Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Aerospace-Grade Aluminum by SRB-Enriched Biofilms Isolated from the Mars Analog Lake Salda
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Physicochemical Analyses of Lake Water
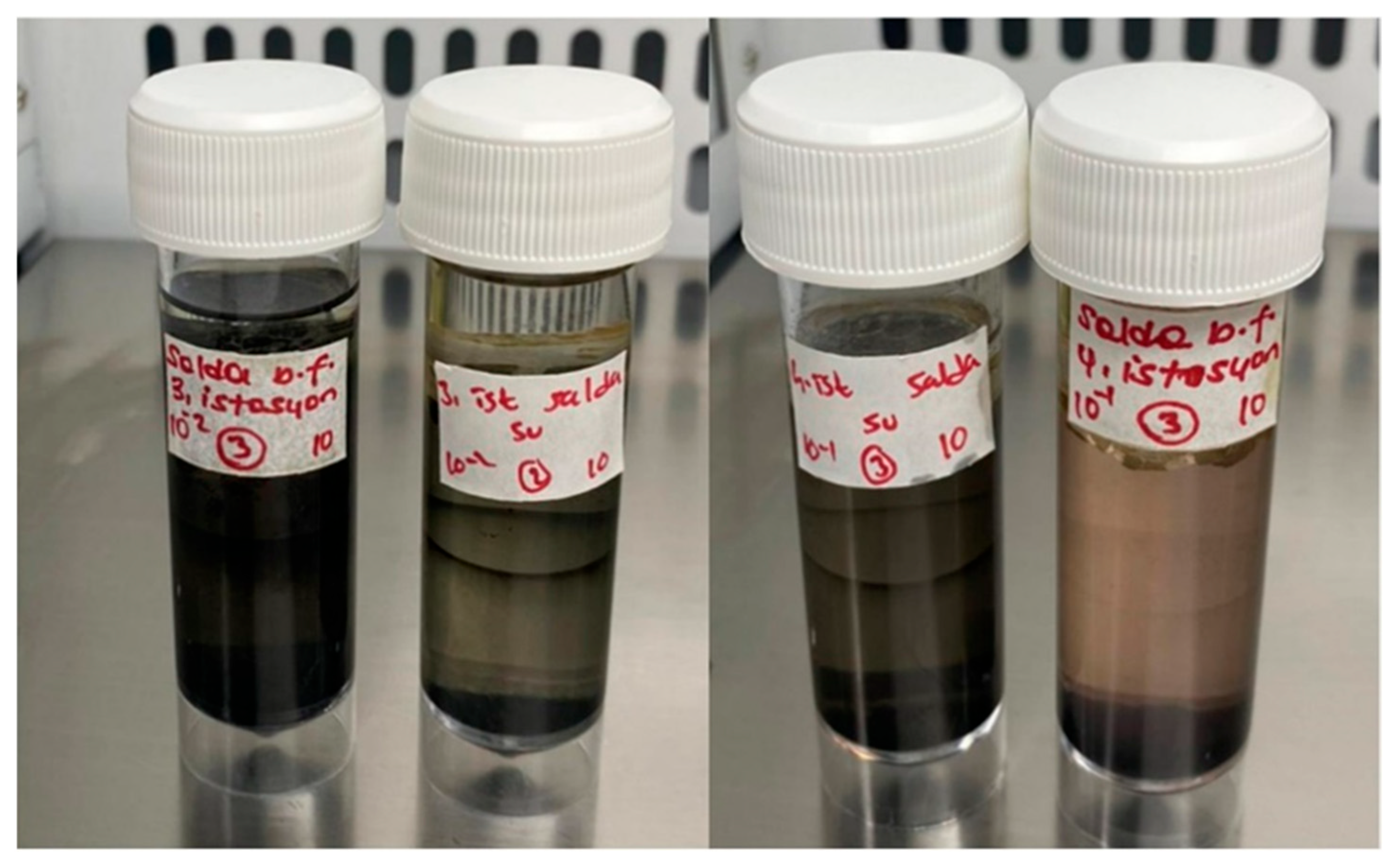
2.3. SRB Enrichment Culture and Cell Count
2.4. Microscopic Examination of Stromatolites
2.5. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS)
2.6. Coupons and Test Condition
2.7. Enumeration of Sessile Cells
2.8. Electrochemical Analyses
2.9. Weight Loss Test
- K = 3.45 × 106
- W = mass loss (g)
- A = surface area (cm2)
- t = time (h)
- d = density (g/cm3)
2.10. FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared) Analysis
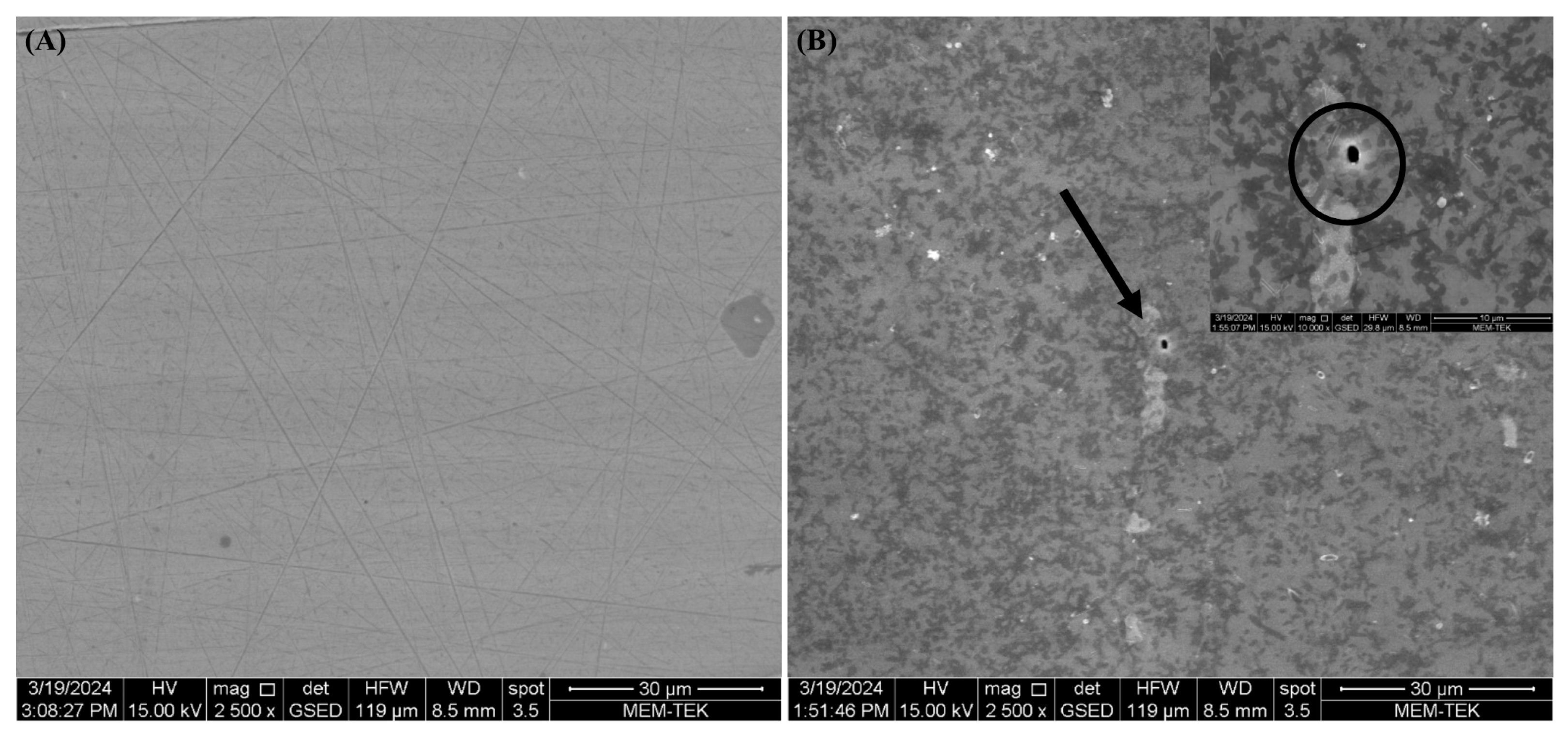
2.11. Surface Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Analyses of Lake Water
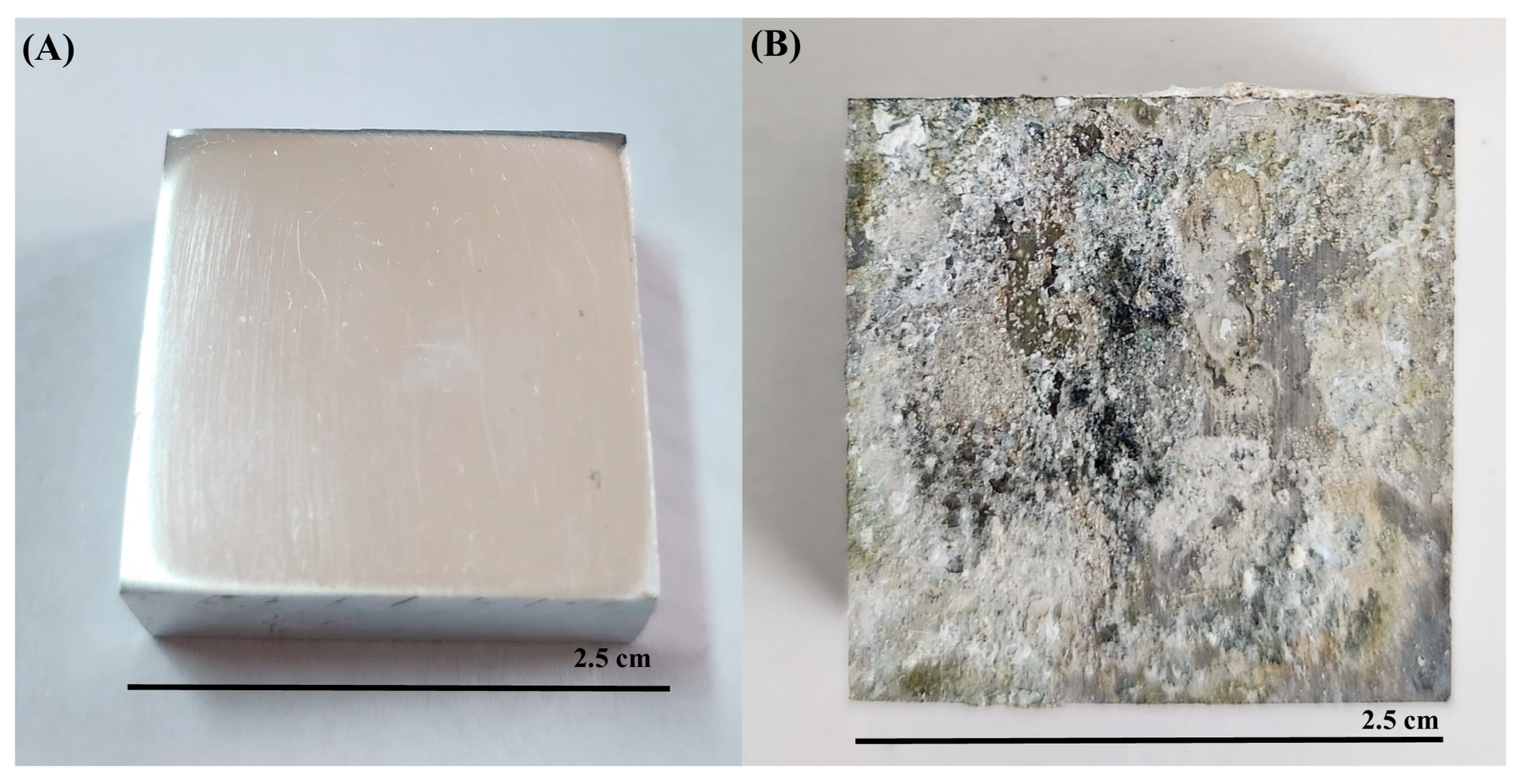
3.2. Microscopic Examination of Stromatolites
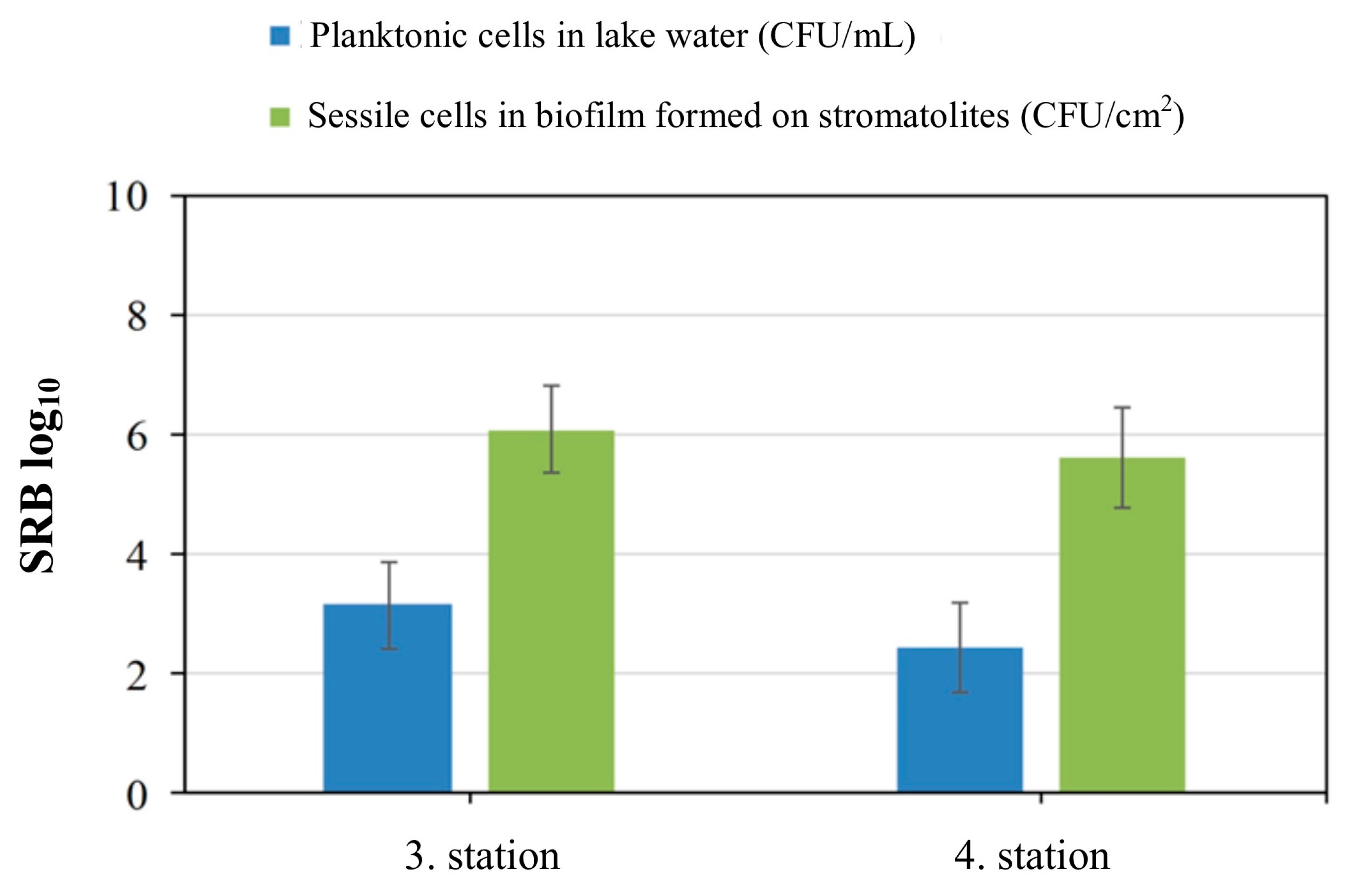
3.3. SRB Enrichment Culture and Cell Count in Biofilm and Lake Water
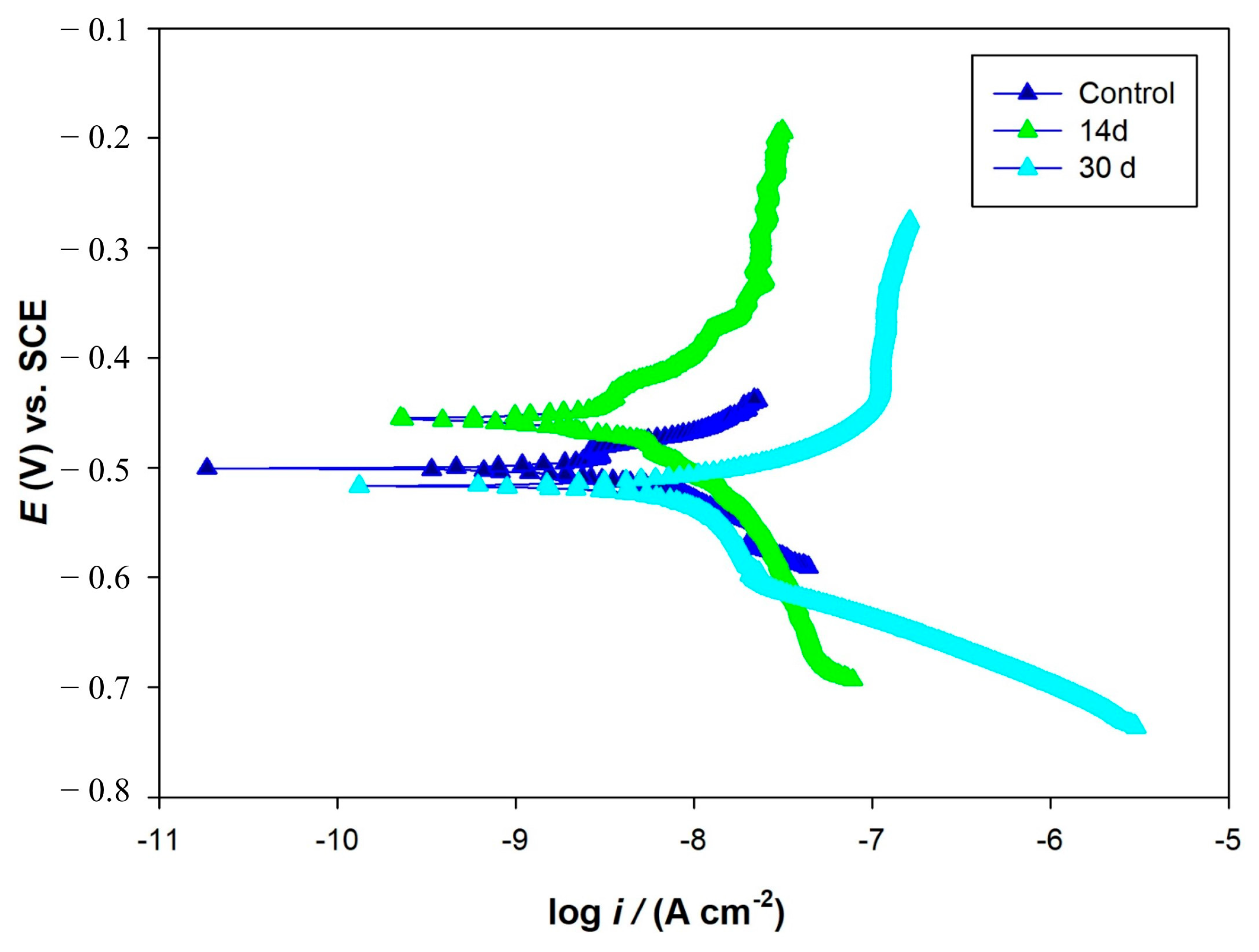
3.4. Biofilm Observations, Cell Count and Corrosion Analyses
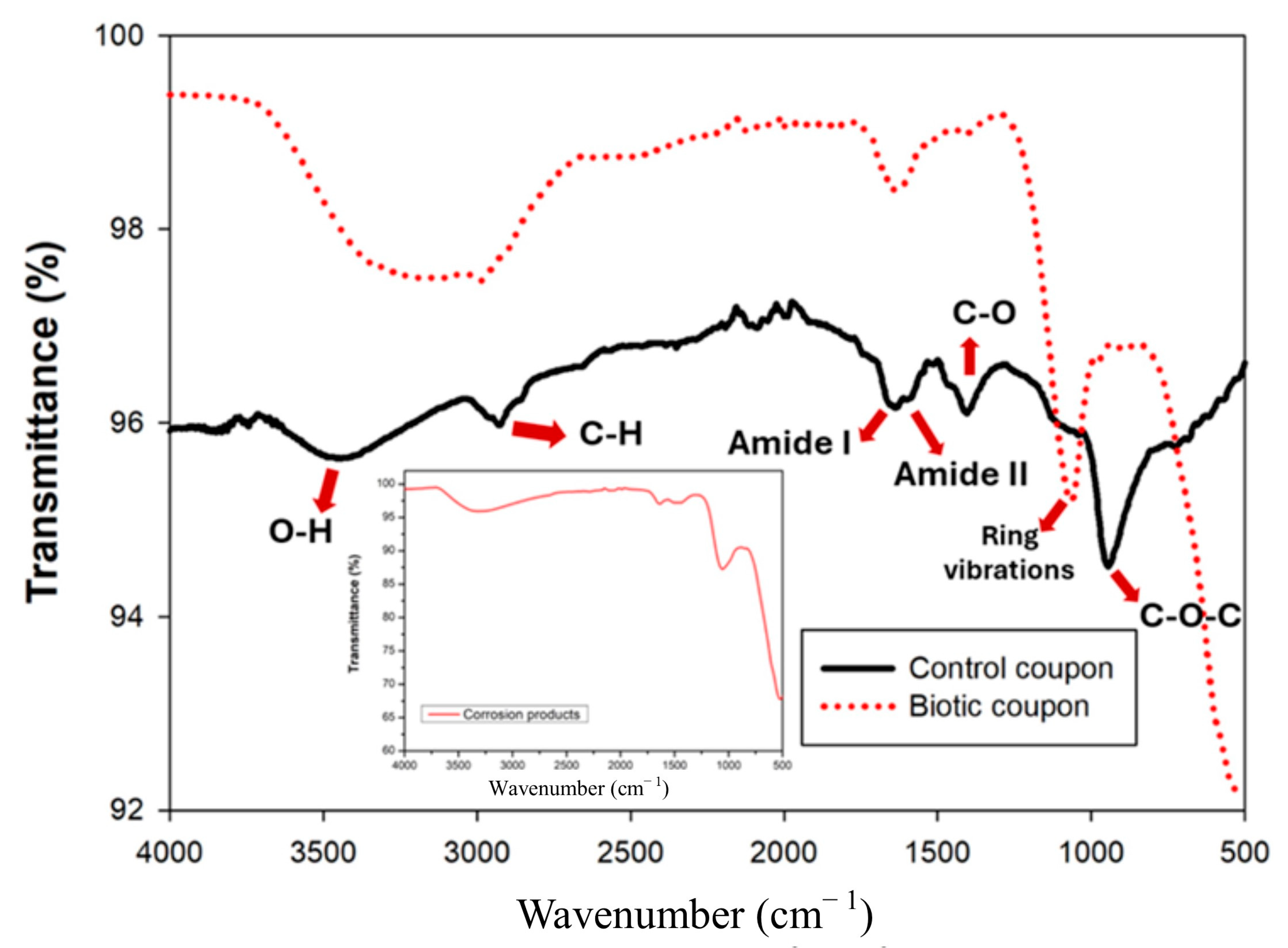
3.5. FTIR Analyses
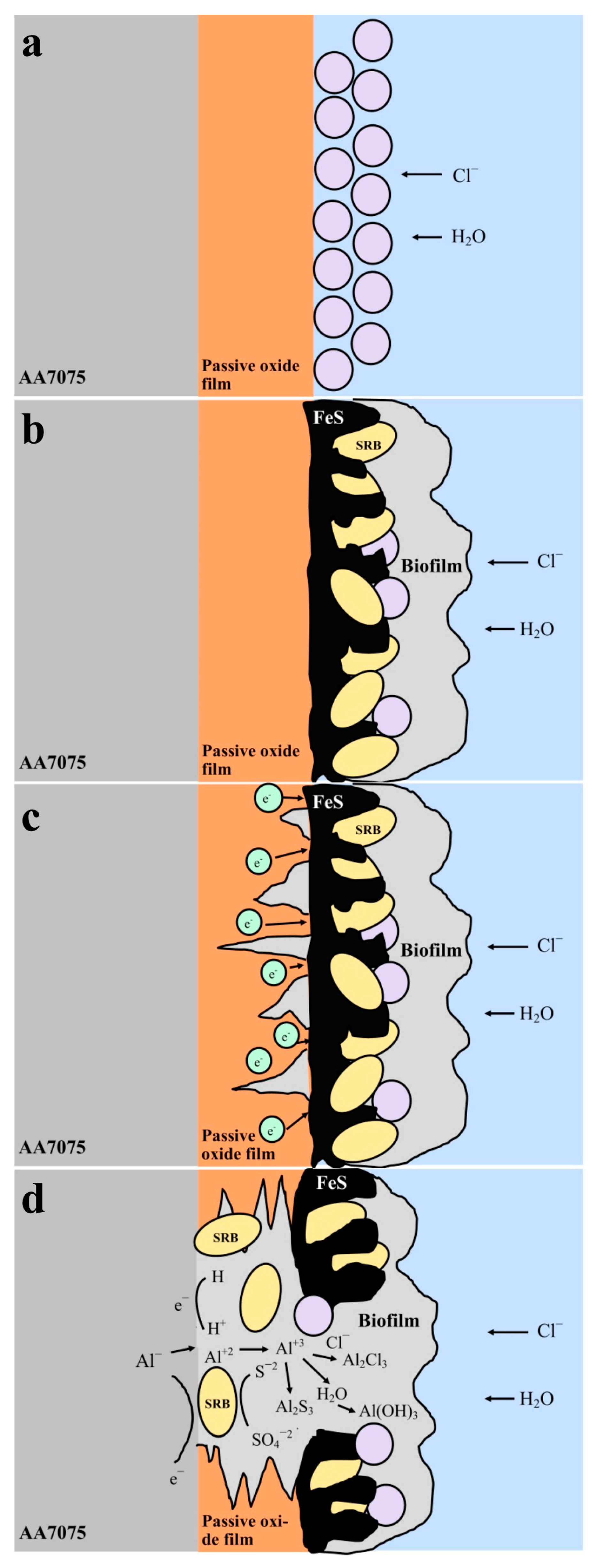
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schreier, J.E.; Reysenbach, A.-L. Deep-Sea Ridges, Microbiology. In Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences, 3rd ed.; Cochran, J.K., Bokuniewicz, H.J., Yager, P.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 291–298. [Google Scholar]
