In-House IgM Dot-Blot Assay for Serodiagnosis of Human Leptospirosis: Development, Standardisation, and Performance Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Routine Leptospirosis Diagnosis
2.2.1. PanbioTM Leptospira IgM ELISA (IgM ELISA)
2.2.2. Microscopic Agglutination Test (MAT)
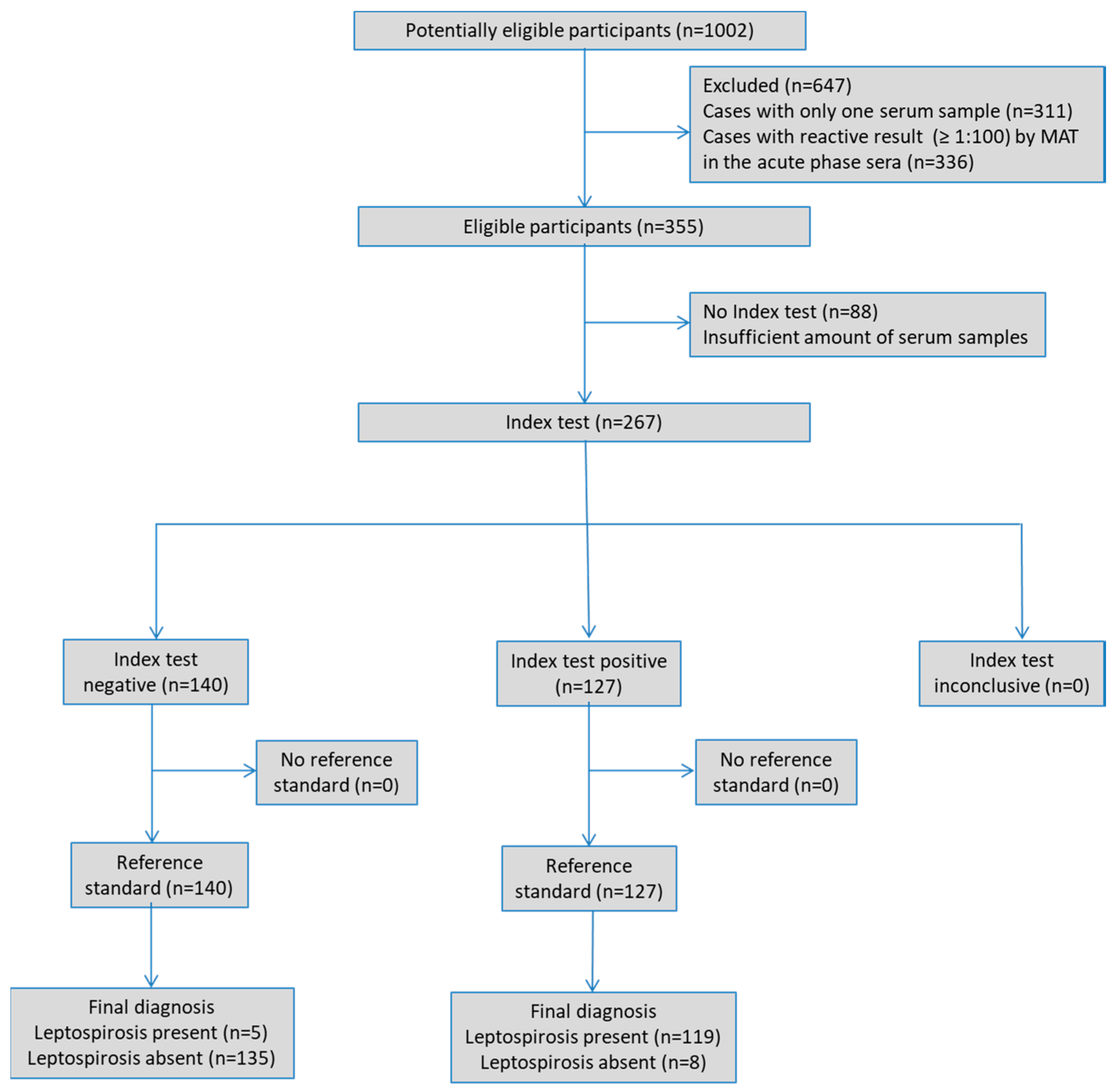
2.3. Serum Samples
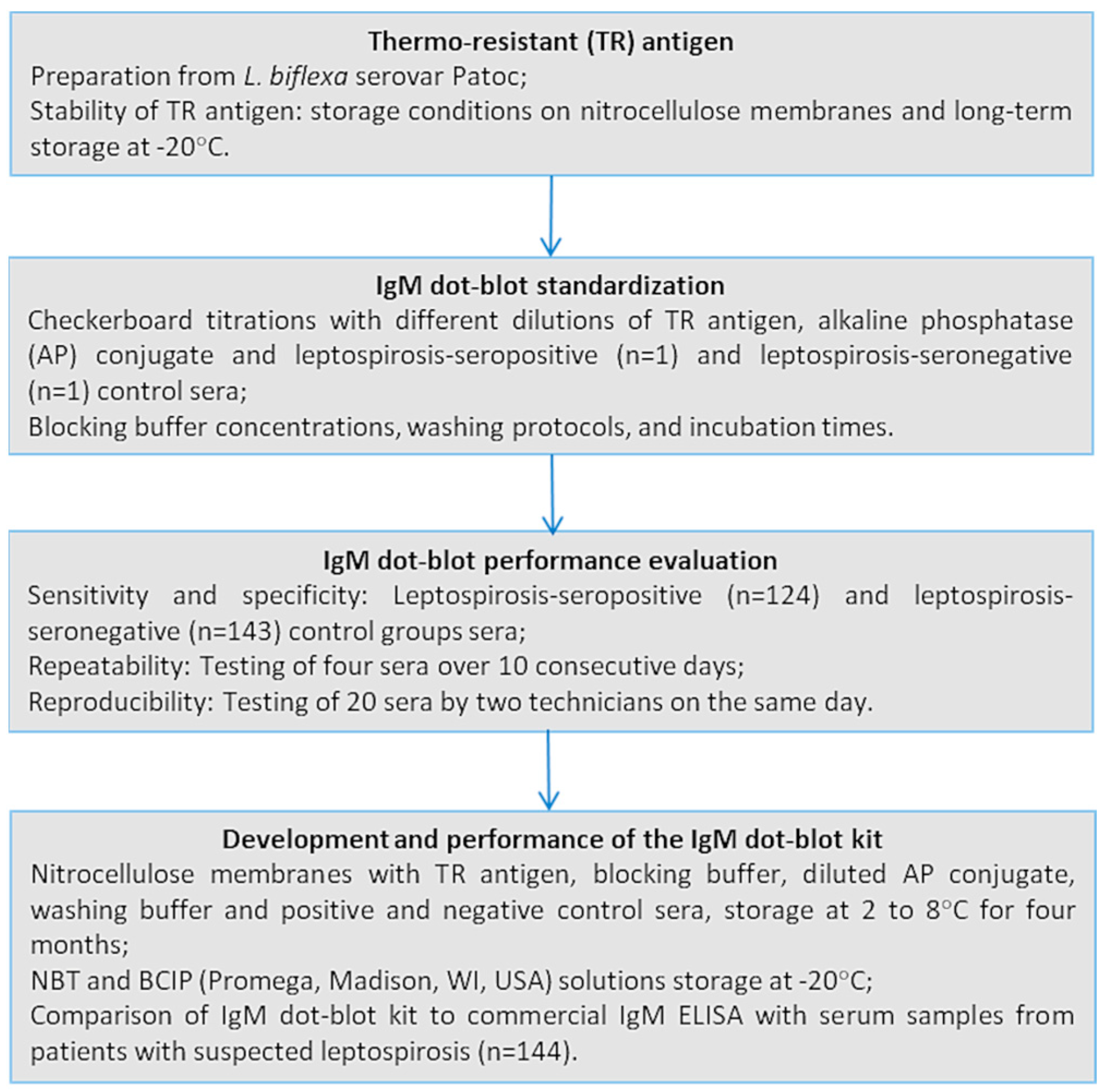
2.4. IgM Dot-Blot Assay
2.4.1. Antigen Preparation
2.4.2. Assay Protocol
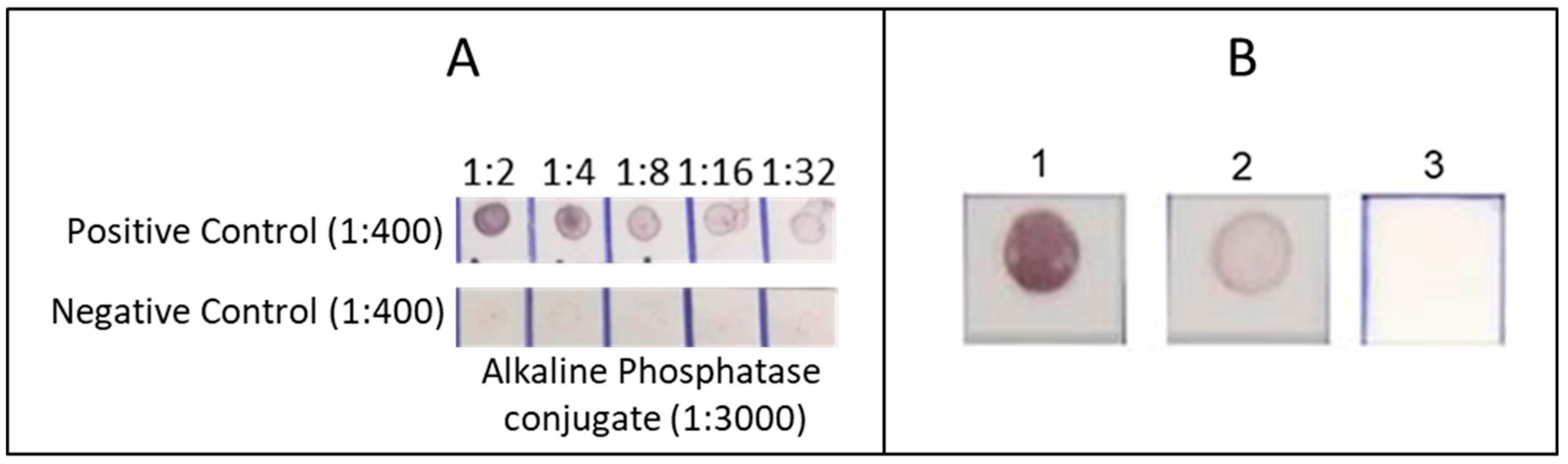
2.4.3. Standardisation
2.4.4. Performance
2.4.5. Stability of the TR Antigen
2.5. Development and Performance of the IgM Dot-Blot Kit
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Antigen Yield and Dot-Blot Standardisation
3.2. Performance
3.3. Stability
3.4. Development and Performance of the IgM Dot-Blot Kit
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MAT | Microscopic Agglutination Test |
| LACENs | Central Public Health Reference Laboratories |
| STARD | Standards for Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy |
| TR | Thermo-resistant antigen |
| EMJH | Ellinghausen-McCullough-Johnson-Harris |
| AP | Alkaline Phosphatase |
| NBT | Nitroblue tetrazolium |
| BCIP | 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PBS-T | PBS + 0.1% tween 20 |
| M-PBS | Skimmed milk in PBS |
| M-PBS-T | Skimmed milk in PBS-T |
References
- Teles, A.J.; Bohm, B.C.; Silva, S.C.M.; Bruhn, F.R.P. Socio-Geographical Factors and Vulnerability to Leptospirosis in South Brazil. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, I.d.O.C.; Landi, M.F.d.A.; Lima, E.M.M.d.; Cruz, L.M.; Bofill, M.I.R.; Santos, D.E.d.; Castro, M.B. de Socio-Epidemiological Characterization of Human Leptospirosis in the Federal District, Brazil, 2011-2015. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2018, 51, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, V.J.d.; De Jesus, T.A.; Da Silva, M.V.G.; De Navasquez, L.M.L.; Sousa, L.d.D.; Rodrigues, H.L.d.S.; Siqueira, A.B.; De Assis, G.D.M.; De Faria, G.G.; Sampaio, M.H.S. Epidemiological Aspects of Leptospirosis in the Brazilian Population (2007-2022) and Its Relationship with Pets. Rev. Unimontes Científica 2024, 26, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministério da Saúde. Situação Epidemiológica Da Leptospirose; Ministério da Saúde: Brasília, Brazil, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hagan, J.E.; Moraga, P.; Costa, F.; Capian, N.; Ribeiro, G.S.; Wunder, E.A.; Felzemburgh, R.D.M.; Reis, R.B.; Nery, N.; Santana, F.S.; et al. Spatiotemporal Determinants of Urban Leptospirosis Transmission: Four-Year Prospective Cohort Study of Slum Residents in Brazil. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 10, e0004275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, K.P.; Sacramento, G.A.; Cruz, J.S.; de Oliveira, D.; Nery, N.; Lindow, J.C.; Carvalho, M.; Hagan, J.; Diggle, P.J.; Begon, M.; et al. Influence of Rainfall on Leptospira Infection and Disease in a Tropical Urban Setting, Brazil. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2020, 26, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haake, D.A.; Levett, P.N. Leptospirosis in Humans. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 387, 65–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samrot, A.V.; Sean, T.C.; Bhavya, K.S.; Sahithya, C.S.; Chan-drasekaran, S.; Palanisamy, R.; Robinson, E.R.; Subbiah, S.K.; Mok, P.L. Leptospiral Infection, Pathogenesis and Its Diagnosis—A Review. Pathogens 2021, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, A.B.; Dore, M.M. Leptospirosis: A Clinical Review of Evidence Based Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention. World J. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 6, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musso, D.; La Scola, B. Laboratory Diagnosis of Leptospirosis: A Challenge. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2013, 46, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picardeau, M. Diagnosis and Epidemiology of Leptospirosis. Med. Mal. Infect. 2013, 43, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajani, M.D.; Ashford, D.A.; Bragg, S.L.; Woods, C.W.; Aye, T.; Spiegel, R.A.; Plikaytis, D.; Perkins, B.A.; Phelan, M.; Paul, N.; et al. Evaluation of Four Commercially Available Rapid Serologic Tests for Diagnosis of Leptospirosis Evaluation of Four Commercially Available Rapid Serologic Tests for Diagnosis of Leptospirosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 803–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effler, P.V.; Domen, H.; Bragg, S.L.; Aye, T.; Sasaki, D.M. Evaluation of the Indirect Hemagglutination Assay for Diagnosis of Acute Leptospirosis in Hawaii. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 1081–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levett, P.N. Leptospirosis. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 14, 296–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maze, M.J.; Sharples, K.J.; Allan, K.J.; Rubach, M.P.; Crump, J.A. Diagnostic Accuracy of Leptospirosis Whole-Cell Lateral Flow Assays: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, M.I.; Reis, M.F.d.; Simon, C.; Dondossola, E.; Alexandre, M.C.; Colonetti, T.; Meller, F.O. IgM ELISA for Leptospirosis Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cien. Saude Colet. 