Bioprospecting of Marine Organisms: Exploring Antibacterial Activities in Aqueous and Organic Extracts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Collection
2.2. Aqueous Extraction
2.3. Organic Extraction
2.4. Bacteria and Culture Conditions
2.4.1. Antibiogram Assay
2.4.2. Statistical Analysis
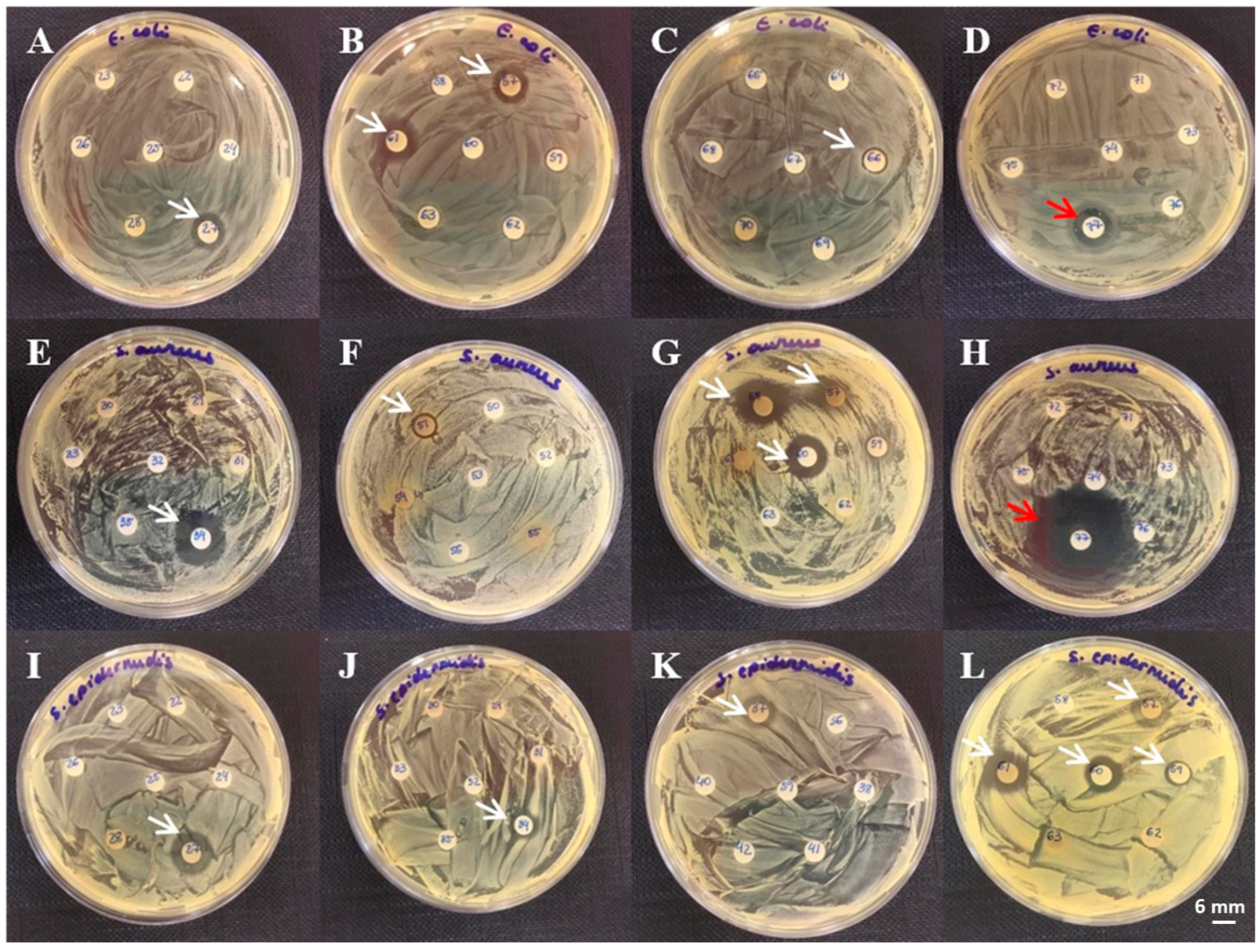
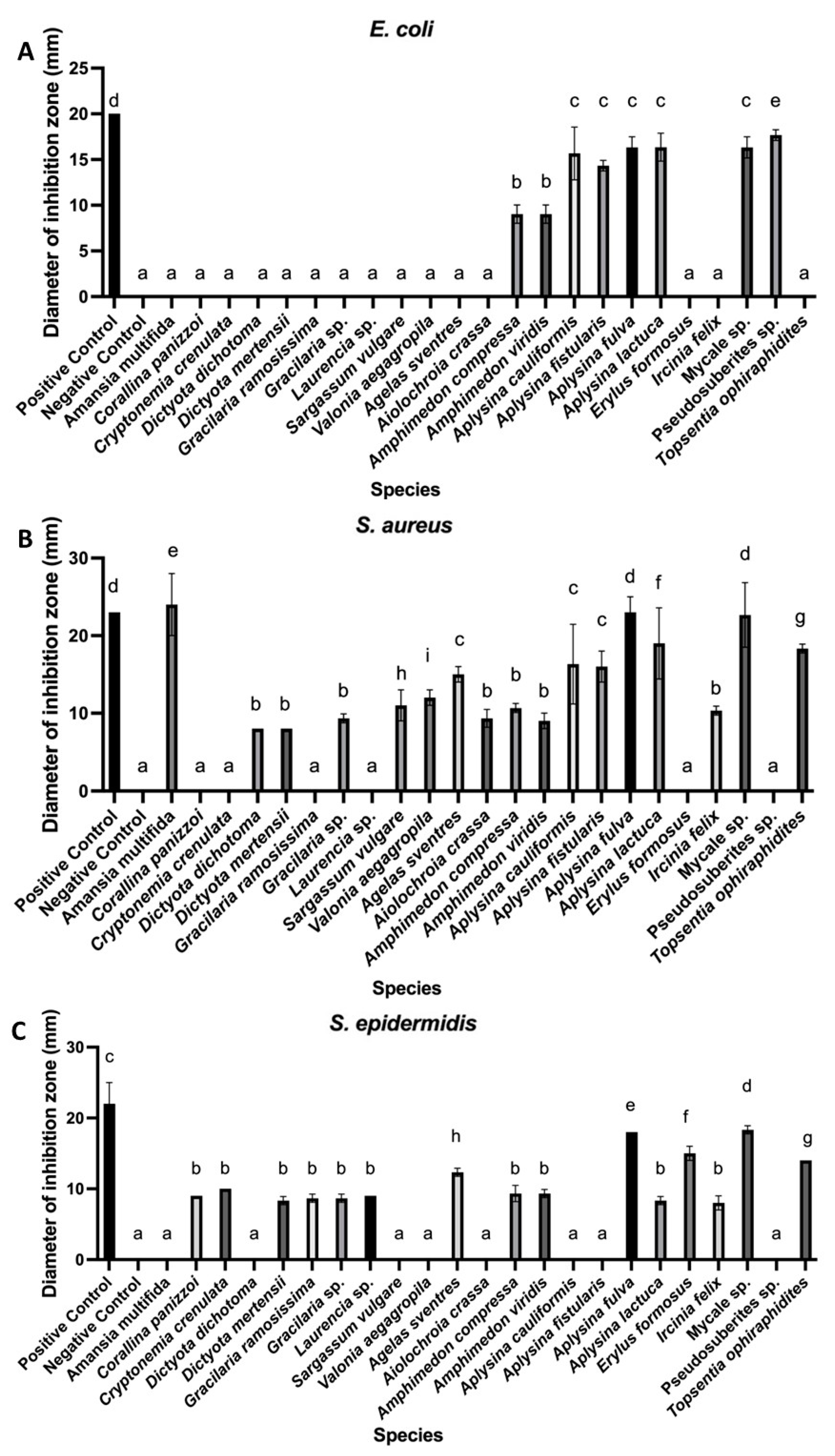
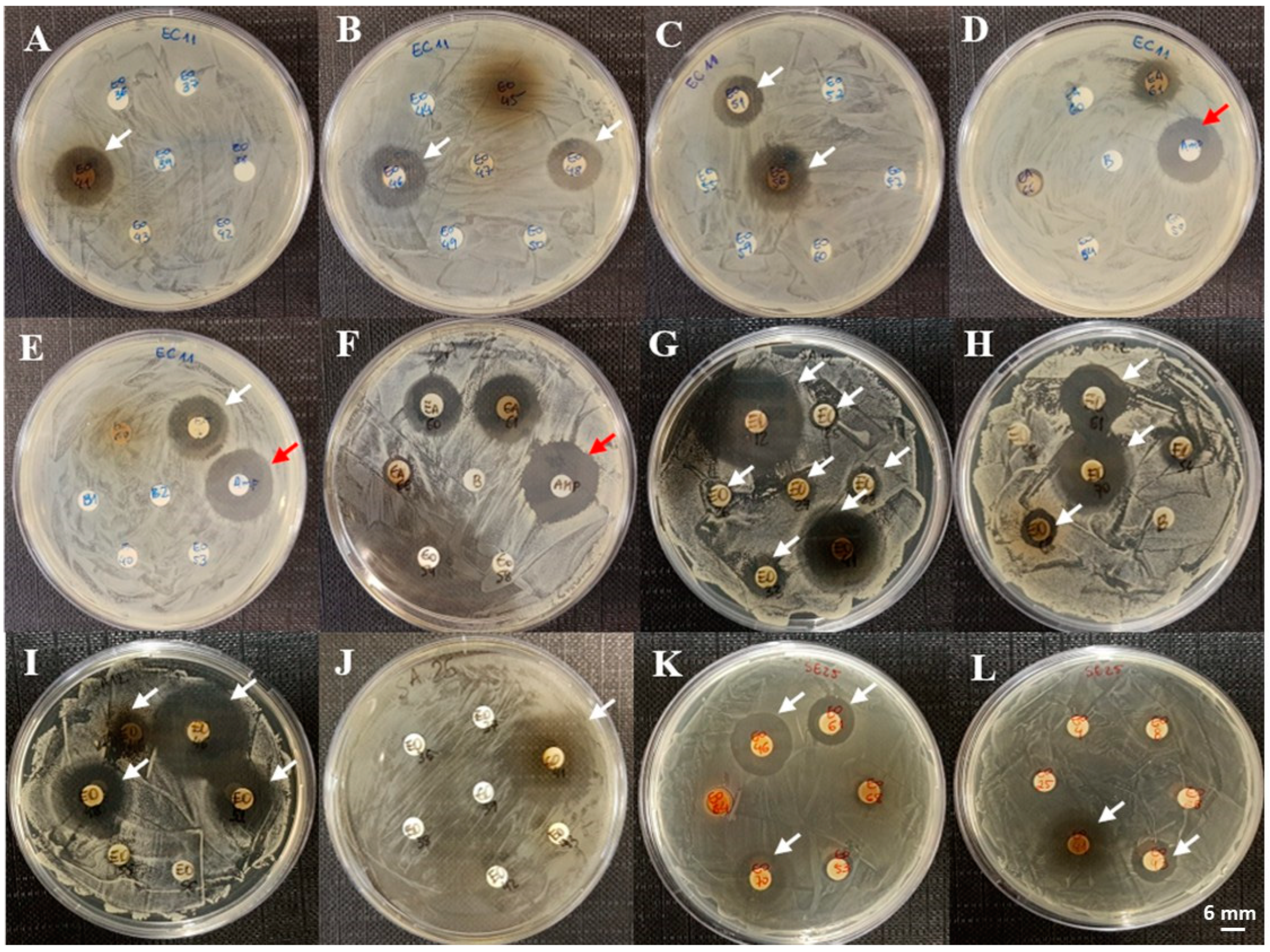
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Gu, Y.C.; Su, M.Z.; Guo, Y.W. Chemistry and bioactivity of secondary metabolites from South China Sea marine fauna and flora: Recent research advances and perspective. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 3062–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.K.; Albarico, F.P.J.B.; Perumal, P.K.; Vadrale, A.P.; Nian, C.T.; Chau, H.T.B.; Anwar, C.; Wani, H.M.U.D.; Pal, A.; Saini, R.; et al. Algae as an emerging source of bioactive pigments. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 126910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Kannappan, A.; Shi, C.; Lin, X. Marine Bacterial Secondary Metabolites: A Treasure House for Structurally Unique and Effective Antimicrobial Compounds. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharathi, D.; Lee, J.T. Recent Advances in Marine-Derived Compounds as Potent Antibacterial and Antifungal Agents: A Comprehensive Review. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhiravel, S.; Dave, D.; Shahidi, F. Bioactives from marine resources as natural health products: A review. Pharmacol. Rev. 2024, 77, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malve, H. Exploring the ocean for new drug developments: Marine pharmacology. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2016, 8, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, A.M.S.; Rodríguez, A.D.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Fusetani, N. Marine pharmacology in 2009–2011: Marine compounds with antibacterial, antidiabetic, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, antiprotozoal, antituberculosis, and antiviral activities; affecting the immune and nervous systems, and other miscellaneous mechanisms of action. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 2510–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, M.J.; Melby, M.K.; Lock, M.; Nichter, M. Accounting for variation in and overuse of antibiotics among humans. Bioessays 2021, 43, 2000163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beesoo, R.; Bhagooli, R.; Neergheen-Bhujun, V.S.; Li, W.W.; Kagansky, A.; Bahorun, T. Antibacterial and antibiotic potentiating activities of tropical marine sponge extracts. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 196, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamayeli, H.; Hassanshahian, M.; Hesni, M.A. The antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of sea anemone (Stichodactyla haddoni) against antibiotic-resistant bacteria and characterization of bioactive metabolites. Int. Aquat. Res. 2019, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkour, F.; El-Shoubaky, G.; Ebada, M. Antibacterial activity of some seaweeds from the Red Sea coast of Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Biol. Fish. 2019, 23, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, A.; Harahap, I.A.; Ardiansyah, A.; Bayu, A.; Rasyid, A.; Murniasih, T.; Setyastuti, A.; Putra, M.Y. Antioxidant and antibacterial activities in 21 species of Indonesian sea cucumbers. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, B.; Al-Mariri, A. Antimicrobial Activity of the Marine Algal Extracts against Selected Pathogens. J. Agr. Sci. Tech-Iran. 2017, 19, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick, S.R.; Garvey, M.; Jordan, K.; Flynn, J.; O’Brien, B.; Gleeson, D. Screening commercial teat disinfectants against bacteria isolated from bovine milk using disk diffusion. Vet. World 2019, 12, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vennila, K.K.; Chitra, P.S.; Hilda, K.; Janarthanan, S.; Martin, P. Screening of Anti-Bacterial Activity of Brown Seaweeds from South East Coast of India. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2020, 11, 3993–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedo, M.W.F.S.; da Cunha, N.B.; Carneiro, J.A.; da Costa, R.A.; de Alencar, S.A.; Cardoso, M.H.; Franco, O.L.; Dias, S.C. Marine Organisms as a Rich Source of Biologically Active Peptides. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 667764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.M.; Antony, S.P. Marine Antimicrobial Peptides: An Emerging Nightmare to the Life-Threatening Pathogens. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2024, 16, 552–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, H.; Xing, R.; Li, P. Characterization, Preparation, and Purification of Marine Bioactive Peptides. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 9746720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiney, E.; Reginald, M.; Wilsy, J.I. Antibacterial activity and phytochemical screening of marine macro algae amphiroa anceps using three solvent extracts. Int. J. Pharmacogn. 2014, 1, 605–608. [Google Scholar]
- Varier, K.M.; Milton, M.C.J.; Arulvasu, C.; Gajendran, B. Evaluation of antibacterial properties of selected red seaweeds from Rameshwaram, Tamil Nadu, India. J. Acad. Ind. Res. 2013, 1, 667–670. [Google Scholar]
- Bianco, E.M.; de Oliveira, S.Q.; Rigotto, C.; Tonini, M.L.; da Rosa Guimaraes, T.; Bittencourt, F.; Gouvea, L.P.; Aresi, C.; de Almeida, M.T.; Moritz, M.I.; et al. Anti-infective potential of marine invertebrates and seaweeds from the Brazilian coast. Molecules 2013, 18, 5761–5778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, M.; Sobou, M.; Vilchéze, C.; Baughn, A.; Hashizume, H.; Pruksakorn, P.; Ishida, S.; Matsumoto, M.; Jacobs, W.R.; Kobayashi, M. Halicyclamine A, a marine spongean alkaloid as a lead for anti-tuberculosis agent. Bioorgan Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 6732–6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarisit, W.; Abdjul, D.B.; Yamazaki, H.; Kato, H.; Rotinsulu, H.; Wewengkang, D.S.; Sumilat, D.A.; Kapojos, M.M.; Ukai, K.; Namikoshi, M. Anti-mycobacterial alkaloids, cyclic 3-alkyl pyridinium dimers, from the Indonesian marine sponge Haliclona sp. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 3503–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazemi, M.; Alidoust Salimi, M.; Alidoust Salimi, P.; Motallebi, A.; Tamadoni Jahromi, S.; Ahmadzadeh, O. Antifungal and antibacterial activity of Haliclona sp. from the Persian Gulf, Iran. J. Mycol. Med. 2014, 24, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shushizadeh, M.R.; Behroozi, S.; Behfar, A.A.; Nazemi, M. Antibacterial activity and Gc-mass analysis of organic extract from