Bacillus subtilis PE7-Mediated Alleviation of Phosphate Starvation and Growth Promotion of Netted Melon (Cucumis melo L. var. reticulatus Naud.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microbial Strains, Culture Conditions, and Inoculum Preparation
2.2. Quantitative Analysis of P-Solubilizing Activity of B. subtilis PE7 by UV Spectrophotometry and Detection of Organic Acids by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.3. Phytase Activity on Agar Medium
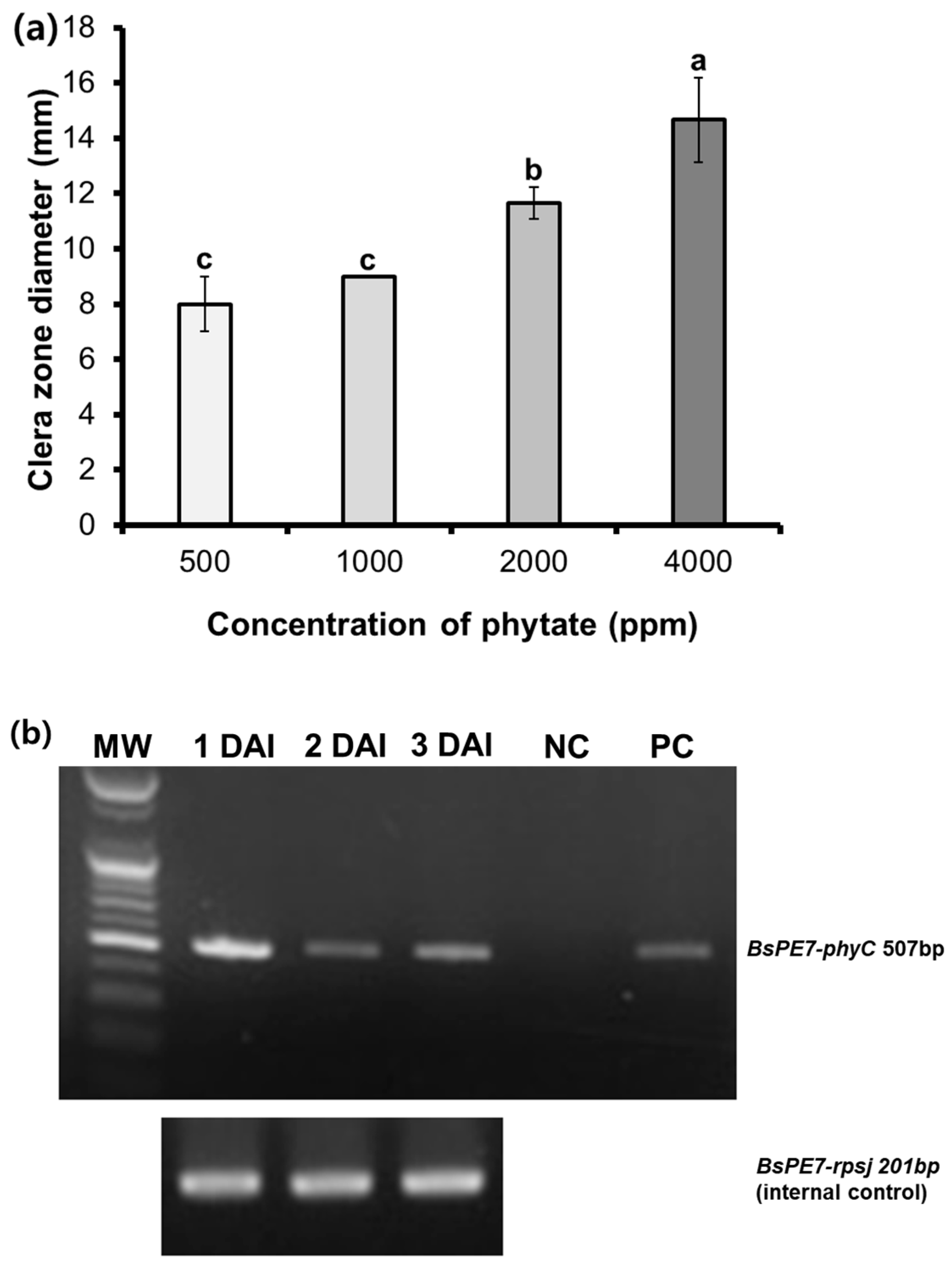
2.4. Phytase Gene Expression Analysis
2.5. Effect of Different Concentrations of KH2PO4 on Biofilm Formation
2.6. Motility Assay
2.7. Preparation of Hoagland’s Solution, Viable Cells, and Broth Culture of B. subtilis PE7 for Pot Experiment
2.8. Pot Experiment
2.9. Analysis of Nutrient Contents in Melon Plants
2.10. Investigation of Root Colonization of B. subtilis PE7 Using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.11. Evaluation of B. subtilis PE7 Population in Pot
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. P-Solubilizing Activity and Organic Acid Production of B. subtilis PE7
3.2. Phytase Activity of B. subtilis PE7 on PSA Medium and Phytase Gene Expression
3.3. Effect of Soluble P Concentration on Biofilm Formation of B. subtilis PE7
3.4. Motility of B. subtilis PE7
3.5. Effect of Cell Concentration and Broth Culture of B. subtilis PE7 on Melon Growth
3.6. Macronutrient and Micronutrient Contents in Melon Plants
3.7. Root Colonization Pattern of B. subtilis PE7
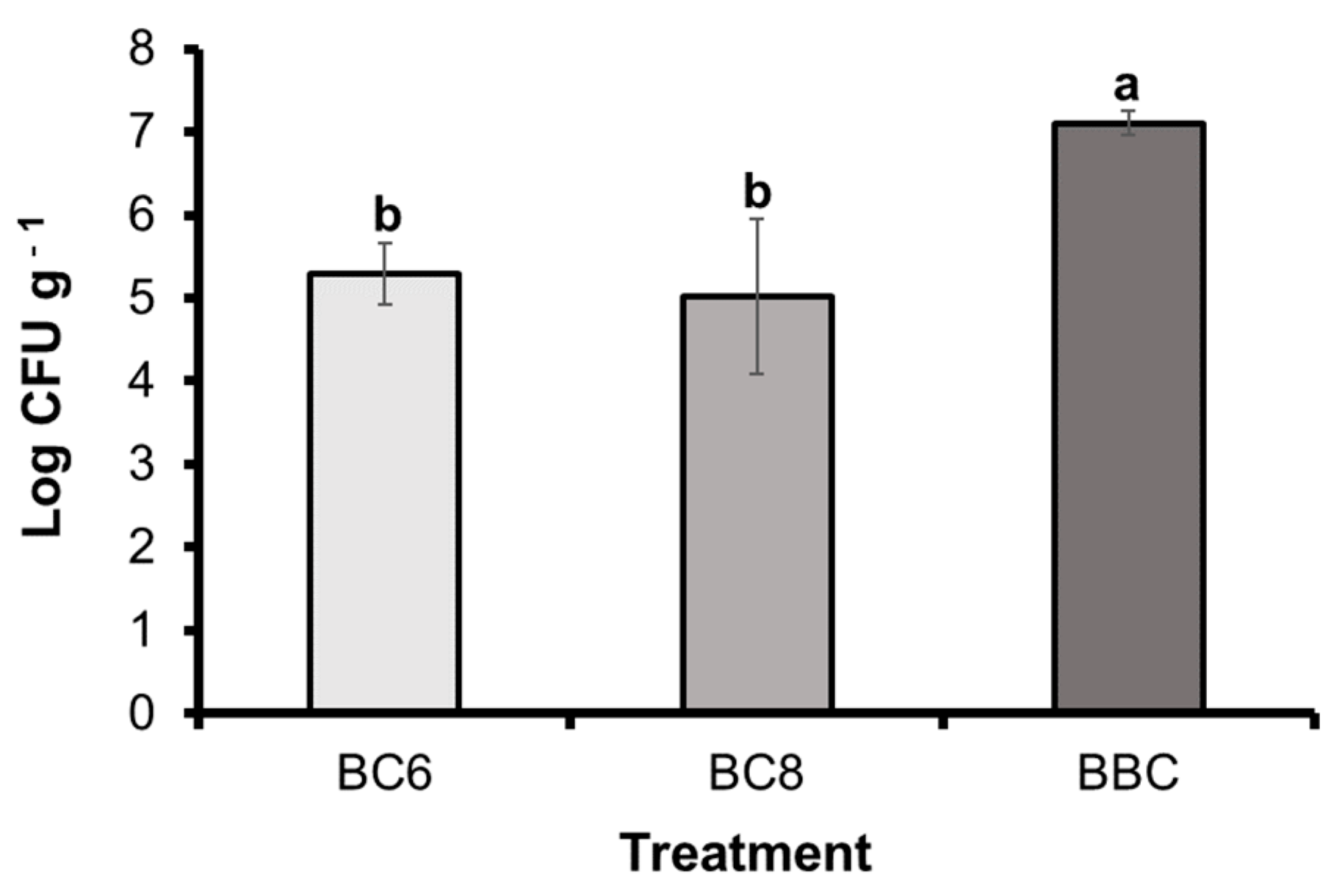
3.8. Population Density of B. subtilis PE7 in the Pot Soil of Melon Plants
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, F.; Harvey, P.R.; Wang, L.; Fan, S.; Xie, X.; Li, F.; Zhou, H.; et al. Identification of the phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria strain JP233 and its effects on soil phosphorus leaching loss and crop growth. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 892533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanif, M.K.; Hameed, S.; Imran, A.; Naqqash, T.; Shahid, M.; Elsas, J.D.V. Isolation and characterization of a beta-propeller gene containing phosphobacterium Bacillus subtilis strain KPS-11 for growth promotion of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuluaga, M.Y.A.; Oliveira, A.L.M.D.; Valentinuzzi, F.; Jayme, N.S.; Monterisi, S.; Fattorini, R.; Cesco, S.; Pii, Y. An insight into the role of the organic acids produced by Enterobacter sp. strain 15S in solubilizing tricalcium phosphate: In situ study on cucumber. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khourchi, S.; Oukarroum, A.; Tika, A.; Delaplace, P.; Bargaz, A. Polyphosphate application influences morpho-physiological root traits involved in P acquisition and durum wheat growth performance. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalayu, G. Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms: Promising approach as biofertilizers. In. J. Agron. 2019, 4917256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Liao, W.H.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, H.T.; Wang, X.J.; Na, M.E.N.G. Effect of phopshate fertilizer and manure on crop yield, soil P accumulation, and the environmental risk assessment. Agr. Sci. China 2007, 6, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, A.M.; Galyamova, M.R.; Sedykh, S.E. Plant growth-promoting soil bacteria: Nitrogen fixation, phosphate solubilization, siderophore production, and other biological activities. Plants 2023, 12, 4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Torres, M.; Romero-Perdomo, F.; Mendoza-Labrador, J.; Gutiérrez, A.Y.; Vargas, C.; Castro-Rincon, E.; Caro-Quintero, A.; Uribe-Velez, D.; Estrada-Bonilla, G.A. Genomic and phenotypic analysis of rock phosphate-solubilizing rhizobacteria. Rhizosphere 2021, 17, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargaz, A.; Elhaissoufi, W.; Khourchi, S.; Benmrid, B.; Borden, K.A.; Rchiad, Z. Benefits of phosphate solubilizing bacteria on belowground crop performance for improved crop acquisition of phosphorus. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 252, 126842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, D.F.; Shang, C.; Zelazny, L.W. Measurement of phytase activity in soil using a chromophoric tethered phytic acid probe. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwanuddin, S.; Kumar, V.; Singh, P.; Naik, B.; Mishra, S.; Chauhan, M.; Saris, P.E.J.; Verma, A.; Kumar, V. Insight into phytase-producing microorganisms for phytate solubilization and soil sustainability. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1127249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Narayanan, M.; Shi, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Ma, Y. Phosphate-solubilizing bacteria: Their agroecological function and optimistic application for enhancing agro-productivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 166468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Vargas, A.; Rodriguez-Gacha, L.M.; Sanchez-Castro, N.; Garzon-Jaramillo, R.; Pedroza-Camacho, L.D.; Poutou-Pinales, R.A.; Rivera-Hoyos, C.M.; Diaz-Ariza, L.A.; Pedroza-Rodriguez, A.M. Phosphate-solubilizing Pseudomonas sp., and Serratia sp., co-culture for Allium cepa L. growth promotion. Heliyon 2020, 6, 05218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Zhao, C.; Wang, E.; Raza, A.; Yin, C. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens as an excellent agent for biofertilizer and biocontrol in agriculture: An overview for its mechanisms. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 259, 127016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.; Mirza, M.S.; Zaheer, A.; Dimitrov, M.R.; Smidt, H.; Hameed, S. Isolation and identification of phosphate solubilizer Azospirillum, Bacillus and Enterobacter strains by 16SrRNA sequence analysis and their effect on growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar]
