Impact of Kefir on the Gut–Brain Axis: Serotonin Metabolism and Signaling in Pediatric Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics, Animals and Protocols
2.2. Gene Expressions of SLC6A4, 5-HT, 5-HTR4, 5-HTR3A, 5-HTR2B, TPH1, and VMAT2 with Real—Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.3. Determination of 5-HT, TPH1, TPH2, 5-HTR3-A, 5-HTR2B, and 5-HIAA by ELISA Assay
2.4. Evaulation of 5-HT and TPH1 Expressions by Western Blot
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
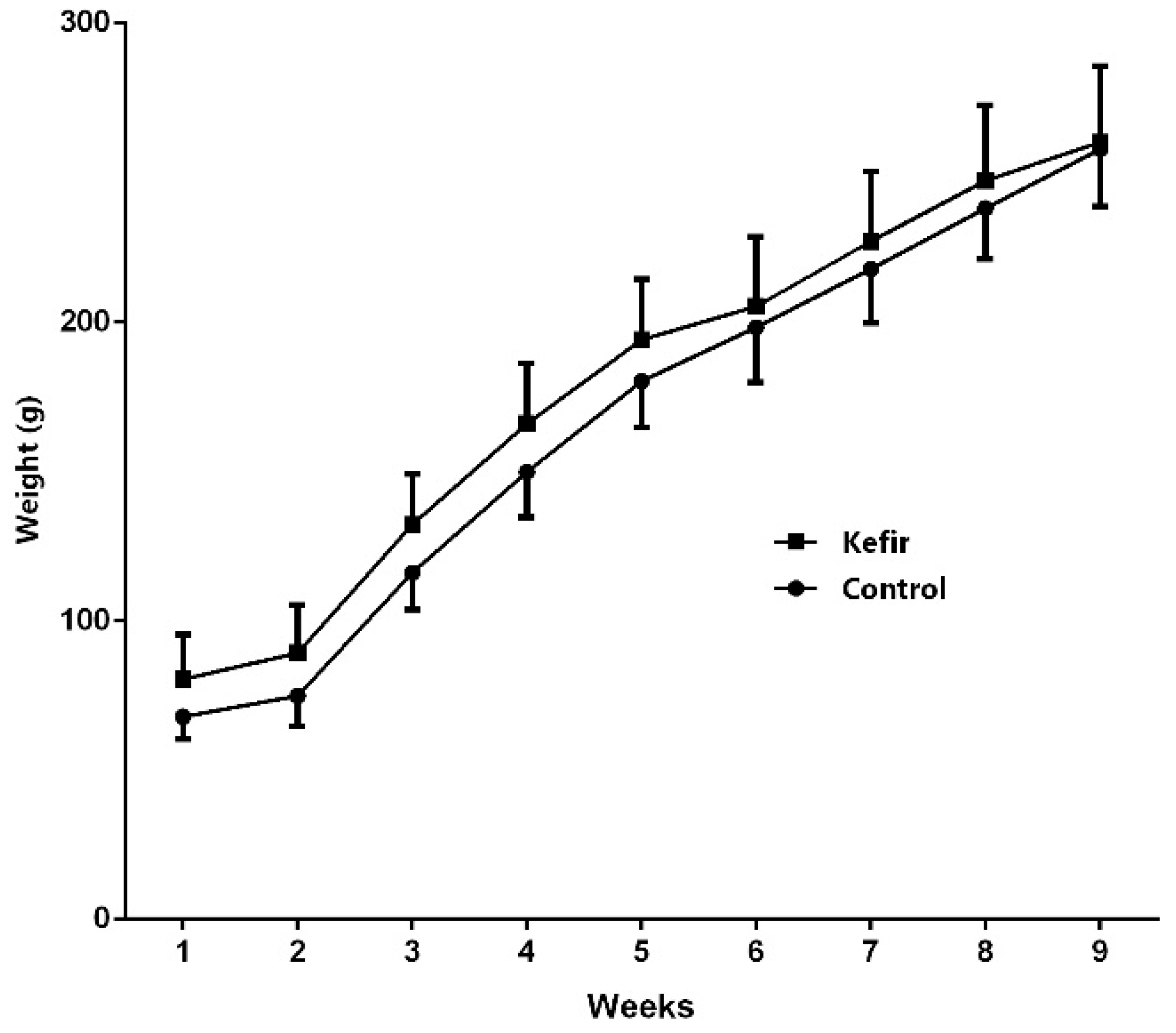
3.1. Initial and the Final Body Weights
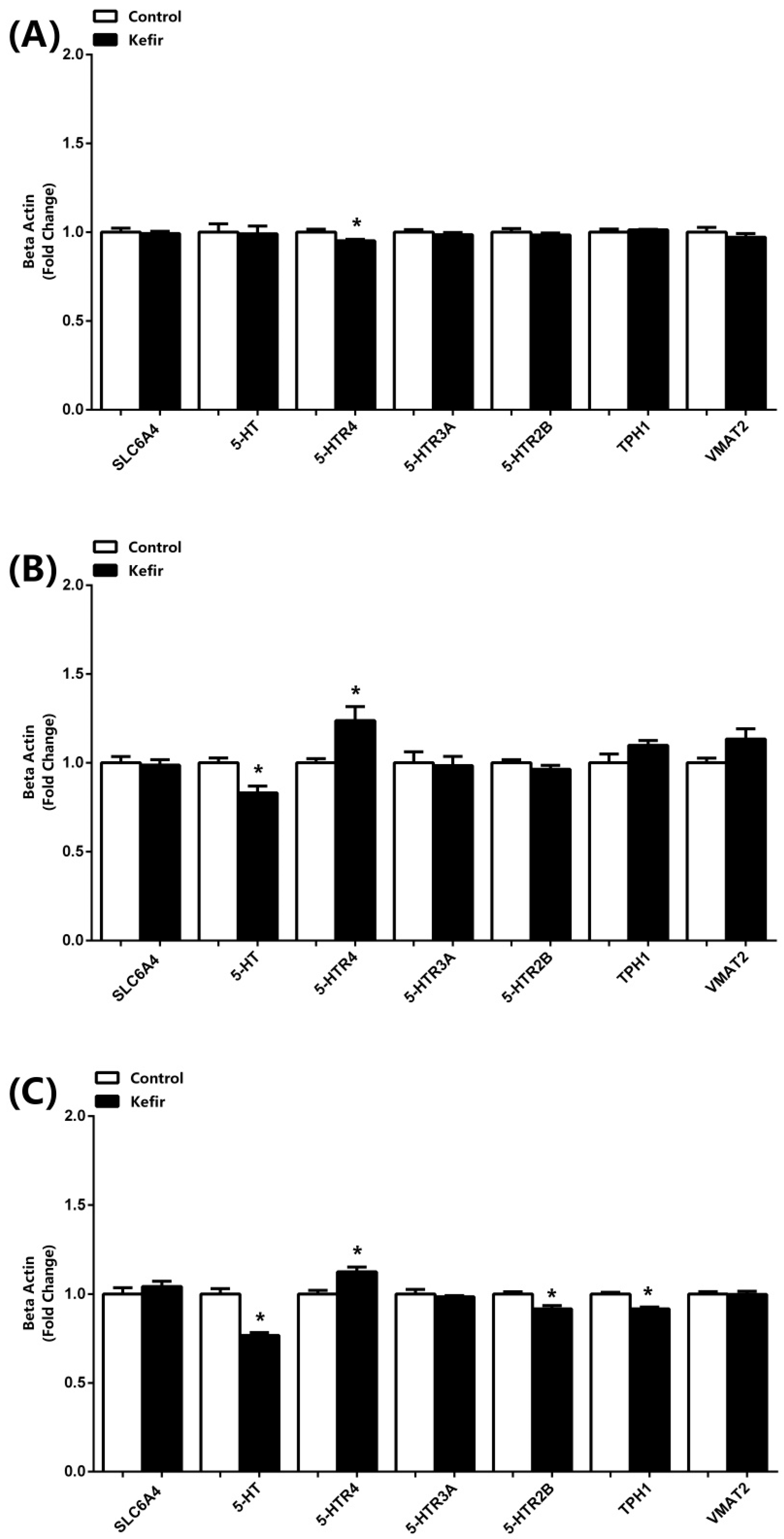
3.2. mRNA Expressions of SLC6A4, 5-HT, 5-HTR4, 5-HTR3A, 5-HTR2B, TPH1, and VMAT2
3.3. 5-HT, TPH1, TPH2, 5-HTR3-A, 5-HTR2B, and 5-HIAA Levels Detected by ELISA Kits
3.4. Western Blot Analyses
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Nichols, D.E.; Nichols, C.D. Serotonin Receptors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 1614–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Galen, K.A.; ter Horst, K.W.; Serlie, M.J. Serotonin, Food Intake, and Obesity. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCorvy, J.D.; Roth, B.L. Structure and Function of Serotonin G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 150, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, D.J.; Gardier, A.M. The Pharmacological Basis of the Serotonin System: Application to Antidepressant Response. Encephale 2016, 42, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arredondo Montero, J.; Bueso Asfura, O.E.; Pérez Riveros, B.P.; López Burgos, E.; Rico Jiménez, M. Diagnostic Performance of Urinary 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic Acid in Acute Appendicitis: A Systematic Review and Diagnostic Test Accuracy Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2023, 38, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donovan, M.H.; Tecott, L.H. Serotonin and the Regulation of Mammalian Energy Balance. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.-M.; Park, S.; Kim, H. Serotonin as a New Therapeutic Target for Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity. Diabetes Metab. J. 2016, 40, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silić, A.; Vukojević, J.; Peitl, V.; De Hert, M.; Karlović, D. Major Depressive Disorder: A Possible Typisation According to Serotonin, Inflammation, and Metabolic Syndrome. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2022, 34, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, T.; Lyons, D.; Heisler, L.K. Role of Serotonin in Body Weight, Insulin Secretion and Glycaemic Control. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2021, 33, e12960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Han, D.; Hao, Y.; Song, Z.; Sun, Z.; Dai, Z. Linking Serotonin Homeostasis to Gut Function: Nutrition, Gut Microbiota and Beyond. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 64, 7291–7310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, D.M.; Dawes, M.A.; Mathias, C.W.; Acheson, A.; Hill-Kapturczak, N.; Dougherty, D.M. L -Tryptophan: Basic Metabolic Functions, Behavioral Research and Therapeutic Indications. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2009, 2, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, R.; Schneider, E.; Gunnigle, E.; Cotter, P.D.; Cryan, J.F. Fermented Foods: Harnessing Their Potential to Modulate the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis for Mental Health. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 158, 105562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, K.G.; Cryan, J.F.; Mayer, E.A. The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis: From Motility to Mood. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 1486–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appleton, J. The Gut-Brain Axis: Influence of Microbiota on Mood and Mental Health. Integr. Med. 2018, 17, 28–32. [Google Scholar]
- Heijtz, R.D.; Wang, S.; Anuar, F.; Qian, Y.; Björkholm, B.; Samuelsson, A.; Hibberd, M.L.; Forssberg, H.; Pettersson, S. Normal Gut Microbiota Modulates Brain Development and Behavior. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3047–3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Riordan, K.J.; Moloney, G.M.; Keane, L.; Clarke, G.; Cryan, J.F. The Gut Microbiota-Immune-Brain Axis: Therapeutic Implications. Cell Reports Med. 2025, 6, 101982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, N.K.; Al-Beltagi, M.; Bediwy, A.S.; El-Sawaf, Y.; Toema, O. Gut Microbiota in Various Childhood Disorders: Implication and Indications. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 1875–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, N.F.; Kumar, M.R.; Yeap, S.K.; Abdullah, J.O.; Khalid, M.; Omar, A.R.; Osman, M.A.; Mortadza, S.A.S.; Alitheen, N.B. Kefir and Its Biological Activities. Foods 2021, 10, 1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima Barros, S.