Microorganisms in Macroalgae Cultivation Ecosystems: A Systematic Review and Future Prospects Based on Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
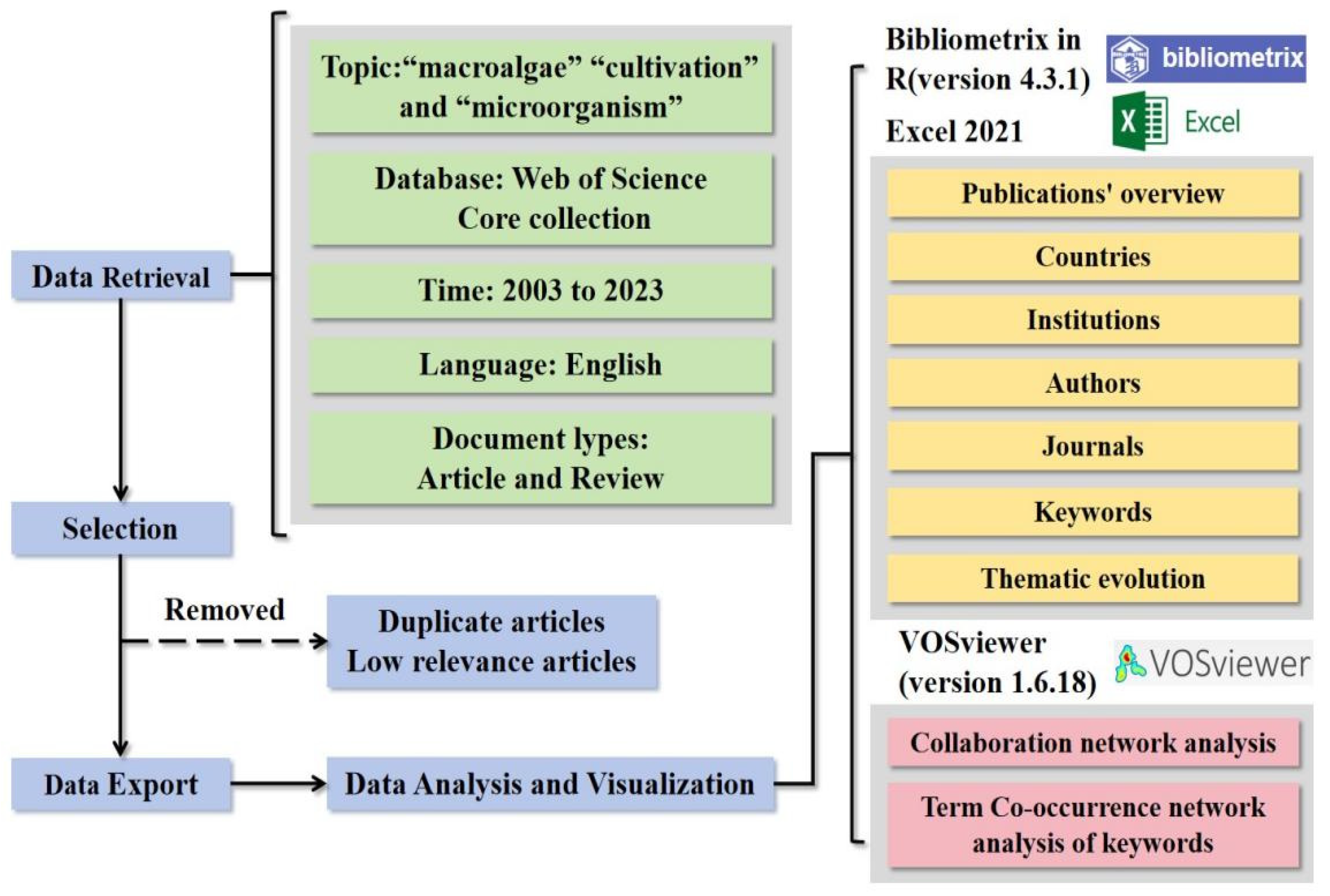
2.1. Study Framework and Data Sources
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Data Analysis and Visualization
3. Results and Discussions
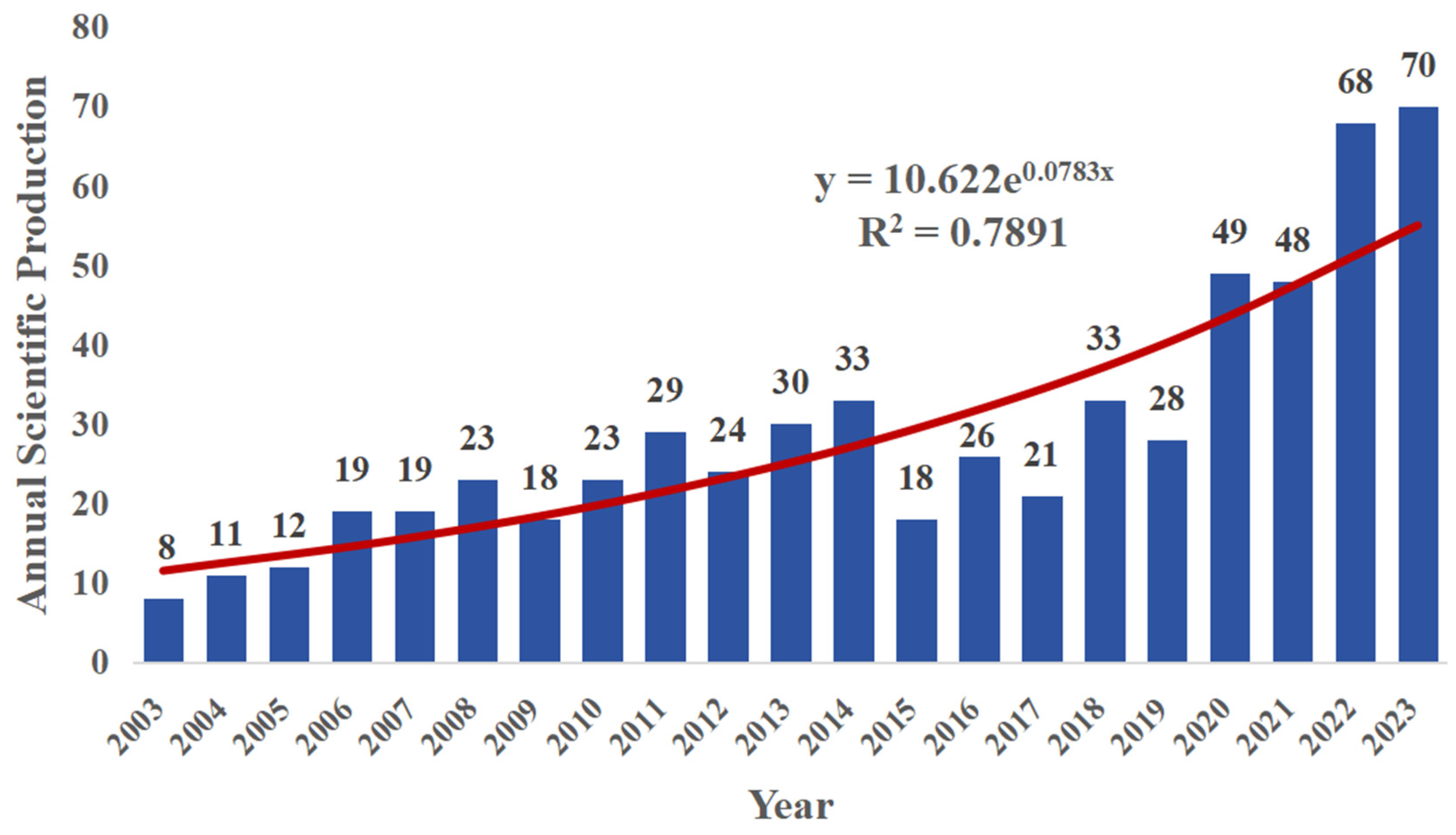
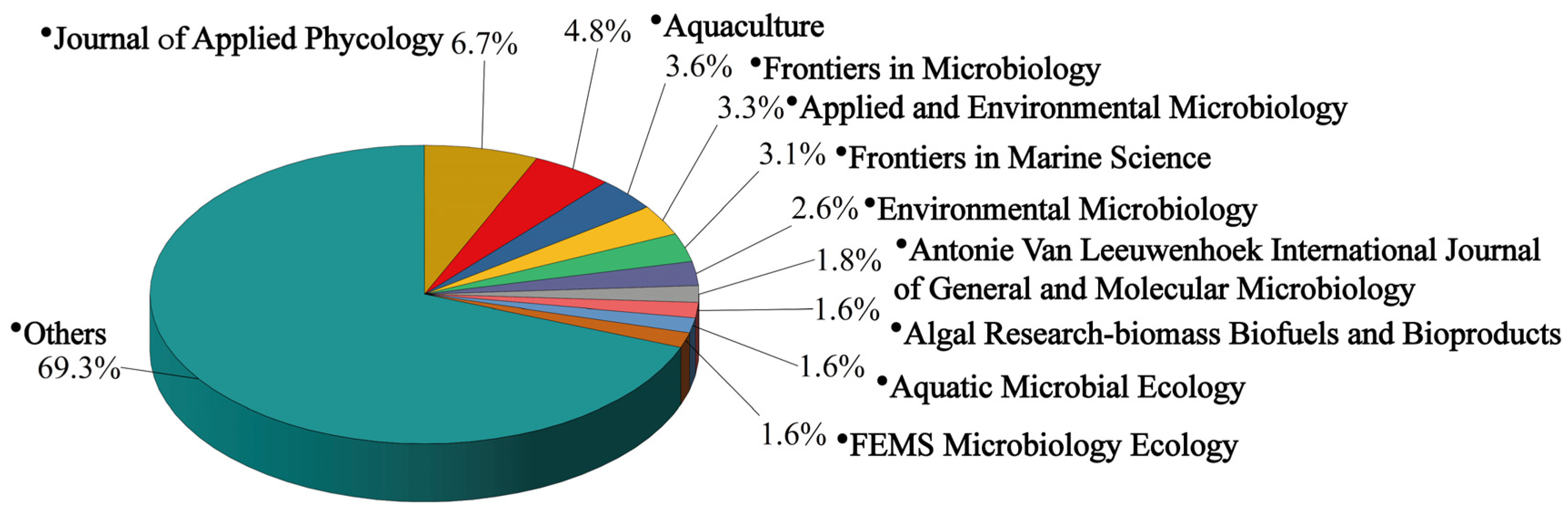
3.1. Quantitative Analysis of the Publications
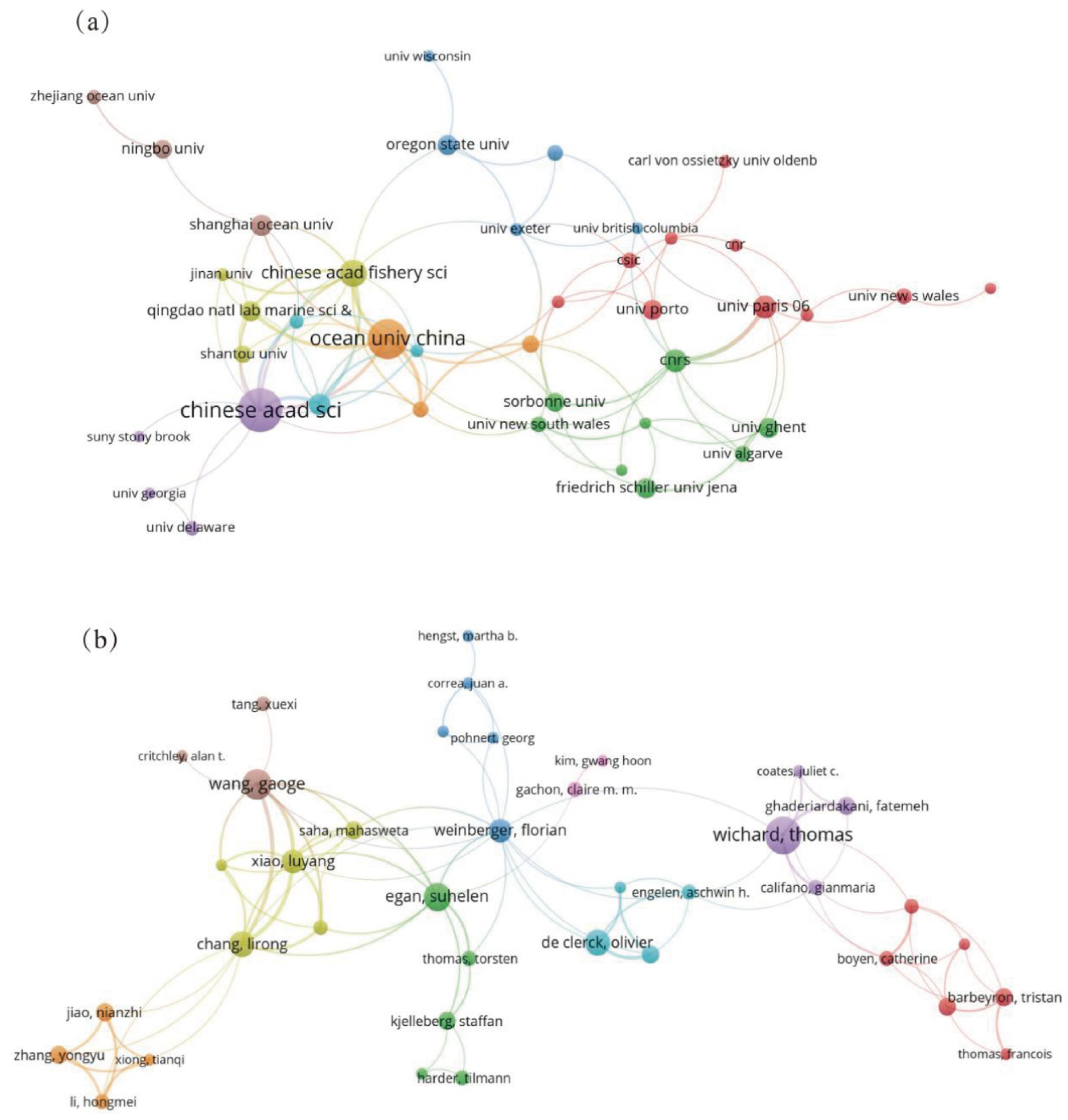
