Eucalyptus globulus Pyroligneous Extract as Dietary Additive for Nile Tilapia Health: In Vitro and In Vivo Assessments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. MIC, MBC, and Antibiogram
2.3. Fish, Feeds, and Experimental Conditions
2.4. Hematology
2.5. Phagocytosis Assay
2.6. Zootechnical Parameters
2.7. Bacterial Challenge
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. MIC and MBC
3.2. Antibiogram
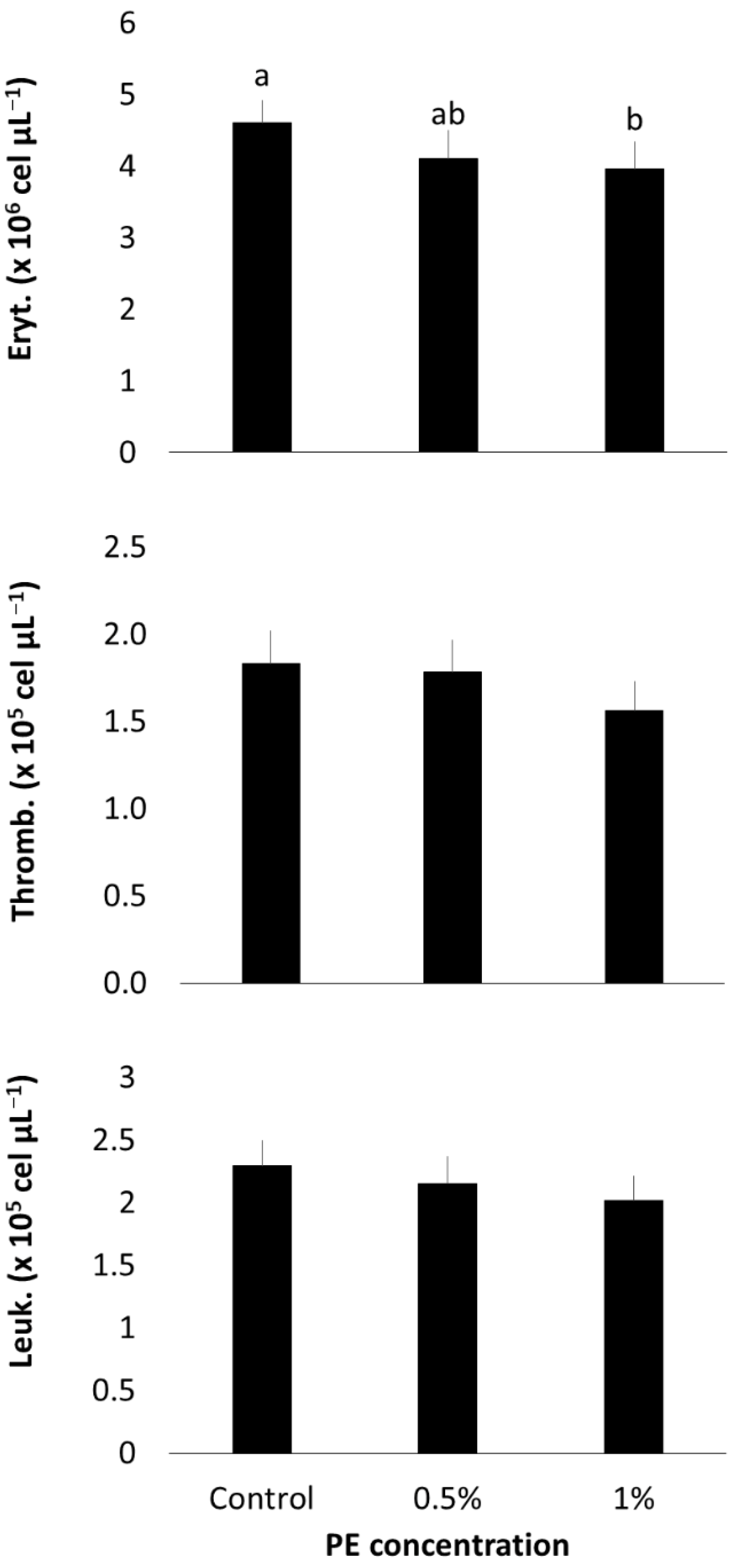
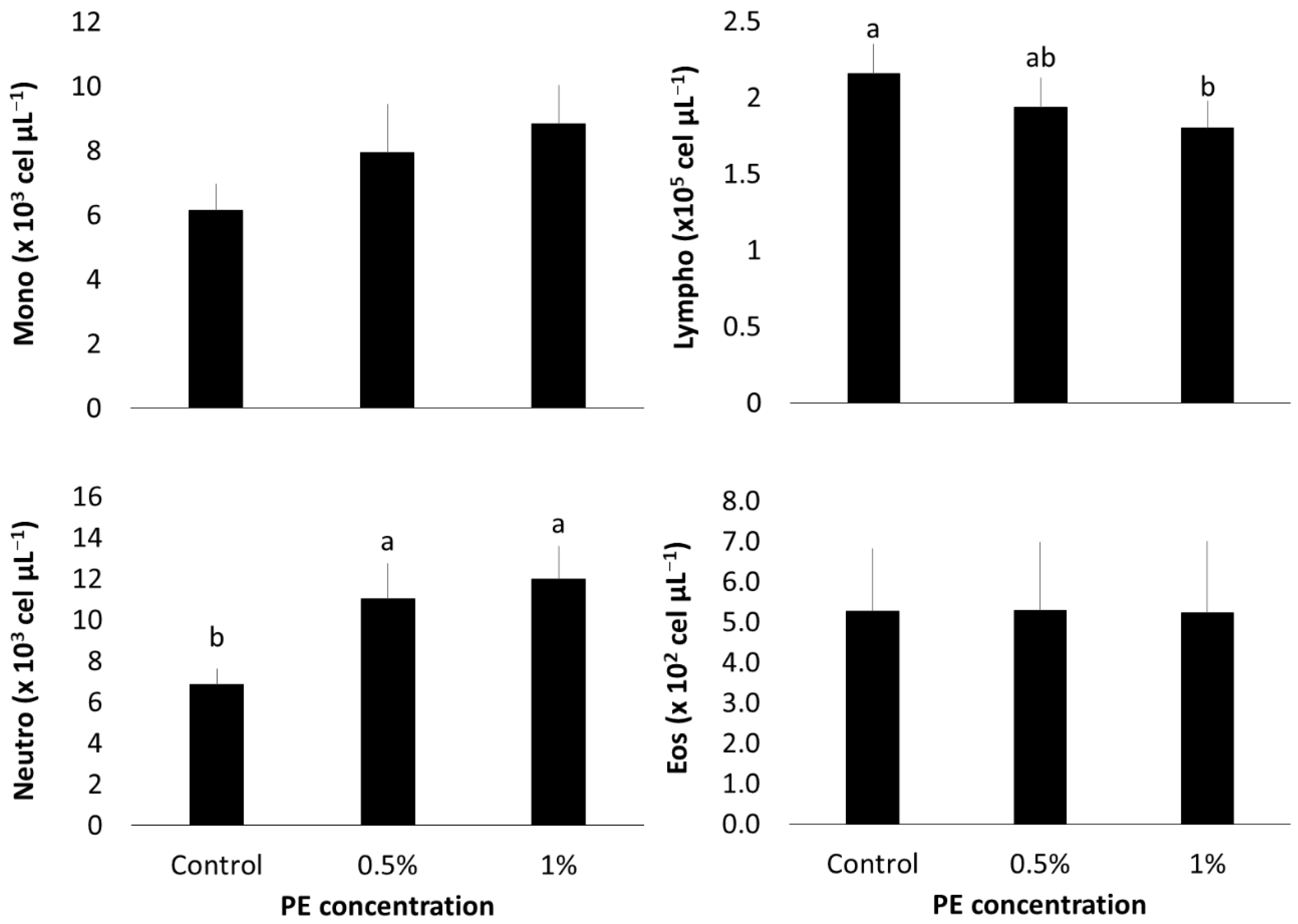
3.3. Hematological Profile
3.4. Phagocytosis
3.5. Zootechnical Results
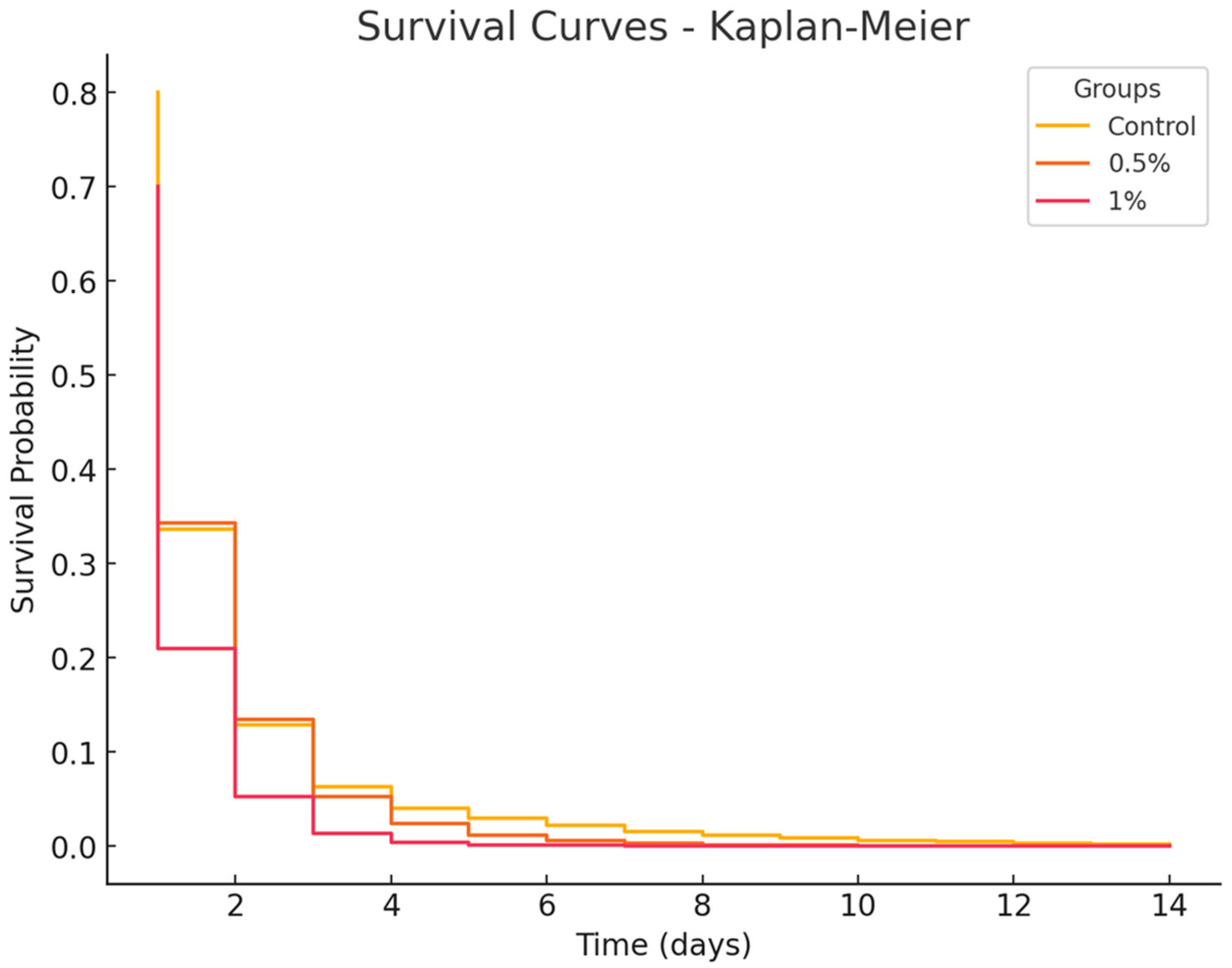
3.6. Bacterial Challenge Survival
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022; FAO: Roma, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Mian, G.F.; Godoy, D.T.; Leal, C.A.G.; Yuhara, T.Y.; Costa, G.M.; Figueiredo, H.C.P. Aspects of the natural history and virulence of S. agalactiae infection in Nile tilapia. Vet. Microbiol. 2009, 136, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, N.W.; Van Der Kraak, G. Effects of stress on reproduction and growth in fish. Fish Stress Health Aquac. 1997, 1, 73–94. [Google Scholar]
- Alderman, D.J.; Hastings, T.S. Antibiotic use in aquaculture: Development of antibiotic resistance—Potential for consumer health risks. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 33, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, L.; Civitareale, C.; Brambilla, G.; Dojmi Di Delupis, G. Toxicity of several important agricultural antibiotics to Artemia. Water Res. 1997, 31, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Pauzi, N.; Mohamad, N.; Azzam-Sayuti, M.; Md Yasin, I.S.; Saad, M.Z.; Nasruddin, N.S.; Azmai, M.N.A. Antibiotic susceptibility and pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from red hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus×Oreochromis mossambicus) in Malaysia. Vet. World. 