Effect of Funneliformis mosseae and Cu Additives on the Astragalus sinicus Root Growth and Cd Uptake Under the Modeled Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials and Design
2.2. Growth Parameters Measurement
2.3. Heavy Metal Cd Content Measurement
2.4. Osmotic Regulator Measurement
2.5. Malondialdehyde (MDA) and Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) Contents Measurement
2.6. Antioxidant Activity Measurements
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results
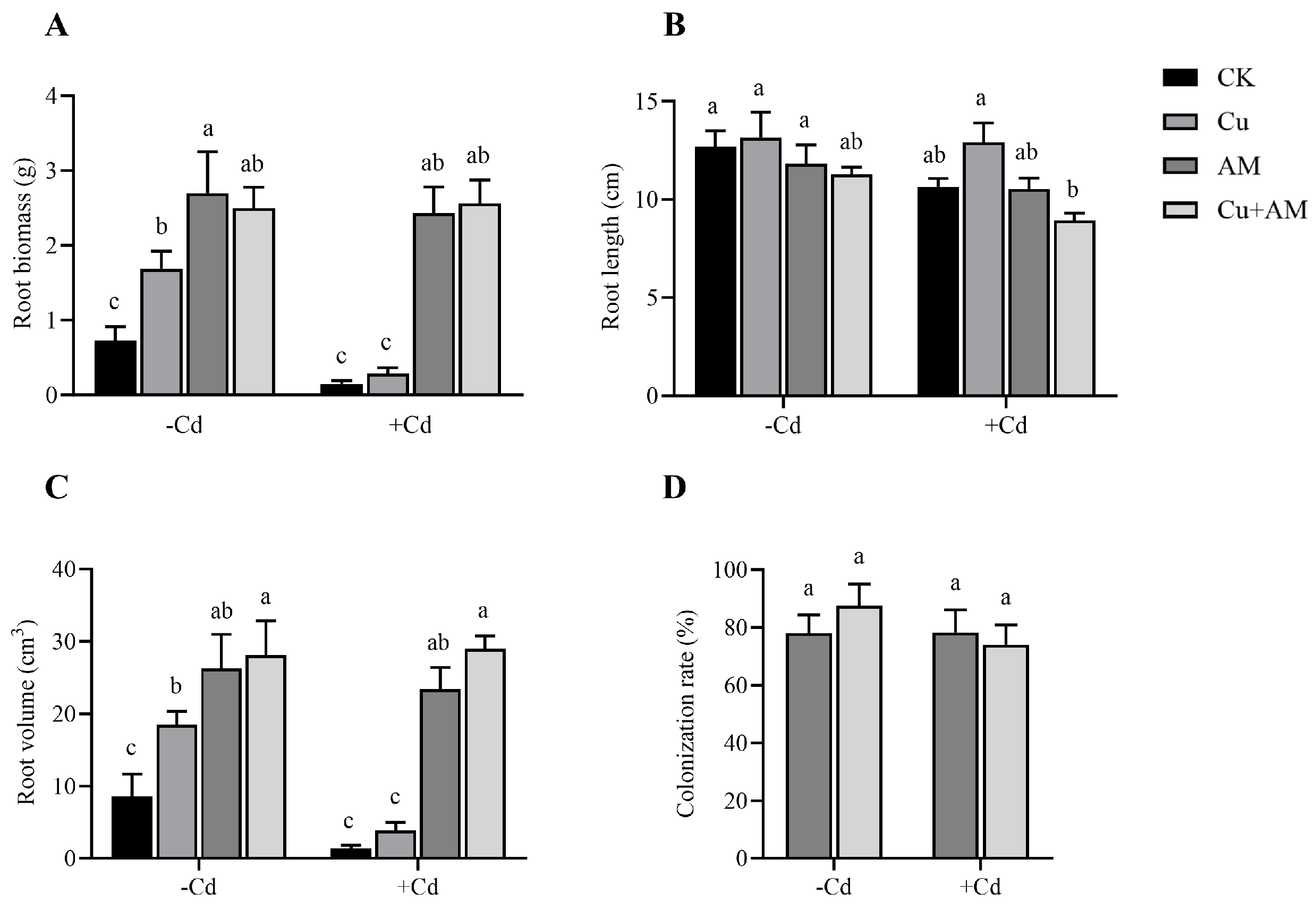
3.1. Effects of Different Treatments on Root Growth of A. sinicus
3.2. Effects of Different Treatments on Cd Concentration, Translocation, and Bioconcentration in the Roots of A. sinicus
3.3. Changes in the Contents of Osmotic Regulatory Substances in the Roots of A. sinicus Under Different Treatments
3.4. Changes in Malondialdehyde (MDA) Content in the Roots of A. sinicus Under Different Treatments