Persian gulf Haliclona SP. J. Pharmacophore 2018, 9, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Bianco, E.M.; Krug, J.L.; Zimath, P.L.; Kroger, A.; Paganelli, C.J.; Boeder, A.M.; dos Santos, L.; Tenfen, A.; Ribeiro, S.M.; Kuroshima, K.N. Antimicrobial (including antimollicutes), antioxidant and anticholinesterase activities of Brazilian and Spanish marine organisms–evaluation of extracts and pure compounds. Rev. Bras. De Farmacogn. 2015, 25, 668–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperstad, S.V.; Haug, T.; Blencke, H.M.; Styrvold, O.B.; Li, C.; Stensvag, K. Antimicrobial peptides from marine invertebrates: Challenges and perspectives in marine antimicrobial peptide discovery. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, T.; Cubero, J.; Lanz, Z.; Gomez-Guinan, Y.; Segnini-Bravo, M.I. Antimicrobial activity of organic extracts isolated from Aplysina fistularis (Demospongiae: Aplysinidae). Rev. Biol. Trop. 2000, 48 (Suppl. S1), 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, M.J.; Li, M.; Ma, H.; Li, P.L.; Li, G.Q. Secondary metabolites from marine sponges of the genus Agelas: A comprehensive update insight on structural diversity and bioactivity. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 7789–7820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indraningrat, A.A.G.; Micheller, S.; Runderkamp, M.; Sauerland, I.; Becking, L.E.; Smidt, H.; Sipkema, D. Cultivation of Sponge-Associated Bacteria from Agelas sventres and Xestospongia muta Collected from Different Depths. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shady, N.H.; Fouad, M.A.; Salah Kamel, M.; Schirmeister, T.; Abdelmohsen, U.R. Natural Product Repertoire of the Genus Amphimedon. Mar. Drugs 2018, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widyani, K.A.M.; Wewengkang, D.; Rumondor, E. THE POTENCY OF Mycale vansoesti SPONGE EXTRACT AND FRACTIONS FROM MANADO TUA ISLAND WATERS AGAINST THE GROWTH OF Staphylococcus aureus AND Escherichia coli. Pharmacon 2022, 11, 1583–1590. [Google Scholar]