2020, 13, 2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, W. Medical consequences of antibiotics use in agriculture. Science 1998, 279, 996–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Ding, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Zeng, Z. Antibiotics, Antibiotic Resistance Genes, and Bacterial Community Composition in Fresh Water Aquaculture Environment in China. Microb. Ecol. 2015, 70, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, G.; Ouraji, H.; Khalesi, M.K.; Sudagar, M.; Barari, A.; Dangesaraki, M.Z.; Khalili, K.H. Effects of a prebiotic, Immunogen®, on feed utilization, body composition, immunity and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila infection in the common carp Cyprinus carpio (Linnaeus) fingerlings. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2012, 96, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.B.; Hashim, R.; Chai, Y.H.; Marsh, T.L.; Mohd Nor, S.A. Dietary prebiotics and probiotics influence growth performance, nutrient digestibility and the expression of immune regulatory genes in snakehead (Channa striata) fingerlings. Aquaculture 2016, 460, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, S.S.; Sukumaran, V. Potential probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum VSG3 improves the growth, immunity, and disease resistance of tropical freshwater fish, Labeo rohita. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 34, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.L.; Park, C.-I.; Kim, D.-H. Improved growth rate and disease resistance in olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus, by probiotic Lactococcus lactis WFLU12 isolated from wild marine fish. Aquaculture 2017, 471, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.Y.; Chen, S.-W.; Hu, S.-Y. Improvements in the growth performance, immunity, disease resistance, and gut microbiota by the probiotic Rummeliibacillus stabekisii in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2019, 92, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, X.W.; Liu, L.L.; Cao, Y.C.; Zhu, H. Dietary oregano essential oil improved the immune response, activity of digestive enzymes, and intestinal microbiota of the koi carp, Cyprinus carpio. Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.L.; Tan, J.Y.W.