3.2. Collaboration Network Analysis
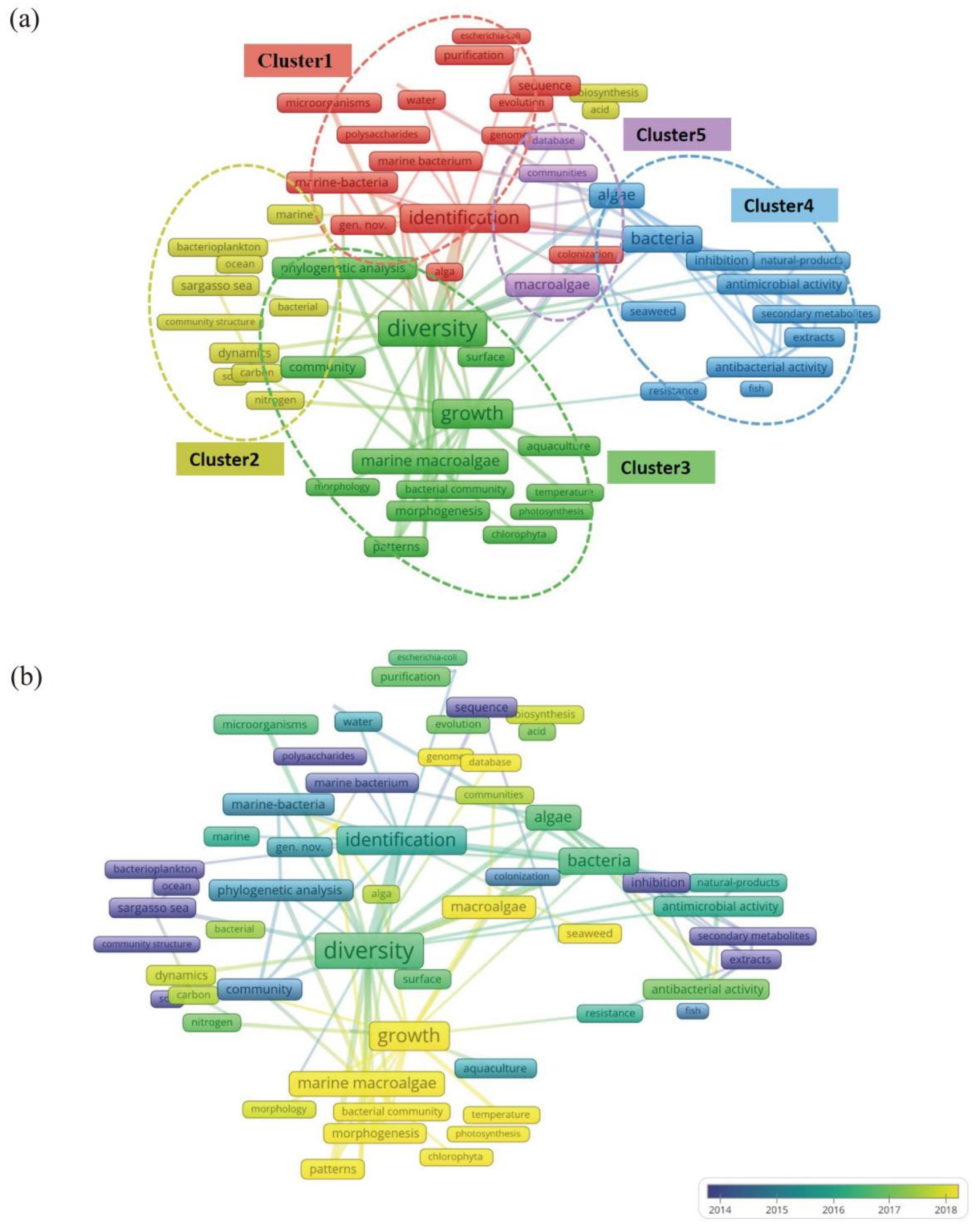
3.3. Term Co-Occurrence Network Analysis of Keywords
3.3.1. Cluster 1: Identification of Microbial Species and Functional Genes
3.3.2. Cluster 2: Biogeochemical Cycles of Carbon in Microbial Communities
3.3.3. Cluster 3: Interactions Between Microorganisms and Macroalgae in Macroalgal Cultivation Environments
3.3.4. Cluster 4: Microbial Resistance and Bioactive Substances in Cultivation Ecosystems of Macroalgae