2017, 22, 4001–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niloofa, R.; Karunanayake, L.; de Silva, H.J.; Premawansa, S.; Rajapakse, S.; Handunnetti, S. Development of In-House ELISAs as an Alternative Method for the Serodiagnosis of Leptospirosis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2021, 105, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picardeau, M.; Bertherat, E.; Jancloes, M.; Skouloudis, A.N.; Durski, K.; Hartskeerl, R.A. Rapid Tests for Diagnosis of Leptospirosis: Current Tools and Emerging Technologies. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 78, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, K.P.; Sharma, S.; Sherchand, J.B.; Upadhyay, B.P.; Bhatta, D.R. Detection of Anti- Leptospira IgM Antibody in Serum Samples of Suspected Patients Visiting National Public Health Laboratory, Teku, Kathmandu. Int. J. Microbiol. 2016, 2016, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Chaudhry, R.; Gupta, N.; Arif, N.; Bhadur, T. Decreasing Trend of Seroprevalence of Leptospirosis at All India Institute of Medical Sciences New Delhi: 2014–2018. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2018, 7, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maneewatchararangsri, S.; Doungchawee, G.; Kalambaheti, T.; Luvira, V.; Soonthornworasiri, N.; Vattanatham, P.; Chaisri, U.; Adisakwattana, P. Evaluation of a Genus-Specific RGroEL1-524 IgM-ELISA and Commercial ELISA Kits during the Course of Leptospirosis in Thailand. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hii, K.-C.; Robie, E.R.; Saihidi, I.; Berita, A.; Alarja, N.A.; Xiu, L.; Merchant, J.A.; Binder, R.A.; Goh, J.K.-T.; Guernier-Cambert, V.; et al. Leptospirosis Infections among Hospital Patients, Sarawak, Malaysia. Trop. Dis. Travel Med. Vaccines 2021, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhawan, S.; Althaus, T.; Lubell, Y.; Suwancharoen, D.; Blacksell, S.D. Evaluation of the Panbio Leptospira IgM ELISA among Outpatients Attending Primary Care in Southeast Asia. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 104, 1777–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zida, S.; Kania, D.; Bolloré, K.; Bandaogo, O.; Pisoni, A.; Dicko, A.; Tinto, B.; Traoré, J.; Van de Perre, P.; Ouédraogo, H.G.; et al. Leptospirosis Cases among Outpatients with Non-Malaria Fever Attending Primary Care Clinics during the Rainy Season in Bobo Dioulasso, Burkina Faso. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2024, 110, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, M.G. Recent Applications of the Dot-ELISA in Immunoparasitology. Vet. Parasitol. 1988, 29, 105–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, P.M.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Glasziou, P.P.; Irwig, L.M.; Lijmer, J.G.; Moher, D.; Rennie, D.; de Vet, H.C.W. Towards of Studies of Diagnostic Accuracy: The STARD Initiative. BMJ 2003, 326, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, P.M.; Reitsma, J.B.; Bruns, D.E.; Gatsonis, C.A.; Glasziou, P.P.; Irwig, L.; Lijmer, J.G.; Moher, D.; Rennie, D.; de Vet, H.C.W.; et al. STARD 2015: An Updated List of Essential Items for Reporting Diagnostic Accuracy Studies. BMJ 2015, 351, h5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goris, M.G.A.; Hartskeerl, R.A. Leptospirosis Serodiagnosis by the Microscopic Agglutination Test. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2014, 32, 12E.5.1–12E.5.18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization, WHO. Human Leptospirosis: Guidance for Diagnosis, Surveillance and Control; 2003. Available online: https://wkc.who.int/resources/publications/i/item/human-leptospirosis-guidance-for-diagnosis-surveillance-and-control (accessed on 29 January 2024).
