Improving the Quality of Ensiling High-Moisture Alfalfa with Peanut Vine in Different Additives: Fermentation, Nutritional Quality, and Microbial Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Forage Harvesting and Silage Preparation
2.2. Fermentation Performance, Chemical Composition, and Microbial Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Compositions of Mixed Alfalfa with Peanut Vine Silage of Before Ensiling
3.2. Effects of Different Additives on Fermentation Quality of Silage Mixed Alfalfa with Peanut Vine
3.3. Effects of Additives on Chemical Composition of Mixed Alfalfa and Peanut Vine Silage
3.4. Effects of Additives on Nitrogen Fractions and CNCPS Composition of Mixed Alfalfa and Peanut Vine Silage
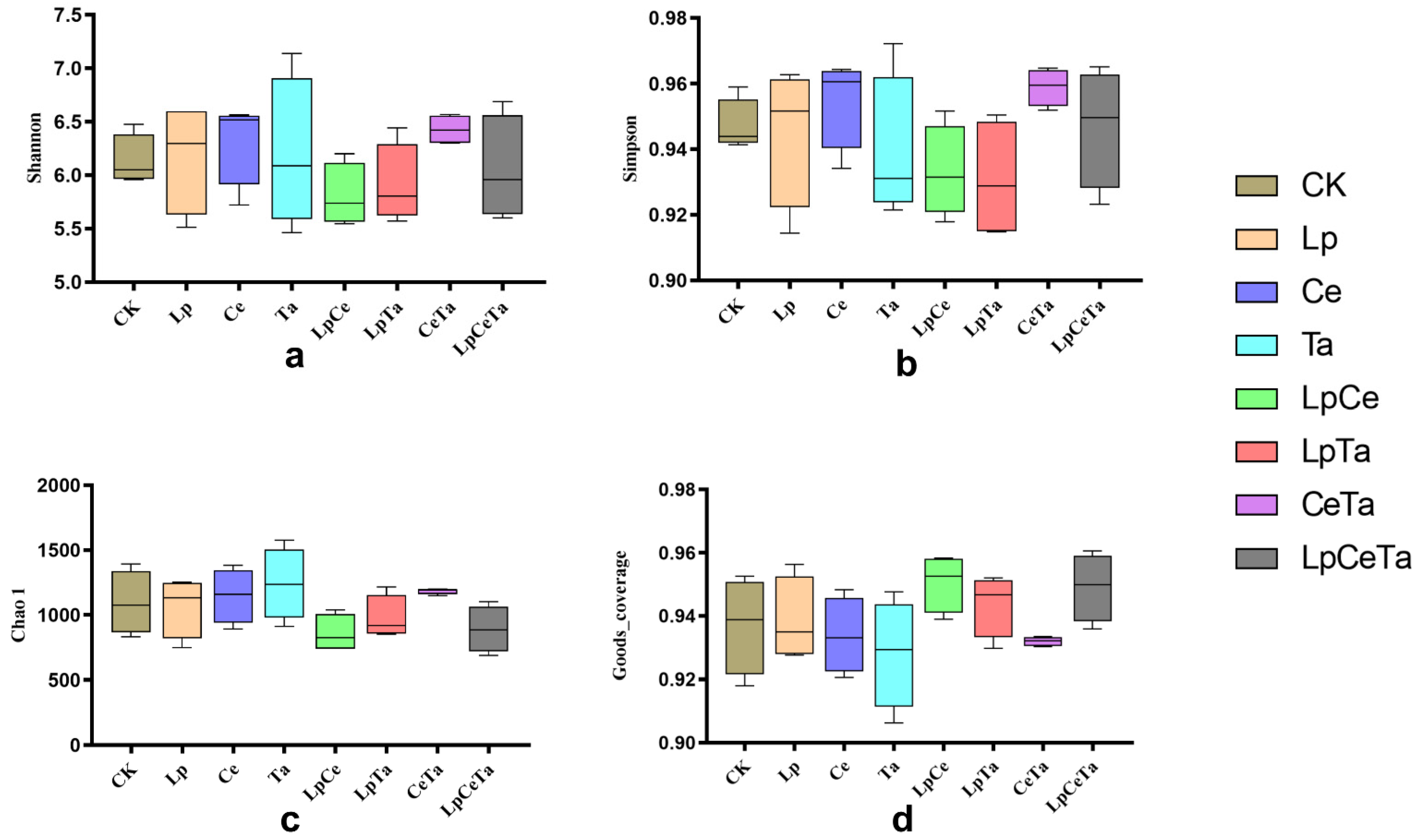
3.5. Bacterial Community of Mixed Alfalfa and Peanut Vine Silage
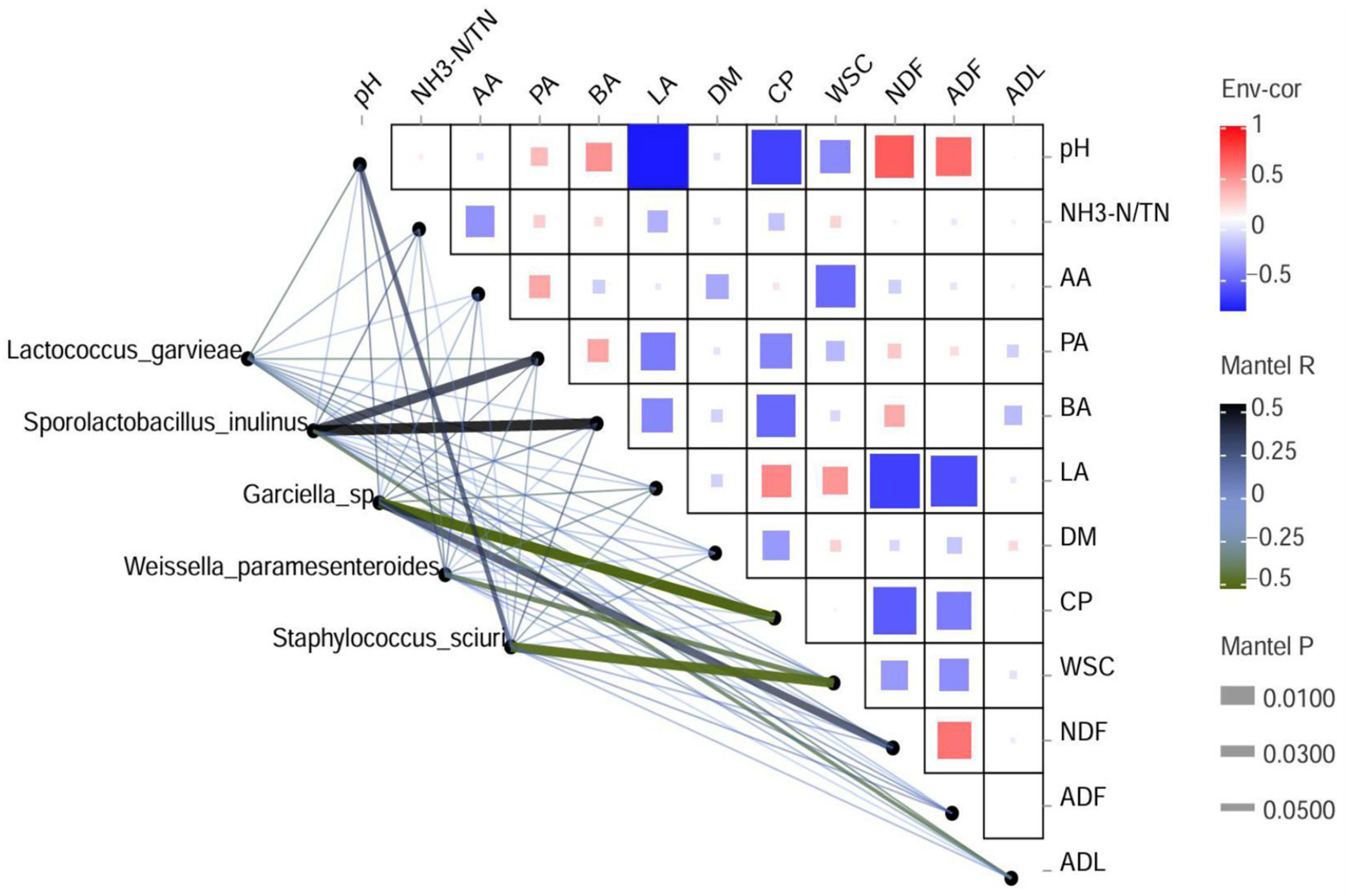
3.6. Correlation Analysis Between Bacterial Community and Various Parameters
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Dunière, L.; Sindo, J.; Chaucheyras-Durand, F.; Chevallier, I.; Thévenot-Sergentet, D. Silage processing and strategies to prevent persistence of undesirable microorganisms. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2013, 182, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarussi, M.C.N.; Pereira, O.G.; da Silva, V.P.; Leandro, E.S.; Ribeiro, K.G.; Santos, S.A. Fermentative profile and lactic acid bacterial dynamics in non-wilted and wilted alfalfa silage in tropical conditions. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zheng, M.; Wu, S.; Zou, X.; Chen, X.; Ge, L.; Zhang, Q. Effects of Gallic Acid on Fermentation Parameters, Protein Fraction, and Bacterial Community of Whole Plant Soybean Silage. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 662966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borreani, G.; Tabacco, E.; Schmidt, R.; Holmes, B.; Muck, R. Silage review: Factors affecting dry matter and quality losses in silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3952–3979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yu, Z. Effects of moisture content and additives on the ensiling quality and vitamins changes of alfalfa silage with or without rain damage. Anim. Sci. J. 2020, 91, e13379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, M.-Z.; Shen, Y.