Impact of Exposure to Disinfectants on Presence of Efflux Pump Genes and Antibiotic Resistance Profiles in Escherichia coli Isolates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Study Design and Sampling
2.3. Bacterial Isolation and Identification
2.4. DNA Extraction and PCR Assays
2.5. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Disinfectant Resistance Genes
3.2. Antibiotic Resistance Phenotypes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barcellos, D.E.S.N.; Marques, B.M.F.P.P.; Mores, T.J.; Coelho, C.F.; Borowski, S.M. Aspectos práticos sobre o uso de antimicrobianos em suinocultura. Acta Sci. Vet. 2009, 37 (Suppl. S1), s151–s155. [Google Scholar]
- Bragg, R.; Jansen, A.; Coetzee, M.; van der Westhuizen, W.; Boucher, C. Bacterial resistance to quaternary ammonium compounds (QAC) disinfectants. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 808, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gerba, C.P. Quaternary ammonium biocides: Efficacy in application. Am. Soc. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasil, Segurança do Paciente em Serviços de Saúde: Limpeza e Desinfecção de Superfícies. 2012. Available online: www.anvisa.gov.br (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Jiang, L.; Li, M.; Tang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, H.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Feng, T.; Zhang, X. Effect of different disinfectants on bacterial aerosol diversity in poultry houses. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brasil Ministério da Agricultura e Pecuária. Instrução Normativa No 45, de 22 de Novembro de 2016. Diário Oficial da União, 30 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Canal do Ovo. Programa de Biosseguridade de Bastos Youtube. 2016. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=FEMMwTY6Q84&t=34s&ab_channel=CanaldoOvo (accessed on 23 May 2025).
- WHO. The WHO AWaRe (Access, Watch, Reserve) Antibiotic Book; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. WHO Global Strategy for Containment of Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Santajit, S.; Indrawattana, N. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance in ESKAPE Pathogens. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 1, 2475067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belter, B.; McCarlie, S.J.; Boucher-van Jaarsveld, C.E.; Bragg, R.R. Investigation into the Metabolism of Quaternary Ammonium Compound Disinfectants by Bacteria. Microb. Drug Resist. 