Observations of the Fine Structural Changes Associated with Merogony and Gametogony in Eimeria necatrix and Localization of Two Gametocyte Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Parasites and Animals
2.2. Polyclonal Antibodies
2.3. Tissue Processing
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy Observation
2.5. Immunoelectron Microscopy Observation
3. Results
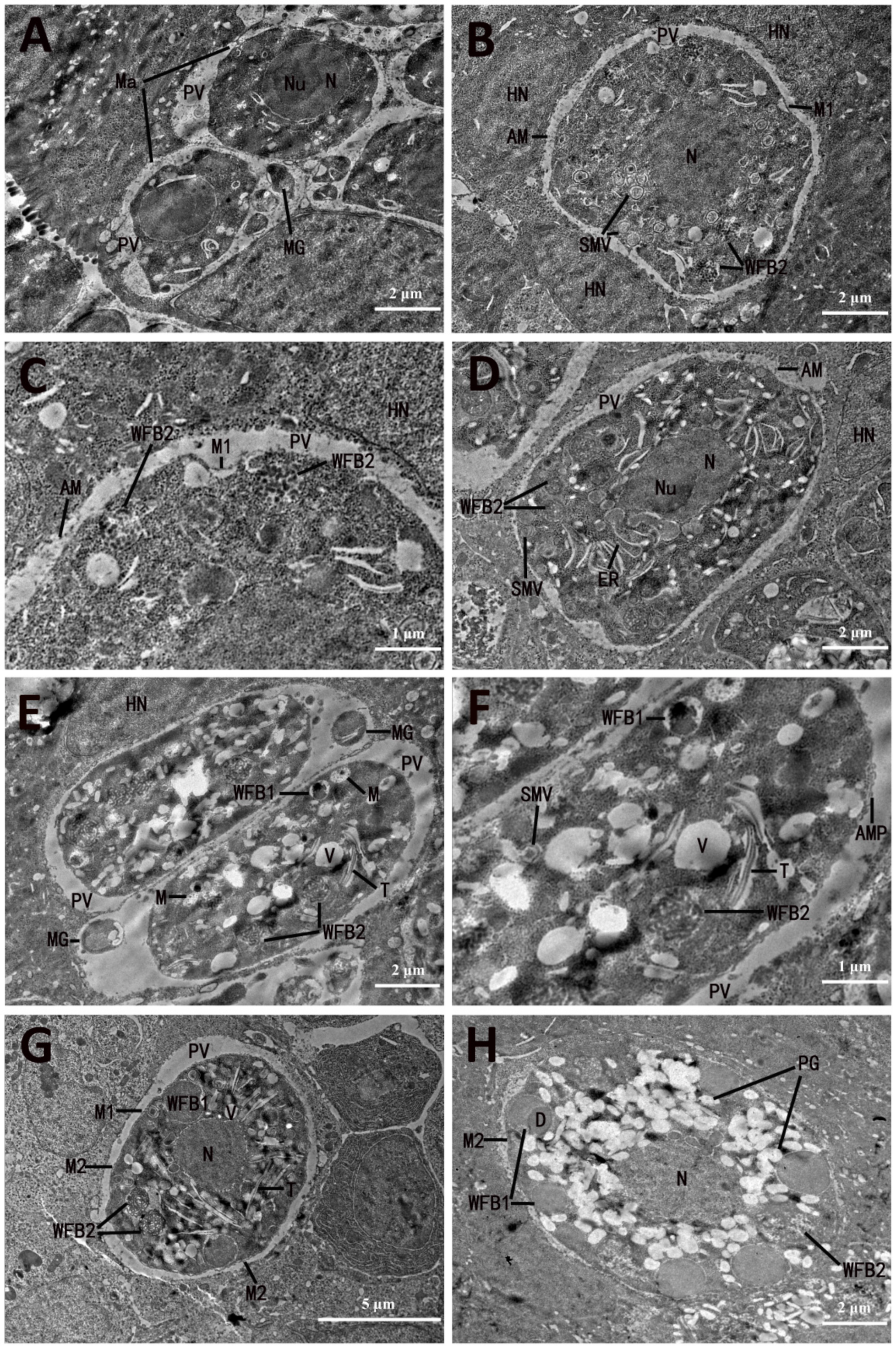
3.1. Development and Ultrastructure of Third-Generation Meronts and Merozoites
3.2. Microgametocyte Ultrastructure and Microgamete Formation
3.3. Development and Ultrastructure of Macrogametocyte and Oocyst Wall Formation
3.3.1. Macrogametocyte Development
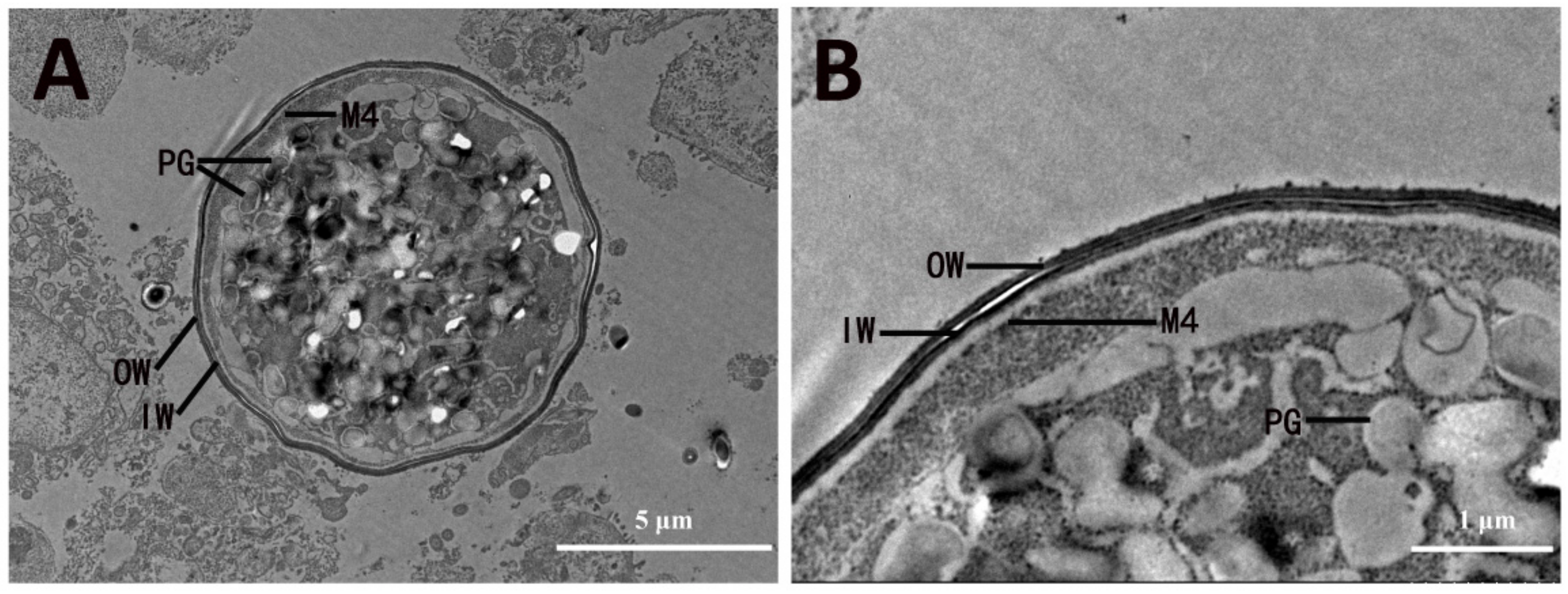
3.3.2. Oocyst Wall Formation
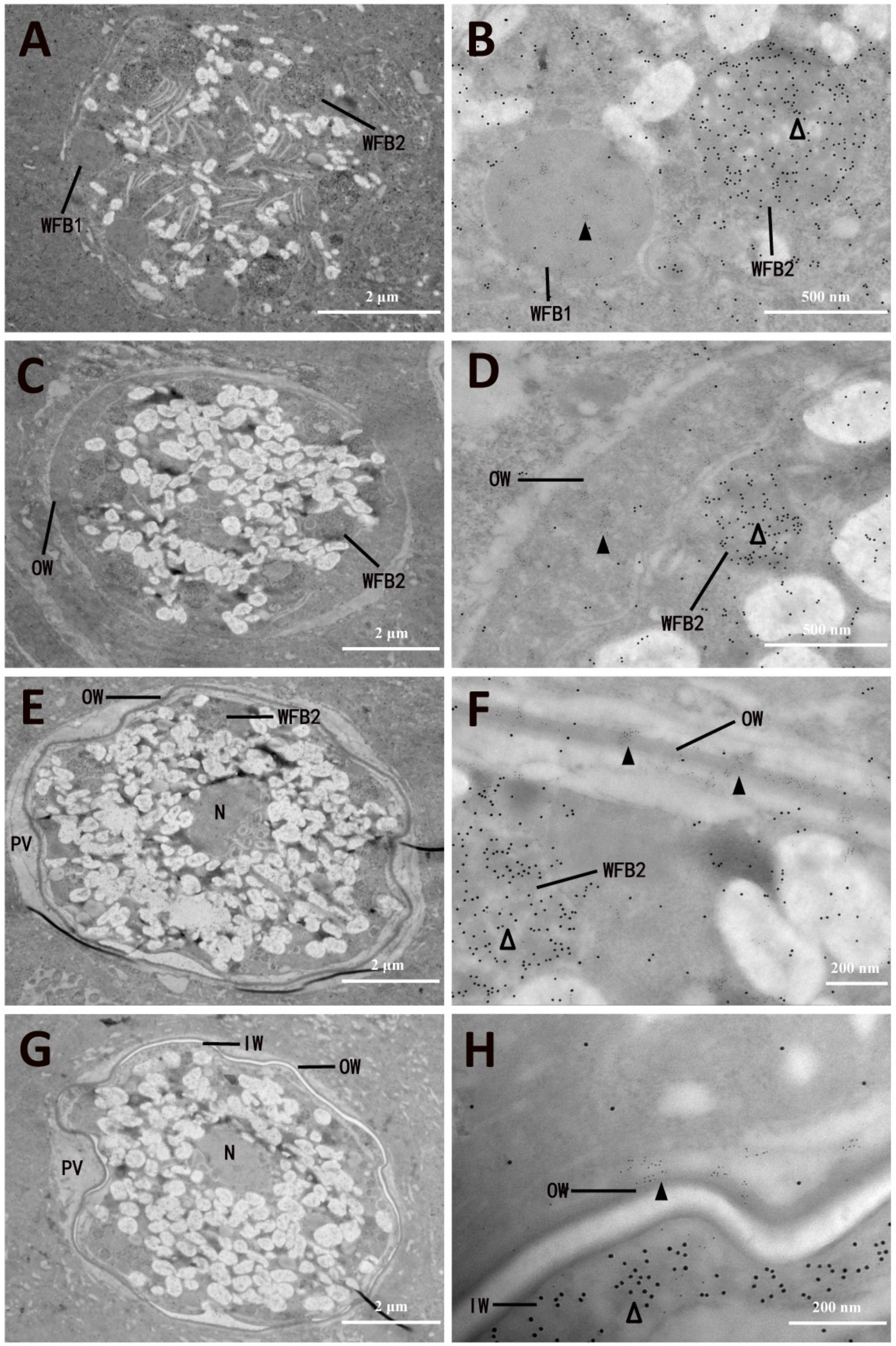
3.4. Ultrastructural Localization of EnGAM22 and EnGAM59 Proteins
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blake, D.P.; Knox, J.; Dehaeck, B.; Huntington, B.; Rathinam, T.; Ravipati, V.; Ayoade, S.; Gilbert, W.; Adebambo, A.O.; Jatau, I.D.; et al. Re-calculating the cost of coccidiosis in chickens. Vet. Res. 2020, 51, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walker, R.A.; Ferguson, D.J.; Miller, C.M.; Smith, N.C. Sex and Eimeria: A molecular perspective. Parasitology 2013, 140, 1701–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDougald, L.R.; Cervantes, H.M.; Jenkins, M.C.; Hess, M.; Beckstead, R. Protozoal Infections. In Diseases of Poultry; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1192–1254. [Google Scholar]
- Mesa-Pineda, C.; Navarro-Ruíz, J.L.; López-Osorio, S.; Chaparro-Gutiérrez, J.J.; Gómez-Osorio, L.M. Chicken Coccidiosis: From the Parasite Lifecycle to Control of the Disease. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 787653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, S.I.; Smith, N.C.; Ferguson, D.J. The coccidian oocyst: A tough nut to crack! Trends Parasitol. 2006, 22, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferguson, D.J.; Belli, S.I.; Smith, N.C.; Wallach, M.G. The development of the macrogamete and oocyst wall in Eimeria maxima: Immuno-light and electron microscopy. Int. J. Parasitol. 2003, 33, 1329–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, K.; Sharman, P.A.; Walker, R.A.; Katrib, M.; De Souza, D.; McConville, M.J.; Wallach, M.G.; Belli, S.I.; Ferguson, D.J.; Smith, N.C. Oocyst wall formation and composition in coccidian parasites. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2009, 104, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, S.I.; Wallach, M.G.; Luxford, C.; Davies, M.J.; Smith, N.C. Roles of tyrosine-rich precursor glycoproteins and dityrosine- and 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine-mediated protein cross-linking in development of the oocyst wall in the coccidian parasite Eimeria maxima. Eukaryot. Cell 2003, 2, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, D.; Gao, Y.; Hou, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, W.; Zhang, A.; Xu, J.; Hu, J.; et al. Examination of gametocyte protein 22 localization and oocyst wall formation in Eimeria necatrix using laser confocal microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. Parasit. Vectors 2023, 16, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmer, S.; Buder, U.; Bleischwitz, S.; Kurth, M. Distribution and Processing of Eimeria nieschulzi OWP13, a New Protein of the COWP Family. J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 2018, 65, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallach, M.G.; Mencher, D.; Yarus, S.; Pillemer, G.; Halabi, A.; Pugatsch, T. Eimeria maxima: Identification of gametocyte protein antigens. Exp. Parasitol. 1989, 68, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallach, M. The importance of transmission-blocking immunity in the control of infections by apicomplexan parasites. Int. J. Parasitol. 1997, 27, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubremetz, J.F.; Yvore, P. Oocystic wall formation in the coccidia Eimeria necatrix Johnson 1930 (Sporozoa, Coccidiomorpha). Study with electronic microscope. C. R. Seances Soc. Biol. Fil. 1971, 165, 862–866. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Regal, D.S. Light and electron microscopic studies on the development of Eimeria necatrix in the chicken. Zentralbl. Vet. B 1976, 23, 744–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Cao, L.; Zhu, Y.; Deng, C.; Su, S.; Xu, J.; Jin, W.; Li, J.; Wu, L.; Tao, J. Cloning and characterization of an Eimeria necatrix gene encoding a gametocyte protein and associated with oocyst wall formation. Parasit. Vectors 2014, 7, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, V.; Rose, M.E. Eimeria tenella and E. necatrix: A third generation of schizogony is an obligatory part of the developmental cycle. J. Parasitol. 