-X. Effect of Application of a Bacteria Inoculant and Wheat Bran on Fermentation Quality of Peanut Vine Ensiled Alone or with Corn Stover. J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 12, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, C.; Zu, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Chen, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, M.; Li, Q. Effect of Mixing Peanut Vine on Fermentation Quality, Nitrogen Fraction and Microbial Community of High-Moisture Alfalfa Silage. Fermentation 2023, 9, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaashikaa, P.R.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Varjani, S. Valorization of agro-industrial wastes for biorefinery process and circular bi-oeconomy: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, R.; Wang, C.; Dong, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X. Effects of Cellulase and Lactobacillus plantarum on Fermentation Quality, Chemical Composition, and Microbial Community of Mixed Silage of Whole-Plant Corn and Peanut Vines. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022, 194, 2465–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.E.; Nadeau, E.M.G.; McAllister, T.A.; Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Santos, M.C.; Kung, L., Jr. Silage review: Recent advances and future uses of silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3980–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinschmit, D.H.; Kung, L. A Meta-Analysis of the Effects of Lactobacillus buchneri on the Fermentation and Aerobic Stability of Corn and Grass and Small-Grain Silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 4005–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Q.; Wang, Z.; Liu, W.; Liu, M.; Ge, G.; Jia, Y.; Du, S. Influence of Cellulase or Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on the Ensiling Performance and Bacterial Community in Mixed Silage of Alfalfa and Leymus chinensis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z.; Ishii, M.; Igarashi, Y.; Cui, Z. Rice straw fermentation using lactic acid bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 2742–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Liu, N.; Diao, X.; He, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, W. Effects of Cellulase and Xylanase on Fermentation Characteristics, Chemical Composition and Bacterial Community of the Mixed Silage of King Grass and Rice Straw. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, Z.; Wu, J.; Deng, M.; Wang, M.; Tian, H.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.; Sun, B.; Guo, Y. Effects of Cellulase and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on the Fermentation Parameters, Nutrients, and Bacterial Community in Cassia alata Silage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 926065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khota, W.; Pholsen, S.; Higgs, D.; Cai, Y. Natural lactic acid bacteria population of tropical grasses and their fermentation factor analysis of silage prepared with cellulase and inoculant. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 9768–9781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckardt, J.; Sepperer, T.; Cesprini, E.; Šket, P.; Tondi, G. Comparing Condensed and Hydrolysable Tannins for Mechanical Foaming of Furanic Foams: Synthesis and Characterization. Molecules 2023, 28, 2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, G.A.; Kang, J.H. Automated Simultaneous Determination of Ammonia and Total Amino Acids in Ruminal Fluid and In Vitro Media. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for Dietary Fiber, Neutral Detergent Fiber, and Nonstarch Polysaccharides in Relation to Animal Nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva, A.; Quintana, A.; Sánchez, M.; Rodríguez, E.N.; Cremata, J.; Sánchez, J.C. Rapid and sensitive anthrone–sulfuric acid assay in microplate format to quantify carbo hydrate in biopharmaceutical products: Method development and validation. Biologicals 2008, 36, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohweder, D.A.; Barnes, R.F.; Jorgensen, N. Proposed hay grading standards based on laboratory analyses for evaluating quality. J. Anim. Sci. 1978, 47, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licitra, G.; Hernandez, T.M.; Van Soest, P.J. Standardization of procedures for nitrogen fractionation of ruminant feeds. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1996, 57, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, W.C.; Ding, W.R.; Ding, L.M.; Xu, D.M.; Zhang, P.; Li, F.H.; Guo, X.S. Influences of malic acid isomers and their application levels on fermentation quality and biochemical characteristics of alfalfa silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2018, 245, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dineen, M.; McCarthy, B.; Ross, D.; Ortega, A.; Dillon, P.; Van Amburgh, M. Characterization of the nutritive value of perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.) dominated pastures using updated chemical methods with application for the Cornell Net Carbohydrate and Protein System. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2021, 272, 114752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Wang, Z.; You, J.; Zhu, G.; Wang, H.; Wang, F. Comparison of in vitro digestibility and chemical composition among four crop straws treated by Pleurotus ostreatus. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; He, L.; Xing, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Fermentation quality and microbial community of alfalfa and stylo silage mixed with Moringa oleifera leaves. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 284, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, X.; Feng, H.; Guo, G.; Huo, W.; Li, Q.; Xu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Chen, L. Effects of laccase and lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation quality, nutrient composition, enzymatic hydrolysis, and bacterial community of alfalfa silage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1035942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasco-Correa, J.; Li, Y. Solid-state anaerobic digestion of fungal pretreated Miscanthus sinensis harvested in two different seasons. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 185, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gennatos, K.; Lazaridou, T.B. Silage yield and protein content of forage legumes intercropping with cereals in two spatial arrangements. Agrofor 2021, 6, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaudeau, D.; Jensen, S.K.; Ambye-Jensen, M.; Adler, S.; Bani, P.; Juncker, E.; Stødkilde, L. Nutritional values of forage-legume-based silages and protein concentrates for growing pigs. Animal 2022, 16, 100572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Xiong, H.; Wen, Z.; Tian, H.; Chen, Y.; Wu, L.; Guo, Y.; Sun, B. Effects of Different Concentrations of Lactobacillus plantarum and Bacillus licheni formis on Silage Quality, In Vitro Fermentation and Microbial Community of Hybrid Pennisetum. Animals 2022, 12, 1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Zhang, G.; Xiao, M.; Dong, C.; Zhang, R.; Du, L.; Zheng, Y.; Wei, M.; Wu, B. Effects of cellulase and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on the fermentation quality, microbial diversity, gene function prediction, and in vitro rumen fermentation parameters of Caragana korshinskii silage. Front. Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 2, 1108043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Bao, X.; Guo, G.; Huo, W.; Xu, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, Q. Treatment of alfalfa silage with tannin acid at different levels modulates ensiling characteristics, methane mitigation, ruminal fermentation patterns and microbiota. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2021, 278, 114997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabacco, E.; Borreani, G.; Crovetto, G.; Galassi, G.; Colombo, D.; Cavallarin, L. Effect of Chestnut Tannin on Fermentation Quality, Proteolysis, and Protein Rumen Degradability of Alfalfa Silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 4736–4746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.; Barry, T.; Attwood, G.; McNabb, W. The effect of condensed tannins on the nutrition and health of ruminants fed fresh temperate forages: A review. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2003, 106, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunade, I.M.; Jiang, Y.; Pech Cervantes, A.A.; Kim, D.H.; Oliveira, A.S.; Vyas, D.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Jeong, K.C.; Adesogan, A.T. Bacterial diversity and composition of alfalfa silage as analyzed by Illumina MiSeq sequencing: Effects of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 2048–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Li, J.; Dong, Z.; Shao, T. The reconstitution mechanism of napier grass microiota during the ensiling of alfalfa and their contributions to fermentation quality of silage. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Huan, H.; Gu, H.; Xu, N.; Shen, Q.; Ding, C. Dynamics of a microbial community during ensiling and upon aerobic exposure in lactic acid bacteria inoculation-treated and untreated barley silages. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 273, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qu, H.; Bai, S.; Yan, L.; You, M.; Gou, W.; Li, P.; Gao, F. Effect of wet sea buckthorn pomace utilized as an additive on silage fermentation profile and bacterial community composition of alfalfa. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, J. Spraying sugars, growth temperatures and N application levels change epiphytic lactic acid bacteria composition on Italian ryegrass. Grassl. Sci. 2022, 68, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Items | Alfalfa | Peanut Vine | Mixture |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry matter (g/kg FW) | 225.2 ± 0.76 | 928.6 ± 0.75 | 436.2 ± 0.48 |
| Crude protein (g/kg DM) | 165.7 ± 0.34 | 72.4 ± 0.77 | 137.7 ± 0.07 |
| Neutral detergent fiber (g/kg DM) | 512.4 ± 4.24 | 575.2 ± 7.69 | 531.2 ± 1.87 |
| Acid detergent fiber (g/kg DM) | 498.4 ± 2.42 | 466.7 ± 2.73 | 488.9 ± 1.48 |
| Water-soluble carbohydrate (g/kg DM) | 37.8 ± 0.55 | 39.3 ± 1.09 | 38.2 ± 0.20 |
| Crude ash (g/kg DM) | 127.3 ± 0.47 | 86.5 ± 0.87 | 115.01 ± 0.20 |
| pH | Lactic Acid (g/kg DM) | NH3-N (g/kg TN) | Acetic Acid (g/kg DM) | Propionic Acid (g/kg DM) | Butyric Acid (g/kg DM) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 5.87 ± 0.29 a | 9.40 ± 0.33 c | 44.49 ± 0.19 a | 17.15 ± 0.51 abc | 1.78 ± 0.19 | 0.70 ± 0.03 a |
