Early Life Factors Influencing Children Gut Microbiota at 3.5 Years from Two French Birth Cohorts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. EPIPAGE 2 and ELFE Cohorts
2.2. Ethics
2.3. Participants
2.4. Maternal and Child Data Collection
2.5. Exposures of Interest
- -
- gestational age: maternal age, maternal level of education, household income and, preconceptional maternal BMI.
- -
- delivery mode: gestational age, maternal age, maternal level of education, household income, country of birth of the mother and preconceptional maternal BMI.
- -
- early neonatal antibiotics: delivery mode, gestational age, maternal level of education and skin-to-skin contact.
- -
- human milk consumption: maternal age, maternal level of education, household income, country of birth of the mother, gestational age, delivery mode and household siblings at 1 year.
- -
- skin-to-skin contact: Country of birth of the mother, gestational age and human milk consumption.
- -
- preconceptional maternal BMI: country of birth of the mother.
- -
- daycare exposure at 1 year: maternal level of education, household income, country of birth of the mother and household sibling at 1 year.
- -
- household sibling at 1 year and environment (rural/urban): maternal age, maternal level of education and household income.
- -
- country of birth of the mother: none.
- -
- antibiotherapy during pregnancy: none
- -
- antibiotherapy during delivery: antibiotherapy during pregnancy.
- -
- age at complementary feeding + age at first introduction of vegetables, fruits, meat, and fish: maternal age, maternal level of education, household income, country of birth of the mother, preconceptional maternal BMI, human milk consumption, daycare exposure at 1 year and household siblings at 1 year.
- -
- PNNS and pregnancy scores: maternal age, maternal level of education, country of birth of the mother, household income, preconceptional maternal BMI, environment (rural/urban), and household siblings at 1 year.
- -
- antibiotherapy during the first year of life: maternal age, maternal level of education, daycare exposure at 1 year and household siblings at 1 year.
2.6. Samples Collection, DNA Extraction, Sequencing and Data Processing
2.7. Microbiota Diversity and Composition
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
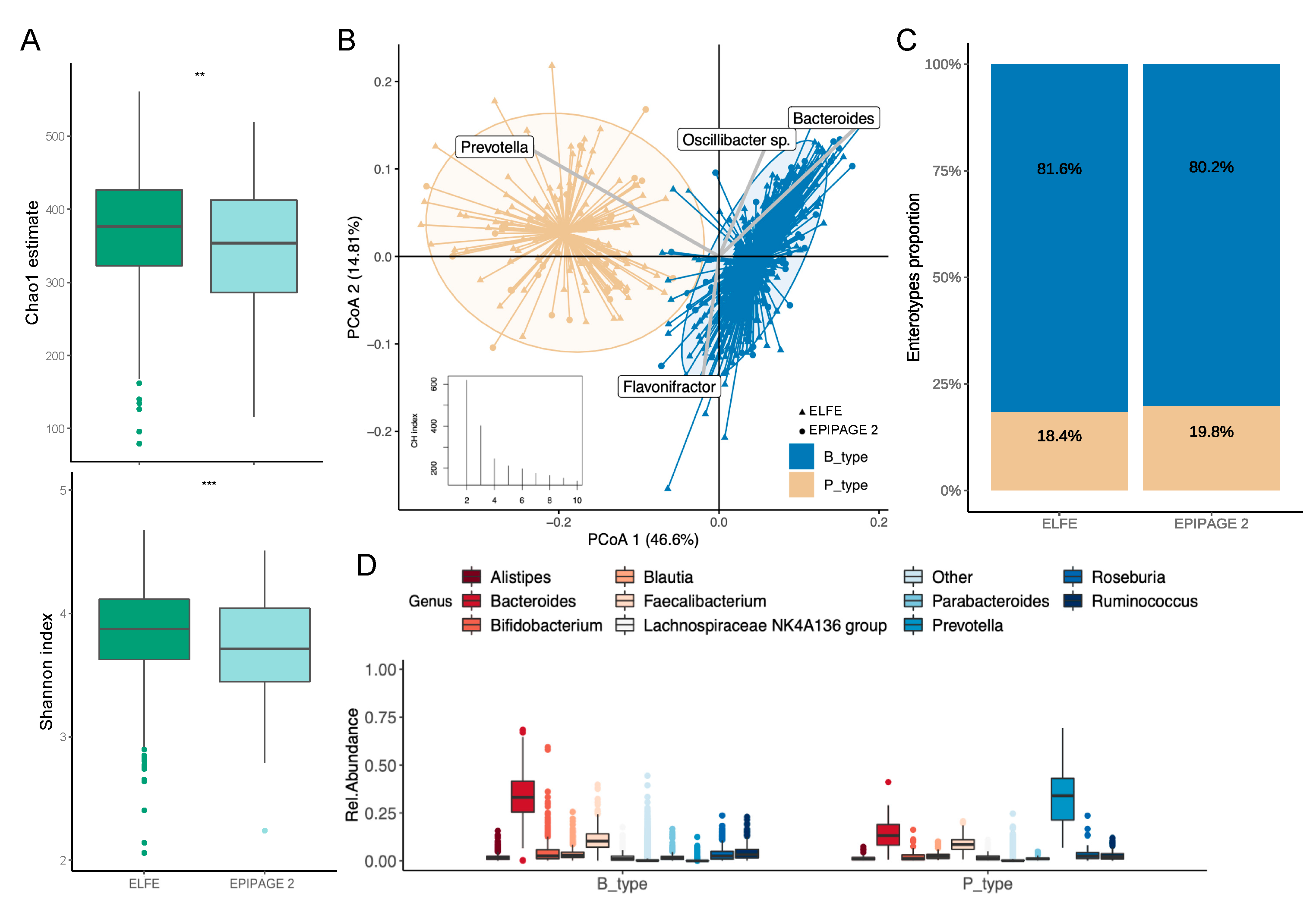
3.1. Gut Microbiota Description of Children at 3.5 Years of Age
3.2. Enterotypes Association with Early Life Factors
3.3. Early Life Factors Influencing Gut Microbiota Diversity at 3.5 Years of Age
3.3.1. Alpha Diversity
3.3.2. Beta Diversity
3.4. Differential Abundance Testing
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
Study Limitation and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomaa, E.Z. Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and diseases: A review. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 2019–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K. The developing world of DOHaD. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2018, 9, 266–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butel, M.J.; Waligora-Dupriet, A.J.; Wydau-Dematteis, S. The developing gut microbiota and its consequences for health. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2018, 9, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Yoo, J.Y.; Valeria Ozorio Dutra, S.; Morgan, K.H.; Groer, M. The Association between Early-Life Gut Microbiota and Long-Term Health and Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, S.; Shen, N.; Wu, H.C.; Clemente, J.C. The microbiome in early life: Implications for health outcomes. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, M.; Alvarez, A.-S.; de Vos, W.M. The Gut Microbiota in the First Decade of Life. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.J.; Ajami, N.J.; O’brien, J.L.; Hutchinson, D.S.; Smith, D.P.; Wong, M.C.; Ross, M.C.; Lloyd, R.E.; Doddapaneni, H.; Metcalf, G.A.; et al. Temporal development of the gut microbiome in early childhood from the TEDDY study. Nature 2018, 562, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpela, K.; de Vos, W.M. Early life colonization of the human gut: Microbes matter everywhere. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 44, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Penders, J.; Shi, Z.; Ren, H.; Cai, K.; Fang, C.; Ding, Q.; Thijs, C.; Blaak, E.E.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; et al. Impact of early events and lifestyle on the gut microbiota and metabolic phenotypes in young school-age children. Microbiome 2019, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roswall, J.; Olsson, L.M.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Nilsson, S.; Tremaroli, V.; Simon, M.-C.; Kiilerich, P.; Akrami, R.; Krämer, M.; Uhlén, M.; et al. Developmental trajectory of the healthy human gut microbiota during the first 5 years of life. Cell Host Microbe 2021, 29, 765–776.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorthe, E.; Benhammou, V.; Marchand-Martin, L.; Pierrat, V.; Lebeaux, C.; Durox, M.; Goffinet, F.; Kaminski, M.; Ancel, P.-Y.; Astruc, D.; et al. Cohort Profile: The Etude Epidémiologique sur les Petits Ages Gestationnels-2 (EPIPAGE-2) preterm birth cohort. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 50, dyaa282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, M.A.; Thierry, X.; Lanoe, J.-L.; Bois, C.; Dufourg, M.-N.; Popa, R.; Cheminat, M.; Zaros, C.; Geay, B. Cohort Profile: The French national cohort of children (ELFE): Birth to 5 years. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 49, 368–369j. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hercberg, S. Le Programme National Nutrition Santé (PNNS): Un vrai programme de santé publique. Cah. Nutr. Diététique 2011, 46, S5–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadawathagedara, M.; Kersuzan, C.; Wagner, S.; Tichit, C.; Gojard, S.; Charles, M.A.; Lioret, S.; de Lauzon-Guillain, B. Adéquation des consommations alimentaires des femmes enceintes de l’étude ELFE aux recommandations du Programme national nutrition santé. Cah. Nutr. Diététique 2017, 52, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, J.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Levenez, F.; Pelletier, E.; Alberti, A.; Bertrand, L.; Bork, P.; Costea, P.I.; Sunagawa, S.; Guarner, F.; et al. HMS_SOP_07_V1: Standard Operating Procedure for Fecal Samples DNA Extraction, Protocol H. International Human Microbiome Standards. 2015. [En ligne]. Available online: http://www.microbiome-standards.org (accessed on 10 October 2020).
