | 36 | 23.59 | 24.62 | risperidone | YES | YES | |
| 12 | 21 | 124 | 40 | 30.10 | 30.10 | haloperidol | YES | NO | |
| 13 | 39 | 161 | 53 | 22.40 | 21.77 | haloperidol (1) | risperidone | YES | NO |
| 14 | 25 | 180 | 103 | 31.80 | 40.00 | risperidone, quietapine | YES | NO | |
| 15 | 35 | 90 | 35 | 23.08 | 23.66 | haloperidol (3) | olanzapine, haloperidol | YES | YES |
| 16 | 22 | 110 | 63 | 23.78 | 23.78 | haloperidol (2) | olanzapine, haloperidol | YES | NO |
| 17 | 21 | 113 | 55 | 20.50 | 20.58 | aripiprazole, haloperidol | YES | YES | |
| 18 | 20 | 75 | 43 | 25.24 | 27.45 | risperidone (3) | risperidone, escitalopram | NO | YES |
| 19 | 24 | 98 | 62 | 20.56 | NA | olanzapine | YES | NO | |
| 20 | 24 | 89 | 55 | 27.50 | 27.60 | aripiprazole (13) | aripiprazole | NO | YES |
| Mean | 25.95 | 101.95 | 54.80 | 24.49 | 25.90 | 4.50 | |||
| SD | 5.61 | 30.27 | 16.47 | 3.54 | 4.65 | 4.44 | |||
2.3. Cytokine Measurements
2.4. Nucleic Acid Extraction
2.5. 16s rRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing
2.6. Quality Control and Taxonomic Assignment
2.7. Measurement of Microbiome Diversity and Differential Taxa Abundance
2.8. Functional Analysis
2.9. Quantification of Bacterial Load in DNA Samples
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics and Classification of the Study Sample
| Descriptive Statistics | Remitters (R+) | Non-Remitters (R−) | p-Value (R+ vs. R−) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| t0 | ||||
| AGE | Median (IQR) | 26 (7.75) | 23.5 (7) | 0.510 a |
| PANSS | Mean (SD) | 90 (23.4) | 109.91 (32.57) | 0.120 b |
| BMI | Mean (SD) | 25.01 (2.71) | 24.15 (4.08) | 0.580 b |
| t1 | ||||
| PANSS | Mean (SD) | 43.63 (7.89) | 62.25 (16.65) | 0.003 b |
| BMI | Mean (SD) | 25.83 (2.70) | 25.96 (5.92) | 0.950 b |
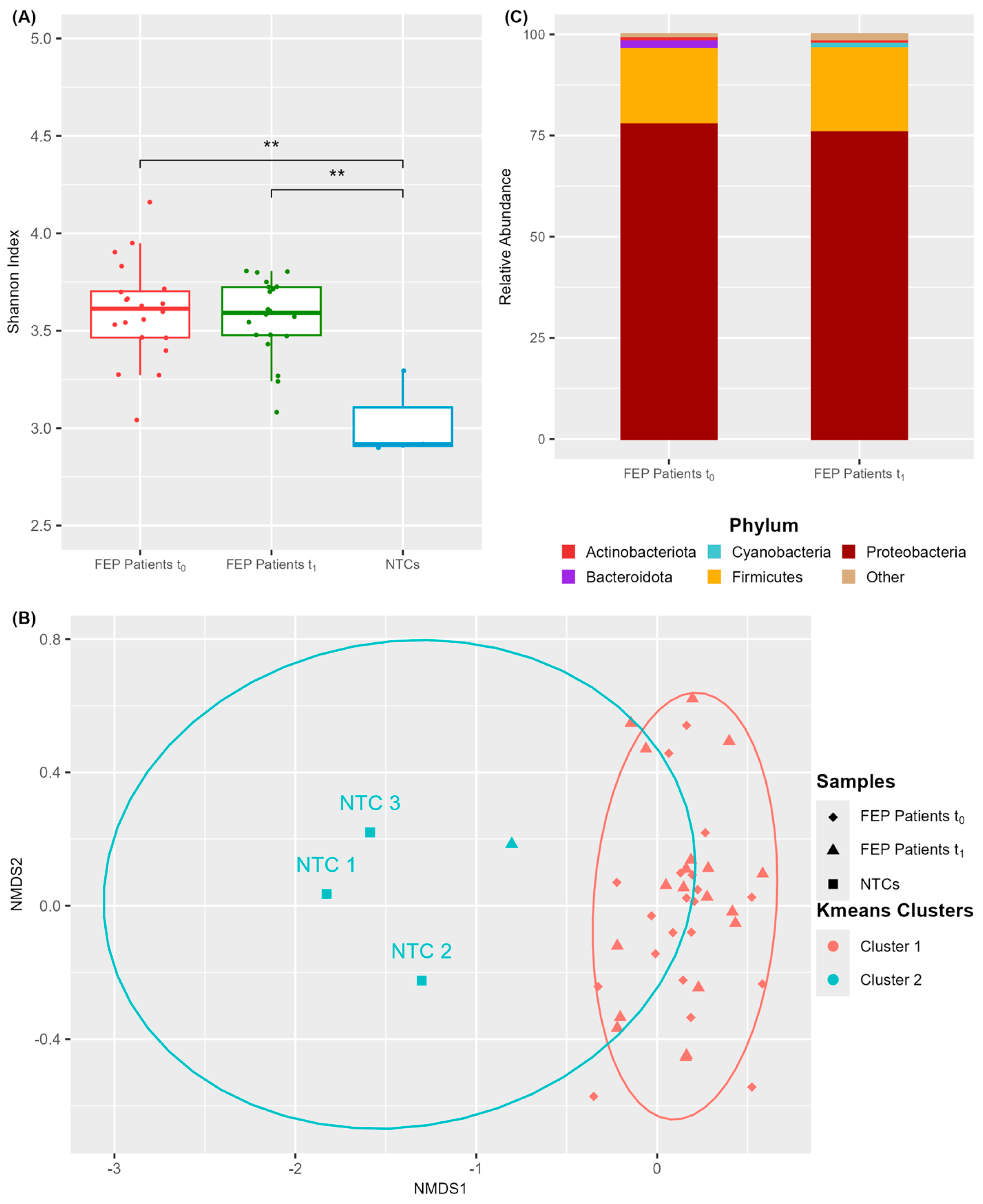
3.2. A Discrete Microbial Community Inhabits the Blood of FEP Patients
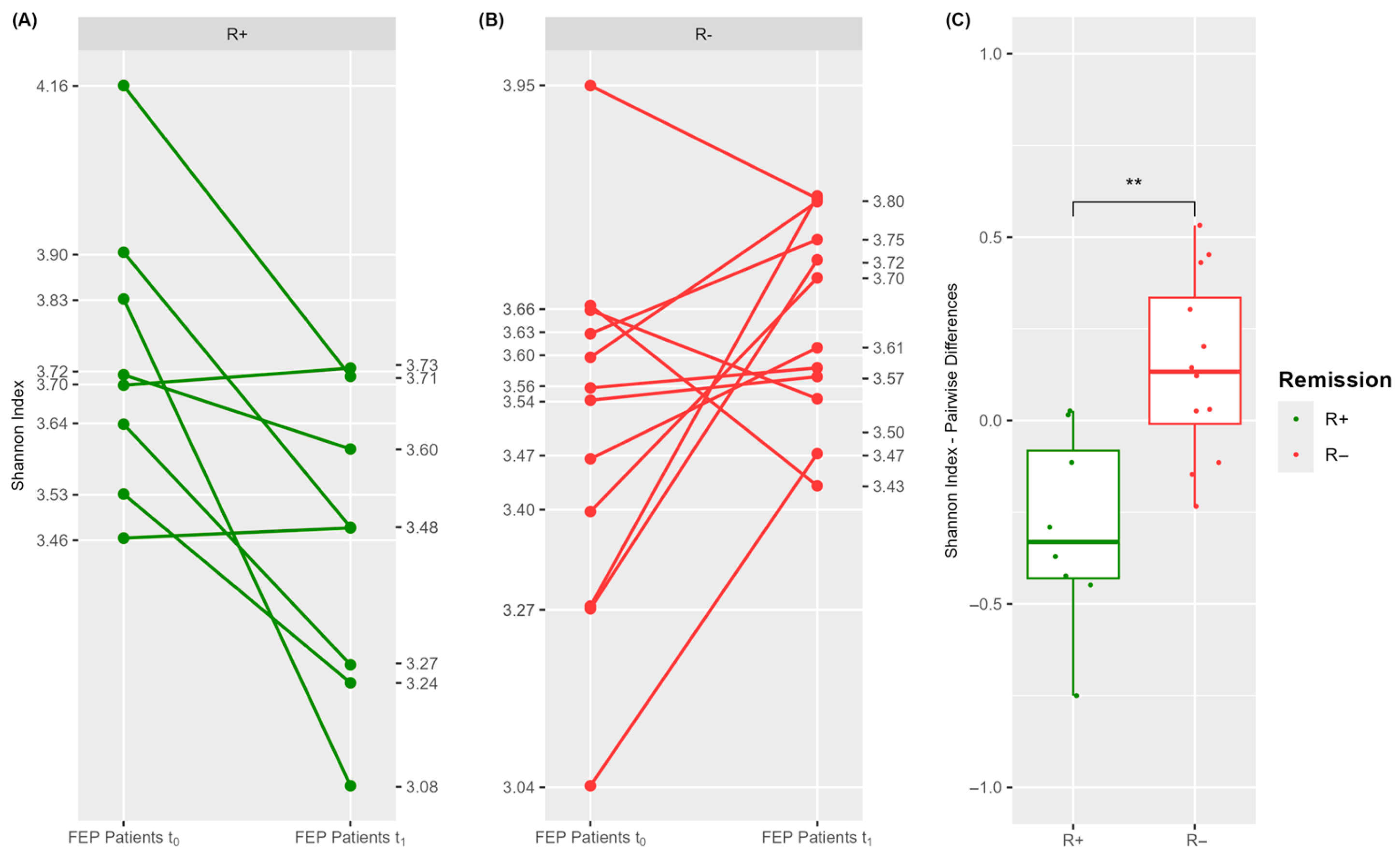
3.3. The Blood Microbiome Composition of FEP Patients Is Related to Treatment Outcome
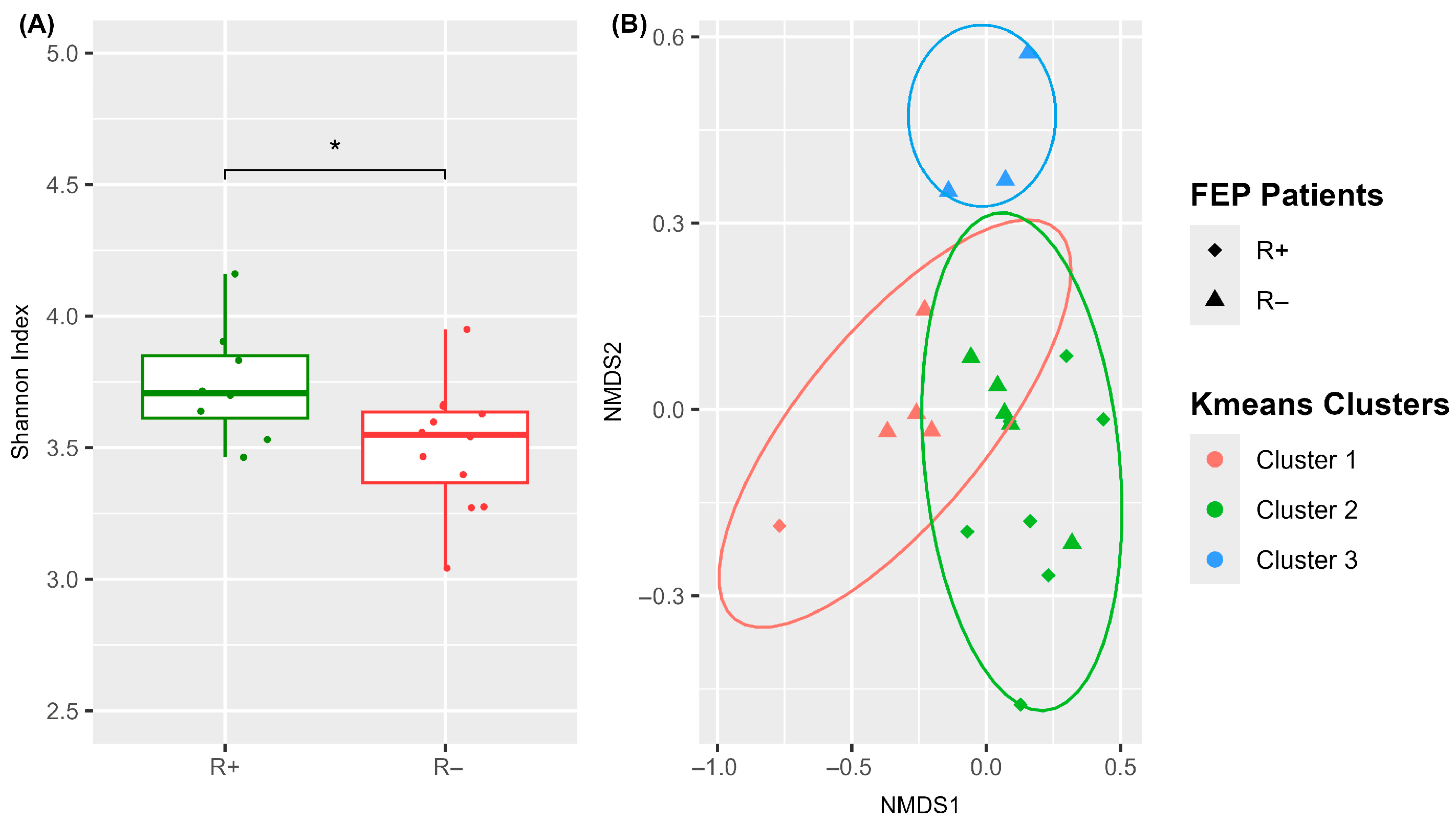
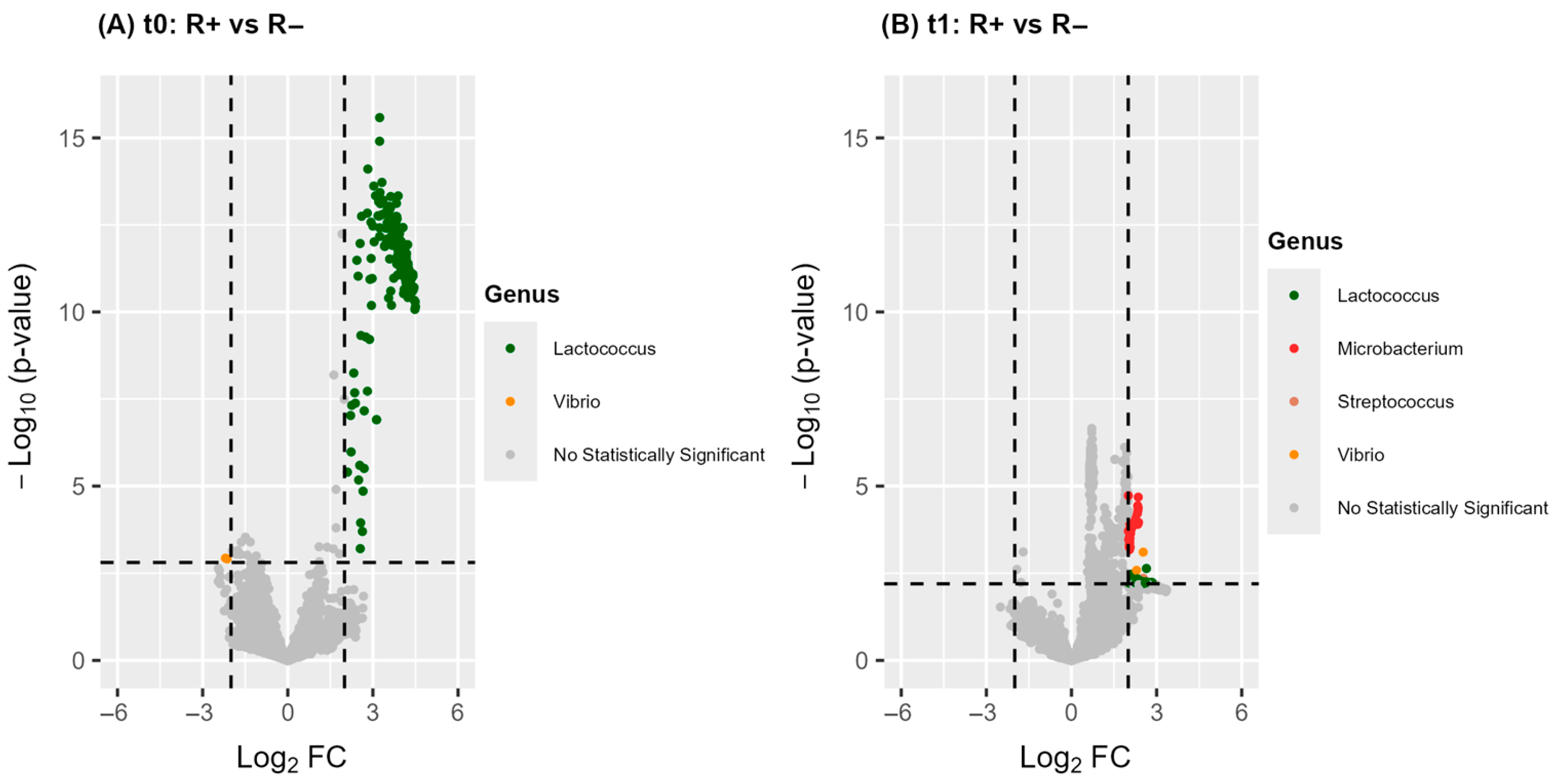
3.3.1. A Significantly Distinct Blood Microbiome Structure Characterizes R+ Versus R− at Baseline
| Phylum | Genus | ASV | log2FC a | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t0 b: R+ c vs. R− d | t1 e: R+ vs. R− | R+: t1 vs. t0 | R−: t1 vs. t0 | |||
| Proteobacteria | Acinetobacter | ASV 59 | −2.1 | −2.4 | ||
| ASV 62 | 3.0 | |||||
| ASV 106 | −1.7 | −1.7 | ||||
| Aeromonas | ASV 77 | −2.5 | ||||
| Aliidiomarina | ASV 57 | 2.8 | ||||
| Caulobacter | ASV 30 | −2.9 | ||||
| Enhydrobacter | ASV 50 | 2.5 | ||||
| Escherichia-Shigella | ASV 44 | 2.5 | 1.9 | |||
| Methylobacterium-Methylorubrum | ASV 45 | 2.2 | ||||
| ASV 68 | −1.8 | |||||
| ASV 81 | −2.3 | |||||
| Morganella | ASV 89 | 2.1 | ||||
| Paracoccus | ASV 94 | −1.9 | 2.6 | |||
| Firmicutes | Anoxybacillus | ASV 87 | −1.7 | |||
| Bacillus | ASV 39 | 2.4 | ||||
| Lactococcus | ASV 35 | 4.5 | ||||
| ASV 69 | −2.7 | |||||
| Staphylococcus | ASV 46 | −1.9 | −1.8 | |||
| ASV 105 | −1.5 | −2.2 | ||||
| Streptococcus | ASV 58 | −2.9 | −1.9 | |||
| Bacteroidota | Cloacibacterium | ASV 47 | −1.5 | |||
| ASV 84 | −1.7 | |||||
3.3.2. Antipsychotics Differentially Impact the Blood Microbiome Structure in R+ Versus R− FEP Patients
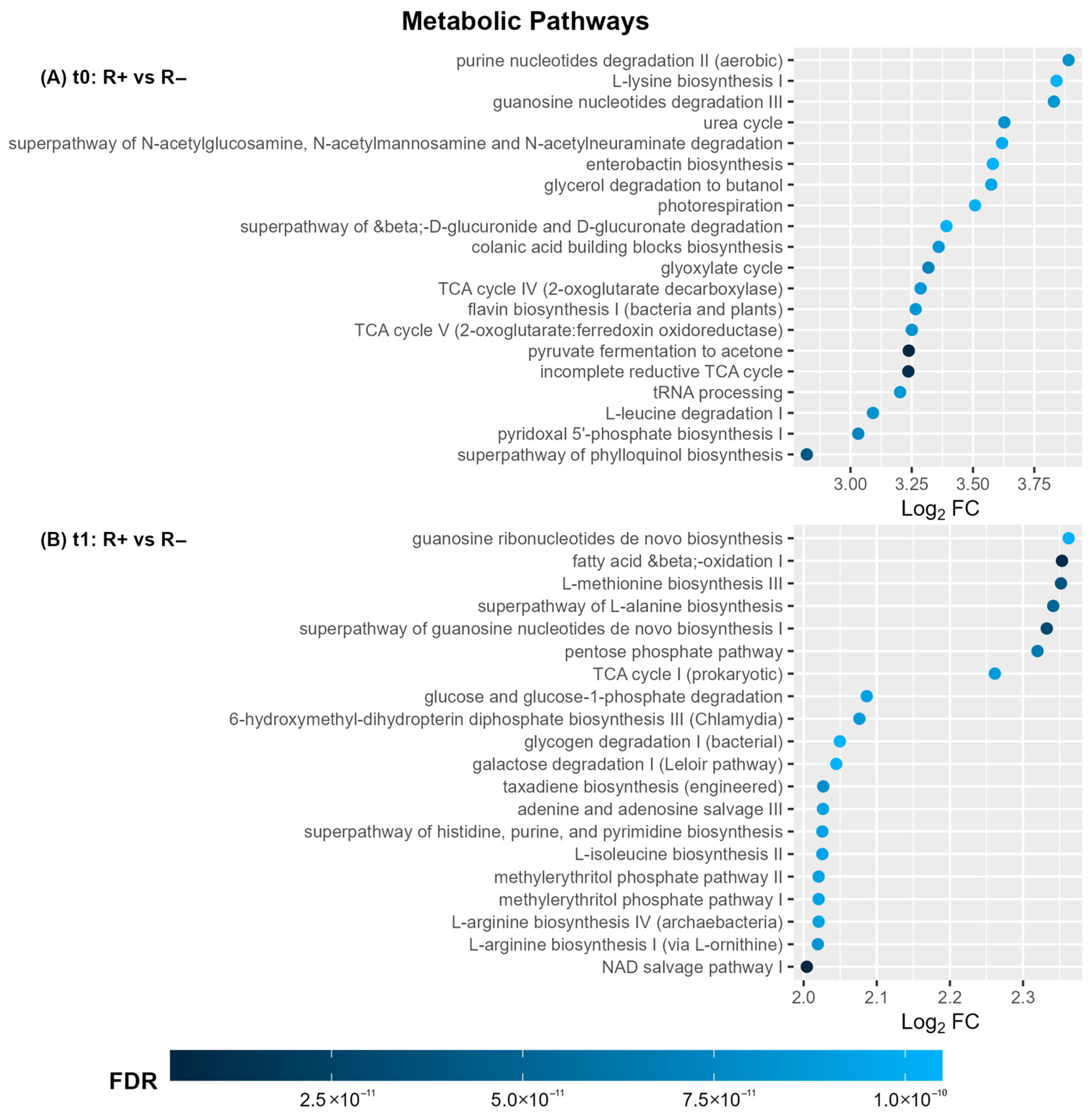
3.4. Functional Diversity of Blood Microbiome in R+ Versus R− Patients
3.5. Integration of Blood Microbiome and Peripheral Cytokine Data
| Time Point | Genus | ASV | Cytokine | Pearson Ro | p-Value | FDR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t0 a | Cloacibacterium | ASV 47 | TNF-α | 0.60 | 0.038 | 0.418 |
| Escherichia-Shigella | ASV 44 | IL10 | −0.58 | 0.038 | 0.514 | |
| Methylobacterium-Methylorubrum | ASV 45 | TNF-α | −0.63 | 0.028 | 0.418 | |
| Methylobacterium-Methylorubrum | ASV 68 | IL10 | −0.56 | 0.047 | 0.514 | |
| Paracoccus | ASV 94 | IL1β | 0.57 | 0.042 | 0.928 | |
