Genomic Characterization of Marine Staphylococcus shinii Strain SC-M1C: Potential Genetic Adaptations and Ecological Role
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Strain Isolation
2.2. DNA Extraction and Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.3. Reads Preprocessing and Assembly
2.4. Strain Typing and Phylogeny
2.5. Reference-Guided Scaffolding and SC-M1C Genome Annotation
3. Results
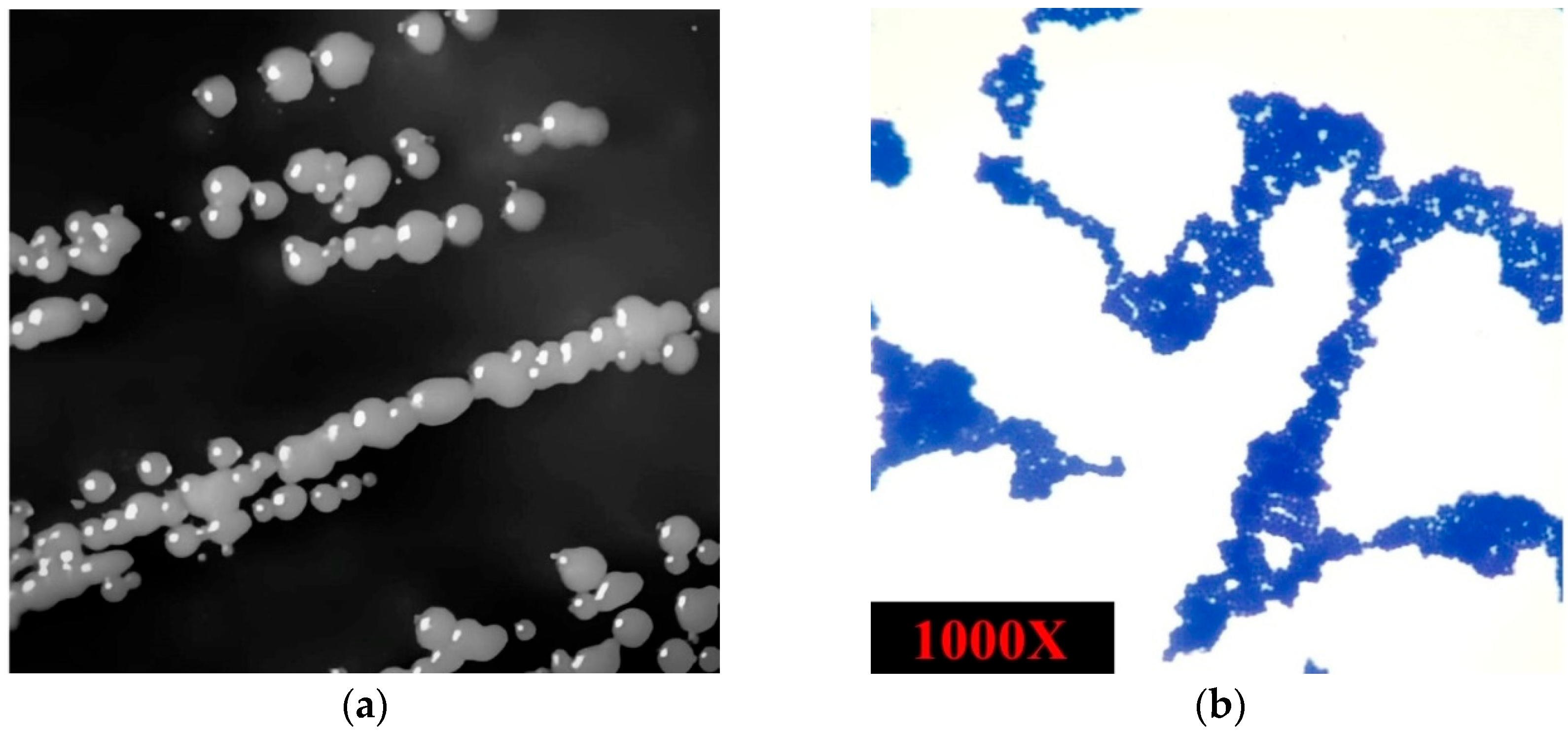
3.1. The Isolated Strain’s Phenotypic Characteristics
3.2. Genome Characteristics and Strain Typing of Isolate SC-M1C
3.3. S. shinii Strain SC-M1C Genome Annotation and Genome Mapping
3.4. Antimicrobial Resistance and Horizontal Gene Transfer
3.5. Reconstruction of S. shinii Strain SC-M1C Metabolic Pathways
3.5.1. Osmoregulation and Salt Tolerance
3.5.2. Nutrient Acquisition
3.5.3. Stress Response and Resistance
3.5.4. Aromatic Hydrocarbon Degradation
3.5.5. Two-Component Systems in S. shinii Strain SC-M1C
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibarbalz, F.M.; Henry, N.; Brandão, M.C.; Martini, S.; Busseni, G.; Byrne, H.; Coelho, L.P.; Endo, H.; Gasol, J.M.; Gregory, A.C.; et al. Global Trends in Marine Plankton Diversity across Kingdoms of Life. Cell 2019, 179, 1084–1097.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshino, T.; Doi, H.; Uramoto, G.I.; Wörmer, L.; Adhikari, R.R.; Xiao, N.; Morono, Y.; D’Hondt, S.; Hinrichs, K.U.; Inagaki, F. Global Diversity of Microbial Communities in Marine Sediment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 27587–27597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauritano, C.; Coppola, D. Biotechnological Applications of Products Released by Marine Microorganisms for Cold Adaptation Strategies: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids, Antioxidants, and Antifreeze Proteins. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arromrak, B.S.; Li, Z.; Gaitán-Espitia, J.D. Adaptive Strategies and Evolutionary Responses of Microbial Organisms to Changing Oceans. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 864797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedeek, A.M.; Elfeky, H.; Hanora, A.S.; Solyman, S.M. Genomic Insights into Biosynthesis and Adaptation in the Bioactive Marine Bacterium Streptomyces Albidoflavus VIP-1 from the Red Sea. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, H.L.; Hanora, A.; Solyman, S.M. Metataxanomic, Bioactivity and Microbiome Analysis of Red Sea Marine Sponges from Egypt. Mar. Genom. 2022, 61, 100920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Samak, M.; Zakeer, S.; Hanora, A.; Solyman, S.M. Metagenomic and Metatranscriptomic Exploration of the Egyptian Red Sea Sponge Theonella Sp. Associated Microbial Community. Mar. Genom. 2023, 70, 101032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.W.; Radax, R.; Steger, D.; Wagner, M. Sponge-Associated Microorganisms: Evolution, Ecology, and Biotechnological Potential. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 295–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentati, D.; Cheffi, M.; Hadrich, F.; Makhloufi, N.; Rabanal, F.; Manresa, A.; Sayadi, S.; Chamkha, M. Investigation of Halotolerant Marine Staphylococcus Sp. CO100, as a Promising Hydrocarbon-Degrading and Biosurfactant-Producing Bacterium, under Saline Conditions. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumurthy, K.; Kaliyamoorthy, K.; Kandasamy, K.; Ponnuvel, M.; Viyakarn, V.; Chavanich, S.; Dufossé, L. Antioxidant and Anti-Breast Cancer Properties of Hyaluronidase from Marine Staphylococcus Aureus (CASMTK1). J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaton, C.J.; Gerbig, G.R.; Sensius, L.D.; Patel, V.; Smith, T.C. Staphylococcus Aureus Epidemiology in Wildlife: A Systematic Review. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soge, O.O.; Meschke, J.S.; No, D.B.; Roberts, M.C. Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus and Methicillin-Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus Spp. Isolated from US West Coast Public Marine Beaches. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapaliya, D.; Hellwig, E.J.; Kadariya, J.; Grenier, D.; Jefferson, A.J.; Dalman, M.; Kennedy, K.; DiPerna, M.; Orihill, A.; Taha, M.; et al. Prevalence and Characterization of Staphylococcus Aureus and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus on Public Recreational Beaches in Northeast Ohio. GeoHealth 2017, 1, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstein, R.; Götz, F. What Distinguishes Highly Pathogenic Staphylococci from Medium- and Non-Pathogenic? In Between Pathogenicity and Commensalism; Dobrindt, U., Hacker, J., Svanborg, C., Eds.; Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 33–89. [Google Scholar]
- Amelia, T.S.M.; Amirul, A.-A.A.; Saidin, J.; Bhubalan, K. Identification of Cultivable Bacteria from Tropical Marine Sponges and Their Biotechnological Potentials. Trop. Life Sci. Res. 2018, 29, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anteneh, Y.S.; Yang, Q.; Brown, M.H.; Franco, C.M.M. Factors Affecting the Isolation and Diversity of Marine Sponge-Associated Bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 1729–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anteneh, Y.S.; Yang, Q.; Brown, M.H.; Franco, C.M.M. Antimicrobial Activities of Marine Sponge-Associated Bacteria. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, G.-S.; Li, B.; Brinks, E.; Franz, C.M.A.P. Characterization of Antibiotic-Resistant, Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci from Fresh Produce and Description of Staphylococcus Shinii Sp. Nov. Isolated from Chives. J. Microbiol. 2022, 60, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arreguin-Perez, C.A.; Cossio-Bayugar, R.; Aguilar-Diaz, H.; Miranda-Miranda, E. In Situ Localization of Staphylococcus Shinii and Staphylococcus Succinus in Infected Rhipicephalus Microplus Ticks: Implications for Biocontrol Strategies. Pathogens 2024, 13, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sosa-Fajardo, A.; Díaz-Muñoz, C.; Van der Veken, D.; Pradal, I.; Verce, M.; Weckx, S.; Leroy, F. Genomic Exploration of the Fermented Meat Isolate Staphylococcus Shinii IMDO-S216 with a Focus on Competitiveness-Enhancing Secondary Metabolites. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Xu, H.; Su, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, L.; Guo, Z.; Wu, J.; Cheng, C.; Feng, J. Horizontal Gene Transfer Contributes to Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance of Vibrio Harveyi 345 Based on Complete Genome Sequence Analysis. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, P.M.; Butler, J.; Randhawa, G.S.; Soltysiak, M.P.M.; Hill, K.A.; Kari, L. Environment and Taxonomy Shape the Genomic Signature of Prokaryotic Extremophiles. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, S.R.; Goering, R.V.; Witten, A.; Harmsen, D.; Mellmann, A. Bacterial Whole-Genome Sequencing Revisited: Portable, Scalable, and Standardized Analysis for Typing and Detection of Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance Genes. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 2365–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Göker, M. TYGS Is an Automated High-Throughput Platform for State-of-the-Art Genome-Based Taxonomy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Unicycler: Resolving Bacterial Genome Assemblies from Short and Long Sequencing Reads. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R.; Oliver Glöckner, F.; Peplies, J. JSpeciesWS: A Web Server for Prokaryotic Species Circumscription Based on Pairwise Genome Comparison. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 929–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Auch, A.F.; Klenk, H.P.; Göker, M. Genome Sequence-Based Species Delimitation with Confidence Intervals and Improved Distance Functions. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonge, M.; Soyk, S.; Ramakrishnan, S.; Wang, X.; Goodwin, S.; Sedlazeck, F.J.; Lippman, Z.B.; Schatz, M.C. RaGOO: Fast and Accurate Reference-Guided Scaffolding of Draft Genomes. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid Annotations Using Subsystems Technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid Prokaryotic Genome Annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattam, A.R.; Abraham, D.; Dalay, O.; Disz, T.L.; Driscoll, T.; Gabbard, J.L.; Gillespie, J.J.; Gough, R.; Hix, D.; Kenyon, R.; et al. PATRIC, the Bacterial Bioinformatics Database and Analysis Resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D581–D591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcock, B.P.; Huynh, W.; Chalil, R.; Smith, K.W.; Raphenya, A.R.; Wlodarski, M.A.; Edalatmand, A.; Petkau, A.; Syed, S.A.; Tsang, K.K.; et al. CARD 2023: Expanded Curation, Support for Machine Learning, and Resistome Prediction at the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D690–D699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelli, C.; Laird, M.R.; Williams, K.P.; Lau, B.Y.; Hoad, G.; Winsor, G.L.; Brinkman, F.S. IslandViewer 4: Expanded Prediction of Genomic Islands for Larger-Scale Datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W30–W35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG Tools for Functional Characterization of Genome and Metagenome Sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatusov, R.L.; Fedorova, N.D.; Jackson, J.D.; Jacobs, A.R.; Kiryutin, B.; Koonin, E.V.; Krylov, D.M.; Mazumder, R.; Smirnov, S.; Nikolskaya, A.N.; et al. The COG Database: An Updated Vesion Includes Eukaryotes. BMC Bioinform. 2003, 4, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmids Using PlasmidFinder and Plasmid Multilocus Sequence Typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blin, K.; Shaw, S.; Kloosterman, A.M.; Charlop-Powers, Z.; van Wezel, G.P.; Medema, M.H.; Weber, T. AntiSMASH 6.0: Improving Cluster Detection and Comparison Capabilities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W29–W35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, B.; Zheng, D.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. VFDB 2025: An Integrated Resource for Exploring Anti-Virulence Compounds. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D871–D877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, D.; Sleator, R.D. A Genomic Analysis of Osmotolerance in Staphylococcus Aureus. Gene 2021, 767, 145268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prágai, Z.; Eschevins, C.; Bron, S.; Harwood, C.R. Bacillus Subtilis NhaC, an Na+/H+ Antiporter, Influences Expression of the PhoPR Operon and Production of Alkaline Phosphatases. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 2505–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, C.; Bremer, E.; Krämer, R. The BCCT Family of Carriers: From Physiology to Crystal Structure. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 78, 13–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadaba, N.S.; Kaiser, J.T.; Johnson, E.; Lee, A.; Rees, D.C. The High-Affinity E. Coli Methionine ABC Transporter: Structure and Allosteric Regulation. Science 2008, 321, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, K.; Akagawa, E.; Yamane, K.; Sun, Z.W.; LaCelle, M.; Zuber, P.; Nakano, M.M. The NasB Operon and NasA Gene Are Required for Nitrate/Nitrite Assimilation in Bacillus Subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 1409–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.T.; Goldman, B.S.; Stewart, V. The NasFEDCBA Operon for Nitrate and Nitrite Assimilation in Klebsiella Pneumoniae M5al. J. Bacteriol. 1994, 176, 2551–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, N.; Shilova, I.N.; Zehr, J.P. Use of the High-affinity Phosphate Transporter Gene, PstS, as an Indicator for Phosphorus Stress in the Marine Diazotroph Crocosphaera watsonii (Chroococcales, Cyanobacteria). J. Phycol. 2019, 55, 752–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Letelier, A.; Olmedo, G.; Eguiarte, L.E.; Martinez-Castilla, L.; Souza, V. Parallel Evolution and Horizontal Gene Transfer of the Pst Operon in Firmicutes from Oligotrophic Environments. Int. J. Evol. Biol. 2011, 2011, 781642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schyns, G.; Potot, S.; Geng, Y.; Barbosa, T.M.; Henriques, A.; Perkins, J.B. Isolation and Characterization of New Thiamine-Deregulated Mutants of Bacillus Subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 8127–8136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josts, I.; Almeida Hernandez, Y.; Andreeva, A.; Tidow, H. Crystal Structure of a Group I Energy Coupling Factor Vitamin Transporter S Component in Complex with Its Cognate Substrate. Cell Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podkowa, K.J.; Briere, L.-A.K.; Heinrichs, D.E.; Shilton, B.H. Crystal and Solution Structure Analysis of FhuD2 from Staphylococcus Aureus in Multiple Unliganded Conformations and Bound to Ferrioxamine-B. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 2017–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebulsky, M.T.; Heinrichs, D.E. Identification and Characterization of FhuD1 and FhuD2, Two Genes Involved in Iron-Hydroxamate Uptake in Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 4994–5000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, B.; Cunningham, R.P. Genetic Mapping of Nth, a Gene Affecting Endonuclease III (Thymine Glycol-DNA Glycosylase) in Escherichia Coli K-12. J. Bacteriol. 1985, 162, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario-Cruz, Z.; Eletsky, A.; Daigham, N.S.; Al-Tameemi, H.; Swapna, G.V.; Kahn, P.C.; Szyperski, T.; Montelione, G.T.; Boyd, J.M. The CopBL Operon Protects Staphylococcus Aureus from Copper Toxicity: CopL Is an Extracellular Membrane–Associated Copper-Binding Protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 4027–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, M.V.; Nesterova, L.Y.; Mihailovskaya, V.S.; Selivanova, P.A.; Kochergina, D.A.; Karipova, M.O.; Valtsifer, I.V.; Averkina, A.S.; Starčič Erjavec, M. Nosocomial Escherichia Coli, Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, and Staphylococcus Aureus: Sensitivity to Chlorhexidine-Based Biocides and Prevalence of Efflux Pump Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, S.S.; Viveiros, M.; Amaral, L.; Couto, I. Multidrug Efflux Pumps in Staphylococcus Aureus: An Update. Open Microbiol. J. 2013, 7, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Blancas, G.Y.; Reyna-Terán, J.D.; Hernández-Eligio, J.A.; Ortuño-Pineda, C.; Toribio-Jiménez, J.; Rodríguez-Barrera, M.