- Dupont, J.; Lozano, P. Earth: An Oxidative Planet with Limited Atom Resources and Rich Chemistry. Angew. Chem. 2025, 137, e202416459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, B.J.; Ray, R.I.; Pope, R.K. Relationship between Corrosion and the Biological Sulfur Cycle: A Review. Corrosion 2000, 56, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, V.; Morzfeld, M.; Manga, M. Liquid Water in the Martian Mid-Crust. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2409983121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanedar, A.; Tanık, A. Presenting Water Quality Characteristics of Lake Salda, Turkey. EJEAS 2023, 6, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcı, N.; Demirel, C. Salda Gölünün Jeomikrobiyolojisi ve Güncel Stromatolit Oluşumunda Mikrobiyal Etkiler/Geomicrobiology of Lake Salda and Microbial Influences on Present-Day Stromatolite Formation. Yerbilimleri 2018, 39, 19–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ilhan-Sungur, E.; Ozuolmez, D.; Çotuk, A.; Cansever, N.; Muyzer, G. Isolation of a Sulfide-Producing Bacterial Consortium from Cooling-Tower Water: Evaluation of Corrosive Effects on Galvanized Steel. Anaerobe 2017, 43, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, B.C.; Kolb, V.M.; Steele, A.; House, C.H.; Lanza, N.L.; Gasda, P.J.; VanBommel, S.J.; Newsom, H.E.; Martínez-Frías, J. Origin of Life on Mars: Suitability and Opportunities. Life 2021, 11, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurowitz, J.A.; Tice, M.M.; Allwood, A.C.; Cable, M.L.; Hand, K.P.; Murphy, A.E.; Uckert, K.; Bell, J.F.; Bosak, T.; Broz, A.P.; et al. Redox-Driven Mineral and Organic Associations in Jezero Crater, Mars. Nature 2025, 645, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calle, L.M.; Li, W.; Johansen, M.R.; Buhrow, J.W.; Calle, C.I. Corrosion on Mars: An