Antibiotic Abuse in Ornamental Fish: An Overlooked Reservoir for Antibiotic Resistance
Abstract
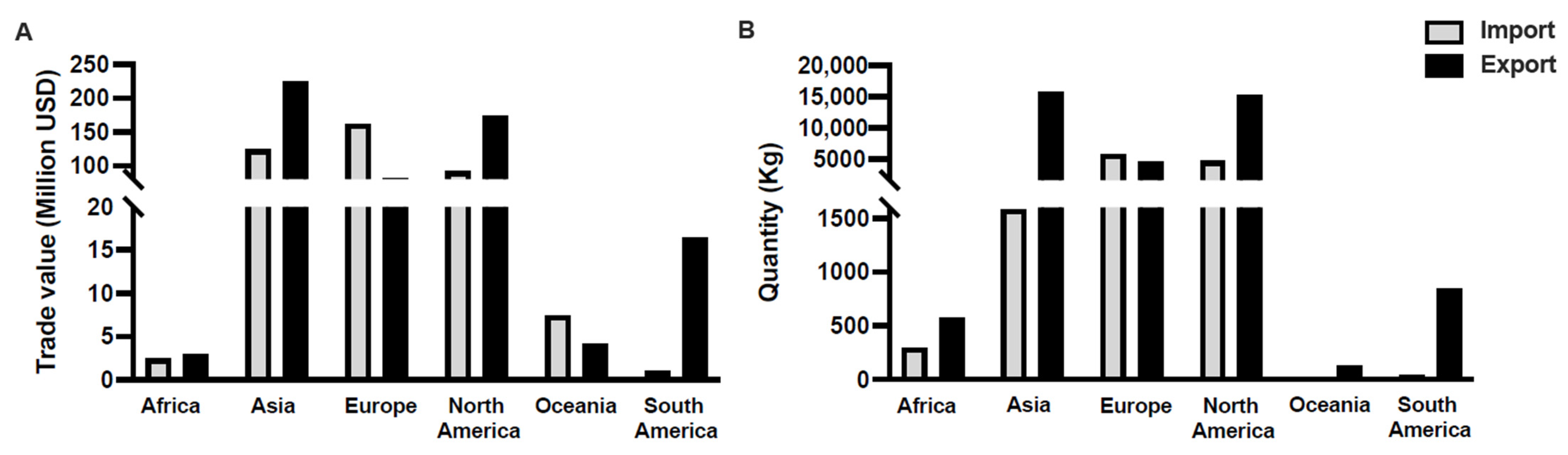
1. The Ornamental Fish Industry: An Overview
2. Antibiotic Use and Resistance in Ornamental Fish
2.1. Antibiotic Practices in the Industry
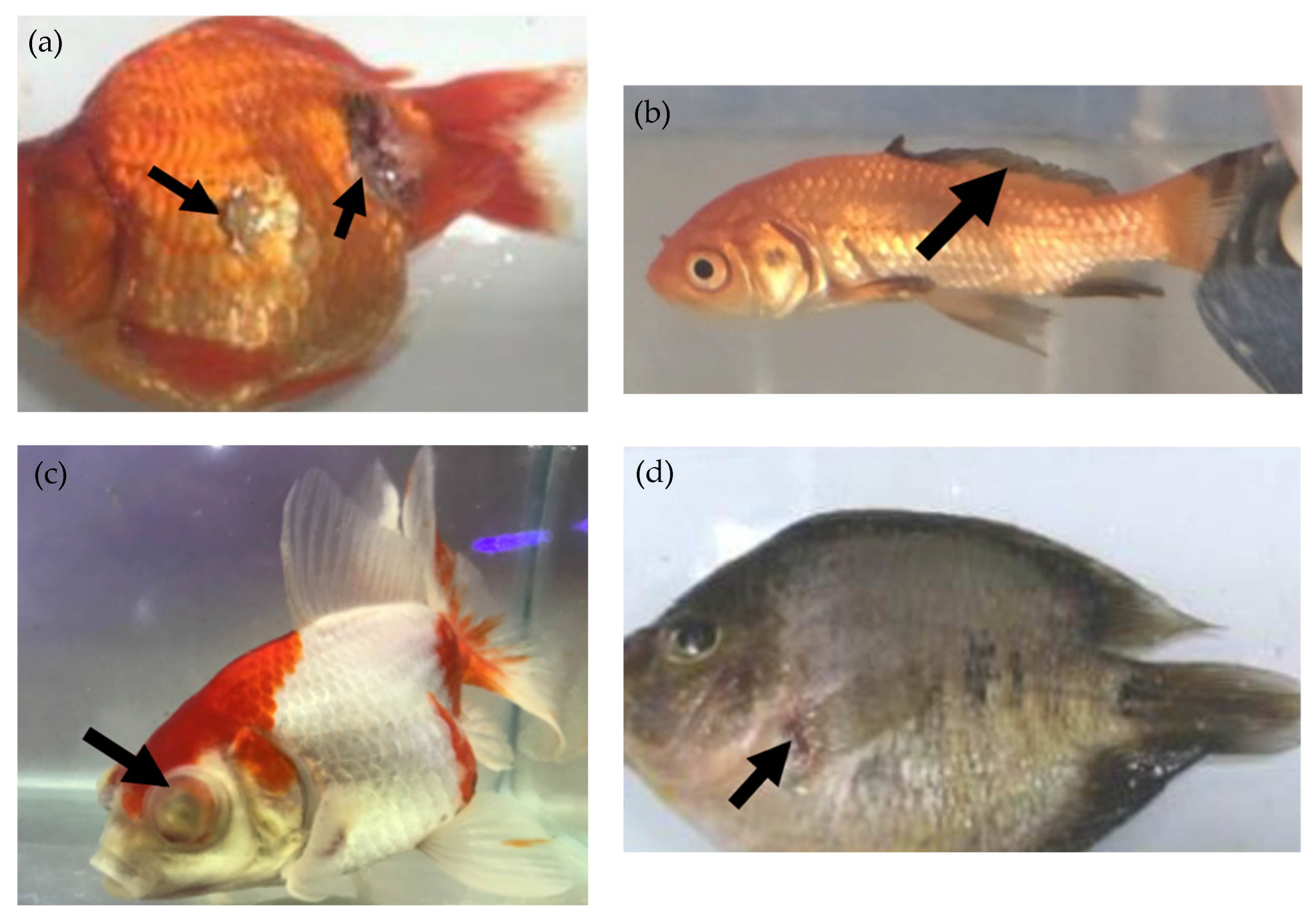
2.2. Bacterial Diseases and Resistance in Ornamental Fish
2.3. Antibiotic Resistance Genes
| Category | Bacterial Genus | Diseases | Symptoms | Host Range | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-negative bacteria | Aeromonas spp. | Aeromonosis | Sloughing of scales, skin, fins, abdominal dropsy, hemorrhage. | Wide range of ornamentals | [19,46,80] |
| Citrobacter spp. | Granulomatous diseases, meningitis | Lethargy, hemorrhagic septicemia, enteritis exophthalmia, and bleeding in eyes. | Angelfish, doctor fish, stingray | [81,82,83] | |
| Edwardsiella spp. | Edwardsiella septicemia | Discolored skin patches, external and enteric septicemia, erratic swimming, exophthalmia. | Koi, goldfish, zebrafish, and catfishes. | [84,85,86] | |
| Flavobacterium spp. | Flavobacteriosis | Yellowy white filamentous lesions predominantly affecting skin, gills, and fins. | Wide range of freshwater ornamentals | [49,50,87,88,89] | |
| Klebsiella spp. | Skin lesion | Cyprinus carpio | [90] | ||
| Vibrio spp. | Vibriosis | Ulceration and hemorrhagic septicemia. | Wide range of ornamentals | [44,51,52] | |
| Pseudomonas spp. | Pseudomoniasis | Tail and fin rot, hemorrhage, and ulceration. | Wide range of ornamentals | [91] | |
| Gram-positive bacteria | Streptococcus spp. | Streptococcosis | Hemorrhages, exophthalmia, ulceration, and erratic spiral swimming | Cyprinids and cichlids, such as red-tail black sharks, rainbow sharks, oscar, and blueram | [58,59,92] |
| Acid-fast bacteria | Mycobacterium spp. | Mycobacteriosis | Ulceration, swollen abdomen, and exophthalmia | Most ornamentals | [93,94] |
| Nocardia spp. | Nocardiosis | Presence of granulomas in skin, muscles and various internal organs. | Neon tetras, oscar, goldfish, and Chinese high-fin banded sharks | [53,54] |
| Antibiotic Class | Related Antibiotic Resistance Genes | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta-lactam | blaOXA1 | blaDHA1, blaTEM | blaP1 # | blaTEM-1, blaOXA7 | ||||||||
| Chloramphenicol | floR | cat, cmA1, floR | catB3 #, cmlA1 #, cmlA2 # | cmlA, floR, cfr | floR | |||||||
| Macrolide- lincosamide-streptogramine | mphA | ereA # | ||||||||||
| (Fluoro) quinolone | qnrS2, qnrB17, aac(6′)-Ib-cr | qnrVC1 # | qnrS, qnrB, aac(6′)-Ib-cr | qnrB, qnrS, qepA | qnrA, qnrS | qnrS, qnrS2 | qnrB, qnrS | |||||
| Sulfonamide /Trimethoprim | sul1, dfrA17 # | sul1, sul2 | dfrA12, dfrA14, sul1, sul2 | dfr2d #, dfr16 #, dfrA1 #, dfrA5 #, dfrA12 #, dfrA15 #, dfrA21 #, dfrA22 #, dfrA27 #, dfrA32 #, dfrB3 #, dhfrXVb #, sul1, sul2 | sul1, sul2, sul3 | sul1, dfr12, dfr13, dfrA1 | ||||||
| Tetracycline | tetA, tetD, tetE | tetA, tetB, tetD, tetE | tetA | tetA, tetB, tetG | tetA, tetE | tetA, tetB, tetM, tetO, tetW | tetA, tetC | tetD, tetE, tetG | tetA, tetB, tetM, tetS, tetW | tetA, tetB, tetE | ||