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhou, X.H.; Xiang, X.; Wang, K.Y. Evaluation of oregano essential oil (Origanum heracleoticum L.) on growth, antioxidant effect and resistance against Aeromonas hydrophila in channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus). Aquaculture 2009, 292, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, R.S.R.; Taccini, M.M.; Moura, L.F.; Ceribelli, U.L.; Brito, J.O.; Gloria, E.M. Potential of Pyroligneous Extract of Eucalyptus Wood as a Preservative of Cosmetic and Sanitizing Products. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Moraes França Ferreira, P.; da Silva Nascimento, L.; Coelho Dias, D.; da Veiga Moreira, D.M.; Lúcia Salaro, A.; Duca de Freitas, M.B.; Souza Carneiro, A.P.; Sampaio Zuanon, J.A. Essential Oregano Oil as a Growth Promoter for the Yellowtail Tetra, Astyanax Altiparanae. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2014, 45, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, E.G.; Fauller, H.; Magalhães, M.; Guirardi, B.; Martins, M.A. Potential use of wood pyrolysis coproducts: A review. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2022, 41, e13705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bektaş, S.; Murat, Ö. Antibacterial activity of eucalyptus (Eucalyptus camaldulensis) essential oil against fish pathogen bacterium, Aeromonas caviae. Mar. Sci. Tech. Bull. 2022, 11, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseeharan, B.; Thaya, R. Medicinal plant derivatives as immunostimulants: An alternative to chemotherapeutics and antibiotics in aquaculture. Aquac. Int. 2014, 22, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamadi, M.; Zamini, A.A.; Vahabzadeh, H. Evaluation of Antibacterial Properties of Eucalyptus spp and Plelargonium roseum Extracts in Common carp, Cyprinus carpio and Their Effectson Blood Indices. Mid-East J. Sci. Res. 2013, 15, 723–731. [Google Scholar]