1987, 73, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaren, D.J. Observations on the fine structural changes associated with schizogony and gametogony in Eimeria tenella. Parasitology 1969, 59, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitz-Coy, S.H.; Edgar, S.A.; Mora, E.C. Ultrastructure of schizonts and merozoites of Eimeria mitis and E. mivati of the chicken. Avian Dis. 1989, 33, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtyseck, E. Electron microscopic studies on schizogony in coccidia (Eimeria perforans and E. stiedae). Z. Parasitenkd. 1965, 26, 50–62. [Google Scholar]
- Regal, D.S. Light-and electron microscopic studies on developmental stages od schozigony and gametogony of the chicken coccidium Eimera necatrix. Zentralbl. Vet. B 1977, 24, 297–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtyseck, E. The microgamete development of Eimeria perforans. Z. Zellforsch. Mikrosk. Anat. 1965, 66, 625–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colley, F.C. Fine structure of microgametocytes and macrogametes of Eimeria nieschulzi. J. Protozool. 1967, 14, 663–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, D.M.; Scholtyseck, E.; Chobotar, B. Fine structural study of the microgametogenesis of Eimeria auburnensis. Z. Parasitenkd. 1969, 33, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haberkorn, A. Host specificity of Eimeria contorta n. sp. (Sporozoa: Eimeriidae). Z. Parasitenkd. 1971, 37, 303–314. [Google Scholar]
- Scholtyseck, E.; Mehlhorn, H.; Hammond, D.M. Electron microscope studies of microgametogenesis in Coccidia and related groups. Z. Parasitenkd. 1972, 38, 95–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlhorn, H. Electron microscopy studies on the developmental stages of Eimeria maxima (Sporozoa, Coccidia). I. Ultrastructure of macrogametes. Z. Parasitenkd. 1972, 39, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, S.J.; Pittilo, R.M.; Joyner, L.P.; Norton, C.C. Scanning and transmission electron microscopy of Eimeria maxima microgametogenesis. Parasitology 1981, 82, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, C.A.; Danforth, H.D. Fine-structural aspects of microgametogenesis of Eimeria magna in rabbits and in kidney cell cultures. J. Protozool. 1976, 23, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, D.J.; Birch-Andersen, A.; Hutchison, W.M.; Siim, J.C. Ultrastructural studies on the endogenous development of Eimeria brunetti. II. Microgametogony and the microgamete. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. B 1977, 85B, 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Madden, P.A.; Vetterling, J.M. Scanning electron microscopy of Eimeria tenella microgametogenesis and fertilization. J. Parasitol. 1977, 63, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regal, D.S. Light and electron microscopic studies on the formation of the oocyst shell of Eimeria necatrix. Zentralbl. Vet. B 1977, 24, 708–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtyseck, E.; Mehlhorn, H.; Hammond, D.M. Fine structure of macrogametes and oocysts of Coccidia and related organisms. Z. Parasitenkd. 1971, 37, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michael, E. The formation and final structure of the oocyst wall of Eimeria acervulina: A transmission and scanning electron microscope study. Z. Parasitenkd. 1978, 57, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefu, Z.; Yingying, W.; Mei, C.; Lihong, W.; Shuichun, H.; Jun, Z.; Renhai, L.; Hong, X. Eimeria tenella: Further studies on the development of the oocyst. Exp. Parasitol. 2006, 113, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedmer, P.; Jung, T.; Castro, J.P.; Pomatto, L.C.D.; Sun, P.Y.; Davies, K.J.A.; Grune, T. Sarcopenia—Molecular mechanisms and open questions. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 65, 101200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittilo, R.M.; Ball, S.J. The fine structure of the developing macrogamete of Eimeria maxima. Parasitology 1979, 79, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, D.J.; Birch-Andersen, A.; Hutchison, W.M.; Siim, J.C. Ultrastructural studies on the endogenous development of Eimeria brunetti. IV. Formation and structure of the oocyst wall. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. B 1977, 85, 201–211. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, D.J.; Birch-Andersen, A.; Hutchison, W.M.; Siim, J.C. Ultrastructural studies on the endogenous development of Eimeria brunetti. III. Macrogametogony and the macrogamete. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. B 1977, 85B, 78–88. [Google Scholar]
