Probiotic Properties of Lactic Acid Bacteria Newly Isolated from Algerian Raw Cow’s Milk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Strains, Growth Conditions, and Identification
2.3. MALDI-TOF MS Identification
2.4. Strain Survival to the In Vitro Simulated Gastrointestinal Conditions
2.5. Determination of Biological Activities of the Strains
2.5.1. Antimicrobial Activity
2.5.2. Antioxidant Activity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of a Total of Nine Selected LAB Isolates Reveals Eight Putative Strains Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and One Putative Strain Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus, as Confirmed by Molecular (PCR-16) and Proteomic (MALDI-TOF) Identification
3.2. The Isolated Strains Have Shown an Interesting Probiotic Profile
3.2.1. Gastric Fluid and Bile Salts Tolerance
3.2.2. Antioxidant Activity
3.2.3. Antimicrobial Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ait Abdeslam, A.; Desmasures, N.; Bensoltane, A. Identification of indigenous Lactobacillus isolated from artisanal Algerian dairy product by 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry. South Asian J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 9, 193–206. [Google Scholar]
- Oberg, T.S.; McMahon, D.J.; Culumber, M.D.; McAuliffe, O.; Oberg, C.J. Invited review: Review of taxonomic changes in dairy-related lactobacilli. J. Dairy Sci. 2022, 105, 2750–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Guarner, F.; Reid, G.; Gibson, G.R.; Merenstein, D.J.; Pot, B.; Morelli, L.; Canani, R.B.; Flint, H.J.; Salminen, S.; et al. Expert Consensus Document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics Consensus Statement on the Scope and Appropriate Use of the Term Probiotic. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 11, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Zhang, F.; Wan, C.; Xiong, Y.; Shah, N.P.; Wei, H.; Tao, X. Evaluation of probiotic properties of Lactobacillus plantarum WLPL04 isolated from human breast milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, R.; Mine, Y.; Yumisashi, Y.; Yoshioka, R.; Hamaoka, M.; Taji, T.; Murayama, T.; Nikawa, H. In Vivo Efficacy of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus L8020 in a Mouse Model of Oral Candidiasis. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyash, M.M.; Abdalla, A.K.; AlKalbani, N.S.; Baig, M.A.; Turner, M.S.; Liu, S.Q.; Shah, N.P. Invited review: Characterization of new probiotics from dairy and non dairyproducts-Insights into acid tolerance, bile metabolism and tolerance, and adhesion capability. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 8363–8379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, N.; Manan, H.; Sallehhuddin, M.; Musa, N.; Ikhwanuddin, M. Screening of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Giant Freshwater Prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) as Potential Probiotics. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorizzo, M.; Albanese, G.; Letizia, F.; Testa, B.; Tremonte, P.; Vergalito, F.; Lombardi, S.J.; Succi, M.; Coppola, R.; Sorrentino, E. Probiotic Potentiality from Versatile Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Strains as Resource to Enhance Freshwater Fish Health. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.A.; Bong, Y.J.; Kim, H.; Jeong, J.K.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Park, K.Y. Effect of nanometric Lactobacillus plantarum in kimchi on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. J. Med. Food 2015, 18, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 765474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, W.P.; Vogel, R.F. The genus Lactobacillus. In Lactic Acid Bacteria; Wood, B.J.B., Holzapfel, W.H., Eds.; Blackie Academic and Professional: London, UK, 1995; Volume 2, pp. 19–54. [Google Scholar]
