Seroepidemiology of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection in Blood Donors from Western Romania, August–September 2023
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Data and Questionnaire
2.3. Serologic Tests
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethics and Informed Consents
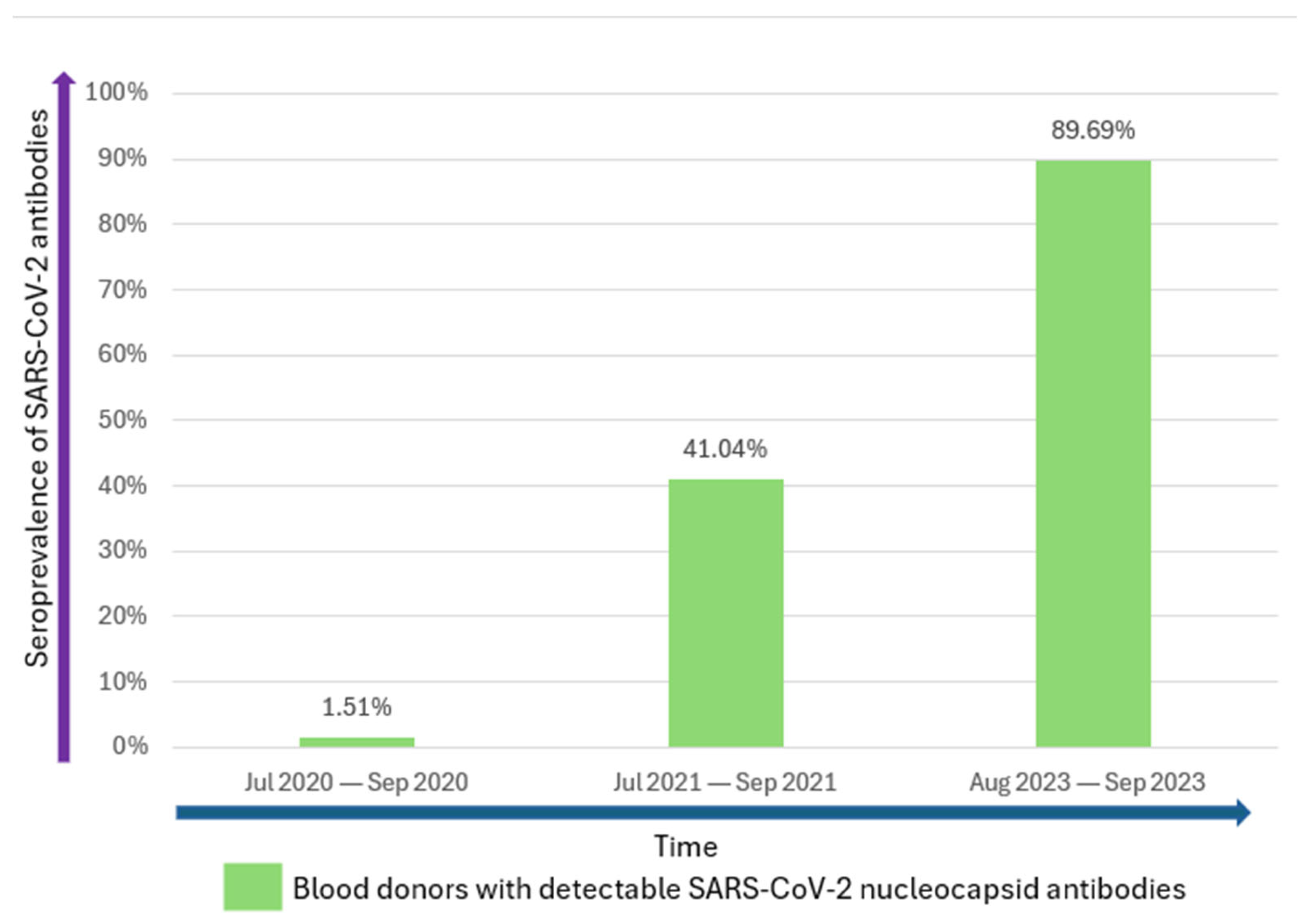
3. Results
| Variables | Total Investigated n = 1048 | n with Detectable SARS-CoV-2 N Antibodies (%) | cOR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age groups (years) | |||||
| 18–29 | 328 | 301 (91.77) | Ref. | ||
| 30–39 | 363 | 326 (89.81) | 0.79 | 0.47–1.33 | 0.38 |
| 40–49 | 232 | 205 (88.36) | 0.68 | 0.39–1.19 | 0.18 |
| 50–64 | 125 | 108 (86.4) | 0.57 | 0.3–1.09 | 0.09 |
| Gender | |||||
| Female | 402 | 365 (90.8) | Ref. | ||
| Male | 646 | 575 (89.01) | 0.82 | 0.54–1.25 | 0.36 |
| Area of residence | |||||
| Rural | 291 | 270 (92.78) | Ref. | ||
| Urban | 757 | 670 (88.51) | 0.6 | 0.36–0.98 | 0.04 |
| ABO blood group | |||||
| O | 416 | 374 (89.9) | Ref. | ||
| A | 410 | 372 (90.73) | 1.10 | 0.69–1.74 | 0.69 |
| B | 160 | 140 (87.5) | 0.79 | 0.45–1.39 | 0.41 |
| AB | 62 | 54 (87.1) | 0.76 | 0.34–1.7 | 0 |
| Rh | |||||
| Rh negative | 165 | 151 (91.52) | Ref. | ||
| Rh positive | 883 | 789 (89.35) | 0.78 | 0.43–1.4 | 0.4 |
| BMI | |||||
| Underweight (<18.5) | 8 | 8 (100%) | - | ||
| Normal weight (18.5–24.9) | 430 | 381 (88.6) | 0.71 | 0.4–1.26 | 0.24 |
| Overweight (25–29.9) | 406 | 364 (89.66) | 0.79 | 0.44–1.42 | 0.43 |
| Obese (>30) | 204 | 187 (91.67) | Ref. | ||
| Total | 1048 | 940 (89.69) | |||
| Potential Exposure to Risk Factors | Total | n with Detectable SARS-CoV-2 N Antibodies (%) | cOR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cat ownership | n = 1048 | ||||
| No | 757 | 684 (90.36) | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 291 | 256 (87.97) | 0.78 | 0.51–1.2 | 0.26 |
| Dog ownership | n = 1046 | ||||
| No | 679 | 606 (89.25) | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 367 | 332 (90.46) | 1.14 | 0.75–1.75 | 0.54 |
| Alcohol consumption | n = 1046 | ||||
| No | 356 | 325 (91.29) | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 690 | 613 (88.84) | 0.76 | 0.49–1.18 | 0.22 |
| Current smoker | n = 1047 | ||||
| No | 745 | 685 (91.95) | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 302 | 254 (84.11) | 0.46 | 0.31–0.7 | <0.001 |
| Former smoker | n = 734 | ||||
| No | 482 | 446 (92.53) | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 252 | 227 (90.08) | 0.73 | 0.43–1.25 | 0.26 |
| Education level | n = 1043 | ||||
