Effects of Treadmill Exercise on Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer’s Disease Model Mice and Wild-Type Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Exercise Intervention Scheme
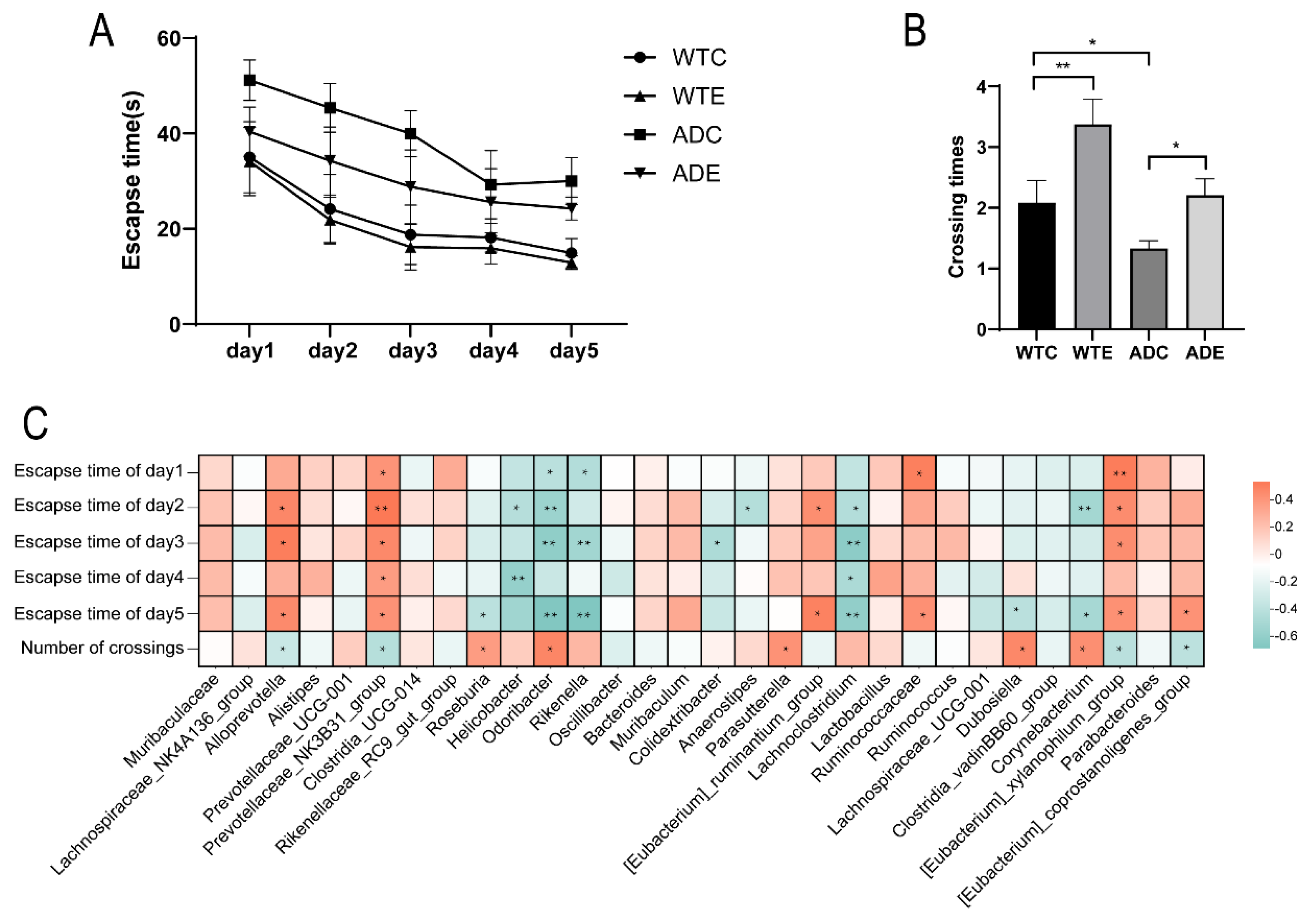
2.3. Morris Water Maze Test
2.4. 16S rDNA Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sequencing Data
3.2. Analysis of Murine Gut Microbial Diversity
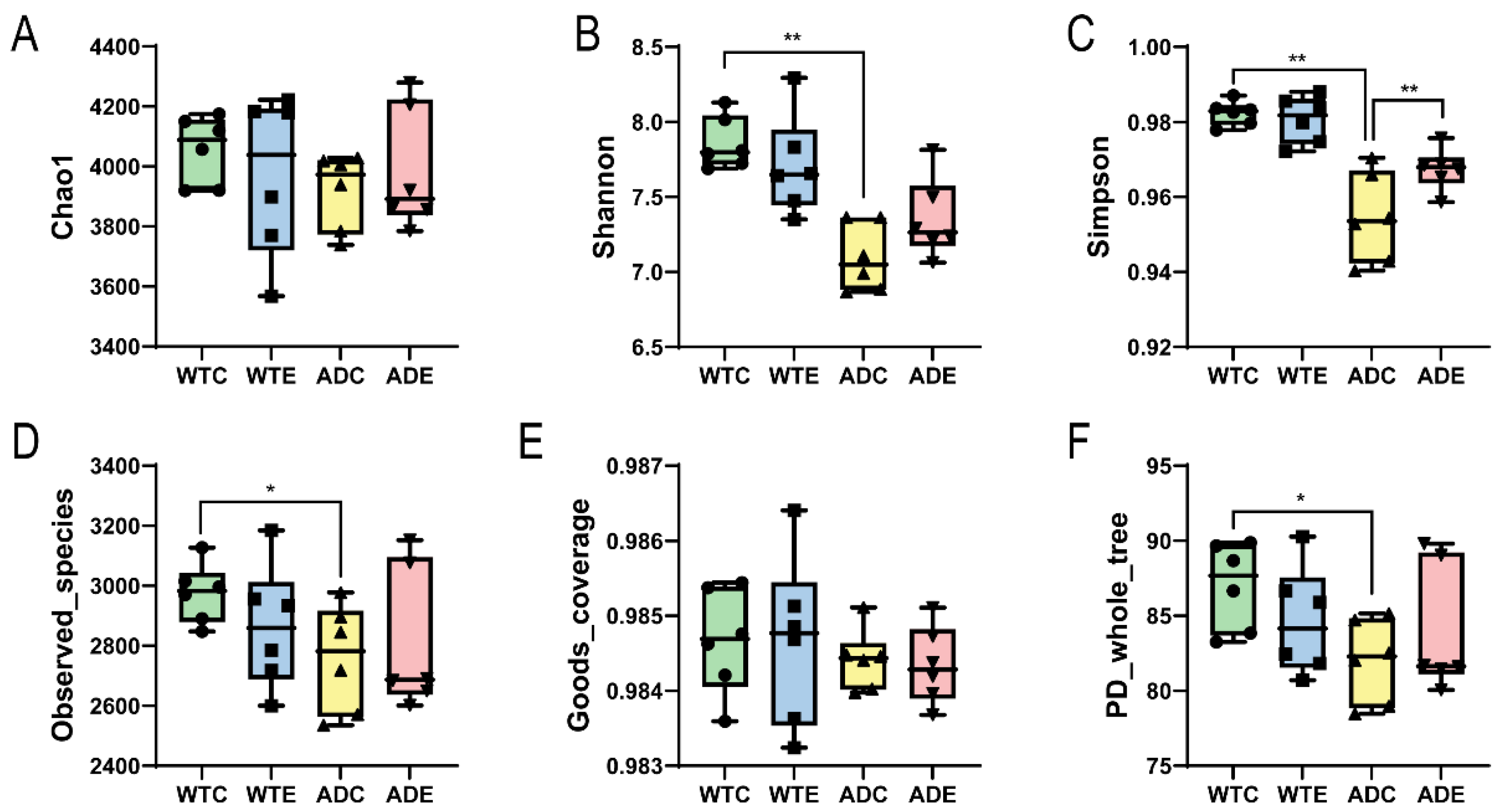
3.2.1. α Diversity Analysis
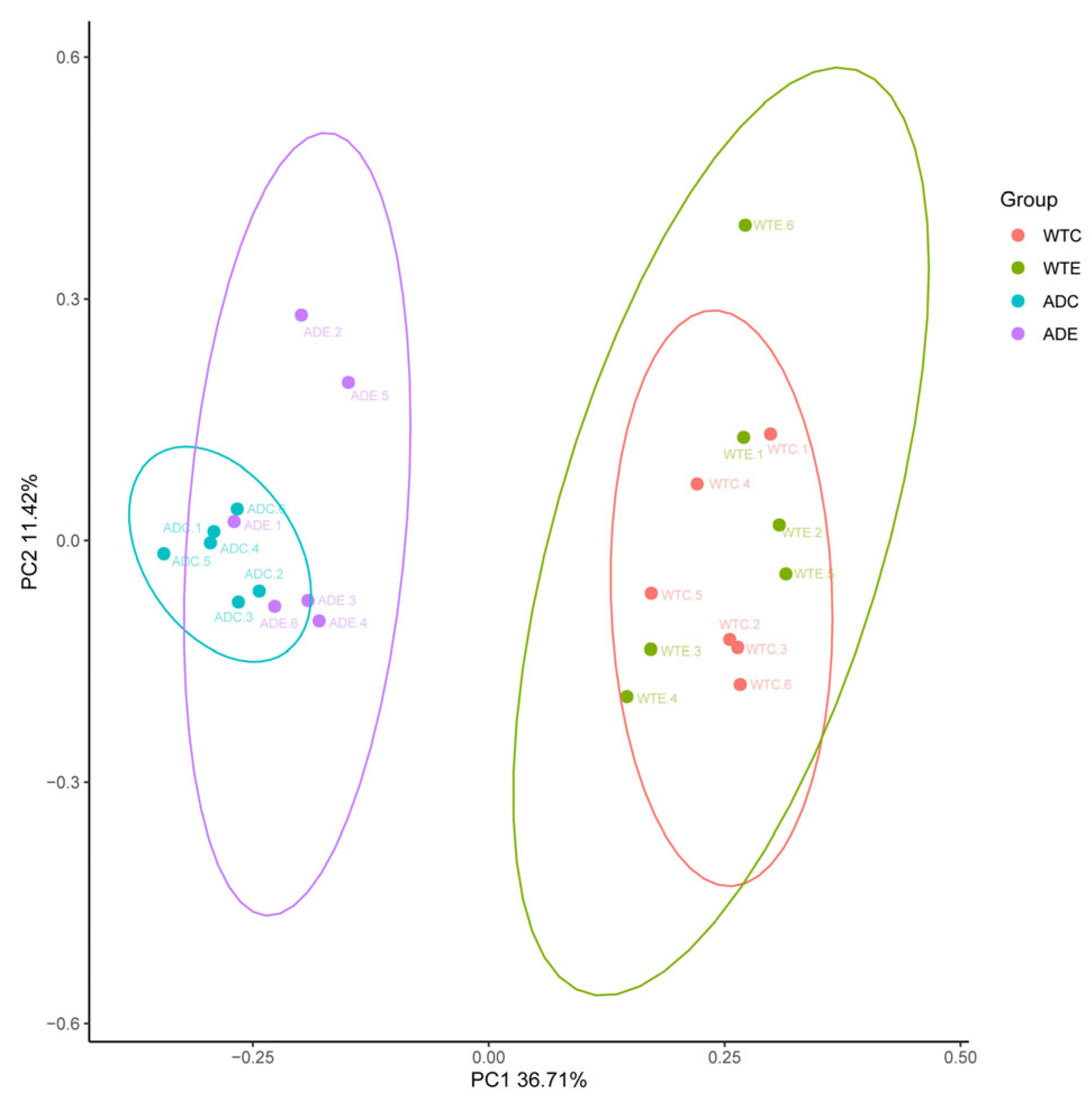
3.2.2. β Diversity Analysis
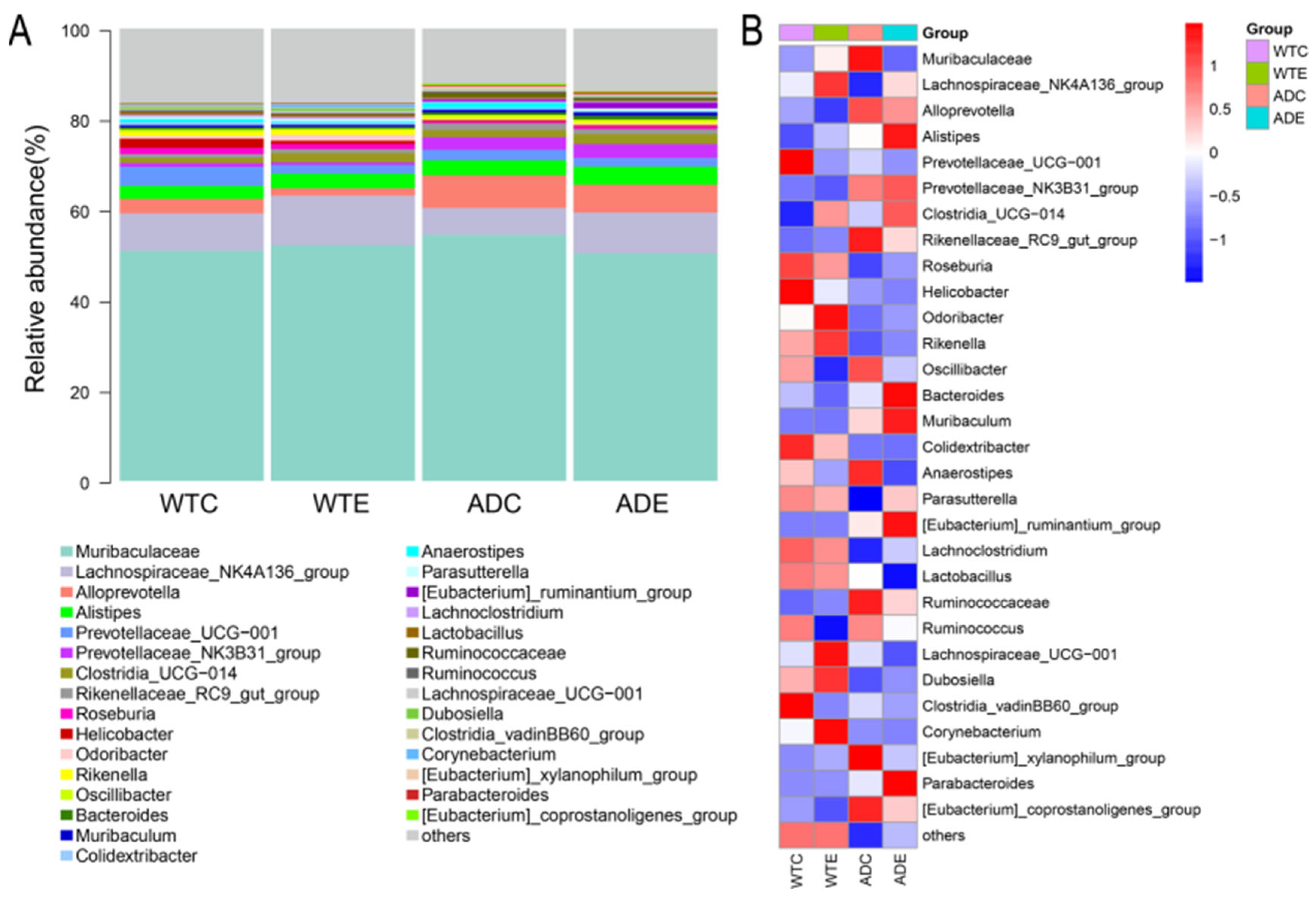
3.3. Analysis of the Composition of the Murine Gut Microbiota
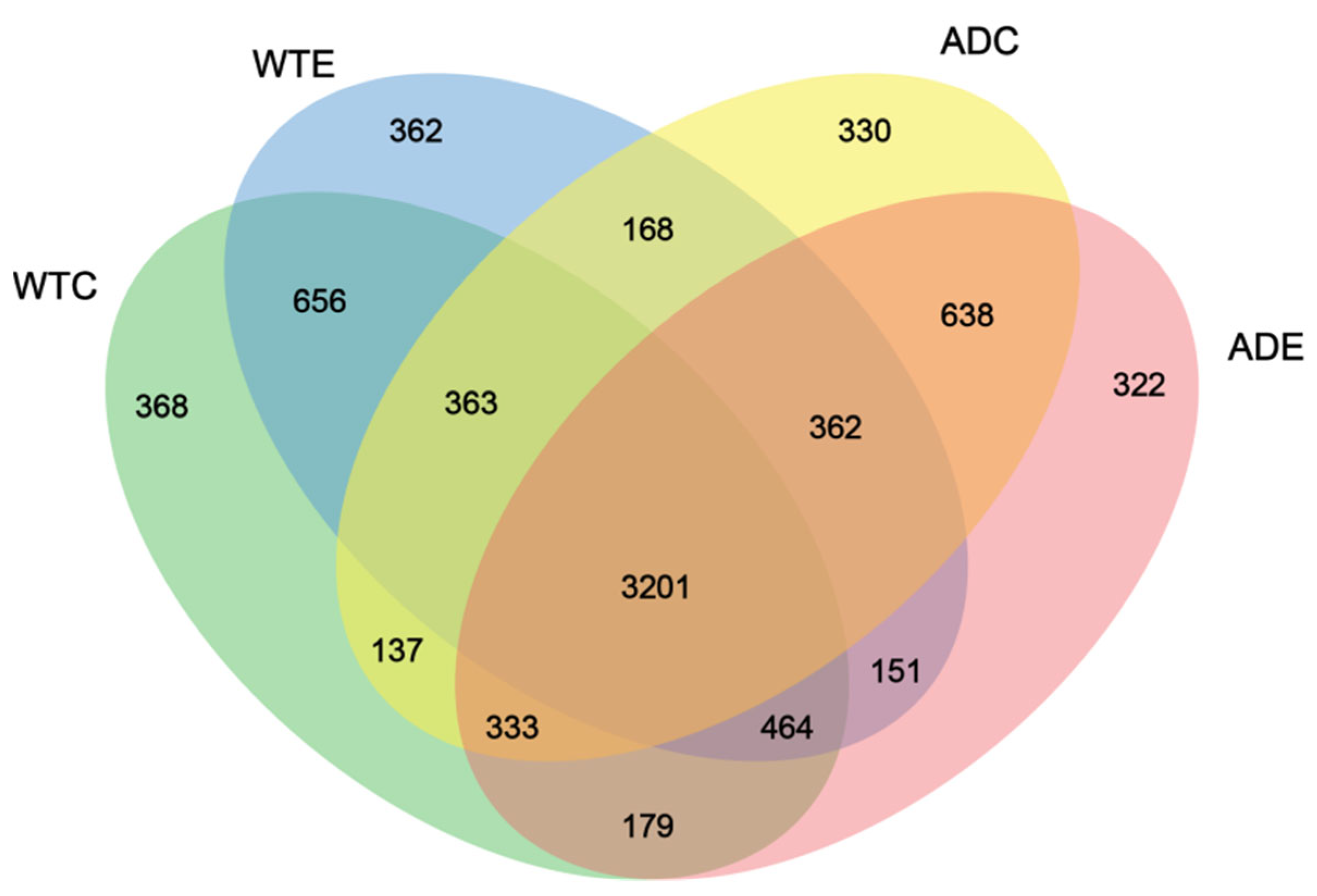
3.3.1. Venn Diagram Analysis of the Species
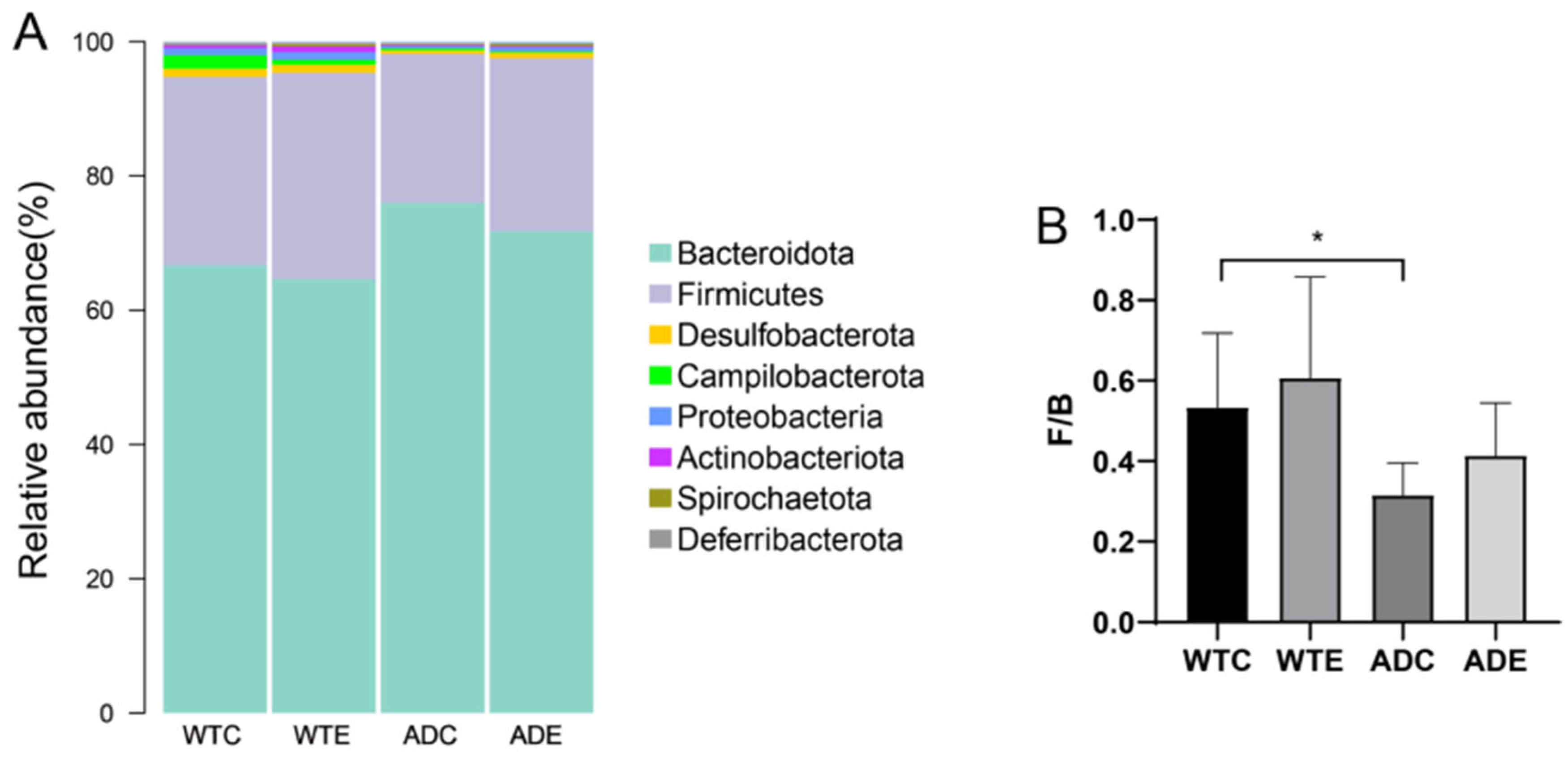
3.3.2. Species Composition of the Murine Gut Microbiota at the Phylum Level
3.3.3. Species Composition of the Murine Gut Microbiota at the Genus Level
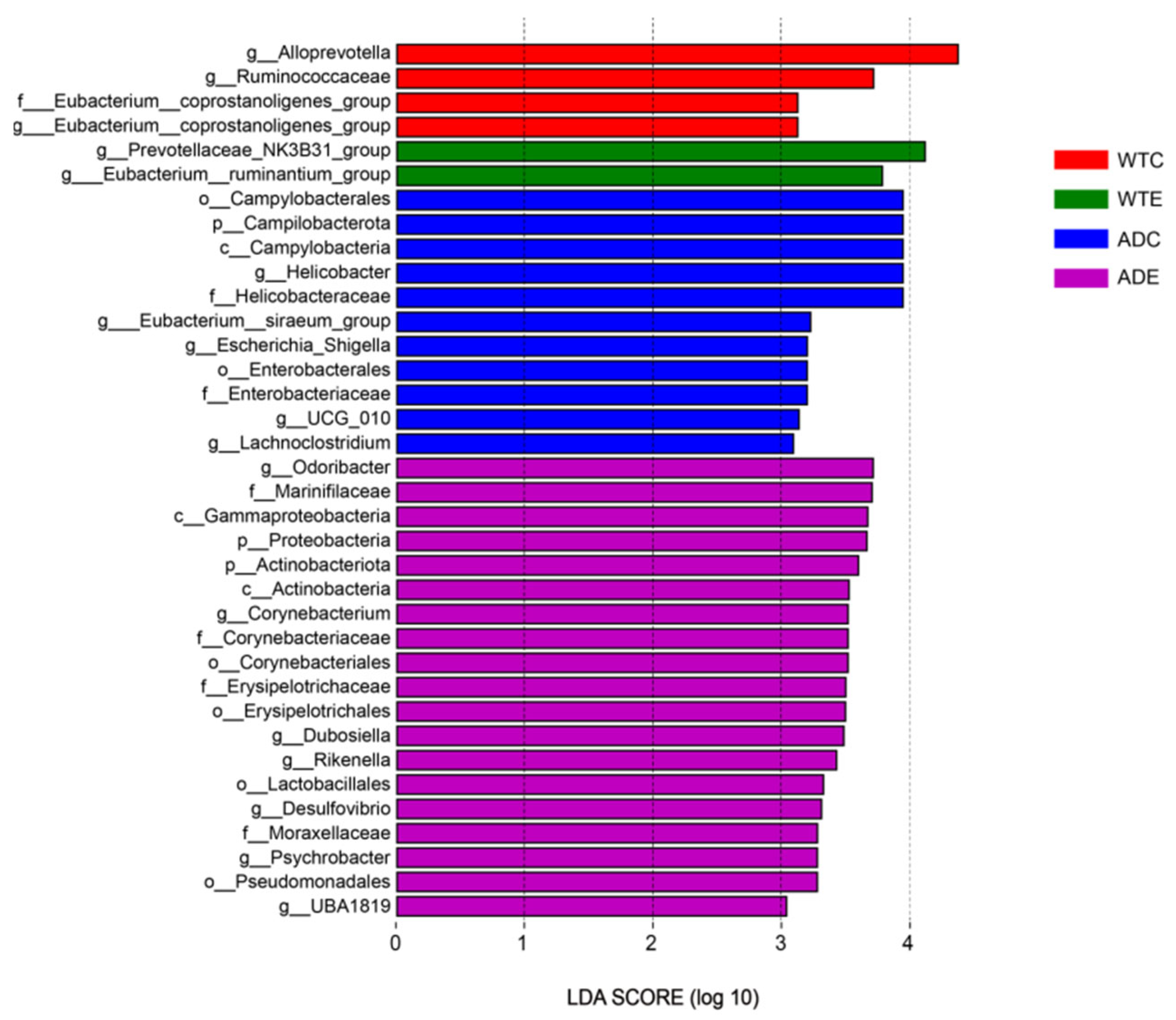
3.4. LEfSe Analysis of Murine Gut Microbiota
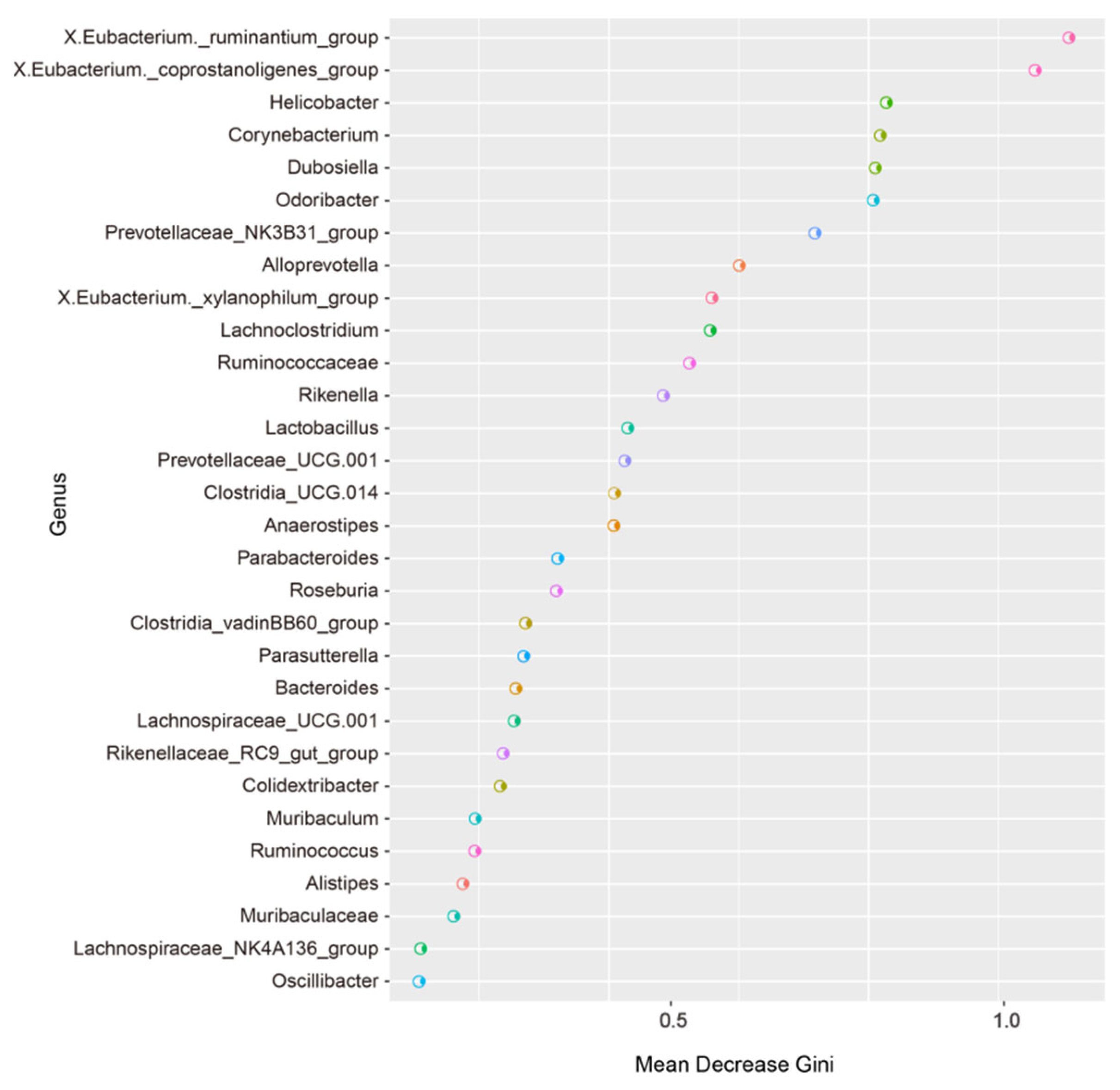
3.5. Random Forest Analysis of the Murine Gut Microbiota
3.6. Gene Function Analysis of the Murine Gut Microbiota
3.7. Correlation Analysis Between Gut Microbiota and Morris Water Maze Performance in Mice
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tiwari, S.; Atluri, V.; Kaushik, A.; Yndart, A.; Nair, M. Alzheimer’s disease: Pathogenesis, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 5541–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhanawat, M.; Malik, G.; Wilson, K.; Gupta, S.; Gupta, N.; Sardana, S. The Gut Microbiota-Brain Axis: A New Frontier in Alzheimer’s Disease Pathology. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2025, 24, 7–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocahan, S.; Doğan, Z. Mechanisms of Alzheimer’s Disease Pathogenesis and Prevention: The Brain, Neural Pathology, N-methyl-D-aspartate Receptors, Tau Protein and Other Risk Factors. Clin. Psychopharmacol. Neurosci. 