Antibiotic Susceptibility Profiles of Bacterial Isolates Recovered from Abscesses in Cattle and Sheep at a Slaughterhouse in Algeria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Origin of Isolates
2.2. Microbiological Methods
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and MIC Determination
2.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatic Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Number
3. Results
3.1. Abscess Characteristics
3.2. Bacterial Isolates
3.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
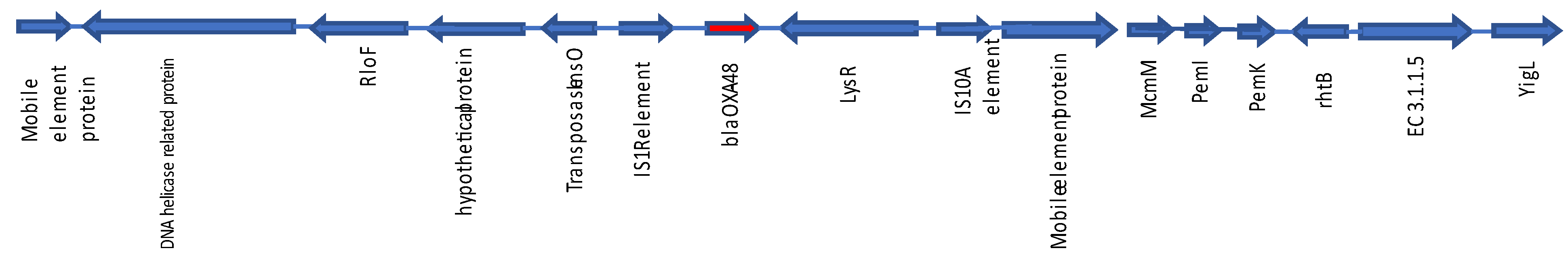
3.4. Resistome, MLST, Plasmidome, and O-Serogroups
3.5. Virulome
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Misk, T.N.; El-Sherry, T.; Misk, N.A. Retrospective study on body surface abscesses in farm animals. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2020, 66, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariappan, S.; Mydeen, S.N.M.; Samuel, S.J.R.; Jegathambigai, J.; Rajan, K.E.; Sudhakar, S. Bacillus sp. Causing Abscessation in Sheep and Goat Population. Curr. Sci. 2012, 103, 921–925. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, A.; Awadin, W.F. Pathological and bacteriological studies on some recorded internal abscesses in slaughtered cattle. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2016, 63, 52–61. [Google Scholar]
- Nagati, S.F.; El Shafii, S.S.A.; Abd El Mawgoud, S.R.A. Effectiveness of Disinfectants on Environmental Multidrug Resistance Contaminants Causing Skin Abscess in Farm Animals. Am. J. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2021, 16, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavassoli, M.; Imani, A.; Yousefnia, M.; Tukmechi, A.; Tajik, H. Bacteria associated with subcutaneous abscesses of cattle caused by Hypoderma spp. larvae in north of Iran. Vet. Res. Forum 2010, 1, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- AL-Tuffyli, Y.K.; Shekhan, M.I. Clinical and Bacteriological Study of Subcutaneous Abscesses Caused by Gram Positive Bacteria in Cow and Sheep in Al-Qadissiyia Province. Al-Qadisiyah J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2012, 11, 17–24. [Google Scholar]
- Ninios, T.; Lundén, J.; Korkeala, H.; Fredriksson-Ahomaa, M. Meat Inspection and Control in the Slaughter House, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2014; pp. 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Aljameel, M.A.; Halima, M.O.; ElTigani-Asil, E.A.; El-Eragi, A.M. Bacteriological and histopathological studies on pulmonary abscesses in camels (Camelus dromedarius) slaughtered at Nyala Slaughterhouse, South Darfur State, Sudan. J. Vet. Med. Anim. Prod. 2013, 4, 26–38. [Google Scholar]
- Herenda, D.; Chambers, P.G.; Ettriqui, A.; Seneviratna, P.; Da Silva, T.J.P. Manuel on Meat Inspection for Developing Countries; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1994; pp. 58–60. [Google Scholar]
- Buba, D.M.; Gurumyen, G.Y.; Oragwa, O.A.; Oziegbe, S.D.; Patrobas, M.N.; Dunka, H.I. Retrospective Analysis of Cutaneous Abscess in Cattle, Goats and Pigs Slaughtered at the Jos Abattoir, Nigeria. Sokoto J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 17, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-nakeeb, N.K.; HameedAl-Fetly, D.R. Anaerobic Bacterial Isolation with Histopatholgical Exam of Liver Abscesses in Cattle, Sheep, and Camels in Al-Qadisiyah Province. Al-Qadisiyah J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2016, 15, 40–46. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, C.; Sauermann, R.; Joukhadar, C. Principles of Antibiotic Penetration into Abscess Fluid. Pharmacology 2006, 78, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alloui, M.N.; Kaba, J.; Alloui, N. Prevalence and risk factors of caseous lymphadenitis in sheep and goats of Batna area (Algeria). Res. Opin. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2011, 1, 162–164. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, A.; Monteiro, J.M.; Vieira-Pinto, M. The Importance of Subcutaneous Abscess Infection by Pasteurella spp. and Staphylococcus aureus as a Cause of Meat Condemnation in Slaughtered Commercial Rabbits. World Rabbit. Sci. 2014, 22, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadi, C. Les Motifs de Saisie des Viandes Rouges et Abats les Plus Fréquents au Niveau de L’abattoir de Frère Ben Aissa Biskra. Master’s Thesis, University Mohamed Khider Biskra, Biskra, Algeria, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Palacios, P.; Girlich, D.; Soraa, N.; Lamrani, A.; Maoulainine, F.M.R.; Bennaoui, F.; Amri, H.; El Idrissi, N.S.S.; Bouskraoui, M.; Birer, A.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant Enterobacterales Responsible for Septicaemia in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit in Morocco. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2023, 33, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubert, D.; Naas, T.; Héritier, C.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Functional Characterization of IS1999, an IS4 Family Element Involved in Mobilization and Expression of β-Lactam Resistance Genes. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 6506–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnin, R.A.; Nordmann, P.; Carattoli, A.; Poirel, L. Comparative Genomics of IncL/M-Type Plasmids: Evolution by Acquisition of Resistance Genes and Insertion Sequences. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferriol-González, C.; Domingo-Calap, P. Phage Therapy in Livestock and Companion Animals. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Qi, J.F.; Qin, R.; Ding, K.; Graham, D.W.; Zhu, Y.G. Intensified Livestock Farming Increases Antibiotic Resistance Genotypes and Phenotypes in Animal Feces. Commun. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatem, M.E.; Arab, R.H.; Ata, S. Nagwa Bacterial Abscessationin Sheep and Goat in Giza Governorate with Full Antibiogram Screening. Glob. Vet. 2013, 10, 372–381. [Google Scholar]
- Tamai, I.A.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Mahmoodi, P.; Pakbin, B.; Salehi, T.Z. Antimicrobial Susceptibility, Virulence Genes and Genomic Characterization of Trueperella Pyogenes Isolated from Abscesses in Dairy Cattle. Res. Vet. Sci. 2023, 154, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.M.; Martins, T.O.; Procópio, D.P. Economic Loss from the Main Causes of Whole Bovine Carcass Condemnation in Slaughterhouses Supervised by the Federal Inspection Service in São Paulo State from 2010 to 2019. Acta Sci. 2022, 44, e55220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, K.B. Prevalence and Etiology of Abscess Disease of Sheep and Goats at Qassim Region, Saudi Arabia. Vet. World 2011, 4, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar Ali, A.S.; Mohammed, Z.M.A. Gross and Histopathological Findings on Lung Abscesses in Slaughtered Sheep in Libya. Eur. J. Vet. Med. 2023, 3, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcvey, D.S.; Kennedy, M.; Chengappa, M.M. Veterinary Microbiology, 3rd ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2013; pp. 184–194. [Google Scholar]
- Madhav Mugale, N.; Balachandran, C.; Dillibabu, V.; Kirubharan, J.; Dhinakar Raj, G.; Sridhar, R.; Selvasubramaniam, S. Hepatic Abscess in Sheep and Goat Caused by O26 Escherichia Coli Serotype: An Emerging Pathogen. Indian Vet. J. 2015, 92, 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Anbagi, N.A. Isolaton and Identification some bacterial causes of lung abscesses sheep by chromogenic media. Basrah J. Vet. Res. 2016, 15, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didkowska, A.; Żmuda, P.; Kwiecień, E.; Rzewuska, M.; Klich, D.; Wędzina, M.K.; Witkowski, L.; Żychska, M.; Kaczmarkowska, A.; Orłowska, B.; et al. Microbiological Assessment of Sheep Lymph Nodes with Lymphadenitis Found during Post—Mortem Examination of Slaughtered Sheep: Implications for Veterinary—Sanitary Meat Control. Acta Vet. Scand. 