- Toubon, G.; Butel, M.J.; Rozé, J.C.; Lepage, P.; Delannoy, J.; Ancel, P.Y. Very Preterm Children Gut Microbiota Comparison at the Neonatal Period of 1 Month and 3.5 Years of Life. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudié, F.; Auer, L.; Bernard, M.; Mariadassou, M.; Cauquil, L.; Vidal, K.; Maman, S.; Hernandez-Raquet, G.; Combes, S.; Pascal, G. FROGS: Find, Rapidly, OTUs with Galaxy Solution. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, M.; Raes, J.; Pelletier, E.; Le Paslier, D.; Yamada, T.; Mende, D.R.; Fernandes, G.R.; Tap, J.; Bruls, T.; Batto, J.M.; et al. Enterotypes of the human gut microbiome. Nature 2011, 473, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.J. Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance (PERMANOVA). In Wiley StatsRef: Statistics Reference Online, 1st ed.; Balakrishnan, N., Colton, T., Everitt, B., Piegorsch, W., Ruggeri, F., Teugels, J.L., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-J.; Satten, G.A. Testing hypotheses about the microbiome using the linear decomposition model (LDM). Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 4106–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Das Peddada, S. Analysis of compositions of microbiomes with bias correction. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, A.D.; Reid, J.N.; Macklaim, J.M.; McMurrough, T.A.; Edgell, D.R.; Gloor, G.B. Unifying the analysis of high-throughput sequencing datasets: Characterizing RNA-seq, 16S rRNA gene sequencing and selective growth experiments by compositional data analysis. Microbiome 2014, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stekhoven, D.J.; Bühlmann, P. MissForest—Non-parametric missing value imputation for mixed-type data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nearing, J.T.; Douglas, G.M.; Hayes, M.; MacDonald, J.; Desai, D.; Allward, N.; Jones, C.M.A.; Wright, R.; Dhanani, A.; Comeau, A.M.; et al. Microbiome differential abundance methods produce disturbingly different results across 38 datasets. Bioinformatics 2021, preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouhy, F.; Watkins, C.; Hill, C.J.; O’Shea, C.-A.; Nagle, B.; Dempsey, E.M.; O’Toole, P.W.; Ross, R.; Ryan, C.A.; Stanton, C. Perinatal factors affect the gut microbiota up to four years after birth. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Wang, J.; Zheng, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, F. Deterministic transition of enterotypes shapes the infant gut microbiome at an early age. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Moles, L.; Espinosa-Martos, I.; Bustos, G.; De Vos, W.M.; Fernández, L.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Fuentes, S.; Jiménez, E. Bacteriological and Immunological Profiling of Meconium and Fecal Samples from Preterm Infants: A Two-Year Follow-Up Study. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saturio, S.; Nogacka, A.M.; Suárez, M.; Fernández, N.; Mantecón, L.; Mancabelli, L.; Milani, C.; Ventura, M.; Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.d.L.; Solís, G.; et al. Early-Life Development of the Bifidobacterial Community in the Infant Gut. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.-L.; Xiong, Y.; Hu, T.-G.; Zong, M.-H.; Wu, H. Bifidobacterium spp. as functional foods: A review of current status, challenges, and strategies. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 23, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saturio, S.; Nogacka, A.M.; Alvarado-Jasso, G.M.; Salazar, N.; Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.d.L.; Gueimonde, M.; Arboleya, S. Role of Bifidobacteria on Infant Health. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou-Yang, M.-C.; Sun, Y.; Liebowitz, M.; Chen, C.-C.; Fang, M.-L.; Dai, W.; Chuang, T.-W.; Chen, J.-L.; Dai, W. Accelerated weight gain, prematurity, and the risk of childhood obesity: A meta-analysis and systematic review. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, J.L.Y.; Burnett, A.C.; Treyvaud, K.; Spittle, A.J. Early environment and long-term outcomes of preterm infants. J. Neural Transm. 2020, 127, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Sitarik, A.R.; Woodcroft, K.; Johnson, C.C.; Zoratti, E. Birth Mode, Breastfeeding, Pet Exposure, and Antibiotic Use: Associations With the Gut Microbiome and Sensitization in Children. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2019, 19, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandall, J.; Tribe, R.M.; Avery, L.; Mola, G.; Visser, G.H.; Homer, C.S.; Gibbons, D.; Kelly, N.M.; Kennedy, H.P.; Kidanto, H.; et al. Short-term and long-term effects of caesarean section on the health of women and children. Lancet 2018, 392, 1349–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falony, G.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Raes, J. Richness and ecosystem development across faecal snapshots of the gut microbiota. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.; Kolodziejczyk, A.A.; Thaiss, C.A.; Elinav, E. Dysbiosis and the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumbhare, S.V.; Patangia, D.V.; Patil, R.H.; Shouche, Y.S.; Patil, N.P. Factors influencing the gut microbiome in children: From infancy to childhood. J. Biosci. 2019, 44, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galazzo, G.; van Best, N.; Bervoets, L.; Dapaah, I.O.; Savelkoul, P.H.; Hornef, M.W.; Lau, S.; Hamelmann, E.; Penders, J.; Hutton, E.K.; et al. Development of the Microbiota and Associations with Birth Mode, Diet, and Atopic Disorders in a Longitudinal Analysis of Stool Samples, Collected From Infancy Through Early Childhood. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1584–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, J.; Watanabe, K.; Jiang, J.; Matsuda, K.; Chao, S.-H.; Haryono, P.; La-Ongkham, O.; Sarwoko, M.-A.; Sujaya, I.N.; Zhao, L.; et al. Diversity in gut bacterial community of school-age children in Asia. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Salazar, E.O.; Ortiz-López, M.G.; Granados-Silvestre, M.D.L.; Palacios-González, B.; Menjivar, M. Altered Gut Microbiota and Compositional Changes in Firmicutes and Proteobacteria in Mexican Undernourished and Obese Children. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, A.; Skov, T.H.; Bahl, M.I.; Roager, H.M.; Christensen, L.B.; Ejlerskov, K.T.; Mølgaard, C.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Licht, T.R. Establishment of Intestinal Microbiota during Early Life: A Longitudinal, Explorative Study of a Large Cohort of Danish Infants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 2889–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, Y.; Belzer, C.; Smidt, H.; de Weerth, C. Development of the gut microbiota in healthy children in the first ten years of life: Associations with internalizing and externalizing behavior. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2038853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Tapia, M.; Tovar, A.R.; Torres, N. Diet as Regulator of Gut Microbiota and its Role in Health and Disease. Arch. Med. Res. 2019, 50, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, V.; Gouda, M.; Moncivaiz, J.; Gordon, A.; Reo, N.V.; Hussein, L.; Paliy, O. Differences in Gut Metabolites and Microbial Composition and Functions between Egyptian and U.S. Children Are Consistent with Their Diets. mSystems 2017, 2, e00169-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsigalou, C.; Paraschaki, A.; Karvelas, A.; Kantartzi, K.; Gagali, K.; Tsairidis, D.; Bezirtzoglou, E. Gut microbiome and Mediterranean diet in the context of obesity. Current knowledge, perspectives and potential therapeutic targets. Metab. Open 2021, 9, 100081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemsen, Y.; Beijers, R.; Vasquez, A.A.; de Weerth, C. Do Breastfeeding History and Diet Quality Predict Inhibitory Control at Preschool Age? Nutrients 2021, 13, 2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieger, A.J.; Scott, J.; Cobiac, L. Dietary patterns and breast-feeding in Australian children. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 1939–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, M.F.; Zachariassen, G.; Bahl, M.I.; Bergström, A.; Høst, A.; Michaelsen, K.F.; Licht, T.R. Having older siblings is associated with gut microbiota development during early childhood. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, G.C.; Chee, K.K.; Hong, P.-Y.; Lay, C.; Satria, C.D.; Sumadiono; Soenarto, Y.; Haksari, E.L.; Aw, M.; Shek, L.P.-C.; et al. Evaluation of stool microbiota signatures in two cohorts of Asian (Singapore and Indonesia) newborns at risk of atopy. BMC Microbiol. 2011, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir, A.; Erez-Granat, O.; Braun, T.; Sosnovski, K.; Hadar, R.; BenShoshan, M.; Heiman, S.; Abbas-Egbariya, H.; Saar, E.G.; Efroni, G.; et al. Gut microbiome development in early childhood is affected by day care attendance. Npj Biofilms Microbiomes 2022, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, E.D.; Hjelmsø, M.H.; Thorsen, J.; Shah, S.; Redgwell, T.; Poulsen, C.E.; Trivedi, U.; Russel, J.; Gupta, S.; Chawes, B.L.; et al. The developing airway and gut microbiota in early life is influenced by age of older siblings. Microbiome 2022, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tap, J.; Derrien, M.; Törnblom, H.; Brazeilles, R.; Cools-Portier, S.; Doré, J.; Störsrud, S.; Le Nevé, B.; Öhman, L.; Simrén, M. Identification of an Intestinal Microbiota Signature Associated With Severity of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 111–123.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gacesa, R.; Kurilshikov, A.; Vila, A.V.; Sinha, T.; Klaassen, M.A.Y.; Bolte, L.A.; Andreu-Sánchez, S.; Chen, L.; Collij, V.; Hu, S.; et al. Environmental factors shaping the gut microbiome in a Dutch population. Nature 2022, 604, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murri, M.; Leiva, I.; Gomez-Zumaquero, J.M.; Tinahones, F.J.; Cardona, F.; Soriguer, F.; Queipo-Ortuño, M.I. Gut microbiota in children with type 1 diabetes differs from that in healthy children: A case-control study. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohir, W.; Ratcliffe, E.M.; Sloboda, D.M. Of the bugs that shape us: Maternal obesity, the gut microbiome, and long-term disease risk. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 77, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanislawski, M.A.; Dabelea, D.; Wagner, B.D.; Sontag, M.K.; Lozupone, C.A.; Eggesbø, M. Pre-pregnancy weight, gestational weight gain, and the gut microbiota of mothers and their infants. Microbiome 2017, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galley, J.D.; Bailey, M.; Dush, C.K.; Schoppe-Sullivan, S.; Christian, L. Maternal Obesity Is Associated with Alterations in the Gut Microbiome in Toddlers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, H.M.; Bridgman, S.L.; Chari, R.; Field, C.J.; Guttman, D.S.; Becker, A.B.; Mandhane, P.J.; Turvey, S.E.; Subbarao, P.; Sears, M.R.; et al. Roles of Birth Mode and Infant Gut Microbiota in Intergenerational Transmission of Overweight and Obesity From Mother to Offspring. JAMA Pediatr. 2018, 172, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Enterotype P_type vs. B_type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | OR a | 95% CI | p-Value | |