| Integron | intl1 | intl1 | intl1, intl2 | intl1 | intl1, intl2 | intl1 | intl1 | intl1 | ||||
| References | [74] | [95] | [69] | [75] | [76] | [96] | [97] | [32] | [41] | [77] | [98] | [99] |
3. Human Health Risks from Ornamental Fish Keeping
3.1. Sources of Antibiotic Residues in Aquaria
3.1.1. Tap Water Contamination
3.1.2. Antibiotics in Fish Feed
3.1.3. Intentional Antibiotic Use
3.2. Pathways of Human Exposure
3.2.1. Bioaerosols from Aeration
3.2.2. Direct Contact and Environmental Exposure
3.2.3. Zoonotic Risks
4. Challenges and Management in the Industry
4.1. Surveillance and Management Challenges
4.2. Environmental Impact and Resistance Spreading
4.3. Strategic Regulatory and Management Approaches
4.3.1. Education and Awareness Initiatives
4.3.2. Regulatory Measures
4.3.3. Alternative Disease Prevention Strategies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller-Morgan, T. A brief overview of the ornamental fish industry and hobby. In Fundamentals of Ornamental Fish Health; Roberts, H.E., Ed.; Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Raghavan, R.; Dahanukar, N.; Tlusty, M.; Rhyne, A.; Krishna, K.; Molur, S.; Rosser, A. Uncovering an obscure trade: Threatened freshwater fishes and the aquarium pet markets. Biol. Conserv. 2013, 164, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penning, M.; Reid, G.; Koldewey, H.; Dick, G.; Andrews, B.; Arai, K.; Garratt, P.; Gendron, S.; Lange, J.; Tanner, K.; et al. Turning the Tide: A Global Aquarium Strategy for Conservation and Sustainability; World Association of Zoos and Aquariums: Bern, Switzerland, 2009; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Ekaratne, S.U.K. A Review of the Status and Trends of Exported Ornamental Fish Resources and Their Habitats in Sri Lanka-BOBP/REP/88; Bay of Bengal Programme: Chennai, India, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Maceda-Veiga, A.; Domínguez-Domínguez, O.; Escribano-Alacid, J.; Lyons, J. The aquarium hobby: Can sinners become saints in freshwater fish conservation? Fish Fish. 2016, 17, 860–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, H.G.; Pinnegar, H.G.; Taylor, M.I. Where are they all from?–sources and sustainability in the ornamental freshwater fish trade. J. Fish Biol. 2019, 94, 909–916. [Google Scholar]
- World Integrated Trade Solution. Live Ornamental Fish Exports by Country 2023. Available online: https://wits.worldbank.org/trade/comtrade/en/country/ALL/year/2023/tradeflow/Exports/partner/WLD/product/030110 (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Monticini, P. The Ornamental Fish Trade. Production and Commerce of Ornamental Fish. Technical-Managerial and Legislative Aspects; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2010; p. 102. [Google Scholar]
- World Integrated Trade Solution. Live Ornamental Fish Import by Country 2023. Available online: https://wits.worldbank.org/trade/comtrade/en/country/ALL/year/2023/tradeflow/Imports/partner/WLD/product/030110# (accessed on 6 April 2025).
