Drinking Water Supplementation of trans-Cinnamaldehyde-Miglyol Microemulsions Reduces Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Heidelberg in Turkey Poults and Augments the Antibacterial Effect of Oxytetracycline
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Bacterial Strain and Culture Conditions
2.3. Plant-Derived Antimicrobial (PDA)
2.4. Oxytetracycline (OTC)
2.5. Experimental Design and Animal Management
2.6. Determination of S. Heidelberg in the Cecum, Liver, and Spleen of Turkey Poults
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dewi, G.; Manjankattil, S.; Peichel, C.; Johnson, T.J.; Noll, S.; Cardona, C.; Kollanoor Johny, A. Combination of autochthonous Lactobacillus strains and trans-Cinnamaldehyde in water reduces Salmonella Heidelberg in turkey poults. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1337428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.V.T.; Thomas, J.V.; Noll, S.; Porter, R., Jr.; Kollanoor Johny, A. Effect of various inoculum levels of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Heidelberg on cecal colonization, internal organ dissemination, and skeletal muscle deposition in turkeys after oral challenge. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjankattil, S.; Dewi, G.; Peichel, C.; Creek, M.; Bina, P.; Lerohl, K.; Deniz, K.; Akhtar, L.; Porter, R., Jr.; Noll, S.; et al. Dairy-origin Propionibacterium freudenreichii, turkey-origin Lactobacillus salivarius, and a Salmonella Typhimurium vaccine elicit comparable colonization resistance on drug-resistant Salmonella serotype cocktail in commercial turkeys. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2024, 33, 100428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjankattil, S.; Dewi, G.; Peichel, C.; Creek, M.; Bina, P.; Johnson, T.J.; Cox, R.; Noll, S.; Kollanoor Johny, A. Effect of Pimenta essential oil and peracetic acid as pre-grind dip treatments on emerging Salmonella, spoilage bacteria, and quality of ground turkey during chilled storage. Poult. Sci. 2025, 104, 104829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peichel, C.; Nair, D.; Manjankattil, S.; Reed, K.; Cox, R.B.; Donoghue, A.; Kollanoor Johny, A. Effect of trans-cinnamaldehyde and peracetic acid alone or combined on multidrug-resistant Salmonella Heidelberg on broiler drumsticks with scalding, chilling and storage. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2025, 34, 100508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, G.; Nair, D.V.T.; Peichel, C.; Johnson, T.J.; Noll, S.; Kollanoor Johny, A. Effect of lemongrass essential oil against multidrug-resistant Salmonella Heidelberg and its attachment to chicken skin and meat. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 101116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, G.; Manjankattil, S.; Peichel, C.; Jia, S.; Nair, D.V.T.; Vickers, Z.; Johnson, T.J.; Cardona, C.; Noll, S.; Kollanoor Johny, A. Effect of plant-derived antimicrobials against multidrug-resistant Salmonella Heidelberg in ground turkey. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 101581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutil, L.; Irwin, R.; Finley, R.; Ng, L.K.; Avery, B.; Boerlin, P.; Bourgault, A.M.; Cole, L.; Daignault, D.; Desruisseau, A.; et al. Ceftiofur resistance in Salmonella enterica serovar Heidelberg from chicken meat and humans, Canada. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Ye, Y.; Lan, P.; Han, X.; Quan, J.; Zhou, M.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, Y. Prevalence and characteristics of ceftriaxone-resistant Salmonella in Hangzhou children’s hospital. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 764787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. FACT SHEET: Veterinary Feed Directive Final Rule and Next Steps. 2024. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/animal-veterinary/development-approval-process/fact-sheet-veterinary-feed-directive-final-rule-and-next-steps (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- Kollanoor-Johny, A.; Mattson, T.; Baskaran, S.A.; Amalaradjou, M.A.; Babapoor, S.M.; March, B.; Valipe, S.; Darre, M.; Hoagland, T.; Schreiber, D.; et al. Reduction of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis colonization in 20-day-old broiler chickens by trans-cinnamaldehyde and eugenol. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 2981–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollanoor-Johny, A.; Upadhyay, A.; Baskaran, S.A.; Upadhyaya, I.; Mooyottu, S.; Mishra, N.; Darre, M.J.; Khan, M.I.; Donoghue, A.M.; Donoghue, D.J.; et al. Effect of therapeutic supplementation of the plant compounds trans-cinnamaldehyde and eugenol on Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis colonization in market-age broiler chickens. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2012, 21, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollanoor Johny, A.; Frye, J.G.; Donoghue, A.; Donoghue, D.J.; Porwollik, S.; McClelland, M.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Gene expression response of Salmonella enterica serotype Enteritidis phage type 8 to subinhibitory concentrations of the plant-derived compounds trans-cinnamaldehyde and eugenol. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USPEA. Antibiotic Stewardship Within U.S. Poultry Production, 2013–2023 Report. 2024. Available online: https://www.uspoultry.org/poultry-antibiotic-use-report/docs/USPOULTRY-AntibioticStewardshipReport-2024.pdf (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- FARAD. Approved Combinations of VFD Labels for Poultry. 2024. Available online: http://www.farad.org/vetgram/vfd_poultry.asp (accessed on 11 July 2025).