- Pittilo, R.M.; Ball, S.J. The ultrastructural development of the oocyst wall of Eimeria maxima. Parasitology 1980, 81, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittilo, R.M.; Ball, S.J. Electron microscopy of Eimeria acervulina macrogametogony and oocyst wall formation. Parasitology 1984, 89 Pt 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtyseck, E. Comparative studies on the nuclear relations and growth of coccidiomorphs with special reference to Eimeria maxima. Z. Parasitenkd. 1963, 22, 428–474. [Google Scholar]
- Scholtyseck, E.; Hammond, D.M. Electron microscope studies of macrogametes and fertilization in Eimeria bovis. Z. Parasitenkd. 1970, 34, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwasila, M. The fine structure of an early stage in the process of fertilization of Eimeria maxima (apicomplexa, eimeriina). Z. Parasitenkd. 1983, 69, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boykins, L.G.; Jones, J.C.; Estrano, C.E.; Schwartzbach, S.D.; Skalli, O. Pre-embedding Double-Label Immunoelectron Microscopy of Chemically Fixed Tissue Culture Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1474, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, L.; Feng, Q.; Wang, F.; Xue, N.; Hou, Z.; Xu, J.; Hu, J.; Tao, J. Observations of the Fine Structural Changes Associated with Merogony and Gametogony in Eimeria necatrix and Localization of Two Gametocyte Proteins. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051135
Zhu Y, Liu D, Wang L, Feng Q, Wang F, Xue N, Hou Z, Xu J, Hu J, Tao J. Observations of the Fine Structural Changes Associated with Merogony and Gametogony in Eimeria necatrix and Localization of Two Gametocyte Proteins. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(5):1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051135
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yu, Dandan Liu, Lele Wang, Qianqian Feng, Feiyan Wang, Nianyu Xue, Zhaofeng Hou, Jinjun Xu, Junjie Hu, and Jianping Tao. 2025. "Observations of the Fine Structural Changes Associated with Merogony and Gametogony in Eimeria necatrix and Localization of Two Gametocyte Proteins" Microorganisms 13, no. 5: 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051135
APA StyleZhu, Y., Liu, D., Wang, L., Feng, Q., Wang, F., Xue, N., Hou, Z., Xu, J., Hu, J., & Tao, J. (2025). Observations of the Fine Structural Changes Associated with Merogony and Gametogony in Eimeria necatrix and Localization of Two Gametocyte Proteins. Microorganisms, 13(5), 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051135