| No formal education | 1 | 1 (100) | - | ||
| Primary education | 5 | 5 (100) | - | ||
| Gymnasium education | 28 | 24 (85.71) | 0.65 | 0.22–1.92 | 0.44 |
| Vocational education | 5 | 3 (60) | 0.16 | 0.03–0.99 | 0.05 |
| High school education | 307 | 275 (89.58) | 0.93 | 0.6–1.45 | 0.75 |
| University or post-university | 697 | 629 (90.24) | Ref. | ||
| Income level in RON (EUR) | n = 967 | ||||
| <1200 (240) | 20 | 18 (90) | Ref. | ||
| 1200–2500 (240–500) | 71 | 62 (87.32) | 0.77 | 0.15–3.87 | 0.75 |
| 2500–5000 (500–1000) | 360 | 324 (90%) | 1 | 0.22–4.49 | 1 |
| >5000 (>1000) | 516 | 467 (90.5) | 1.06 | 0.24–4.7 | 0.94 |
| Confirmed past SARS-CoV-2 infection | n = 1046 | ||||
| No | 520 | 446 (85.77) | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 526 | 493 (93.73) | 2.48 | 1.61–3.81 | <0.001 |
| No. of SARS-CoV-2 infections | n = 527 | ||||
| 0 | 2 | 2 (100) | - | ||
| 1 | 389 | 360 (92.54) | 0.73 | 0.09–5.68 | 0.76 |
| 2 | 116 | 113 (97.41) | 2.22 | 0.22–22.54 | 0.5 |
| 3 | 18 | 17 (94.44) | Ref. | ||
| 4 | 2 | 2 (100) | - | ||
| Vaccination Status | n = 1042 | ||||
| No | 211 | 200 (94.79) | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 831 | 735 (88.45) | 0.42 | 0.22–0.80 | 0.008 |
| Signs/Symptoms | n | n with Detectable SARS-CoV-2 N Antibodies (%) | cOR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fever | |||||
| No | 730 | 640 (87.67) | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 318 | 300 (94.34) | 2.34 | 1.39–3.96 | 0.001 |
| Cough | |||||
| No | 820 | 723 (88.17) | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 228 | 217 (95.18) | 2.65 | 1.39–5.03 | 0.003 |
| Respiratory Distress | |||||
| No | 970 | 866 (89.28) | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 78 | 74 (94.87) | 2.22 | 0.8–6.2 | 0.13 |
| Chest Pain | |||||
| No | 982 | 879 (89.51) | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 66 | 61 (92.42) | 1.43 | 0.56–3.64 | 0.45 |
| Headache | |||||
| No | 800 | 707 (88.38) | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 248 | 233 (93.95) | 2.04 | 1.16–3.6 | 0.013 |
| Anosmia (Loss of Smell) | |||||
| No | 835 | 736 (88.14) | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 213 | 204 (95.77) | 3.05 | 1.51–6.14 | 0.002 |
| Ageusia (Loss of Taste) | |||||
| No | 851 | 750 (88.13) | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 197 | 190 (96.45) | 3.66 | 1.67–7.99 | 0.001 |
| Gastrointestinal Symptoms | |||||
| No | 1006 | 903 (89.76) | Ref. | ||
| Yes | 42 | 37 (88.1) | 0.84 | 0.32–2.2 | 0.73 |
| Total | 1048 | 940 (89.69) | |||
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus Disease 2019 |