- Nair, D.V.T.; Kollanoor Johny, A. Food grade pimenta leaf essential oil reduces Salmonella enterica serovar Heidelberg (2011 ground turkey outbreak isolate) attachment onto turkey skin. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.V.T.; Kollanoor-Johny, A. Effect of Propionibacterium freudenreichii on Salmonella multiplication, motility, and association with avian epithelial cells. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.V.T.; Kollanoor Johny, A. Characterizing the antimicrobial function of dairy-origin probiotic Propionibacterium freudenreichii subsp. freudenreichii against multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Heidelberg in turkey poults. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.V.T.; Thomas, J.V.; Dewi, G.; Noll, S.; Brannon, J.; Kollanoor Johny, A. Reduction of multidrug-resistant Salmonella Heidelberg using dairy-origin probiotic Propionibacterium freudenreichii B3523 in growing turkeys. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2019, 28, 356–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.V.T.; Johnson, T.J.; Noll, S.L.; Kollanoor Johny, A. Effect of supplementation of dairy-origin probiotic Propionibacterium freudenreichii subsp. freudenreichii on the cecal microbiome of turkeys challenged with multidrug-resistant Salmonella Heidelberg. Poult. Sci. 2021, 100, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, D.V.T.; Thomas, J.V.; Dewi, G.; Brannon, J.; Noll, S.; Johnson, T.J.; Cox, R.B.; Kollanoor Johny, A. Propionibacterium freudenreichii B3523 reduces cecal colonization and internal organ dissemination of multidrug-resistant Salmonella Heidelberg in finishing turkeys. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2021, 30, 100107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakaran, D.M.; Kollanoor Johny, A.; Nair, D.V.T.; Johnson, T.J.; Noll, S.; Reed, K.M. Beneficial cecal microbiome modulation in turkeys exposed to probiotics and vaccine after multidrug-resistant Salmonella Heidelberg challenge. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, G.; Ramanathan, R.; Kollanoor Johny, A. Cecal metabolome profiles of turkey poults in response to Salmonella Heidelberg challenge with or without turkey-derived Lactobacillus probiotic and trans-cinnamaldehyde. Animals 2025, 15, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollanoor Johny, A.; Hoagland, T.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Effect of subinhibitory concentrations of plant-derived molecules in increasing the sensitivity of multidrug-resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium DT104 to antibiotics. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadfield, M.; Hinton, M. Evaluation of treatment and prophylaxis with nitrofurans and comparison with alternative antimicrobial agents in experimental Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis infection in chicks. Vet. Res. Commun. 2003, 27, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, I.; Upadhyay, A.; Kollanoor-Johny, A.; Mooyottu, S.; Baskaran, S.A.; Yin, H.; Schreiber, D.T.; Khan, M.I.; Darre, M.J.; Curtis, P.A.; et al. In-feed supplementation of trans-cinnamaldehyde reduces layer-chicken egg-borne transmission of Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 2985–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Russell, R.M.; Pifer, R.; Menezes-Garcia, Z.; Cuesta, S.; Narayanan, S.; MacMillan, J.B.; Sperandio, V. The serotonin neurotransmitter modulates virulence of enteric pathogens. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28, 41–53.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-T.; Chen, P.-F.; Chang, S.-C. Antibacterial activity of leaf essential oils and their constituents from Cinnamomum osmophloeum. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2001, 77, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michiels, J.; Missotten, J.A.M.; Fremaut, D.; De Smet, S.; Dierick, N.A. In vitro characterisation of the antimicrobial activity of selected essential oil components and binary combinations against pig gut flora. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2009, 151, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantala, M. Nitrovin and tetracycline: A comparison of their effect on salmonellosis in chicks. Br. Poult. Sci. 1974, 15, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nivas, S.C.; York, M.D.; Pomeroy, B.S. Effects of different levels of chlortetracycline in the diet of turkey poults artificially infected with Salmonella typhimurium. Poult. Sci. 1976, 55, 2176–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seuna, E.; Nurmi, E. Therapeutical trials with antimicrobial agents and cultured cecal microflora in Salmonella infantis infections in chickens. Poult. Sci. 1979, 58, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.W.; Tucker, J.F. The effect of antibiotic therapy on the faecal excretion of Salmonella typhimurium by experimentally infected chickens. J. Hyg. 1975, 75, 275–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, F.; Lauteri, C.; Rossi, C.; Ferri, G.; Serio, A.; Vergara, A.; Paparella, A. Combined effect of tetracycline compounds and essential oils on antimicrobial-resistant Salmonella enterica isolated from the swine food chain. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1439286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
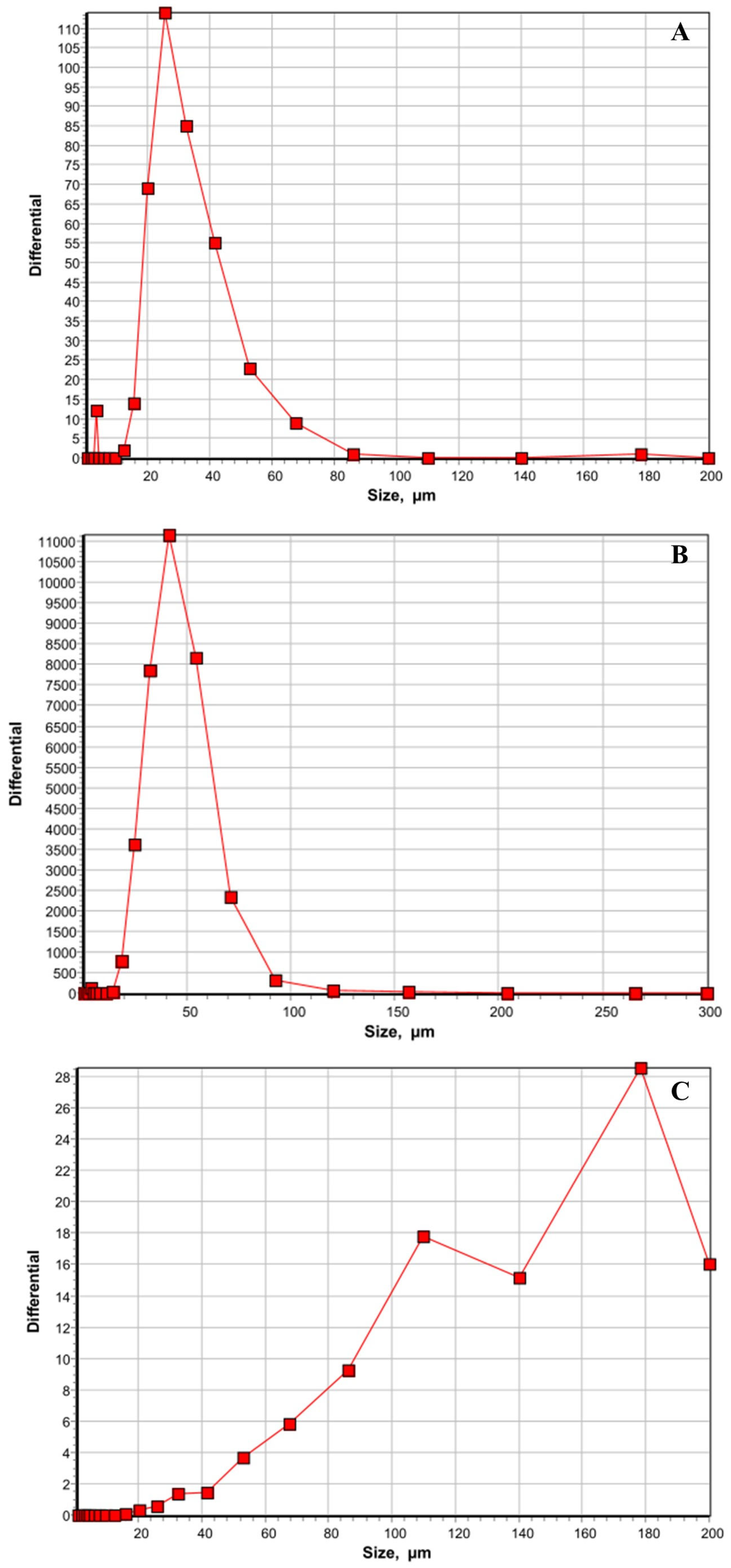
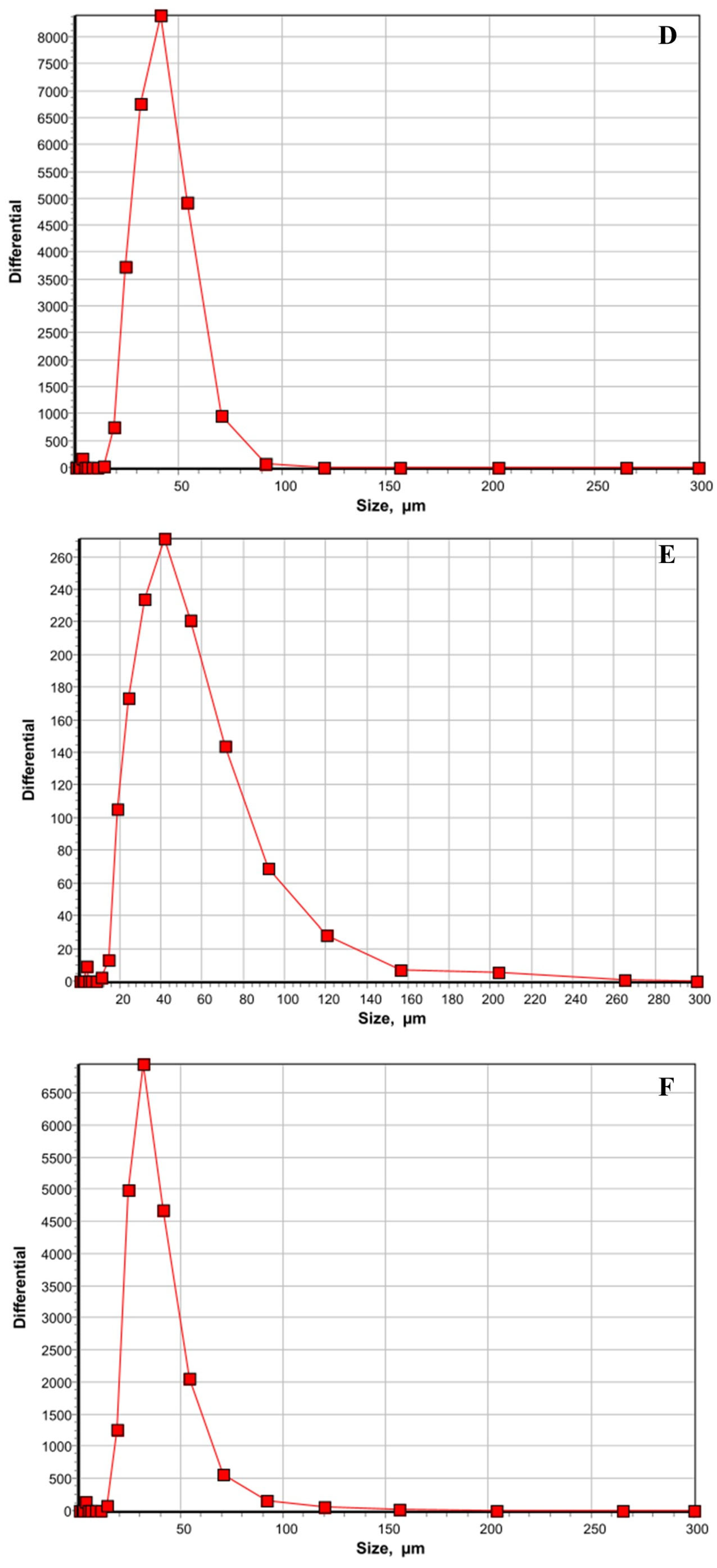
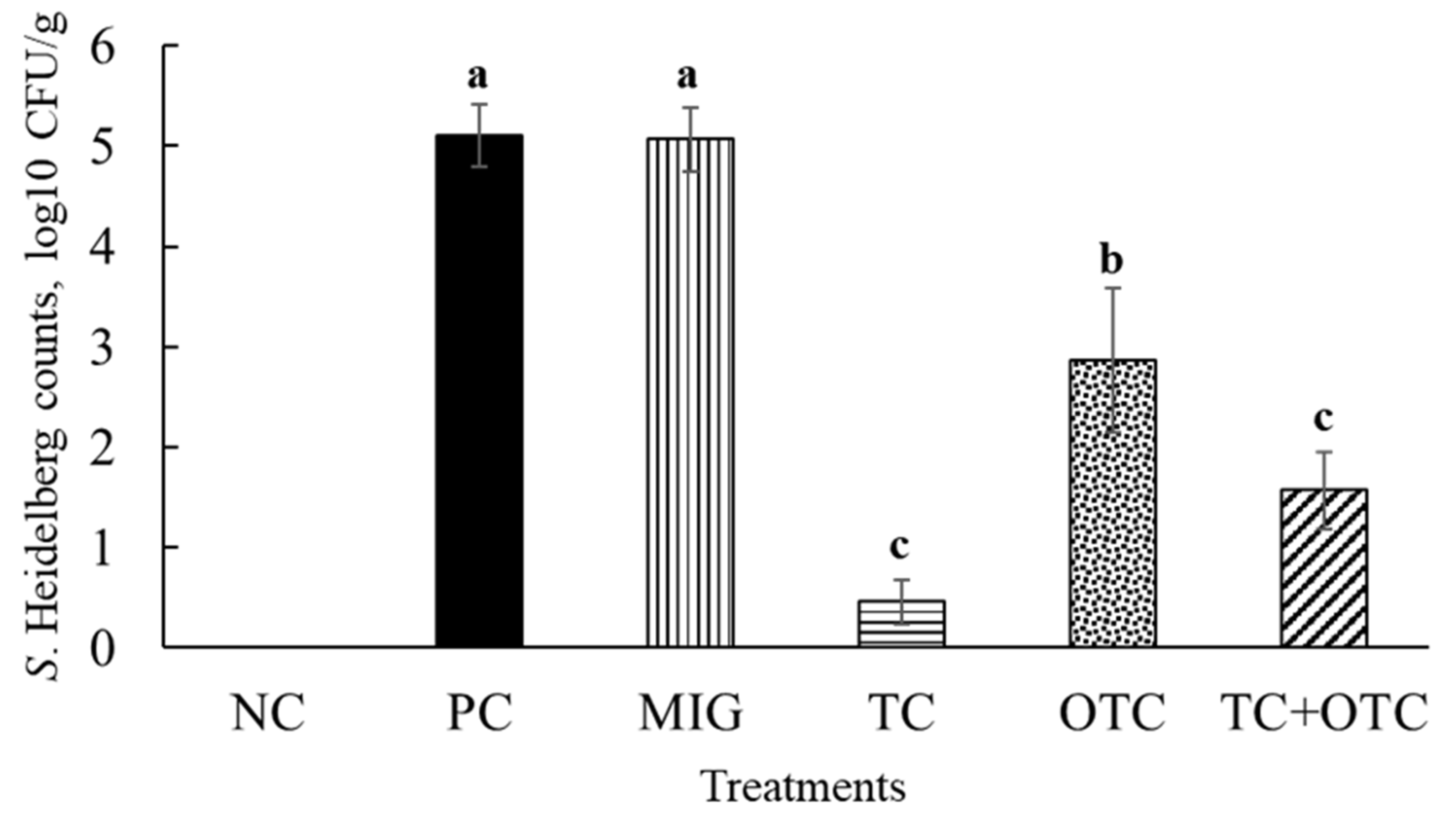