- Saeid, A.; Prochownik, E.; Dobrowolska-Iwanek, J. Phosphorus solubilization by Bacillus species. Molecules 2018, 23, 2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakki, M.; Banane, B.; Marhane, O.; Esmaeel, Q.; Hatimi, A.; Barka, E.A.; Azim, K.; Bouizgarne, B. Phosphate solubilizing Pseudomonas and Bacillus combined with rock phosphates promoting tomato growth and reducing bacterial canker disease. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1289466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, Z.; Ahmad, M.; Raza, M.A.; Hilger, T.; Rasche, F. Phosphate-solubilizing Bacillus sp. modulate soil exoenzyme activities and improve wheat growth. Microb. Ecol. 2024, 87, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Liu, X.; Bao, Y.; Wang, Y. Solubilization of K and P nutrients from coal gangue by Bacillus velezensis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, e01538-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, B.K.; Tarafdar, J.C. Efficiency of Bacillus coagulans as P bioferilizer to mobilize native soil organic and poorly soluble phosphates and increase crop yield. Arch. Agron. Soil. Sci. 2012, 58, 1099–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, A.; Sharma, S.K.; Joshi, O.P.; Khan, I.R. Phytase, phosphatase activity and P-nutrition of soybean as influenced by inoculation of Bacillus. Indian J. Microbiol. 2011, 51, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, C.N.G.; Pang, J.K.Y.; Gottardi, M.; Kracun, S.K.; Svendsen, B.A.; Nielsen, K.F.; Kovacs, A.T.; Moelbak, L.; Fimognari, L.; Husted, S.; et al. Bacillus subtilis promotes plant phosphorus (P) acquisition through P solubilization and stimulation of root and root hair growth. Physiol. Plant. 2024, 176, 14338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, V.P.; Marriel, I.E.; Sousa, S.M.; Lana, U.G.P.; Mattos, B.B.; Oliveira, C.A.; Gomes, E.A. Endophytic Bacillus strains enhance pearl millet growth and nutrient uptake under low-P. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepo, D.M.; Ahn, Y.J.; Eom, H.J.; Hahn, D.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Choi, E.K.; Hwang, U.S.; Lim, K.B. Comparison of the functional components in netted and cantaloupe melons. J. Agric. Life Sci. 2023, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fam, V.W.; Charoenwoodhipong, P.; Sivamani, R.K.; Holt, R.R.; Keen, C.L.; Hackman, R.M. Plant-based foods for skin health: A narrative review. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2022, 122, 614–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.E.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, K.Y.; Maung, C.E.H. Role of an antagonistic bacterium, Bacillus subtilis PE7, in growth promotion of netted melon (Cucumis melo L. var. reticulatus Naud.). Can. J. Microbiol. 2023, 70, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Weng, J.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, L.; Yao, Q.; Chang, L.; Niu, Q. Physiological and biochemical responses of Cucumis melo L. chloroplasts to low-phosphate stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martuscelli, M.; Mattia, C.D.; Stagnari, F.; Speca, S.; Pisante, M.; Mastrocola, D. Influence of phosphorus management on melon (Cucumis melo L.) fruit quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2715–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Wu, X.; Wen, X. Effects of soluble phosphate on phosphate-solubilizing characteristics and expression of gcd gene in Pseudomonas frederiksbergensis JW-SD2. Curr. Microbiol. 2016, 72, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerovuo, J.; Lauraeus, M.; Nurminen, P.; Kalkkinen, N.; Apajalahti, J. Isolation, characterization, molecular gene cloning, and sequencing of a novel phytase from Bacillus subtilis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2079–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, C.T.; Lorda, G.S.; Ludueña, L.M.; Anzuay, M.S.; Taurian, T. Motility and biofilm production involved in the interaction of phosphate solubilizing endophytic strains with peanut, maize and soybean plants. Rhizosphere 2020, 15, 100228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzantini, D.; Celandroni, F.; Salvetti, S.; Gueye, S.A.; Lupetti, A.; Senesi, S.; Ghelardi, E. FlhF Is Required for swarming motility and full pathogenicity of Bacillus cereus. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pande, A.; Pandey, P.; Mehra, S.; Singh, M.; Kaushik, S. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of phosphate solubilizing bacteria and their efficiency on the growth of maize. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2017, 15, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirkan, E.; Baygin, E.; Usta, A. Screening of phytate hydrolysis Bacillus sp. isolated from soil and optimization of the certain nutritional and physical parameters on the production of phytase. Turk. J. Biochem. 2014, 39, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, R.; Barman, S.; Mandal, N.C. Phosphate deficiency induced biofilm formation of Burkholderia on insoluble phosphate granules plays a pivotal role for maximum release of soluble phosphate. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leggett, J.E.; Frere, M.H. Growth and nutrient uptake by soybean plants in nutrient solutions of graded concentrations. Plant Physiol. 1971, 48, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msaad, H.; Lamsaadi, N.; Farssi, O.; Oubenali, A.; Lahmaoui, S.; Boulli, A.; Ghoulam, C.; Moukhtari, A.E.; Farissi, M. Biofertilizer and biostimulant potentials of phosphate-solubilizing Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis M1 strain and silicon in improving low phosphorus availability tolerance in rosemary. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2024, 77, ovae072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaraj, P.U.; Dahale, S. Mineral phosphate solubilization: Concepts and prospects in sustainable agriculture. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2014, 80, 389–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassileva, M.; Mendes, G.D.O.; Deriu, M.A.; Benedetto, G.D.; Flor-Peregrin, E.; Mocali, S.; Martos, V.; Vassilev, N. Fungi, P-Solubilization, and plant nutrition. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joudaki, H.; Aria, N.; Moravej, R.; Yazdi, M.R.; Emami-Karvani, Z.; Hamblin, M.R. Microbial Phytases: Properties and applications in the food industry. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z.; Wu, J.; Chen, L.; Dong, W. Isolated Bacillus subtilis strain 330–2 and its antagonistic genes identified by the removing PCR. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Narayanan, M.; Shi, X.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Ma, Y. Biofilms formation in plant growth-promoting bacteria for alleviating agro-environmental stress. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsin, M.Z.; Omer, R.; Huang, J.; Mohsin, A.; Guo, M.; Qian, J.; Zhuang, Y. Advances in engineered Bacillus subtilis biofilms and spores, and their applications in bioremediation, biocatalysis, and biomaterials. Synth. Syst. Biotechnol. 2021, 6, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gingichashvili, S.; Duanis-Assaf, D.; Shemesh, M.; Featherstone, J.D.B.; Feuerstein, O.; Steinberg, D. The adaptive morphology of Bacillus subtilis biofilms: A defense mechanism against bacterial starvation. Microorganisms 2019, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, Q.; Ayaz, M.; Mu, G.; Hussain, A.; Qiu, Y.; Yu, C.; Xu, Y.; Manghwar, H.; Gu, Q.; Wu, H.; et al. Revealing plant growth-promoting mechanisms of Bacillus strains in elevating rice growth and its interaction with salt stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 994902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çam, S.; Badilli, I. The effect of NaCl, pH, and phosphate on biofilm formation and exopolysaccharide production by high biofilm producers of Bacillus strains. Folia Microbiol. 