The Effects of Lactococcus garvieae and Pediococcus pentosaceus on the Characteristics and Microbial Community of Urtica cannabina Silage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Characteristics of Wilted and Ensiled Nettle
2.4. Bacterial Community Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nutritional Quality and Fermentation Characteristics of Nettle Silage
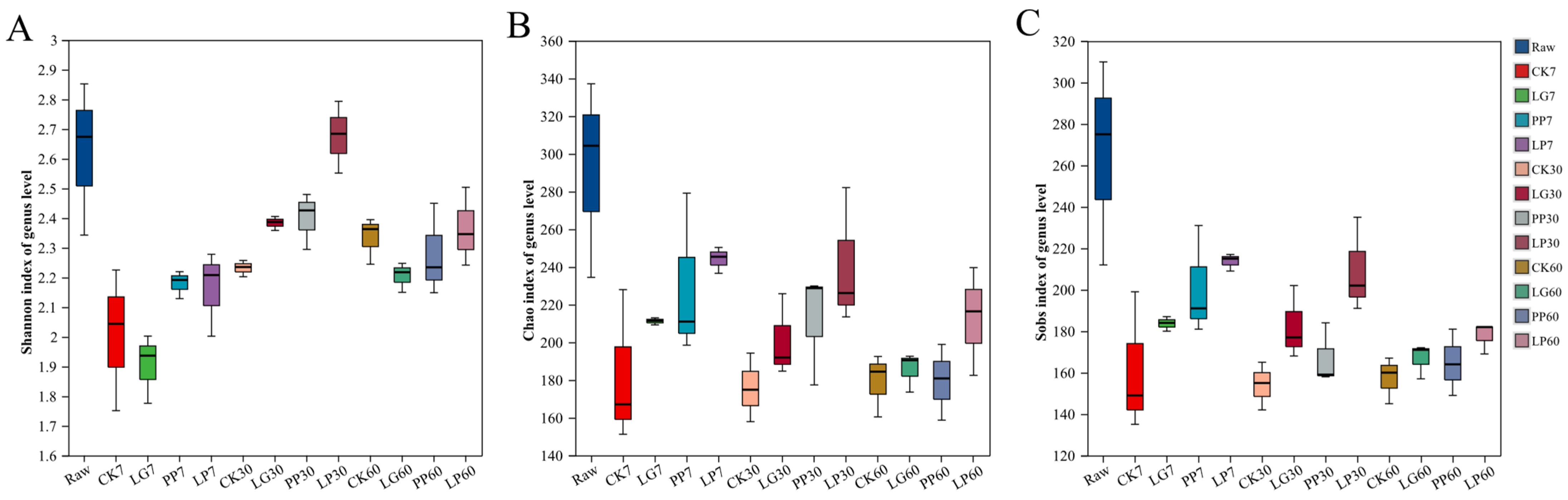
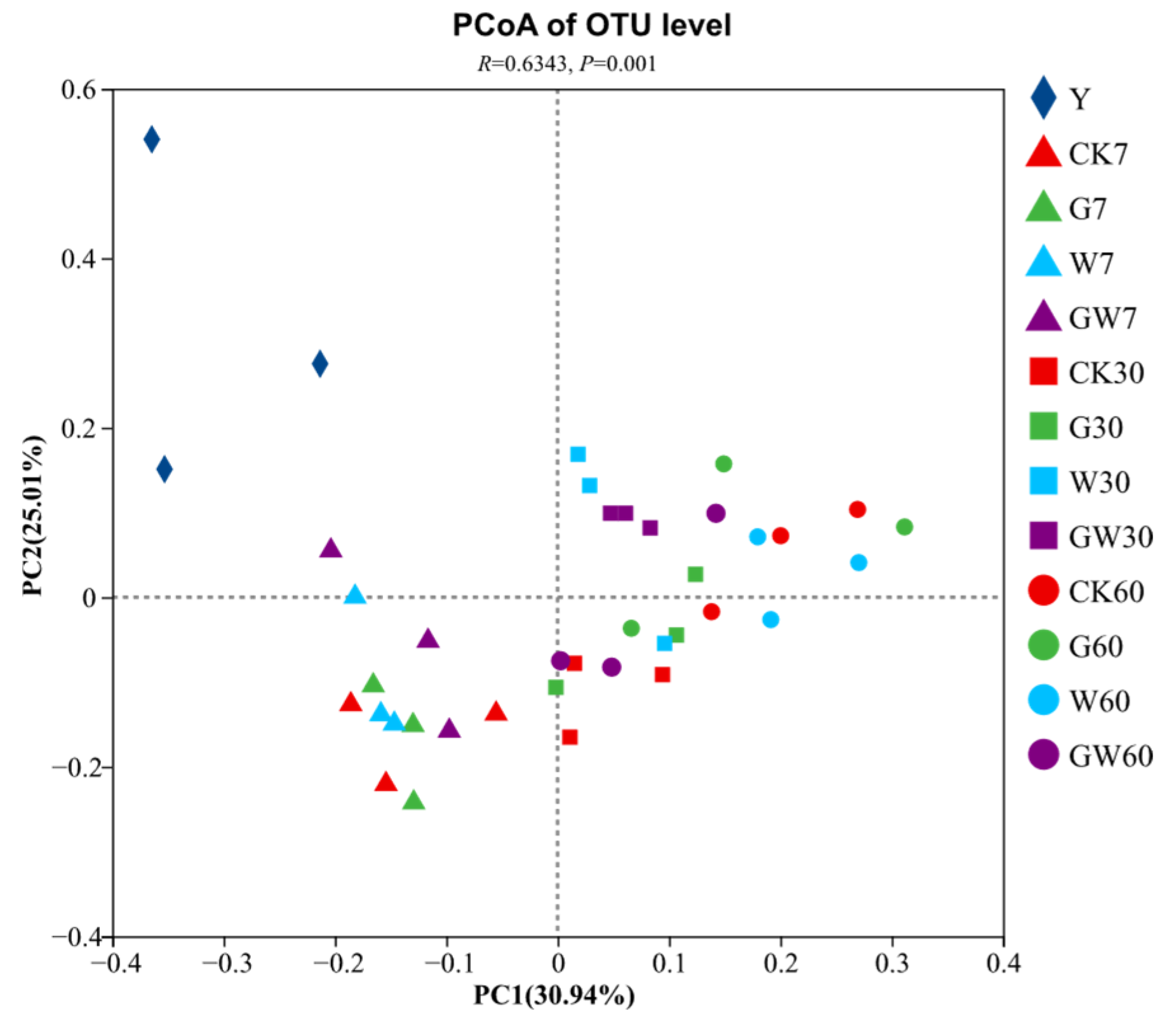
3.2. Alpha Diversity Analysis of Nettle Silage and Beta Diversity Analysis
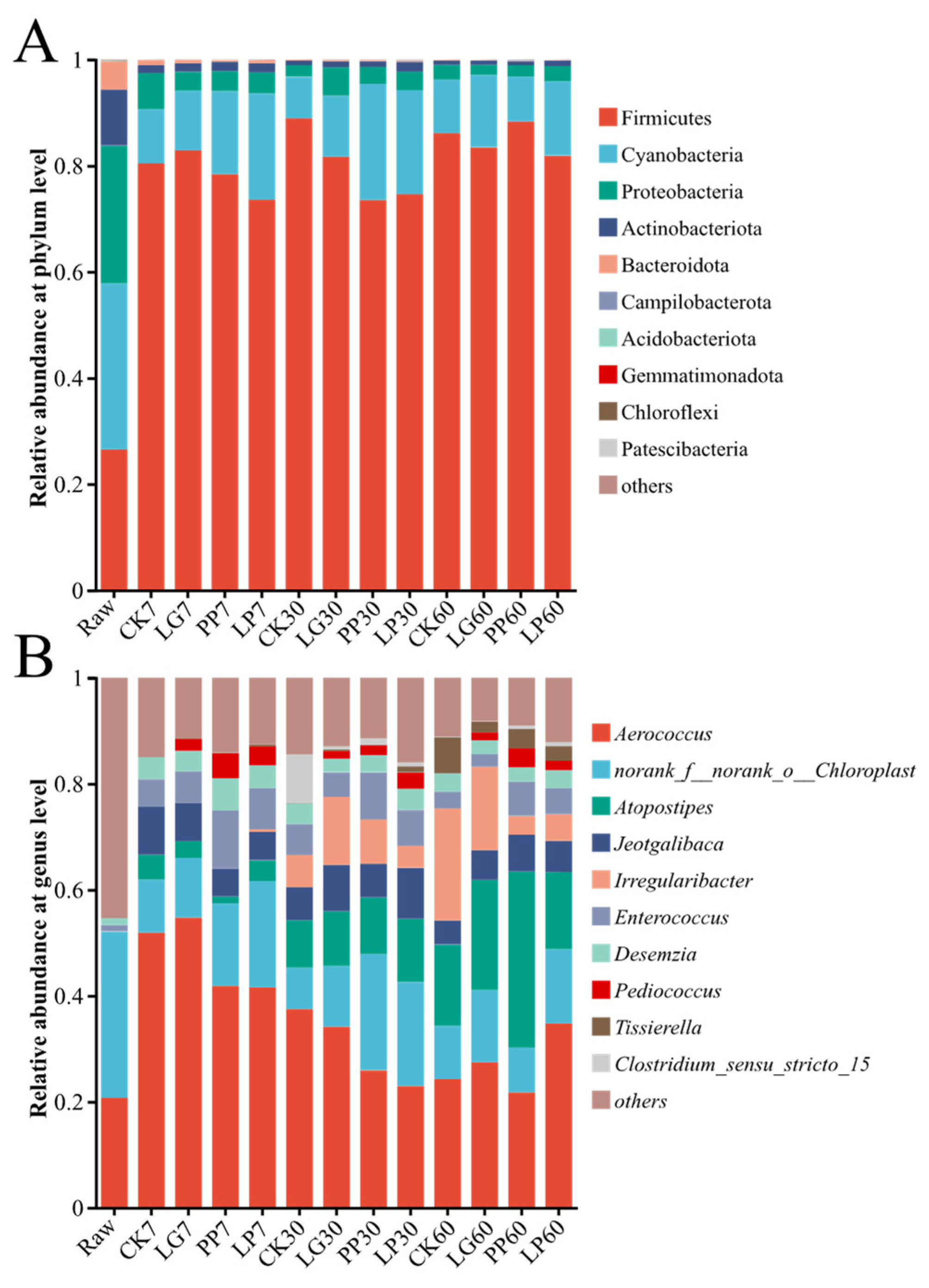
3.3. Analysis of Microbial Community Composition of LAB Inoculated with Urtica cannabinae
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Inoculating LAB from Urtica cannabinae on Nutritional and Fermentation Quality of Nettle Silage
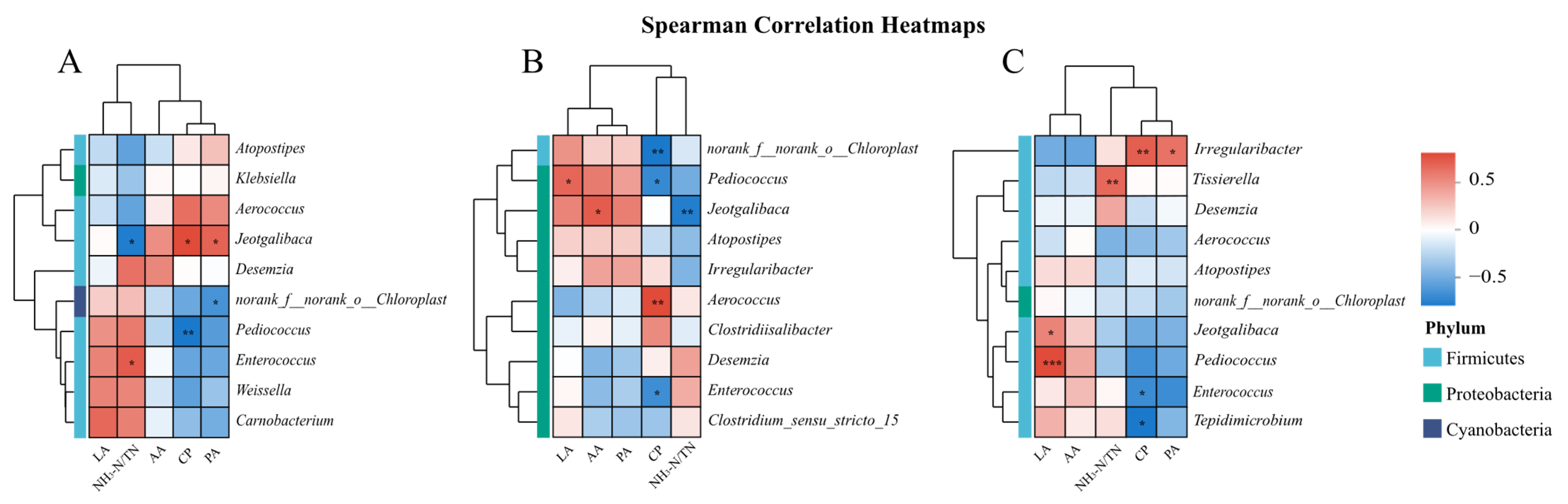
4.2. Effect of Inoculating LAB Derived from Urtica cannabinae on Composition of Nettle Silage Microbiota
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| LAB | Lactic acid bacteria |
| WSC | Water-soluble carbohydrate |
| CK | Control group |
| DM | Dry matter |
| CP | Crude protein |
| NDF | Neutral detergent fiber |
| ADF | Acid detergent fiber |
| EE | Ether extract |
| AA | Acetic acid |
| PA | Propionic acid |
| BA | Butyric acid |
References
- Kregiel, D.; Pawlikowska, E.; Antolak, H. Urtica spp.: Ordinary plants with extraordinary properties. Molecules 2018, 23, 1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y. Natural Grassland Resources and Utilization of Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- He, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Effect of applying lactic acid bacteria and cellulase on the fermentation quality, nutritive value, tannins profile and in vitro digestibility of Neolamarckia cadamba leaves silage. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhusal, K.K.; Magar, S.K.; Thapa, R.; Lamsal, A.; Bhandari, S.; Maharjan, R.; Shrestha, J. Nutritional and pharmacological importance of stinging nettle (Urtica dioica L.): A review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Chen, Y.; Ma, C.; Chai, Y.; Jia, S.; Zhang, F. Potential factors causing failure of whole plant nettle (Urtica cannabina) silages. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1113050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shao, T.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z. Fermentation profiles, bacterial community compositions, and their predicted functional characteristics of grass silage in response to epiphytic microbiota on legume forages. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 830888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung Jr, L.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage review: Interpretation of chemical, microbial, and organoleptic components of silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, C.O.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Jiang, J. The performance of lactic acid bacteria in silage production: A review of modern biotechnology for silage improvement. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 266, 127212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soundharrajan, I.; Park, H.S.; Rengasamy, S.; Sivanesan, R.; Choi, K.C. Application and future prospective of lactic acid bacteria as natural additives for silage production—A review. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Nag, M.; Lahiri, D.; Sarkar, T.; Pati, S.; Kari, Z.A.; Ray, R.R. Engineered biofilm: Innovative nextgen strategy for quality enhancement of fermented foods. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 808630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Yuan, X.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Guo, G.; Bai, Y.; Shao, T. Characteristics of isolated lactic acid bacteria and their effects on the silage quality. Asian—Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Du, S.; Ge, G.; Wan, T.; Jia, Y. Selection of lactic acid bacteria from native grass silage and its effects as inoculant on silage fermentation. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 3169–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, Y.; Yin, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Pan, Q. Effects of nettle cube diet on rumen bacterial community structure, fermentation parameters and growth performance of Tibetan Sheep. Chin. J. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 34, 1683–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jin, Y.; Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Li, P. Effect of corn flour on the quality of Urtica cannabina silage. Acta Pratac. Sin. 2015, 24, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, S.; Chai, Y.; Yang, H.J.; Zhang, F.; Ma, C. Isolation and identification of dominant lactic acid bacteria from Urtica cannabina silage. Pratac. Sci. 2023, 40, 1410–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.; Huang, R.; Wang, X.; Ma, C.; Zhang, F. Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Lactiplantibacillus brevis on fermentation, aerobic stability, and the bacterial community of paper mulberry silage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1063914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Qiu, R.; Sun, L.; Bao, J.; Liu, Y.; Ge, G.; Wang, Z. Effect isolated lactic acid bacteria inoculation on the quality, bacterial composition and metabolic characterization of Caragana korshinskii silage. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2024, 11, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xiong, H.; Wen, Z.; Tian, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, L.; Sun, B. Effects of different concentrations of Lactobacillus plantarum and Bacillus licheniformis on silage quality, in vitro fermentation and microbial community of hybrid Pennisetum. Animals 2022, 12, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherburn, M.W. Phenol-hypochlorite reaction for determination of ammonia. Anal. Chem. 1967, 39, 971–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Feng, Y.; Pei, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Fu, S.; Peng, Z. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum additive and temperature on the ensiling quality and microbial community dynamics of cauliflower leaf silages. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Xu, J.; Li, M.; Xi, Y.; Sun, H.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, Y. Synergistic effects of ferulic acid esterase-producing lactic acid bacteria, cellulase and xylanase on the fermentation characteristics, fibre and nitrogen components and microbial community structure of Broussonetia papyrifera during ensiling. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024, 104, 3543–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Huang, B.; Lin, J.; Yang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Liu, D.; Sun, B. Isolation and screening of high biofilm producing lactic acid bacteria, and exploration of its effects on the microbial hazard in corn straw silage. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 136009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Lindow, S.E.; Zhang, J. Lactobacillus parafarraginis ZH1 producing anti-yeast substances to improve the aerobic stability of silage. Anim. Sci. J. 2018, 89, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Hao, J.; Zhao, M.; Yan, X.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ge, G. Effects of different temperature and density on quality and microbial population of wilted alfalfa silage. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauschild, A.H. Selective effect of pH on the production of exocellular protein by Clostridium perfringens type D. J. Bacteriol. 1966, 92, 800–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Trijp, M.P.; Rösch, C.; An, R.; Keshtkar, S.; Logtenberg, M.J.; Hermes, G.D.; Hooiveld, G.J. Fermentation kinetics of selected dietary fibers by human small intestinal microbiota depend on the type of fiber and subject. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 2000455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, Z.; Shi, S.; Lin, M. Lignocellulose degradation patterns, structural changes, and enzyme secretion by Inonotus obliquus on straw biomass under submerged fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, G.; Jiang, X.; Yang, J.; Lv, J.; Zhang, Y. Cellulase interacts with lactic acid bacteria to affect fermentation quality, microbial community, and ruminal degradability in mixed silage of soybean residue and corn stover. Animals 2021, 11, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Peng, Z.; Xiao, M.; Huang, T.; Yang, S.; Liu, K.; Xiong, T. Modulation of the microbiome-fat-liver axis by lactic acid bacteria: A potential alleviated role in high-fat-diet-induced obese mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 10361–10374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Bai, Y.; Jia, Y.; Shao, T. Ensiling as pretreatment of rice straw: The effect of hemicellulase and Lactobacillus plantarum on hemicellulose degradation and cellulose conversion. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zi, X.; Zhou, H.; Lv, R.; Tang, J.; Cai, Y. Silage fermentation and ruminal degradation of cassava foliage prepared with microbial additive. AMB Express 2019, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comino, L.; Tabacco, E.; Righi, F.; Revello-Chion, A.; Quarantelli, A.; Borreani, G. Effects of an inoculant containing a Lactobacillus buchneri that produces ferulate-esterase on fermentation products, aerobic stability, and fibre digestibility of maize silage harvested at different stages of maturity. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2014, 198, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Du, S.; Sun, L.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Sun, P.; Wang, Z. Volatile metabolomics and metagenomics reveal the effects of lactic acid bacteria on alfalfa silage quality, microbial communities, and volatile organic compounds. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; He, L.; Xing, Y.; Zhou, W.; Pian, R.; Yang, F.; Zhang, Q. Bacterial diversity and fermentation quality of Moringa oleifera leaves silage prepared with lactic acid bacteria inoculants and stored at different temperatures. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 284, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oloyede, G.K.; Oyelola, M.S. Chrysen-2-ol derivative from west indian wood nettle Laportea aestuans (L.) chew inhibits oxidation and microbial growth in vitro. Excli J. 2013, 12, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bobis, O.; Dezmirean, D.S.; Tomos, L.; Chirila, F.; Al Marghitas, L. Influence of phytochemical profile on antibacterial activity of different medicinal plants against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2015, 51, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zheng, P.; Zou, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Influence of pyroligneous acid on fermentation parameters. CO2 production and bacterial communities of rice straw and stylo silage, Front. Microbiol. 