Exosome-Modified AAV Gene Therapy Attenuates Autoimmune Hepatitis via Enhanced Regulatory T Cell Targeting and Immune Modulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mice
2.2. Experimental Design in AIH Mouse Model
2.3. Histology
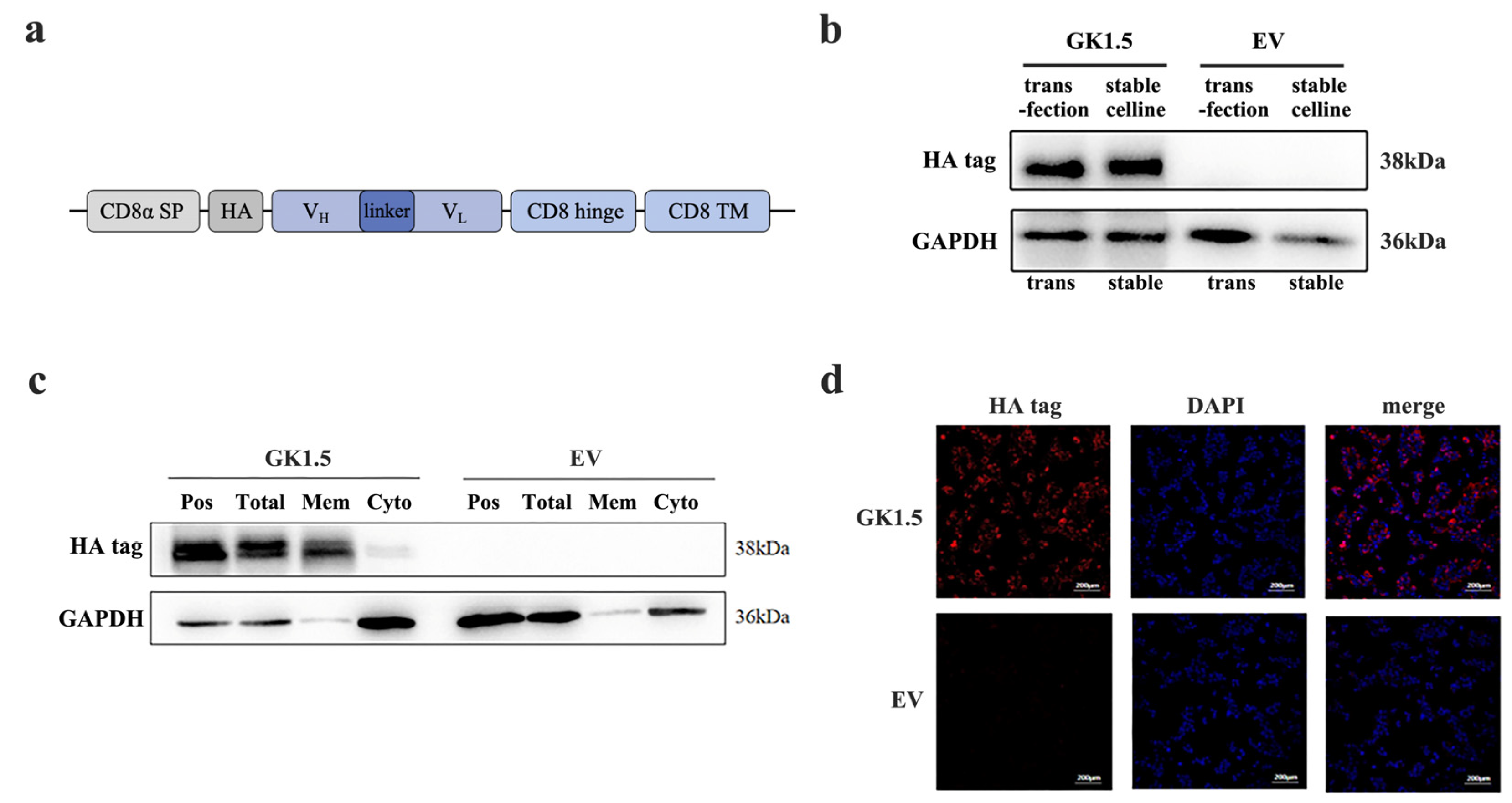
2.4. Lentivirus Packaging and Stable Cell Line Construction
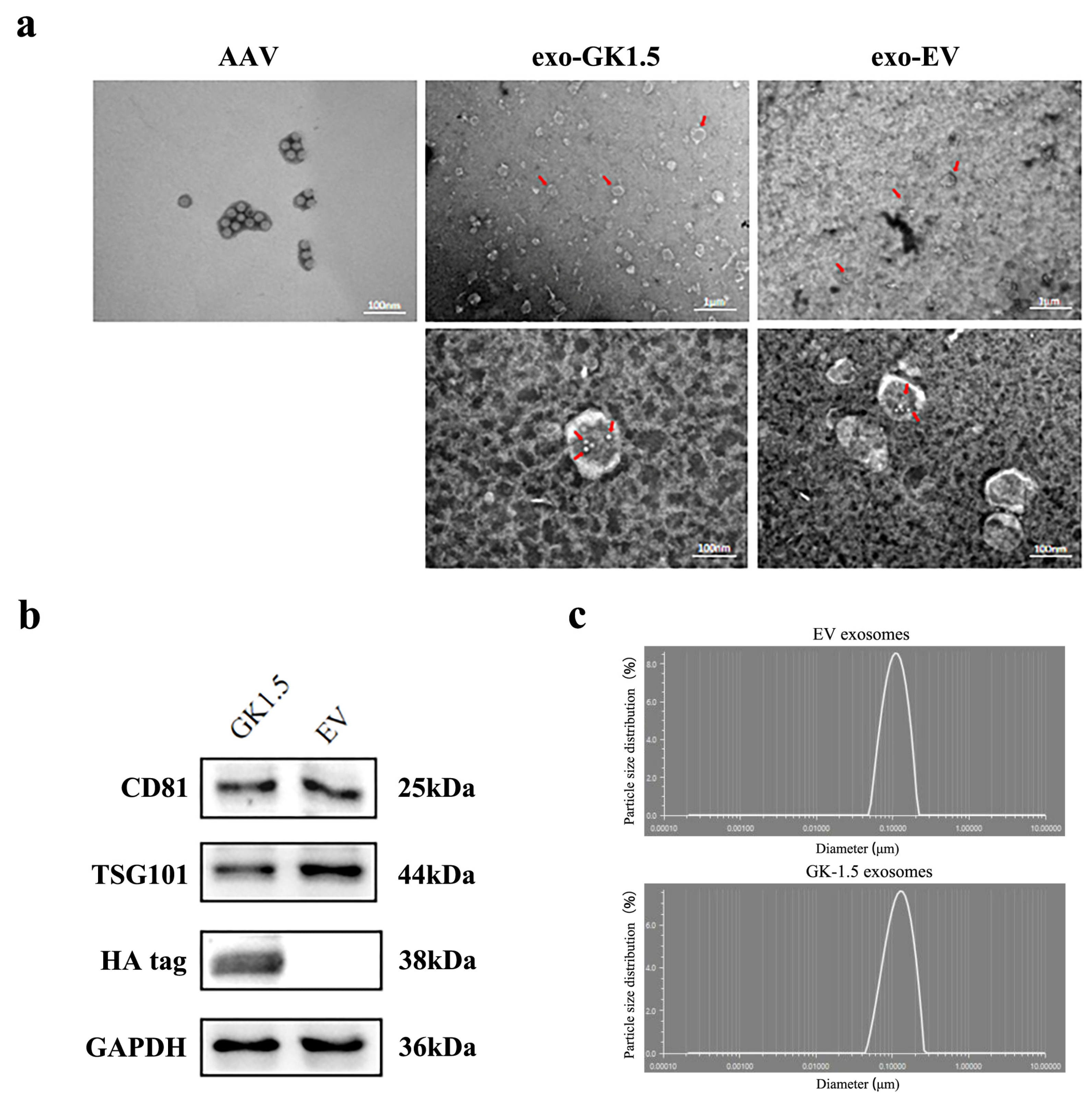
2.5. Exo-AAV and AAV Preparations
2.6. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.7. ELISA
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Establishment and Verification of Stable Transfected Cell Line Overexpressing CD4-Binding Protein
3.2. Exo-AAV Identification
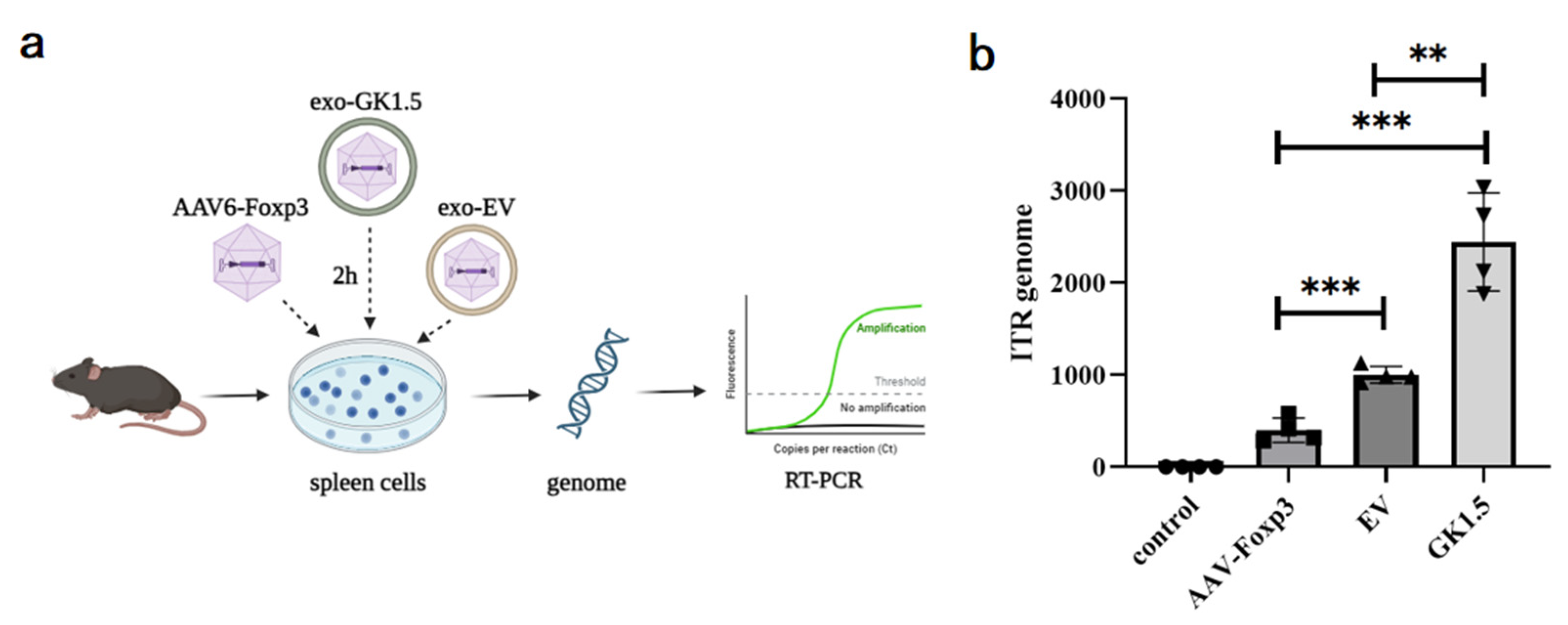
3.3. Detection of Exo-AAV Binding Ability In Vitro
3.4. Examination of Liver Damage in AIH Mice After Exo-AAV Treatment
3.5. Detection of Immune Cells and Inflammatory Cytokines in AIH Mice Liver After Exo-AAV Treatment
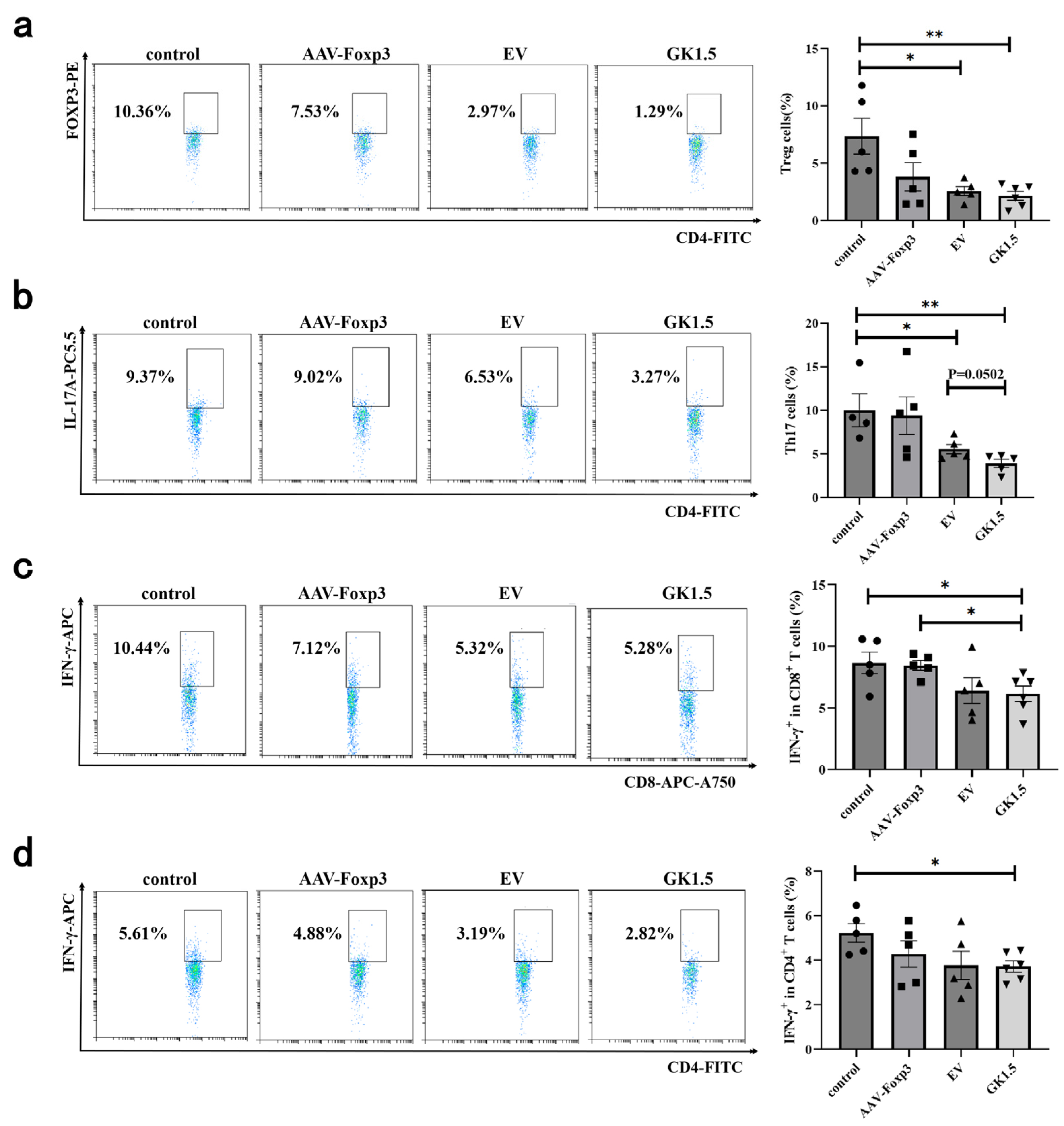
3.6. Identification of Spleen T Cells in AIH Mice After Exo-AAV Treatment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moy, L.; Levine, J. Autoimmune hepatitis: A classic autoimmune liver disease. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care 2014, 44, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiler-Normann, C.; Schramm, C.; Quaas, A.; Wiegard, C.; Glaubke, C.; Pannicke, N.; Moller, S.; Lohse, A.W. Infliximab as a rescue treatment in difficult-to-treat autoimmune hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, R.; Marenco-Flores, A.; Alsaqa, M.; Barba, R.; Cuellar-Lobo, M.; Barberan, C.; Sierra, L. Autoimmune Hepatitis Management: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Livers 2024, 4, 240–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiffman, M.L. Autoimmune Hepatitis: Epidemiology, Subtypes, and Presentation. Clin. Liver Dis. 2024, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, R.