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2024-Blue Transformation in Action; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Stevens, C.H.; Croft, D.P.; Paull, G.C.; Tyler, C.R. Stress and welfare in ornamental fishes: What can be learned from aquaculture? J. Fish Biol. 2017, 91, 409–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larcombe, E.; Alexander, M.E.; Snellgrove, D.; Henriquez, F.L.; Sloman, K.A. Current disease treatments for the ornamental pet fish trade and their associated problems. Rev. Aquac. 2025, 17, e12948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamloo, K.; Akhavan, S.R.; Fallah, F.J.; Henry, M.A. Variations of physiological and innate immunological responses in goldfish (Carassius auratus) subjected to recurrent acute stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014, 37, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fast, M.D.; Hosoya, S.; Johnson, S.C.; Afonso, L.O. Cortisol response and immune-related effects of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar Linnaeus) subjected to short- and long-term stress. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2008, 24, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Sun, J.; Jiang, B.; Hu, X.; Lv, A.; Chen, L.; Guo, Y. Concurrent infections of Aeromonas veronii and Vibrio cholerae in koi carp (Cyprinus carpio var. koi). Aquaculture 2021, 535, 736395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sewaminathan, T.R.; Kumar, R.G. Mass mortality in ornamental fish, Cyprinus carpio koi caused by a bacterial pathogen, Proteus hauseri. Acta Trop. 2015, 149, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preena, P.G.; Dharmaratnam, A.; Swaminathan, T.R. A peek into mass mortality caused by antimicrobial resistant Edwardsiella tarda in goldfish, Carassius auratus in Kerala. Biologia 2022, 77, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjur, N.; Sarbran, S.F.; Daud, H.M.; Othman, N.Z. An update on the ornamental fish industry in Malaysia: Aeromonas hydrophila-associated disease and its treatment control. Vet. World 2021, 14, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, S.; Heo, G.J. Ornamental fish: A potential source of pathogenic and multidrug-resistant motile Aeromonas spp. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 72, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, P.H.M.; Moreno, L.Z.; de Oliveira, C.H.; Gomes, V.T.M.; Silva, A.P.S.; Barbosa, M.R.F.; Sato, M.I.Z.; Balian, S.C.; Moreno, A.M. Main bacterial species causing clinical disease in ornamental freshwater fish in Brazil. Folia Microbiol. 2021, 66, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Alexander, M.E.; Snellgrove, D.; Smith, P.; Bramhall, S.; Carey, P.; Henriquez, F.L.; McLellan, I.; Sloman, K.A. How should we monitor welfare in the ornamental fish trade? Rev. Aquac. 2022, 14, 770–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narendrakumar, L.; Geetha Preena, P.; Swaminathan, T.R. Antimicrobial resistance in ornamental fisheries: Causes and preventive measures. In Handbook on Antimicrobial Resistance: Current States, Trends in Detection and Mitigation, 1st ed.; Mothadaka, M.P., Vaiyapuri, M., Rao Badireddy, M., Nagarajrao Ravishankar, C., Bhatia, R., Jena, J., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 149–163. [Google Scholar]
- Karreman, G.A.; Gaunt, P.S.; Endris, R.G.; Saint-Erne, N. Therapeutants for Fish. In Fish Diseases and Medicine, 1st ed.; Smith, S.A., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 321–348. [Google Scholar]
- Chanda, M.; Paul, M.; Maity, J.; Dash, G.; Gupta, S.S. The use of antibiotics and disinfectants in ornamental fish farms of West Bengal, India. J. Nat. Sci. Biol. Med. 2011, 2, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, B.D.; Francis-Floyd, R.; Yanong, R.P.E. Management of Aquarium Fish. Available online: https://www.merckvetmanual.com/exotic-and-laboratory-animals/aquarium-fish/management-of-aquarium-fish (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. Approved Aquaculture Drugs. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/animal-veterinary/aquaculture/approved-aquaculture-drugs (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Weir, M.; Rajić, A.; Dutil, L.; Cernicchiaro, N.; Uhland, F.C.; Mercier, B.; Tuśevljak, N. Zoonotic bacteria, antimicrobial use and antimicrobial resistance in ornamental fish: A systematic review of the existing research and survey of aquaculture-allied professionals. Epidemiol. Infect. 2012, 140, 192–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au-Yeung, C.; Lam, K.L.; Chan, K.W.; Mo, W.Y. Uses of antibiotics in ornamental fish in Hong Kong and the antibiotic resistance in the associated zoonotic pathogens. J. Xenobiot. 2022, 12, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au-Yeung, C.; Lam, K.L.; Choi, M.H.; Chan, K.W.; Cheung, Y.S.; Tsui, Y.L.; Mo, W.Y. Impact of prophylactic antibiotic use in ornamental fish tanks on microbial communities and pathogen selection in carriage water in Hong Kong retail shops. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenen, O.L.M.; Veldman, K.T.; Ceccarelli, D.; Tafro, N.; Zuidema, T.; Mevius, D. Potential transfer of antimicrobial resistance and zoonotic bacteria through global ornamental fish trade. Asian Fish. Sci. 2020, 33, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleingeld, D.W.; Braune, S.; Slotfeldt, H.J.; Albrecht, I. Bacterial isolations, resistance development and risk analysis in the ornamental fish trade. Bull. Inst. Océanogr. 2001, 20, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes in wastewater collected from ornamental fish market in northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 271, 116316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, P.K.S.; Wu, K.R.; Ruan, P.Y. Provision of Service for Laboratory Analysis of Antibiotics in Ambient River and Marine Water Samples; City University of Hong Kong: Hong Kong, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Guruge, K.S.; Goswami, P.; Tanoue, R.; Nomiyama, K.; Wijesekara, R.G.S.; Dharmaratne, T.S. First nationwide investigation and environmental risk assessment of 72 pharmaceuticals and personal care products from Sri Lankan surface waterways. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, P.S. Degradation of oxytetracycline hydrochloride in fresh and seawater. Asian Fish. Sci. 1994, 7, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrower, J.; McNaughtan, M.; Hunter, C.; Hough, R.; Zhang, Z.; Helwig, K. Chemical fate and partitioning behavior of antibiotics in the aquatic environment—A review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 3275–3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D. Microbiological effects of sublethal levels of antibiotics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 465–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenni, P.; Ancona, V.; Caracciolo, A.B. Ecological effects of antibiotics on natural ecosystems: A review. Microchem. J. 2018, 136, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernier, S.P.; Surette, M.G. Concentration-dependent activity of antibiotics in natural environments. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullberg, E.; Cao, S.; Berg, O.G.; Ilbäck, C.; Sandegren, L.; Hughes, D.; Andersson, D.I. Selection of resistant bacteria at very low antibiotic concentrations. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Fang, H.; Mao, Q.; Bai, Y.; Ye, Z.; Hu, D.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Ye, N.; Zhang, S.; et al. Low concentrations of antibiotics alter microbial communities and induce high abundances of antibiotic-resistant genes in ornamental water. Water 2023, 15, 3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, N.; Hatha, A.A.M. Distribution, extracellular virulence factors and drug resistance of motile aeromonads in fresh water ornamental fishes and associated carriage water. Int. J. Aquac. 2013, 3, 92–100. [Google Scholar]