3.5. Changes in H2O2 Content and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in the Roots of A. sinicus Under Different Treatments
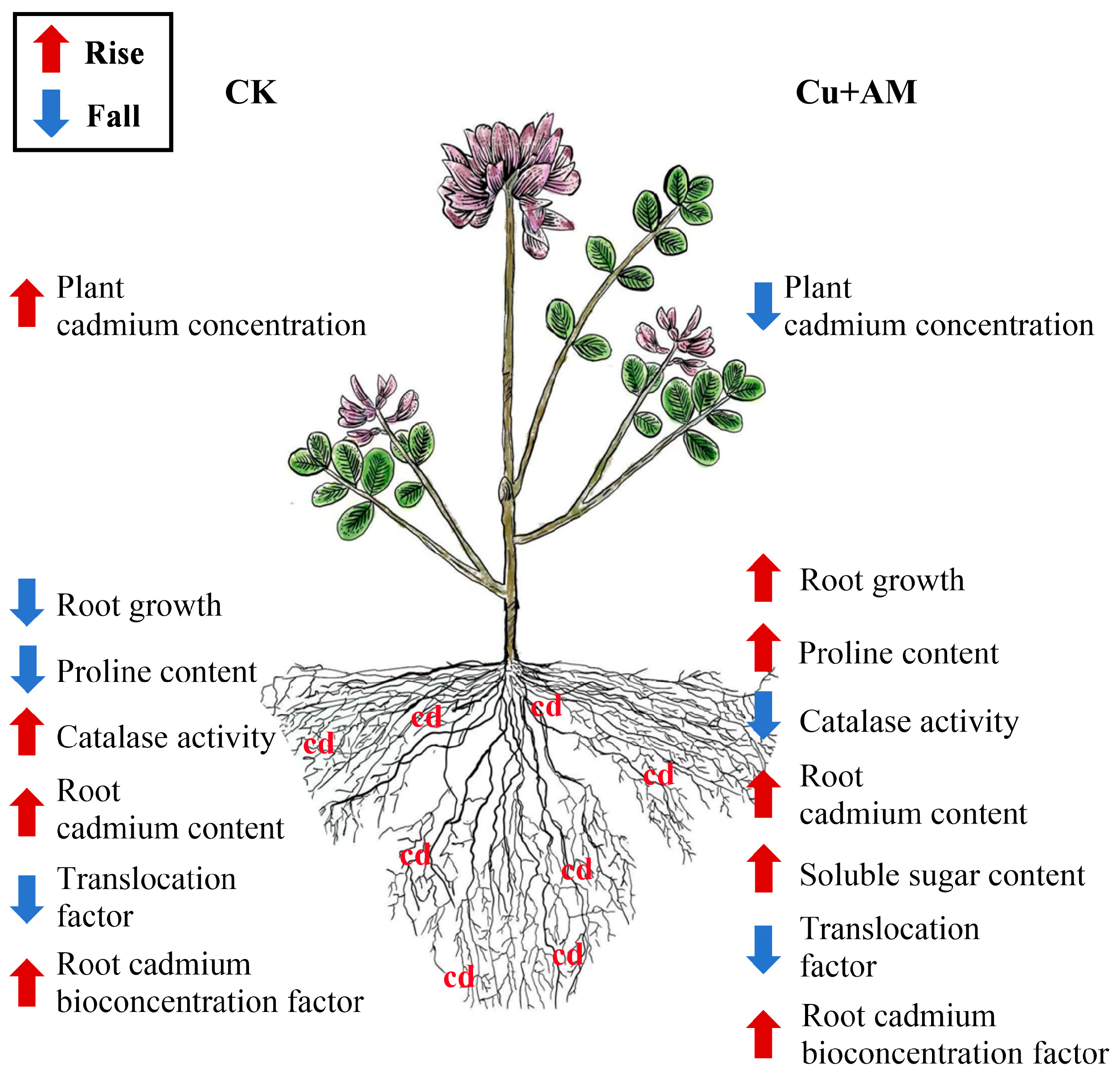
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, D.Y.; Jia, X.Y.; Wang, L.W.; McGrath, S.P.; Zhu, Y.G.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, F.J.; Bank, M.S.; O’Connor, D.; Nriagu, J. Global soil pollution by toxic metals threatens agriculture and human health. Science 2025, 388, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, G.; Hermann, T.; Szatmári, G.; Pásztor, L. Maps of heavy metals in the soils of the European Union and proposed priority areas for detailed assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1054–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Report on the national general survey of soil contamination. China Environ. Prot. Ind. 2014, 5, 10–11.