É.; dos Santos Rocha, C.; de Moura, M.S.B.; Barcelos, M.P.; de Paula da Silva, C.H.T.; da Silva Hage-Melim, L.I. Potential Beneficial Effects of Kefir and Its Postbiotic, Kefiran, on Child Food Allergy. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 3770–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamida, R.S.; Shami, A.; Ali, M.A.; Almohawes, Z.N.; Mohammed, A.E.; Bin-Meferij, M.M. Kefir: A Protective Dietary Supplementation against Viral Infection. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pektaş, M.B.; Aslan, E.; Güzel, H.; Korkmaz, Ö.A.; Çeleğen, K.; Pektaş, A.; Bostanci, A.; Sadi, G. Kefir Protects the Liver against High Fructose Corn Syrup Induced Phosphodiesterase Hyperactivity. Turkish J. Biochem. 2022, 47, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, E.; Sadi, G.; Guzel, H.; Karaca, C.; Korkmaz, O.; Pektas, M.; Celegen, M.; Aladag, T.; Oncu, S.; Pektas, M. Kefir Prevents Adipose Tissue Growth through the Induction of Apoptotic Elements in High-Fructose Corn Syrup-Fed Rats. Polish J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2023, 73, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, O.; Aslan, E.; Guzel, H.; Korkmaz, O.A.; Sadi, G.; Gurol, A.M.; Boyaci, M.G.; Pektas, M.B. Kefir Alters Craniomandibular Bone Development in Rats Fed Excess Dose of High Fructose Corn Syrup. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2022, 40, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekici, Ö.; Aslan, E.; Aladağ, T.; Güzel, H.; Korkmaz, Ö.A.; Bostancı, A.; Sadi, G.; Pektaş, M.B. Masseter Muscle and Gingival Tissue Inflammatory Response Following Treatment with High-fructose Corn Syrup in Rats: Anti-inflammatory and Antioxidant Effects of Kefir. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e13732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, F.S.; Luaces-Regueira, M.; Ton, A.M.; Campagnaro, B.P.; Campos-Toimil, M.; Pereira, T.M.; Vasquez, E.C. Mechanisms of Action of Kefir in Chronic Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 1901–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, C.; Gökmen, V. Determination of Tryptophan Derivatives in Kynurenine Pathway in Fermented Foods Using Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2018, 243, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akar, F.; Güney, C.; Özer, H.; Pektaş, M.; Koca, H.; Kocabaş, A.; Sadi, G. The Inverse Association between ANGPTL8 and PI3K-MTOR- PPARγ Expressions in Adipose Tissue of High-Fructose- Fed Rats: The Modulatory Effect of Kefir. İstanbul J. Pharm. 