- Lewbart, G.A. Bacteria and ornamental fish. Semin. Avian Exot. Pet Med. 2001, 10, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, H.E.; Palmeiro, B.; Scott, W.E. Bacterial and parasitic diseases of pet fish. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2009, 12, 609–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, C.; Mota, V.; Martinez-Murcia, A.; Saaverdra, M.J. Antimicrobial resistance patterns of Aeromonas spp. isolated from ornamental fish. J. Aquac. Res. Dev. 2012, 3, 131. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, S.; De Silva, B.C.J.; Dahanayake, P.S.; De Zoysa, M.; Heo, G.J. Phylogenetic characteristics, virulence properties and antibiogram profile of motile Aeromonas spp. isolated from ornamental guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shameena, S.S.; Kumar, K.; Kumar, S.; Rathore, G. Virulence characteristics of Aeromonas veronii biovars isolated from infected freshwater goldfish (Carassius auratus). Aquaculture 2020, 518, 734819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, S.; Patra, A.; Adikesavalu, H.; Abraham, T.J. Flavobacteriosis in cultured freshwater ornamental goldfish Carassius auratus. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2016, 5, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decostere, A.; Ducatelle, R.; Haesebrouck, F. Flavobacterium columnare (Flexibacter columnaris) associated with severe gill necrosis in koi carp (Cyprinus carpio L). Vet. Rec. 2002, 150, 694–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decostere, A.; Haesebrouck, F.; Devriese, L.A. Characterization of four Flavobacterium columnare (Flexibacter columnaris) strains isolated from tropical fish. Vet. Microbiol. 1998, 62, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastuszka, A.; Guz, L.; Michalk, K.; Pietras-Ożga, D.; Puk, K. Vibrio infection in freshwater fish in Poland. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2024, 27, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Deen, A.G.S.; Elkamel, A.A. Clinical and experimental study on vibriosis in ornamental fish. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2015, 61, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Najmeh, S.; Tayebeh, F.; Katayoon, N. Nocardiosis in some ornamental fishes in Iran. J. Zoonotic Dis. 2020, 4, 28–34. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, W.X.; Tseng, Y.H.; Huang, W.R.; Cheng, L.W.; Wang, P.C.; Chen, S.C. Nocardiosis and other common diseases of cultured golden pompano (Trachinotus blochii) in Taiwan. J. Fish Dis. 2024, 47, e13894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beran, V.; Matlova, L.; Dvorska, L.; Svastova, P.; Pavlik, I. Distribution of mycobacteria in clinically healthy ornamental fish and their aquarium environment. J. Fish Dis. 2006, 29, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puk, K.; Guz, L. Occurrence of Mycobacterium spp. in ornamental fish. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2020, 27, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokulraj, A.; Praveenraj, J.; Gnanadesikan, R.; Arumugam, U. Mycobacterial infection in ornamental fishes farmed in low saline waters of Tiruvallur District, India. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 86, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazado, C.C.; Fridman, S.; Sinai, T.; Zilberg, D. First report of Streptococcus parauberis in a cultured freshwater ornamental fish, the ram cichlid Mikrogeophagus ramirezi (Myers & Harry, 1948). J. Fish Dis. 2017, 41, 161–164. [Google Scholar]
- Raissy, M.; Zandi, S.; Ahmadi, A.; Foroutan, M.S.; Fadaeifard, F. Experimental evaluation of pathogenicity of Streptococcus iniae in Silver Shark and Rainbow Shark. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 6, 3560–3563. [Google Scholar]
- Ruppé, É.; Woerther, P.; Barbier, F. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in Gram-negative bacilli. Ann. Intensive Care 2015, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.A. Bacterial Fish Pathogens: Disease of Farmed and Wild Fish, 6th ed.; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Stock, I.; Wiedemann, B. Natural antibiotic susceptibilities of Edwardsiella tarda, E. ictaluri, and E. hoshinae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 2245–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trust, T.J.; Whitby, J.L. Antibiotic Resistance of Bacteria in Water Containing Ornamental Fishes. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1976, 10, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guz, L.; Puk, K. Antibiotic susceptibility of mycobacteria isolated from ornamental fish. J. Vet. Res. 2022, 66, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Hu, X.; Lü, A.; Sun, J.; Yiksung, Y.; Pei, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, L. Isolaiton and characterization of Aeromonas veronii from ornamental fish species in China. Isr. J. Aquac.-Bamidgeh 2017, 69, 1446. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Schwarz, S.; Wu, C.; Shen, J.; Walsh, T.R.; Wang, Y. Farm animals and aquaculture: Significant reservoirs of mobile colistin resistance genes. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 2469–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhodes, G.; Huys, G.; Swings, J.; Mcgann, P.; Hiney, M.; Smith, P.; Pickup, R.W. Distribution of oxytetracycline resistance plasmids between Aeromonads in hospital and aquaculture environments: Implication of Tn1721 in dissemination of the tetracycline resistance determinant Tet A. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3883–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile genetic elements associated with antimicrobial resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobiasova, H.; Kutilova, I.; Piackova, V.; Vesely, T.; Cizek, A.; Dolejska, M. Ornamental fish as a source of plasmid-mediated quinolone resistance genes and antibiotic resistance plasmids. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantas, L.; Midtlyng, P.J.; Sørum, H. Impact of antibiotic treatments on the expression of the R plasmid tra genes and on the host innate immune activity during pRAS1 bearing Aeromonas hydrophila infection in zebrafish (Danio rerio). BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamminen, M.; Karkman, A.; Lõhmus, A.; Muziasari, W.I.; Takasu, H.; Wada, S.; Suzuki, S.; Virta, M. Tetracycline Resistance Genes Persist at Aquaculture Farms in the Absence of Selection Pressure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, K.; Nomura, N.; Suzuki, S. Biofilms: Hot spots of horizontal gene transfer (HGT) in aquatic environments, with a focus on a new HGT mechanism. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2020, 96, fiaa031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirfard, K.D.; Moriyama, M.; Suzuki, S.; Sano, D. Effect of environmental factors on conjugative transfer of antibiotic resistance genes in aquatic settings. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 135, lxae129. [Google Scholar]
- Čížek, A.; Dolejská, M.; Sochorová, R.; Strachotová, K.; Piačková, V.; Veselý, T. Antimicrobial resistance and its genetic determinants in aeromonads isolated in ornamental (koi) carp (Cyprinus carpio koi) and common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 142, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Ni, P.; Wang, Y.; Jin, S.; Jiang, Z.; Ye, S.; Li, R. Delineating the origins of the multidrug-resistant pathogens in ornamental fish farms by multilocus sequence typing and identification of a novel multidrug-resistant plasmid. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerzova, L.; Videnska, P.; Faldynova, M.; Sedlar, K.; Provaznik, I.; Cizek, A.; Rychlik, I. Characterization of microbiota composition and presence of selected antibiotic resistance genes in carriage water of ornamental fish. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verner-Jeffreys, D.W.; Welch, T.J.; Schwarz, T.; Pond, M.J.; Woodward, M.J.; Haig, S.J.; Rimmer, G.S.E.; Roberts, E.; Morrison, V.; Baker-Austin, C. High prevalence of multidrug-tolerant bacteria and associated antimicrobial resistance genes isolated from ornamental fish and their carriage water. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e8388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, J.A.; Wright, G.D. The antibiotic resistance “mobilome”: Searching for the link between environment and clinic. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, M.; Popowska, M. Prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes among Aeromonas species in aquatic environments. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 921–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; De Silva, B.C.J.; Wimalasena, S.H.M.P.; Pathirana, H.N.K.S.; Dahnayake, P.S.; Heo, G.J. Characterization of virulence determinants and multiple antimicrobial resistance profiles in motile Aeromonas spp. isolated from ornamental goldfish (Carassius auratus). J. Exot. Pet Med. 2019, 29, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeck, G.W.; Kim, J.H.; Choresca, C., Jr.; Gomez, D.K.; Shin, S.P.; Han, J.E.; Park, S.C. Mass mortality of doctor fish (Garra rufa obtusa) caused by Citrobacter freundii infection. J. Vet. Clin. 2009, 26, 150–154. [Google Scholar]