2020, 62, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haenni, M.; Lupo, A.; Madec, J.-Y. Résistance Aux Carbapénèmes Chez Les Animaux En l’absence d’usage. Bull. Acad. Vet. Fr. 2018, 171, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S. The Crisis of Carbapenemase-Mediated Carbapenem Resistance across the Human–Animal–Environmental Interface in India. Infect. Dis. Now 2023, 53, 104628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Castillo, F.Y.; Guerrero-Barrera, A.L.; Avelar-González, F.J. An Overview of Carbapenem-Resistant Organisms from Food-Producing Animals, Seafood, Aquaculture, Companion Animals, and Wildlife. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1158588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norizuki, C.; Kawamura, K.; Wachino, J.I.; Suzuki, M.; Nagano, N.; Kondo, T.; Arakawa, Y. Detection of Escherichia coli Producing CTX-M-1-Group Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamases from Pigs in Aichi Prefecture, Japan, between 2015 and 2016. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 71, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naas, T.; Dabos, L.; Bonnin, R.A. β-Lactamase Genes without Limits. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madec, J.Y.; Haenni, M.; Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase/AmpC- and Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Animals: A Threat for Humans? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uyanik, T.; Çadirci, Ö.; Gücükoğlu, A.; Can, C. Investigation of Major Carbapenemase Genes in ESBL-Producing Escherichia Coli and Klebsiella Pneumoniae Strains Isolated from Raw Milk in Black Sea Region of Turkey. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 128, 105315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaici, L.; Haenni, M.; Saras, E.; Boudehouche, W.; Touati, A.; Madec, J.Y. Bla NDM-5-Carrying IncX3 Plasmid in Escherichia Coli ST1284 Isolated from Raw Milk Collected in a Dairy Farm in Algeria. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2671–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loucif, L.; Chelaghma, W.; Bendjama, E.; Cherak, Z.; Khellaf, M.; Khemri, A.; Rolain, J.M. Detection of blaOXA-48 and mcr-1 Genes in Escherichia Coli Isolates from Pigeon (Columba livia) in Algeria. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loucif, L.; Chelaghma, W.; Cherak, Z.; Bendjama, E.; Beroual, F.; Rolain, J.M. Detection of NDM-5 and MCR-1 Antibiotic Resistance Encoding Genes in Enterobacterales in Long-Distance Migratory Bird Species Ciconia ciconia, Algeria. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 814, 152861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamprecht, A.; Sommer, J.; Willmann, M.; Brender, C.; Stelzer, Y.; Krause, F.F.; Tsvetkov, T.; Wild, F.; Riedel-Christ, S.; Kutschenreuter, J.; et al. Pathogenicity of Clinical OXA-48 Isolates and Impact of the OXA-48 IncL Plasmid on Virulence and Bacterial Fitness. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.; Gibbon, M.J.; Couto, N.; Kakar, K.; Habib, S.; Samad, A.; Munir, A.; Fatima, F.; Mohsin, M.; Feil, E.J. The Diversity, Resistance Profiles and Plasmid Content of Klebsiella spp. Recovered from Dairy Farms Located around Three Cities in Pakistan. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenk, S.; Rakovitsky, N.; Temkin, E.; Schechner, V.; Cohen, R.; Kloyzner, B.S.; Schwaber, M.J.; Solter, E.; Cohen, S.; Stepansky, S.; et al. Investigation of Outbreaks of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae in Three Neonatal Intensive Care Units Using Whole Genome Sequencing. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepuschitz, S.; Schill, S.; Stoeger, A.; Pekard-Amenitsch, S.; Huhulescu, S.; Inreiter, N.; Hartl, R.; Kerschner, H.; Sorschag, S.; Springer, B.; et al. Whole genome sequencing reveals resemblance between ESBL-producing and carbapenem resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates from Austrian rivers and clinical isolates from hospitals. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordmann, P.; Poirel, L. Strategies for Identification of Carbapenemase-Producing Enterobacteriaceae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 487–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirel, L.; Bonnin, R.A.; Nordmann, P. Genetic Features of the Widespread Plasmid Coding for the Carbapenemase OXA-48. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickx, A.P.A.; Landman, F.; de Haan, A.; Witteveen, S.; van Santen-Verheuvel, M.G.; Schouls, L.M. blaOXA-48-like Genome Architecture among Carbapenemase-Producing Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae in The Netherlands. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 000512. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Kim, Y.B.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Global Dissemination of Carbapenemase-Producing Klebsiella Pneumoniae: Epidemiology, Genetic Context, Treatment Options, and Detection Methods. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mairi, A.; Pantel, A.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.P.; Touati, A. OXA-48-like Carbapenemases Producing Enterobacteriaceae in Different Niches. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 37, 587–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, R.; Marchandin, H.; Chanal, C.; Sirot, D.; Labia, R.; De Champs, C.; Jumas-Bilak, E.; Sirot, J. Chromosome-Encoded Class D β-Lactamase OXA-23 in Proteus Mirabilis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2004–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyrouthy, R.; Robin, F.; Delmas, J.; Gibold, L.; Dalmasso, G.; Dabboussi, F.; Hamzé, M.; Bonnet, R. IS1R-Mediated Plasticity of IncL/M Plasmids Leads to the Insertion of BlaOXA-48 into the Escherichia Coli Chromosome. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3785–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venugopal, N.; Mitra, S.; Tewari, R.; Ganaie, F.; Shome, R.; Rahman, H.; Shome, B.R. Molecular Detection and Typing of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus and Methicillin-Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Cattle, Animal Handlers, and Their Environment from Karnataka, Southern Province of India. Vet. World 2019, 12, 1760–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaher, H.A.; El Baz, S.; Alothaim, A.S.; Alsalamah, S.A.; Alghonaim, M.I.; Alawam, A.S.; Eraqi, M.M. Molecular Basis of Methicillin and Vancomycin Resistance in Staphylococcus Aureus from Cattle, Sheep Carcasses and Slaughterhouse Workers. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.; Araújo, S.; Monteiro, A.; Eira, J.; Pereira, J.E.; Maltez, L.; Igrejas, G.; Lemsaddek, T.S.; Poeta, P. Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA in Livestock: Antimicrobial Resistance and Genetic Lineages. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouiller, K.; Bertrand, X.; Hocquet, D.; Chirouze, C. Human Infection of Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus aureus CC398: A Review. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonvegna, M.; Grego, E.; Sona, B.; Stella, M.C.; Nebbia, P.; Mannelli, A.; Tomassone, L. Occurrence of Methicillin-Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci (Mrcons) and Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from Pigs and Farm Environment in Northwestern Italy. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chajęcka-Wierzchowska, W.; Gajewska, J.; Zadernowska, A.; Randazzo, C.L.; Caggia, C. A Comprehensive Study on Antibiotic Resistance among Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci (CoNS) Strains Isolated from Ready-to-Eat Food Served in Bars and Restaurants. Foods 2023, 12, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chenouf, N.S.; Mama, O.M.; Messaï, C.R.; Ruiz-Ripa, L.; Fernández-Fernández, R.; Carvalho, I.; Zitouni, A.; Hakem, A.; Torres, C. Detection of Methicillin-Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci and PVL/MecA Genes in Cefoxitin-Susceptible Staphylococcus Aureus (T044/ST80) from Unpasteurized Milk Sold in Stores in Djelfa, Algeria. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 2684–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, K.; Zhang, Y. Multidrug-Resistant Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci in Food Animals. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujňáková, D.; Puvača, N.; Ćirković, I. Virulence factors and antibiotic resistance of enterobacterales. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakbin, B.; Brück, W.M.; Rossen, J.W. Virulence factors of enteric pathogenic Escherichia coli: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaalal, N.; Touati, A.; Bakour, S.; Aissa, M.A.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Pantel, A. Spread of OXA-48 and NDM-1-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae ST48 and ST101 in Chicken Meat in Western Algeria. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, M.; Brooks, B.D.; Brooks, A.E. The complex relationship between virulence and antibiotic resistance. Genes 2017, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beceiro, A.; Tomás, M.; Bou, G. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence: A successful or deleterious association in the bacterial world? Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 185–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranda-Estrada, L.I.; Ruíz-Rosas, M.; Molina-López, J.; Parra-Rojas, I.; González-Villalobos, E.; Castro-Alarcón, N. Relationship between virulence factors, resistance to antibiotics and phylogenetic groups of uropathogenic Escherichia coli in two locations in Mexico. Enfermedades Infecc. Microbiol. Clin. (Engl. Ed.) 2017, 35, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, G.; Santos, M.L.; Ramalho, J.F.; Duarte, A.; Caneiras, C. Virulence factors in carbapenem-resistant hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1325077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sheep | Cattle | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | Months | 2 Years | Years | ||
| Male | 97 | / | 18 | / | 1 |
| Female | / | 3 | / | 3 | 1 |
| Pus Characteristics | Staphylococcus aureus | Staphylococcus Coagulase negative | Aeromonas spp. | Bacillus spp. | Enterobacterales | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | ||||||
| Consistency | Grumbling viscous Homogeneous viscous | Homogeneous viscous Homogeneous fluid | Homogeneous viscous Thick homogeneous | Homogeneous viscous Thick homogeneous | Grumbling fluid Grumbling viscous Homogeneous fluid Homogeneous viscous Thick grumbling Thick homogeneous Viscous grumbling hemorrhagic | |
| Color | White Light yellow | Light yellow Yellow white Green | Green White Yellow | Green Yellow | Green White Yellow | |
| Odor | Fade | Fade | Fade | Fade | Nauseating Fade | |
| Bacterial Species | Animal Species | Total | Percentage (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sheep | Cattle | |||
| Escherichia coli | 56 | 14 | 70 | 61.3% |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 5 | 2 | 7 | 6.1% |
| Aeromonas veronii | 3 | 3 | 6 | 5.2% |
| Aeromonas hydrophila | 1 | 3 | 4 | 3.5% |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | 3 | 3 | 2.6% | |
| Morganella morganii | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2.6% |
| Staphylococcus epidermidis | 3 | 3 | 2.6% | |
| Klebsiella oxytoca | 2 | 2 | 1.7% | |
| Citrobacter brackii | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Citrobacter freundii | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Enterobacter spp. | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Serratia marcescens | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Proteus vulgaris | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Lelliottia spp. | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Staphylococcus lentus | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Staphylococcus cohnii | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Staphylococcus simulans | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Staphylococcus pasteuri | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Staphylococcus vitulinus | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Aeromonas bestiarum | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Aeromonas salmonicida | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Aeromonas eucrenophila | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Bacillus cereus | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Bacillus mojavensis | 1 | 1 | 0.9% | |