- Seradj, S.H.; Hashemi, S.Z.; Zomorodian, K.; Moein, M.R. Antimicrobial effects of some Persian gulf marine sponges. Iran. South Med. J. 2020, 23, 494–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeano, E.; Martínez, A. Antimicrobial activity of marine sponges from Urabá Gulf, Colombian Caribbean region. J. Mycol. Medicale 2007, 17, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, J.; Brango-Vanegas, J.; Costa, G.M.; Castellanos, L.; Arévalo, C.; Duque, C. Marine organisms as source of extracts to disrupt bacterial communication: Bioguided isolation and identification of quorum sensing inhibitors from. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2015, 25, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.C.C.; Merces, P.F.F.; Souza, I.R.A.; Almeida, C.M.A.; Lima, V.L.M.; Correia, M.T.S.; Silva, M.V.; Silva, A.G. Antimicrobial activity of seaweeds of Pernambuco, northeastern coast of Brazil. J. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 10, 312–318. [Google Scholar]
- Bakar, K.; Mohamad, H.; Tan, H.S.; Latip, J. Sterols compositions, antibacterial, and antifouling properties from two Malaysian seaweeds: Dictyota dichotoma and Sargassum granuliferum. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 9, 047–053. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Saif, S.S.; Abdel-Raouf, N.; El-Wazanani, H.A.; Aref, I.A. Antibacterial substances from marine algae isolated from Jeddah coast of Red sea, Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 21, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima-Filho, J.V.M.; Carvalho, A.F.F.U.; Freitas, S.M.; Melo, V.M.M. Antibacterial activity of extracts of six macroalgae from the northeastern brazilian coast. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2002, 33, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berne, S.; Kalauz, M.; Lapat, M.; Savin, L.; Janussen, D.; Kersken, D.; Avgutin, J.A.; Jokhadar, S.Z.; Jaklic, D.; Gunde-Cimerman, N.; et al. Screening of the Antarctic marine sponges (Porifera) as a source of bioactive compounds. Polar Biol. 2016, 39, 947–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibungu, W.C.; Clarke, A.M.; Fri, J.; Njom, H.A. Antimicrobial Potential and Phytochemical Screening of Clathria sp. 1 and Tedania (Tedania) stylonychaeta Sponge Crude Extracts Obtained from the South East Coast of South Africa. Biomed. Res. Int-Uk 2021, 2021, 6697944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquina-Lemonche, L.; Burns, J.; Turner, R.D.; Kumar, S.; Tank, R.; Mullin, N.; Wilson, J.S.; Chakrabarti, B.; Bullough, P.A.; Foster, S.J.; et