| t1 b | Acinetobacter | ASV 106 | IL10 | 0.80 | 0.001 | 0.023 |
| Escherichia-Shigella | ASV 44 | IL1β | −0.60 | 0.030 | 0.515 | |
| Methylobacterium-Methylorubrum | ASV 81 | TNF-α | −0.58 | 0.036 | 0.558 | |
| Methylobacterium-Methylorubrum | ASV 68 | IL10 | 0.67 | 0.012 | 0.133 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASV | Amplicon Sequence Variant |
| BCAA | Branched-Chain Amino Acid |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| FC | Fold Change |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| FEP | First-Episode Psychosis |
| NMDS | Non-metric Multidimensional Scaling |
| NTC | No Template Control |
| PANSS | Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative Realt-Time PCR |
| SCZ | Schizophrenia |
References
- McCutcheon, R.A.; Reis Marques, T.; Howes, O.D. Schizophrenia-An Overview. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhar, S.; Johnstone, M.; McKenna, P.J. Schizophrenia. Lancet 2022, 399, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasrallah, H.A. The Daunting Challenge of Schizophrenia: Hundreds of Biotypes and Dozens of Theories. Curr. Psychiatr. 2018, 7, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Martinuzzi, E.; Barbosa, S.; Daoudlarian, D.; Bel Haj Ali, W.; Gilet, C.; Fillatre, L.; Khalfallah, O.; Troudet, R.; Jamain, S.; Fond, G.; et al. Stratification and Prediction of Remission in First-Episode Psychosis Patients: The OPTiMiSE Cohort Study. Transl. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, C.L.; Peters, B.J.; Foster, J.A. Microbes and Mental Health: Can the Microbiome Help Explain Clinical Heterogeneity in Psychiatry? Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2020, 58, 100849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, V.L.; Smith, M.R.B.; Hall, L.J.; Cleare, A.J.; Stone, J.M.; Young, A.H. Perturbations in Gut Microbiota Composition in Psychiatric Disorders. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.; Ju, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Q.; Guo, R.; Ma, Q.; Sun, Q.; Fan, Y.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Z.; et al. Metagenome-Wide Association of Gut Microbiome Features for Schizophrenia. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeligowski, T.; Yun, A.L.; Lennox, B.R.; Burnet, P.W.J. The Gut Microbiome and Schizophrenia: The Current State of the Field and Clinical Applications. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, A.J.; Davis, J.A.; Dawson, S.L.; Loughman, A.; Collier, F.; O’Hely, M.; Simpson, C.A.; Green, J.; Marx, W.; Hair, C.; et al. A Systematic Review of Gut Microbiota Composition in Observational Studies of Major Depressive Disorder, Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 1920–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, E.; Maukonen, J.; Hyytiäinen, T.; Kieseppä, T.; Orešič, M.; Sabunciyan, S.; Mantere, O.; Saarela, M.; Yolken, R.; Suvisaari, J. Analysis of Microbiota in First Episode Psychosis Identifies Preliminary Associations with Symptom Severity and Treatment Response. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 192, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuncio-Mora, L.; Lanzagorta, N.; Nicolini, H.; Sarmiento, E.; Ortiz, G.; Sosa, F.; Genis-Mendoza, A.D. The Role of the Microbiome in First Episode of Psychosis. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, P.; Prandovszky, E.; Honkanen, J.K.; Chen, O.; Yolken, R.; Suvisaari, J. Dysregulation of Microbiota in Patients With First-Episode Psychosis Is Associated With Symptom Severity and Treatment Response. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 95, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchia, M.; Fontana, A.; Panebianco, C.; Paribello, P.; Arzedi, C.; Cossu, E.; Garzilli, M.; Montis, M.A.; Mura, A.; Pisanu, C.; et al. Involvement of Gut Microbiota in Schizophrenia and Treatment Resistance to Antipsychotics. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minichino, A.; Preston, T.; Fanshawe, J.B.; Fusar-Poli, P.; McGuire, P.; Burnet, P.W.J.; Lennox, B.R. Psycho-Pharmacomicrobiomics: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biol. Psychiatry 2024, 95, 611–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Kumar, B.U.; Hei, G.; Lv, L.; Huang, X.-F.; Fan, X.; et al. Changes in Metabolism and Microbiota after 24-Week Risperidone Treatment in Drug Naïve, Normal Weight Patients with First Episode Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 201, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cussotto, S.; Walsh, J.; Golubeva, A.V.; Zhdanov, A.V.; Strain, C.R.; Fouhy, F.; Stanton, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Hyland, N.P.; Clarke, G.; et al. The Gut Microbiome Influences the Bioavailability of Olanzapine in Rats. eBioMedicine 2021, 66, 103307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klünemann, M.; Andrejev, S.; Blasche, S.; Mateus, A.; Phapale, P.; Devendran, S.; Vappiani, J.; Simon, B.; Scott, T.A.; Kafkia, E.; et al. Bioaccumulation of Therapeutic Drugs by Human Gut Bacteria. Nature 2021, 597, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsamakis, K.; Galinaki, S.; Alevyzakis, E.; Hortis, I.; Tsiptsios, D.; Kollintza, E.; Kympouropoulos, S.; Triantafyllou, K.; Smyrnis, N.; Rizos, E. Gut Microbiome: A Brief Review on Its Role in Schizophrenia and First Episode of Psychosis. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misera, A.; Łoniewski, I.; Palma, J.; Kulaszyńska, M.; Czarnecka, W.; Kaczmarczyk, M.; Liśkiewicz, P.; Samochowiec, J.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K. Clinical Significance of Microbiota Changes under the Influence of Psychotropic Drugs. An Updated Narrative Review. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1125022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lizano, P.; Lutz, O.; Xu, Y.; Rubin, L.H.; Paskowitz, L.; Lee, A.M.; Eum, S.; Keedy, S.K.; Hill, S.K.; Reilly, J.L.; et al. Multivariate Relationships between Peripheral Inflammatory Marker Subtypes and Cognitive and Brain Structural Measures in Psychosis. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 3430–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fond, G.; Lançon, C.; Korchia, T.; Auquier, P.; Boyer, L. The Role of Inflammation in the Treatment of Schizophrenia. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 11, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Baek, S.-H.; Kim, J.-W.; Ryu, S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kim, J.-M.; Chung, Y.-C.; Kim, S.-W. Inflammatory Markers of Symptomatic Remission at 6 Months in Patients with First-Episode Schizophrenia. Schizophrenia 2023, 9, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermakov, E.A.; Melamud, M.M.; Buneva, V.N.; Ivanova, S.A. Immune System Abnormalities in Schizophrenia: An Integrative View and Translational Perspectives. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 880568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzimanolis, A.; Foteli, S.; Xenaki, L.-A.; Selakovic, M.; Dimitrakopoulos, S.; Vlachos, I.; Kosteletos, I.; Soldatos, R.-F.; Gazouli, M.; Chatzipanagiotou, S.; et al. Elevated Serum Kynurenic Acid in Individuals with First-Episode Psychosis and Insufficient Response to Antipsychotics. Schizophrenia 2024, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, R.; Christensen, R.H.B.; Pedersen, E.M.J.; Nordentoft, M.; Hjorthøj, C.; Köhler-Forsberg, O.; Benros, M.E. Efficacy and Safety of Anti-Inflammatory Agents in Treatment of Psychotic Disorders—A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 90, 364–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severance, E.G.; Gressitt, K.L.; Stallings, C.R.; Origoni, A.E.; Khushalani, S.; Leweke, F.M.; Dickerson, F.B.; Yolken, R.H. Discordant Patterns of Bacterial Translocation Markers and Implications for Innate Immune Imbalances in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2013, 148, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, T.; He, L.; Fu, J.