Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Effects of Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Plant Extraction Preparation
2.3. Green Synthesis of ZnO and TiO2 NPs with C. procera Leaf Extract
2.3.1. Synthesis of ZnO NPs
2.3.2. Green Synthesis of TiO2 NPs
2.4. Characterization of ZnO and TiO2 NPs
2.5. Bacterial Strains
2.6. Antibacterial Activity of ZnO and TiO2 NPs
2.7. Synergistic Effects of NPs with Antibiotics against Clinical Isolates
2.8. Antioxidant Potential of ZnO and TiO2 NPs by DPPH Method
2.9. In Vivo Study
2.9.1. Ethical Approval
2.9.2. Experimental Animals and Toxicity Evaluation of Green Synthesized ZnO and TiO2 Nanoparticles
2.9.3. Histological Examinations
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characterizations of ZnO and TiO2 NPs
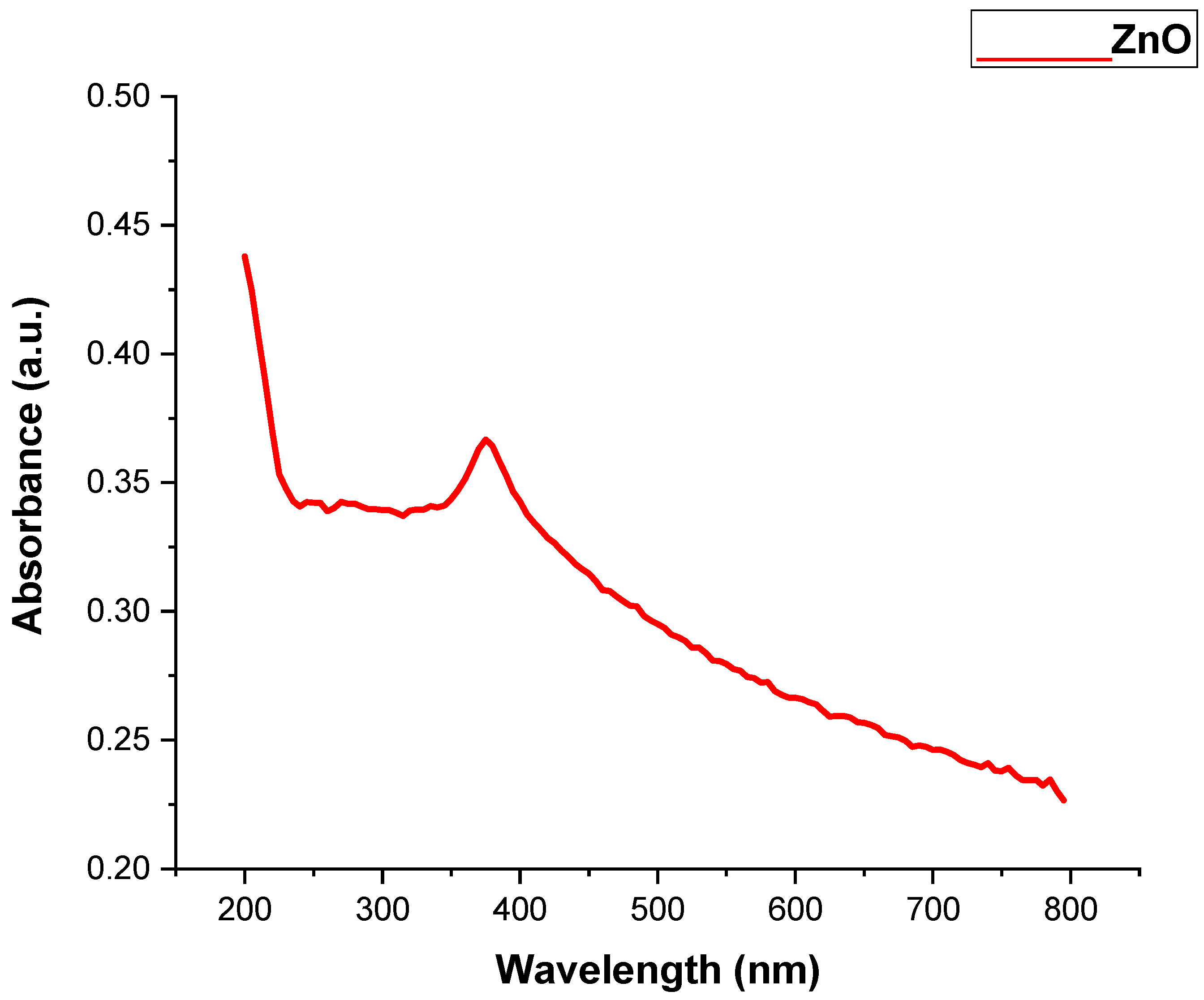
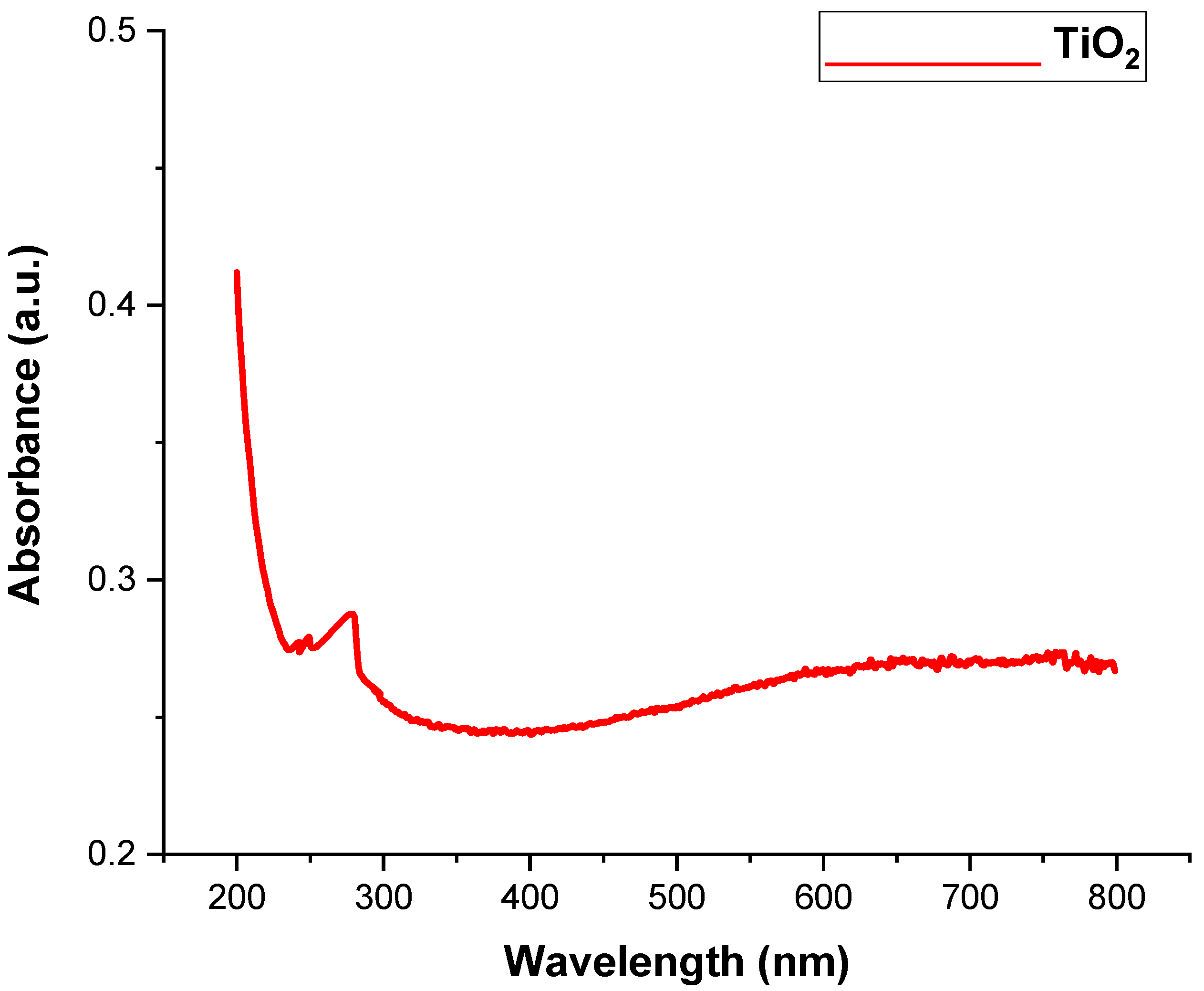
3.1.1. UV-Visible Spectroscopy
3.1.2. X-ray Diffraction
3.1.3. FT-IR Spectroscopic Analysis of the ZnO and TiO2 NPs