| Lp | 5.18 ± 0.16 bc | 21.90 ± 0.16 b | 34.81 ± 0.29 de | 20.43 ± 0.31 a | 1.28 ± 0.08 | 0.31 ± 0.01 bc |
| Ce | 4.96 ± 0.19 cd | 42.78 ± 0.40 a | 39.02 ± 0.38 bcd | 14.99 ± 0.27 bc | 0.79 ± 0.02 | 0.48 ± 0.03 ab |
| Ta | 5.34 ± 0.09 bc | 22.50 ± 0.44 b | 42.87 ± 0.40 ab | 13.53 ± 0.14 c | 1.20 ± 0.03 | 0.26 ± 0.01 bc |
| LpCe | 4.74 ± 0.06 d | 45.77 ± 0.17 a | 31.36 ± 0.11 e | 17.42 ± 0.13 abc | 0.58 ± 0.01 | 0.13 ± 0.00 c |
| LpTa | 5.40 ± 0.07 b | 20.67 ± 0.06 b | 38.65 ± 0.18 bcd | 17.44 ± 0.24 abc | 1.71 ± 0.05 | 0.31 ± 0.01 bc |
| CeTa | 5.06 ± 0.09 cd | 26.02 ± 0.67 b | 40.59 ± 0.23 abc | 15.82 ± 0.21 bc | 1.52 ± 0.08 | 0.44 ± 0.01 b |
| LpCeTa | 4.79 ± 0.03 d | 45.65 ± 0.41 a | 37.47 ± 0.25 cd | 19.51 ± 0.20 ab | 1.27 ± 0.02 | 0.30 ± 0.02 bc |
| DM (g/kg FW) | CP (g/kg DM) | NDF (g/kg DM) | ADF (g/kg DM) | EE (g/kg DM) | WSC (g/kg DM) | RFV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 420.6 ± 0.22 bc | 131.5 ± 0.31 d | 575.7 ± 3.33 a | 476.1 ± 2.29 a | 20.0 ± 0.03 c | 19.2 ± 0.11 d | 840.2 ± 7.21 d |
| Lp | 417.2 ± 0.75 c | 140.4 ± 0.17 ab | 538.4 ± 2.09 b | 451.2 ± 1.43 bc | 27.4 ± 0.06 a | 16.4 ± 0.07 e | 929.2 ± 1.88 cd |
| Ce | 426.4 ± 0.38 ab | 139.4 ± 0.17 bc | 529.7 ± 1.67 b | 427.6 ± 1.38 d | 27.1 ± 0.12 a | 30.1 ± 0.13 a | 977.3 ± 4.35 ab |
| Ta | 429.4 ± 0.19 a | 129.6 ± 0.06 d | 554.7 ± 2.64 ab | 463.5 ± 0.45 ab | 22.4 ± 0.10 b | 26.6 ± 0.03 b | 886.6 ± 3.85 cd |
| LpCe | 414.8 ± 0.48 c | 141.6 ± 0.17 ab | 531.7 ± 2.27 b | 445.5 ± 1.33 bcd | 27.4 ± 0.06 a | 26.9 ± 0.14 b | 949.1 ± 2.53 ab |
| LpTa | 430.7 ± 0.06 a | 137.3 ± 0.13 c | 535.6 ± 1.85 b | 437.3 ± 0.59 cd | 21.9 ± 0.24 bc | 24.4 ± 0.09 c | 953.1 ± 2.53 ab |
| CeTa | 425.6 ± 0.37 ab | 140.1 ± 0.10 ab | 544.5 ± 1.09 ab | 439.1 ± 1.15 cd | 25.7 ± 0.25 a | 27.1 ± 0.11 b | 934.7 ± 2.70 abc |
| LpCeTa | 417.5 ± 0.25 c | 142.5 ± 0.04 a | 521.5 ± 1.11 b | 425.9 ± 0.34 d | 22.7 ± 0.13 b | 23.2 ± 0.17 c | 994.2 ± 1.84 a |
| TP (g/kg CP) | NPN (g/kg CP) | SP (g/kg CP) | ADIP (g/kg CP) | NDIP (g/kg CP) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 437.4 ± 1.23 d | 562.6 ± 1.23 a | 578.7 ± 1.14 ab | 141.8 ± 0.25 d | 162.6 ± 0.37 c |
| Lp | 446.7 ± 1.12 d | 553.4 ± 1.12 a | 575.6 ± 1.19 ab | 132.3 ± 0.32 e | 144.6 ± 0.36 e |
| Ce | 471.7 ± 0.86 c | 528.3 ± 0.86 b | 582.9 ± 0.93 a | 136.7 ± 0.14 e | 140.4 ± 0.19 e |
| Ta | 478.7 ± 1.06 bc | 521.3 ± 1.06 bc | 538.0 ± 0.93 c | 168.1 ± 0.28 a | 171.8 ± 0.29 b |
| LpCe | 471.0 ± 0.77 c | 530.0 ± 0.77 b | 565.8 ± 0.66 b | 145.4 ± 0.55 cd | 168.8 ± 0.72 b |
| LpTa | 495.8 ± 0.79 a | 504.2 ± 0.79 d | 525.5 ± 0.80 c | 161.7 ± 0.25 b | 177.7 ± 0.43 a |
