Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus D1 Fermented Milk Confers Protection Against Typhoid Fever Through Immunomodulation and Gut Microbiota Regulation in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains, Culture Conditions and Fermented Milk
2.2. Mice
2.3. Treatment, Typhoid Fever Induction and Sample Collection
2.4. Determination of Salmonella Translocation and Hepatic Inflammatory Foci
2.5. Relative Expression of Cytokines and Antimicrobial Peptides in Ileum
2.6. Ileum Microbiota Screening Through 16S rDNA Gene Sequencing
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
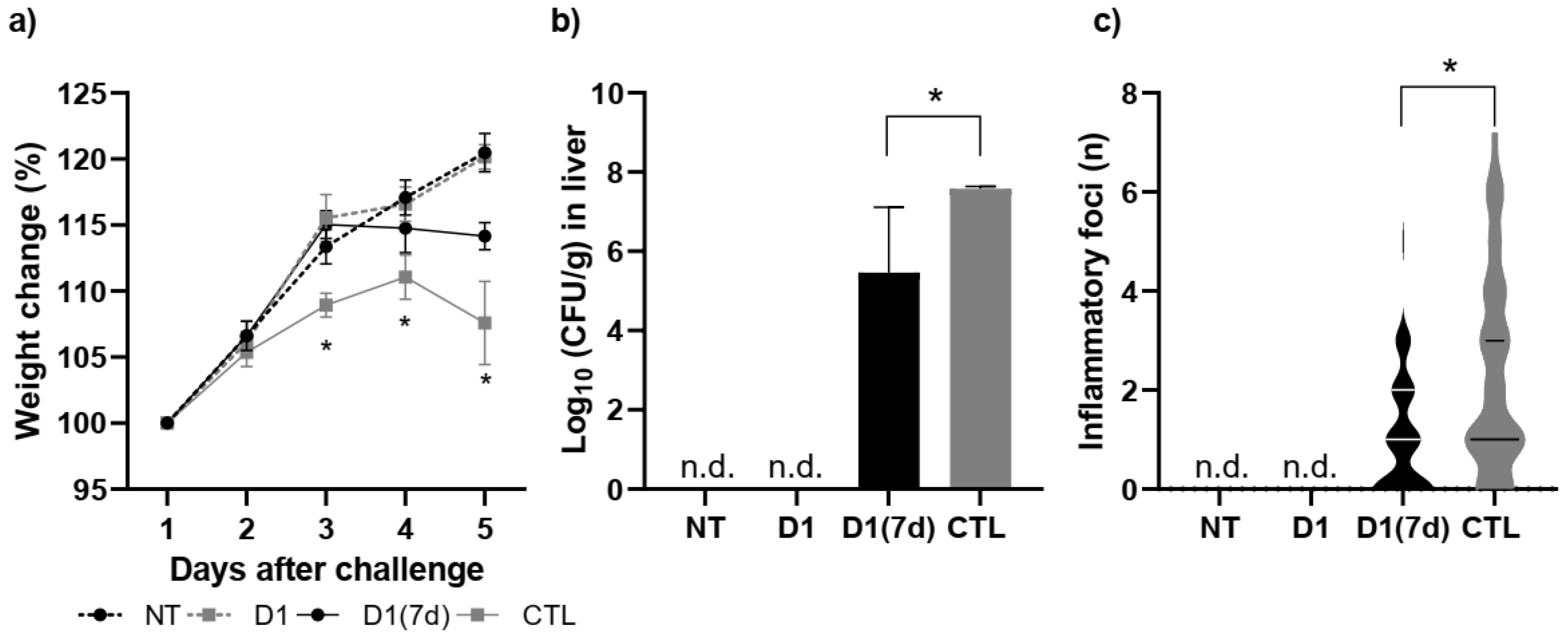
3.1. Consumption of Milk Fermented by L. rhmanosus D1 Reduced the Mortality Rate of Mice Infected with S. Typhimurium
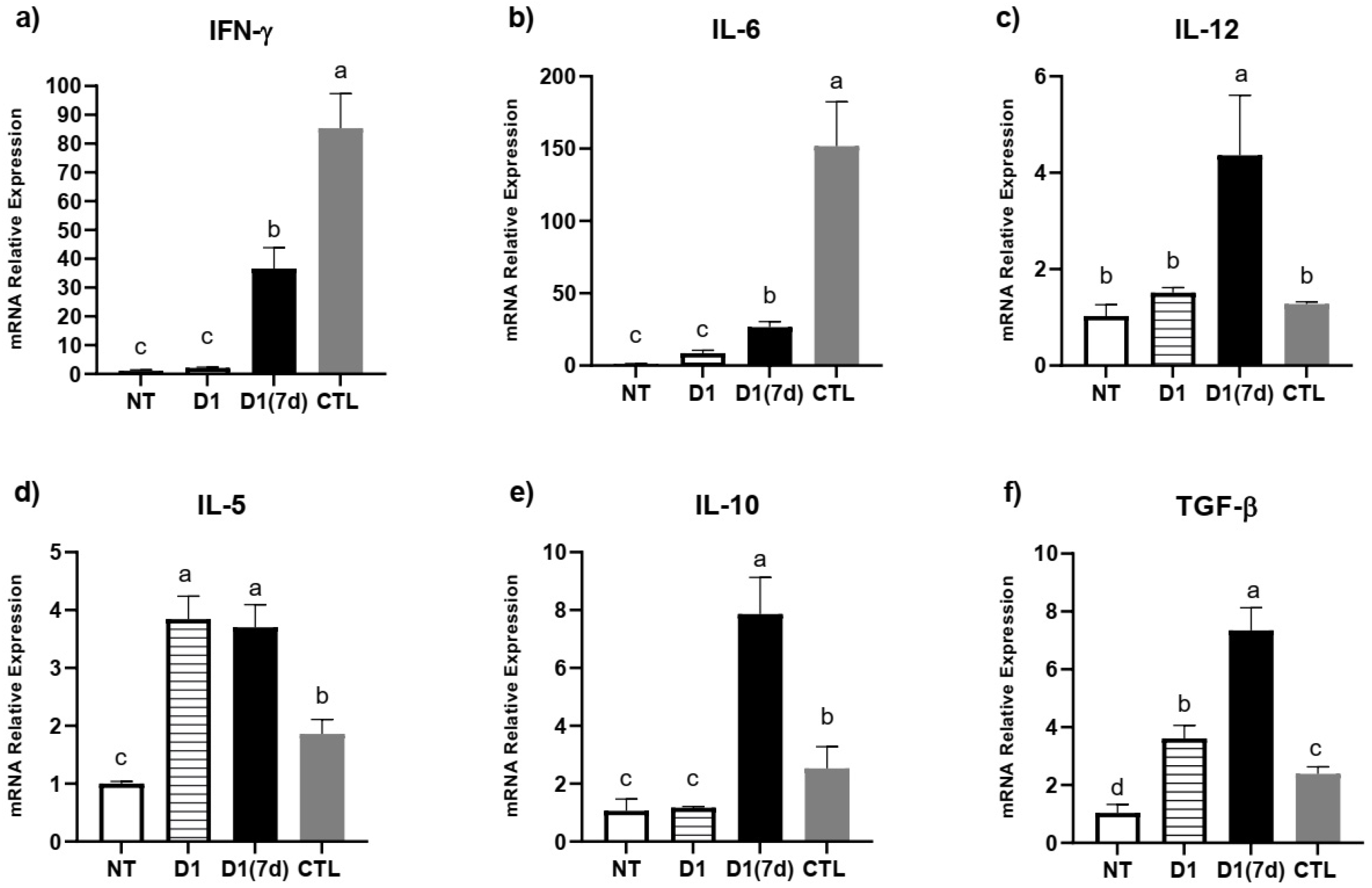
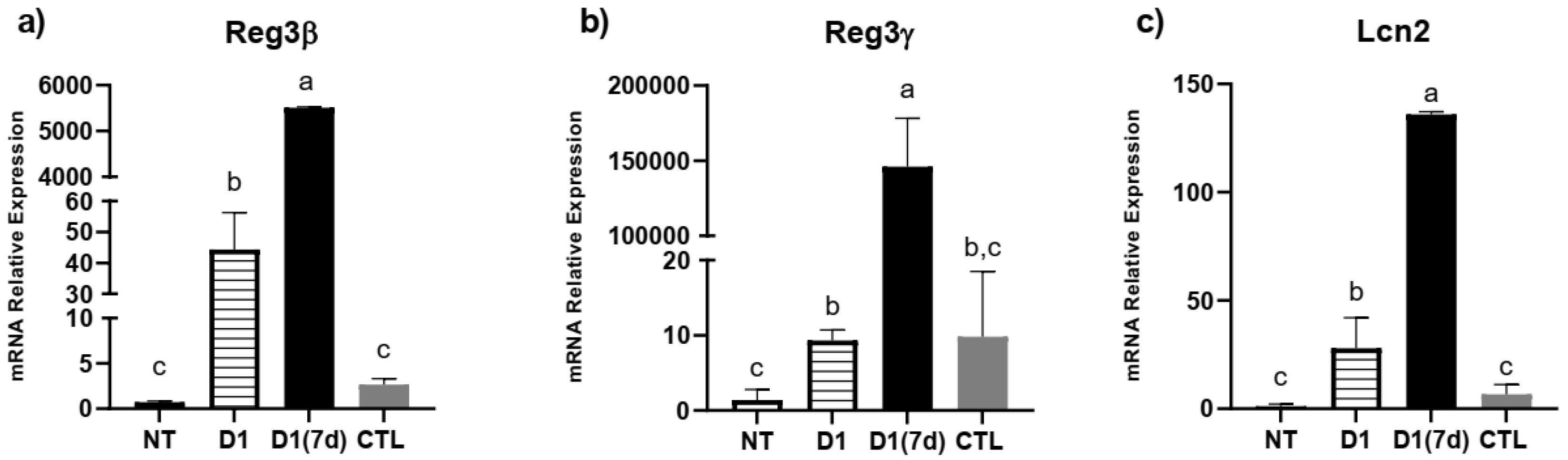
3.2. Consumption of Milk Fermented by L. rhmanosus D1 Reduced Disease Severity in Infected Mice Through Epithelial Barrier Maintenance and Modulation of Cytokines and Antimicrobial Peptides in Ileum
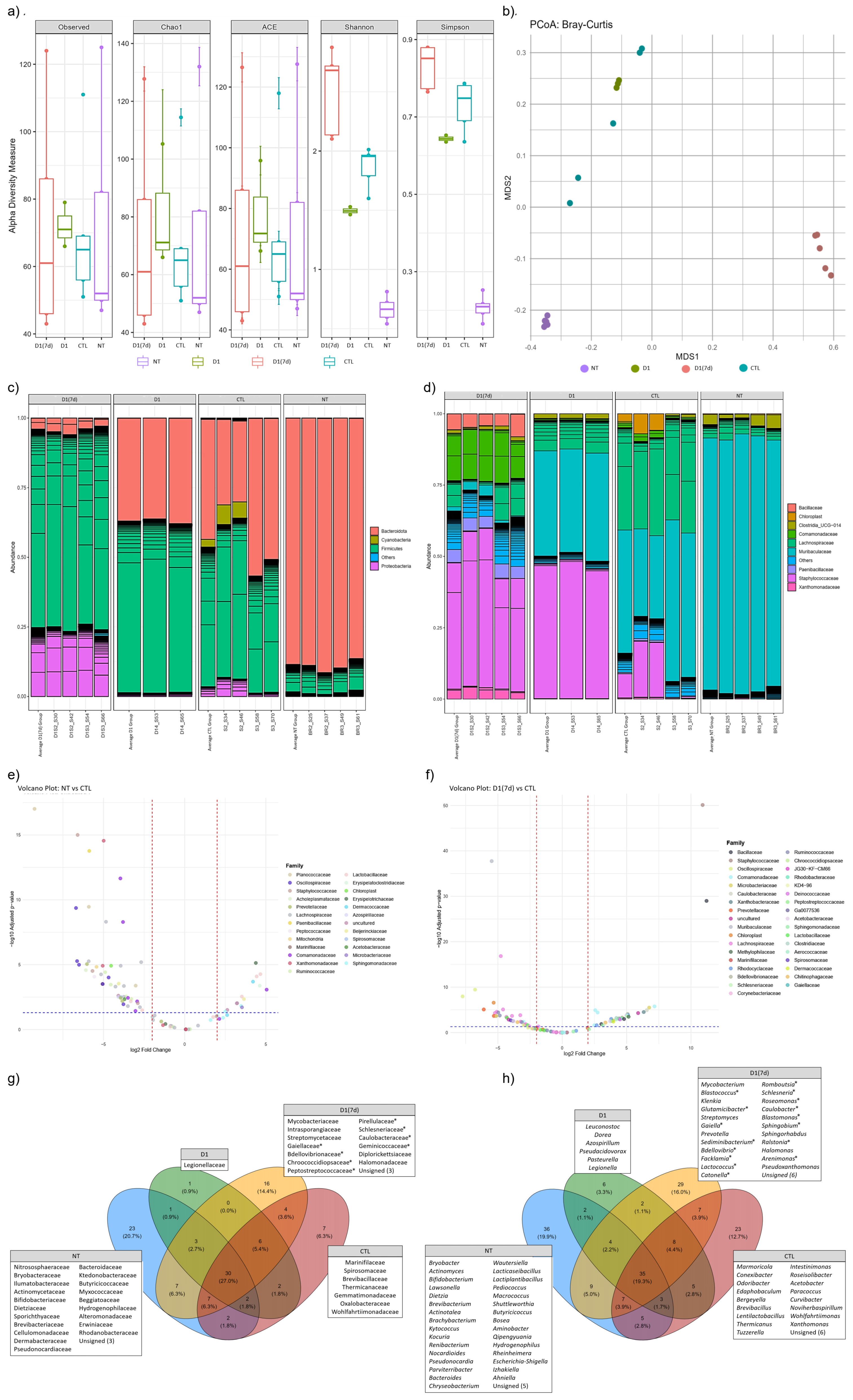
3.3. Consumption of Milk Fermented by L. rhmanosus D1 Changed Ileum Microbiota in Infected Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mastroeni, P.; Bryant, C. Cytokines in Salmonellosis. EcoSal Plus 2004, 1, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayyaz, A.; Fatima, J.; Mahmood, S.; Khurram, Y.; Naz, G.; Aslam, R.S.; Sarwar, A.; Sarwar, F.; Israr, Y.; Israr, A.; et al. Role of Probiotics in the Control of Salmonella Infections in Animals and Humans. Lett. Anim. Biol. 2025, 5, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, B.M.; Melo-Gonzalez, F.; Salazar, G.A.; Porto, B.N.; Riedel, C.A.; Kalergis, A.M.; Bueno, S.M. New Insights on the Early Interaction Between Typhoid and Non-Typhoid Salmonella Serovars and the Host Cells. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 647044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galán, J.E. Salmonella Typhimurium and Inflammation: A Pathogen-Centric Affair. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzymajlo, K. The Game for Three: Salmonella–Host–Microbiota Interaction Models. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 854112. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S.; Pathak, S.; Sarikhani, M.; Majumdar, S.; Ray, S.; Chandrasekar, B.S.; Adiga, V.; Sundaresan, N.R.; Nandi, D. Nitric Oxide Synthase 2 Enhances the Survival of Mice during Salmonella Typhimurium Infection-Induced Sepsis by Increasing Reactive Oxygen Species, Inflammatory Cytokines and Recruitment of Neutrophils to the Peritoneal Cavity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 116, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzilă, E.R.; Dorneanu, O.S.; Trofin, F.; Sima, C.M.; Iancu, L.S. Assessing Salmonella Typhi Pathogenicity and Prevention: The Crucial Role of Vaccination in Combating Typhoid Fever. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakir, M.; Khan, M.; Umar, M.I.; Murtaza, G.; Ashraf, M.; Shamim, S. Emerging Trends of Multidrug-Resistant (Mdr) and Extensively Drug-Resistant (Xdr) Salmonella Typhi in a Tertiary Care Hospital of Lahore, Pakistan. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkangara, M. Prevention and Control of Human Salmonella Enterica Infections: An Implication in Food Safety. Int. J. Food Sci. 2023, 2023, 8899596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, A. Antibiotic Resistome of Salmonella Typhi: Molecular Determinants for the Emergence of Drug Resistance. Front. Med. 2021, 15, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acurcio, L.B.; Wuyts, S.; de Cicco Sandes, S.H.; Sant’anna, F.M.; Pedroso, S.H.S.P.; Bastos, R.W.; dos Reis, D.C.; Vieira, A.F.; Cassali, G.D.; Lebeer, S.; et al. Milk Fermented by Lactobacillus Paracasei NCC 2461 (ST11) Modulates the Immune Response and Microbiota to Exert Its Protective Effects Against Salmonella Typhimurium Infection in Mice. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 1398–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abatemarco Júnior, M.; Sandes, S.H.C.; Ricci, M.F.; Arantes, R.M.E.; Nunes, Á.C.; Nicoli, J.R.; Neumann, E. Protective Effect of Lactobacillus Diolivorans 1Z, Isolated From Brazilian Kefir, Against Salmonella Enterica Serovar Typhimurium in Experimental Murine Models. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarita, B.; Samadhan, D.; Hassan, M.Z.; Kovaleva, E.G. A Comprehensive Review of Probiotics and Human Health-Current Prospective and Applications. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1487641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.H.; Sun, A.Q.; Liao, Y.; Tang, Z.X.; Zhang, S.H.; Shan, X.; Hu, J.T. Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum Regulated Intestinal Microbial Community and Cytokines to Inhibit Salmonella Typhimurium Infection. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 1355–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryaznova, M.; Dvoretskaya, Y.; Burakova, I.; Syromyatnikov, M.; Popov, E.; Kokina, A.; Mikhaylov, E.; Popov, V. Dynamics of Changes in the Gut Microbiota of Healthy Mice Fed with Lactic Acid Bacteria and Bifidobacteria. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Hu, A.; Ma, S.; Liu, J.; Yao, X.; Ye, T.; Han, M.; Yang, C.; Zhang, R.; Xiao, X.; et al. Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum Postbiotic Protects against Salmonella Infection in Broilers via Modulating NLRP3 Inflammasome and Gut Microbiota. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 103483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; He, F.; Yu, D.; Xu, H.; Li, N.; Cao, Z.; Wen, J. 16S RRNA Gene Amplicon Sequencing of Gut Microbiota Affected by Four Probiotic Strains in Mice. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Zhang, X.; Hao, H.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Liang, X.; Liu, T.; Gong, P.; Zhang, L.; Zhai, Z.; et al. Lactobacillus Rhamnosus Gg Derived Extracellular Vesicles Modulate Gut Microbiota and Attenuate Inflammatory in Dss-Induced Colitis Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheem, A.; Liang, L.; Zhang, G.; Cui, S. Modulatory Effects of Probiotics During Pathogenic Infections with Emphasis on Immune Regulation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 616713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandes, S.; Figueiredo, N.; Pedroso, S.; Sant’Anna, F.; Acurcio, L.; Abatemarco Junior, M.; Barros, P.; Oliveira, F.; Cardoso, V.; Generoso, S.; et al. Weissella Paramesenteroides WpK4 Plays an Immunobiotic Role in Gut-Brain Axis, Reducing Gut Permeability, Anxiety-like and Depressive-like Behaviors in Murine Models of Colitis and Chronic Stress. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaid, M.; Lu, H.; Din, A.U.; Yu, B.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Yan, J.; Qi, Z. Deciphering Microbiome, Transcriptome, and Metabolic Interactions in the Presence of Probiotic Lactobacillus acidophilus Against Salmonella Typhimurium in a Murine Model. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acurcio, L.B.; Bastos, R.W.; Sandes, S.H.d.C.; Guimarães, A.C.d.C.; Alves, C.G.; Reis, D.C.d.; Wuyts, S.; Nunes, Á.C.; Cassali, G.D.; Lebeer, S.; et al. Protective Effects of Milk Fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum B7 from Brazilian Artisanal Cheese on a Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Infection in BALB/c Mice. J. Funct. Foods 2017, 33, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Hooper, L.V. Antimicrobial Defense of the Intestine. Immunity 2015, 42, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Mo, Q.; Wan, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Li, W. Antimicrobial Peptide AP2 Ameliorates Salmonella Typhimurium Infection by Modulating Gut Microbiota. BMC Microbiol. 2025, 25, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.H.; Bozadjieva-Kramer, N.; Seeley, R.J. Reg3γ: Current Understanding and Future Therapeutic Opportunities in Metabolic Disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1672–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, M.F.S.; Costa, H.H.S.; Andrade, E.H.P.; Acúrcio, L.B.; Drummond, A.F.; Cunha, A.F.; Nunes, A.C.; Moreira, J.L.S.; Penna, F.A.M.; Souza, M.R. Queijo de Minas Artesanal Da Serra Da Canastra: Influência Da Altitude Das Queijarias Nas Populações de Bactérias Acidolácticas [Influence of Altitute on Lactic Acid Bacteria Population of Minas Artisanal Cheese from Serra Da Canastra]. Arq. Bras. Med. Veterinária Zootec. 2011, 63, 1567–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelter, C.; Käppeli, R.; König, C.; Krah, A.; Hardt, W.D.; Stecher, B.; Bumann, D. Salmonella-Induced Mucosal Lectin RegIIIβ Kills Competing Gut Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deriu, E.; Liu, J.Z.; Pezeshki, M.; Edwards, R.A.; Ochoa, R.J.; Contreras, H.; Libby, S.; Fang, F.; Raffatellu, M. Probiotic bacteria reduce Salmonella Typhimurium intestinal colonization by competing for iron. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 14, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, I.; Atarashi, K.; Manel, N.; Brodie, E.; Shima, T.; Karaoz, U.; Wei, D.; Goldfarb, K.; Santee, C.; Lynch, S.; et al. Induction of Intestinal Th17 Cells by Segmented Filamentous Bacteria. Cell 2009, 139, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, R.; Oh, H.; Zhang, D.; Park, S.G.; Seo, J.; Koblansky, A.; Hayden, M.; Ghosh, S. A mouse model of Salmonella Typhi infection. Cell 2012, 151, 590–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buras, J.A.; Holzmann, B.; Sitkovsky, M. Model Organisms: Animal Models of Sepsis: Setting the Stage. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 854–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagato, E.; Mileti, E.; Massimiliano, L.; Fasano, F.; Budelli, A.; Penna, G.; Rescigno, M. Lactobacillus paracasei CBA L74 Metabolic Products and Fermented Milk for Infant Formula Have Anti-Inflammatory Activity on Dendritic Cells In Vitro and Protective Effects Against Colitis and an Enteric Pathogen In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Qiao, L.; Chang, J.; Yan, S.; Song, X.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Q.; Xu, C. Lactobacillus casei ATCC 393 and it’s metabolites alleviate dextran sulphate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice through the NLRP3-(Caspase-1)/IL-1β pathway. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 12022–12035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Peng, H.; Liao, Y.; Li, J.; Yin, Y.; Peng, H.; Wang, L.; Tan, Y.; Li, C.; Bai, H.; et al. The Prophylactic Protection of Salmonella Typhimurium Infection by Lentilactobacillus buchneri GX0328-6 in Mice. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 16, 2054–2072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.Y.; Son, Y.H.; Yoo, J.W.; Joo, M.K.; Kim, D.H. Tight Junction Protein Expression-Inducing Probiotics Alleviate TNBS-Induced Cognitive Impairment with Colitis in Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsholi, D.M.; Yacoub, G.S.; Rehman, A.U.; Ullah, H.; Khan, A.I.; Deng, T.; Siddiqui, N.Z.; Alioui, Y.; Farooqui, N.A.; Elkharti, M.; et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus Attenuates Cisplatin-Induced Intestinal Mucositis in Mice via Modulating the Gut Microbiota and Improving Intestinal Inflammation. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naso, A.M.; Lizier, M.; Correale, C.; Silvestri, A.; Penna, G.; Brescia, P.; Rescigno, M. A Multi-Strain Probiotic Formulation Preserves Intestinal Epithelial and Vascular Barriers During Enteropathogenic Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1631322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofori, F.; Dargenio, V.N.; Dargenio, C.; Miniello, V.L.; Barone, M.; Francavilla, R. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Effects of Probiotics in Gut Inflammation: A Door to the Body. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 578386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klüber, P.; Meurer, S.K.; Lambertz, J.; Schwarz, R.; Zechel-Gran, S.; Braunschweig, T.; Hurka, S.; Domann, E.; Weiskirchen, R. Depletion of Lipocalin 2 (LCN2) in Mice Leads to Dysbiosis and Persistent Colonization with Segmented Filamentous Bacteria. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, S.K.; Gasterich, N.; Weiskirchen, S.; Weiskirchen, R. Lipocalin 2 Receptors: Facts, Fictions, and Myths. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1229885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, M.; Celano, G.; Calabrese, F.M.; Portincasa, P.; Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M. The Controversial Role of Human Gut Lachnospiraceae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Liu, L.; Miao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, X. The Response of Cecal Microbiota to Inflammatory State Induced by Salmonella Enterica Serovar Enteritidis. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 963678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, S.G.; Kothari, D.; Lee, W.D.; Kim, J.I.; Kim, K.I.; Kim, Y.G.; Ga, G.W.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, S.K. Potential Probiotic Acceptability of a Novel Strain of Paenibacillus konkukensis SK 3146 and Its Dietary Effects on Growth Performance, Intestinal Microbiota, and Meat Quality in Broilers. Animals 2022, 12, 1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekim, B.; Calik, A.; Ceylan, A.; Saçaklı, P. Effects of Paenibacillus Xylanexedens on Growth Performance, Intestinal Histomorphology, Intestinal Microflora, and Immune Response in Broiler Chickens Challenged with Escherichia coli K88. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.; Oh, H.; An, J.; Chang, S.; Cho, H.; Park, S.; Jeon, K.; Yoon, Y.; et al. Effects of Dietary Supplementation of Pediococcus pentosaceus Strains from Kimchi in Weaned Piglet Challenged with Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2023, 65, 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Cai, L.; Lv, L.; Li, L. Pediococcus pentosaceus, a Future Additive or Probiotic Candidate. Microb. Cell Fact. 2021, 20, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göksel, Ş.; Akçelik, N.; Özdemir, C.; Akçelik, M. The