Investigation of Corrosion Mechanisms Under Relevant Simulated Martian Environments 2017; No. NASA/TP-2017-219743; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Calle, L.M. Corrosion on Mars: Effect of the Mars Environment on Spacecraft Materials 2019; No. NASA/TP-2019-220238; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dursun, T.; Soutis, C. Recent Developments in Advanced Aircraft Aluminium Alloys. Mater. Des. 2014, 56, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, A.; Rodriguez-Millan, M.; Satish Shenoy, B. Aerospace Grade Aluminum Alloys. In Aluminum Technologies in Aerospace Applications; Gürgen, S., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 1–13. ISBN 978-3-031-82447-0. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, T.; Jia, R.; Unsal, T.; Xu, D. Toward a Better Understanding of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion Caused by Sulfate Reducing Bacteria. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2019, 35, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, F.; Zhai, X.; Duan, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, K.; Hou, B. Influence of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria on the Corrosion Behavior of 5052 Aluminum Alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 316, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; APHA: Washington DC, USA, 1981; ISBN 087553-091-5. [Google Scholar]
- Postgate, J.R. The Sulphate-Reducing Bacteria, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1984; ISBN 978-0-521-25791-6. [Google Scholar]
- Kramar, M.K.; Tinta, T.; Lučić, D.; Malej, A.; Turk, V. Bacteria Associated with Moon Jellyfish during Bloom and Post-Bloom Periods in the Gulf of Trieste (Northern Adriatic). PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0198056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glöckner, F.O. Evaluation of General 16S Ribosomal RNA Gene PCR Primers for Classical and Next-Generation Sequencing-Based Diversity Studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R. PyNAST: A Flexible Tool for Aligning Sequences to a Template Alignment. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 266–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rognes, T.; Flouri, T.; Nichols, B.; Quince, C.; Mahé, F. VSEARCH: A Versatile Open Source Tool for Metagenomics. PeerJ 2016, 4, e2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R. Usearch; Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL): Berkeley, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM G1-11; Standard Practice for Preparing, Cleaning and Evaluating Corrosion Test Specimen. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Theophil Anand, G.; John Sundaram, S.; Kanimozhi, K.; Nithiyavathi, R.; Kaviyarasu, K. Microwave Assisted Green Synthesis of CuO Nanoparticles for Environmental Applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 36, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, J.; Flemming, H.-C. FTIR-Spectroscopy in Microbial and Material Analysis. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 1998, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahzadeh, M. Biopolymer-Based Metal Nanoparticle Chemistry for Sustainable Applications: Volume 1: Classification, Properties and Synthesis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; ISBN 978-0-12-822123-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kazanci, N.; Girgin, S.; Dügel, M. On the Limnology of Salda Lake, a Large and Deep Soda Lake in Southwestern Turkey: Future Management Proposals. Aquat. Conserv. Mar. Freshw. Ecosyst. 