Microbiota of Peri-Implant Healthy Tissues, Peri-Implant Mucositis, and Peri-Implantitis: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Microbiological Sampling and Analysis of Peri-Implant Microbiota
2.1. Microbiological Sampling at Peri-Implant Sites
2.2. Microbiological Analysis of Peri-Implant Microbiota
3. Peri-Implant Microbiota
3.1. Microbial Profile of Healthy Peri-Implant Sites
3.2. Peri-Implant Mucositis-Associated Microbiota
3.3. Peri-Implantitis-Associated Microbiota
3.3.1. Candida albicans in Peri-Implantitis
3.3.2. Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) in Peri-Implantitis
3.3.3. Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) in Peri-Implantitis
4. Discussion
4.1. Microbial Profile of Healthy Peri-Implant Sites
4.2. Peri-Implant Mucositis-Associated Microbiota
4.3. Peri-Implantitis-Associated Microbiota
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malchiodi, L.; Fiorino, A.; Merlino, L.; Cucchi, A.; Zotti, F.; Nocini, P.F. Analysis of Ultra-Short Implants with Different Angulations: A Retrospective Case–Control Study with 2 to 9 Years of Follow-Up. Clin. Oral Investig. 2024, 28, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazil, V.; Bandiaky, O.N.; Renard, E.; Idiri, K.; Struillou, X.; Soueidan, A. Current Data on Oral Peri-Implant and Periodontal Microbiota and Its Pathological Changes: A Systematic Review. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, M.G.; Lindhe, J. Peri-implant Health. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S249–S256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglundh, T.; Armitage, G.; Araujo, M.G.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Blanco, J.; Camargo, P.M.; Chen, S.; Cochran, D.; Derks, J.; Figuero, E.; et al. Peri-implant Diseases and Conditions: Consensus Report of Workgroup 4 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, S286–S291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Amo, F.S.L.; Yu, S.H.; Sammartino, G.; Sculean, A.; Zucchelli, G.; Rasperini, G.; Felice, P.; Pagni, G.; Iorio-Siciliano, V.; Grusovin, M.G.; et al. Peri-implant Soft Tissue Management: Cairo Opinion Consensus Conference. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, F.; Derks, J.; Monje, A.; Wang, H. Peri-implantitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, S246–S266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucchi, A.; Maiani, F.; Franceschi, D.; Sassano, M.; Fiorino, A.; Urban, I.A.; Corinaldesi, G. The Influence of Vertical Ridge Augmentation Techniques on Peri-implant Bone Loss: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2024, 26, 15–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, M. Oral Dysbiosis and Systemic Diseases: A Two-Way Relationship? Medicina 2023, 59, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosio, F.; Santella, B.; Di Palo, M.P.; Giordano, F.; Lo Giudice, R. Characterization of the Oral Microbiome in Wearers of Fixed and Removable Implant or Non-Implant-Supported Prostheses in Healthy and Pathological Oral Conditions: A Narrative Review. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almohareb, T.; Alhamoudi, N.; Al Deeb, M.; Bin-Shuwaish, M.S.; Mokeem, S.A.; Saad Shafqat, S.; Vohra, F.; Abduljabbar, T. Clinical Efficacy of Photodynamic Therapy as an Adjunct to Mechanical Debridement in the Treatment of Per-Implantitis with Abscess. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 30, 101750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombeccari, G.P.; Guzzi, G.; Gualini, F.; Gualini, S.; Santoro, F.; Spadari, F. Photodynamic Therapy to Treat Periimplantitis. Implant. Dent. 2013, 22, 631–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birang, E.; Talebi Ardekani, M.R.; Rajabzadeh, M.; Sarmadi, G.; Birang, R.; Gutknecht, N. Evaluation of Effectiveness of Photodynamic Therapy with Low-Level Diode Laser in Nonsurgical Treatment of Peri-Implantitis. J. Lasers Med. Sci. 2017, 8, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.-H.; Lin, Y.-C.; Kung, J.-C.; Yan, D.-Y.; Chen, I.-H.; Jheng, Y.-S.; Lai, C.-H.; Wu, Y.-M.; Lee, K.-T. Efficacy of Er:YAG Laser for the Peri-Implantitis Treatment and Microbiological Changes: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Lasers Med. Sci. 2022, 37, 3517–3525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arısan, V.; Karabuda, Z.C.; Arıcı, S.V.; Topçuoğlu, N.; Külekçi, G. A Randomized Clinical Trial of an Adjunct Diode Laser Application for the Nonsurgical Treatment of Peri-Implantitis. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2015, 33, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passariello, C.; Lucchese, A.; Pera, F.; Gigola, P. Clinical, Microbiological and Inflammatory Evidence of the Efficacy of Combination Therapy Including Serratiopeptidase in the Treatment of Periimplantitis. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2012, 10, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, M.; Schär, D.; Wicki, B.; Eick, S.; Ramseier, C.A.; Arweiler, N.B.; Sculean, A.; Salvi, G.E. Anti-infective Therapy of Peri-implantitis with Adjunctive Local Drug Delivery or Photodynamic Therapy: 12-month Outcomes of a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laleman, I.; Pauwels, M.; Quirynen, M.; Teughels, W. The Usage of a Lactobacilli Probiotic in the Non-Surgical Therapy of Peri-Implantitis: A Randomized Pilot Study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2020, 31, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, J.K.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, C.S. Surgical Therapy of Peri-Implantitis with Local Minocycline: A 6-Month Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. J. Dent. Res. 2019, 98, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galofré, M.; Palao, D.; Vicario, M.; Nart, J.; Violant, D. Clinical and Microbiological Evaluation of the Effect of Lactobacillus reuteri in the Treatment of Mucositis and Peri-implantitis: A Triple-blind Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Periodontal Res. 2018, 53, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibli, J.A.; Ferrari, D.S.; Siroma, R.S.; Figueiredo, L.C.d.; Faveri, M.D.; Feres, M. Microbiological and Clinical Effects of Adjunctive Systemic Metronidazole and Amoxicillin in the Non-Surgical Treatment of Peri-Implantitis: 1 Year Follow-Up. Braz. Oral Res. 2019, 33, e080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socransky, S.S.; Haffajee, A.D.; Cugini, M.A.; Smith, C.; Kent, R.L. Microbial Complexes in Subgingival Plaque. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1998, 25, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socransky, S.S.; Haffajee, A.D. Periodontal Microbial Ecology. Periodontology 2005, 38, 135–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Persson, G.R.; Pirih, F.Q.; Camargo, P.M. Peri-implant Health, Peri-implant Mucositis, and Peri-implantitis: Case Definitions and Diagnostic Considerations. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89, S304–S312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, G.R.; Renvert, S. Cluster of Bacteria Associated with Peri-Implantitis. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, J.; Nishimura, M.; Yamazaki, M.; Yoshida, K.; Kurashige, Y.; Saitoh, M.; Abiko, Y. Expression Profile of Drosomycin-like Defensin in Oral Epithelium and Oral Carcinoma Cell Lines. Arch. Oral Biol. 2013, 58, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Martin, I.; Doolittle-Hall, J.; Teles, R.P.; Patel, M.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Jung, R.E.; Teles, F.R.F. Exploring the Microbiome of Healthy and Diseased Peri-implant Sites Using Illumina Sequencing. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Tong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Si, M.; He, F. Microbial Profiles of Peri-implant Mucositis and Peri-implantitis: Submucosal Microbial Dysbiosis Correlates with Disease Severity. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2022, 33, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobi, M.; Stumpp, S.; Stiesch, M.; Eberhard, J.; Heuer, W. The Peri-Implant and Periodontal Microbiota in Patients with and without Clinical Signs of Inflammation. Dent. J. 2015, 3, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonhardt, Å.; Gröndahl, K.; Bergström, C.; Lekholm, U. Long-term Follow-up of Osseointegrated Titanium Implants Using Clinical, Radiographic and Microbiological Parameters. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2002, 13, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, V.; Nibali, L.; Spratt, D.; Dopico, J.; Mardas, N.; Petrie, A.; Donos, N. Peri-implant and Periodontal Microbiome Diversity in Aggressive Periodontitis Patients: A Pilot Study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 558–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mombelli, A.; van Oosten, M.A.C.; Schürch, E.; Lang, N.P. The Microbiota Associated with Successful or Failing Osseointegrated Titanium Implants. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 1987, 2, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, E.S.C.; Feres, M.; Figueiredo, L.C.; Shibli, J.A.; Ramiro, F.S.; Faveri, M. Microbiological Diversity of Peri-implantitis Biofilm by S Anger Sequencing. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2014, 25, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun Giok, K.; Menon, R.K. The Microbiome of Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review of Next-Generation Sequencing Studies. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogunseitan, O. Microbial Diversity; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; ISBN 9780632047086. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Xu, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, T.; Lin, J.; Chen, F. Subgingival Microbiome in Patients with Healthy and Ailing Dental Implants. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahrmann, P.; Gilli, F.; Wiedemeier, D.B.; Attin, T.; Schmidlin, P.R.; Karygianni, L. The Microbiome of Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.J.; Lee, W. Difference in Microbiome Compositions of Healthy Peri-Implant Sulcus and Peri-Implantitis Sulcus from the Same Patient. Heliyon 2023, 9, e20303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosio, F.; Amato, A.; Chiacchio, A.; Sisalli, L.; Giordano, F. Do Systemic Diseases and Medications Influence Dental Implant Osseointegration and Dental Implant Health? An Umbrella Review. Dent. J. 2023, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canullo, L.; Peñarrocha-Oltra, D.; Covani, U.; Rossetti, P. Microbiologic and Clinical Findings of Implants in Healthy Condition and with Peri-Implantitis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2015, 30, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Spirito, F.; Giordano, F.; Di Palo, M.P.; Cannatà, D.; Orio, M.; Coppola, N.; Santoro, R. Reliability and Accuracy of YouTube Peri-Implantitis Videos as an Educational Source for Patients in Population-Based Prevention Strategies. Healthcare 2023, 11, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisano, M.; Giordano, F.; Sangiovanni, G.; Capuano, N.; Acerra, A.; D’Ambrosio, F. The Interaction between the Oral Microbiome and Systemic Diseases: A Narrative Review. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 14, 1862–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D′Ambrosio, F.; Caggiano, M.; Acerra, A.; Pisano, M.; Giordano, F. Is Ozone a Valid Adjuvant Therapy for Periodontitis and Peri-Implantitis? A Systematic Review. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boccia, G.; Di Spirito, F.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Di Palo, M.P.; Giordano, F.; Amato, M. Local and Systemic Antibiotics in Peri-Implantitis Management: An Umbrella Review. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capuano, N.; Amato, A.; Dell’Annunziata, F.; Giordano, F.; Folliero, V.; Di Spirito, F.; More, P.R.; De Filippis, A.; Martina, S.; Amato, M.; et al. Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Application in Endodontics. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salerno, C.; Pascale, M.; Contaldo, M.; Esposito, V.; Busciolano, M.; Milillo, L.; Guida, A.; Petruzzi, M.; Serpico, R. Candida-Associated Denture Stomatitis. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2011, 16, e139–e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, M.; Romano, A.; Di Palo, M.P.; Baroni, A.; Serpico, R.; Contaldo, M. Oral Candidiasis in Adult and Pediatric Patients with COVID-19. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Chaparro, P.J.; Duarte, P.M.; Shibli, J.A.; Montenegro, S.; Lacerda Heluy, S.; Figueiredo, L.C.; Faveri, M.; Feres, M. The Current Weight of Evidence of the Microbiologic Profile Associated with Peri-Implantitis: A Systematic Review. J. Periodontol. 2016, 87, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthiban, S.; Ahmed, N.; Ramakrishnan, T.; Balakumar, V.; Raja, M.; Shekhar, H. Herpes Simplex 1 and Periopathogen Role in Peri-Implantitis. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract. 2017, 18, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vignoletti, F.; Discepoli, N.; Müller, A.; de Sanctis, M.; Muñoz, F.; Sanz, M. Bone Modelling at Fresh Extraction Sockets: Immediate Implant Placement versus Spontaneous Healing. An Experimental Study in the Beagle Dog. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2012, 39, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canullo, L.; Pesce, P.; Botticelli, D.; Covani, U.; Jankovic, S.; Jovanovic, T.; Rakic, M. What Is the Impact of Epstein-Barr Virus in Peri-Implant Infection? Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Spirito, F.; Caggiano, M.; Di Palo, M.P.; Contaldo, M.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Martina, S.; Amato, A. Oral Lesions in Pediatric Subjects: SARS-CoV-2 Infection and COVID-19 Vaccination. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pussinen, P.J.; Könönen, E.; Paju, S.; Hyvärinen, K.; Gursoy, U.K.; Huumonen, S.; Knuuttila, M.; Suominen, A.L. Periodontal Pathogen Carriage, Rather than Periodontitis, Determines the Serum Antibody Levels. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trombelli, L.; Farina, R.; Silva, C.O.; Tatakis, D.N. Plaque-induced Gingivitis: Case Definition and Diagnostic Considerations. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, S44–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mombelli, A. Microbial Colonization of the Periodontal Pocket and Its Significance for Periodontal Therapy. Periodontology 2018, 76, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheiham, A.; James, W.P.T. Diet and Dental Caries. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, D.R.; London, R.M. Restorative Design and Associated Risks for Peri-implant Diseases. Periodontology 2019, 81, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belibasakis, G.N.; Charalampakis, G.; Bostanci, N.; Stadlinger, B. Peri-Implant Infections of Oral Biofilm Etiology. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 830, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Belibasakis, G.N.; Manoil, D. Microbial Community-Driven Etiopathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wehrbein, H. Bone Quality in the Midpalate for Temporary Anchorage Devices. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, G.A.; Croce, D.E.D.; Casadoumecq, A.C.; Richard, S.B.; Takara, D. Characterization of the Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca-ATPase from Rabbit Temporalis Muscle. Arch. Oral Biol. 2012, 57, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Dahlin, C.; Jemt, T.; Sennerby, L.; Turri, A.; Wennerberg, A. Is Marginal Bone Loss around Oral Implants the Result of a Provoked Foreign Body Reaction? Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.W.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, S.; Li, S.K.; Zhang, C.; Chu, C.-H. Treatment Time for Non-Surgical Endodontic Therapy with or without a Magnifying Loupe. BMC Oral Health 2015, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakic, M.; Grusovin, M.; Canullo, L. The Microbiologic Profile Associated with Peri-Implantitis in Humans: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2016, 31, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Lamont, R.J. Beyond the Red Complex and into More Complexity: The Polymicrobial Synergy and Dysbiosis (PSD) Model of Periodontal Disease Etiology. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2012, 27, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorn, B.R.; Leung, K.-P.; Progulske-Fox, A. Invasion of Human Oral Epithelial Cells by Prevotella intermedia. Infect. Immun. 1998, 66, 6054–6057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostanci, N.; Belibasakis, G.N. Porphyromonas Gingivalis: An Invasive and Evasive Opportunistic Oral Pathogen. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 333, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apaydin, A.; Yazdirduyev, B.; Can, T.; Keklikoglu, N. Soft Tissue Changes during Distraction Osteogenesis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 40, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandu, A. Dental Implant Tourism: Author’s Reply. Aust. Dent. J. 2011, 56, 344–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisano, M.; Sangiovanni, G.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Romano, A.; Di Spirito, F. Oral Care in a Patient with Long Arm Deletion Syndrome of Chromosome 18: A Narrative Review and Case Presentation. Am. J. Case Rep. 2022, 23, e936142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caggiano, M.; Gasparro, R.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Pisano, M.; Di Palo, M.P.; Contaldo, M. Smoking Cessation on Periodontal and Peri-Implant Health Status: A Systematic Review. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ambrosio, F.; Pisano, M.; Amato, A.; Iandolo, A.; Caggiano, M.; Martina, S. Periodontal and Peri-Implant Health Status in Traditional vs. Heat-Not-Burn Tobacco and Electronic Cigarettes Smokers: A Systematic Review. Dent. J. 2022, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.; Di Spirito, F.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Boccia, G.; Moccia, G.; De Caro, F. Probiotics in Periodontal and Peri-Implant Health Management: Biofilm Control, Dysbiosis Reversal, and Host Modulation. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, M.; Di Spirito, F.; Martina, S.; Sangiovanni, G.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Iandolo, A. Intentional Replantation of Single-Rooted and Multi-Rooted Teeth: A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2022, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paduano, S.; Uomo, R.; Amato, M.; Riccitiello, F.; Simeone, M.; Valletta, R. Cyst-like periapical lesion healing in an orthodontic patient: A case report with five-year follow-up. G. Ital. Endod. 2013, 27, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengo, C.; Fiorino, A.; Cucchi, A.; Nappo, A.; Randellini, E.; Calamai, P.; Ferrari, M. Patient-reported outcomes and complication rates after lateral maxillary sinus floor elevation: A prospective study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 4431–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkhateeb, E.; Virtanen, S. Influence of Surface Self-modification in Ringer’s Solution on the Passive Behavior of Titanium. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2005, 75A, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata-Ali, J.; Candel-Marti, M.E.; Flichy-Fernandez, A.J.; Penarrocha-Oltra, D.; Balaguer-Martinez, J.; Penarrocha, M.A. Peri-Implantitis: Associated Microbiota and Treatment. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2011, 16, e937–e943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
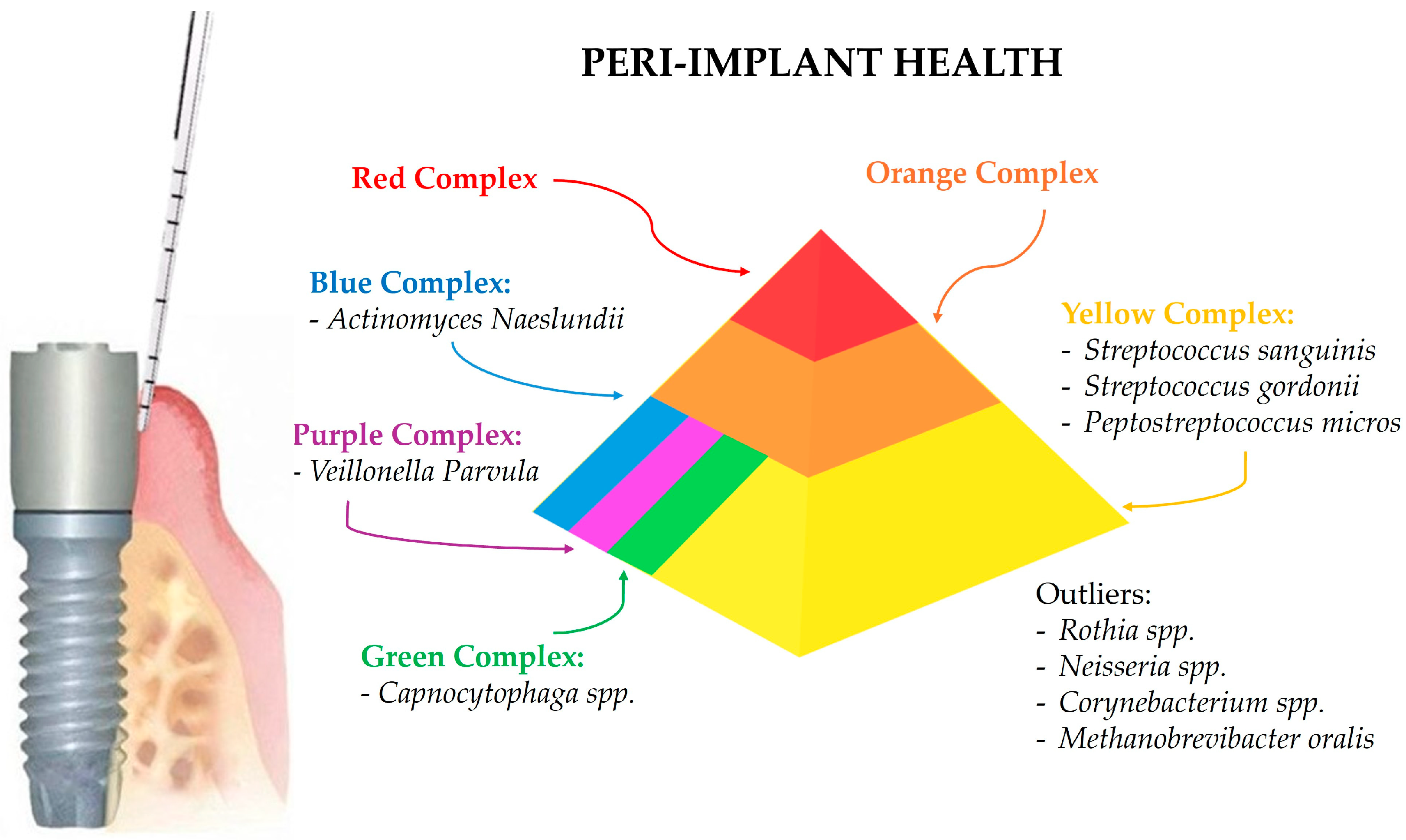
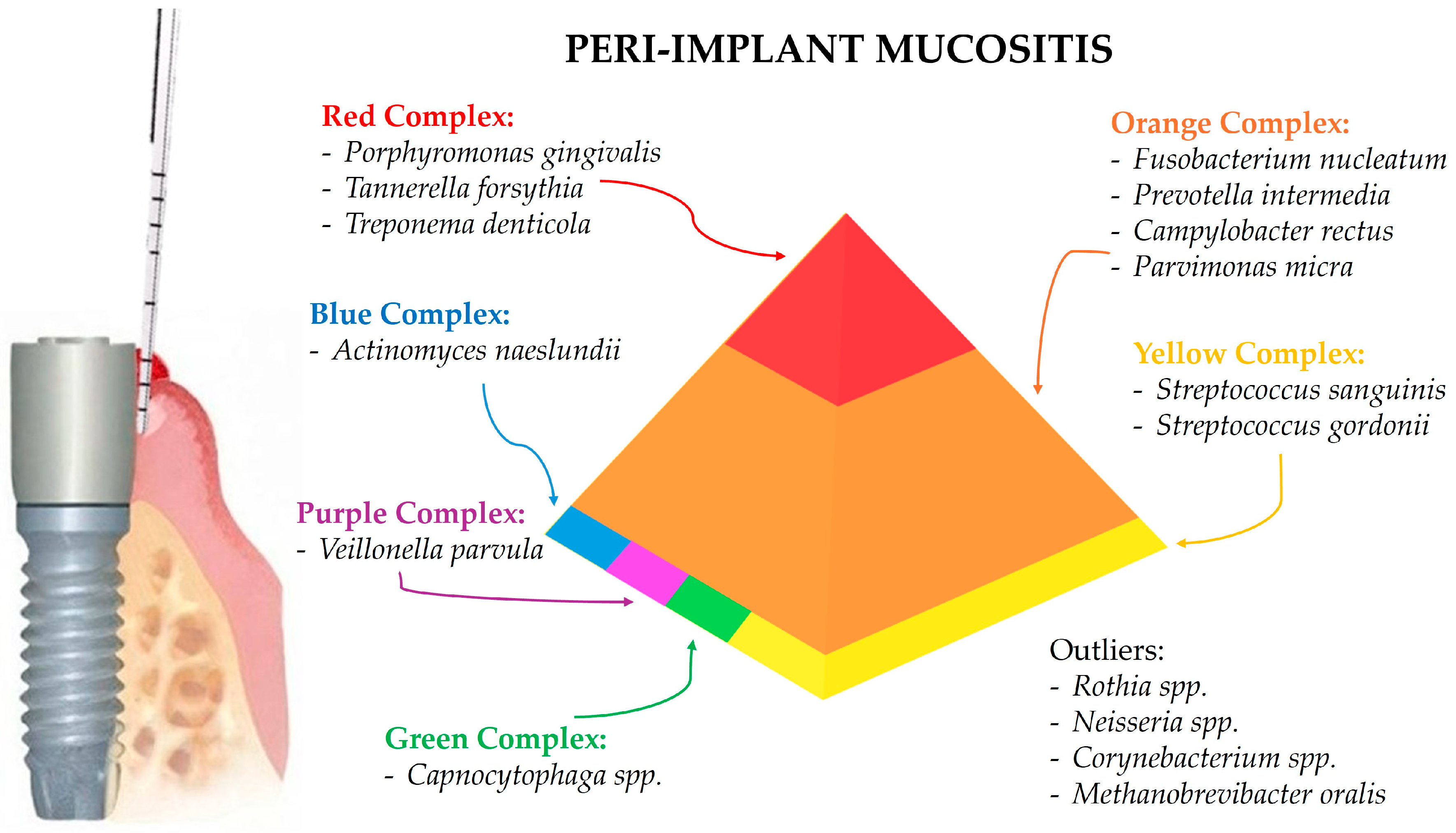
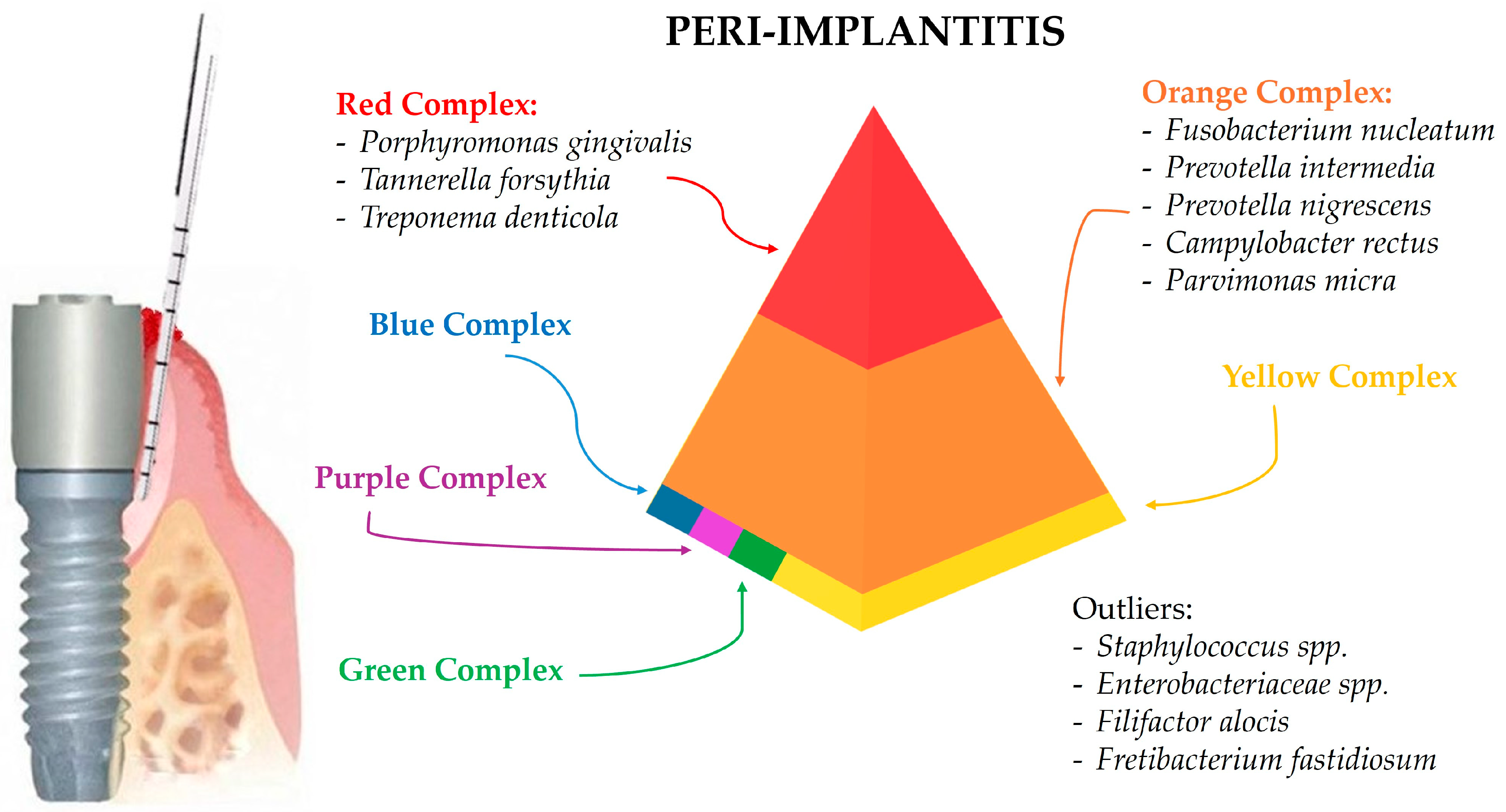
| Bacteria | Genus | Phylogenetic Tree | Features | Adherence and Toxin Production | Antimicrobial Susceptibility | Antibiotic Resistance | Role in Peri-Implant Health and Diseases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actinomyces naeslundii | Genus Actinomyces, family Actinomycetaceae | Closely related to Actinomyces oris and Actinomyces johnsonii | Anaerobic or microaerophilic, Gram-positive, rod-shaped, non-spore forming | Adheres to oral surfaces, contributing to initial biofilm formation | Susceptible to penicillin and other beta-lactam antibiotics | Generally low, but resistance can occur via beta-lactamase production | Associated with good oral health; early colonizer of dental biofilms, contributes to biofilm stability. |
| Campylobacter rectus | Genus Campylobacter, family Campylobacteraceae | Initially classified as Wolinella recta, reclassified based on rRNA analysis | Facultative anaerobe, Gram-negative, rod-shaped, motile | Adheres to periodontal tissues, forms biofilms, moves using a single flagellum | Susceptible to multiple antibiotic classes, including macrolides and beta-lactams | MD | Detected in peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis, contributing to the pathogenic microbial community. |
| Capnocytophaga | Genus Capnocytophaga, family Flavobacteriaceae | Part of the family Flavobacteriaceae | Capnophilic, anaerobic, Gram-negative, fusiform bacilli | Adheres to oral tissues, uses gliding motility for movement | Generally susceptible to antibiotics | Beta-lactam resistance due to beta-lactamase production | Generally associated with health or early stage disease; found in lower abundance in peri-implant mucositis. |