| SARS-CoV-2 | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 |
References
- Wu, J.T.; Leung, K.; Leung, G.M. Nowcasting and Forecasting the Potential Domestic and International Spread of the 2019-nCoV Outbreak Originating in Wuhan, China: A Modelling Study. Lancet 2020, 395, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COVID-19 Epidemiological Update, Edition 176. 2025. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-epidemiological-update-edition-176?utm (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- Olariu, T.R.; Lighezan, R.; Ursoniu, S.; Craciun, A.C.; Mihu, A.G.; Lupu, M.A. High SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence in Blood Donors from Romania after the Third COVID-19 Pandemic Wave. Infect. Dis. 2022, 54, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olariu, T.R.; Craciun, A.C.; Vlad, D.C.; Dumitrascu, V.; Marincu, I.; Lupu, M.A. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence in Western Romania, March to June 2021. Medicina 2021, 58, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmandad, H.; Lim, T.Y.; Sterman, J. Behavioral Dynamics of COVID-19: Estimating Underreporting, Multiple Waves, and Adherence Fatigue across 92 Nations. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2021, 37, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteón, V.; Pérez, F.L.; Hernández, V.P.; Pacheco, A.O.; Guzman, P.F.; Torres, G.I.G. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Blood Donors during the Third Wave of Infection in Campeche Mexico. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2022, 61, 103374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harker, S.; James, S.E.; Murphy, J.; Davies, B.; Moore, C.; Tennant, B.P.; Geen, J.; Thomas, D. Serosurveillance of SARS-CoV-2 in Welsh Blood Donors: Establishment of the Surveillance System and Results up to November 2022. Eurosurveillance 2023, 28, 2200473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Red Cross Lifeblood Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibodies Among Australian Blood Donors: Round 2 Update. 2022. Available online: https://www.kirby.unsw.edu.au/sites/default/files/documents/COVID19-Blood-Donor-Report-Round2-May-Jun-2022%5B1%5D.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Australian Red Cross Lifeblood Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibodies Among Australian Blood Donors: Round 4 Update. 2023. Available online: https://www.kirby.unsw.edu.au/sites/default/files/documents/COVID19-Blood-Donor-Report-Round4-Nov-Dec-2022%5B1%5D.pdf (accessed on 10 November 2024).