2022, 28, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Long, M.; Huang, Y.; Wu, G.; Deng, W.; Yang, X.; Li, B.; Meng, Y.; Cheng, L.; Fan, L.; et al. Antimicrobial and disinfectant resistance of Escherichia coli isolated from giant pandas. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buffet-Bataillon, S.; Tattevin, P.; Bonnaure-Mallet, M.; Jolivet-Gougeon, A. Emergence of resistance to antibacterial agents: The role of quaternary ammonium compounds—A critical review. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2012, 39, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Zhou, Z.C.; Zhu, L.; Wei, Y.Y.; Feng, W.Q.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.J.; Shuai, X.Y.; Zhang, Z.J.; et al. The impact and mechanism of quaternary ammonium compounds on the transmission of antibiotic resistance genes. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 28352–28360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhnert, P.; Bisgaard, M.; Korczak, B.M.; Schwendener, S.; Christensen, H.; Frey, J. Identification of animal Pasteurellaceae by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. J. Microbiol. Methods 2012, 89, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Liu, L.; Wang, H.; Tian, J.; Ying, H.; Shi, L.; Yu, T. Characterization and horizontal transfer of qacH-associated class 1 integrons in Escherichia coli isolated from retail meats. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 258, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillings, M.R.; Xuejun, D.; Hardwick, S.A.; Holley, M.P.; Stokes, H.W. Gene cassettes encoding resistance to quaternary ammonium compounds: A role in the origin of clinical class 1 integrons? ISME J. 2009, 3, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, L.; Meng, J.; McDermott, P.F.; Wang, F.; Yang, Q.; Cao, G.; Hoffmann, M.; Zhao, S. Presence of disinfectant resistance genes in Escherichia coli isolated from retail meats in the USA. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2644–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, M.P.V. Determinantes Emergentes de Resistência Antimicrobiana Em Escherichia coli de Origem Clínica, Fecal, e de Carne de Aves e Suínos. Ph.D. Thesis, University of São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals. In CLSI Supplement VET01S 2020, 5th ed.; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020; Volume 40. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, C.; Hu, H.; Chen, G.; Li, Z.; Li, A.; Zhang, J. Disinfectant resistance in bacteria: Mechanisms, spread, and resolution strategies. Environ. Res. 2021, 195, 110897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slipski, C.J.; Jamieson, T.R.; Zhanel, G.G.; Bay, D.C. Riboswitch-associated guanidinium-selective efflux pumps frequently transmitted on proteobacterial plasmids increase Escherichia coli biofilm tolerance to disinfectants. J. Bacteriol. 2020, 202, e00104-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Group | Production Type | Sample Year | Disinfection Protocol | Disinfection Dilution | Frequency of Disinfection | № of Samples |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-exposed | Free-range | 2022 | Without disinfection | - | - | 28 |
| Protocol 1 | Caged | 2021 | QAC, glutaraldehyde, ethanolic aldehyde, and chemical enhancers | 1:400 L | Three times a week | 20 |
| Protocol 2 | Caged | 2021 | QAC and glutaraldehyde | 1:100 L | Every other day | 53 |
| Protocol 3 | Caged | 2021 | QAC, glutaraldehyde, ethanolic aldehyde, and chemical enhancers | 1:100 L | Twice a day | 22 |
| Total | 123 |
| Gene | Sequence (5′–3′) | Description | Annealing (°C) | Amplicon (pb) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| emrE | CCTGTTATGGGCGGTAGAC TTCGTGCTCACCTTTCCTT | Efflux pumps (multidrug) | 54 | 310 | [16] |
| qacE | AGCCCCATACCTACAAAG AGCTTGCCCCTTCCGC | Efflux pumps (QAC) | 55 | 194 | [17] |
| qacEΔ1 | AAGTAATCGCAACATCCG ATAAGCAACACCGACAGG | Efflux pumps (QAC) | 49 | 140 | [16] |
| qacH | TTTGGTGAGGTCGTCGCA GCCAGCCCAAACAGCATA | Efflux pumps (QAC) | 54 | 162 | [16] |
| sugE(c) | CTGCTGGAAGTGGTATGGG GCATCGGGTTAGCGGACT | Efflux pumps (QAC)—chromosomal | 55 | 226 | [18] |
| ydgE | GGCAATCGTGCTGGAAAT GGCGGCAATACCAAACCC | Efflux pumps (multidrug) | 54 | 184 | [16] |
| ydgF | ATTACCTTGTTTAGCGTTTT GGTTCACCTCCAGTTCAG | Efflux pumps (multidrug) | 49 | 139 | [16] |
| intl1 | ACGAGCGCAAGGTTTCGGT GAAAGGTCTGGTCATACATG | Class 1 integron | 54 | 150 | [19] |
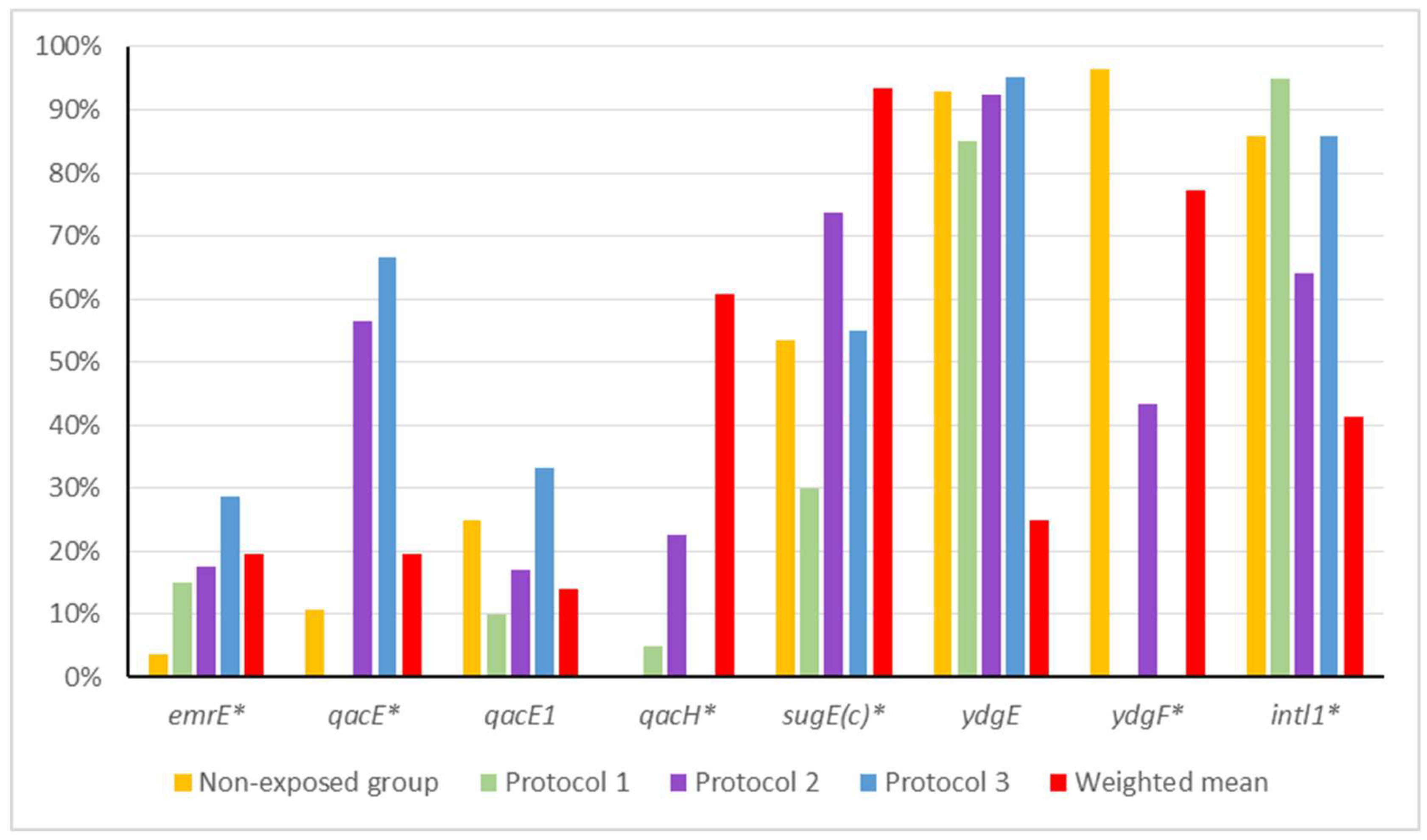
| Group | emrE | qacE | qacEΔ1 | qacH | sugE(c) | ydgE | ydgF | intl1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-exposed | 3.57% | 10.71% | 25.00% | 0% | 53.57% | 92.86% | 96.43% | 85.71% |
| Protocol 1 | 15.00% | 0% | 10.00% | 5.00% | 30.00% | 85.00% | 0% | 95.00% |
| Protocol 2 | 16.98% | 56.60% | 16.98% | 22.64% | 73.58% | 92.45% | 43.40% | 64.15% |
| Protocol 3 | 27.27% * | 36.36% | 31.82% | 0% | 50.00% | 90.91% | 0% | 81.82% |
| Weighted mean (protocols 1 to 3) | 18.95% | 40% | 18.95% | 13.68% | 58.95% | 90.53% | 24.21% | 74.74% |
| p-value (Non-exposed vs. weighted mean) | 0.0708 | 0.0031 * | 0.5932 | 0.0385 * | 0.6664 | 1 | <0.0001 * | 0.3073 |