Á.; Toledo-Hernández, E.; Rojas-Aparicio, A.; Romero-Ramírez, Y. The CatE Gene of Bacillus Licheniformis M2-7 Is Essential for Growth in Benzopyrene, and Its Expression Is Regulated by the Csr System. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 39, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tago, K.; Sato, J.; Takesa, H.; Kawagishi, H.; Hayatsu, M. Characterization of Methylhydroquinone-Metabolizing Oxygenase Genes Encoded on Plasmid in Burkholderia Sp. NF100. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2005, 100, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwudulue, U.M.; Barger, N.; Dubovis, M.; Luzzatto Knaan, T. Natural Products and Pharmacological Properties of Symbiotic Bacillota (Firmicutes) of Marine Macroalgae. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedeek, A.M.; Ismail, M.M.; Elsayed, T.R.; Ramadan, M.A. Evaluation of the Marine Bacterial Population in the Great Bitter Lake, Egypt, as a Source of Antimicrobial Secondary Metabolites. Fermentation 2022, 8, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.; Robb, A.; Paterson, G.K. Isolation and Genome Sequencing of Staphylococcus Schleiferi Subspecies Coagulans from Antarctic and North Sea Seals. Access Microbiol. 2020, 2, e000162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.T.; Abdulrahman, I.; Amran, R.H.; Al-Matary, M.A.; Satheesh, S. Complete Genome Sequencing and Antibiofilm Activity of an Endophytic Bacterium Associated with Marine Sponge Hyrtios Erectus Collected from the Red Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2025, 12, 1588772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminov, R.I. Horizontal Gene Exchange in Environmental Microbiota. Front. Microbiol. 2011, 2, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carraro, N.; Rivard, N.; Burrus, V.; Ceccarelli, D. Mobilizable Genomic Islands, Different Strategies for the Dissemination of Multidrug Resistance and Other Adaptive Traits. Mob. Genet. Elem. 2017, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuda, M.; Shintani, M. Microbial Evolution through Horizontal Gene Transfer by Mobile Genetic Elements. Microb. Biotechnol. 2024, 17, e14408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Kaur, J. Comparative Genomics of Seven Genomes of Genus Idiomarina Reveals Important Halo Adaptations and Genes for Stress Response. 3 Biotech 2024, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, I.; Singh, V.; Alzahrani, K.J.; Chu, D.-T. (Eds.) Microbial Genomic Islands in Adaptation and Pathogenicity; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; ISBN 978-981-19-9341-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wei, H.-M.; Yuan, J.-L.; Xu, L.; Sun, J.-Q. A Comprehensive Genomic Analysis Provides Insights on the High Environmental Adaptability of Acinetobacter Strains. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1177951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufmann, H.; Salvador, C.; Salazar, V.W.; Cruz, N.; Dias, G.M.; Tschoeke, D.; Campos, L.; Sawabe, T.; Miyazaki, M.; Maruyama, F.; et al. Genomic Repertoire of Twenty-Two Novel Vibrionaceae Species Isolated from Marine Sediments. Microb. Ecol. 2025, 88, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
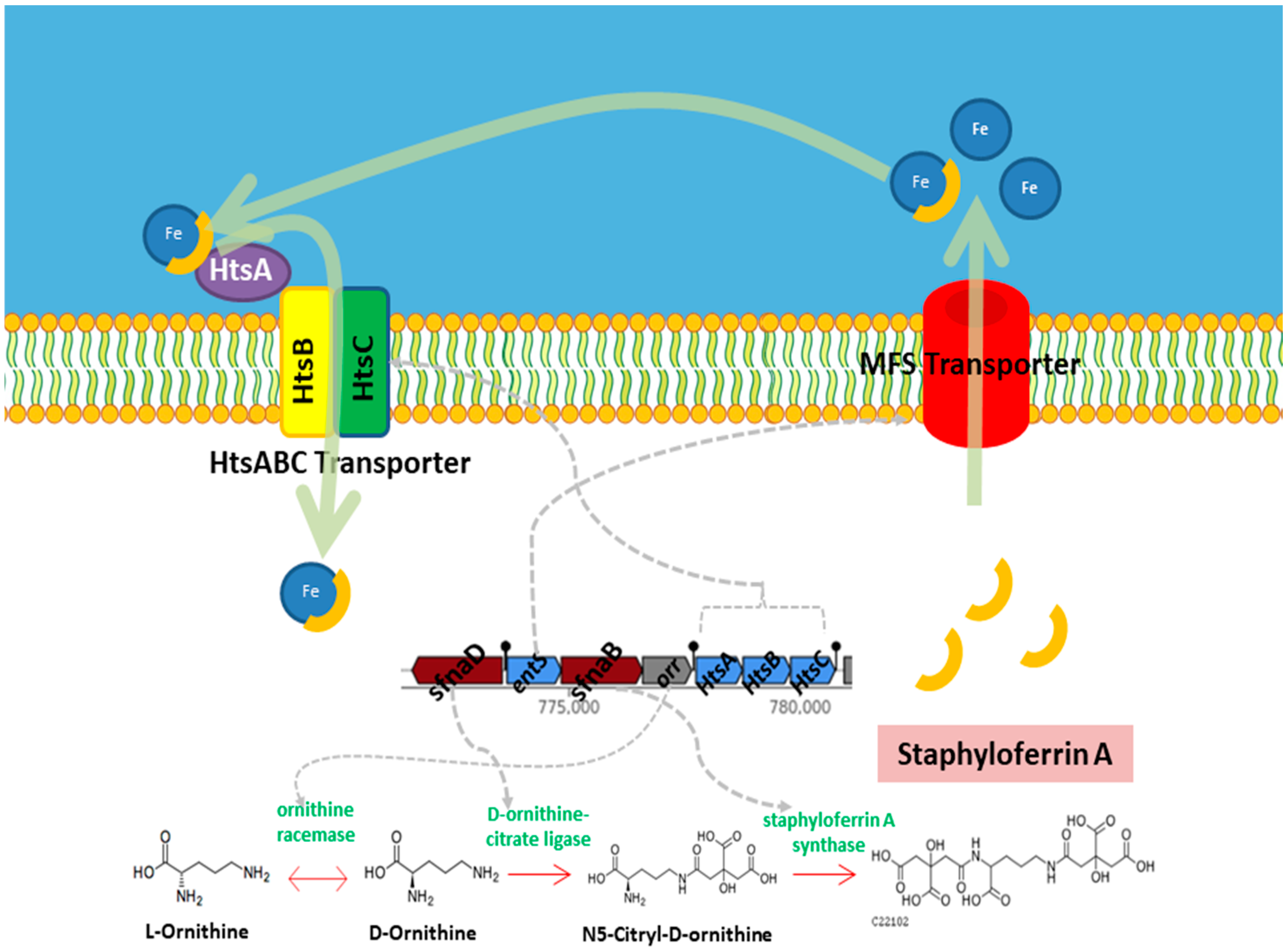
