Effect of Cordyceps militaris Residue and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on Fermentation Quality and Bacterial Community of Alfalfa Silage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Silage Preparation
2.2. Fermentation Quality and Nutrient Composition Analyses
2.3. Bacterial Community Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical and Microbial Characteristics of Alfalfa and Cordyceps militaris Residue Before Ensiling
3.2. Fermentation Quality of Alfalfa Silage
3.3. Chemical Composition of Alfalfa Silage
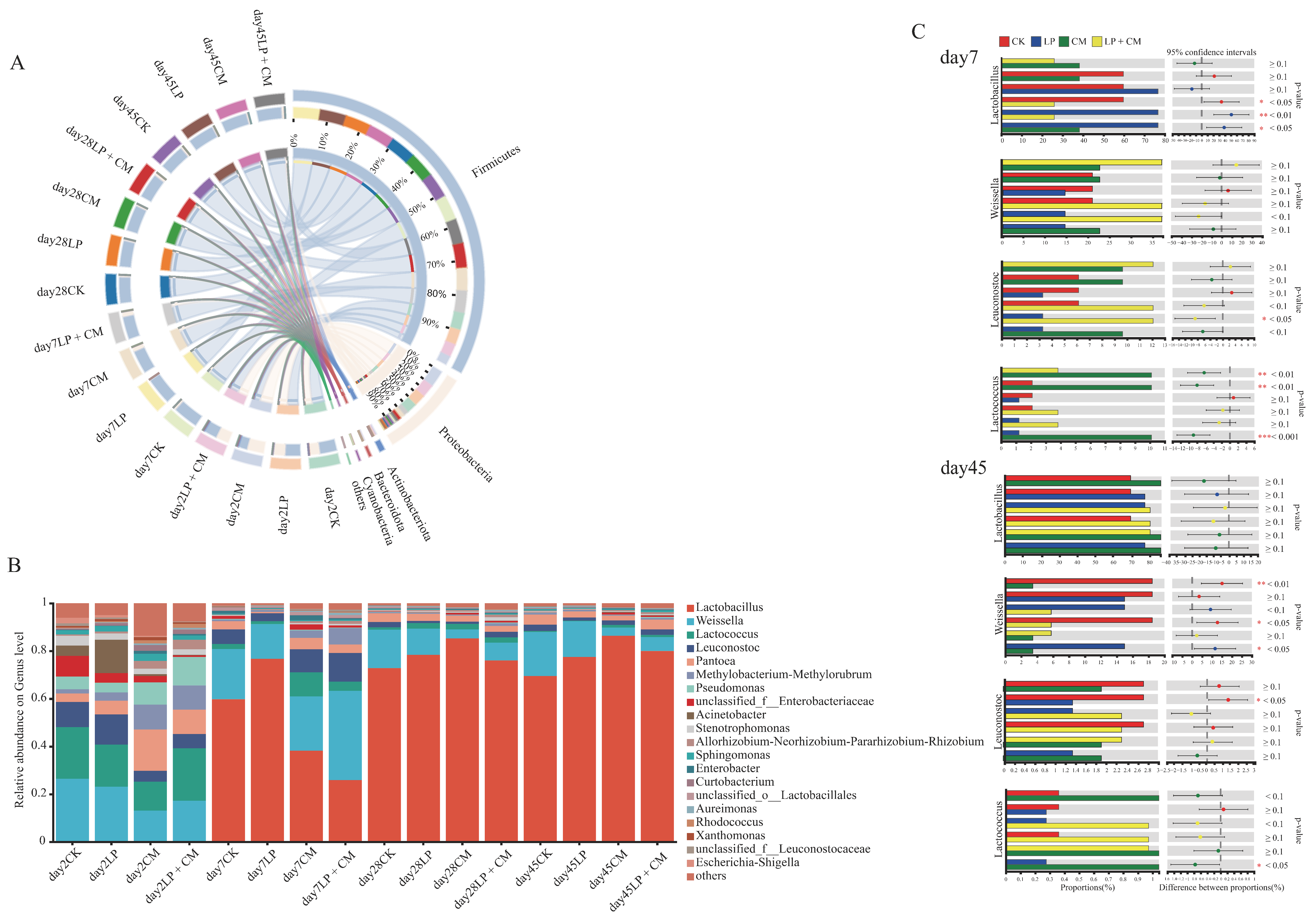
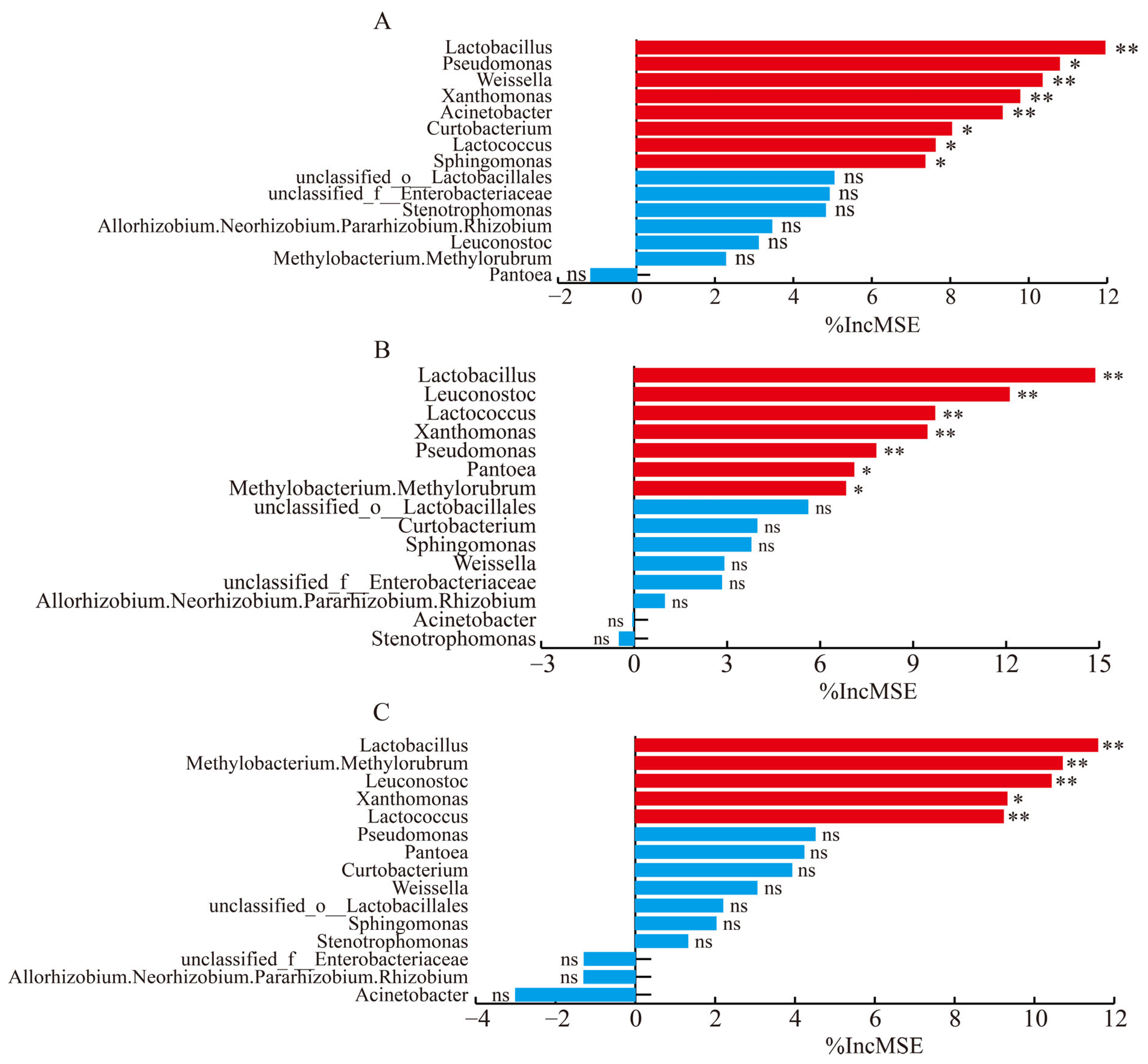
3.4. The Microbial Community of Alfalfa Silage During Ensiling
4. Discussion
4.1. The Characteristics of Raw Material
4.2. Fermentation Quality and Chemical Composition of Alfalfa Silage
4.3. The Microbial Community of Alfalfa Silage
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Q.; Xu, N.; Zhou, M.Z.; Gao, B.; Wang, C.; Shi, Y. Fermenting liquid vinegar with higher taste, flavor and healthy value by using discarded Cordyceps militaris solid culture medium. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 98, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, K.V.; Balasubramanian, B.; Park, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Sebastian, J.K.; Liu, W.C.; Pappuswamy, M.; Meyyazhagan, A.; Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S.; et al. Conservation of Endangered Cordyceps sinensis Through Artificial Cultivation Strategies of C. militaris, an Alternate. Mol. Biotechnol. 2025, 67, 1382–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Insights, C.M. Cordyceps Sinensis and Militaris Extract Market Analysis & Forecast 2032. Available online: https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/market-insight/cordyceps-sinensis-and-militaris-extract-market-2578 (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Zhu, Z.Y.; Liu, X.C.; Dong, F.Y.; Guo, M.Z.; Wang, X.T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.M. Influence of fermentation conditions on polysaccharide production and the activities of enzymes involved in the polysaccharide synthesis of Cordyceps militaris. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 3909–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.Q.; Li, Y.L.; Ren, J.H.; Qin, N. Yield, Nutritional Contant, and Antioxidant Activity of Pleurotus ostreatus on Corncobs Supplemented with Herb Residues. Mycobiology 2018, 46, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.Y.; Long, L.K.; Wu, L.L.; Zhang, F.L.; Wu, S.L.; Zhang, W.M.; Sun, X.M. Evaluation of different agricultural wastes for the production of fruiting bodies and bioactive compounds by medicinal mushroom Cordyceps militaris. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 3476–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.J.; Yang, S.G.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.T.; Wang, X.L.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhang, R.J.; Shen, L. Reclamation of Chinese herb residues using probiotics and evaluation of their beneficial effect on pathogen infection. J. Infect. Public Health 2017, 10, 749–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.C.; Chen, Y.L.; Chang, S.M.; Shih, I.L. Cultivation of Medicinal Caterpillar Fungus, Cordyceps militaris (Ascomycetes), and Production of Cordycepin Using the Spent Medium from Levan Fermentation. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2013, 15, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.; Ya, W.; Yi-Lin, Z.; Zhen, Z. The Reutilization Of Herbal Residues. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Energy and Environmental Protection (ICEEP), Guilin, China, 19–21 April 2013; pp. 2993–2996. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.Y.; Qu, H.; Bai, S.Q.; Yan, L.J.; You, M.H.; Gou, W.L.; Li, P.; Gao, F.Q. Effect of wet sea buckthorn pomace utilized as an additive on silage fermentation profile and bacterial community composition of alfalfa. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Wang, J.C.H.; Cheng, Q.M.; Long, Z.F.; Chen, C.; Xie, Y.X.; Lei, Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.Y.; He, X.J.; et al. The potential of biogas production and effects of alfalfa silage under the synergistic influence of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Rosa roxburghii pomace waste on the fermentation quality and bacterial community. mSphere 2025, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Chen, F.; Xu, J.J.; Guo, L.N.; Xiong, Y.; Lin, Y.L.; Ni, K.K.; Yang, F.Y. Exploring the Addition of Herbal Residues on Fermentation Quality, Bacterial Communities, and Ruminal Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Paper Mulberry Silage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 820011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, K.K.; Wang, X.K.; Lu, Y.; Guo, L.N.; Li, X.M.; Yang, F.Y. Exploring the silage quality of alfalfa ensiled with the residues of astragalus and hawthorn. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 297, 122249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barido, F.H.; Lee, S.K. Tenderness-related index and proteolytic enzyme response to the marination of spent hen breast by a protease extracted from Cordyceps militaris mushroom. Anim. Biosci. 2021, 34, 1859–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.B.; An, L.P.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhao, N.X.; Yuan, G.X.; Du, P.G. Extraction methods and sedative-hypnotic effects of polysaccharide and total flavonoids of Cordyceps militaris. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.-Y.; Park, E.-H. Anti-inflammatory and related pharmacological activities of cultured mycelia and fruiting bodies of Cordyceps militaris. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 96, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcdonald, P.; Henderson, A.R.; Heron, S.J.E. The Biochemistry of Silage; Chalcombe Publications: Marlow, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, L.M.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage review: Interpretation of chemical, microbial, and organoleptic components of silages. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 4020–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.S.; Ke, W.C.; Ding, W.R.; Ding, L.M.; Xu, D.M.; Wang, W.W.; Zhang, P.; Yang, F.Y. Profiling of metabolome and bacterial community dynamics in ensiled Medicago sativa inoculated without or with Lactobacillus plantarum or Lactobacillus buchneri. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.Y.; Zhao, S.S.; Wang, Y.; Fan, X.M.; Wang, Y.P.; Feng, C.S. Assessment of Bacterial Community Composition and Dynamics in Alfalfa Silages With and Without Lactobacillus plantarum Inoculation Using Absolute Quantification 16S rRNA Sequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 629894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarussi, M.C.N.; Pereira, O.G.; Silva, V.P.D.; Leandro, E.S.; Santos, S.A. Fermentative profile and lactic acid bacterial dynamics in non-wilted and wilted alfalfa silage in tropical conditions. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2019, 46, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.J.; Park, S.J.; Lee, S.G.; Shin, S.C.; Choi, D.H. Cordycepin: Selective growth inhibitor derived from liquid culture of Cordyceps militaris against Clostridium spp. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2744–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Lou, Z.X.; Wang, H.X.; Chen, C. Antimicrobial effect and proposed action mechanism of cordycepin against Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.X.; Zhou, T.S. Biosorption of methylene blue from wastewater by an extraction residue of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bge. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Na, N.; Li, X.M.; Li, Z.Q.; Wang, C.; Wu, X.G.; Xiao, Y.Z.; Yin, G.M.; Liu, S.B.; Liu, Z.P.; et al. Impact of Packing Density on the Bacterial Community, Fermentation, and In Vitro Digestibility of Whole-Crop Barley Silage. Agriculture 2021, 11, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthur Thomas, T. An automated procedure for the determination of soluble carbohydrates in herbage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1977, 28, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.X.; Ke, W.C.; Bai, J.; Li, F.H.; Xu, D.M.; Ding, Z.T.; Guo, X.S. The effect of Pediococcus acidilactici J17 with high-antioxidant activity on antioxidant, α-tocopherol, β-carotene, fatty acids, and fermentation profiles of alfalfa silage ensiled at two different dry matter contents. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2020, 268, 114614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.S.; Pan, G.; Leng, R.X.; Ni, W.H.; Yang, J.Y.; Sun, J.J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Z.G.; Xue, Y.L. Effect of Ensiling Density and Storage Temperature on Fermentation Quality, Bacterial Community, and Nitrate Concentration of Sorghum-Sudangrass Silage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 828320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.X.; Zhang, J.; Ling, W.Q.; Degen, A.A.; Zhou, Y.; Ge, C.Y.; Yang, F.L.; Zhou, J. Ensiling hybrid Pennisetum with lactic acid bacteria or organic acids improved the fermentation quality and bacterial community. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1216722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Benno, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Kumai, S. Effect of applying lactic acid bacteria isolated from forage crops on fermentation characteristics and aerobic deterioration of silage. J. Dairy Sci. 1999, 82, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.H.; Li, X.M.; Guan, H.; Huang, L.K.; Ma, X.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z.; Nie, G.; Zhou, J.Q.; Yang, W.Y.; et al. Microbial community and fermentation characteristic of Italian ryegrass silage prepared with corn stover and lactic acid bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 279, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhou, W.; Yang, F.Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, Q. Effects of Wilting and Lactobacillus plantarum Addition on the Fermentation Quality and Microbial Community of Moringa oleifera Leaf Silage. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Benno, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Ohmomo, S.; Kumai, S.; Nakase, T. Influence of Lactobacillus spp. from An inoculant and of weissella and leuconostoc spp. from forage crops on silage fermentation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2982–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhao, S.S.; Wang, Y.P.; Yang, F.Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, X.M.; Feng, C.S. The Effect of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum ZZU203, Cellulase-Producing Bacillus methylotrophicus, and Their Combinations on Alfalfa Silage Quality and Bacterial Community. Fermentation 2023, 9, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besharati, M.; Palangi, V.; Salem, A.Z.M.; De Palo, P.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Maggiolino, A. Substitution of raw lucerne with raw citrus lemon by-product in silage: In vitro apparent digestibility and gas production. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 1006581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markkinen, N.; Laaksonen, O.; Nahku, R.; Kuldjärv, R.; Yang, B. Impact of lactic acid fermentation on acids, sugars, and phenolic compounds in black chokeberry and sea buckthorn juices. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, E.B.; Smith, M.L.; Savage, R.M.; Polukis, S.A.; Drouin, P.; Kung, L. Effects of Lactobacillus hilgardii 4785 and Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 on the bacterial community, fermentation and aerobic stability of high-moisture corn silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 1481–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, L.; Xie, Z.; Hu, L.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Z. Lactobacillus plantarum and molasses alter dynamic chemical composition, microbial community, and aerobic stability of mixed (amaranth and rice straw) silage. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 5225–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, L., Jr.; Myers, C.L.; Neylon, J.M.; Taylor, C.C.; Lazartic, J.; Mills, J.A.; Whiter, A.G. The effects of buffered propionic acid-based additives alone or combined with microbial inoculation on the fermentation of high moisture corn and whole-crop barley. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Xie, L.L.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Wang, Q.Q.; Feng, L.; Li, Y.; Lei, Y.H.; Sun, Y.F. Effect of Lactiplantibacillus and sea buckthorn pomace on the fermentation quality and microbial community of paper mulberry silage. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1412759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.E.; Nadeau, E.M.G.; McAllister, T.A.; Contreras-Govea, F.E.; Santos, M.C.; Kung, L. Silage review: Recent advances and future uses of silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3980–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Yuan, X.J.; Guo, G.; Li, J.F.; Bai, Y.F.; Shao, T. Effects of molasses on the fermentation characteristics of mixed silage prepared with rice straw, local vegetable by-products and alfalfa in Southeast China. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, F.; Wang, X.; Xiong, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Ni, K.; Yang, F. Innovative utilization of herbal residues: Exploring the diversity of mechanisms beneficial to regulate anaerobic fermentation of alfalfa. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 360, 127249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.R.F.; Scott, M.B.; Tweed, J.K.S.; Minchin, F.R.; Davies, D.R. Effects of polyphenol oxidase on lipolysis and proteolysis of red clover silage with and without a silage inoculant (Lactobacillus plantarum L54). Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2008, 144, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.W.; Lv, H.J.; Xing, Y.Q.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, Q. Intrinsic tannins affect ensiling characteristics and proteolysis of Neolamarckia cadamba leaf silage by largely altering bacterial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 311, 123496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Gao, L.; Chen, D.D.; Xue, Y.L.; Kholif, A.E.; Zhou, W.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, Q. Effects of Forestry Waste Neolamarckia cadamba Leaf Meal as an Additive on Fermentation Quality, Antioxidant Activity, and Bacterial Community of High-Moisture Stylo Silage. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 925400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Q.; Wang, Z.J.; Liu, W.; Liu, M.J.; Ge, G.T.; Jia, Y.S.; Du, S. Influence of Cellulase or Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on the Ensiling Performance and Bacterial Community in Mixed Silage of Alfalfa and Leymus chinensis. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarvey, J.A.; Franco, R.B.; Palumbo, J.D.; Hnasko, R.; Stanker, L.; Mitloehner, F.M. Bacterial population dynamics during the ensiling of Medicago sativa (alfalfa) and subsequent exposure to air. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 114, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Wang, S.R.; Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.H.; Li, J.F.; Nazar, M.; Shao, T. Microbial diversity and fermentation profile of red clover silage inoculated with reconstituted indigenous and exogenous epiphytic microbiota. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 314, 123606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshri, J.; Chen, Y.R.; Pinto, R.; Kroupitski, Y.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Sela, S. Microbiome dynamics during ensiling of corn with and without Lactobacillus plantarum inoculant. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 4025–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.R.; Zhang, H.Y.; Pan, G.; Yin, H.; Sun, J.J.; Yu, Z.; Bai, C.S.; Xue, Y.L. Effect of exogenous microorganisms on the fermentation quality, nitrate degradation and bacterial community of sorghum-sudangrass silage. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1052837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunade, I.M.; Kim, D.H.; Jiang, Y.; Weinberg, Z.G.; Jeong, K.C.; Adesogan, A.T. Control of Escherichia coli O157:H7 in contaminated alfalfa silage: Effects of silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 4427–4436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.M.; Du, Z.M.; Yamasaki, S.; Nguluve, D.; Tinga, B.; Macome, F.; Oya, T. Community of natural lactic acid bacteria and silage fermentation of corn stover and sugarcane tops in Africa. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2020, 33, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhang, Y.; Gou, W.L.; Cheng, Q.M.; Bai, S.Q.; Cai, Y.M. Silage fermentation and bacterial community of bur clover, annual ryegrass and their mixtures prepared with microbial inoculant and chemical additive. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2019, 247, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.T.; Xie, H.D.; Zeng, F.Q.; Luo, X.Q.; Peng, L.J.; Sun, X.W.; Wang, X.F.; Yang, C.J. An Assessment on the Fermentation Quality and Bacterial Community of Corn Straw Silage with Pineapple Residue. Fermentation 2024, 10, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Item | Alfalfa | Cordyceps militaris Residue | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry matter (%FM) | 21.33 ± 0.18 | 89.80 ± 0.09 | <0.001 |
| CP (%DM) | 21.09 ± 0.32 | 22.53 ± 0.33 | 0.006 |
| NDF (%DM) | 37.42 ± 1.35 | 33.11 ± 0.92 | 0.010 |
| ADF (%DM) | 27.00 ± 1.20 | 17.19 ± 0.59 | <0.001 |
| WSC (%DM) | 8.76 ± 1.77 | 6.90 ± 0.46 | 0.152 |
| Lactic acid bacteria (log10 cfu/g) | 5.40 ± 0.31 | 4.74 ± 0.12 | 0.026 |
| Yeasts (log10 cfu/g) | 5.82 ± 0.22 | 4.83 ± 0.11 | 0.002 |
| Item | Treatment | Ensiling Days | SEM | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 7 | 28 | 45 | T | D | T*D | |||
| pH | CK | 4.89 Aa | 4.47 b | 4.49 Ab | 4.41 Bb | 0.006 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| LP | 4.91 Aa | 4.39 c | 4.46 Ab | 4.49 Ab | |||||
| CM | 4.77 Ba | 4.47 b | 4.23 Bc | 4.16 Cc | |||||
| LP + CM | 4.72 Ba | 4.41 b | 4.17 Bc | 4.14 Cc | |||||
| Lactic acid (%DM) | CK | 2.11 Bb | 2.74 Bb | 6.64 Ba | 7.13 Ba | 0.028 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.031 |
| LP | 2.18 ABd | 4.08 Ac | 6.72 ABb | 8.23 Aa | |||||
| CM | 2.27 Ad | 3.69 Ac | 7.00 ABb | 8.45 Aa | |||||
| LP + CM | 2.25 Ad | 3.72 Ac | 7.06 Ab | 8.19 Aa | |||||
| Acetic acid (%DM) | CK | 1.02 b | 1.87 Aa | 2.41 Aa | 2.31 Aa | 0.040 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.132 |
| LP | 1.47 b | 1.43 ABb | 2.25 Aa | 2.51 Aa | |||||
| CM | 1.15 b | 1.08 Bb | 1.69 Ba | 1.92 Ba | |||||
| LP + CM | 1.01 c | 0.96 Bc | 1.69 Bb | 2.00 Ba | |||||
| 1, 2 propylene glycol (%DM) | CK | 0.00 b | 0.00 b | 0.00 b | 0.26 Ba | 0.005 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| LP | 0.00 b | 0.00 b | 0.00 b | 0.29 Aa | |||||
| CM | 0.00 c | 0.00 c | 0.01 b | 0.04 Ca | |||||
| LP + CM | 0.00 b | 0.00 b | 0.01 b | 0.05 Ca | |||||
| Ethanol (%DM) | CK | 0.86 b | 1.13 b | 1.25 BCa | 1.16 Ca | 0.017 | 0.002 | <0.001 | 0.412 |
| LP | 0.92 c | 1.08 b | 1.32 Ba | 1.35 ABa | |||||
| CM | 0.93 b | 1.12 b | 1.42 Aa | 1.50 Aa | |||||
| LP + CM | 0.84 b | 0.92 b | 1.22 Ca | 1.24B Ca | |||||
| NH3-N %TN | CK | 0.57 c | 2.14 b | 4.75 Aa | 5.01 Aa | 0.034 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| LP | 0.86 d | 1.79 c | 4.79 Aa | 3.52 Cb | |||||
| CM | 0.72 d | 1.50 c | 2.97 Bb | 4.02 Ba | |||||
| LP + CM | 0.82 c | 1.50 b | 2.84 Ba | 3.05 Da | |||||
| Lactic acid bacteria, log10 cfu/g FM | CK | 7.37 Bb | 10.05 ABa | 9.69 a | 9.49 Ca | 0.061 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| LP | 7.92 Bb | 9.42 Ba | 9.79 a | 9.68 ABa | |||||