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, X.; Huang, Y.; Xie, W.; Wei, H. Amelioration of concanavalin A-induced autoimmune hepatitis by magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate through inhibition of CD4+CD25−CD69+ subset proliferation. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Feng, X.; Yan, W.; Tian, D. Regulatory T Cells in Autoimmune Hepatitis: Unveiling Their Roles in Mouse Models and Patients. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 575572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratori, L.; Lohse, A.W.; Lenzi, M. Diagnosis and management of autoimmune hepatitis. BMJ 2023, 380, e070201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Rivera, C.; Ling, S.C.; Ahmed, N.; Yap, J.; Aglipay, M.; Barrowman, N.; Graitson, S.; Critch, J.; Rashid, M.; Ng, V.L.; et al. Incidence and Characteristics of Autoimmune Hepatitis. Pediatrics 2015, 136, e1237–e1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Kwo, P. Treatment of Autoimmune Hepatitis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2024, 28, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Gerven, N.M.; Verwer, B.J.; Witte, B.I.; van Hoek, B.; Coenraad, M.J.; van Erpecum, K.J.; Beuers, U.; van Buuren, H.R.; de Man, R.A.; Drenth, J.P.; et al. Relapse is almost universal after withdrawal of immunosuppressive medication in patients with autoimmune hepatitis in remission. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli, B.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D. Autoimmune hepatitis: Standard treatment and systematic review of alternative treatments. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 6030–6048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawitt, E.L. Autoimmune hepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassim, S.; Bilodeau, M.; Vincent, C.; Lapierre, P. Novel Immunotherapies for Autoimmune Hepatitis. Front. Pediatr. 