| Treatments | Positive Liver Samples (%) | Positive Spleen Samples (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Negative Control | 0 (0/16) | 0 (0/16) |
| Positive Control | 56 (9/16) a | 38 (6/16) a |
| MIG control | 69 (11/16) a | 63 (10/16) a |
| TC group | 6 (1/16) b | 6 (1/16) b |
| OTC group | 0 (0/16) b | 13 (2/16) b |
| TC+OTC group | 6 (1/16) b | 0 (0/16) b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nair, D.V.T.; Kollanoor Johny, A. Drinking Water Supplementation of trans-Cinnamaldehyde-Miglyol Microemulsions Reduces Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Heidelberg in Turkey Poults and Augments the Antibacterial Effect of Oxytetracycline. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2703. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122703
Nair DVT, Kollanoor Johny A. Drinking Water Supplementation of trans-Cinnamaldehyde-Miglyol Microemulsions Reduces Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Heidelberg in Turkey Poults and Augments the Antibacterial Effect of Oxytetracycline. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(12):2703. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122703
Chicago/Turabian StyleNair, Divek V. T., and Anup Kollanoor Johny. 2025. "Drinking Water Supplementation of trans-Cinnamaldehyde-Miglyol Microemulsions Reduces Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Heidelberg in Turkey Poults and Augments the Antibacterial Effect of Oxytetracycline" Microorganisms 13, no. 12: 2703. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122703
APA StyleNair, D. V. T., & Kollanoor Johny, A. (2025). Drinking Water Supplementation of trans-Cinnamaldehyde-Miglyol Microemulsions Reduces Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Heidelberg in Turkey Poults and Augments the Antibacterial Effect of Oxytetracycline. Microorganisms, 13(12), 2703. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122703