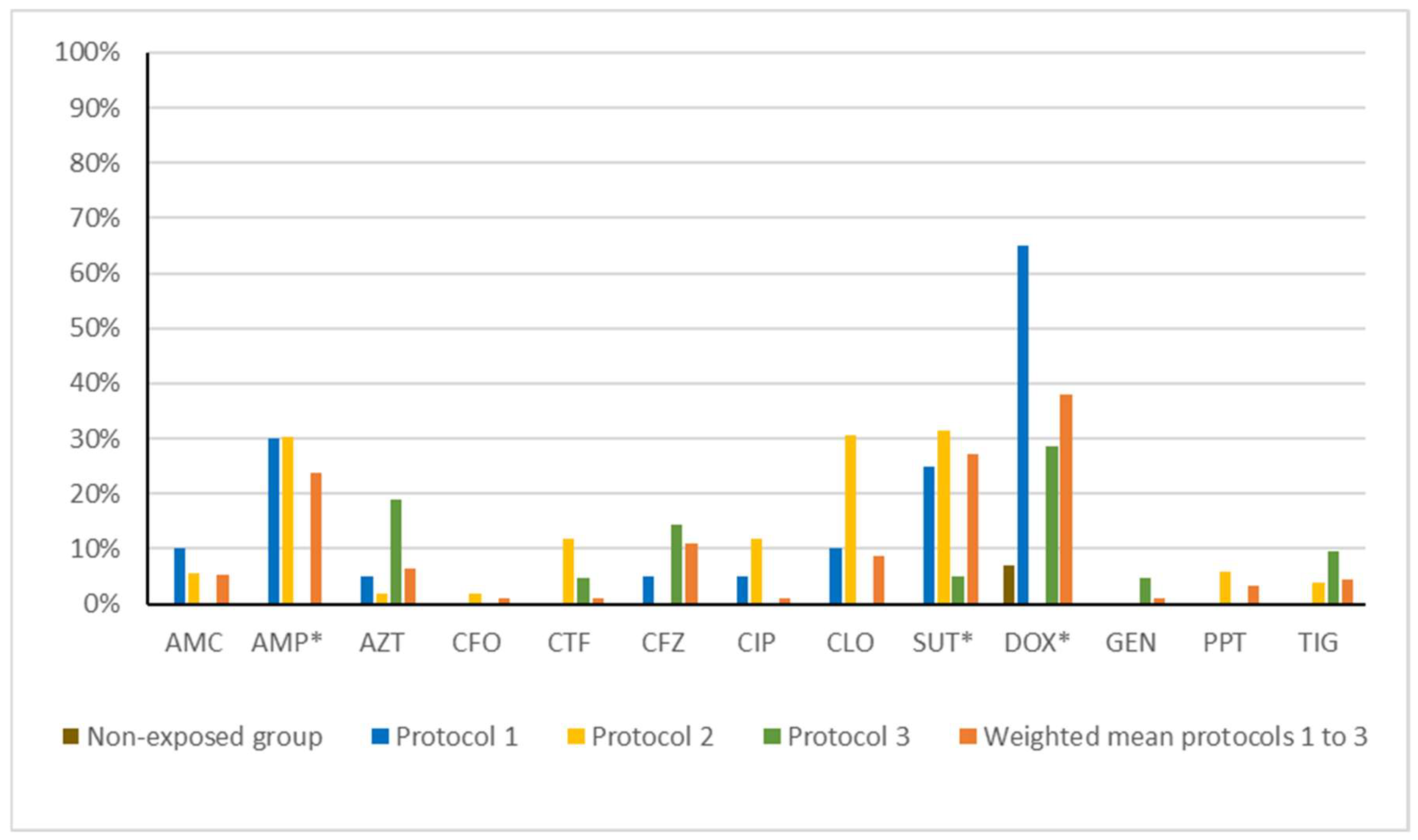
| Group | AMC | AMP | AZT | CFO | CTF | CFZ | CIP | CLO | SUT | DOX | GEN | PPT | TIG |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-exposed | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 7.14% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Protocol 1 | 10.0% | 30.00% | 5.00% | 0% | 0% | 5.00% | 5.00% | 10.00% | 25.00% | 65.00% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Protocol 2 | 5.66% | 30.19% | 1.89% | 1.89% | 0% | 11.32% | 0% | 11.32% | 35.85% | 30.19% | 0% | 5.66% | 3.77% |
| Protocol 3 | 0% | 0% | 18.18% | 0% | 4.55% | 13.64% | 0% | 0% | 4.55% | 27.27% | 4.55% | 0% | 9.09% |
| Weighted mean (protocols 1 to 3) | 5.26% | 23.16% | 6.32% | 1.05% | 1.05% | 10.53% | 1.05% | 8.42% | 26.32% | 36.84% | 1.05% | 3.16% | 4.21% |
| p-value (Non-exposed vs. weighted mean) | 0.5875 | 0.0035 * | 0.335 | 1 | 1 | 0.1145 | 1 | 0.1963 | 0.0009 * | 0.002 * | 1 | 1 | 0.5731 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbosa, F.B.; Takeda, B.R.; Vicentini, G.G.I.; Gandolfi, G.; Rocha, V.G.P.; Franco, L.S.; Cunha, M.P.V.; Knöbl, T. Impact of Exposure to Disinfectants on Presence of Efflux Pump Genes and Antibiotic Resistance Profiles in Escherichia coli Isolates. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122700
Barbosa FB, Takeda BR, Vicentini GGI, Gandolfi G, Rocha VGP, Franco LS, Cunha MPV, Knöbl T. Impact of Exposure to Disinfectants on Presence of Efflux Pump Genes and Antibiotic Resistance Profiles in Escherichia coli Isolates. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(12):2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122700
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbosa, Fernanda Borges, Beatriz Rodrigues Takeda, Gabriella Garcia Ilion Vicentini, Gabriel Gandolfi, Victória Galdino Pavlenco Rocha, Leticia Soares Franco, Marcos Paulo Vieira Cunha, and Terezinha Knöbl. 2025. "Impact of Exposure to Disinfectants on Presence of Efflux Pump Genes and Antibiotic Resistance Profiles in Escherichia coli Isolates" Microorganisms 13, no. 12: 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122700
APA StyleBarbosa, F. B., Takeda, B. R., Vicentini, G. G. I., Gandolfi, G., Rocha, V. G. P., Franco, L. S., Cunha, M. P. V., & Knöbl, T. (2025). Impact of Exposure to Disinfectants on Presence of Efflux Pump Genes and Antibiotic Resistance Profiles in Escherichia coli Isolates. Microorganisms, 13(12), 2700. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13122700