| CeTa | 495.7 ± 1.26 a | 504.4 ± 1.26 d | 534.3 ± 1.53 c | 146.5 ± 0.36 cd | 159.7 ± 0.15 c |
| LpCeTa | 490.0 ± 0.99 ab | 510.1 ± 0.99 cd | 538.3 ± 1.07 c | 146.9 ± 0.22 c | 152.1 ± 0.09 d |
| PA (g/kg CP) | PB1 (g/kg CP) | PB2 (g/kg CP) | PB3 (g/kg CP) | PC (g/kg CP) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 562.6 ± 1.23 a | 16.1 ± 0.09 e | 257.6 ± 1.39 d | 20.8 ± 0.13 a | 141.8 ± 0.25 d |
| Lp | 553.4 ± 1.12 a | 22.2 ± 0.08 d | 271.9 ± 2.01 cd | 12.3 ± 0.27 c | 132.3 ± 0.32 e |
| Ce | 528.3 ± 0.86 b | 54.6 ± 0.09 a | 281.3 ± 0.93 bc | 3.7 ± 0.11 d | 136.7 ± 0.14 e |
| Ta | 521.3 ± 1.06 bc | 16.7 ± 0.17 e | 288.6 ± 1.16 abc | 3.6 ± 0.11 d | 168.1 ± 0.28 a |
| LpCe | 529.0 ± 0.77 b | 36.8 ± 0.16 b | 270.0 ± 1.32 cd | 23.5 ± 0.28 a | 145.4 ± 0.55 cd |
| LpTa | 504.2 ± 0.79 d | 21.3 ± 0.20 d | 295.5 ± 0.76 ab | 16.0 ± 0.26 b | 161.7 ± 0.25 b |
| CeTa | 504.4 ± 1.26 d | 29.9 ± 0.35 c | 305.8 ± 1.11 a | 13.3 ± 0.23 bc | 146.5 ± 0.36 cd |
| LpCeTa | 510.1 ± 0.99 cd | 28.2 ± 0.17 c | 300.4 ± 1.61 ab | 5.2 ± 0.16 d | 146.9 ± 0.22 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, H.; Wu, C.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Y.; He, Y.; Chen, H.; Zu, X.; Wang, L.; Gao, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. Improving the Quality of Ensiling High-Moisture Alfalfa with Peanut Vine in Different Additives: Fermentation, Nutritional Quality, and Microbial Communities. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102228
Jia H, Wu C, Liu Z, Sun Y, He Y, Chen H, Zu X, Wang L, Gao Y, Wang M, et al. Improving the Quality of Ensiling High-Moisture Alfalfa with Peanut Vine in Different Additives: Fermentation, Nutritional Quality, and Microbial Communities. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(10):2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102228
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Haikuo, Chunhui Wu, Zhenling Liu, Yu Sun, Ying He, Huan Chen, Xiaowei Zu, Lixin Wang, Yanxia Gao, Mingya Wang, and et al. 2025. "Improving the Quality of Ensiling High-Moisture Alfalfa with Peanut Vine in Different Additives: Fermentation, Nutritional Quality, and Microbial Communities" Microorganisms 13, no. 10: 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102228
APA StyleJia, H., Wu, C., Liu, Z., Sun, Y., He, Y., Chen, H., Zu, X., Wang, L., Gao, Y., Wang, M., & Li, Q. (2025). Improving the Quality of Ensiling High-Moisture Alfalfa with Peanut Vine in Different Additives: Fermentation, Nutritional Quality, and Microbial Communities. Microorganisms, 13(10), 2228. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13102228