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, M.; Cai, R.; Miao, Y.; Zhu, X. Heavy metals potentially drive co-selection of antibiotic resistance genes by shifting soil bacterial communities in paddy soils along the middle and lower Yangtze River. Pedosphere 2024, 34, 606–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Teng, Y.G.; Lu, S.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, J.S. Contamination features and health risk of soil heavy metals in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 512, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Q.R.; Li, X.C.; Huang, X.F. A critical review on chemical analysis of heavy metal complexes in water/wastewater and the mechanism of treatment methods. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 429, 131688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Y.Q.; Wang, L.; Ju, C.; Wang, G.; Ma, F.; Wang, Y.J.; Yang, D.G. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth and toxic element uptake of Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud under zinc/cadmium stress. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 213, 112023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osonubi, O. Comparative effects of vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculation and phosphorus fertilization on growth and phosphorus uptake of maize (Zea mays L.) and sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) plants under drought-stressed conditions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1994, 18, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahadur, A.; Batool, A.; Nasir, F.; Jiang, S.; Mingsen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Pan, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, H. Mechanistic insights into arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-mediated drought stress tolerance in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouallal, I.; Abbas, Y.; ElYacoubi, H.; Imtara, H.; Al Zain, M.N.; Ouajdi, M.; El Goumi, Y.; Alzamel, N.M.; Mohammed Noman, O.; Rochdi, A. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal inoculation by indigenous fungal complexes on the morpho-physiological behavior of Argania spinosa subjected to water deficit stress. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Huang, C.H.; Luo, J.; Peng, F.; Xue, X. Effects of salt stress on plant and the mechanism of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhancing salt tolerance of plants. Adv. Earth Sci. 2018, 33, 361. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.R. The Mechanisms by Which Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi (AMF) Enhance Phytoremediation of Soil Heavy Metal Pb Contamination; Northwest A&F University: Xianyang, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, Q.Q.; Wu, Y.J.; Gao, Y.M.; An, T.T.; Liu, S.; Liang, L.Y.; Xu, B.C.; Zhang, S.Q.; Yu, M.; Shabala, S. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi mitigate cadmium stress in maize. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 289, 117600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ef, A.; Abeer, H.; Alqarawi, A.; Hend, A.A. Alleviation of adverse impact of cadmium stress in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Pak. J. Bot. 2015, 47, 785–795. [Google Scholar]
- Vilela, L.A.F.; Barbosa, M.V. Contribution of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi in Promoting Cadmium Tolerance in Plants, Cadmium Tolerance in Plants; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hashem, A.; Abd_Allah, E.; Alqarawi, A.; Al Huqail, A.A.; Egamberdieva, D.; Wirth, S. Alleviation of cadmium stress in Solanum lycopersicum L. by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi via induction of acquired systemic tolerance. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.R.; Du, X.R.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Feng, F.J.; Zhang, J.M. Rhizosphere interface microbiome reassembly by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi weakens cadmium migration dynamics. Imeta 2023, 2, e133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, M.; Kamran, M.; Fang, Y.Z.; Wang, Q.Q.; Cao, H.Y.; Yang, G.L.; Deng, L.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Anastopoulos, I.; et al. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-induced mitigation of heavy metal phytotoxicity in metal contaminated soils: A critical review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.P.; Yan, L.; Kamran, M.; Liu, S.S.; Riaz, M. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi-assisted phytoremediation: A promising strategy for cadmium-contaminated soils. Plants 2024, 13, 3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhalaria, R.; Kumar, D.; Kumar, H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuča, K.; Torequl Islam, M.; Verma, R. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi as potential agents in ameliorating heavy metal stress in plants. Agronomy 2020, 10, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zveushe, O.K.; Dong, F.Q.; Ling, Q.; Chen, Y.; Sajid, S.; Zhou, L.; de Dios, V.R. Unraveling the effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on cadmium uptake and detoxification mechanisms in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, N.C.; Wolf, J.; Koch, G.W. Interactions among mycorrhizae, atmospheric CO2 and soil N impact plant community composition. Ecol. Lett. 2003, 6, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, E.D.; Liu, Y.Y.; Gu, D.F.; Zhan, X.C.; Li, J.Y.; Zhou, K.N.; Zhang, P.J.; Zou, Y. Molecular mechanisms of plant responses to copper: From deficiency to excess. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migocka, M.; Malas, K. Plant responses to copper: Molecular and regulatory mechanisms of copper uptake, distribution and accumulation in plants. In Plant Micronutrient Use Efficiency: Molecular and Genomic Perspectives in Crop Plants; Hossain, M.A., Kamiya, T., Burritt, D.J., Tran, L.P., Fujiwara, T., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 71–86. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Q.; Li, Z.H.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.Y.; Kang, Q.; Niu, D.D. Gibberellic acid application on biomass, oxidative stress response, and photosynthesis in spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) seedlings under copper stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 53594–53604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrees, M.; Ali, S.; Rizwan, M.; Ibrahim, M.; Abbas, F.; Farid, M.; Zia-ur-Rehman, M.; Irshad, M.K.; Bharwana, S.A. The effect of excess copper on growth and physiology of important food crops: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 8148–8162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscitti, M.; Arango, M.; Beltrano, J. Improvement of copper stress tolerance in pepper plants (Capsicum annuum L.) by inoculation with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. Theor. Exp. Plant Physiol. 2017, 29, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Z.; Jin, Z.X.; Li, Y.L.; Gu, Y.F. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation on the photosynthetic pigment contents, anti-oxidation capacity and membrane lipid peroxidation of Elsholtzia splendens leaves under copper stress. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 7699–7708. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, R.; Tapia, Y.; Antilén, M.; Ruiz, A.; Pimentel, P.; Santander, C.; Aponte, H.; González, F.; Cornejo, P. Beneficial interactive effects provided by an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and yeast on the growth of Oenothera picensis established on Cu mine tailings. Plants 2023, 12, 4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.H.; Zhao, B. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi mediated uptake of lanthanum in Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.). Chemosphere 2007, 68, 1548–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Shi, P.; Zhao, B. The effect of Cd on mycorrhizal development and enzyme activity of Glomus mosseae and Glomus intraradices in Astragalus sinicus L. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Li, Y.; Shi, P.; Chen, X.H.; Lin, H.; Zhao, B. The differential behavior of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in interaction with Astragalus sinicus L. under salt stress. Mycorrhiza 2011, 21, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Řezáčová, V.; Némethová, E.; Stehlíková, I.; Czakó, A.; Gryndler, M. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Funneliformis mosseae improves soybean growth even in soils with good nutrition. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 1252–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Ban, Y.; Belvett, N. Positive effects of Funneliformis mosseae inoculation on reed seedlings under water and TiO2 nanoparticles stresses. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, R.R.; Hu, Z.H.; Zhang, Q.L.; Li, Y.Q.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.L.; Wu, X.N.; Yang, J.T.; Zhang, L.Q.; Jing, Y.X. The effect of Funneliformis mosseae on the plant growth, Cd translocation and accumulation in the new Cd-hyperaccumulator Sphagneticola calendulacea. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 203, 110988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Song, F.; Xu, H. Influence of arbuscular mycorrhiza on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activity of maize plants under temperature stress. Mycorrhiza 2010, 20, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, M.; Tao, K.; Zhu, X. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on growth and reactive oxygen metabolism of tomato fruits under low saline conditions. Biocell 2022, 46, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miransari, M. Hyperaccumulators, arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and stress of heavy metals. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pogrzeba, M. Inoculation with Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi supports the uptake of macronutrients and promotes the growth of Festuca ovina L. and Trifolium medium L., a candidate species for green urban infrastructure. Plants 2024, 13, 2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, N.; Singh, S.; Kashyap, L. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and heavy metal tolerance in plants: An insight into physiological and molecular mechanisms. In Mycorrhiza-Nutrient Uptake, Biocontrol, Ecorestoration; Varma, A., Prasad, R., Tuteja, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2017; pp. 75–97. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.J.; Ouyang, X.L.; Yang, A.H.; Liu, T.Y.; Liu, L.P.; Zhou, H. Growth and physiological response of Cinnamomum camphora (L.) Presl to copper stress and analysis of copper enrichment and transport characteristics. Plant Sci. J. 2024, 42, 232–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zahangeer, A.M.; Rabia, C.T.; Mridha, M.A.U. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhance biomass growth, mineral content, and antioxidant activity in tomato plants under drought stress. J. Food Qual. 2023, 2023, 2581608. [Google Scholar]