- Gallani, S.U.; Sebastiao, F.D.A.; Valladao, G.M.; Boaratti, A.Z.; Pilarski, F. Pathogenesis of mixed infection by Spironucleus sp. and Citrobacter freundii in freshwater angelfish Pterophyllum scalare. Microb. Pathog. 2016, 100, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; Cao, X.H.; Jiang, Y.F.; Ni, L.Y.; Mo, Z.Q.; Qin, Q.W.; Li, Y.W.; Dan, X.M. Outbreak of a novel disease associated with Citrobacter freundii infection in freshwater cultured stingray, Potamotrygon motoro. Aquaculture 2018, 49, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yan, M.; Mu, C.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Pan, G.; Wang, X. FucP promotes the pathogenicity of Edwardsiella piscicida to infect zebrafish. Aquac. Rep. 2021, 20, 100665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawke, J.P.; Mcwhorter, A.C.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Brenner, D.J. Edwardsiella ictaluri sp. nov., the causative agent of enteric septicemia of catfish. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 1981, 31, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, C.; Palmeiro, B. Updates on Selected Emerging Infectious Diseases of Ornamental Fish. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2020, 23, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altinok, I. Toxicity and therapeutic effects of chloramine-T for treating Flavobacterium columnare infection of goldfish. Aquaculture 2004, 239, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Declercq, A.M.; Haesebrouck, F.; Broeck, W.V.D.; Bossier, P.; Decostere, A. Columnaris disease in fish: A review with emphasis on bacterium-host interactions. Vet. Res. 2013, 44, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Hatai, K.; Kubota, S.S. Studies on columnaris disease in guppy (Poecilia reticulata), 2: Therapeutic effects of some drugs against Flexibacter columnaris. Bull. Nippon Vet. Zootech. Coll. 1990, 39, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, R.V.; Peixoto, P.G.; Ribeiro, D.D.C.; Aroujo, M.C.; Santos, C.D.; Hayashi, C.; Pedreira, M.M.; Pelli, A. Klebsiella pneumoniae as a main cause of infection in Nishikigoi cyprinus carpio (Carp) by inadequate handling. Braz. J. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 7, 86–88. [Google Scholar]
- Duman, M.; Jorge, L.; Saticioglu, I.B.; Mulet, M.; Gomila, M.; Altun, S.; Ajmi, N.; García-Valdés, E. Description of three new Pseudomonas species isolated from aquarium fish: Pseudomonas auratipiscis sp. nov., Pseudomonas carassii sp. nov. and Pseudomonas ulcerans sp. nov. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 47, 126552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, R.; Mitchell, H.; Yanong, R.P. Characterization of Streptococcus iniae isolated from ornamental cyprinid fishes and development of challenge models. Aquaculture 2006, 256, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, D.T.; Rhodes, M.W. Mycobacteriosis in fishes: A review. Vet. J. 2009, 180, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdanmanesh, M.; Tadayon, K.; Koshkghazi, D.B.; Mosavari, N. Isolation and identification of non-tuberculous mycobacteria from aquarium fish in Ilam, Iran. J. Clin. Tuberc. Other Mycobact. Dis. 2024, 37, 100478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Tan, A.; Zhang, R.; Luo, L. Multi-drug resistance mediated by class 1 integrons in Aeromonas isolated from farmed freshwater animals. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemamalini, N.; Shanmugam, S.A.; Kathirvelpandian, A.; Deepak, A.; Kaliyamurthi, V.; Suresh, E.; Ezhilmathi, S. Prevalence, antimicrobial susceptibility and resistance gene detection in bacteria isolated from Goldfish and Tiger Barb from ornamental fish farms of Tamil Nadu. Indian J. Microbiol. 2022, 62, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; De Silva, B.C.J.; Wimalasena, S.H.M.P.; Pathirana, H.N.K.S.; Dahanayake, P.S.; Heo, G.J. Distribution of antimicrobial resistance genes and class 1 integron gene cassette arrays in motile Aeromonas spp. isolated from goldfish (Carassius auratus). Microb. Drug Resist. 2018, 24, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnupriya, V.; Swaminathan, T.R.; Dharmarathnam, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Preena, P.G. Virulent and multi-drug-resistant Edwardsiella tarda infection in Oscar fish: Unveiling the threat of mass mortality and AMR dissemination. Curr. Microbiol. 2024, 81, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, S.; De Silva, B.C.J.; Wickramanayake, M.V.K.S.; Dahanayake, P.S.; Wimalasena, S.H.M.P.; Heo, G.J. Incidence of antimicrobial resistance genes and class 1 integron gene cassettes in multidrug–Resistant motile Aeromonas sp. isolated from ornamental guppy (Poecilia reticulata). Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 69, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centre for Food Safety. Is Ornamental Fish Meant for Consumption? Available online: https://www.cfs.gov.hk/english/multimedia/multimedia_pub/multimedia_pub_fsf_196_03.html (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Rose, S.; Hill, R.; Bermudez, L.E.; Miller-Morgan, T. Imported ornamental fish are colonized with antibiotic-resistant bacteria. J. Fish Dis. 2013, 36, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicuro, B.; Pastorino, P.; Barisone, S.; Dellerba, D.; Menconi, V.; Righetti, M.; Vita, V.D.; Prearo, M. Prevalence and antibiotic sensitivity of bacteria isolated from imported ornamental fish in Italy: A translocation of resistant strains? Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 175, 104880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lázár, V.; Nagy, I.; Spohn, R.; Csörgo, B.; Györkei, Á.; Nyerges, Á.; Horváth, B.; Vörös, A.; Busa-Fekete, R.; Hrtyan, M.; et al. Genome-wide analysis captures the determinants of the antibiotic cross-resistance interaction network. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majcherczyk, P.A.; Barblan, J.L.; Moreillon, P.; Entenza, J.M. Development of glycopeptide-intermediate resistance by Staphylococcus aureus leads to attenuated infectivity in a rat model of endocarditis. Microb. Pathog. 2008, 45, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, L.P.; Bagnall, M.C.; Karatzas, K.A.; Coldham, N.C.; Piddock, L.J.; Woodward, M.J. Fitness and dissemination of disinfectant-selected multiple-antibiotic-resistant (MAR) strains of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium in chickens. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2008, 61, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, Y.; Hu, M.; Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Wong, M.H.; Wang, M.; Andrews, C.B.; Zheng, C. Efficient detection and assessment of human exposure to trace antibiotic residues in drinking water. Water Res. 2020, 175, 115699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, A.M.; Ciorba, P.; Döhla, M.; Exner, M.; Felder, C.; Lenz-Plet, F.; Sib, E.; Skutlarek, D.; Schmithausen, R.M.; Faerber, H.A. The investigation of antibiotic residues, antibiotic resistance genes and antibiotic-resistant organisms in a drinking water reservoir system in Germany. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2020, 224, 113449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilca, F.Z.; Galarza, N.C.; Tejedo, J.R.; Cuba, W.A.Z.; Quiróz, C.N.C.; Tornisielo, V.L. Occurrence of residues of veterinary antibiotics in water, sediment and trout tissue (Oncorhynchus mykiss) in the southern area of Lake Titicaca, Peru. J. Great Lakes Res. 2021, 47, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Lv, K.; Lu, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, X. Removal of antibiotic-resistant genes during drinking water treatment: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 163, 415–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.; Zheng, S.; Ye, C.; Hu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dao, H.; Chen, S.; Yu, X. Ancient Oriental Wisdom still Works: Removing ARGs in Drinking Water by Boiling as compared to Chlorination. Water Res. 2022, 209, 117902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, M.; Mirzaei, R.; Kalantary, R.R.; Sabzali, A.; Gatei, F. Performance evaluation of reverse osmosis technology for selected antibiotics removal from synthetic pharmaceutical wastewater. Iran. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2012, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Ho, K.W.; Ying, G.G.; Deng, W.J. Veterinary antibiotics in food, drinking water, and the urine of preschool children in Hong Kong. Environ. Int. 2017, 108, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wistrand-Yuen, E.; Knopp, M.; Hjort, K.; Koskiniemi, S.; Berg, O.G.; Andersson, D.I. Evolution of high-level resistance during low-level antibiotic exposure. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Xu, X.R.; Diao, Z.H.; Sun, K.F.; Hao, Q.W.; Liu, S.S.; Ying, G.G. Tissue distribution, bioaccumulation characteristics and health risk of antibiotics in cultured fish from a typical aquaculture area. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 343, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, H.; Xu, J.; Chen, Z. Antibiotics in aquaculture ponds from Guilin, South of China: Occurrence, distribution, and health risk assessment. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, M.; Wang, R.; Qian, Y. Protective effect of moderate dietary cellulose against antibiotic–Induced growth retardation, blood deterioration and immunosuppression in juvenile yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco). Aquac. Res. 2021, 52, 6000–6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Wen, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yin, J. Antibiotics in cultured freshwater products in Eastern China: Occurrence, human health risks, sources, and bioaccumulation potential. Chemosphere 2021, 264, 128441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, W.Y.; Chen, Z.; Leung, H.M.; Leung, A.O.W. Application of veterinary antibiotics in China’s aquaculture industry and their potential human health risks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 8978–8989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Song, G.; Lim, W. A review of the toxicity in fish exposed to antibiotics. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 237, 108840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Q.; Chen, B.; Zhang, J.P.; Chen, N.; Liu, C.Z.; Hu, C.Q. Liver toxicity of macrolide antibiotics in zebrafish. Toxicology 2020, 441, 152501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, M.; Marti, E.; Balcázar, J.L.; Boy-Roura, M.; Busquets, A.; Colón, J.; Sànchez-Melsió, A.; Lekunberri, I.; Borrego, C.M.; Ponsá, S.; et al. Fate of pharmaceuticals and antibiotic resistance genes in a full-scale on-farm livestock waste treatment plant. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 378, 120716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Dong, H. Dispersion of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) from stored swine manure biogas digestate to the atmosphere. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 761, 144108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.L.; Shao, M.F.; Luo, Y.; Dong, Y.F.; Ouyang, F.; Dong, W.Y.; Li, J. Airborne bacterial contaminations in typical Chinese wet market with live poultry trade. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Mao, D.; Luo, Y. Significant higher airborne antibiotic resistance genes and the associated inhalation risk in the indoor than the outdoor. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 268, 115620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Cheng, X.; Meng, L.; Dong, P.; Yang, H.; Chen, S.; Zhu, J. Revealing the distribution characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes and bacterial communities in animal-aerosol-human in a chicken farm: From One-Health perspective. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 224, 112687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruglyakova, E.; Mirskaya, E.; Agranovski, I.E. Bioaerosol release from concentrated microbial suspensions in bubbling processes. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremonesini, D.; Thomson, A. Lung colonization with Aeromonas hydrophila in cystic fibrosis believed to have come from a tropical fish tank. J. R. Soc. Med. 2008, 101 (Suppl. 1), 44–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisamichi, M.; Yokoyama, T.; Yazawa, M.; Kaneshiro, N.; Sakurada, T.; Konno, Y.; Shibagaki, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Kimura, K. A rare case of peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis caused by goldfish water tankderived Aeromonas hydrophila. Clin. Nephrol. 2015, 84, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooster, G.A.; Bowser, P.R. The aerobiological pathway of a fish pathogen: Survival and dissemination of Aeromonas salmonicida in aerosols and its implications in fish health management. J. World Aquac. Soc. 1996, 27, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifton, I.J.; Peckham, D.G. Defining routes of airborne transmission of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in people with cystic fibrosis. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2010, 4, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaerewijck, M.J.; Huys, G.; Palomino, J.C.; Swings, J.; Portaels, F. Mycobacteria in drinking water distribution systems: Ecology and significance for human health. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 911–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centre for Health Protection. Invasive Group B Streptococcus Infection Associated with Sequence Type 283 (ST283). Available online: https://www.chp.gov.hk/en/healthtopics/content/24/105002.html (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Balagué, N.; Uçkay, I.; Vostrel, P.; Hinrikson, H.; Van Aaken, I.; Beaulieu, J.Y. Non-tuberculous mycobacterial infections of the hand. Chir. Main 2015, 34, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajanchi, B.K.; Fadl, A.A.; Borchardt, M.A.; Berg, R.L.; Horneman, A.J.; Stemper, M.E.; Joseph, S.W.; Moyer, N.P.; Sha, J.; Chopra, A.K. Distribution of virulence factors and molecular fingerprinting of Aeromonas Species isolates from water and clinical samples: Suggestive evidence of water-to-human transmission. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 2313–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Alexander, J. Aeromonas hydrophilia infection in an immunocompromised host. Cureus 2021, 13, e20834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Yuwono, C.; Tay, A.C.Y.; Wehrhahn, M.C.; Riordan, S.M.; Zhang, L. Analysis of global Aeromonas veronii genomes provides novel information on source of infection and virulence in human gastrointestinal diseases. BMC Genom. 2022, 23, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuwono, C.; Wehrhahn, M.C.; Liu, F.; Riordan, S.M.; Zhang, L. The isolation of Aeromonas species and other common enteric bacterial pathogens from patients with gastroenteritis in an Australian population. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Banerjee, S.; Konar, J.; Datta, P.; Sahu, C.; Naha, A. Necrotizing soft tissue infection caused by Aeromonas caviae: A case report. J. Evol. Med. Dent. Sci. 2015, 4, 2589–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Chatterjee, M.; Bandyopadhyay, M.K.; Bandyopadhyay, M.; Ghosh, T.; Samaddar, D. Necrotizing fasciitis caused by Aeromonas caviae. Avicenna J. Med. 2012, 2, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochedez, P.; Hope-Rapp, E.; Olive, C.; Nicolas, M.; Beaucaire, G.; Cabié, A. Bacteremia caused by Aeromonas hydrophila complex in the Caribbean Islands of Martinique and Guadeloupe. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 83, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcarcel, B.; De-la-Cruz-Ku, G.; Malpica, L.; Enriquez-Vera, D. Clinical features and outcome of Aeromonas sobria bacteremia in pediatric and adult patients with hematologic malignancies: A single-center retrospective study in Peru. PLoS ONE 2021, 6, e0255910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, A.R.; Nunes, O.C.; Manaia, C.M. Quinolone resistant Aeromonas spp. as carriers and potential tracers of acquired antibiotic resistance in hospital and municipal wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 665–671. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.; Sun, C.; Hulth, A.; Li, J.; Nilsson, L.E.; Zhou, Y.; Börjesson, S.; Bi, Z.; Bi, Z.; Sun, Q.; et al. Mobile colistin resistance gene mcr-5 in porcine Aeromonas hydrophila. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1777–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimanpour, S.; Mosavari, N.; Asl, D.H.; Tadayon, K.; Farazi, A.A. Zoonotic tuberculosis caused by Mycobacterium bovis, Central province. Iran. J. Lung. Pulm. Respir. Res. 2015, 2, 0054. [Google Scholar]