al. The architecture of the Gram-positive bacterial cell wall. Nature 2020, 582, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, E.R.; Billings, G.; Odermatt, P.D.; Auer, G.K.; Zhu, L.; Miguel, A.; Chang, F.; Weibel, D.B.; Theriot, J.A.; Huang, K.C. The outer membrane is an essential load-bearing element in Gram-negative bacteria. Nature 2018, 559, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Plesiat, P.; Nikaido, H. The challenge of efflux-mediated antibiotic resistance in Gram-negative bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 337–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Menezes, V.P.P.; Silva Filho, A.M.d.; Costa, A.J.; Nascimento, E.; Pinheiro, U.S.; Chaves, R.P.; Andrade, A.L.; Vasconcelos, M.A.d.; Teixeira, E.H.; Sampaio, A.H.; et al. Bioprospecting of Marine Organisms: Exploring Antibacterial Activities in Aqueous and Organic Extracts. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040940
Menezes VPP, Silva Filho AMd, Costa AJ, Nascimento E, Pinheiro US, Chaves RP, Andrade AL, Vasconcelos MAd, Teixeira EH, Sampaio AH, et al. Bioprospecting of Marine Organisms: Exploring Antibacterial Activities in Aqueous and Organic Extracts. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):940. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040940
Chicago/Turabian StyleMenezes, Vinícius Paulino Pinto, Aldeni Moreira da Silva Filho, Aline Jeferson Costa, Elielton Nascimento, Ulisses Santos Pinheiro, Renata Pinheiro Chaves, Alexandre Lopes Andrade, Mayron Alves de Vasconcelos, Edson Holanda Teixeira, Alexandre Holanda Sampaio, and et al. 2025. "Bioprospecting of Marine Organisms: Exploring Antibacterial Activities in Aqueous and Organic Extracts" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040940
APA StyleMenezes, V. P. P., Silva Filho, A. M. d., Costa, A. J., Nascimento, E., Pinheiro, U. S., Chaves, R. P., Andrade, A. L., Vasconcelos, M. A. d., Teixeira, E. H., Sampaio, A. H., Nagano, C. S., & Carneiro, R. F. (2025). Bioprospecting of Marine Organisms: Exploring Antibacterial Activities in Aqueous and Organic Extracts. Microorganisms, 13(4), 940. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040940