- Hammer, N.D.; Skaar, E.P. Molecular Mechanisms of Staphylococcus Aureus Iron Acquisition. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 65, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiwes, J.; Fiedler, H.-P.; Haag, H.; Zähner, H.; Konetschny-Rapp, S.; Jung, G. Isolation and Characterization of Staphyloferrin A, a Compound with Siderophore Activity from Staphylococcus Hyicus DSM 20459. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1990, 67, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wang, B.; Sun, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H. Chemistry and Biology of Siderophores from Marine Microbes. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
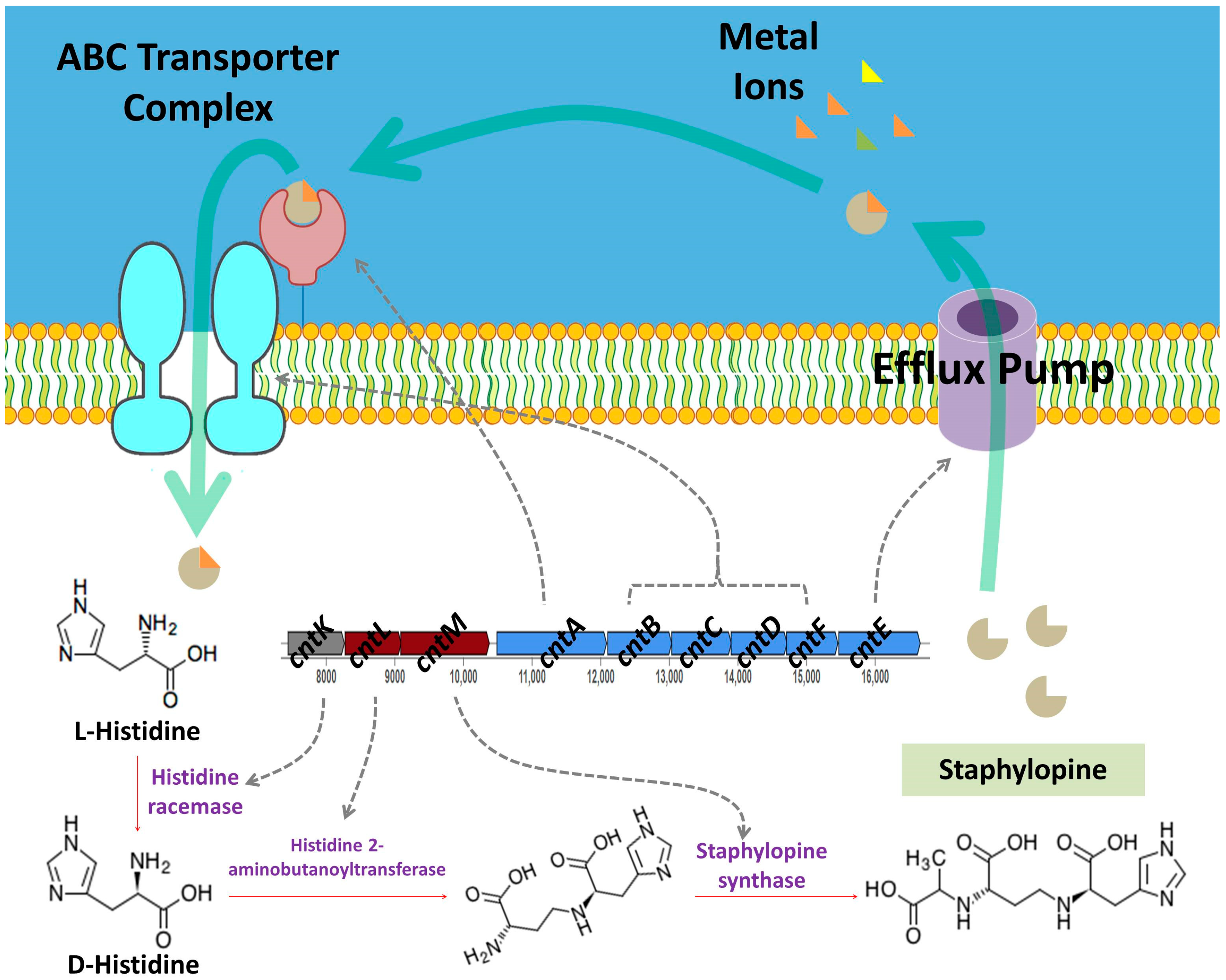
- Grim, K.P.; San Francisco, B.; Radin, J.N.; Brazel, E.B.; Kelliher, J.L.; Párraga Solórzano, P.K.; Kim, P.C.; McDevitt, C.A.; Kehl-Fie, T.E. The Metallophore Staphylopine Enables Staphylococcus Aureus To Compete with the Host for Zinc and Overcome Nutritional Immunity. MBio 2017, 8, e01281-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Bai, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhou, J.; Lei, X. Total Syntheses of Natural Metallophores Staphylopine and Aspergillomarasmine A. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 82, 13643–13648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghssein, G.; Ezzeddine, Z. The Key Element Role of Metallophores in the Pathogenicity and Virulence of Staphylococcus Aureus: A Review. Biology 2022, 11, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carini, P.; Steindler, L.; Beszteri, S.; Giovannoni, S.J. Nutrient Requirements for Growth of the Extreme Oligotroph “Candidatus Pelagibacter Ubique” HTCC1062 on a Defined Medium. ISME J. 2013, 7, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, V.J.; Irla, M.; Gil López, M.; Brautaset, T.; Fernandes Brito, L. Unravelling Formaldehyde Metabolism in Bacteria: Road towards Synthetic Methylotrophy. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaish, M.; Price-Whelan, A.; Reyes-Robles, T.; Liu, J.; Jereen, A.; Christie, S.; Alonzo, F.; Benson, M.A.; Torres, V.J.; Krulwich, T.A. Roles of Staphylococcus Aureus Mnh1 and Mnh2 Antiporters in Salt Tolerance, Alkali Tolerance, and Pathogenesis. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200, e00611-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, T.; Bremer, E. Guardians in a Stressful World: The Opu Family of Compatible Solute Transporters from Bacillus Subtilis. Biol. Chem. 2017, 398, 193–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.T.; Parales, R.E. Aromatic Hydrocarbon Dioxygenases in Environmental Biotechnology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2000, 11, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widada, H.; Nojiri, K.; Kasuga, T.; Yo, J. Molecular Detection and Diversity of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon-Degrading Bacteria Isolated from Geographically Diverse Sites. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 58, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.-S.; Keum, Y.-S.; Li, Q.X. Bacterial Degradation of Aromatic Compounds. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2009, 6, 278–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropel, D.; van der Meer, J.R. Bacterial Transcriptional Regulators for Degradation Pathways of Aromatic Compounds. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 474–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tierney, A.R.; Rather, P.N. Roles of Two-Component Regulatory Systems in Antibiotic Resistance. Future Microbiol. 2019, 14, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirakawa, H.; Kurushima, J.; Hashimoto, Y.; Tomita, H. Progress Overview of Bacterial Two-Component Regulatory Systems as Potential Targets for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
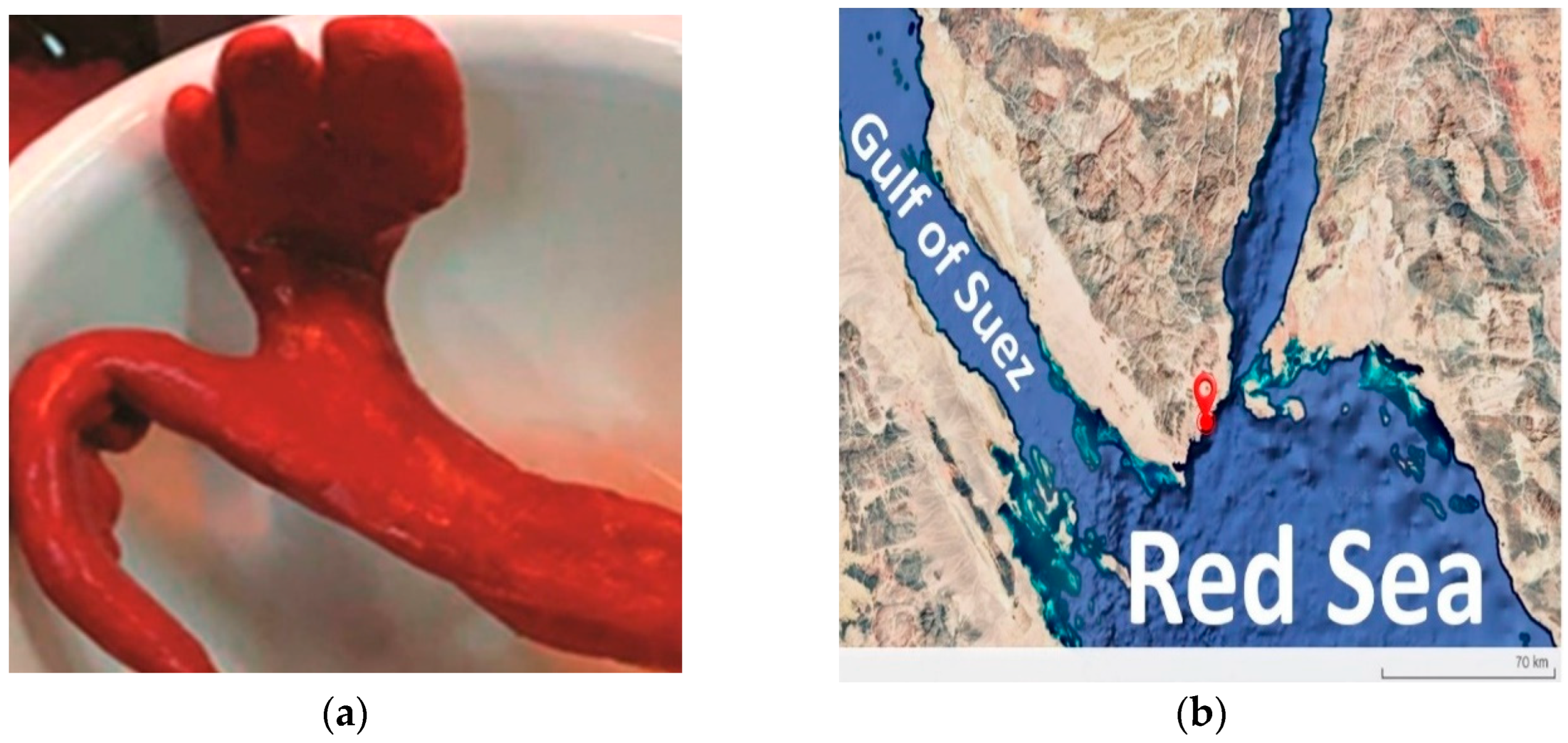

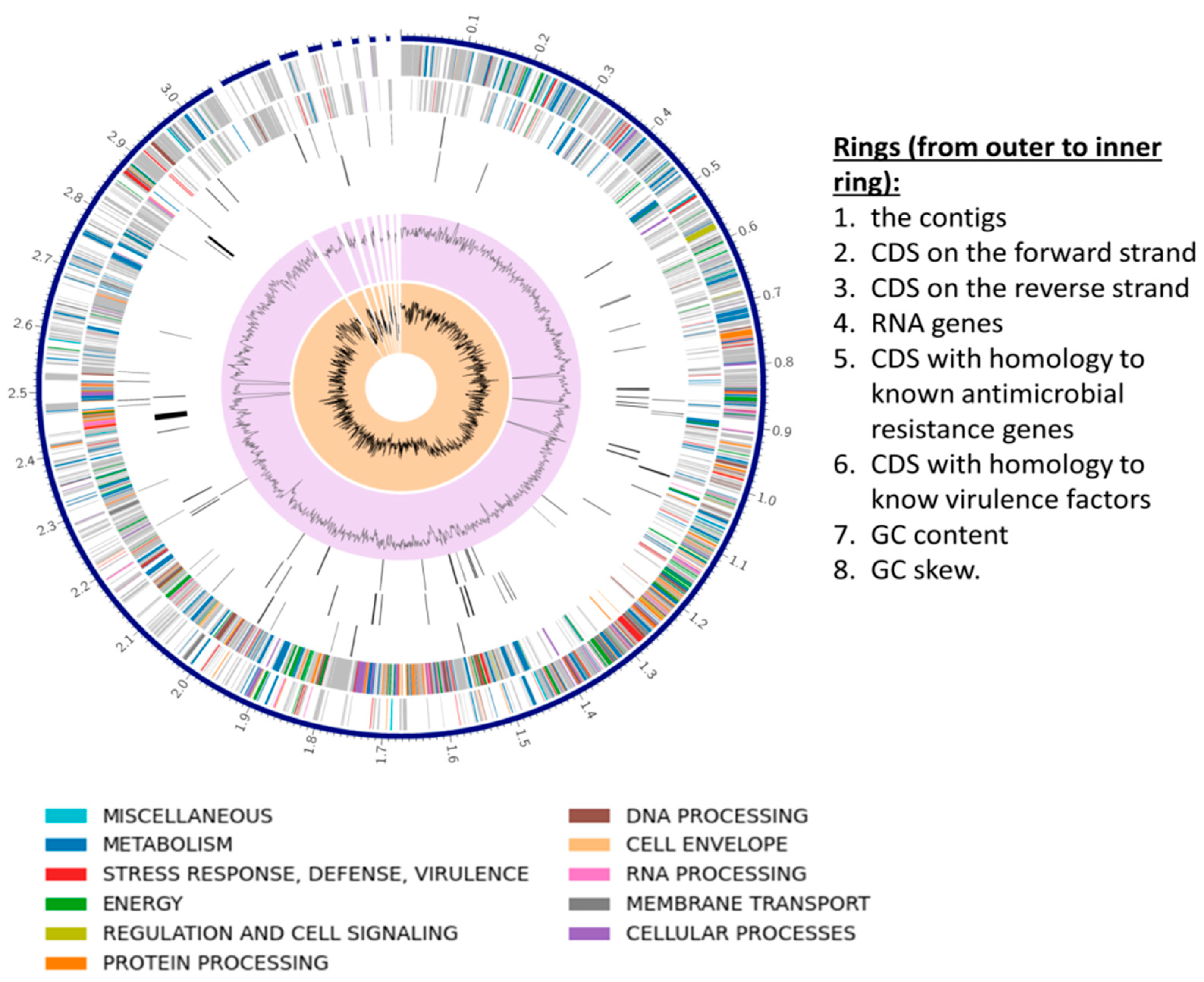