| Pooled sample | ||||
| Gestational age (weeks) | 708 | 1.02 | 0.97, 1.08 | 0.39 |
| Delivery mode | 697 | 0.61 | ||
| Vaginal | — | — | ||
| Cesarean | 0.88 | 0.53, 1.43 | ||
| Early neonatal antibiotics | 704 | 0.75 | ||
| No | — | — | ||
| Yes | 0.87 | 0.38, 1.97 | ||
| Human milk consumption | 632 | 0.015 | ||
| No | — | — | ||
| Yes | 1.99 | 1.14, 3.68 | ||
| Duration of human milk consumption (months) | 632 | 1.01 | 0.97, 1.05 | 0.60 |
| Skin-to-skin practice | 695 | 0.51 | ||
| Yes | — | — | ||
| No | 0.81 | 0.41, 1.52 | ||
| Maternal prepregnancy BMI | 777 | 0.34 | ||
| Underweight | 0.90 | 0.40, 1.82 | ||
| Normal | — | — | ||
| Overweight | 1.17 | 0.71, 1.87 | ||
| Obese | 1.75 | 0.92, 3.18 | ||
| Daycare exposure at 1 year | 722 | <0.001 | ||
| Family | — | — | ||
| Childcare assistant/Paid home help | 0.69 | 0.43, 1.10 | ||
| Daycare centre | 2.05 | 1.15, 3.65 | ||
| Household siblings at 1 year | 728 | 0.045 | ||
| No | — | — | ||
| At least 1 | 1.51 | 1.01, 2.28 | ||
| Mother born in France | 798 | 0.46 | ||
| Yes | — | — | ||
| No | 1.26 | 0.67, 2.25 | ||
| ELFE | ||||
| Age at complementary feeding | 493 | 0.83 | ||
| ≤6 months | — | — | ||
| >6 months | 1.08 | 0.52, 2.14 | ||
| Age at first vegetables introduction | 492 | 0.45 | ||
| ≤6 months | — | — | ||
| >6 months | 0.79 | 0.42, 1.43 | ||
| Age at first fruits introduction | 493 | 0.24 | ||
| ≤6 months | — | — | ||
| >6 months | 0.72 | 0.40, 1.24 | ||
| Age at first meat introduction | 483 | 0.092 | ||
| ≤6 months | — | — | ||
| >6 months | 0.60 | 0.33, 1.09 | ||
| Age at first fish introduction | 477 | 0.019 | ||
| ≤6 months | — | — | ||
| >6 months | 0.45 | 0.24, 0.88 | ||
| Maternal pregnancy diet (PNSS score) * | 560 | 0.17 | ||
| ≤7.80 | — | — | ||
| >7.80 | 1.37 | 0.87, 2.17 | ||
| Maternal pregnancy diet (Pregnancy score) * | 560 | 0.43 | ||
| ≤7.75 | — | — | ||
| >7.75 | 1.21 | 0.76, 1.93 | ||
| Antibiotics in the first year | 609 | 0.17 | ||
| Yes | — | — | ||
| No | 0.74 | 0.47, 1.14 | ||
| Environment | 607 | 0.37 | ||
| Rural | — | — | ||
| Urban | 1.24 | 0.78, 2.03 | ||
| EPIPAGE 2 | ||||
| Antibiotics during delivery | 149 | 0.072 | ||
| No | — | — | ||
| Yes | 0.41 | 0.14, 1.08 | ||
| Antibiotics during pregnancy | 149 | 0.79 | ||
| No | — | — | ||
| Yes | 1.13 | 0.47, 2.70 | ||
| Chao1 Estimate | Shannon Index | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pooled Sample | N | Beta a | 95% CI | p-Value | Beta a | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Gestational age (weeks) | 708 | 1.8 | 0.27, 3.3 | 0.021 | 0.00 | 0.00, 0.01 | 0.31 |
| Delivery mode | 697 | 0.004 | <0.001 | ||||
| Vaginal | — | — | — | — | |||
| Cesarean | −22 | −37, −7.1 | −0.12 | −0.20, −0.05 | |||
| Early neonatal antibiotics | 704 | 0.28 | 0.11 | ||||
| No | — | — | — | — | |||
| Yes | 14 | −11, 40 | 0.10 | −0.02, 0.23 | |||
| Human milk consumption | 632 | 0.41 | 0.79 | ||||
| No | — | — | — | — | |||
| Yes | 6.4 | −8.9, 22 | 0.01 | −0.08, 0.06 | |||
| Duration of human milk consumption (months) | 632 | 0.52 | −0.69, 1.7 | 0.40 | 0.01 | 0.00, 0.01 | 0.076 |
| Skin-to-skin practice | 695 | 0.89 | 0.56 | ||||
| Yes | — | — | — | — | |||
| No | −1.4 | −21, 19 | 0.03 | −0.07, 0.13 | |||
| Maternal prepregnancy BMI | 777 | 0.007 | 0.039 | ||||