Effects of Lactic Acid Bacteria on Salmonella Biofilms. Microbiology 2022, 91, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.W. Proteobacteria: Microbial Signature of Dysbiosis in Gut Microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazkour, S.; Shekarforoush, S.S.; Basiri, S.; Namazi, F.; Zarei-Kordshouli, F. Protective Effects of Oral Administration of Mixed Probiotic Spores of Bacillus subtilis and Bacillus coagulans on Gut Microbiota Changes and Intestinal and Liver Damage of Rats Infected with Salmonella Typhimurium. J. Food Saf. 2022, 42, e12981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, Z.; Gu, X.; Zhao, J.; Guo, T.; Kong, J. Probiotic Bacillus Subtilis LF11 Protects Intestinal Epithelium Against Salmonella Infection. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 837886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Ma, K.; Nie, K.; Deng, M.; Luo, W.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X. Assessment of the Safety and Probiotic Properties of Roseburia Intestinalis: A Potential “Next Generation Probiotic”. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 973046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampanelli, E.; Romp, N.; Troise, A.D.; Ananthasabesan, J.; Wu, H.; Gül, I.S.; De Pascale, S.; Scaloni, A.; Bäckhed, F.; Fogliano, V.; et al. Gut Bacterium Intestinimonas butyriciproducens Improves Host Metabolic Health: Evidence from Cohort and Animal Intervention Studies. Microbiome 2025, 13, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, K.; Ma, K.; Luo, W.; Shen, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xiao, M.; Tong, T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X. Roseburia Intestinalis: A Beneficial Gut Organism from the Discoveries in Genus and Species. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 757718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kang, S.; Wu, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Wen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.; et al. Muribaculum intestinale Restricts Salmonella Typhimurium Colonization by Converting Succinate to Propionate. ISME J. 2025, 19, wraf069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atterbury, R.J.; Hobley, L.; Till, R.; Lambert, C.; Capeness, M.J.; Lerner, T.R.; Fenton, A.K.; Barrow, P.; Sockett, R.E. Effects of Orally Administered Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus on the Well-Being and Salmonella Colonization of Young Chicks. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 5794–5803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waso, M.; Reyneke, B.; Havenga, B.; Khan, S.; Khan, W. Insights into Bdellovibrio spp. Mechanisms of Action and Potential Applications. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.M.S.; Almeida, A.M.D.S.; Borsanelli, A.C.; de Athayde, F.R.F.; Nascente, E.d.P.; Batista, J.M.M.; Gouveia, A.B.V.S.; Stringhini, J.H.; Leandro, N.S.M.; Café, M.B. Intestinal Microbiome Profiles in Broiler Chickens Raised with Different Probiotic Strains. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acurcio, L.; Sandes, S.; Rios, D.; Sant’Anna, F.; Pedroso, S.; Bastos, R.; Souza, M.; Nicoli, J. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus D1 Fermented Milk Confers Protection Against Typhoid Fever Through Immunomodulation and Gut Microbiota Regulation in Mice. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2348. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102348
Acurcio L, Sandes S, Rios D, Sant’Anna F, Pedroso S, Bastos R, Souza M, Nicoli J. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus D1 Fermented Milk Confers Protection Against Typhoid Fever Through Immunomodulation and Gut Microbiota Regulation in Mice. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(10):2348. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102348
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcurcio, Leonardo, Sávio Sandes, Diego Rios, Felipe Sant’Anna, Silvia Pedroso, Rafael Bastos, Marcelo Souza, and Jacques Nicoli. 2025. "Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus D1 Fermented Milk Confers Protection Against Typhoid Fever Through Immunomodulation and Gut Microbiota Regulation in Mice" Microorganisms 13, no. 10: 2348. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102348
APA StyleAcurcio, L., Sandes, S., Rios, D., Sant’Anna, F., Pedroso, S., Bastos, R., Souza, M., & Nicoli, J. (2025). Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus D1 Fermented Milk Confers Protection Against Typhoid Fever Through Immunomodulation and Gut Microbiota Regulation in Mice. Microorganisms, 13(10), 2348. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102348