- Saboor, A.; Ali, M.A.; Hussain, S.; El Enshasy, H.A.; Hussain, S.; Ahmed, N.; Gafur, A.; Sayyed, R.; Fahad, S.; Danish, S. Zinc nutrition and arbuscular mycorrhizal symbiosis effects on maize (Zea mays L.) growth and productivity. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 6339–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalloufi, M.; Martínez-Andújar, C.; Lachaâl, M.; Karray-Bouraoui, N.; Pérez-Alfocea, F.; Albacete, A. The interaction between foliar GA3 application and arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi inoculation improves growth in salinized tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) plants by modifying the hormonal balance. J. Plant Physiol. 2017, 214, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.C.; Yang, L.; Zou, Y.N.; Wu, Q.S. Root-associated endophytic fungi modulate endogenous auxin and cytokinin levels to improve plant biomass and root morphology of trifoliate orange. Hortic. Plant J. 2023, 9, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, D.J.; Srivastava, A.; Wu, Q.S.; Zou, Y.N. Mycorrhiza stimulates root-hair growth and IAA synthesis and transport in trifoliate orange under drought stress. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bücking, H.; Kafle, A. Role of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in the nitrogen uptake of plants: Current knowledge and research gaps. Agronomy 2015, 5, 587–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Bei, S.K.; Li, C.J.; Dong, Y.; Li, H.G.; Christie, P.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.L. Enhancement of faba bean competitive ability by arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi is highly correlated with dynamic nutrient acquisition by competing wheat. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, N.; Fan, J.Q.; Wang, F.; George, T.S.; Feng, G. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi stimulate organic phosphate mobilization associated with changing bacterial community structure under field conditions. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 2639–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.Q.; Zhang, B.G.; Li, J.X.; Lai, B. Decontamination of heavy metal complexes by advanced oxidation processes: A review. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2575–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, K.Y.; Zou, R.; Wang, L.; Huo, W.M.; Fan, H.L. Cellular distribution of cadmium in two amaranth (Amaranthus mangostanus L.) cultivars differing in cadmium accumulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 22147–22158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Y.F. Translocation and accumulation of heavy metals from the rhizoshphere soil to the medicinal plant (Paeonia Lactiflora Pall.) grown in Bozhou, Anhui Province, China. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2023, 35, 2223768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, K.; Kohli, S.K.; Ohri, P.; Bhardwaj, R.; Ahmad, P. Agroecotoxicological aspect of Cd in soil–plant system: Uptake, translocation and amelioration strategies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 30908–30934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rask, K.A.; Johansen, J.L.; Kjøller, R.; Ekelund, F. Differences in arbuscular mycorrhizal colonisation influence cadmium uptake in plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 162, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.Y.; Wang, L.; Shi, Z.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Song, Z.M. Effects of AM inoculation and organic amendment, alone or in combination, on growth, P nutrition, and heavy-metal uptake of tobacco in Pb-Cd-contaminated soil. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2012, 31, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, F.D.; Li, B.; Jiang, M.; Li, T.G.; He, Y.M.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.S. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth and heavy metal accumulation of bermudagrass [Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers.] grown in a lead–zinc mine wasteland. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2019, 21, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.Q.; Nie, Q.K.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Z.C.; Huang, W.X. The studies on cadmium and its chelate related transporters in plants. Crops 2018, 3, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yruela, I. Copper in plants: Acquisition, transport and interactions. Funct. Plant Biol. 2009, 36, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, I.; Fontaine, J.; Sahraoui, A.L.H. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal responses to abiotic stresses: A review. Phytochemistry 2016, 123, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Ali, S.; Zandi, P.; Mehmood, A.; Ullah, S.; Ikram, M.; Ismail, I.; Babar, M. Role of sugars, amino acids and organic acids in improving plant abiotic stress tolerance. Pak. J. Bot. 2020, 52, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yooyongwech, S.; Samphumphuang, T.; Tisarum, R.; Theerawitaya, C.; Cha-Um, S. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) improved water deficit tolerance in two different sweet potato genotypes involves osmotic adjustments via soluble sugar and free proline. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 198, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.H.; Zeng, Z.F.; Wu, X.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, F.Q.; Yang, J.; Li, X. Jasmonic acid negatively regulation of root growth in Japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.) under cadmium treatment. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 98, 651–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, S.; Chaudhary, N.; Singh, N.K. Role of soluble sugars in metabolism and sensing under abiotic stress. In Plant Growth Regulators: Signalling Under Stress Conditions; Aftab, T., Hakeem, K.R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Germany, 2021; pp. 305–334. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.M.; Wu, X.B.; Li, X.Y.; Li, X.H. Responses of growth, functional enzyme activity in biomembrane of tomato seedlings to excessive copper, cadmium and the alleviating effect of exogenous nitric oxide. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2011, 17, 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.H.; Wei, M.; Li, Y.P.; Tang, M.; Zhang, H.Q. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi improve growth and tolerance of Platycladus orientalis under lead stress. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2023, 25, 1967–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.H.; Wang, H.; Li, H. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi enhance drought stress tolerance by regulating osmotic balance, the antioxidant system, and the expression of drought-responsive genes in vitis vinifera L. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2023, 2023, 7208341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Hossain, M.A.; da Silva, J.A.T.; Fujita, M. Plant response and tolerance to abiotic oxidative stress: Antioxidant defense is a key factor. In Crop Stress and Its Management: Perspectives and Strategies; Bandi, V., Shanker, A.K., Shanker, C., Mandapaka, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 261–316. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.M.; Hashem, A.; Abd-Allah, E.F.; Wu, Q.S. Root-associated symbiotic fungi enhance waterlogging tolerance of peach seedlings by increasing flavonoids and activities and gene expression of antioxidant enzymes. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2023, 10, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.L.; Wang, L.T.; Chen, K.K.; Sun, H.; Wang, P.C. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on the growth and physiological performance of Sophora davidii seedling under low-phosphorus stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 43, 2383–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Wei, X.W.; Wang, Y.; Dong, J.X.; Yang, X.C. Mechanism of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in enhancing lead stress resistance in poplar trees. Forests 2025, 16, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, A.M.; Fulekar, M. Antioxidant enzyme responses of plants to heavy metal stress. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 11, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.; Sun, X.; Mo, C.; Hao, M.; Wei, X.; Ma, A. Relationship between antioxidant enzymes and sclerotial formation of Pleurotus tuber-regium under abiotic stress. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 1391–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, D.; Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Romero, R.; Prasad, R.; Singh, J. Antioxidant enzymes regulation in plants in reference to reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS). Plant Gene 2019, 19, 100182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anass, K.; Zoulfa, R.; Azzouz, K.; Nada, N.; Abdelhamid, E.; Bouchra, B.; Ayoub, K.; Mohammed, E.M.; Naima, N.; Nhiri, M. Effects of mycorrhizal symbiosis and Ulva lactuca seaweed extract on growth, carbon/nitrogen metabolism, and antioxidant response in cadmium-stressed sorghum plant. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2024, 30, 605–618. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.T.; Chen, K.; Li, Q.; Tang, Y.L.; Jiang, Y.Y.; Su, Y. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on alleviating cadmium stress in Medicago truncatula Gaertn. Plants 2023, 12, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Du, C.Q.; Riaz, M.; Jiang, C.C. Boron mitigates citrus root injuries by regulating intracellular pH and reactive oxygen species to resist H+-toxicity. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 255, 113254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, D.; Saritha, B.; Janeeshma, E.; Gusain, P.; Khoshru, B.; Nouh, F.A.A.; Rani, A.; Olatunbosun, A.N.; Ruparelia, J.; Rabari, A. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal association boosted the arsenic resistance in crops with special responsiveness to rice plant. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 193, 104681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Anand, G.; Singh, N.; Kapoor, R. Arbuscular mycorrhiza augments arsenic tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by strengthening antioxidant defense system and thiol metabolism. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Cai, R.; Hu, J.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X. Effect of Funneliformis mosseae and Cu Additives on the Astragalus sinicus Root Growth and Cd Uptake Under the Modeled Conditions. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051109
Li Y, Cai R, Hu J, Liu H, Zhu X. Effect of Funneliformis mosseae and Cu Additives on the Astragalus sinicus Root Growth and Cd Uptake Under the Modeled Conditions. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(5):1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051109
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yuxin, Rui Cai, Jindian Hu, Hongling Liu, and Xiancan Zhu. 2025. "Effect of Funneliformis mosseae and Cu Additives on the Astragalus sinicus Root Growth and Cd Uptake Under the Modeled Conditions" Microorganisms 13, no. 5: 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051109
APA StyleLi, Y., Cai, R., Hu, J., Liu, H., & Zhu, X. (2025). Effect of Funneliformis mosseae and Cu Additives on the Astragalus sinicus Root Growth and Cd Uptake Under the Modeled Conditions. Microorganisms, 13(5), 1109. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13051109