2021, 8, 701434121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulahal, N.; Degraeve, P. Phenolic-rich plant extracts with antimicrobial activity: An alternative to food preservatives and biocides? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 753518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Lee, H.J. Antimicrobial activity of probiotic bacteria isolated from plants: A review. Foods 2025, 14, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Jia, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Lin, Y.; Yang, F.; Ni, K. Characterization of phyllosphere endophytic lactic acid bacteria reveals a potential novel route to enhance silage fermentation quality. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Index | Time | Treatment | p-Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | LG | PP | LP | Treatment | Time | Treatment × Time | ||
| DM | 7 d | 37.72 ± 0.29 Aa | 38.74 ± 0.13 Aa | 38.63 ± 0.32 Aa | 38.64 ± 0.32 Aa | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.909 |
| 15 d | 36.68 ± 0.31 Bab | 37.58 ± 0.52 ABb | 37.27 ± 0.58 ABb | 37.86 ± 0.21 Aa | ||||
| 30 d | 36.33 ± 0.25 Abc | 37.12 ± 0.46 Ab | 36.89 ± 1.4 Ab | 36.67 ± 0.53 Ab | ||||
| 60 d | 35.45 ± 0.52 Ac | 36.52 ± 0.39 Ab | 36.38 ± 0.59 Ab | 36.1 ± 0.16 Ab | ||||
| CP (% DM) | 7 d | 16.23 ± 0 Aa | 16.08 ± 0.06 ABa | 15.95 ± 0.02 Ba | 16.08 ± 0.13 ABa | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 15 d | 15.82 ± 0.04 BCb | 16 ± 0.03 Aa | 15.93 ± 0.15 ABa | 15.69 ± 0.21 Cb | ||||
| 30 d | 15.27 ± 0.01 Ac | 15.19 ± 0.02 Ab | 15.14 ± 0 Ab | 14.21 ± 0.08 Bc | ||||
| 60 d | 13.27 ± 0.01 Ad | 13.23 ± 0.03 Ac | 12.37 ± 0.01 Bc | 13.11 ± 0.03 Ad | ||||
| NDF (% DM) | 7 d | 28.03 ± 1.18 Aa | 27.81 ± 1.36 Aa | 27.97 ± 0.43 Aa | 28.22 ± 1.17 Aa | 0.597 | 0.000 | 0.133 |
| 15 d | 27.45 ± 0.84 Aa | 27.14 ± 1.36 Aab | 27.43 ± 2.54 Aab | 27.41 ± 2.78 Aab | ||||
| 30 d | 27.77 ± 2.64 Aa | 26.57 ± 1.01 Bab | 26.35 ± 0.92 Bb | 26.47 ± 2.4 Bb | ||||
| 60 d | 25.59 ± 0.9 Bb | 26.22 ± 2.84 Ab | 26.31 ± 0.16 Ab | 26.46 ± 1.55 Ab | ||||
| ADF (% DM) | 7 d | 19 ± 1.36 Aa | 19.01 ± 0.63 Aa | 19.16 ± 0.45 Aa | 19.24 ± 0.79 Aa | 0.014 | 0.000 | 0.351 |
| 15 d | 18.11 ± 0.32 Aa | 18.37 ± 0.71 Aa | 18.98 ± 0.84 Aab | 18.63 ± 1.34 Aab | ||||