3.1.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.2. Antibacterial and Synergistic Effects of Green Synthesized ZnO and TiO2 NPs
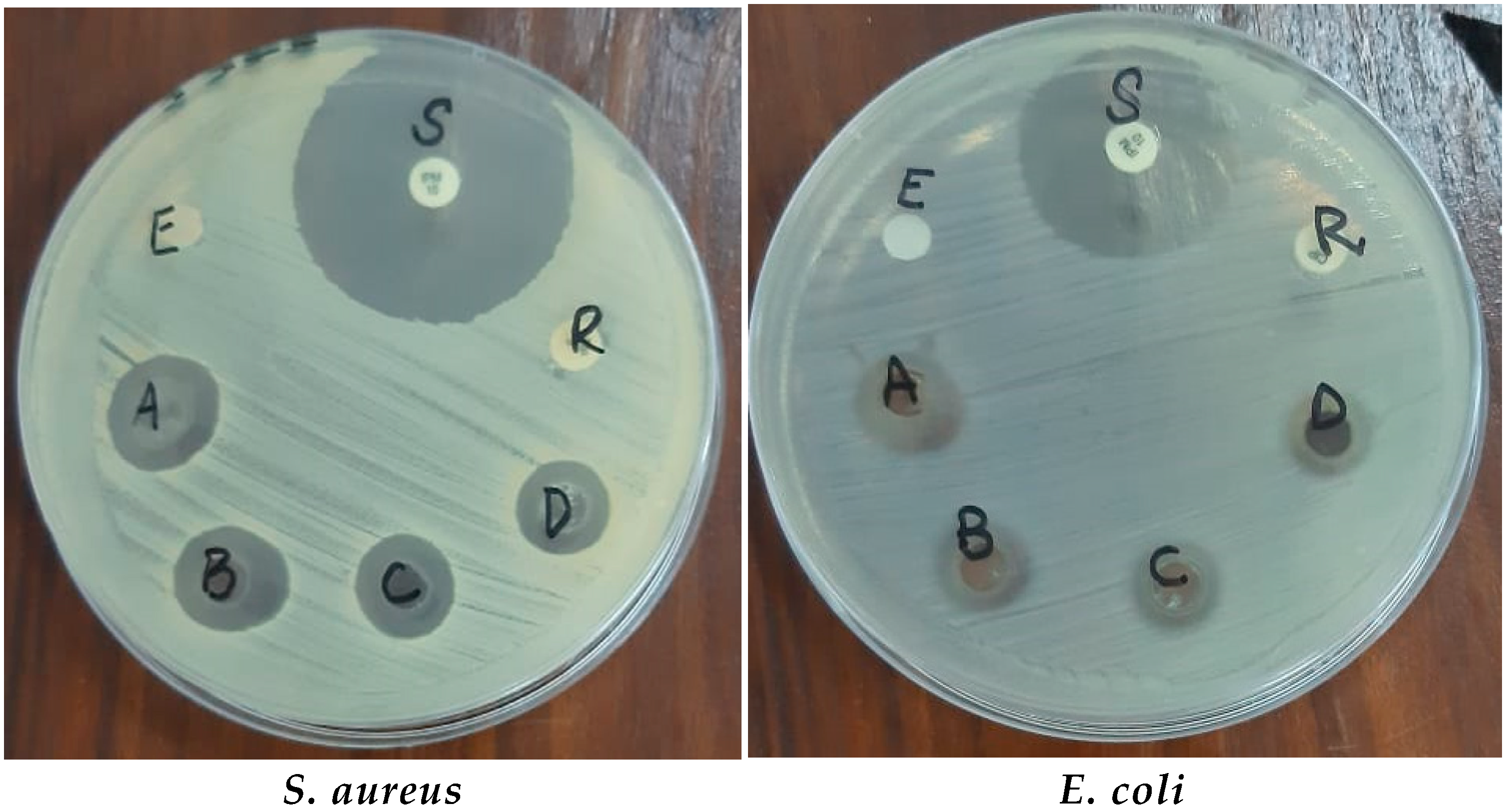
3.2.1. Antibacterial Activity and Synergistic Effects of ZnO NPs against Bacterial Strains