2017, 15, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreiro, A.L.; Choi, J.; Ryou, J.; Newcomer, E.P.; Thompson, R.; Bollinger, R.M.; Hall-Moore, C.; Ndao, I.M.; Sax, L.; Benzinger, T.L.S.; et al. Gut microbiome composition may be an indicator of preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabo2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heravi, F.S.; Naseri, K.; Hu, H. Gut Microbiota Composition in Patients with Neurodegenerative Disorders (Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s) and Healthy Controls: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, A.; Cattane, N.; Galluzzi, S.; Provasi, S.; Lopizzo, N.; Festari, C.; Ferrari, C.; Guerra, U.P.; Paghera, B.; Muscio, C.; et al. Association of brain amyloidosis with pro-inflammatory gut bacterial taxa and peripheral inflammation markers in cognitively impaired elderly. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 49, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Berk, M.; Carvalho, A.; Caso, J.R.; Sanz, Y.; Walder, K.; Maes, M. The Role of the Microbial Metabolites Including Tryptophan Catabolites and Short Chain Fatty Acids in the Pathophysiology of Immune-Inflammatory and Neuroimmune Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 4432–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harach, T.; Marungruang, N.; Duthilleul, N.; Cheatham, V.; Mc Coy, K.D.; Frisoni, G.; Neher, J.J.; Fåk, F.; Jucker, M.; Lasser, T.; et al. Reduction of Abeta amyloid pathology in APPPS1 transgenic mice in the absence of gut microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minter, M.R.; Zhang, C.; Leone, V.; Ringus, D.L.; Zhang, X.; Oyler-Castrillo, P.; Musch, M.W.; Liao, F.; Ward, J.F.; Holtzman, D.M.; et al. Antibiotic-induced perturbations in gut microbial diversity influences neuro-inflammation and amyloidosis in a murine model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augusto-Oliveira, M.; Arrifano, G.P.; Leal-Nazaré, C.G.; Santos-Sacramento, L.; Lopes-Araújo, A.; Royes, L.F.F.; Crespo-Lopez, M.E. Exercise Reshapes the Brain: Molecular, Cellular, and Structural Changes Associated with Cognitive Improvements. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 6950–6974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, T. Preventive Strategies for Cognitive Decline and Dementia: Benefits of Aerobic Physical Activity, Especially Open-Skill Exercise. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marttinen, M.; Ala-Jaakkola, R.; Laitila, A.; Lehtinen, M.J. Gut Microbiota, Probiotics and Physical Performance in Athletes and Physically Active Individuals. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredi, J.N.; Gupta, S.K.; Vyavahare, S.; Deak, F.; Lu, X.; Buddha, L.; Wankhade, U.; Lohakare, J.; Isales, C.; Fulzele, S. Gut microbiota dysbiosis in Alzheimer’s disease (AD): Insights from human clinical studies and the mouse AD models. Physiol. Behav. 2025, 290, 114778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yuan, S.; Jian, Y.; Lei, Y.; Hu, Z.; Yang, Q.; Yan, X.; Zheng, L.; Li, J.; Liu, W. Aerobic exercise regulates GPR81 signal pathway and mediates complement- microglia axis homeostasis on synaptic protection in the early stage of Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2023, 331, 122042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, B.; Biswas, P.; Gulati, M.; Rani, P.; Gupta, R. Gut microbiome and Alzheimer’s disease: What we know and what remains to be explored. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 102, 102570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junyi, L.; Yueyang, W.; Bin, L.; Xiaohong, D.; Wenhui, C.; Ning, Z.; Hong, Z. Gut Microbiota Mediates Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease: Unraveling Key Factors and Mechanistic Insights. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 3746–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Gao, G.; Kwok, L.-Y.; Sun, Z. Gut microbiome-targeted therapies for Alzheimer’s disease. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2271613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Feng, Q.; Liang, S.; Sonne, S.B.; Xia, Z.; Qiu, X.; Li, X.; Long, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; et al. A catalog of the mouse gut metagenome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, S.; Rao, S.; Khattak, A.; Zamir, F.; Chaari, A. Physical Exercise and the Gut Microbiome: A Bidirectional Relationship Influencing Health and Performance. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Zhu, M.; Yan, X.; Cheng, Y.; Shao, L.; Liu, X.; Jiang, R.; Wu, S. Structural and Functional Dysbiosis of Fecal Microbiota in Chinese Patients With Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 634069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, N.M.; Kerby, R.L.; Dill-Mcfarland, K.A.; Harding, S.J.; Merluzzi, A.P.; Johnson, S.C.; Carlsson, C.M.; Asthana, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; et al. Gut microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.N.; Momeni, N.; Chiti, H.; Mahmoodnasab, H.; Ahmadi, M.; Heidarzadeh, S. Higher gut Bacteroidetes and Actinobacteria population in early pregnancy is associated with lower risk of gestational diabetes in the second trimester. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2025, 25, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Yang, T.; Tian, Z.; Shi, C.; Yan, C.; Li, H.; Du, Y.; Li, G. Progress in the investigation of the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio as a potential pathogenic factor in ulcerative colitis. J. Med. Microbiol. 2025, 74, 001966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhang, X.; Akbar, M.T.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhi, L.; Shen, Q. Exploration of the Muribaculaceae Family in the Gut Microbiota: Diversity, Metabolism, and Function. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, T.; Zhu, X.; Feng, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cui, T.; Li, M. Jiedu Yizhi Formula Improves Cognitive Function by Regulating the Gut Dysbiosis and TLR4/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2023, 19, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Huang, S.-H.; Ding, H.-F.; Kwek, E.; Liu, J.-H.; Chen, Z.-X.; Ma, K.Y.; Chen, Z.-Y. Adverse effect of oxidized cholesterol exposure on colitis is mediated by modulation of gut microbiota. J. Hazard Mater. 2023, 459, 132057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Mao, B.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y. Serum metabolomics combined with gut microbiota reveals the effects of Polygala tenuifolia polysaccharide on the metabolic and microbial profiles in SAMP8 mouse. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 251, 116442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Cao, Z.; Du, Y.; Xu, G.; Wang, J.; Zheng, J.; Lu, Y. Bidirectional Two-Sample, Two-Step Mendelian Randomisation Study Reveals Mediating Role of Gut Microbiota Between Vitamin B Supplementation and Alzheimer’s Disease. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suolang, Q.; Basang, Z.; Silang, W.; Nima, C.; Yang, Q.; Da, W. Study on intestinal microbial communities of three different cattle populations on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0312314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Precup, G.; Vodnar, D.-C. Gut Prevotella as a possible biomarker of diet and its eubiotic versus dysbiotic roles: A comprehensive literature review. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 122, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.; Guo, Y.; Chen, M.; Lu, X.; Guo, Z.; Zheng, B. Gut microbiome-serum metabolic profiles: Insight into the hypoglycemic effect of Porphyra haitanensis glycoprotein on hyperglycemic mice. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 7977–7991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.-Y.; Chou, P.-L.; Yang, J.-C.; Chien, C.-T. Silicon-containing water intake confers antioxidant effect, gastrointestinal protection, and gut microbiota modulation in the rodents. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Ma, Y.; Xiong, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Y.; Ma, A. Ameliorating Effects of Vitamin K2 on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukari, Z.; Emmanuel, T.; Woodward, J.; Ferguson, R.; Ezughara, M.; Darga, N.; Lopes, B.S. The Global Challenge of Campylobacter: Antimicrobial Resistance and Emerging Intervention Strategies. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2025, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Liu, X.; Han, F.; Zhang, L.; Bu, J.; Wu, S.; Wang, J. Helicobacter pylori CagA+ strains modulate colorectal pathology by regulating intestinal flora. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025, 25, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, A.; Lordan, C.; Ross, R.P.; Cotter, P.D. Gut microbes from the phylogenetically diverse genus Eubacterium and their various contributions to gut health. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1802866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Che, X.; Ma, K.; Guo, W.; Wang, S.; Sun, Z.P.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Y. Chronic Cr(VI) exposure-induced biotoxicity involved in liver microbiota-gut axis disruption in Phoxinus lagowskii Dybowski based on multi-omics technologies. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 368, 125759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, X.-N.; Long, D.-P.; Yin, S.-S.; Qing, R.-Y.; Chi, Z.-Z.; Gao, M.-Q.; Zhu, M.-Q. The efficient separation of bioactive components from Eucommia ulmoides Oliver using membrane filtration technology and its mechanisms in preventing alcoholic liver disease. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 351, 123100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Yu, X. Gut microbiota in patients with sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1513253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Q.; Pan, R.; Li, X.; Christian, M.; Zhu, P.; Zhao, J. Chrysanthemum extract mitigates high-fat diet-induced inflammation, intestinal barrier damage and gut microbiota disorder. Food Funct. 2025, 16, 1347–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurakawa, T.; Kani, K.; Chudan, S.; Nishikawa, M.; Tabuchi, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Nagai, Y.; Ikushiro, S.; Furusawa, Y. Rice Kefiran Ameliorates Obesity and Hepatic Steatosis Through the Change in Gut Microbiota. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Jin, Y.; Chu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, X. Genetic prediction of blood metabolites mediating the relationship between gut microbiota and Alzheimer’s disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Front Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1414977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubeda, C.; Vázquez-Carretero, M.D.; Luque-Tirado, A.; Ríos-Reina, R.; Rubio-Sánchez, R.; Franco-Macías, E.; García-Miranda, P.; Calonge, M.L.; Peral, M.J. Fecal Volatile Organic Compounds and Microbiota Associated with the