- Olea-Popelka, F.; Muwonge, A.; Perera, A.; Dean, A.S.; Mumford, E.; Erlacher-Vindel, E.; Forcella, S.; Silk, B.J.; Ditiu, L.; El Idrissi, A.; et al. Zoonotic tuberculosis in human beings caused by Mycobacterium bovis—A call for action. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e21–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, A.; Chosidow, O.; Caumes, E.; Robert, J.; Cambau, E. Sixty-three cases of Mycobacterium marinum infection: Clinical features, treatment, and antibiotic susceptibility of causative isolates. Arch. Intern. Med. 2002, 162, 1746–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jernigan, J.A.; Farr, B.M. Incubation period and sources of exposure for cutaneous Mycobacterium marinum infection: Case report and review of the literature. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 31, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traore, S.G.; Bonfoh, B.; Krabi, R.; Odermatt, P.; Utzinger, J.; Rose, K.N.; Tanner, M.; Frey, J.; Quilici, M.L.; Koussémon, M. Risk of Vibrio transmission linked to the consumption of Crustaceans in Coastal Towns of Côte d’Ivoire. J. Food Prot. 2012, 75, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loo, K.Y.; Law, J.W.F.; Tan, L.T.H.; Pusparajah, P.; Wong, S.H.; Chan, K.G.; Lee, L.H.; Letchumanan, V. The burden of Vibrio sp. infections–A scoping review. Prog. Microbes Mol. Biol. 2023, 6, a0000340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sims, J.; Isokpehi, R.D.; Cooper, G.A.; Bass, M.P.; Brown, S.D.; John, A.L.S.; Gulig, P.A.; Cohly, H.H.P. Visual analytics of surveillance data on foodborne vibriosis, United States 1973–2010. Environ. Health Insights 2011, 5, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzulli, L.; Brettar, I.; Pezzati, E.; Reid, P.C.; Colwell, R.R.; Höfle, M.G.; Pruzzo, C. Long-term effects of ocean warming on the prokaryotic community: Evidence from the vibrios. ISME J. 2012, 6, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavallo, R.A.; Acquaviva, M.I.; Stabili, L.; Cecere, E.; Petrocelli, A.; Narracci, M. Antibacterial activity of marine macroalgae against fish pathogenic Vibrio species. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2013, 8, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenen, O.L.M.; Evans, J.J.; Berthe, F. Bacterial infections from aquatic species: Potential for and prevention of contact zoonoses. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz. 2013, 32, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. 4 Steps to Food Safety. Available online: https://www.foodsafety.gov/keep-food-safe/4-steps-to-food-safety (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- World Health Organization. Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance; WHO Document Production Services: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Caputo, A.; Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; Karunasagar, I.; Hao, B.; Gaunt, P.; Verner-Jeffreys, D.; Fridman, S.; Dorado-Garcia, A. Antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture: A global analysis of literature and national action plans. Rev. Aquac. 2023, 15, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, A.C.; da Cunha, M.A. International legislation on drugs and biological products used in the sanitary management of aquatic animals. In Aquaculture Pharmacology; Kibenge, F.S.B., Baldisserotto, B., Chong, R.S.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Chapter 9; pp. 347–392. [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Food & Drug Administration. The Index of Legally Marketed Unapproved New Animal Drugs for Minor Species. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/animal-veterinary/minor-useminor-species/index-legally-marketed-unapproved-new-animal-drugs-minor-species (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Veterinary Surgeons Act, in c.36. 1966. Available online: https://faolex.fao.org/docs/pdf/uk143988.pdf (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Animal Welfare Act, in c.45. 2006. Available online: https://faolex.fao.org/docs/pdf/uk75239.pdf (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Veterinary Medicines Regulations, in S.I. 2013/2033. Available online: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2013/2033/pdfs/uksi_20132033_en.pdf (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- National Veterinary Assay Laboratory, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries. Reports on the Japanese Veterinary Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System 2016–2017; JVARM-Japanese Veterinary: Tokyo, Japan, 2020.
- The Beijing Municipal Administration for Market Regulation. Technical Specification for Ornamental Fish Farming; The Beijing Municipal Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Loftin, K.A.; Adams, C.D.; Meyer, M.T.; Surampalli, R. Effects of ionic strength, temperature, and pH on degradation of selected antibiotics. J. Environ. Qual. 2008, 37, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, A.M.; Stoskopf, M.K. The kinetics of oxytetracycline degradation in deionized water under varying temperature, pH, light, substrate, and organic matter. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 2000, 12, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Mao, D.; Luo, Y.; Xu, L. Sulfamethoxazole biodegradation and biotransformation in the water–sediment system of a natural river. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7069–7076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreozzi, R.; Caprio, V.; Ciniglia, C.; de Champdoré, M.; Lo Giudice, R.; Marotta, R.; Zuccato, E. Antibiotics in the environment: Occurrence in Italian STPs, fate, and preliminary assessment on algal toxicity of amoxicillin. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6832–6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Dong, G.; Zhao, H.; Chen, M.; Quan, W.; Qu, B. Occurrence and risk assessment of fluoroquinolones and tetracyclines in cultured fish from a coastal region of northern China. Envrion. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 8035–8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Huang, H.; Ren, T. Antibiotic residues in liquid manure from swine feedlot and their effects on nearby groundwater in regions of North China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11565–11575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delalay, G.; Berezowski, J.A.; Diserens, N.; Schmidt-Posthaus, H. An understated danger: Antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture and pet fish in Switzerland, a retrospective study from 2000 to 2017. J. Fish Dis. 2020, 43, 1299–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Yin, G.; Liu, M.; Zhou, J.; Zheng, Y.; Gao, J.; Zong, H.; Yang, Y.; Gao, L.; Tong, C. Effects of sulfamethazine on denitrification and the associated N2O release in estuarine and coastal sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roose-Amsaleg, C.; Laverman, A.M. Do antibiotics have environmental side-effects? Impact of synthetic antibiotics on biogeochemical processes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 4000–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharmaratnam, A.; Swaminathan, T.R.; Kumar, R.; Basheer, V.S. Aeromonas hydrophila associated with mass mortality of adult Goldfish, Carassius auratus (Linnaeus 1758) in ornamental farms in India. Indian J. Fish. 2018, 65, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 19 EU/EEA Countries in 2010. Second ESVAC Report 2012; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012.
- European Medicines Agency. Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 31 European Countries in 2022. Trends from 2010 to 2022. Thirteenth ESVAC Report; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022.