-Y.; Deng, H.-X.; Xue, X.-L.; Chen, B.-T. Bacterial Translocation Associates With Aggression in Schizophrenia Inpatients. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 704069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, S.B.; Sheikh, M.A.; Akkouh, I.A.; Szabo, A.; O’Connell, K.S.; Lekva, T.; Engh, J.A.; Agartz, I.; Elvsåshagen, T.; Ormerod, M.B.E.G.; et al. Elevated Systemic Levels of Markers Reflecting Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction and Inflammasome Activation Are Correlated in Severe Mental Illness. Schizophr. Bull. 2023, 49, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potgieter, M.; Bester, J.; Kell, D.B.; Pretorius, E. The Dormant Blood Microbiome in Chronic, Inflammatory Diseases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 567–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikkari, S.; McLaughlin, I.J.; Bi, W.; Dodge, D.E.; Relman, D.A. Does Blood of Healthy Subjects Contain Bacterial Ribosomal DNA? J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 1956–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Païssé, S.; Valle, C.; Servant, F.; Courtney, M.; Burcelin, R.; Amar, J.; Lelouvier, B. Comprehensive Description of Blood Microbiome from Healthy Donors Assessed by 16S Targeted Metagenomic Sequencing. Transfusion 2016, 56, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.S.; Tan, S.P.; Wong, D.M.K.; Koo, W.L.Y.; Wong, S.H.; Tan, N.S. The Blood Microbiome and Health: Current Evidence, Controversies, and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, B.; Snow, M.; Herrman, E.; Ray, N.; Mansukhani, K.; Patel, K.A.; Said-Al-Naief, N.; Maier, T.; Machida, C.A. Interconnections Between the Oral and Gut Microbiomes: Reversal of Microbial Dysbiosis and the Balance Between Systemic Health and Disease. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciarra, F.; Franceschini, E.; Campolo, F.; Venneri, M.A. The Diagnostic Potential of the Human Blood Microbiome: Are We Dreaming or Awake? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Vincenzo, F.; Del Gaudio, A.; Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.R.; Scaldaferri, F. Gut Microbiota, Intestinal Permeability, and Systemic Inflammation: A Narrative Review. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olde Loohuis, L.M.; Mangul, S.; Ori, A.P.S.; Jospin, G.; Koslicki, D.; Yang, H.T.; Wu, T.; Boks, M.P.; Lomen-Hoerth, C.; Wiedau-Pazos, M.; et al. Transcriptome Analysis in Whole Blood Reveals Increased Microbial Diversity in Schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ma, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, B.; He, X.; Yang, J.; Yan, B.; Gao, F.; Qian, L.; et al. Multi-Omics Analysis Reveals Aberrant Gut-Metabolome-Immune Network in Schizophrenia. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 812293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jauhar, S.; Veronese, M.; Nour, M.M.; Rogdaki, M.; Hathway, P.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Stone, J.; Egerton, A.; McGuire, P.; Kapur, S.; et al. Determinants of Treatment Response in First-Episode Psychosis: An 18F-DOPA PET Study. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1502–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xenaki, L.-A.; Kollias, C.T.; Stefanatou, P.; Ralli, I.; Soldatos, R.-F.; Dimitrakopoulos, S.; Hatzimanolis, A.; Triantafyllou, T.-F.; Kosteletos, I.; Vlachos, I.I.; et al. Organization Framework and Preliminary Findings from the Athens First-Episode Psychosis Research Study. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2020, 14, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders: Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Kay, S.R.; Fiszbein, A.; Opler, L.A. The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 1987, 13, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, N.C.; Carpenter, W.T.; Kane, J.M.; Lasser, R.A.; Marder, S.R.; Weinberger, D.R. Remission in Schizophrenia: Proposed Criteria and Rationale for Consensus. Am. J. Psychiatry 2005, 162, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.; Krueger, F.; Segonds-Pichon, A.; Biggins, L.; Krueger, C.; Wingett, S. FastQC; Illumina: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schliep, K.; Potts, A.J.; Morrison, D.A.; Grimm, G.W. Intertwining Phylogenetic Trees and Networks. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2017, 8, 1212–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, N.M.; Proctor, D.M.; Holmes, S.P.; Relman, D.A.; Callahan, B.J. Simple Statistical Identification and Removal of Contaminant Sequences in Marker-Gene and Metagenomics Data. Microbiome 2018, 6, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleine Bardenhorst, S.; Vital, M.; Karch, A.; Rübsamen, N. Richness Estimation in Microbiome Data Obtained from Denoising Pipelines. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricotta, C.; Podani, J. On Some Properties of the Bray-Curtis Dissimilarity and Their Ecological Meaning. Ecol. Complex. 2017, 31, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchin, P.R. An Evaluation of the Relative Robustness of Techniques for Ecological Ordination. Vegetatio 1987, 69, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseeuw, P.J. Silhouettes: A Graphical Aid to the Interpretation and Validation of Cluster Analysis. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 1987, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; Oshlack, A. A Scaling Normalization Method for Differential Expression Analysis of RNA-Seq Data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Peddada, S. Das Analysis of Compositions of Microbiomes with Bias Correction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Peddada, S. Das Analysis of Microbial Compositions: A Review of Normalization and Differential Abundance Analysis. npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2020, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for Prediction of Metagenome Functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, R.J.; Milillo, M.; Prestwood, J.; Quintero, R.; Zurawski, D.V.; Kwak, Y.I.; Waterman, P.E.; Lesho, E.P.; Mc Gann, P. Detection of Bacterial 16S RRNA and Identification of Four Clinically Important Bacteria by Real-Time PCR. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhofer, R.; Minich, J.J.; Marotz, C.; Cooper, A.; Knight, R.; Weyrich, L.S. Contamination in Low Microbial Biomass Microbiome Studies: Issues and Recommendations. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.; Xu, L.; Cui, G.; Sun, L.; Hu, X.; Yang, X.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, T.; et al. Salivary Microbiome Profiling Reveals a Dysbiotic Schizophrenia-Associated Microbiota. npj Schizophr. 2021, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.C.S.; Ko, K.K.K.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Loh, M.; SG10K_Health Consortium; Chia, M.; Nagarajan, N. No Evidence for a Common Blood Microbiome Based on a Population Study of 9,770 Healthy Humans. Nat. Microbiol. 2023, 8, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, F.; Daniel, C.; Thomas, M.; Singer, E.; Guilbaud, A.; Tessier, F.J.; Revol-Junelles, A.-M.; Borges, F.; Foligné, B. Occurrence and Dynamism of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Distinct Ecological Niches: A Multifaceted Functional Health Perspective. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Faas, M.M.; de Vos, P. Disease Managing Capacities and Mechanisms of Host Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1365–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, V.L.; da Silva, T.F.; de Jesus, L.C.L.; Tapia-Costa, A.P.; Drumond, M.M.; Azevedo, V.; Mancha-Agresti, P. Lactic Acid Bacteria as Delivery Vehicle for Therapeutics Applications. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2183, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifa, A.; Ibrahim, H.-I.M.; Sheikh, A.; Khalil, H.E. Attenuation of Immunogenicity in MOG-Induced Oligodendrocytes by the Probiotic Bacterium Lactococcus sp. PO3. Medicina 2023, 59, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krzyściak, W.; Karcz, P.; Bystrowska, B.; Szwajca, M.; Bryll, A.; Śmierciak, N.; Ligęzka, A.; Turek, A.; Kozicz, T.; Skalniak, A.E.; et al. The Association of the Oral Microbiota with the Effects of Acid Stress Induced by an Increase of Brain Lactate in Schizophrenia Patients. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Ferreiro, V.; García-Fernández, L.; Romero, C.; De la Fuente, M.; Diaz-del Cerro, E.; Scala, M.; González-Soltero, R.; Álvarez-Mon, M.A.; Peñuelas-Calvo, I.; Rodriguez-Jimenez, R. Impact of Probiotic Treatment on Clinical Symptom Reduction in Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2025, 182, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Foulon, A.; El Hage, W.; Dufour-Rainfray, D.; Denis, F. Is There a Link between Oropharyngeal Microbiome and Schizophrenia? A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y. Regulation of Neurotransmitters by the Gut Microbiota and Effects on Cognition in Neurological Disorders. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäki-Marttunen, V.; Andreassen, O.A.; Espeseth, T. The Role of Norepinephrine in the Pathophysiology of Schizophrenia. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 118, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, P.K.; Gaur, S.; Roy, R.G.; Samkaria, A.; Ingole, R.; Goel, A. Schizophrenia, Bipolar and Major Depressive Disorders: Overview of Clinical Features, Neurotransmitter Alterations, Pharmacological Interventions, and Impact of Oxidative Stress in the Disease Process. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 2784–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjerkenstedt, L.; Edman, G.; Hagenfeldt, L.; Sedvall, G.; Wiesel, F.A. Plasma Amino Acids in Relation to Cerebrospinal Fluid Monoamine Metabolites in Schizophrenic Patients and Healthy Controls. Br. J. Psychiatry 1985, 147, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reveley, M.A.; De Belleroche, J.; Recordati, A.; Hirsch, S.R. Increased CSF Amino Acids and Ventricular Enlargement in Schizophrenia: A Preliminary Study. Biol. Psychiatry 1987, 22, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorella, A.; Monteleone, P.; Fabrazzo, M.; Viggiano, A.; De Luca, B.; Maj, M. Plasma Concentrations of Amino Acids in Chronic Schizophrenics Treated with Clozapine. Neuropsychobiology 2001, 44, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernstrom, J.D. Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Brain Function. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 1539S–1546S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Marinelli, L.; Blottière, H.M.; Larraufie, P.; Lapaque, N. SCFA: Mechanisms and Functional Importance in the Gut. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, S.; Shin, Y.; Han, S.; Kwon, J.; Choi, T.G.; Kang, I.; Kim, S.S. The Gut-Brain Axis in Schizophrenia: The Implications of the Gut Microbiome and SCFA Production. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothman, D.L.; De Feyter, H.M.; de Graaf, R.A.; Mason, G.F.; Behar, K.L. 13C MRS Studies of Neuroenergetics and Neurotransmitter Cycling in Humans. NMR Biomed. 