3.3.5. Cluster 5: High-Throughput Sequencing and Database Utilization in Microorganisms in the Cultivation Ecosystems of Macroalgae
3.4. Thematic Evolution
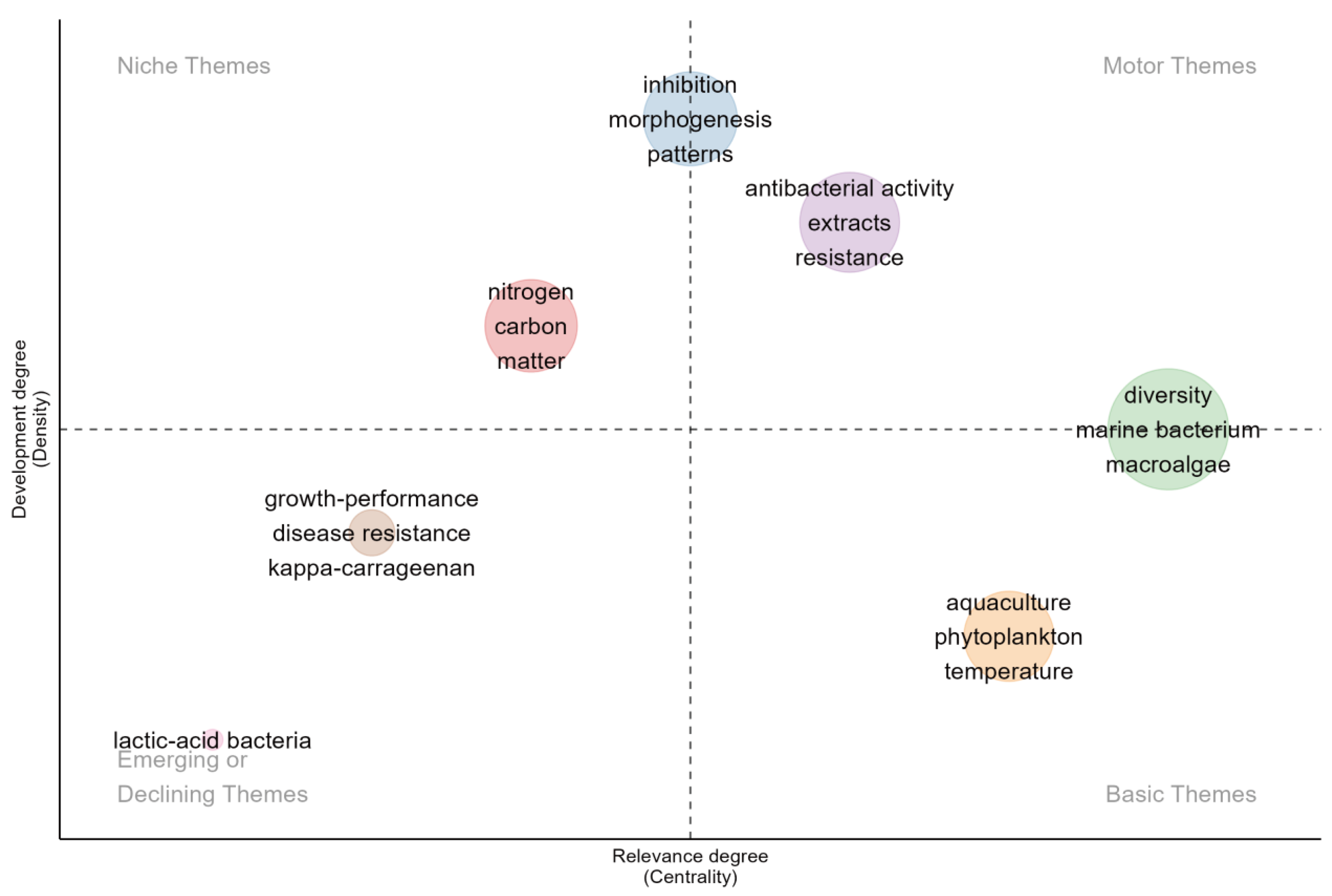
3.5. Thematic Map
3.6. Prospects of the Environmental Microbiology of Macroalgae Aquaculture
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, J.; Lovatelli, A.; Aguilar-Manjarrez, J.; Cornish, L.; Dabbadie, L.; Desrochers, A.; Diffey, S.; Garrido Gamarro, E.; Geehan, J.; Hurtado, A.; et al. Seaweeds and Microalgae: An Overview for Unlocking Their Potential in Global Aquaculture Development; FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Circular No. 1229; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lead, J.C.; Gamarro, E.G.; Geehan, J.A.; Lucente, D.; Mair, G.C.; Miao, W.; Reantaso, M.B.; Roubach, R.; Yuan, X.; Potin, P. Seaweeds and Microalgae: An Overview for Unlocking their Potential in Global Aquaculture Development; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021; Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/handle/20.500.14283/cb5670en (accessed on 8 May 2025).