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation. FAO Project FMM/Ras/298/MUL: Strengthening Capacities, Policies and National Action Plans on Prudent and Responsible Use of Antimicrobials in Fisheries: Final Workshops, Concorde Hotel, Singapore, 12–14 December 2017; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation. Recommendations for Prudent and Responsible Use of Veterinary Medicines in Aquaculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; Lavilla-Pitogo, C.; Lopez, M.M.L.; Hao, B. Guidance in development of aquaculture component of a National Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance. Asian Fish. Sci. 2020, 33, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordin, W.N.; Misol, G., Jr.; Johari, R. Aquaculture component of national action plan on antimicrobial resistance in Malaysia. Asian Fish. Sci. 2020, 33, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López Nadal, A.; Peggs, D.; Wiegertjes, G.F.; Brugman, S. Exposure to antibiotics affects saponin immersion-induced immune stimulation and shift in microbial composition in zebrafish larvae. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wei, T.; Wu, X.; Zhong, H.; Qiu, W.; Zheng, Y. Early exposure to environmental levels of sulfamethoxazole triggers immune and inflammatory response of healthy zebrafish larvae. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddik, M.A.; Pham, H.D.; Francis, D.S.; Vo, B.V.; Shahjahan, M. Dietary supplementation of fish protein hydrolysate in high plant protein diets modulates growth, liver and kidney health, and immunity of barramundi (Lates calcarifer). Aquac. Nutr. 2021, 27, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totewad, N.D.; Gyananath, G. Effect of probiotic rnterococcus gallinarum N3 supplemented feed on growth performance of freshwater fish Cyprinus carpio. Agric. Sci. Dig. 2024, 44, 174. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez Cruz, P.; Ibáñez, A.L.; Monroy, H.O.A.; Ramírez Saad, H.C.; Mitsumori, M.; Kingsley, D.H. Use of probiotics in aquaculture. ISRN Microbiol. 2012, 2012, 916845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, V.; Gomez-Chiarri, M.; Roy, C.; Smith, K.; Amaral-Zettler, L. Subtle microbiome manipulation using probiotics reduces Aantibiotic-associated mortality in fish. Msystems 2017, 2, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondad-Reantaso, M.G.; MacKinnon, B.; Karunasagar, I.; Fridman, S.; Alday-Sanz, V.; Brun, E.; Le Groumellec, M.; Li, A.; Surachetpong, W.; Karunasagar, I.; et al. Review of alternatives to antibiotic use in aquaculture. Rev Aquac. 2023, 15, 1421–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadifard, N.; Rezaei Aminlooi, V.; Tukmechi, A.; Agh, N. Evaluation of the impacts of long-term enriched Artemia with Bacillus subtilis on growth performance, reproduction, intestinal microflora, and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila of ornamental fish Poecilia latipinna. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2019, 11, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadnia-Motlagh, H.; Hajimoradlo, A.; Gorbani, R.; Agh, N.; Safari, O.; Lashkarizadeh-Bami, M. Reproductive performance and intestinal bacterial changes of Carassuis auratus fed supplemented lactoferrin and Lactobacillus rhamnosus PTCC 1637 diet. Iran. J. Ichthyol. 2017, 4, 150–161. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Campos, L.C.; Li, J.; Karu, K.; Ciric, L. Removal of antibiotics in sand, GAC, GAC sandwich and anthracite/sand biofiltration systems. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 130004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayatri, R.; Agustina, T.E.; Bahrin, D.; Moeksin, R.; Gustini, G. Preparation and characterization of ZnO-Zeolite nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation by ultraviolet light. J. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 22, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sbardella, L.; Comas, J.; Fenu, A.; Rodriguez-Roda, I.; Weemaes, M. Advanced biological activated carbon filter for removing pharmaceutically active compounds from treated wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulkowska, A.; Leung, H.W.; So, M.K.; Taniyasu, S.; Yamashita, N.; Yeung, L.W.Y.; Richardson, B.J.; Lei, A.P.; Giesy, J.P.; Lam, P.K.S. Removal of antibiotics from wastewater by sewage treatment facilities in Hong Kong and Shenzhen, China. Water Res. 2008, 42, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Family | Species | Common Name |
|---|---|---|
| Characidae | Hyphessobrycon megalopterus | Black phantom tetra |
| Paracheirodon innesi | Neon tetra | |
| Cichlidae | Astronotus ocellatus | Oscar |
| Pterophyllum altum | Angelfish | |
| Cyprinidae | Carassius auratus | Goldfish |
| Cyprinus rubrofuscus | Koi | |
| Gasteropelecidae | Gasteropelecus sternicla | Hatchetfish |
| Loricariidae | Ancistrus spinosus | Armored catfish |
| Hypostomus plecotomus | Suckermouth catfish | |
| Poeciliidae | Poecilia reticulata | Guppy |
| Xiphophorus maculatus | Platies |
| Antibiotic Class | Region/Country | Detected Antibiotics | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibiotic class | Amphenicol | Mainland China, PRC | Chloramphenicol | [32] |
| The Netherlands | Chloramphenicol | [30] | ||
| Macrolide- lincosamide-streptogramine | Hong Kong, PRC | Clarithromycin, roxithromycin | [29] | |
| Nitrofuran | The Netherlands | Ciprofloxacin, enrofloxacin, oxalinic acid | [30] | |
| (Fluoro) quinolone | Germany | Enrofloxacin | [31] | |
| Mainland China, PRC | Ciprofloxacin, enrofloxacin, norfloxacin | [32] | ||
| The Netherlands | [30] | |||
| Hong Kong, PRC | Ciprofloxacin, enrofloxacin, oxalinic acid | [28,29] | ||
| Sulfonamide /Trimethoprim | Mainland China, PRC | Sulfadimethoxine, sulfadiazine, sulfameter, sulfamethazine, sulfathiazole | [32] | |
| Tetracycline | Germany | Tetracycline | [31] | |
| Mainland China, PRC | Chlortetracycline, oxytetracycline, tetracycline | [32] | ||
| The Netherlands | [30] | |||
| Hong Kong, PRC | Chlortetracycline, doxycycline, oxytetracycline, tetracycline | [28,29] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Au-Yeung, C.; Tsui, Y.-L.; Choi, M.-H.; Chan, K.-W.; Wong, S.-N.; Ling, Y.-K.; Lam, C.-M.; Lam, K.-L.; Mo, W.-Y. Antibiotic Abuse in Ornamental Fish: An Overlooked Reservoir for Antibiotic Resistance. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040937
Au-Yeung C, Tsui Y-L, Choi M-H, Chan K-W, Wong S-N, Ling Y-K, Lam C-M, Lam K-L, Mo W-Y. Antibiotic Abuse in Ornamental Fish: An Overlooked Reservoir for Antibiotic Resistance. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):937. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040937
Chicago/Turabian StyleAu-Yeung, Chun, Yat-Lai Tsui, Man-Hay Choi, Ka-Wai Chan, Sze-Nga Wong, Yuk-Ki Ling, Cheuk-Ming Lam, Kit-Ling Lam, and Wing-Yin Mo. 2025. "Antibiotic Abuse in Ornamental Fish: An Overlooked Reservoir for Antibiotic Resistance" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040937
APA StyleAu-Yeung, C., Tsui, Y.-L., Choi, M.-H., Chan, K.-W., Wong, S.-N., Ling, Y.-K., Lam, C.-M., Lam, K.-L., & Mo, W.-Y. (2025). Antibiotic Abuse in Ornamental Fish: An Overlooked Reservoir for Antibiotic Resistance. Microorganisms, 13(4), 937. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040937