| 30 d | 17.51 ± 1.88 Aa | 17.73 ± 0.9 Aa | 18.19 ± 0.58 Aab | 18.08 ± 0.78 Aab | ||||
| 60 d | 15.7 ± 0.11 Bb | 17.78 ± 1.89 Aa | 17.61 ± 0.17 Ab | 17.63 ± 1.14 Ab | ||||
| EE (% DM) | 7 d | 6.26 ± 0.25 Aa | 6.94 ± 0.34 Aab | 6.59 ± 0.55 Aab | 7.04 ± 0.23 Aa | 0.006 | 0.000 | 0.014 |
| 15 d | 6.93 ± 0.87 Aa | 7.07 ± 0.81 Aa | 7.59 ± 0.6 Aa | 7.74 ± 0.42 Aa | ||||
| 30 d | 6.44 ± 0.44 Ba | 5.81 ± 0.97 Bbc | 5.45 ± 0.57 Bbc | 7.63 ± 0.64 Aa | ||||
| 60 d | 4.07 ± 0.32 Ab | 4.79 ± 0.19 Ac | 4.51 ± 0.18 Ac | 4.39 ± 0.15 Ab | ||||
| WSCs (% DM) | 7 d | 4.92 ± 0.45 Aa | 4.8 ± 0.3 Aa | 4.83 ± 0.1 Aa | 4.74 ± 0.03 Aa | 0.908 | 0.000 | 0.998 |
| 15 d | 3.61 ± 0.11 Ab | 3.6 ± 0.24 Ab | 3.58 ± 0.19 Ab | 3.59 ± 0.09 Ab | ||||
| 30 d | 2.69 ± 0.01 Ac | 2.67 ± 0.03 Ac | 2.67 ± 0.03 Ac | 2.69 ± 0.11 Ac | ||||
| 60 d | 1.69 ± 0.07 Ad | 1.7 ± 0.13 Ad | 1.74 ± 0.16 Ad | 1.67 ± 0.12 Ad | ||||
| Index | Time | Treatment | p-Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | LG | PP | LP | Treatment | Time | Treatment × Time | ||
| pH | 7 d | 7.85 ± 0.03 Ab | 7.43 ± 0.02 Ba | 7.46 ± 0.02 Ba | 7.53 ± 0.03 Ba | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 15 d | 7.77 ± 0.12 Ab | 7.07 ± 0.03 Cb | 7.14 ± 0.08 Cb | 7.29 ± 0.05 Bb | ||||
| 30 d | 8.35 ± 0.04 Aa | 6.35 ± 0.06 Cc | 6.42 ± 0.04 BCc | 6.56 ± 0.03 Bc | ||||
| 60 d | 8.47 ± 0.17 Aa | 5.01 ± 0.04 Bd | 5.24 ± 0.05 Cd | 5.78 ± 0.02 Dd | ||||
| LA (g/kg DM) | 7 d | 2.68 ± 0.35 Ab | 3.02 ± 0.15 Ab | 2.8 ± 0.12 Ab | 3.06 ± 0.06 Aa | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 15 d | 3.47 ± 0.07 ABa | 3.58 ± 0.54 Aab | 3.47 ± 0.07 ABa | 2.89 ± 0.06 Ba | ||||
| 30 d | 1.39 ± 0.15 Bc | 3.64 ± 0.71 Aa | 3.54 ± 0.06 Aa | 3.27 ± 0.07 Aa | ||||
| 60 d | 0.25 ± 0.01 Bd | 3.68 ± 0.37 Aa | 3.62 ± 0.17 Aa | 3.47 ± 0.15 Aa | ||||
| AA (g/kg DM) | 7 d | 1.86 ± 0.06 Aa | 1.49 ± 0.04 Cc | 1.49 ± 0.08 Cc | 1.61 ± 0.01 Ba | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 15 d | 1.92 ± 0.03 Ca | 2.05 ± 0.01 Ba | 2.26 ± 0.02 Aa | 1.66 ± 0.03 Da | ||||
| 30 d | 0.94 ± 0.04 Cb | 1.79 ± 0.13 Ab | 1.66 ± 0.05 Bb | 1.61 ± 0.01 Ba | ||||
| 60 d | 0.63 ± 0.03 Bc | 1.6 ± 0.08 Ac | 1.6 ± 0.03 Abc | 1.63 ± 0.04 Aa | ||||
| PA (g/kg DM) | 7 d | 0.06 ± 0.01 Ab | 0.06 ± 0.01 Ab | 0.04 ± 0 Ab | 0.05 ± 0.02 Aa | 0.348 | 0.000 | 0.005 |