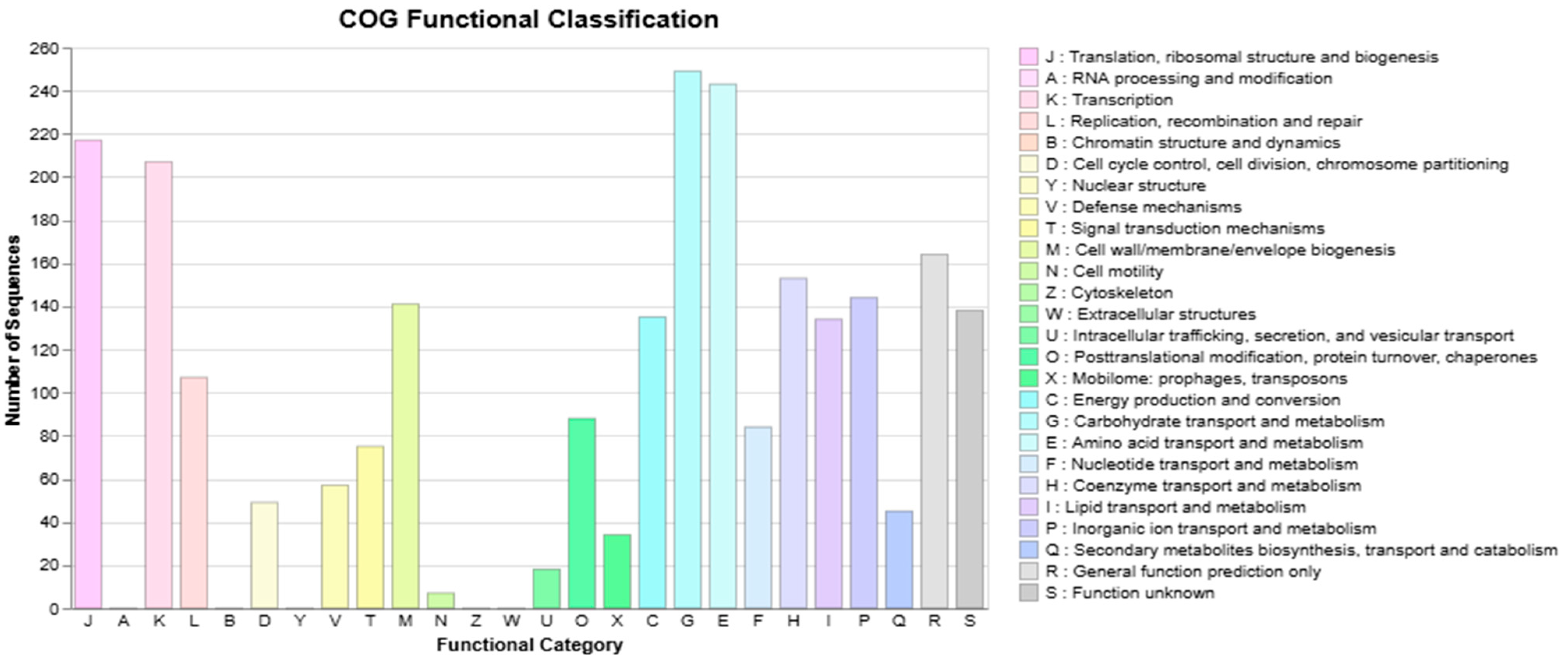
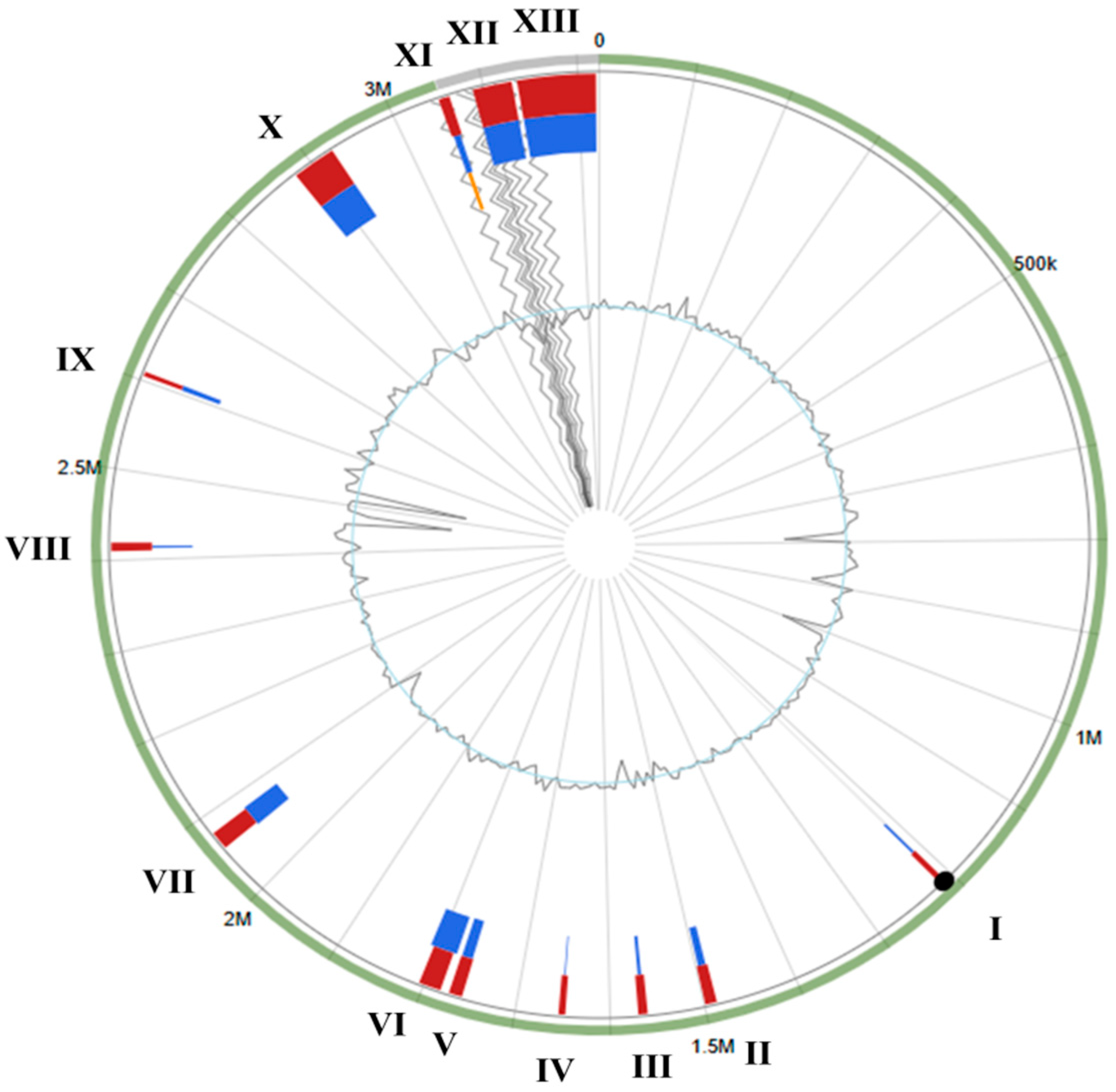
| Strain | NCBI Accession | ANIm (%) | ANIb (%) | dDDH (%) | GC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Staphylococcus shinii K22-5M | GCF_017583065.1 | 99.40 | 99.09 | 94.8 | 0.15 |
| Staphylococcus pseudoxylosus S04009 | GCF_003697915.1 | 91.94 | 91.15 | 44.3 | 0.46 |
| Staphylococcus xylosus CCM 2738 | GCF_002732165.1 | 91.16 | 90.70 | 41.5 | 0.33 |
| Staphylococcus saprophyticus CCUG 38042 | GCF_002902545.1 | 85.04 | 80.71 | 24.8 | 0.65 |
| Staphylococcus saprophyticus ATCC 15305 | GCF_000010125.1 | 85.00 | 80.72 | 24.6 | 0.85 |
| Staphylococcus edaphicus CCM 8730 | GCF_002614725.1 | 84.76 | 80.34 | 24 | 0.92 |
| Staphylococcus caeli 82B | GCF_900097965.1 | 84.79 | 79.70 | 23.7 | 0.95 |
| Staphylococcus equorum NCTC 12414 | GCF_003970515.1 | 84.60 | 79.77 | 23.7 | 0.77 |
| Staphylococcus equorum subsp. linens DSM 15097 | GCF_002901955.1 | 84.38 | 79.58 | 23.4 | 0.67 |
| Staphylococcus nepalensis DSM 15150 | GCF_002902745.1 | 84.81 | 78.57 | 23.3 | 0.63 |
| Staphylococcus nepalensis CCM 7045 | GCF_014635045.1 | 84.70 | 78.40 | 22.9 | 0.59 |
| Staphylococcus ureilyticus DSM 6718 | GCF_002902235.1 | 84.41 | 78.12 | 22.6 | 0.16 |
| Staphylococcus cohnii NCTC 11041 | GCF_002902365.1 | 84.22 | 78.32 | 22.4 | 0.1 |
| RAST | Prokka | |
|---|---|---|
| Total CDs | 3077 | 3032 |
| CDs with functional assignment | 2285 | 1946 |
| Hypothetical CDs | 792 | 1086 |
| rRNA | 2 | 1 |
| tRNA | 42 | 38 |
| Virulence Class | Virulence Factor | Associated Gene(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Adherence | Autolysin; elastin-binding protein; fibronectin-binding proteins | atl; ebp; fnbA |
| Enzyme | Lipase; serine V8 protease; thermonuclease | geh; sspA; nuc |
| Immune evasion | Capsule; polyglutamic acid capsule (Bacillus); polysaccharide capsule (Bacillus) | —; capB, capC; galE |
| Iron uptake | Periplasmic-binding protein-dependent ABC transport system (Vibrio-like) | vctC |
| Nutritional factor | Allantoin utilization (Klebsiella-like) | — |
| AMR Mechanism | Gene | Antibiotic Class |
|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic inactivation enzyme | BlaZ family | β-lactams |
| FosB | Fosfomycin | |
| Mph(C) family | Macrolides | |
| Antibiotic resistance gene cluster, cassette, or operon | TcaB, TcaB2, TcaR | Glycopeptides |
| Antibiotic target modification or protection | Alr | Cell wall synthesis inhibitors |
| Antibiotic target modification or protection | Ddl | Cell wall synthesis inhibitors |
| EF-G, EF-Tu | Protein synthesis inhibitors | |
| folA, Dfr, folP | Antifolates | |
| gyrA, gyrB | Fluoroquinolones | |
| inhA, fabI | Fatty acid synthesis inhibitors | |
| Iso-tRNA | Protein synthesis inhibitors | |
| kasA | Fatty acid synthesis inhibitors | |
| MurA | Cell wall synthesis inhibitors | |
| Rho | Transcription inhibitors | |
| rpoB, rpoC | Rifamycins | |
| S10p, S12p | Aminoglycosides | |
| Efflux pumps conferring antibiotic resistance | NorA | Fluoroquinolones |
| YkkCD | Multidrug efflux | |
| Gene conferring resistance via absence | gidB | Aminoglycosides (loss of methylation) |
| Protein-altering cell wall charge | GdpD, MprF, PgsA | Cationic antimicrobial peptides |
| Regulator modulating antibiotic resistance gene expression | BceR, BceS, LiaF, LiaR, LiaS | Glycopeptides and antimicrobial peptides |
| BGC | Type | Size (bp) | Most Similar Known Cluster | Identity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Opine-like metallophore, terpene | 37,511 | Staphylopine | 100% |
| 2 | RiPP-like | 10,281 | ||
| 3 | T3PKS | 41,169 | ||