2017, 5, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiegs, G.; Hentschel, J.; Wendel, A. A T cell-dependent experimental liver injury in mice inducible by concanavalin A. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heymann, F.; Hamesch, K.; Weiskirchen, R.; Tacke, F. The concanavalin A model of acute hepatitis in mice. Lab. Anim. 2015, 49, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varrin-Doyer, M.; Shetty, A.; Spencer, C.M.; Schulze-Topphoff, U.; Weber, M.S.; Bernard, C.C.; Forsthuber, T.; Cree, B.A.; Slavin, A.J.; Zamvil, S.S. MOG transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains contain highly stimulatory T-cell epitopes in MS. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2014, 1, e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeler, G.D.; Kumar, S.; Palaschak, B.; Silverberg, E.L.; Markusic, D.M.; Jones, N.T.; Hoffman, B.E. Gene Therapy-Induced Antigen-Specific Tregs Inhibit Neuro-inflammation and Reverse Disease in a Mouse Model of Multiple Sclerosis. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Yang, P.; Lei, B.; Shao, J.; Wang, C.; Xiang, Q.; Wei, L.; Peng, Z.; Kijlstra, A. AAV2-mediated subretinal gene transfer of hIFN-alpha attenuates experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis in mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, L.; Xu, J. TIPE2 Alleviates Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Through Regulating Macrophage Polarization. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowles, D.E.; McPhee, S.W.; Li, C.; Gray, S.J.; Samulski, J.J.; Camp, A.S.; Li, J.; Wang, B.; Monahan, P.E.; Rabinowitz, J.E.; et al. Phase 1 gene therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy using a translational optimized AAV vector. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Xiao, W.; Conlon, T.; Hughes, J.; Agbandje-McKenna, M.; Ferkol, T.; Flotte, T.; Muzyczka, N. Mutational analysis of the adeno-associated virus type 2 (AAV2) capsid gene and construction of AAV2 vectors with altered tropism. J. Virol. 