| CM | 8.91 Ac | 10.81 Aa | 9.95 b | 9.61 ABb | |||||
| LP + CM | 9.33 Ab | 9.64 Bab | 10.19 a | 9.77 Aab | |||||
| Yeasts, log10 cfu/g FM | CK | 5.67 a | 3.22 b | 3.10 b | 1.80 c | - | - | - | - |
| LP | 5.34 | <2.00 | <2.00 | 3.73 | |||||
| CM | 5.56 | 3.55 | <2.00 | 3.82 | |||||
| LP + CM | 5.55 | 3.18 | 3.92 | <2.00 | |||||
| Item | Treatments | SEM | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | LP | CM | LP + CM | |||
| DM (%FM) | 21.69 c | 22.13 c | 24.84 a | 23.99 b | 0.404 | <0.001 |
| CP (% DM) | 21.90 b | 21.85 b | 22.80 a | 22.72 a | 0.164 | 0.024 |
| NDF (% DM) | 33.93 | 34.90 | 33.90 | 34.33 | 0.345 | 0.770 |
| ADF (%DM) | 25.08 | 26.23 | 24.21 | 24.87 | 0.346 | 0.227 |
| WSC (% DM) | 1.35 c | 1.20 c | 2.10 a | 1.71 b | 0.372 | <0.001 |
| Item | Treatment | Ensiling Days | SEM | p-Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 7 | 28 | 45 | T | D | T*D | |||
| Shannon | CK | 2.14 Ba | 1.35 Bb | 1.02 b | 1.09 b | 0.039 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.002 |
| LP | 2.15 Ba | 0.85 Bb | 0.93 b | 0.85 b | |||||
| CM | 2.91 Aa | 1.96 Ab | 0.79 c | 0.76 c | |||||
| LP + CM | 2.55 ABa | 1.94 Ab | 1.17 c | 0.99 c | |||||
| Chao | CK | 175.15 B | 147.15 | 113.81 B | 147.28 | 4.571 | 0.039 | <0.001 | 0.009 |
| LP | 174.77 B | 111.14 | 134.53 AB | 117.40 | |||||
| CM | 274.73 Aa | 141.28 b | 98.16 Bb | 96.15 b | |||||
| LP + CM | 225.56 ABa | 153.94 b | 168.53 Aab | 143.91 b | |||||
| Ace | CK | 215.27 | 196.15 | 138.83 C | 153.33 A | 5.059 | 0.203 | <0.001 | 0.003 |
| LP | 187.87 | 127.29 | 173.40 B | 148.05 A | |||||
| CM | 277.05 a | 192.29 b | 111.10 Dc | 98.36 Bc | |||||
| LP + CM | 213.89 | 168.72 | 202.39 A | 175.17 A | |||||
| Coverage | CK | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.000 | 0.245 | <0.001 | 0.019 |
| LP | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |||||
| CM | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |||||
| LP + CM | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.99 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, L.; Zhao, M.; Song, J.; Gao, D.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Yu, Z.; Bai, C. Effect of Cordyceps militaris Residue and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on Fermentation Quality and Bacterial Community of Alfalfa Silage. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081919
Wei L, Zhao M, Song J, Gao D, Li X, Sun J, Yu Z, Bai C. Effect of Cordyceps militaris Residue and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on Fermentation Quality and Bacterial Community of Alfalfa Silage. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081919
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Luheng, Meirong Zhao, Jia Song, Duo Gao, Xinnan Li, Juanjuan Sun, Zhu Yu, and Chunsheng Bai. 2025. "Effect of Cordyceps militaris Residue and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on Fermentation Quality and Bacterial Community of Alfalfa Silage" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081919
APA StyleWei, L., Zhao, M., Song, J., Gao, D., Li, X., Sun, J., Yu, Z., & Bai, C. (2025). Effect of Cordyceps militaris Residue and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum on Fermentation Quality and Bacterial Community of Alfalfa Silage. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081919