- Olariu, T.R.; Lighezan, R.; Ursoniu, S.; Craciun, A.C.; Paduraru, A.A.; Lupu, M.A. Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in 2115 Blood Donors from Romania. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2021, 27, 817–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanian Ministry of Public Health. ORDER Nr. 1193 of 7 July 2007 for the Approval of the Rules on the Information to Be Provided to Donors of Blood and Blood Components of Human Origin, as Well as the Information to Be Communicated by Donors at Each Donation and the Admissibility of Donors of Human Blood and Blood Components. Available online: https://www.lexmed.ro/doc/Ordin_1193_2007.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2025). (In Romanian)
- Bradley, T.; Grundberg, E.; Selvarangan, R.; LeMaster, C.; Fraley, E.; Banerjee, D.; Belden, B.; Louiselle, D.; Nolte, N.; Biswell, R.; et al. Antibody Responses after a Single Dose of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1959–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Follmann, D.; Janes, H.E.; Buhule, O.D.; Zhou, H.; Girard, B.; Marks, K.; Kotloff, K.; Desjardins, M.; Corey, L.; Neuzil, K.M.; et al. Antinucleocapsid Antibodies After SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the Blinded Phase of the Randomized, Placebo-Controlled mRNA-1273 COVID-19 Vaccine Efficacy Clinical Trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 2022, 175, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, K.; Abe, K.T.; Naimark, D.; Oliver, M.J.; Perl, J.; Leis, J.A.; Bolotin, S.; Tran, V.; Mullin, S.I.; Shadowitz, E.; et al. Evaluation of the SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response to the BNT162b2 Vaccine in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2123622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health England Evaluation of Roche Elecsys Anti SARS-CoV-2 Serology Assay for the Detection of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies. 2021. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/60ae29428fa8f520c3cef62b/Evaluation_of_Roche_Elecsys_anti_SARS_CoV_2_S_assay_PHE.pdf (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Kang, H. The Prevention and Handling of the Missing Data. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2013, 64, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig-Barberà, J.; Natividad-Sancho, A.; Trushakova, S.; Sominina, A.; Pisareva, M.; Ciblak, M.A.; Badur, S.; Yu, H.; Cowling, B.J.; El Guerche-Séblain, C.; et al. Epidemiology of Hospital Admissions with Influenza during the 2013/2014 Northern Hemisphere Influenza Season: Results from the Global Influenza Hospital Surveillance Network. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offergeld, R.; Preußel, K.; Zeiler, T.; Aurich, K.; Baumann-Baretti, B.I.; Ciesek, S.; Corman, V.M.; Dienst, V.; Drosten, C.; Görg, S.; et al. Monitoring the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic: Prevalence of Antibodies in a Large, Repetitive Cross-Sectional Study of Blood Donors in Germany-Results from the SeBluCo Study 2020–2022. Pathogens 2023, 12, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hvalryg, M.; Nissen-Meyer, L.S.H. Sero-Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Blood Donors during the Third Wave of Infection in Norway, Winter/Spring 2021. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2021, 60, 103256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slot, E.; Hogema, B.M.; Reusken, C.B.E.M.; Reimerink, J.H.; Molier, M.; Karregat, J.H.M.; IJlst, J.; Novotný, V.M.J.; van Lier, R.A.W.; Zaaijer, H.L. Low SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence in Blood Donors in the Early COVID-19 Epidemic in the Netherlands. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, L.; Nunhofer, V.; Jungbauer, C.; Hoeggerl, A.D.; Grüner, L.; Grabmer, C.; Zimmermann, G.; Rohde, E.; Laner-Plamberger, S. Seroprevalence of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Total Antibody Is Higher in Younger Austrian Blood Donors. Infection 2021, 49, 1187–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siller, A.; Wachter, G.A.; Neururer, S.; Pfeifer, B.; Astl, M.; Borena, W.; Kimpel, J.; Elmer, S.; Spöck, F.; Vales, A.; et al. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Healthy Blood Donors from the State of Tyrol, Austria, in Summer 2020. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2021, 133, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quee, F.A.; Hogema, B.M.; Molier, M.; Slot, E.; van den Hurk, K.; Zaaijer, H.L. The Elecsys® Anti-SARS-CoV-2 and Elecsys® Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S Antibody Assays: Differentiating between Vaccination and Infection, and Assessing Long-Term Performance. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0305613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Huang, H.; Li, D.; Gu, D.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, T.; Liu, Y.; et al. Relationship Between the ABO Blood Group and the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Susceptibility. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.-B.; Gu, D.-Z.; Yu, J.-N.; Yang, J.; Shen, W.-Q. Association between ABO Blood Groups and COVID-19 Infection, Severity and Demise: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 84, 104485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severe COVID-19 GWAS Group; Ellinghaus, D.; Degenhardt, F.; Bujanda, L.; Buti, M.; Albillos, A.; Invernizzi, P.; Fernández, J.; Prati, D.; Baselli, G.; et al. Genomewide Association Study of Severe Covid-19 with Respiratory Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1522–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, J.G.; Vermeulen, M.J.; Schull, M.J.; Park, A.L. ABO Blood Group, SARS-CoV-2 Infection, and Risk of Venous Thromboembolism: Population-Based Cohort Study. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2021, 27, 10760296211008986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domènech-Montoliu, S.; Puig-Barberà, J.; Guerra-Murcia, O.; Pac-Sa, M.R.; Orrico-Sanchéz, A.; Gómez-Lanas, L.; Sala-Trull, D.; Domènech-Leon, C.; Del Rio-González, A.; Sánchez-Urbano, M.; et al. ABO Blood Groups and Incidence of COVID-19 in the Mass Gathering Events in Borriana (Spain), March 2020: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Epidemiologia 2023, 4, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olariu, T.R.; Ursoniu, S.; Craciun, A.C.; Dumitrascu, V.; Vlad, D.C.; Olariu, A.T.; Mihu, A.G.; Lupu, M.A. SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence and Associated Risk Factors in Adult Outpatients from Western Romania, January to March 2023: A Seroepidemiological Assessment after Three Years of COVID-19 Pandemic. Infect. Dis. 2025, 57, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, C.; Bou Malhab, S.; Sacre, H.; Salameh, P. Smoking and COVID-19: A Scoping Review. Tob. Use Insights 2021, 14, 1179173X21994612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, D.; Shahab, L.; Brown, J.; Perski, O. The Association of Smoking Status with SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Hospitalization and Mortality from COVID-19: A Living Rapid Evidence Review with Bayesian Meta-Analyses (Version 7). Addiction 2021, 116, 1319–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.K.; Charles, W.N.; Sklavounos, A.; Dutt, A.; Seed, P.T.; Khajuria, A. The Effect of Smoking on COVID-19 Severity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patanavanich, R.; Glantz, S.A. Smoking Is Associated With COVID-19 Progression: A Meta-Analysis. Nicotine Tob. Res. 2020, 22, 1653–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, A.N.; Andersson, F.; Thiesmeier, R.; Orsini, N.; Peña, S.; Caspersen, I.H.; Magnusson, C.; Karvonen, S.; Magnus, P.M.; Hergens, M.P.; et al. The Association between Tobacco Use and COVID-19 Diagnoses in Three Nordic Countries: A Pooled Analysis. Eur. J. Public Health 2025, 35, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.; Di Marco, L.; Pivetti, A.; Paduano, S.; Vecchi, C.; Bernabucci, V.; Critelli, R.M.; Lasagni, S.; De Maria, M.; Venturelli, D.; et al. Long-Term SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Seroprevalence in Blood Donors, Italy. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2023, 29, 1479–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enciu, B.G.; Pițigoi, D.; Zaharia, A.; Popescu, R.; Niculcea, A.; Crăciun, M.-D.; Pistol, A. COVID-19 Vaccination in Romania and the Benefits of the National Electronic Registry of Vaccinations. Vaccines 2023, 11, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.M.; Grebe, E.; Lartey, I.; Stone, M.; Spencer, B.R.; Akinseye, A.; Molina Manrique, I.; Fink, R.V.; Green, V.; Saa, P.; et al. Estimated US Trends in SARS-CoV-2 Spike Antibody Concentrations and Correlation to Risk of First-Time Infections Based on Blood Donations, 2022. J. Infect. Dis. 2025, jiaf329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reedman, C.N.; Drews, S.J.; Yi, Q.-L.; Pambrun, C.; O’Brien, S.F. Changing Patterns of SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence among Canadian Blood Donors during the Vaccine Era. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0033922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.M.; Manrique, I.M.; Stone, M.S.; Grebe, E.; Saa, P.; Germanio, C.D.; Spencer, B.R.; Notari, E.; Bravo, M.; Lanteri, M.C.; et al. Estimates of SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence and Incidence of Primary SARS-CoV-2 Infections Among Blood Donors, by COVID-19 Vaccination Status—United States, April 2021–September 2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2023, 72, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quee, F.A.; Hogema, B.M.; Slot, E.; Kruijer, S.; Molier, M.; van den Hurk, K.; Zaaijer, H.L. Booster Vaccinations and Omicron: The Effects on SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Dutch Blood Donors. BMC Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozio, C.H.; Butterfield, K.A.; Briggs Hagen, M.; Grannis, S.; Drawz, P.; Hartmann, E.; Ong, T.C.; Fireman, B.; Natarajan, K.; Dascomb, K.; et al. Protection From COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination and Prior SARS-CoV-2 Infection Against COVID-19-Associated Encounters in Adults During Delta and Omicron Predominance. J. Infect. Dis. 2023, 227, 1348–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levring, M.B.; Holm, D.K.; Nilsson, A.C.; Bauer, J.M.; Jensen, I.S.; Davidsen, J.R.; Rasmussen, L.D.; Sprogøe, U.; Lillevang, S.T. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Kinetics in Blood Donors with a Previously Positive SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Test within a Seroprevalence Survey. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saá, P.; Fink, R.V.; Bakkour, S.; Jin, J.; Simmons, G.; Muench, M.O.; Dawar, H.; Di Germanio, C.; Hui, A.J.; Wright, D.J.; et al. Frequent Detection but Lack of Infectivity of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in Presymptomatic, Infected Blood Donor Plasma. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e159876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanjanaumporn, J.; Aeumjaturapat, S.; Snidvongs, K.; Seresirikachorn, K.; Chusakul, S. Smell and Taste Dysfunction in Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Review of Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Prognosis, and Treatment Options. Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 38, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doty, R.L. The Mechanisms of Smell Loss after SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 693–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, S.; Essel, H.B. Motivational Factors for Blood Donation, Potential Barriers, and Knowledge about Blood Donation in First-Time and Repeat Blood Donors. BMC Hematol. 2018, 18, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, Z. Cross-Sectional Studies: Strengths, Weaknesses, and Recommendations. Chest 2020, 158, S65–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, E. Recall Bias Can Be a Threat to Retrospective and Prospective Research Designs. Internet J. Epidemiol. 2005, 3, 2. [Google Scholar]
| Risk Factor | aOR | 95% CI | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area of residence | 1.68 | 1.01–2.79 | 0.045 |
| Current smoker | 2.07 | 1.36–3.16 | 0.001 |
| Confirmed past SARS-CoV-2 infection | 1.65 | 0.84–3.21 | 0.14 |
| Fever | 1.20 | 0.56–0.59 | 0.64 |
| Cough | 1.47 | 0.66–3.27 | 0.35 |
| Headaches | 0.80 | 0.37–1.73 | 0.57 |
| Anosmia | 0.99 | 0.32–3.05 | 0.98 |
| Ageusia | 2.31 | 0.68–7.87 | 0.18 |
| Vaccination status | 2.59 | 1.35–4.99 | 0.004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olariu, T.R.; Lighezan, R.; Ursoniu, S.; Craciun, A.C.; Olariu, A.T.; Sprintar, S.A.; Oatis, D.A.; Lupu, M.A.; Mihu, A.G. Seroepidemiology of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection in Blood Donors from Western Romania, August–September 2023. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102313
Olariu TR, Lighezan R, Ursoniu S, Craciun AC, Olariu AT, Sprintar SA, Oatis DA, Lupu MA, Mihu AG. Seroepidemiology of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection in Blood Donors from Western Romania, August–September 2023. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(10):2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102313
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlariu, Tudor Rares, Rodica Lighezan, Sorin Ursoniu, Alina Cristiana Craciun, Alexander Tudor Olariu, Sergiu Adrian Sprintar, Daniela Adriana Oatis, Maria Alina Lupu, and Alin Gabriel Mihu. 2025. "Seroepidemiology of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection in Blood Donors from Western Romania, August–September 2023" Microorganisms 13, no. 10: 2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102313
APA StyleOlariu, T. R., Lighezan, R., Ursoniu, S., Craciun, A. C., Olariu, A. T., Sprintar, S. A., Oatis, D. A., Lupu, M. A., & Mihu, A. G. (2025). Seroepidemiology of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection in Blood Donors from Western Romania, August–September 2023. Microorganisms, 13(10), 2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102313