2024, 69, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.; Sun, B.; Shi, H.; Gao, T.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; et al. Sucrose triggers a novel signaling cascade promoting Bacillus subtilis rhizosphere colonization. ISME J. 2021, 15, 2723–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wu, H.; Yu, X.; Qian, L.; Gao, X. Swarming motility plays the major role in migration during tomato root colonization by Bacillus subtilis SWR01. Biol. Control 2016, 98, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessia, A.; Sartori, M.; Garcia, D.; Fernandez, L.; Ponzio, R.; Barros, G.; Nesci, A. In vitro studies of biofilm-forming Bacillus strains, biocontrol agents isolated from the maize phyllosphere. Biofilm 2022, 4, 100097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, S.S.; Hassan, G.I.; Hussain, A.; Faisul-ur-Rasool. Phosphorus availability issue-its fixation and role of phosphate solubilizing bacteria in phosphate solubilization. Res. J. Agric. Sci. 2011, 2, 174–179. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, L.; Tian, X.; Wang, W.; Wu, C. Metabolome and Transcriptome Analysis Reveals Molecular Mechanisms of Soil Amendment (Volcanic Ash) Alleviating Salt–Alkali Stress in Melons (Cucumis melo L.). Agronomy 2024, 14, 2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abel, S.; Ticconi, C.A.; Delatorre, C.A. Phosphate sensing in higher plants. Physiol. Plant. 2002, 115, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Liu, H.; Ning, Z.; Bian, Z.; Zeng, L.; Xie, D. Inoculation with Bacillus cereus DW019 modulates growth, yield and rhizospheric microbial community of cherry tomato. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, C.; Christensen, M.N.; Kovacs, A.T. Molecular aspects of plant growth promotion and protection by Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Plant. Microbe. Interact. 2021, 34, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoyo, G.; Urtis-Flores, C.A.; Loeza-Lara, P.D.; Orozco-Mosqueda, M.D.C.; Glick, B.R. Rhizosphere colonization determinants by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR). Biology 2021, 10, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashan, Y.; de-Bashan, L.E.; Prabhu, S.R.; Hernandez, J.P. Advances in plant growth-promoting bacterial inoculant technology: Formulations and practical perspectives (1998–2013). Plant Soil 2014, 378, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Treatment * | Length (cm) | Fresh Weight (g) | Dry Weight (g) | Leaf Number | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shoot | Root | Shoot | Root | Shoot | Root | ||
| P-Con | 34.68 ± 1.43 a | 32.30 ± 5.77 a | 30.27 ± 1.47 a | 7.68 ± 0.93 a | 3.51 ± 0.13 a | 0.53 ± 0.08 b | 11.00 ± 0.00 a |