Progression of Cognitive Impairment in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 24, 707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiippala, K.; Barreto, G.; Burrello, C.; Diaz-Basabe, A.; Suutarinen, M.; Kainulainen, V.; Bowers, J.R.; Lemmer, D.; Engelthaler, D.M.; Eklund, K.K.; et al. Novel Odoribacter splanchnicus Strain and Its Outer Membrane Vesicles Exert Immunoregulatory Effects in vitro. Front Microbiol. 2020, 11, 575455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber-Ruano, I.; Calvo, E.; Mayneris-Perxachs, J.; Rodríguez-Peña, M.M.; Ceperuelo-Mallafré, V.; Cedó, L.; Núñez-Roa, C.; Miro-Blanch, J.; Arnoriaga-Rodríguez, M.; Balvay, A.; et al. Orally administered Odoribacter laneus improves glucose control and inflammatory profile in obese mice by depleting circulating succinate. Microbiome 2022, 10, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tu, S.; Ji, X.; Wu, J.; Meng, J.; Gao, J.; Shao, X.; Shi, S.; Wang, G.; Qiu, J.; et al. Dubosiella newyorkensis modulates immune tolerance in colitis via the L-lysine-activated AhR-IDO1-Kyn pathway. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Zhu, H.; Li, X.; Shi, W.; Guo, Y.; Du, X.; Zhang, L.; Su, L.; Qin, C. Comparative Metagenomics and Metabolomes Reveals Abnormal Metabolism Activity Is Associated with Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer’s Disease Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.-H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Zhao, L.; Sheng, Y.-Y.; Tao, G.-S.; Xue, Y.-Z. Gut microbial characteristical comparison reveals potential anti-aging function of Dubosiella newyorkensis in mice. Front Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1133167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Ni, D.; Zhang, X.; Hao, W.; Yuan, Q.; Xu, W.; Mu, W.; Wu, D.; Wu, X.; et al. Polymerization of dietary fructans differentially affects interactions among intestinal microbiota of colitis mice. ISME J. 2025, 19, wrae262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovynev, A.; Ying, Z.; Zhang, S.; Olgiati, E.; Lambooij, J.M.; Visentin, C.; Guigas, B.; Ducarmon, Q.R.; Rensen, P.C.N.; Schönke, M. Timing Matters: Late, but Not Early, Exercise Training Ameliorates MASLD in Part by Modulating the Gut-Liver Axis in Mice. J. Pineal. Res. 2024, 76, e70003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-J.; Fu, J.