| Total | 91 | 23 | 114 | 100% |
| Antimicrobial (s) | K. pneumoniae O103B2 * | K. pneumoniae O103B1 * | E. coli O103A10 * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amoxicillin | >32 (R) | >32 (R) | >32 (R) |
| Amoxicillin + CLA | >128 (R) | >128 (R) | >128 (R) |
| Ticarcillin | >32 (R) | >32 (R) | <4 (S) |
| Piperacillin | >32 (R) | >32 (R) | <4 (S) |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | >32 (R) | >32 (R) | <4 (S) |
| Temocillin | 256(R) | 256 (R) | 512 (R) |
| Tigecycline | 1 (R) | 1 (R) | 1 (R) |
| Ceftazidime | 16 (R) | 16 (R) | 0.25 (S) |
| Ceftazidime/Avibactam | 0.25 (S) | 0.25 (S) | 0.25 (S) |
| Cefotaxime | 8 (R) | 8 (R) | 0.5 (S) |
| Ceftolozane/Tazobactam | 16 (R) | 16 (R) | 0.5 (S) |
| Cefepime | 8 (I) | 8 (I) | 0.5 (S) |
| Cefiderocol | 1 (S) | 1 (S) | 0.12 (S) |
| Aztreonam | 16 (R) | 16 (R) | 0.12 (S) |
| Imipenem | 1 (S) | 1 (S) | 0.5 (S) |
| Imipenem/Relebactam | 0.5 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 0.25 (S) |
| Meropenem | 0.5 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 0.12 (S) |
| Meropenem/Vaborbactam | 0.5 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 0.12 (S) |
| Ertapenem | 2 (R) | 2 (R) | 0.5 (S) |
| Ciprofloxacin | 2 (R) | 2 (R) | 0.12 (S) |
| Tobramycin | 8 (R) | 8 (R) | 1 (S) |
| Levofloxacin | 0.5 (S) | 1 (I) | 0.25 (S) |
| Colistin | 0.5 (S) | 0.5 (S) | 0.5 (S) |
| Isolates 1 | Clinical Features | MLST | Serotype | Antibiotic Resistance Genes | Point Mutations | Plasmid Replicon | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta-Lactam | Aminoglycosides | Quinolones | Various | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Animal 2 | Site 3 | Date of Isolation 4 | blaCTX-M-15 | blaSHV-187 | blaTEM-1B | blaTEM-1C | blaOXA-48 | blaOXA-1 | aadA1 | aadA2b | aac(6′)-Ib-cr | aph(3′)-Ia | aph(6)-Id | aph(3″)-Ib | qnrB1 | qnrS1 | sul2 | sul3 | dfrA14 | fosA | tet(A) | tet(B) | catB3 | mph(B) | sitABCD | cmlA1 | IncY | Col | Col156 | IncFIA | IncFIB | IncFII | ColRNAI | IncFIB(K) | IncFII(K) | IncL | ||||
| Ec O103A9 | S | PR | 23/04 | ST1706 | O116:H8 | acrR parC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O103A10 | S | LN | 12/03 | ST10 | O8:H10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kp O103B1 | S | PR | 28/05 | ST985 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kp O103B2 | S | LN | 29/05 | ST985 | acrR ompK36 ompK37 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O104G3 | C | Li | 21/05 | ST88 | O8:H17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O104G4 | S | Li | 16/06 | ST101 | O153:H21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O104G5 | S | Li | 21/05 | ST224 | O42:H8 | gyrA parE parC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O104G6 | C | PR | 09/03 | ST155 | O23:H21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O104G7 | S | L | 22/05 | ST223 | O:123:H21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O104G8 | S | PR | 06/03 | ST206 | O144:H5 | parC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O104H4 | C | L | 28/05 | Unknown | O37:H12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Isolates 1 | Clinical Features | MLST | Antibiotic Resistance Genes | Virulence Factors | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beta-lactams | Aminoglycosides | Fosfomycin | Fusidic acid | Tetracycline | Erythromycin | Adherence | Enzyme | Immune Evasion | Toxin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Animal 2 | Site 3 | Date of Isolation 4 | blaZ | mecA | ant(6) | aph(3′) | fosB | fusB | tet(K) | erm(T) | ebp | sdrC | sdrG | icaA,B,C | hlg | luk D,E | sak | spl | sspA | sspB | sspC | geh | lip | aur | nuc | capB | scn | hlb | sec | sea | sel | cylR2 | ||