2021, 51, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Beyer, A.; Aebersold, R. On the Dependency of Cellular Protein Levels on MRNA Abundance. Cell 2016, 165, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, C.; Marcotte, E.M. Insights into the Regulation of Protein Abundance from Proteomic and Transcriptomic Analyses. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fülling, C.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Gut Microbe to Brain Signaling: What Happens in Vagus. Neuron 2019, 101, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene | Forward Primer Sequence (5′ → 3′) | Reverse Primer Sequence (3′ → 5′) | Product |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLC6A4 | CCGTCATCTGCATCCCTACC | ATGTCCCCACACGGGATTTC | 20 |
| 5-HT | GGACTCCTCCTCTAAGCAAGC | CACGGAAAGAAGTGGTCGGA | 21 |
| 5-HTR4 | GGCTCACGAGGAGATGTCTG | TAGAGGGAGGGTGGGTTCAG | 20 |
| 5-HTR3A | TTGGCCTTGTTCCTTTCCGT | CGCACCCCCTTCTTGTAGTT | 20 |
| 5-HTR2B | ATCTGTCAGGGGAGGGAGTC | TTTCAGAAGATGCTTGTCTGCTT | 23 |
| TPH1 | TGCGACATCAACCGAGAACA | CGGATCCGTACAACAGCACT | 20 |
| VMAT2 | CCATGGCCCTGAGCGATCT | CTGGTGGTCTGGATTTCCGT | 19 |
| β-ACTIN | CCAGGAGTACGATGAGTCCG | ACGCAGCTCAGTAACAGTCC | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boyaci, M.G.; Pektaş, A.; Topal, F.; Önen, N.; Pektaş, B.M. Impact of Kefir on the Gut–Brain Axis: Serotonin Metabolism and Signaling in Pediatric Rats. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112536
Boyaci MG, Pektaş A, Topal F, Önen N, Pektaş BM. Impact of Kefir on the Gut–Brain Axis: Serotonin Metabolism and Signaling in Pediatric Rats. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(11):2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112536
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoyaci, Mehmet Gazi, Ayhan Pektaş, Fadime Topal, Nur Önen, and Bilgehan Mehmet Pektaş. 2025. "Impact of Kefir on the Gut–Brain Axis: Serotonin Metabolism and Signaling in Pediatric Rats" Microorganisms 13, no. 11: 2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112536
APA StyleBoyaci, M. G., Pektaş, A., Topal, F., Önen, N., & Pektaş, B. M. (2025). Impact of Kefir on the Gut–Brain Axis: Serotonin Metabolism and Signaling in Pediatric Rats. Microorganisms, 13(11), 2536. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13112536