-J.; Liao, Z.-Y.; Liu, Y.-X.; He, J.; He, L.-Y.; Bai, J.; Yang, J.-Y.; Niu, S.-Q.; Guo, J.-L. Z-ligustilide alleviates atherosclerosis by reconstructing gut microbiota and sustaining gut barrier integrity through activation of cannabinoid receptor 2. Phytomedicine 2024, 135, 156117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Q.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Z.; Wang, C.; Xia, M.; Chen, B.; Lv, B.; Peres Diaz, L.; Li, X.; Feng, R.; et al. Hydrogen sulfide produced by the gut microbiota impairs host metabolism via reducing GLP-1 levels in male mice. Nat. Metab. 2024, 6, 1601–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, G.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; He, K.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, X.; Xie, B. The gut microbiota and metabolite profiles are altered in patients with spinal cord injury. Mol. Brain 2023, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Wu, X.; Liu, W.; Zheng, L.; Tang, C. Effects of Treadmill Exercise on Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer’s Disease Model Mice and Wild-Type Mice. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081765
Zhao Z, Wu X, Liu W, Zheng L, Tang C. Effects of Treadmill Exercise on Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer’s Disease Model Mice and Wild-Type Mice. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081765
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zhe, Xingqing Wu, Wenfeng Liu, Lan Zheng, and Changfa Tang. 2025. "Effects of Treadmill Exercise on Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer’s Disease Model Mice and Wild-Type Mice" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081765
APA StyleZhao, Z., Wu, X., Liu, W., Zheng, L., & Tang, C. (2025). Effects of Treadmill Exercise on Gut Microbiota in Alzheimer’s Disease Model Mice and Wild-Type Mice. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1765. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081765