- Elumalai, P.; Kurian, A.; Lakshmi, S.; Faggio, C.; Esteban, M.A.; Ringø, E. Herbal Immunomodulators in Aquaculture. Rev. Fish. Sci. Aquac. 2020, 29, 33–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter, M.; Bontemps, N.; Lecchini, D.; Banaigs, B.; Sasal, P. Use of plant extracts in fish aquaculture as an alternative to chemotherapy: Current status and future perspectives. Aquaculture 2014, 433, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hai, N. The use of medicinal plants as immunostimulants in aquaculture: A review. Aquaculture 2015, 446, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.B.G.; Ré-Poppi, N.; Raposo, J.L., Jr. Characterization of pyroligneous acid used in agriculture by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2012, 23, 610–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, A.; Gunupuru, L.R. Production, prospects and potential application of pyroligneous acid in agriculture. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2018, 135, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; El Basuini, M.F.; Yilmaz, S.; Abdel-Latif, H.M.R.; Alagawany, M.; Abdul Kari, Z.A.; Razab, M.K.A.A.; Hamid, N.K.A.; Moonmanee, T.; Doan, H.V. Exploring the Roles of Dietary Herbal Essential Oils in Aquaculture: A Review. Animals 2022, 12, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhzadeh, N.; Soltani, M.; Ebrahimzadeh-Mousavi, H.A.; Shahbazian, N.; Norouzi, M. Effects of Zataria multiflora and Eucalyptus globolus essential oils on haematological parameters and respiratory burst activity in Cyprinus carpio. Iran J. Fish Sci. 2011, 10, 316–323. [Google Scholar]
- Sivaraj, A.; Devagnanaroopan, J.; Palani, B.; Senthilkumar, B. View of Antibacterial activity of Eucalyptus oblique aqueous leaf extract on selective Vibrio species of Penaeus monodon culture hatchery. World J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 2017, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Zarei, S.; Bahador, N.; Mirbakhsh, M.; Pazir, M.K. Antibacterial activity of aqueous extract of Eucalyptus camaldulensis in different salinity and temperature against Vibrio harveyi (PTCC1755) and Vibrio alginolyticus (MK641453.1). J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, 8, 1206–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Ghalem, B.R.; Mohamed, B. Antibacterial activity of leaf essential oils of Eucalyptus globulus and Eucalyptus camaldulensis. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 2, 211–215. [Google Scholar]