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024—Blue Transformation in Action; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Beardall, J.; Jin, P.; Gao, L.; Xie, S.; Gao, K. A review of existing and potential blue carbon contributions to climate change mitigation in the Anthropocene. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 59, 1686–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Gao, L.; Jiang, M.; Jian, A.; He, L. The potential of seaweed cultivation to achieve carbon neutrality and mitigate deoxygenation and eutrophication. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 014018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Jin, R.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Wu, J. The considerable environmental benefits of seaweed aquaculture in China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2019, 33, 1203–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, P.; Marley, A.C.; Froehlich, H.E.; Gaines, S.D.; Ladner, I.; MacAdam-Somer, I.; Bradley, D. A case for seaweed aquaculture inclusion in U.S. nutrient pollution management. Mar. Policy 2021, 129, 104506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.R.; Lilley, M.; Shutler, J.; Lowe, C.; Artioli, Y.; Torres, R.; Berdalet, E.; Tyler, C.R. Assessing risks and mitigating impacts of harmful algal blooms on mariculture and marine fisheries. Rev. Aquac. 2020, 12, 1663–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Reddy, C.R.K. Seaweed–microbial interactions: Key functions of seaweed–associated bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2014, 88, 213–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; He, Z.; Hu, X.; Yin, H.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y. Large–scale seaweed cultivation diverges water and sediment microbial communities in the coast of Nan’ao Island, South China Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, L.; Xu, K.; Xu, Y.; Ji, D.; Chen, C.; Xie, C. The cultivation of Pyropia haitanensis has important impacts on the seawater microbial community. J. Appl. Phycol. 2020, 32, 2561–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Wang, W.; Xu, K.; Xu, Y.; Ji, D.; Chen, C.; Xie, C. Cultivation of different seaweed species and seasonal changes cause divergence of the microbial community in coastal seawaters. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 988743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; He, Z.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y. Diversity, composition and ecological networks of bacterial communities in response to a full cultivation cycle of the seaweed, Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis. Environ. Res. 2024, 240, 117453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, P.; Chatterjee, A.; Kiran, K.J.; Bhowmick, G.D.; Sappati, P.K.; Nagarajan, V. Exploring Seaweed–Associated Marine Microbes: Growth Impacts and Enzymatic Potential for Sustainable Resource Utilization. Indian J. Microbiol. 2024, 64, 593602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, K.; Joint, I.; Callow, M.E.; Callow, J.A. Effect of marine bacterial isolates on the growth and morphology of axenic plantlets of the green alga Ulva linza. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 52, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croft, M.T.; Lawrence, A.D.; Raux-Deery, E.; Warren, M.J.; Smith, A.G. Algae acquire vitamin B12 through a symbiotic relationship with bacteria. Nature 2005, 438, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, P.; Aslam, M.; Wang, H.; Ye, P.; Li, T.; Liang, H.; Lin, Q.; Chen, W.; Du, H. Diversity and ecological function of urease-producing bacteria in the cultivation environment of Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 87, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigel, B.L.; Miranda, K.K.; Fogarty, E.C.; Watson, A.R.; Pfister, C.A. Functional Insights into the Kelp Microbiome from Metagenome–Assembled Genomes. Msystems 2022, 7, e01422-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dittami, S.M.; Duboscq-Bidot, L.; Perennou, M.; Gobet, A.; Corre, E.; Boyen, C.; Tonon, T. Host-microbe interactions as a driver of acclimation to salinity gradients in brown algal cultures. ISME J. 2016, 10, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint, I.; Tait, K.; Wheeler, G. Cross-kingdom signalling: Exploitation of bacterial quorum sensing molecules by the green seaweed Ulva. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2007, 362, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, P.; Luo, X.; Deng, Q.; Yang, Z.; Wu, J.; Xian, W.; Yan, W.; Mou, X.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Community structure and carbon metabolism functions of bacterioplankton in the Guangdong coastal zone. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2024, 6, 547–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, N.; Herndl, G.J.; Hansell, D.A.; Benner, R.; Kattner, G.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Kirchman, D.L.; Weinbauer, M.G.; Luo, T.; Chen, F.; et al. Microbial production of recalcitrant dissolved organic matter: Long-term carbon storage in the global ocean. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 8, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.C.; Wang, F.Q.; Amann, R.I.; Teeling, H.; Du, Z.J. Epiphytic common core bacteria in the microbiomes of co-located green (Ulva), brown (Saccharina) and red (Grateloupia, Gelidium) macroalgae. Microbiome 2023, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Cai, R.; Liu, R.; Liu, G.; Sun, C. Maribellus comscasis sp. nov, a novel deep–sea Bacteroidetes bacterium, possessing a prominent capability of degrading cellulose. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 4561–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.; Wang, R.; Xia, T.; Zhang, S.; Ma, S.; Guo, Z. Natural Products and Biological Activity from Actinomycetes Associated with Marine Algae. Molecules 2023, 28, 5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, C.A.; Altabet, M.A.; Weigel, B.L. Kelp beds and their local effects on seawater chemistry, productivity, and microbial communities. Ecology 2019, 100, e02798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, C.A.; Altabet, M.A. Enhanced microbial nitrogen transformations in association with macrobiota from the rocky intertidal. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Luo, H.; Wang, Q.; He, Z.; Long, A. Large–scale Cultivation of Seaweed is Effective Approach to Increase Marine Carbon Sequestration and Solve Coastal Environmental Problems. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 36, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Criado, A.R. The art of writing literature review: What do we know and what do we need to know? Int. Bus. Rev. 2020, 29, 101717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrone, M.; Linnenluecke, M.K. Interdisciplinary Research Maps: A new technique for visualizing research topics. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwudulue, U.M.; Barger, N.; Dubovis, M.; Luzzatto Knaan, T. Natural products and pharmacological properties of symbiotic Bacillota (Firmicutes) of marine macroalgae. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagarete, A.; Ramos, A.S.; Puntervoll, P.; Allen, M.J.; Verdelho, V. Antiviral potential of algal metabolites-a comprehensive review. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltz, R.H. Genome mining for drug discovery: Progress at the front end. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 48, kuab044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamilla-Tamayo, L.; Escobar-Calderón, F.; Skalický, M. Reviewing the potential of algae species as a green alternative to produce nanoparticles: Findings from a database analysis. Water. 2023, 15, 2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Li, T.; Bi, R.; Sanganyado, E.; Huang, J.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Du, H. A systematic overview, trends and global perspectives on blue carbon: A bibliometric study (2003–2021). Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, X.; Lin, S.; Dong, Y.; Shen, H.; He, Z.; Luo, H.; Zou, L.; Chung, I.K.; Yang, Y. Large-scale seaweed cultivation as a nature solution for carbon-negative economy and restorative environmental stewardship: Lessons from China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2025, 207, 114954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Q.; Song, X.; Yuan, M.; Sun, R.; Zhang, J.; Yin, L.; Pu, Y. Removal of microcystins from water and primary treatment technologies-A comprehensive understanding based on bibliometric and content analysis, 1991–2020. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Huang, J.; Du, H.; Liu, X.; Zhong, C.; Lin, S. Coral bleaching from a nutrient perspective is understudied: A bibliometric survey. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 926783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongeon, P.; Paul-Hus, A. The journal coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: A comparative analysis. Scientometrics 2016, 106, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. VOS: A New Method for Visualizing Similarities Between Objects. In Advances in Data Analysis. Studies in Classification, Data Analysis, and Knowledge Organization; Decker, R., Lenz, H.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verasoundarapandian, G.; Wong, C.; Shaharuddin, N.; Gomez-Fuentes, C.; Zulkharnain, A.; Ahmad, S. A Review and Bibliometric Analysis on Applications of Microbial Degradation of Hydrocarbon Contaminants in Arctic Marine Environment at Metagenomic and Enzymatic Levels. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Majzoub, M.E.; Marzinelli, E.M.; Dai, Z.; Thomas, T.; Egan, S. Bacterial controlled mitigation of dysbiosis in a seaweed disease. ISME J. 2022, 16, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, P.; Aslam, M.; Du, H.; Liang, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, W. Environmental factors shape the epiphytic bacterial communities of Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonnadula, R.; Verma, P.; Shouche, Y.S.; Ghadi, S.C. Characterization of microbulbifer strain CMC-5, a new biochemical variant of microbulbifer elongatus type strain DSM6810T isolated from decomposing seaweeds. Curr. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Shuai, L.; Li, Y.; Lin, W.; Zhao, X.; Duan, D. Phylogenetic analysis of epiphytic marine bacteria on Hole–Rotten diseased sporophytes of Laminaria japonica. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, T.; Pang, S.; Liu, M.; Yue, H. Isolation and identification of bacteria associated with the surfaces of several algal species. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2009, 27, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfatis, A.; Wang, Y.; Twumasi-Ankrah, N.; Moffitt, J.R. Highly multiplexed spatial transcriptomics in bacteria. Science 2025, 387, eadr0932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, J.F.; Gräfe, M.S.; Dhiman, S.; Wienecke, P.; Arndt, H.D.; Wichard, T. Thallusin Quantification in Marine Bacteria and Algae Cultures. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause-Jensen, D.; Duarte, C.M. Substantial role of macroalgae in marine carbon sequestration. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, V.; Fong, J.; Ng, C.S.L.; Huang, D. Temporal and spatial dynamics of tropical macroalgal contributions to blue carbon. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 828, 154369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, A.; Geraldi, N.R.; Alam, I.; Kamau, A.A.; Acinas, S.G.; Logares, R.; Gasol, J.M.; Massana, R.; Krause-Jensen, D.; Duarte, C.M. Important contribution of macroalgae to oceanic carbon sequestration. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.F.; Filbee-Dexter, K.; Norderhaug, K.M.; Fredriksen, S.; Frisk, N.L.; Fagerli, C.W.; Wernberg, T. Detrital carbon production and export in high latitude kelp forests. Oecologia 2020, 192, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; He, C.; Shi, Q.; Jiao, N.; Zhang, Y. DOC dynamics and bacterial community succession during long-term degradation of Ulva prolifera and their implications for the legacy effect of green tides on refractory DOC pool in seawater. Water Res. 2020, 185, 116268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, T.; Li, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhai, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, L.; Chang, L.; Xue, L.; et al. Seaweed farming environments do not always function as CO2 sink under synergistic influence of macroalgae and microorganisms. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 361, 108824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallagher, J.B.; Shelamoff, V.; Layton, C. Seaweed ecosystems may not mitigate CO2 emissions. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2022, 79, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Zhan, S.; Shao, K.; Chen, H.; Fan, J. Spatial distribution characteristics and interaction effects of DOM and microbial communities in kelp cultivation areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 10, 170511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middelburg, J. Chemoautotrophy in the ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L24604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q. Management strategies of marine food resources undermultiple stressors with particular reference of the Yellow Sea large marine ecosystem. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2014, 1, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, P.; Aslam, M.; Yang, C.; Ye, P.; Ke, X.; Liang, Z.; Li, T.; Chen, W.; Du, H. Temporal variations of biological nitrogen fixation and diazotrophic communities associated with artificial seaweed farms. Fron. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1408958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelrazek, H.M.; Shams El-Din, N.G.; Ghozlan, H.A.; Sabry, S.A.; Abouelkheir, S.S. Distribution and functional perspective analysis of epiphytic and endophytic bacterial communities associated with marine seaweeds, Alexandria shores, Egypt. BMC Microbiol. 2024, 24, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichard, T. Exploring bacteria–induced growth and morphogenesis in the green macroalga order Ulvales (Chlorophyta). Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, P.Y.; Cheng, A.; Wang, R.; Zhang, R. Marine biofilms: Diversity, interactions and biofouling. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashen, J.B.; Goff, L.J. Molecular and Ecological Evidence for Species Specificity and Coevolution in a Group of Marine Algal-Bacterial Symbioses. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3024–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.J.; Hwang, M.S.; Park, M.A.; Baek, J.M.; Ha, D.S.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, S.R. Molecular identification of the algal pathogen Pythium chondricola (Oomycetes) from Pyropia yezoensis (Rhodophyta) using ITS and cox1 markers. Algae 2015, 30, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, J.A.; Klochkova, T.A.; Kim, G.H.; Loiseaux–De Goër, S. Olpidiopsis sp., an oomycete from Madagascar that infects Bostrychia and other red algae: Host species susceptibility. Phycol. Res. 2006, 54, 72–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.H.; Klochkova, T.A.; Lee, D.J.; Im, S.H. Chloroplast virus causes green-spot disease in cultivated Pyropia of Korea. Algal Res. 2016, 17, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goecke, F.; Labes, A.; Wiese, J.; Imhoff, J.F. Phylogenetic analysis and antibiotic activity of bacteria isolated from the surface of two co-occurring macroalgae from the Baltic Sea. Eur. J. Phycol. 2013, 48, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvers, P.H.; Gobler, C.J. Mitigation of harmful algal blooms caused by Alexandrium catenella and reduction in saxitoxin accumulation in bivalves using cultivable seaweeds. Harmful Algae 2021, 105, 102056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.; Hu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tang, Y.Z. Interactions between the seaweed Gracilaria and dinoflagellate Akashiwo sanguinea in an indoor co-cultivation system and the interference of bacteria. J. Appl. Phycol. 2021, 33, 3153–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Z.Y.; He, Z.L.; Deng, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.F.; Tang, Y.Z. Cultivation of seaweed Gracilaria lemaneiformis enhanced biodiversity in a eukaryotic plankton community as revealed via metagenomic analyses. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viju, N.; Punitha, S.M.J.; Satheesh, S. An Analysis of Biosynthesis Gene Clusters and Bioactivity of Marine Bacterial Symbionts. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 2522–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, H.M.; Chen, C.W.; Huang, C.Y.; Singhania, R.R.; Sung, Y.J.; Dong, C.; Patel, A.K. Development of Bioactive Peptides Derived from Red Algae for Dermal Care Applications: Recent Advances. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltz, R.H. Gifted microbes for genome mining and natural product discovery. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrell, A.A.; Veličković, D.; Lawrence, T.J.; Bowen, B.P.; Louie, K.B.; Carper, D.L.; Chu, R.K.; Mitchell, H.D.; Orr, G.; Markillie, L.M.; et al. Novel metabolic interactions and environmental conditions mediate the boreal peatmoss-cyanobacteria mutualism. ISME J. 2022, 16, 1074–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, J.Y.; Liu, L.; Hua, Z.S.; Fang, B.Z.; Zhou, E.M.; Salam, N.; Hedlund, B.P.; Li, W.J. Microbial dark matter coming to light: Challenges and opportunities. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, P.; Wang, J.; Zhao, F. RiboFR–Seq: A novel approach to linking 16S rRNA amplicon profiles to metagenomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, S.J.; Tamminen, M.V.; Preheim, S.P.; Guo, M.T.; Briggs, A.W.; Brito, I.L.A.; Weitz, D.; Pitkänen, L.K.; Vigneault, F.; Virta, M.P.; et al. Massively parallel sequencing of single cells by epicPCR links functional genes with phylogenetic markers. ISME J. 2016, 10, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reisky, L.; Préchoux, A.; Zühlke, M.K.; Bäumgen, M.; Robb, C.S.; Gerlach, N.; Roret, T.; Stanetty, C.; Larocque, R.; Michel, G.; et al. A marine bacterial enzymatic cascade degrades the algal polysaccharide ulvan. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KleinJan, H.; Frioux, C.; Califano, G.; Aite, M.; Fremy, E.; Karimi, E.; Corre, E.; Wichard, T.; Siegel, A.; Boyen, C.; et al. Insights into the potential for mutualistic and harmful host–microbe interactions affecting brown alga freshwater acclimation. Mol. Ecol. 2023, 32, 703–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhao, S.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, H.; Needham, D.M.; Evans, E.D.; Dai, C.L.; Lu, P.J.; Alm, E.J.; Weitz, D.A. High–throughput, single–microbe genomics with strain resolution, applied to a human gut microbiome. Science 2022, 376, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hevroni, G.; Vincent, F.; Ku, C.; Sheyn, U.; Vardi, A. Daily turnover of active giant virus infection during algal blooms revealed by single-cell transcriptomics. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadf7971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarone, P.; Laura, G.; Laura, A.; Maria, M.S. Seasonal changes in bacterioplankton nutrient limitation and their effects on bacterial community composition in the NW Mediterranean Sea. Aquat. Microbal Ecol. 2006, 44, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, S.; Marin-Léal, J.C.; Ropert, M.; Lefebvre, S. Effects of oyster farming on macrofaunal assemblages associated with Lanice conchilega tubeworm populations: A trophic analysis using natural stable isotopes. Aquaculture 2007, 271, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, G.; Edlinger, A.; Banerjee, S.; Degrune, F.; García-Palacios, P.; Pescador, D.S.; Herzog, C.; Romdhane, S.; Saghai, A.; Spor, A.; et al. Crop cover is more important than rotational diversity for soil multifunctionality and cereal yields in European cropping systems. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Saini, K.C.; Mallick, A.; Bast, F. Seaweed-associated epiphytic bacteria: Diversity, ecological and economic implications. Aquat. Bot. 2023, 189, 103698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Kasai, H.; Shizuri, Y.; Harayama, S. Isolation and phylogenetic characterization of bacteria capable of inducing differentiation in the green alga Monostroma oxyspermum. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Lin, W.; Liu, J. The characteristics of nutrient removal and inhibitory effect of Ulva clathrata on Vibrio anguillarum 65. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albakosh, M.A.; Naidoo, R.K.; Kirby, B.; Bauer, R. Identification of epiphytic bacterial communities associated with the brown alga Splachnidium rugosum. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penesyan, A.; Kjelleberg, S.; Egan, S. Development of novel drugs from marine surface associated microorganisms. Mar. Drugs. 2010, 8, 438–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penesyan, A.; Marshall-Jones, Z.; Holmstrom, C.; Kjelleberg, S.; Egan, S. Antimicrobial activity observed among cultured marine epiphytic bacteria reflects their potential as a source of new drugs: Research article. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 69, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penesyan, A.; Tebben, J.; Lee, M.; Thomas, T.; Kjelleberg, S.; Harder, T.; Egan, S. Identification of the antibacterial compound produced by the marine epiphytic bacterium Pseudovibrio sp. D323 and related sponge-associated bacteria. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1391–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalini, M.S.; Prakash, H.S. Diversity and bioprospecting of actinomycete endophytes from the medicinal plants. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 64, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulfah, M.; Kasanah, N.; Wijayanti, N. Antivibriosis and cytotoxicity of Actinobacteria associated with red seaweed Gelidiella acerosa. Aquac. Res. 2021, 12, 6786–6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogolitsyn, K.; Dobrodeeva, L.; Samodova, A.; Parshina, A. In vitro Immunostimulant Activity of the Polyphenolic Extract from the Arctic Brown Algae Fucus vesiculosus. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2024, 79, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wei, L.; Yang, J.; Ahmed, W.; Wang, Y.; Fu, L.; Ji, G. Probiotic Consortia: Reshaping the Rhizospheric Microbiome and Its Role in Suppressing Root-Rot Disease of Panax notoginseng. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Jin, H.; Lv, R.; Shi, H.; De, G.; Yang, B.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, H. Probiotics maintain the intestinal microbiome homeostasis of the sailors during a long sea voyage. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 930–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherlach, K.; Hertweck, C. Mining and unearthing hidden biosynthetic potential. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Weinberger, F.; de Nys, R.; Thomas, T.; Egan, S. A pathway to improve seaweed aquaculture through microbiota manipulation. Trends Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
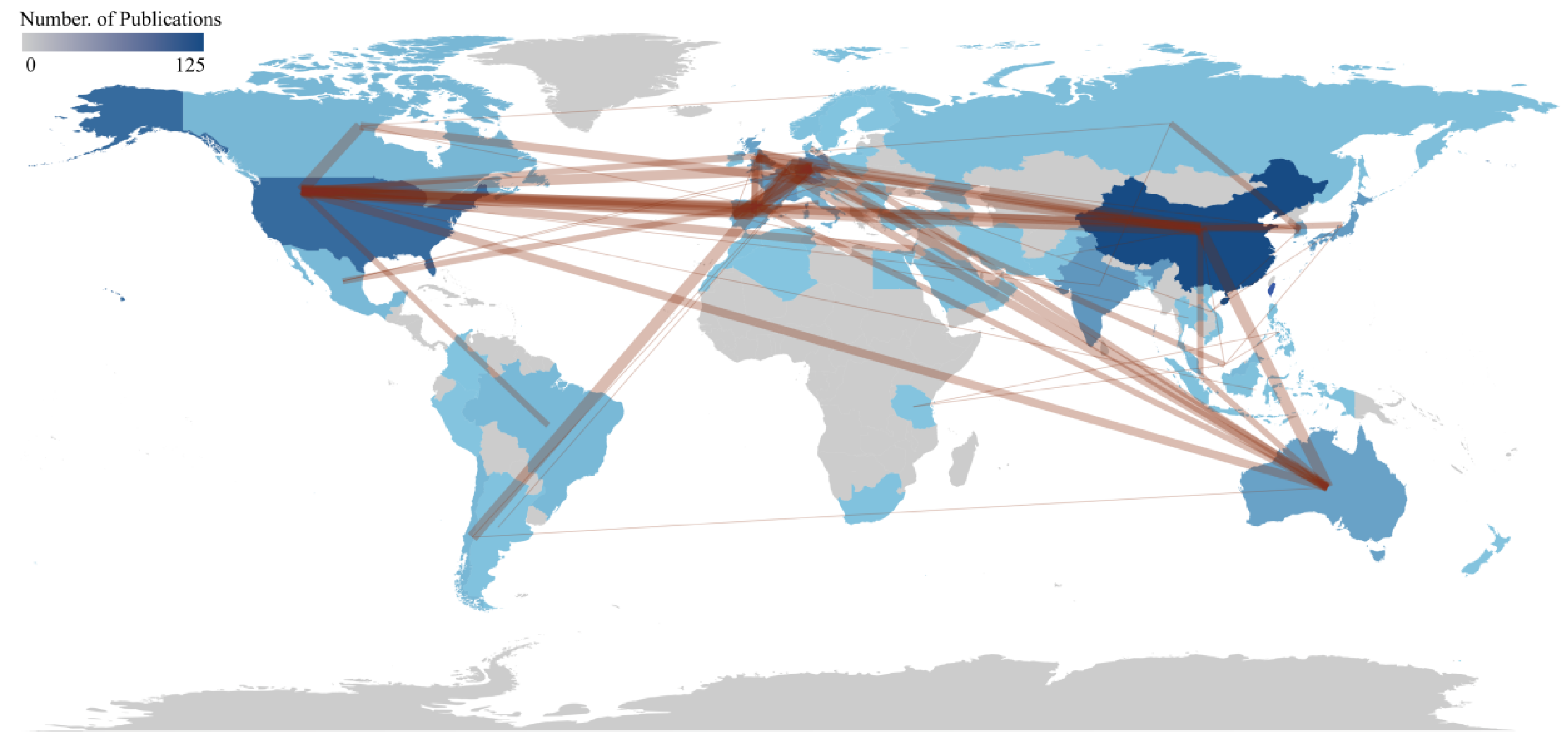

| Country | Articles | SCP | MCP | Freq. | MCP Ratio | TC | AAC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | 125 | 101 | 24 | 0.205 | 0.192 | 2117 | 16.9 |
| USA | 73 | 61 | 12 | 0.12 | 0.164 | 7043 | 96.5 |
| India | 45 | 41 | 4 | 0.074 | 0.089 | 756 | 16.8 |
| Germany | 41 | 19 | 22 | 0.067 | 0.537 | 1660 | 40.5 |
| Japan | 37 | 34 | 3 | 0.061 | 0.081 | 815 | 22 |
| Korea | 25 | 19 | 6 | 0.041 | 0.24 | 581 | 23.2 |
| France | 24 | 16 | 8 | 0.039 | 0.333 | 505 | 21 |
| Australia | 21 | 12 | 9 | 0.034 | 0.429 | 1263 | 60.1 |
| United Kingdom | 20 | 10 | 10 | 0.033 | 0.5 | 774 | 38.7 |
| Italy | 14 | 10 | 4 | 0.023 | 0.286 | 311 | 22.2 |
| Portugal | 14 | 7 | 7 | 0.023 | 0.5 | 529 | 37.8 |
| Spain | 14 | 7 | 7 | 0.023 | 0.5 | 624 | 44.6 |
| Chile | 13 | 8 | 5 | 0.021 | 0.385 | 301 | 23.2 |
| Belgium | 12 | 3 | 9 | 0.02 | 0.75 | 300 | 25 |
| Brazil | 12 | 10 | 2 | 0.02 | 0.167 | 312 | 26 |
| Malaysia | 12 | 6 | 6 | 0.02 | 0.5 | 224 | 18.7 |
| Canada | 11 | 7 | 4 | 0.018 | 0.364 | 309 | 28.1 |
| Denmark | 10 | 5 | 5 | 0.016 | 0.5 | 549 | 54.9 |
| Mexico | 9 | 7 | 2 | 0.015 | 0.222 | 82 | 9.1 |
| Russia | 6 | 4 | 2 | 0.01 | 0.333 | 311 | 51.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Pei, P.; Aslam, M.; Syaifudin, M.; Bi, R.; Li, P.; Du, H. Microorganisms in Macroalgae Cultivation Ecosystems: A Systematic Review and Future Prospects Based on Bibliometric Analysis. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051110
Chen Y, Pei P, Aslam M, Syaifudin M, Bi R, Li P, Du H. Microorganisms in Macroalgae Cultivation Ecosystems: A Systematic Review and Future Prospects Based on Bibliometric Analysis. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(5):1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051110
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yinglong, Pengbing Pei, Muhammad Aslam, Muhamad Syaifudin, Ran Bi, Ping Li, and Hong Du. 2025. "Microorganisms in Macroalgae Cultivation Ecosystems: A Systematic Review and Future Prospects Based on Bibliometric Analysis" Microorganisms 13, no. 5: 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051110
APA StyleChen, Y., Pei, P., Aslam, M., Syaifudin, M., Bi, R., Li, P., & Du, H. (2025). Microorganisms in Macroalgae Cultivation Ecosystems: A Systematic Review and Future Prospects Based on Bibliometric Analysis. Microorganisms, 13(5), 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051110