2004, 14, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boomer, I.; Horne, D.J.; Slipper, I.J. The Use of Ostracods in Palaeoenvironmental Studies, or What Can You Do with an Ostracod Shell? Paleontol. Soc. Pap. 2003, 9, 153–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briceag, A.; Ion, G. Holocene Ostracod and Foraminiferal Assemblages of the Romanian Black Sea Shelf. Quat. Int. 2014, 345, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boomer, I.; Frenzel, P.; Feike, M. Salinity-Driven Size Variability in Cyprideis Torosa (Ostracoda, Crustacea). J. Micropalaeontology 2017, 36, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, L.K.; Reid, R.P.; Dupraz, C.; Decho, A.W.; Buckley, D.H.; Spear, J.R.; Przekop, K.M.; Visscher, P.T. Sulfate Reducing Bacteria in Microbial Mats: Changing Paradigms, New Discoveries. Sediment. Geol. 2006, 185, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Buick, R. The Antiquity of Microbial Sulfate Reduction. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2004, 64, 243–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, R.G.; Planchon, O.; Duxbury, N.S.; Latif, K.; Kidron, G.J.; Consorti, L.; Armstrong, R.A.; Gibson, C.; Schild, R. Oceans, Lakes, and Stromatolites on Mars. Adv. Astron. 2020, 2020, 6959532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, V.; Cantasano, N. Evidence of life on Mars. Cosmology 2014, 17, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Balci, N.; Gunes, Y.; Kaiser, J.; On, S.A.; Eris, K.; Garczynski, B.; Horgan, B.H.N. Biotic