| Corynebacterium | Genus Corynebacterium, family Corynebacteriaceae | Related to genera like Mycobacterium and Streptomyces | Aerobic, some facultatively anaerobic, Gram-positive, rod-shaped | Produces toxins, adheres to epithelial cells | Susceptible to a range of antibiotics | Resistance varies, some strains producing beta-lactamase | Part of normal oral flora; found in healthy peri-implant sites and peri-implant mucositis, contributing to microbial diversity. |
| Enterobacteriaceae | Large family including genera like Escherichia and Salmonella | Part of the order Enterobacterales, class Gammaproteobacteria | Facultative anaerobes, Gram-negative, rod-shaped | Adheres to intestinal cells using fimbriae, some produce exotoxins | Varies widely among species | Common, with many strains producing beta-lactamase or other mechanisms | Includes opportunistic pathogens found in peri-implantitis; contribute to complex biofilm and disease progression. |
| Fusobacterium nucleatum | Genus Fusobacterium, family Fusobacteriaceae | Part of the phylum Fusobacteriota | Obligate anaerobe, Gram-negative, rod-shaped | Adheres to gingival and other epithelial cells, invades endothelial cells | Generally susceptible to metronidazole and beta-lactams | Resistance to some antibiotics reported | Found in peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis, plays a significant role in biofilm formation and disease progression. |
| Neisseria | Genus Neisseria, family Neisseriaceae | Part of the family Neisseriaceae within the phylum Proteobacteria | Aerobic, oxidase-positive, Gram-negative, diplococci | Adheres to mucosal surfaces using pili, produces LOS (lipooligosaccharide) | Varies, some strains showing resistance | Resistance to penicillin, ciprofloxacin, and others due to beta-lactamase | Abundant in healthy peri-implant sites; more prevalent in peri-implant mucositis, indicating involvement in early inflammation. |
| Parvimonas micra | Genus Parvimonas, family Peptostreptococcaceae | Related to other anaerobic Gram-positive cocci | Anaerobic, Gram-positive, coccus-shaped | Adheres to oral and systemic tissues, contributing to abscess formation | Generally susceptible to beta-lactam antibiotics | MD | Frequently associated with peri-implantitis and peri-implant mucositis, involved in early disease stages. |
| Peptostreptococcus | Genus Peptostreptococcus, family Peptostreptococcaceae | Related to other anaerobic Gram-positive cocci | Anaerobic, Gram-positive, small spherical cells | Can form part of mixed infections | Susceptible to beta-lactam antibiotics | Increasing resistance to antimicrobial drugs reported | Present in lower abundance in healthy peri-implant sites; typically found in higher levels in peri-implantitis sites. |
| Porphyromonas gingivalis | Genus Porphyromonas, family Porphyromonadaceae | Part of the Bacteroidota phylum | Anaerobic, Gram-negative, rod-shaped | Adheres to gingival epithelial cells, invades host cells, forms biofilms | Susceptible to metronidazole and other antibiotics | MD | Strongly associated with peri-implantitis; found in peri-implant mucositis, contributing to inflammation and tissue damage. |
| Prevotella intermedia | Genus Prevotella, family Prevotellaceae | Part of the Bacteroidota phylum | Anaerobic, Gram-negative, rod-shaped | Adheres to oral tissues, contributing to inflammation and tissue destruction | Susceptible to various antibiotics | MD | Detected in peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis, contributes to inflammatory response. |