| Underweight | 9.7 | −12, 32 | 0.05 | −0.06, 0.16 | |||
| Normal | — | — | — | — | |||
| Overweight | 22 | 6.6, 37 | 0.10 | 0.02, 0.17 | |||
| Obese | 26 | 4.7, 48 | 0.08 | −0.02, 0.19 | |||
| Daycare exposure at 1 year | 722 | >0.99 | 0.92 | ||||
| Family | — | — | — | — | |||
| Childcare assistant/Paid home help | 0.30 | −14, 14 | 0.00 | −0.07, 0.07 | |||
| Daycare centre | −0.66 | −20, 19 | 0.02 | −0.11, 0.08 | |||
| Household siblings at 1 year | 728 | <0.001 | <0.001 | ||||
| No | — | — | — | — | |||
| At least 1 | 37 | 25, 49 | 0.16 | 0.10, 0.22 | |||
| Mother born in France | 798 | 0.24 | 0.047 | ||||
| Yes | — | — | — | — | |||
| No | −12 | −32, 8.2 | −0.10 | −0.20, 0.00 | |||
| ELFE | |||||||
| Age at complementary feeding | 493 | 0.95 | 0.59 | ||||
| ≤6 months | — | — | — | — | |||
| >6 months | −0.63 | −22, 21 | 0.03 | −0.08, 0.14 | |||
| Age at first vegetables introduction | 492 | 0.92 | 0.46 | ||||
| ≤6 months | — | — | — | — | |||
| >6 months | 0.92 | −17, 19 | 0.03 | −0.06, 0.13 | |||
| Age at first fruits introduction | 493 | 0.92 | 0.83 | ||||
| ≤6 months | — | — | — | — | |||
| >6 months | 0.80 | −15, 17 | 0.01 | −0.07, 0.09 | |||
| Age at first meat introduction | 483 | 0.43 | 0.74 | ||||
| ≤6 months | — | — | — | — | |||
| >6 months | −7.1 | −25, 11 | 0.02 | −0.07, 0.11 | |||
| Age at first fish introduction | 477 | 0.52 | 0.91 | ||||
| ≤6 months | — | — | — | — | |||
| >6 months | −6.7 | −27, 13 | 0.01 | −0.11, 0.10 | |||
| Maternal pregnancy diet (PNNS score) * | 560 | 0.74 | 0.54 | ||||
| ≤7.80 | — | — | — | — | |||
| >7.80 | 2.2 | −11, 15 | 0.02 | −0.04, 0.08 | |||
| Maternal pregnancy diet (Pregnancy score) * | 560 | 0.78 | 0.69 | ||||
| ≤7.75 | — | — | — | — | |||
| >7.75 | 1.9 | −11, 15 | 0.01 | −0.05, 0.08 | |||
| Antibiotics in the first year | 609 | 0.33 | 0.11 | ||||
| Yes | — | — | — | — | |||
| No | 6.5 | −6.4, 19 | 0.05 | −0.01, 0.12 | |||
| Environment | 607 | 0.75 | 0.72 | ||||
| Rural | — | — | — | — | |||
| Urban | −2.3 | −16, 12 | 0.01 | −0.08, 0.06 | |||
| EPIPAGE 2 | |||||||
| Antibiotics during delivery | 149 | 0.50 | 0.72 | ||||
| No | — | — | — | — | |||
| Yes | 12 | −23, 46 | 0.03 | −0.13, 0.19 | |||
| Antibiotics during pregnancy | 149 | 0.99 | 0.33 | ||||
| No | — | — | — | — | |||
| Yes | −0.23 | −33, 33 | 0.08 | −0.08, 0.23 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toubon, G.; Butel, M.-J.; Rozé, J.-C.; Nicolis, I.; Delannoy, J.; Zaros, C.; Ancel, P.-Y.; Aires, J.; Charles, M.-A. Early Life Factors Influencing Children Gut Microbiota at 3.5 Years from Two French Birth Cohorts. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061390
Toubon G, Butel M-J, Rozé J-C, Nicolis I, Delannoy J, Zaros C, Ancel P-Y, Aires J, Charles M-A. Early Life Factors Influencing Children Gut Microbiota at 3.5 Years from Two French Birth Cohorts. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(6):1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061390
Chicago/Turabian StyleToubon, Gaël, Marie-José Butel, Jean-Christophe Rozé, Ioannis Nicolis, Johanne Delannoy, Cécile Zaros, Pierre-Yves Ancel, Julio Aires, and Marie-Aline Charles. 2023. "Early Life Factors Influencing Children Gut Microbiota at 3.5 Years from Two French Birth Cohorts" Microorganisms 11, no. 6: 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061390
APA StyleToubon, G., Butel, M.-J., Rozé, J.-C., Nicolis, I., Delannoy, J., Zaros, C., Ancel, P.-Y., Aires, J., & Charles, M.-A. (2023). Early Life Factors Influencing Children Gut Microbiota at 3.5 Years from Two French Birth Cohorts. Microorganisms, 11(6), 1390. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061390