| Sepi O104F3 | S | PR | 23/04 | ST61 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spas O104G1 | S | NK | 21/05 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sa O104F4 | S | LN | 18/06 | ST522 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sa O104F5 | C | Li | 21/04 | Unk | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sa O104F6 | S | NK | 24/02 | ST522 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sa O104F7 | S | LN | 06/03 | ST700 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sa O104F8 | C | L | 29/05 | ST97 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sa O104F9 | S | LN | 05/03 | ST700 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sa O104F10 | S | LN | 05/05 | ST398 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Virulence Factors | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria 1 | Animal 2 | Site 3 | MLST | Various | Hemolysin | Type 3 Fimbriae | Type 1 Fimbriae | Type IV Pili | Ent Siderophore | Salmochelin | Aerobactin | Yersiniabactin | Two-component Regulatory System | T6SS | Stb | Ferrous iron Transport | AcrAB | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| fimH | F17 A,C,D,G | ompT | terC | csgA | traT | traJ | cia | cvaC | etsC | gad | lpfA | mchF | mchC | nlpI | papC | tia | yeh A,B,C,D | cma | espI | iha | iss | hra | AslA | colE2- like | hlyF | mrkA-J | fimA-K | pilW | entA-F | entS | fepA-D | fepE | fes | iroE | iroN | iutA | iucC | irp1-2 | ybtA, E, Q, S, T, U, X | fyuA | rcsA | rcsB | 23 genes | stbA-D | sit A | sitD | sitC | AcrAB | acrB | ||||
| Ec O103A9 | S | PR | ST1706 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O103A10 | S | LN | ST10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kp O103B1 | S | PR | ST985 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kp O103B2 | S | LN | ST985 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O104G3 | C | Li | ST88 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O104G4 | S | Li | ST101 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O104G5 | S | Li | ST224 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O104G6 | C | PRC | ST155 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O104G7 | S | L | ST223 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O104G8 | S | PR | ST206 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ec O104H4 | C | L | Unk | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yousfi, C.; Oueslati, S.; Daaboul, D.; Girlich, D.; Proust, A.; Bentchouala, C.; Naas, T. Antibiotic Susceptibility Profiles of Bacterial Isolates Recovered from Abscesses in Cattle and Sheep at a Slaughterhouse in Algeria. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030524
Yousfi C, Oueslati S, Daaboul D, Girlich D, Proust A, Bentchouala C, Naas T. Antibiotic Susceptibility Profiles of Bacterial Isolates Recovered from Abscesses in Cattle and Sheep at a Slaughterhouse in Algeria. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(3):524. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030524
Chicago/Turabian StyleYousfi, Chahrazed, Saoussen Oueslati, Dina Daaboul, Delphine Girlich, Alexis Proust, Chafia Bentchouala, and Thierry Naas. 2024. "Antibiotic Susceptibility Profiles of Bacterial Isolates Recovered from Abscesses in Cattle and Sheep at a Slaughterhouse in Algeria" Microorganisms 12, no. 3: 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030524
APA StyleYousfi, C., Oueslati, S., Daaboul, D., Girlich, D., Proust, A., Bentchouala, C., & Naas, T. (2024). Antibiotic Susceptibility Profiles of Bacterial Isolates Recovered from Abscesses in Cattle and Sheep at a Slaughterhouse in Algeria. Microorganisms, 12(3), 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12030524