- Blanco, R.M.; Romero, E.C. Fifteen Years of Human Leptospirosis in São Paulo, Brazil. J. Epidemiol. Res. 2015, 2, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faine, S.; Adler, B.; Bolin, C.; Perolat, P. Leptospira and Leptospirosis, 2nd ed.; Medisci Press: Melbourne, Australia, 1999; ISBN 095863260X, 9780958632607. [Google Scholar]
- Faine, S. Guidelines for the Control of Leptospirosis, 67th ed.; World Health Organization, Ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1982; ISBN 924170067X. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A Rapid and Sensitive Method for the Quantitation of Microgram Quantities of Protein Utilizing the Principle of Protein-Dye Binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, R.; Lima, E.; de Haro, G.; Kamikawa, C.; Blanco, R.; Vincentini, A.; Romero, E. Comparative Analysis of a Novel N -Butanol-Prepared Antigen vs. Thermo-Resistant and Sonicated Antigens for Human Leptospirosis Detection. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 77, ovae004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleiss, J.L.; Levin, B.; Paik, M.C. Statistical Methods for Rates and Proportions; Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; ISBN 0471526290. [Google Scholar]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, A.J.A.; Pereira, F.A.; da Silva, E.D.; de Matos, R.B.; da Silva, E.D.; Ferreira, A.G.P.; Reis, M.G.; Ko, A.I. Evaluation of the EIE-IgM-Leptospirose Assay for the Serodiagnosis of Leptospirosis. Acta Trop. 2007, 102, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goris, M.G.A.; Leeflang, M.M.G.; Loden, M.; Wagenaar, J.F.P.; Klatser, P.R.; Hartskeerl, R.A.; Boer, K.R. Prospective Evaluation of Three Rapid Diagnostic Tests for Diagnosis of Human Leptospirosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2013, 7, e2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabity, S.A.; Hagan, J.E.; Araújo, G.; Damião, A.O.; Cruz, J.S.; Nery, N.; Wunder, E.A.; Reis, M.G.; Ko, A.I.; Ribeiro, G.S. Prospective Evaluation of Accuracy and Clinical Utility of the Dual Path Platform (DPP) Assay for the Point-of-Care Diagnosis of Leptospirosis in Hospitalized Patients. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desakorn, V.; Wuthiekanun, V.; Thanachartwet, V.; Sahassananda, D.; Chierakul, W.; Apiwattanaporn, A.; Day, N.P.; Limmathurotsakul, D.; Peacock, S.J. Accuracy of a Commercial IgM ELISA for the Diagnosis of Human Leptospirosis in Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2012, 86, 524–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization. Technical Report ISO/TR 14468:2010–Selected Illustrations of Attribute Agreement Analysis, 1st ed.; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- NCCLS. User Protocol for Evaluation of Qualitative Test Performance; Approved Guideline. NCCLS Document EP12-A; NCCLS: Wayne, PA, USA, 2002; ISBN 1-56238-468-6. [Google Scholar]
| IgM Dot-Blot Performance | MAT-Confirmed Cases and Controls | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| No. Reactive/Total | Rates | (95% CI) | |
| Sensitivity | |||
| Acute phase | 72/124 | 58.1% | (48.9–66.9) |
| Convalescent phase | 119/124 | 96.0% | (90.8–98.7) |
| Specificity | |||
| Healthy individuals | 6/58 | 89.7% | (78.8–96.1) |
| Other diseases | 2 */85 | 97.6% | (91.8–99.7) |
| Total control group | 8/143 | 94.4% | (89.3–97.6) |
| Performance Measures | No. Matching/Total | Estimate | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | 22/26 | 84.6% | 65.1–95.6% |
| Specificity | 114/118 | 96.6% | 91.6–99.1% |
| Accuracy | 136/144 | 94.4% | 89.4–97.6% |
| Agreement Kappa index | 136/144 | 0.81 | 0.69–0.94 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Blanco, R.M.; dos Santos Lima, E.; Pinhata, J.M.W.; Brandao, A.P.; Romero, E.C. In-House IgM Dot-Blot Assay for Serodiagnosis of Human Leptospirosis: Development, Standardisation, and Performance Evaluation. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061307
Blanco RM, dos Santos Lima E, Pinhata JMW, Brandao AP, Romero EC. In-House IgM Dot-Blot Assay for Serodiagnosis of Human Leptospirosis: Development, Standardisation, and Performance Evaluation. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(6):1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061307
Chicago/Turabian StyleBlanco, Roberta Morozetti, Elaine dos Santos Lima, Juliana Maira Watanabe Pinhata, Angela Pires Brandao, and Eliete Caló Romero. 2025. "In-House IgM Dot-Blot Assay for Serodiagnosis of Human Leptospirosis: Development, Standardisation, and Performance Evaluation" Microorganisms 13, no. 6: 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061307
APA StyleBlanco, R. M., dos Santos Lima, E., Pinhata, J. M. W., Brandao, A. P., & Romero, E. C. (2025). In-House IgM Dot-Blot Assay for Serodiagnosis of Human Leptospirosis: Development, Standardisation, and Performance Evaluation. Microorganisms, 13(6), 1307. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13061307