- Clarridge, J.E., III. Impact of 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis for identification of bacteria on clinical microbiology and infectious diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 840–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nacef, M.; Chevalier, M.; Chollet, S.; Drider, D.; Flahaut, C. MAL-DI-TOF mass spectrometry for the idenificaion of lacic acid bacteria isolated from a French cheese: The Maroilles. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2016, 247, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Man, J.C.; Rogosa, M.; Sharpe, M.E. A medium for the cultivation of lactobacilli. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1960, 23, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nübel, U.; Engelen, B.; Felske, A.; Snaidr, J.; Wieshuber, A.; Amann, R.I.; Ludwig, W.; Backhaus, H. Sequence Heterogeneities of Genes Encoding 16S rRNAs in Paenibacillus polymyxa Detected by Temperature Gradient Gel Electrophoresis. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 5636–5643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Geneics Analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The Neighbor-Joining Method: A New Method for Reconstructing Phylogenetic Trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.G.V.; Franz, C.M.; Schillinger, U.; Holzapfel, W.H. Lactobacillus spp. with in vitro probiotic properties from human faeces and traditional fermented products. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 109, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sensoy, I.A. review on the food digestion in the digestive tract and the used in vitro models. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2021, 4, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyronimus, B.; Le Marrec, C.; HadjSassi, A.; Deschamps, A. Acid and bile tolerance of spore-forming lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 61, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouwehand, A.C.; Tölkkö, S.; Salminen, S. The Effect of Digestive Enzymes on the Adhesion of Probiotic Bacteria In Vitro. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 856–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaalel, A.; Riazi, A.; Dubois-Dauphin, R.; Thonart, P. Screening of plantaricin EF and JK in an Algerian Lactobacillus plantarum isolate. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2015, 5, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blois, M.S. Antioxidant determination by the use of a stable Free radical. Nature 1958, 181, 1199–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Morrison, M. Comparisons of Different Hypervariable Regions of rrs Genes for Use in Fingerprinting of Microbial Communities by PCR-Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 4800–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maragkoudakis, P.A.; Zoumpopoulou, G.; Miaris, C.; Kalantzopoulos, G.; Pot, B.; Tsakalidou, E. Probiotic potential of Lactobacillus strains isolated from dairy products. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhmetsadykova, S.H.; Baubekova, A.; Konuspayeva, G.; Akhmetsadykov, N.; Faye, B.; Loiseau, G. Lactic acid bacteria biodiversity in raw and fermented camel milk. Afr. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 6, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keddar, K.; Ziar, H.; Belmadani, N.; Monnoye, M.; Gérard, P.; Riazi, A. Probiotic Bacteria from Human Milk Can Alleviate Oral Bovine Casein Sensitization in Juvenile Wistar Rats. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasser, F. Safety of lactic acid bacteria and their occurrence in human clinical infections. Bull. Inst. Pasteur 1994, 92, 45–67. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, J.; Wittouck, S.; Salvetti, E.; Franz, C.M.; Harris, H.M.; Mattarelli, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P.; Walter, J.; et al. A taxonomic note on the genus Lactobacillus: Description of 23 novel genera, emended description of the genus Lactobacillus Beijerinck 1901, and union of Lactobacillaceae and Leuconostocaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 2782–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidanza, M.; Panigrahi, P.; Kollmann, T.R. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum–Nomad and Ideal Probiotic. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 712236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiler, E.A.; Klaenhammer, T.R. Role of Transporter Proteins in Bile Tolerance of Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 6013–6016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziar, H.; Gérard, P.; Riazi, A. Effect of prebiotic carbohydrates on growth, bile survival and cholesterol uptake abilities of dairy-related bacteria. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2012, 94, 1184–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Yu, L.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhai, Q. Identification of Novel Bile Salt-Tolerant Genes in Lactobacillus Using Comparative Genomics and Its Application in the Rapid Screening of Tolerant Strains. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Düz, M.; Doğan, Y.N.; Doğan, İ. Antioxidant activitiy of Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus sake and Lactobacillus curvatus strains isolated from fermented Turkish Sucuk. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2020, 92, e20200105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, G.Y.; Choi, S.I.; Park, N.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Kang, C.H.; Kim, G.H. In Vitro Antidiabetic, Antioxidant Activity, and Probiotic Activities of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum and Lacticaseibacillus paracasei Strains. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 3181–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Su, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, Q.; Liang, X.; Lv, J. Antioxidative activity of lactic acid bacteria in yogurt. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2011, 5, 5194–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijan, S. Probiotics and Their Antimicrobial Effect. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
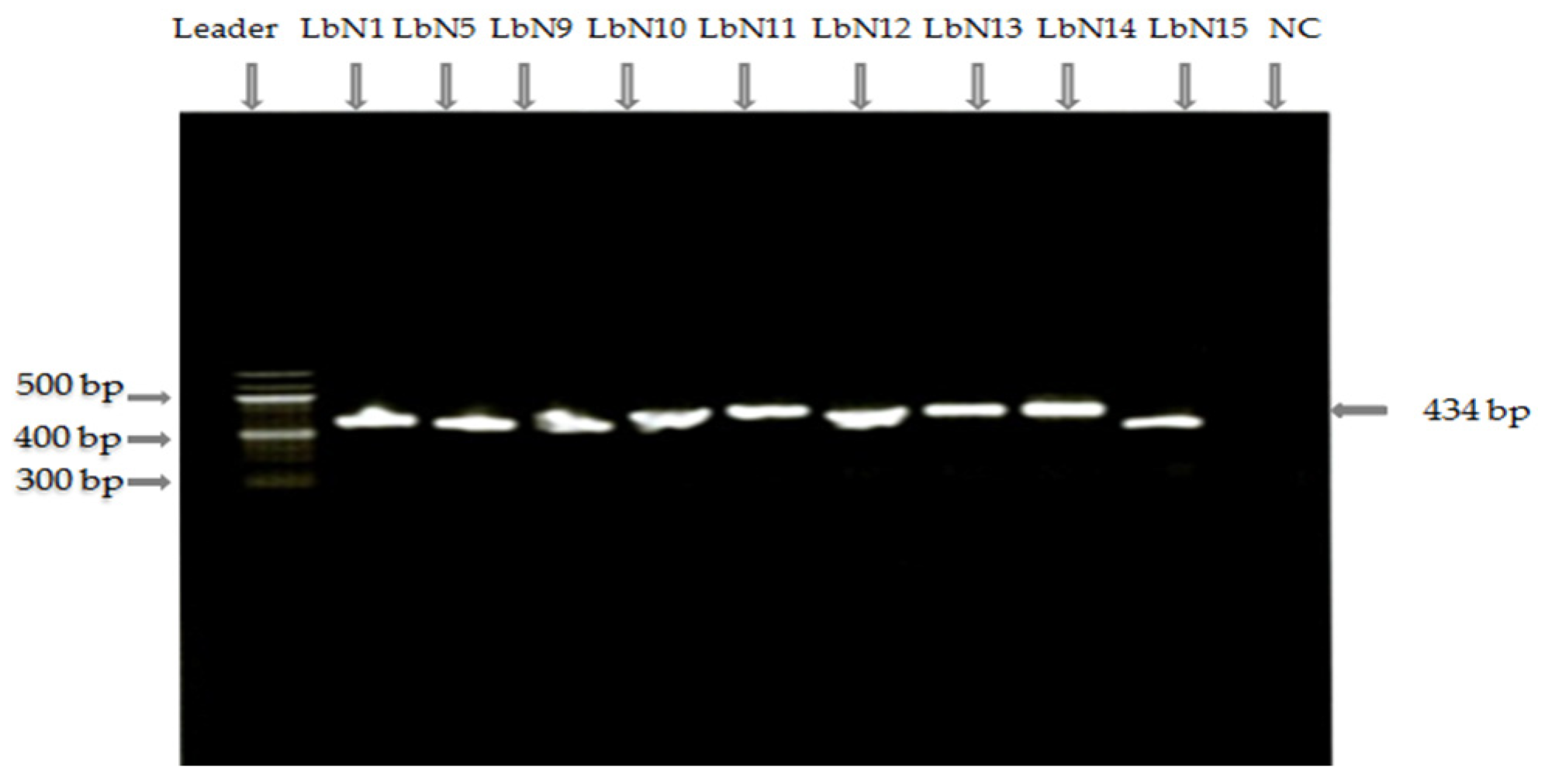

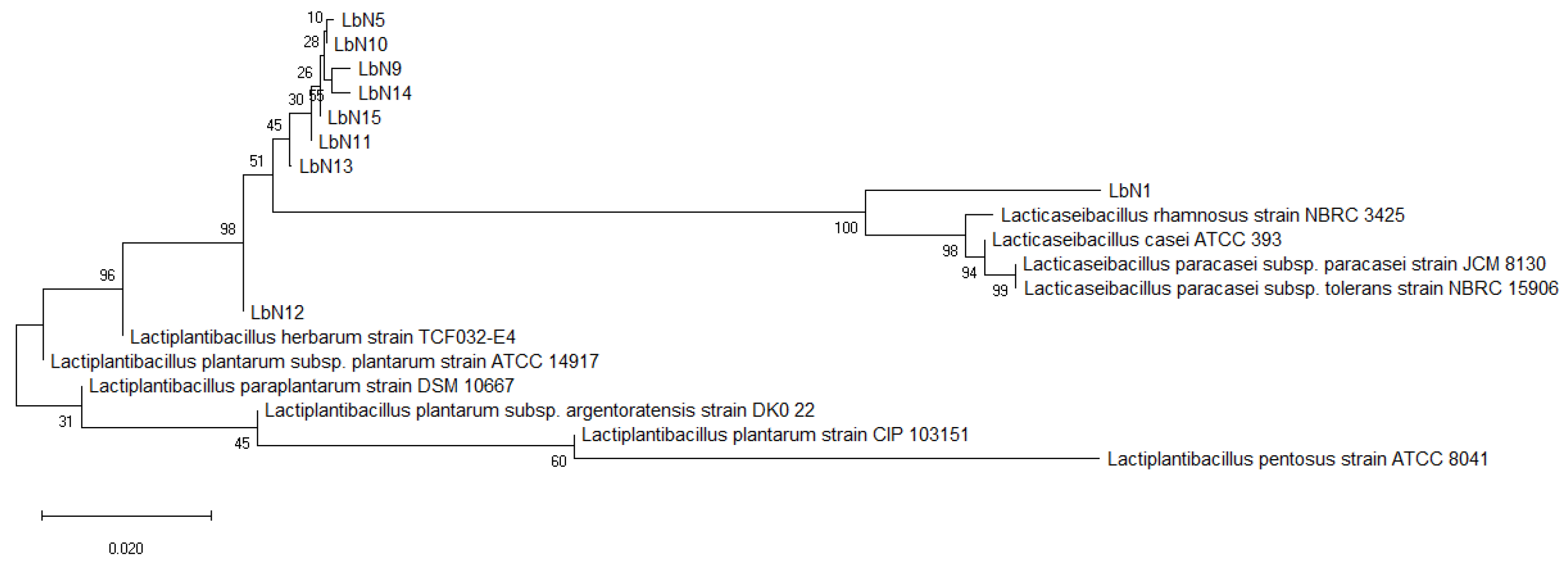
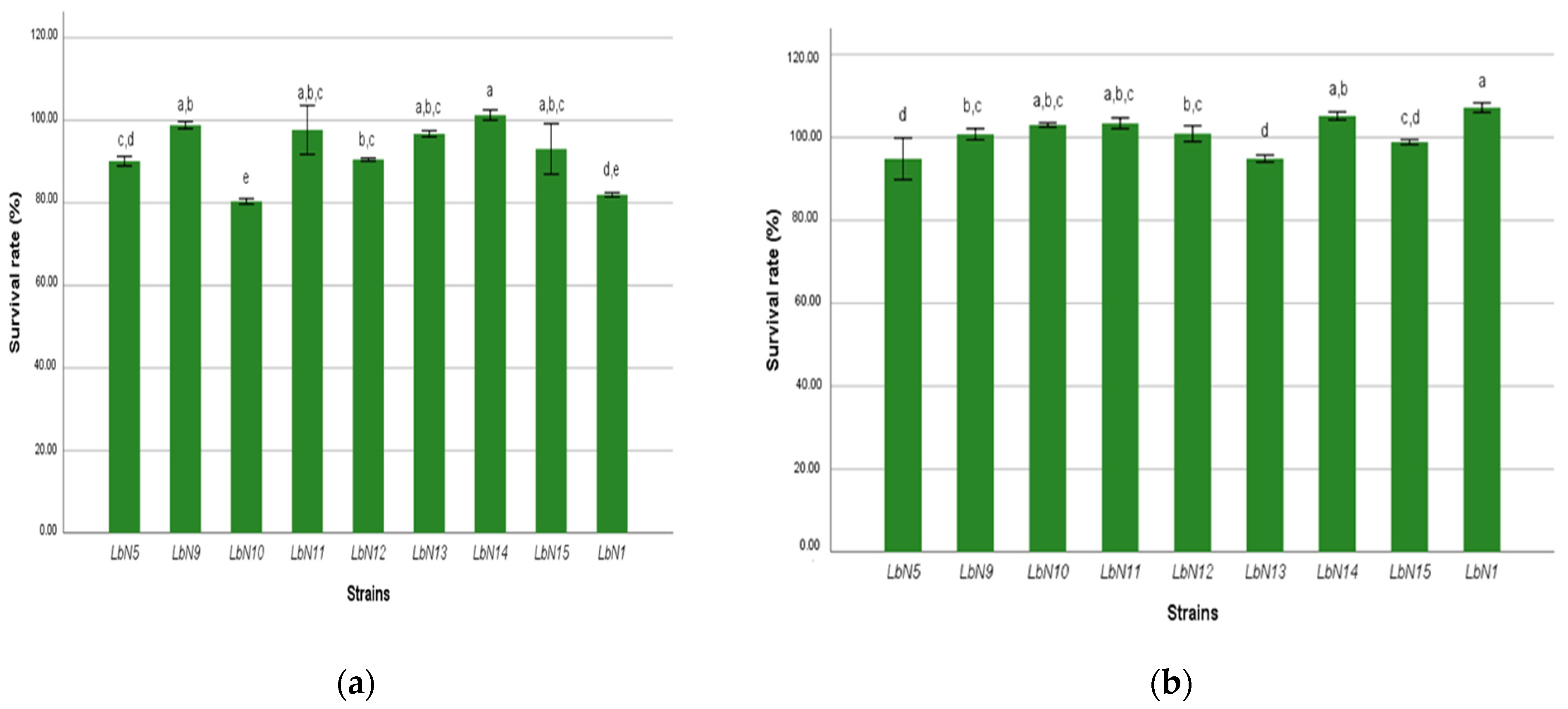
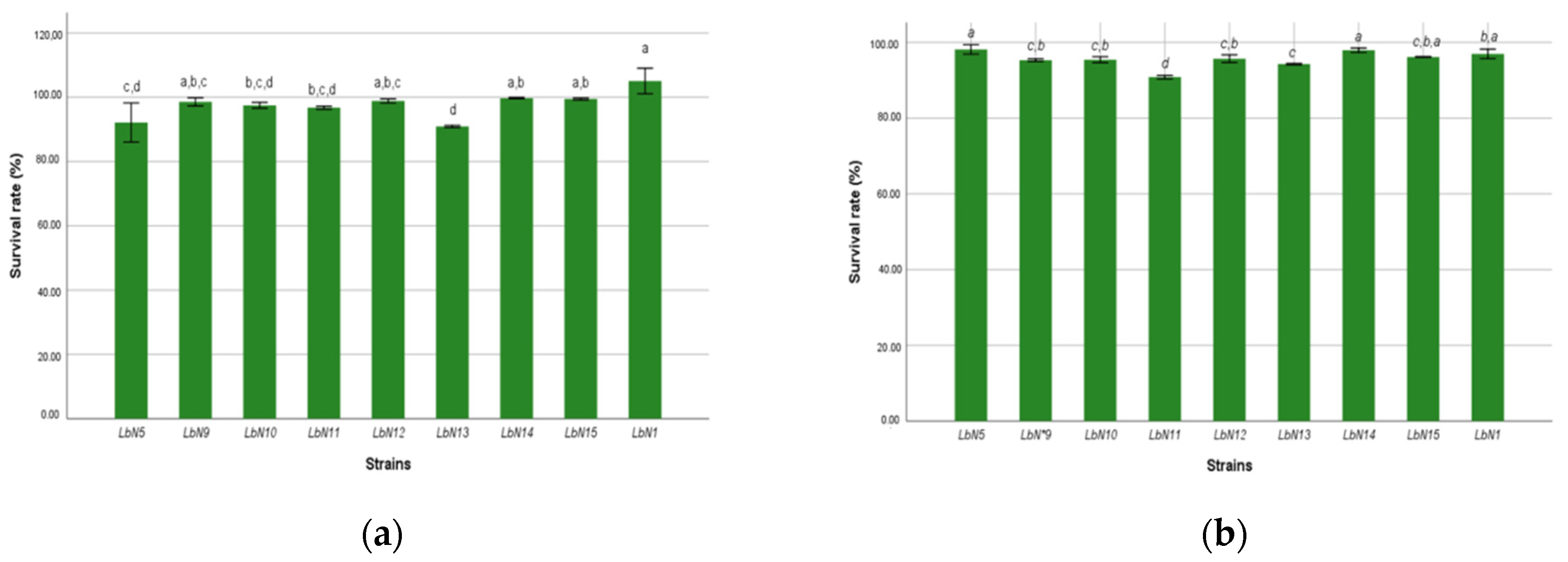
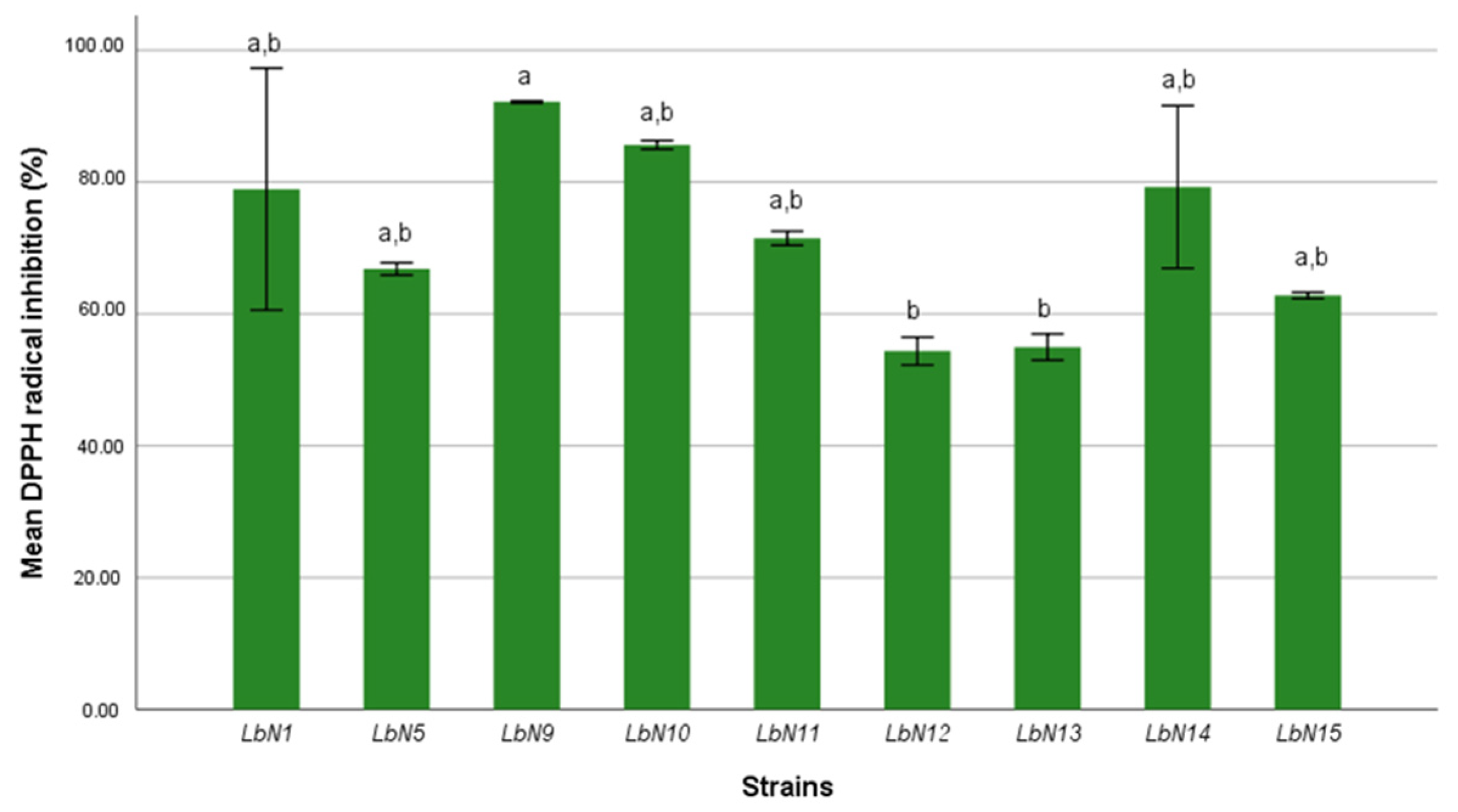
| Isolates Code | Species Identification | Similarity Scores (%) |
|---|---|---|
| LbN1 | Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus | 99.75 |
| LbN5 | Lacticaseibacillus plantarum | 100 |
| LbN9 | Lacticaseibacillus plantarum | 100 |
| LbN10 | Lacticaseibacillus plantarum | 100 |
| LbN11 | Lacticaseibacillus plantarum | 100 |
| LbN12 | Lacticaseibacillus plantarum | 99.75 |
| LbN13 | Lacticaseibacillus plantarum | 100 |
| LbN14 | Lacticaseibacillus plantarum | 100 |
| LbN15 | Lacticaseibacillus plantarum | 100 |
| Isolated LAB Strains | Pathogens/Inhibition Zone (mm) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. subtilis ATCC 6633 | P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853 | E. coli ATCC 25922 | S.aureus ATCC 33862 | C. albicans ATCC 10231 | A. niger ATCC 106404 | |
| LbN1 | 13.10 ± 0.36 a,b,c | 14.20 ± 0.72 b | 12.50 ± 0.5 a,b | 12.03 ± 0.15 b,c | 14.67 ± 0.58 c,d | 6.83 ± 0.76 b,c,d,e |
| LbN5 | 12.07± 0.11 b,c | 14.17± 0.28 b | 11.97 ± 0.95 a,b | 13.50 ± 0.50 a,b | 17.00 ± 1.00 a,b | 8.73 ± 0.46 a,b |
| LbN9 | 13.83 ± 0.28 a,b | 14.40 ± 1.21 b | 13.80 ± 0.38 a | 13.40 ± 0.52 a,b | 14.17 ± 0.28 d | 9.00 ± 0.50 a |