2011, 24, 943–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCutcheon, R.A.; Krystal, J.H.; Howes, O.D. Dopamine and Glutamate in Schizophrenia: Biology, Symptoms and Treatment. World Psychiatry 2020, 19, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möhler, H. The GABA System in Anxiety and Depression and Its Therapeutic Potential. Neuropharmacology 2012, 62, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein-Petersen, A.W.; Köhler-Forsberg, O.; Benros, M.E. Infections, Antibiotic Treatment and the Microbiome in Relation to Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2021, 234, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essali, N.; Miller, B.J. Psychosis as an Adverse Effect of Antibiotics. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2020, 9, 100148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasik, J.; Yolken, R.H.; Bahn, S.; Dickerson, F.B. Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotic Supplementation in Schizophrenia Patients: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Biomark. Insights 2015, 10, BMI.S22007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, A.; Banafshe, H.R.; Mirhosseini, N.; Moradi, M.; Karimi, M.-A.; Mehrzad, F.; Bahmani, F.; Asemi, Z. Clinical and Metabolic Response to Vitamin D plus Probiotic in Schizophrenia Patients. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, Q.X.; Soh, A.Y.S.; Venkatanarayanan, N.; Ho, C.Y.X.; Lim, D.Y.; Yeo, W.-S. A Systematic Review of the Effect of Probiotic Supplementation on Schizophrenia Symptoms. Neuropsychobiology 2019, 78, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawidowski, B.; Górniak, A.; Podwalski, P.; Lebiecka, Z.; Misiak, B.; Samochowiec, J. The Role of Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Schizophrenia. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Chen, K.; Yu, J.; Feng, W.; Fu, W.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Chen, D. Relationship between TNF-α Levels and Psychiatric Symptoms in First-Episode Drug-Naïve Patients with Schizophrenia before and after Risperidone Treatment and in Chronic Patients. BMC Psychiatry 2021, 21, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şimşek, Ş.; Yıldırım, V.; Çim, A.; Kaya, S. Serum IL-4 and IL-10 Levels Correlate with the Symptoms of the Drug-Naive Adolescents with First Episode, Early Onset Schizophrenia. J. Child Adolesc. Psychopharmacol. 2016, 26, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reale, M.; Costantini, E.; Greig, N.H. Cytokine Imbalance in Schizophrenia. From Research to Clinic: Potential Implications for Treatment. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 536257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W. Host Innate Immune Responses to Acinetobacter Baumannii Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassols, J.; Serino, M.; Carreras-Badosa, G.; Burcelin, R.; Blasco-Baque, V.; Lopez-Bermejo, A.; Fernandez-Real, J.-M. Gestational Diabetes Is Associated with Changes in Placental Microbiota and Microbiome. Pediatr. Res. 2016, 80, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, D.; Kleinstein, S.E.; Hanson, B.; Hasturk, H.; Eveloff, R.; Freire, M.; Ramsey, M. Impaired Host Response and the Presence of Acinetobacter Baumannii in the Serum Microbiome of Type-II Diabetic Patients. iScience 2021, 24, 101941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iebba, V.; Guerrieri, F.; Di Gregorio, V.; Levrero, M.; Gagliardi, A.; Santangelo, F.; Sobolev, A.P.; Circi, S.; Giannelli, V.; Mannina, L.; et al. Combining Amplicon Sequencing and Metabolomics in Cirrhotic Patients Highlights Distinctive Microbiota Features Involved in Bacterial Translocation, Systemic Inflammation and Hepatic Encephalopathy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Guo, J.; Liu, R.; Zhang, F.; Wen, S.; Liu, Y.; Ren, W.; Zhang, X.; Shang, Y.; Gao, M.; et al. Predominance of Escherichia-Shigella in Gut Microbiome and Its Potential Correlation with Elevated Level of Plasma Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha in Patients with Tuberculous Meningitis. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0192622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rolig, A.S.; Mittge, E.K.; Ganz, J.; Troll, J.V.; Melancon, E.; Wiles, T.J.; Alligood, K.; Stephens, W.Z.; Eisen, J.S.; Guillemin, K. The Enteric Nervous System Promotes Intestinal Health by Constraining Microbiota Composition. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2000689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Yang, X.; Xu, S.; Wu, C.; Qin, N.; Chen, S.-D.; Xiao, Q. Detection of Microbial 16S RRNA Gene in the Blood of Patients With Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrasso, K.; Chac, D.; Debela, M.D.; Geigel, C.; Steenhaut, A.; Rivera Seda, A.; Dunmire, C.N.; Harris, J.B.; Larocque, R.C.; Midani, F.S.; et al. Impact of a Human Gut Microbe on Vibrio Cholerae Host Colonization through Biofilm Enhancement. eLife 2022, 11, e73010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbrini, M.; Scicchitano, D.; Candela, M.; Turroni, S.; Rampelli, S. Connect the Dots: Sketching out Microbiome Interactions through Networking Approaches. Microbiome Res. Rep. 2023, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shobeiri, P.; Kalantari, A.; Teixeira, A.L.; Rezaei, N. Shedding Light on Biological Sex Differences and Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis: A Comprehensive Review of Its Roles in Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Biol. Sex Differ. 2022, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-L.; Liu, Y.-W.; Wang, P.-N.; Lin, C.-Y.; Lan, T.-H. Gender Differences in Gut Microbiome Composition Between Schizophrenia Patients with Normal Body Weight and Central Obesity. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 836896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Pang, X.; Zhang, H.; Ji, P. The CGAS-STING Pathway in Bacterial Infection and Bacterial Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 814709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Aliyari, S.R.; Parvatiyar, K.; Wang, L.; Zhen, A.; Sun, W.; Han, X.; Zhang, A.; Kato, E.; Shi, H.; et al. STING Directly Interacts with PAR to Promote Apoptosis upon Acute Ionizing Radiation-Mediated DNA Damage. Cell Death Differ. 2025, 32, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, J.B.; Adams, R.I.; Román, C.M.B.; Brooks, B.; Coil, D.A.; Dahlhausen, K.; Ganz, H.H.; Hartmann, E.M.; Hsu, T.; Justice, N.B.; et al. Schrödinger’s Microbes: Tools for Distinguishing the Living from the Dead in Microbial Ecosystems. Microbiome 2017, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Logotheti, M.; Gkekas, T.; Agioutantis, P.C.; Hatzimanolis, A.; Foteli, S.; Mamma, D.; Stefanis, N.C.; Kolisis, F.N.; Loutrari, H. Blood Microbiome Analysis Reveals Biomarkers of Treatment Response in Drug-Naïve Patients with First-Episode Psychosis: A Pilot Study. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081935
Logotheti M, Gkekas T, Agioutantis PC, Hatzimanolis A, Foteli S, Mamma D, Stefanis NC, Kolisis FN, Loutrari H. Blood Microbiome Analysis Reveals Biomarkers of Treatment Response in Drug-Naïve Patients with First-Episode Psychosis: A Pilot Study. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081935
Chicago/Turabian StyleLogotheti, Marianthi, Thomas Gkekas, Panagiotis C. Agioutantis, Alex Hatzimanolis, Stefania Foteli, Diomi Mamma, Nikolaos C. Stefanis, Fragiskos N. Kolisis, and Heleni Loutrari. 2025. "Blood Microbiome Analysis Reveals Biomarkers of Treatment Response in Drug-Naïve Patients with First-Episode Psychosis: A Pilot Study" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081935
APA StyleLogotheti, M., Gkekas, T., Agioutantis, P. C., Hatzimanolis, A., Foteli, S., Mamma, D., Stefanis, N. C., Kolisis, F. N., & Loutrari, H. (2025). Blood Microbiome Analysis Reveals Biomarkers of Treatment Response in Drug-Naïve Patients with First-Episode Psychosis: A Pilot Study. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1935. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081935