- Gholipourkanani, H.; Buller, N.; Lymbery, A. In vitro antibacterial activity of four nano-encapsulated herbal essential oils against three bacterial fish pathogens. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkat-Madouri, L.; Asma, B.; Madani, K.; Bey-Ould Si Said, Z.; Rigou, P.; Grenier, D.; Allalou, H.; Remini, H.; Adjaoud, A.; Boulekbache-Makhlouf, L. Chemical composition, antibacterial and antioxidant activities of essential oil of Eucalyptus globulus from Algeria. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 78, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.W.; Wendt, M.; Heo, G.-J. Antimicrobial activity of essential oil of Eucalyptus globulus against fish pathogenic bacteria. Lab. Anim. Res. 2016, 32, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024; FAO: Roma, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PeixeBR, Anuário 2025—PeixeBR, (2025). Available online: https://www.peixebr.com.br/anuario-2025/ (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Ho, S.P.; Hsu, T.Y.; Chen, M.H.; Wang, W.S. Antibacterial effect of chloramphenicol, thiamphenicol and florfenicol against aquatic animal bacteria. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2000, 62, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulkhaq, M.F.; Budi, D.S.; Rahayu, N.N. The effect of temperature, salinity and antimicrobial agent on growth and viability of Aeromonas hydrophila. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 441, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dairiki, J.K.; Majolo, C.; Chagas, E.C.; Chaves, F.C.M.; de Oliveira, M.R.; Morais, I.D.S. Procedimento para Inclusão de óleos Essenciais em rações para Peixes. 2013. Available online: https://www.sidalc.net/search/Record/dig-infoteca-e-doc-973005/Description (accessed on 2 April 2020).