2000, 74, 8635–8647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asokan, A.; Conway, J.C.; Phillips, J.L.; Li, C.; Hegge, J.; Sinnott, R.; Yadav, S.; DiPrimio, N.; Nam, H.J.; Agbandje-McKenna, M.; et al. Reengineering a receptor footprint of adeno-associated virus enables selective and systemic gene transfer to muscle. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, S.; Horowitz, E.D.; Troupes, A.N.; Brown, S.M.; Pulicherla, N.; Samulski, R.J.; Agbandje-McKenna, M.; Asokan, A. Engraftment of a galactose receptor footprint onto adeno-associated viral capsids improves transduction efficiency. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 28814–28823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabtree, E.; Song, L.; Llanga, T.; Bower, J.J.; Cullen, M.; Salmon, J.H.; Hirsch, M.L.; Gilger, B.C. AAV-mediated expression of HLA-G1/5 reduces severity of experimental autoimmune uveitis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, P.; Murdaca, G.; Puppo, F.; Negrini, S. HLA-G Expressing Immune Cells in Immune Mediated Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre, E.; Rizzo, R.; Bortolotti, D.; Fernandez-Landazuri, S.; Fainardi, E.; Gonzalez, A. Some basic aspects of HLA-G biology. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 657625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakkum, D.J.; Radivojevic, M.; Frey, U.; Franke, F.; Hierlemann, A.; Takahashi, H. Parameters for burst detection. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, J.R.; Chen, B.Y.; Wong, A.; Cheng, D.; Van Arnam, J.S.; Witte, O.N.; Clark, P.M. 18F-FAC PET Selectively Images Liver-Infiltrating CD4 and CD8 T Cells in a Mouse Model of Autoimmune Hepatitis. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 1616–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Yin, S.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Xie, X. CD24 aggravates acute liver injury in autoimmune hepatitis by promoting IFN-gamma production by CD4+ T cells. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapierre, P.; Djilali-Saiah, I.; Vitozzi, S.; Alvarez, F. A murine model of type 2 autoimmune hepatitis: Xenoimmunization with human antigens. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardtke-Wolenski, M.; Fischer, K.; Noyan, F.; Schlue, J.; Falk, C.S.; Stahlhut, M.; Woller, N.; Kuehnel, F.; Taubert, R.; Manns, M.P.; et al. Genetic predisposition and environmental danger signals initiate chronic autoimmune hepatitis driven by CD4+ T cells. Hepatology 2013, 58, 718–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdener, M.; Hintermann, E.; Bayer, M.; Rhode, A.; Rodrigo, E.; Hintereder, G.; Johnson, E.F.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Pfeilschifter, J.; Manns, M.P.; et al. Breaking tolerance to the natural human liver autoantigen cytochrome P450 2D6 by virus infection. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 1409–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhi, M.S.; Meda, F.; Wang, P.; Samyn, M.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D.; Ma, Y. Expansion and de novo generation of potentially therapeutic regulatory T cells in patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 2008, 47, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhi, M.S.; Liberal, R.; Holder, B.; Robson, S.C.; Ma, Y.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D. Inhibition of interleukin-17 promotes differentiation of CD25(-) cells into stable T regulatory cells in patients with autoimmune hepatitis. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1526–1535.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhi, M.S.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D. Regulatory T cells in autoimmune hepatitis: An updated overview. J. Autoimmun. 