and Abiotic Imprints on Mg-Rich Stromatolites: Lessons from Lake Salda, SW Turkey. Geomicrobiol. J. 2020, 37, 401–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Takahashi, A.; Kojima, H.; Miyata, N.; Fukui, M. Desulfofustis limnaeus sp. Nov., a Freshwater Sulfate-Reducing Bacterium Isolated from Marsh Soil. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Xu, C.C.; Zhang, D.; Buchheit, R. Corrosion Protective Film Formation on Mg Alloy AZ31 by Exposure to Dilute Selenite Solutions. Materials 2021, 14, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Li, J.; Ma, J.; Su, Y.; Zheng, X.; Mao, Y.; Zhao, Z. EBSD Characterization of 7075 Aluminum Alloy and Its Corrosion Behaviors in SRB Marine Environment. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vejar, N.D.; Sacre, J.; Collao, B.; Perez-Donoso, J.; Páez, M.A.; Pineda, F.; BenjaminWorker; Sancy, M. Enhanced Corrosion of 7075 Alloy by the Presence of Bacillus megaterium. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 9723–9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, J.; Zheng, L.; Jin, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Gao, Z.; Meng, G.; Liu, H.; Liu, H. Corrosion of Aluminum Alloy 7075 Induced by Marine Aspergillus Terreus with Continued Organic Carbon Starvation. npj Mater. Degrad. 2022, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, F.; Duan, J.; Zhai, X.; Wang, N.; Zhang, J.; Lu, D.; Hou, B. Interaction between Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria and Aluminum Alloys—Corrosion Mechanisms of 5052 and Al-Zn-In-Cd Aluminum Alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2020, 36, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Element | Fe | Si | Cu | Mn | Cr | Ti | Mg | Zn | %Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amount (wt%) | 0.10 | 0.05 | 1.60 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 2.50 | 5.80 | Balance |