- Baba, E.; Acar, Ü.; Öntaş, C.; Kesbiç, O.S.; Yılmaz, S. Evaluation of Citrus limon peels essential oil on growth performance, immune response of Mozambique tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus challenged with Edwardsiella tarda. Aquaculture 2016, 465, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brum, A.; Pereira, S.A.; Owatari, M.S.; Chagas, E.C.; Chaves, F.C.M.; Mouriño, J.L.P.; Martins, M.L.M. Effect of dietary essential oils of clove basil and ginger on Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) following challenge with Streptococcus agalactiae. Aquaculture 2017, 468, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmino, J.P.; Galindo-Villegas, J.; Reyes-López, F.E.; Gisbert, E. Phytogenic bioactive compounds shape fish mucosal immunity. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 695973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranzani-Paiva, M.J.T.; Pádua, S.B.; Tavares-Dias, M.; Egami, M.I. Métodos para Análise Hematológica em Peixes; Editora da Universidade Estadual de Maringá-EDUEM: Maringá, Brazil, 2013; pp. 1–140. [Google Scholar]
- Levy-Pereira, N.; Yasui, G.S.; Evangelista, M.M.; Nascimento, N.F.; Santos, M.P.; Siqueira-Silva, D.H.; Monzani, P.S.; Senhorini, J.A.; Pilarski, F. In vivo phagocytosis and hematology in Astyanax altiparanae, a potential model for surrogate technology. Braz. J. Biol. 2019, 80, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, B.A.; Feijó, F.M.C.; Alves, N.D.; Pimenta, A.S.; Benicio, L.D.M.; Silva-Júnior, E.C.; Santos, C.S.; Pereira, A.F.; Moura, Y.B.F.; Gama, G.S.P.; et al. Use of a product based on wood vinegar of Eucalyptus clone I144 used in the control of bovine mastitis. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 279, 109670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, J.L.S.; Alves, T.; Camerini, L.; Nedel, F.; Campos, A.D.; Lund, R.G. Antimicrobial and cytotoxic capacity of pyroligneous extracts films of Eucalyptus grandis and chitosan for oral applications. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Araújo, E.; Pimenta, A.S.; Feijó, F.M.C.; Castro, R.V.O.; Fasciotti, M.; Monteiro, T.V.C.; de Lima, K.M.G. Antibacterial and antifungal activities of pyroligneous acid from wood of Eucalyptus urograndis and Mimosa tenuiflora. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 124, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological profile for phenol; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2008. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK599448/ (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR). Toxicological Profile for Cresols; Toxicological Profiles; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2008. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK599914/ (accessed on 7 July 2025).
- Pimenta, A.S.; Fasciotti, M.; Monteiro, T.V.C.; Lima, K.M.G. Chemical Composition of Pyroligneous Acid Obtained from Eucalyptus GG100 Clone. Molecules 2018, 23, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurudeen, N.D.; Ayisi, C.L.; Ampofo-Yeboah, A. Effects of Eucalyptus globulus leaf extract on growth performance, feed utilization and blood biochemistry of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Veterinaria 2022, 71, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoseini, S.M.; Mirghaed, A.T.; Iri, Y.; Ghelichpour, M. Effects of dietary cineole administration on growth performance, hematological and biochemical parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2018, 495, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterfalvi, A.; Miko, E.; Nagy, T.; Reger, B.; Simon, D.; Miseta, A.; Czéh, B.; Szereday, L. Much More Than a Pleasant Scent: A Review on Essential Oils Supporting the Immune System. Molecules 2019, 24, 4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, E.; Awaad, A. Role of medicinal plants on growth performance and immune status in fish. Fish. Shell. Immunol. 