| N-Con | 25.27 ± 1.57 d | 28.37 ± 1.57 a | 18.67 ± 1.16 c | 5.82 ± 0.69 b | 2.53 ± 0.22 cd | 0.43 ± 0.04 b | 8.83 ± 0.41 cd |
| BC6 | 27.18 ± 0.41 c | 31.92 ± 5.56 a | 19.59 ± 1.91 c | 6.11 ± 0.79 b | 2.68 ± 0.28 cd | 0.45 ± 0.07 b | 9.17 ± 0.41 bcd |
| BC8 | 30.08 ± 1.41 b | 28.70 ± 4.08 a | 23.68 ± 2.16 b | 7.60 ± 0.87 a | 3.16 ± 0.34 b | 0.72 ± 0.20 a | 9.67 ± 0.52 b |
| BBC | 29.15 ± 1.78 b | 31.75 ± 3.35 a | 19.67 ± 0.87 c | 6.48 ± 0.68 b | 3.01 ± 0.22 b | 0.49 ± 0.07 b | 9.33 ± 0.52 bc |
| Treatment * | Macronutrient (mg plant−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | P | K | Mg | Ca | S | |
| P-Con | 69.26 ± 5.40 a | 1.83 ± 0.18 a | 129.73 ± 1.69 a | 22.35 ± 0.46 a | 106.82 ± 1.25 a | 23.09 ± 11.56 a |
| N-Con | 71.15 ± 4.02 a | 0.24 ± 0.01 c | 89.44 ± 9.42 c | 14.92 ± 2.23 bc | 68.08 ± 5.40 cd | 28.70 ± 14.37 a |
| BC6 | 79.77 ± 13.63 a | 0.27 ± 0.05 c | 87.50 ± 14.57 c | 14.41 ± 2.21 c | 71.76 ± 9.33 c | 1.57 ± 0.23 b |
| BC8 | 74.95 ± 1.07 a | 0.48 ± 0.01 b | 110.97 ± 3.64 b | 20.58 ± 1.20 a | 91.62 ± 3.60 b | 6.27 ± 5.25 b |
| BBC | 50.29 ± 2.12 b | 0.54 ± 0.05 b | 104.51 ± 3.45 b | 17.24 ± 0.36 b | 74.92 ± 3.03 c | 4.33 ± 1.12 b |
| Treatment * | Micronutrient (mg plant−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn | B | Cu | Fe | Mo | |
| P-Con | 0.44 ± 0.07 a | 0.22 ± 0.15 a | 0.48 ± 0.12 a | 3.02 ± 1.15 c | ND |
| N-Con | 0.27 ± 0.05 b | 0.07 ± 0.03 b | 0.15 ± 0.06 b | 1.44 ± 0.38 ab | ND |
| BC6 | 0.30 ± 0.08 b | 0.05 ± 0.02 b | 0.09 ± 0.05 b | 3.42 ± 1.31 a | ND |
| BC8 | 0.40 ± 0.10 ab | 0.05 ± 0.01 b | 0.25 ± 0.17 b | 3.76 ± 1.34 a | ND |
| BBC | 0.37 ± 0.06 ab | 0.11 ± 0.03 ab | 0.23 ± 0.14 b | 2.64 ± 1.30 ab | ND |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, S.E.; Kim, K.Y.; Maung, C.E.H. Bacillus subtilis PE7-Mediated Alleviation of Phosphate Starvation and Growth Promotion of Netted Melon (Cucumis melo L. var. reticulatus Naud.). Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122384
Han SE, Kim KY, Maung CEH. Bacillus subtilis PE7-Mediated Alleviation of Phosphate Starvation and Growth Promotion of Netted Melon (Cucumis melo L. var. reticulatus Naud.). Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122384
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Seong Eun, Kil Yong Kim, and Chaw Ei Htwe Maung. 2024. "Bacillus subtilis PE7-Mediated Alleviation of Phosphate Starvation and Growth Promotion of Netted Melon (Cucumis melo L. var. reticulatus Naud.)" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122384
APA StyleHan, S. E., Kim, K. Y., & Maung, C. E. H. (2024). Bacillus subtilis PE7-Mediated Alleviation of Phosphate Starvation and Growth Promotion of Netted Melon (Cucumis melo L. var. reticulatus Naud.). Microorganisms, 12(12), 2384. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122384