| Parameters | Station 1 | Station 2 | Station 3 | Station 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 10.16 | 10.01 | 10.08 | 10.04 |
| EC (mS/cm) | 1.21 | 1.36 | 1.24 | 1.21 |
| DO (mg/L) | 8.74 | 7.34 | 7.98 | 8.26 |
| TDS (ppm) | 1715 | 1723 | 1610 | 1540 |
| Temperature (°C) | 16.3 | 17.8 | 18.9 | 20.4 |
| TSS (mg/L) | 2 | 2 | 4 | 15 |
| Species | Similarity |
|---|---|
| Entomomonas asaccharolytica | 100 |
| Mycoplasma sp. (ex Biomphalaria glabrata) | 100 |
| Pseudomonas knackmussii | 100 |
| Pseudomonas oryziphila | 100 |
| Salmonella enterica | 100 |
| Pseudomonas mosselii | 100 |
| Escherichia coli | 100 |
| Halopseudomonas litoralis | 100 |
| Mycoplasmoides fastidiosum | 100 |
| Pseudomonas sp. BT-42-2 | 100 |
| Lactiplantibacillus paraplantarum | 100 |
| Comamonas antarctica | 100 |
| Weissella hellenica | 100 |
| Intestinimonas butyriciproducens | 100 |
| Enterococcus faecium | 100 |
| Bacillus thuringiensis | 100 |
| Pseudomonas mediterranea | 100 |
| Pseudomonas sp. Os17 | 100 |
| Halomonas sp. MS1 | 100 |
| Candidatus Pseudomonas adelgestsugas | 100 |
| Kangiella sediminilitoris | 100 |
| Desulfofustis limnaeus | 100 |
| Sample Name | Number of Raw Reads | Reads After Filtering | Number and Proportion of Reads Used in Final Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| SG1 | 294.112 | 122.857 | 187.728 |
| Coupon | Ecorr (mV) vs. SCE | Icorr (nA/cm2) | Ba mV/dec | Bb mV/dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | −500 | 2.4 | 126 | 149 |