2017, 67, 40–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immanuel, G.; Uma, R.P.; Iyapparaj, P.; Citarasu, T.; Peter, S.M.P.; Babu, M.M.; Palavesam, A. Dietary medicinal plant extracts improve growth, immune activity and survival of tilapia Oreochromis mossambicus. J. Fish. Biol. 2009, 74, 1462–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reverter, M.; Tapissier-Bontemps, N.; Sarter, S.; Sasal, P.; Caruso, D. Moving towards more sustainable aquaculture practices: A meta-analysis on the potential of plant-enriched diets to improve fish growth, immunity and disease resistance. Rev. Aquac. 2021, 13, 537–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; An, S.; Zhou, C.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Z.; Feng, J.; Lin, H.; Xun, P.; Yu, W. Effects of eucalyptus essential oil on growth, immunological indicators, disease resistance, intestinal morphology and gut microbiota in Trachinotus ovatus. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Bacterial Strains | Collection Number | Code | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aeromonas hydrophila | 17410018 | INCQS 00318 | 2014 |
| Aeromonas jandaei | 17410036 | LHZ-FZEA-USP#01/19 | 2019 |
| Escherichia coli | 17410013 | INCQS 00171 | 2013 |
| Plesiomonas shigelloides | 17410038 | LHZ-FZEA-USP#03/19 | 2019 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 17410032 | ATCC 00313 | 2018 |
| Salmonella enteritidis | 17410010 | ATCC 13076 | 2009 |
| Streptococcus agalactiae | 17410028 | INCQS 00128 | 2016 |
| Bacterial Strains | MIC (%) | MBC (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Aeromonas hydrophila | 6.25 | 12.5 |
| Aeromonas jandaei | 6.25 | 12.5 |
| Escherichia coli | 6.25 | 12.5 |
| Plesiomonas shigelloides | 3.12 | - |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | 6.25 | 12.5 |
| Salmonella enteritidis | 6.25 | 12.5 |
| Streptococcus agalactiae | 6.25 | 12.5 |
| Treatments | IIW | FIW | IL | FL | Cons | WG | MWG | FCR | MDWG | Growth | K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 13.7 ± 1.1 | 48.2 ± 3.7 | 9.5 ± 0.4 | 13.2 ± 0.3 | 915.7 ± 84.5 | 1036.6 ± 79.9 | 34.5 ± 2.6 | 0.88 ± 0.01 | 1.33 ± 0.1 | 3.7 ± 0.5 | 2.07 ± 0.01 |
| 0.5% | 12.7 ± 0.5 | 41.8 ± 0.9 | 8.6 ± 0.1 | 12.3 ± 0.1 | 868 ± 22.8 | 874 ± 13.1 | 29.1 ± 0.4 | 0.99 ± 0.02 | 1.12 ± 0.01 | 3.7 ± 0.1 | 2.20 ± 0.04 |
| 1% | 11.6 ± 0.3 | 40.8 ± 1.2 | 8.3 ± 0.1 | 12.4 ± 0.1 | 1002 ± 38.8 | 875.6 ± 36.2 | 29.2 ± 1.2 | 1.15 ± 0.09 | 1.12 ± 0.04 | 4.1 ± 0.1 | 2.11 ± 0.03 |
| p-Value | 0.4630 | 0.3530 | 0.1780 | 0.2650 | 0.4830 | 0.3120 | 0.3120 | 0.1810 | 0.3000 | 0.8660 | 0.2650 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
dos Reis, M.F.; Levy-Pereira, N.; de Alcântara Rocha, N.R.; Lazaro, T.M.; de França, M.M.; Nishikawa, S.H.L.; de Godoy, S.H.S.; de Sousa, R.L.M. Eucalyptus globulus Pyroligneous Extract as Dietary Additive for Nile Tilapia Health: In Vitro and In Vivo Assessments. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081773
dos Reis MF, Levy-Pereira N, de Alcântara Rocha NR, Lazaro TM, de França MM, Nishikawa SHL, de Godoy SHS, de Sousa RLM. Eucalyptus globulus Pyroligneous Extract as Dietary Additive for Nile Tilapia Health: In Vitro and In Vivo Assessments. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081773
Chicago/Turabian Styledos Reis, Marcelo Felisberto, Nycolas Levy-Pereira, Nathalia Raissa de Alcântara Rocha, Talita Maria Lazaro, Marisa Matias de França, Sofia Harumi Lopes Nishikawa, Silvia Helena Seraphin de Godoy, and Ricardo Luiz Moro de Sousa. 2025. "Eucalyptus globulus Pyroligneous Extract as Dietary Additive for Nile Tilapia Health: In Vitro and In Vivo Assessments" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081773
APA Styledos Reis, M. F., Levy-Pereira, N., de Alcântara Rocha, N. R., Lazaro, T. M., de França, M. M., Nishikawa, S. H. L., de Godoy, S. H. S., & de Sousa, R. L. M. (2025). Eucalyptus globulus Pyroligneous Extract as Dietary Additive for Nile Tilapia Health: In Vitro and In Vivo Assessments. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1773. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081773