| 4 | NI siderophore | 32,991 | Staphyloferrin A | 100% |
| 5 | Cyclic lactone autoinducer | 20,709 | ||
| 6 | Terpene | 20,818 | ||
| 7 | Terpene precursor | 20,890 | ||
| 8 | Terpene precursor | 20,953 | ||
| 9 | Lanthipeptide class i | 24,084 | ||
| 10 | NRPS | 56,796 | ||
| 11 | NRPS | 44,376 | ||
| 12 | NRPS | 44,328 |
| Function | Genes | COG(s) | Role | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+/H+ antiport system (multi-subunit) | mnhA1, mnhB1, mnhC1, mnhD1, mnhE1, mnhF1, mnhG1 | COG0651, COG2111, COG1006, COG1863, COG2212, COG1320 | Maintains intracellular pH and osmotic balance under high-salinity conditions. | [40] |
| Na+/H+ antiporter | nhaC | COG1757 | Regulates pH and ion homeostasis in saline environments. | [40,41] |
| Compatible solute uptake | opuD | COG1292 | Imports glycine betaine to protect against osmotic stress. | [40,42] |
| Nutrient | Genes | COG(s) | Role | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Methionine | metP, metN2 | COG2011, – | Active transport of methionine in nutrient-poor marine habitats. | [43] |
| Nitrogen (nitrate/nitrite assimilation) | nasD | COG1251 | Reduces nitrite to ammonium for nitrogen assimilation. | [44,45] |
| Phosphate | pstS | – | Scavenges inorganic phosphate in oligotrophic waters. | [46,47] |
| Thiamine | ykoD | COG1122 | Imports thiamine, essential for metabolic processes. | [48,49] |
| Iron | fhuD | – | Facilitates acquisition of iron under limiting conditions. | [50,51] |
| Stress Type | Genes | COG(s) | Role | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oxidative stress and DNA repair | nth, trxB, recA | –, COG0492, – | Protects from oxidative damage and promotes DNA repair. | [52] |
| Heavy metal stress (copper) | copA, copB | – | Exports excess copper to prevent toxicity. | [53] |
| Detoxification and efflux | sepA, mdtD | – | Removes toxic or host-derived compounds. | [54,55] |
| Genes | COG(s) | Role | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| catE | COG2514 | Acts as a key catechol 2,3-dioxygenase, performing meta-cleavage of aromatic rings, a critical step in the breakdown of petroleum hydrocarbons. | [56] |
| mhqR, mhqA, mhqO, mhqD | COG1846, COG0346, COG0400 | This mhq cluster enables the degradation of a variety of aromatic compounds. | [57] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
El Samak, M.; Lotfy, H.; Sedeek, A.M.; Mohamed, Y.S.; Solyman, S.M. Genomic Characterization of Marine Staphylococcus shinii Strain SC-M1C: Potential Genetic Adaptations and Ecological Role. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1866. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081866
El Samak M, Lotfy H, Sedeek AM, Mohamed YS, Solyman SM. Genomic Characterization of Marine Staphylococcus shinii Strain SC-M1C: Potential Genetic Adaptations and Ecological Role. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1866. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081866
Chicago/Turabian StyleEl Samak, Manar, Hasnaa Lotfy, Abdelrahman M. Sedeek, Yehia S. Mohamed, and Samar M. Solyman. 2025. "Genomic Characterization of Marine Staphylococcus shinii Strain SC-M1C: Potential Genetic Adaptations and Ecological Role" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1866. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081866
APA StyleEl Samak, M., Lotfy, H., Sedeek, A. M., Mohamed, Y. S., & Solyman, S. M. (2025). Genomic Characterization of Marine Staphylococcus shinii Strain SC-M1C: Potential Genetic Adaptations and Ecological Role. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1866. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081866