| Biotic (14 d) | −456 | 9.2 | 100 | 834 |
| Biotic (30 d) | −518 | 76.7 | 161 | 77 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Unsal, T.; Yucel, S.; Ongan Rabba, D.; Aksu, A.; Taskin, O.S.; Cetintasoglu, M.E.; Bilgin, R.; Korkmaz, N.; Balcıoglu Ilhan, E.B.; Dur, O.; et al. Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Aerospace-Grade Aluminum by SRB-Enriched Biofilms Isolated from the Mars Analog Lake Salda. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112555
Unsal T, Yucel S, Ongan Rabba D, Aksu A, Taskin OS, Cetintasoglu ME, Bilgin R, Korkmaz N, Balcıoglu Ilhan EB, Dur O, et al. Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Aerospace-Grade Aluminum by SRB-Enriched Biofilms Isolated from the Mars Analog Lake Salda. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112555
Chicago/Turabian StyleUnsal, Tuba, Seben Yucel, Demet Ongan Rabba, Abdullah Aksu, Omer Suat Taskin, Mehmet Emre Cetintasoglu, Rasit Bilgin, Nagihan Korkmaz, Esra Billur Balcıoglu Ilhan, Osman Dur, and et al. 2025. "Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Aerospace-Grade Aluminum by SRB-Enriched Biofilms Isolated from the Mars Analog Lake Salda" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112555
APA StyleUnsal, T., Yucel, S., Ongan Rabba, D., Aksu, A., Taskin, O. S., Cetintasoglu, M. E., Bilgin, R., Korkmaz, N., Balcıoglu Ilhan, E. B., Dur, O., & Caglar Balkis, N. (2025). Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion of Aerospace-Grade Aluminum by SRB-Enriched Biofilms Isolated from the Mars Analog Lake Salda. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2555. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112555