2021, 119, 102619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.R.; Liberal, R.; Holder, B.S.; Cardone, J.; Ma, Y.; Robson, S.C.; Mieli-Vergani, G.; Vergani, D.; Longhi, M.S. Dysfunctional CD39(POS) regulatory T cells and aberrant control of T-helper type 17 cells in autoimmune hepatitis. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1007–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, C.A.; Balaj, L.; Sivaraman, S.; Crommentuijn, M.H.; Ericsson, M.; Mincheva-Nilsson, L.; Baranov, V.; Gianni, D.; Tannous, B.A.; Sena-Esteves, M.; et al. Microvesicle-associated AAV vector as a novel gene delivery system. Mol. Ther. 2012, 20, 960–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, J.A.; Mietzsch, M.; Chipman, P.; Strugatsky, D.; McKenna, R. Structural characterization of an envelope-associated adeno-associated virus type 2 capsid. Virology 2022, 565, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Li, Z.; Huang, S.; Yan, B.; He, S.; Chen, F.; Liang, Y. AAV-Containing Exosomes as a Novel Vector for Improved Gene Delivery to Lung Cancer Cells. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 707607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassmer, S.J.; Carvalho, L.S.; Gyorgy, B.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Maguire, C.A. Exosome-associated AAV2 vector mediates robust gene delivery into the murine retina upon intravitreal injection. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuer, C.B.; Hanlon, K.S.; Natasan, J.S.; Volak, A.; Meliani, A.; Mingozzi, F.; Kleinstiver, B.P.; Moon, J.J.; Maguire, C.A. In vivo engineering of lymphocytes after systemic exosome-associated AAV delivery. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Qian, Q.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Huang, B.; Liang, J.; et al. The Clinical Significance of Hepatic CD69+ CD103+ CD8+ Resident-Memory T Cells in Autoimmune Hepatitis. Hepatology 2021, 74, 847–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, J.; Bromberg, J.S. Regulatory T cell migration during an immune response. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Tu, H.; Yin, X.; Peng, C.; Dou, C.; Yang, W.; Wu, W.; Guan, X.; Li, J.; Yan, H.; et al. Targeting Glutamine Metabolism Ameliorates Autoimmune Hepatitis via Inhibiting T Cell Activation and Differentiation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 880262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yan, F.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; et al. Cornuside improves murine autoimmune hepatitis through inhibition of inflammatory responses. Phytomedicine 2023, 120, 155077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, W.; Huang, W.; Wang, Y.; Sima, H.; Ma, K.; Chen, R.; Han, H.; Yang, Y.; Bao, Y.; Pei, X.; et al. Exosome-Modified AAV Gene Therapy Attenuates Autoimmune Hepatitis via Enhanced Regulatory T Cell Targeting and Immune Modulation. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040823
Shao W, Huang W, Wang Y, Sima H, Ma K, Chen R, Han H, Yang Y, Bao Y, Pei X, et al. Exosome-Modified AAV Gene Therapy Attenuates Autoimmune Hepatitis via Enhanced Regulatory T Cell Targeting and Immune Modulation. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(4):823. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040823
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Wenwei, Weilin Huang, Yixuan Wang, Helin Sima, Kai Ma, Rongtao Chen, Heqiao Han, Yixuan Yang, Yuchen Bao, Xiaolei Pei, and et al. 2025. "Exosome-Modified AAV Gene Therapy Attenuates Autoimmune Hepatitis via Enhanced Regulatory T Cell Targeting and Immune Modulation" Microorganisms 13, no. 4: 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040823
APA StyleShao, W., Huang, W., Wang, Y., Sima, H., Ma, K., Chen, R., Han, H., Yang, Y., Bao, Y., Pei, X., & Zhang, L. (2025). Exosome-Modified AAV Gene Therapy Attenuates Autoimmune Hepatitis via Enhanced Regulatory T Cell Targeting and Immune Modulation. Microorganisms, 13(4), 823. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13040823