| LbN10 | 14.57 ± 0.40 a | 15.03 ±0.55 a,b | 13.10 ± 0.56 a,b | 12.23 ± 1.15 b | 15.77 ± 0.49 b,c | 8.07 ± 1.10 a,b,c,d |
| LbN11 | 14.67 ± 0.57 a | 14.80 ± 0.26 b | 12.10 ± 0.26 a,b | 12.97 ± 0.45 a,b | 15.60 ± 0.60 b,c,d | 4.90 ± 0.36 e |
| LbN12 | 14.50 ± 0.50 a | 14.33 ± 1.15 b | 11.37 ± 0.78 b | 12.63 ± 0.32 a,b | 14.60 ± 0.52 c,d | 8.33 ± 0.58 a,b,c |
| LbN13 | 11.58 ± 0.95 c | 16.17 ± 0.76 a,b | 12.40 ± 0.52 a,b | 10.27 ± 0.64 c | 16.83 ± 0.28 a,b | 7.13 ± 0.32 a,b,c,d |
| LbN14 | 14.49 ± 1.32 a | 15.77 ± 0.93 a,b | 12.80 ± 0.72 a,b | 14.27 ± 1.10 a | 17.47 ± 0.45 a | 6.23 ± 1.12 d,e |
| LbN15 | 14.47 ± 0.55 a | 17.33 ± 1.15 a | 12.83 ± 1.60 a,b | 13.80 ± 0.20 a,b | 14.87 ± 0.41 c,d | 6.43 ± 0.51 c,d,e |
| p value * (MANOVA test) | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.04 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kouadri Boudjelthia, N.; Belabbas, M.; Bekenniche, N.; Monnoye, M.; Gérard, P.; Riazi, A. Probiotic Properties of Lactic Acid Bacteria Newly Isolated from Algerian Raw Cow’s Milk. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082091
Kouadri Boudjelthia N, Belabbas M, Bekenniche N, Monnoye M, Gérard P, Riazi A. Probiotic Properties of Lactic Acid Bacteria Newly Isolated from Algerian Raw Cow’s Milk. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(8):2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082091
Chicago/Turabian StyleKouadri Boudjelthia, Nacima, Meryem Belabbas, Nahla Bekenniche, Magali Monnoye, Philippe Gérard, and Ali Riazi. 2023. "Probiotic Properties of Lactic Acid Bacteria Newly Isolated from Algerian Raw Cow’s Milk" Microorganisms 11, no. 8: 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082091
APA StyleKouadri Boudjelthia, N., Belabbas, M., Bekenniche, N., Monnoye, M., Gérard, P., & Riazi, A. (2023). Probiotic Properties of Lactic Acid Bacteria Newly Isolated from Algerian Raw Cow’s Milk. Microorganisms, 11(8), 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11082091