| 15 d | 0.09 ± 0.01 Bb | 0.09 ± 0.03 Bb | 0.09 ± 0.01 Bab | 0.16 ± 0 Aa | ||||
| 30 d | 0.06 ± 0 Ab | 0.09 ± 0.02 Ab | 0.08 ± 0.01 Aab | 0.07 ± 0.02 Ab | ||||
| 60 d | 0.19 ± 0.05 Aa | 0.18 ± 0.01 ABa | 0.12 ± 0.01 Ba | 0.13 ± 0.08 Bb | ||||
| BA (g/kg DM) | 7 d | ND | ND | ND | ND | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 15 d | ND | ND | ND | ND | ||||
| 30 d | 3.3 ± 0.08 Ab | 2.09 ± 0.01 Cb | 2.8 ± 0.01 Bb | 3.04 ± 0.2 ABb | ||||
| 60 d | 5.41 ± 0.54 Aa | 3.31 ± 0.37 Ba | 3.36 ± 0.17 Ba | 3.68 ± 0.07 Ba | ||||
| NH3-N/TN (%) | 7 d | 1.06 ± 0.06 ABc | 0.34 ± 0.19 Bc | 1.48 ± 0.44 Ab | 1.88 ± 0.1 Ac | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 15 d | 1.91 ± 0.04 Ac | 0.81 ± 0.06 Bc | 1.31 ± 0.01 ABb | 1.49 ± 0.14 ABc | ||||
| 30 d | 6.71 ± 0.18 Ab | 4.4 ± 0.08 Bb | 5.04 ± 0.1 Ba | 5.16 ± 0.01 Bb | ||||
| 60 d | 9.04 ± 0.19 Aa | 5.79 ± 0.11 Ba | 6.13 ± 0.29 Ba | 6.78 ± 1.87 Ba | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Chai, Y.; Jia, S.; Ma, C.; Zhang, F. The Effects of Lactococcus garvieae and Pediococcus pentosaceus on the Characteristics and Microbial Community of Urtica cannabina Silage. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071453
Chen Y, Li S, Sun Y, Chai Y, Jia S, Ma C, Zhang F. The Effects of Lactococcus garvieae and Pediococcus pentosaceus on the Characteristics and Microbial Community of Urtica cannabina Silage. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(7):1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071453
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yongcheng, Shuangming Li, Yingchao Sun, Yuxin Chai, Shuan Jia, Chunhui Ma, and Fanfan Zhang. 2025. "The Effects of Lactococcus garvieae and Pediococcus pentosaceus on the Characteristics and Microbial Community of Urtica cannabina Silage" Microorganisms 13, no. 7: 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071453
APA StyleChen, Y., Li, S., Sun, Y., Chai, Y., Jia, S., Ma, C., & Zhang, F. (2025). The Effects of Lactococcus garvieae and Pediococcus pentosaceus on the Characteristics and Microbial Community of Urtica cannabina Silage. Microorganisms, 13(7), 1453. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13071453