| Prevotella nigrescens | Genus Prevotella, family Prevotellaceae | Part of the Bacteroidota phylum | Anaerobic, Gram-negative, rod-shaped | Adheres to oral tissues, contributing to inflammation and disease | Susceptible to various antibiotics | MD | Often found in peri-implant diseases, triggers immune responses leading to periodontal disease. |
| Rothia | Genus Rothia, family Micrococcaceae | Part of the family Micrococcaceae | Aerobic, Gram-positive, rod-shaped, non-motile | Adheres to oral and gut tissues | Generally susceptible to antibiotics | MD | Associated with oral health; present in healthy peri-implant sites and peri-implant mucositis, suggests role in transition from health to disease. |
| Treponema denticola | Genus Treponema, family Spirochaetaceae | Part of the Spirochaetes phylum, closely related to Treponema pallidum | Anaerobic, Gram-negative, spirochete, motile | Adheres to gingival fibroblasts, invades host cells, produces cytotoxic effects | Generally susceptible to antibiotics | MD | Highly proteolytic; part of the red complex, associated with peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis. |
| Tannerella forsythia | Genus Tannerella, family Bacteroidaceae | Part of the Bacteroidota phylum | Anaerobic, Gram-negative, rod-shaped | Adheres to periodontal tissues, contributing to inflammation and tissue destruction | Generally susceptible to antibiotics | MD | Part of the red complex; found in peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis, involved in inflammatory process. |
| Veillonella parvula | Genus Veillonella, family Veillonellaceae | Part of the Negativicutes class within the Firmicutes phylum | Anaerobic, Gram-negative, coccus-shaped | Adheres to oral tissues, forms biofilms with Streptococcus species | Susceptible to metronidazole, penicillin, cephalosporins, clindamycin, and chloramphenicol | Reports of resistance to various antibiotics in different countries | Part of normal oral flora; involved in early biofilm formation, present in peri-implant mucositis. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Spirito, F.; Giordano, F.; Di Palo, M.P.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Scognamiglio, B.; Sangiovanni, G.; Caggiano, M.; Gasparro, R. Microbiota of Peri-Implant Healthy Tissues, Peri-Implant Mucositis, and Peri-Implantitis: A Comprehensive Review. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12061137
Di Spirito F, Giordano F, Di Palo MP, D’Ambrosio F, Scognamiglio B, Sangiovanni G, Caggiano M, Gasparro R. Microbiota of Peri-Implant Healthy Tissues, Peri-Implant Mucositis, and Peri-Implantitis: A Comprehensive Review. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(6):1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12061137
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Spirito, Federica, Francesco Giordano, Maria Pia Di Palo, Francesco D’Ambrosio, Bruno Scognamiglio, Giuseppe Sangiovanni, Mario Caggiano, and Roberta Gasparro. 2024. "Microbiota of Peri-Implant Healthy Tissues, Peri-Implant Mucositis, and Peri-Implantitis: A Comprehensive Review" Microorganisms 12, no. 6: 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12061137
APA StyleDi Spirito, F., Giordano, F., Di Palo, M. P., D’Ambrosio, F., Scognamiglio, B., Sangiovanni, G., Caggiano, M., & Gasparro, R. (2024). Microbiota of Peri-Implant Healthy Tissues, Peri-Implant Mucositis, and Peri-Implantitis: A Comprehensive Review. Microorganisms, 12(6), 1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12061137