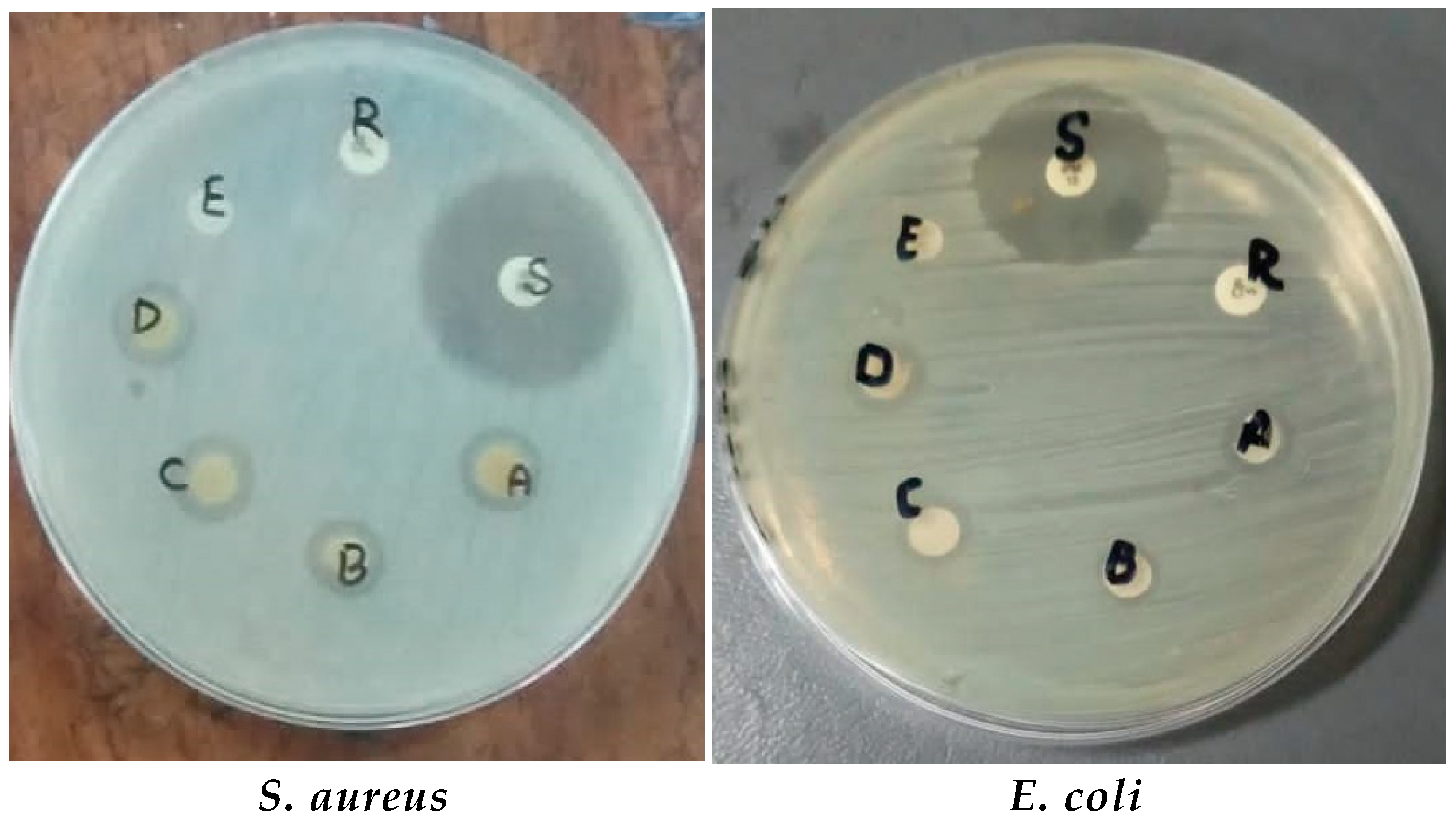
3.2.2. Antibacterial Activity and Synergistic Effects of TiO2 NPs against Bacterial Strains
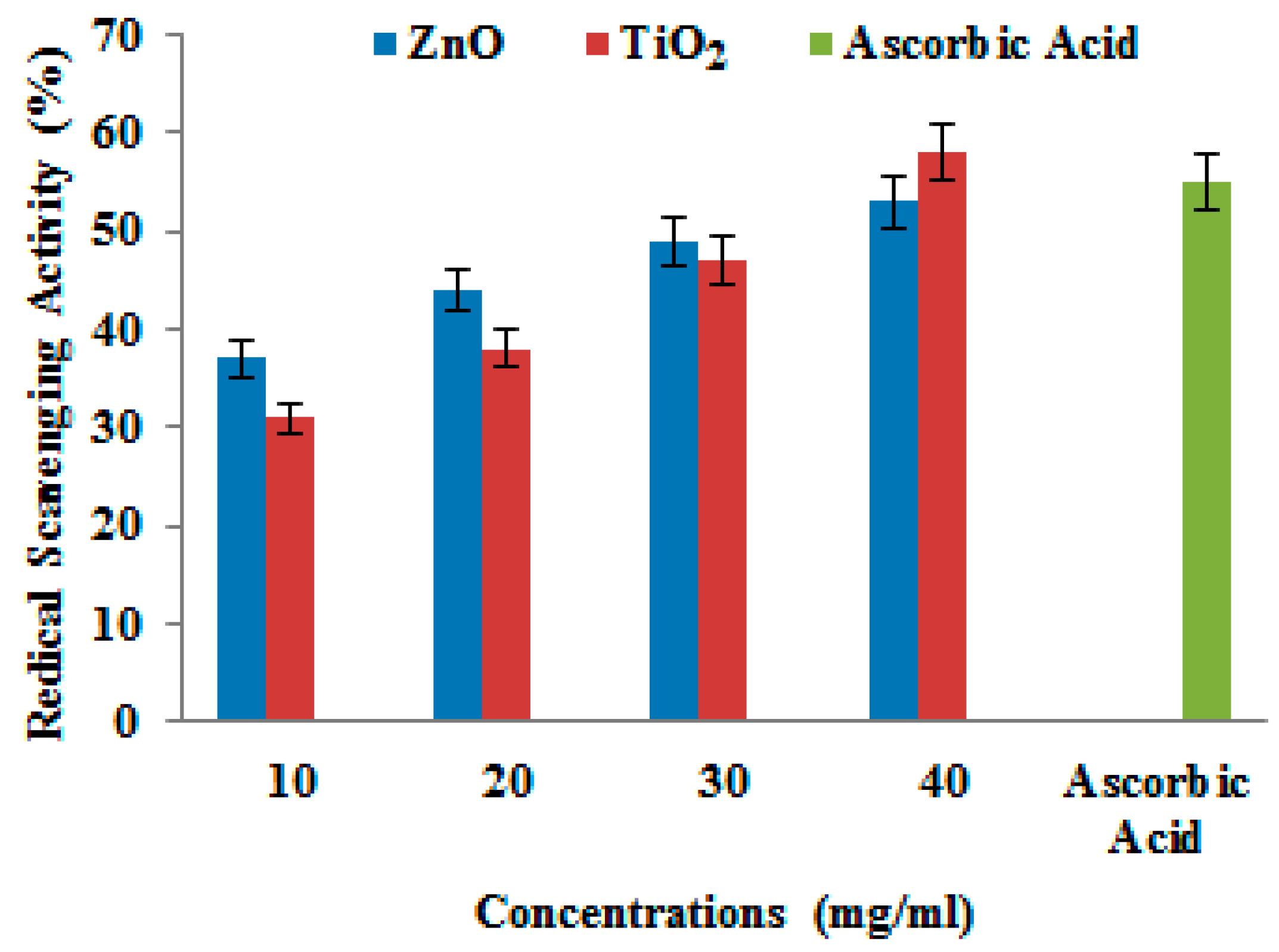
3.3. Antioxidant Activity of ZnO and TiO2 NPs by DPPH Assay
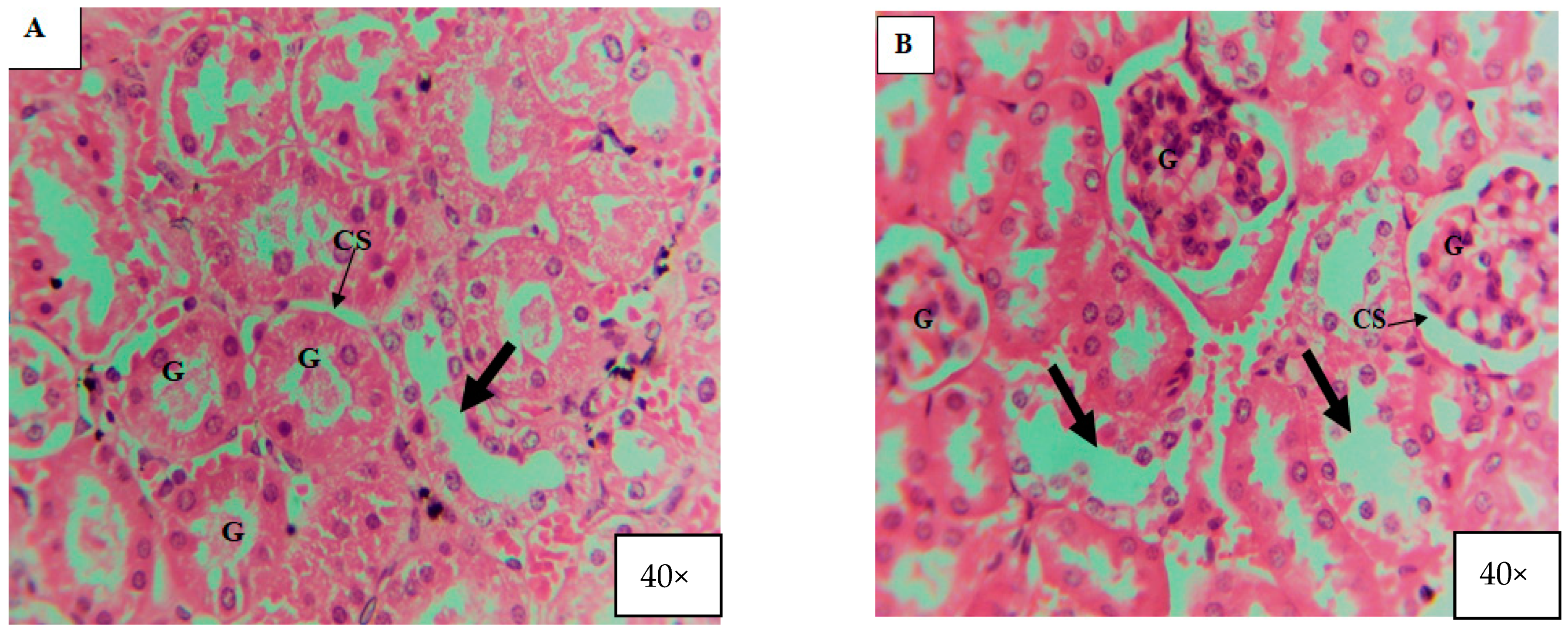
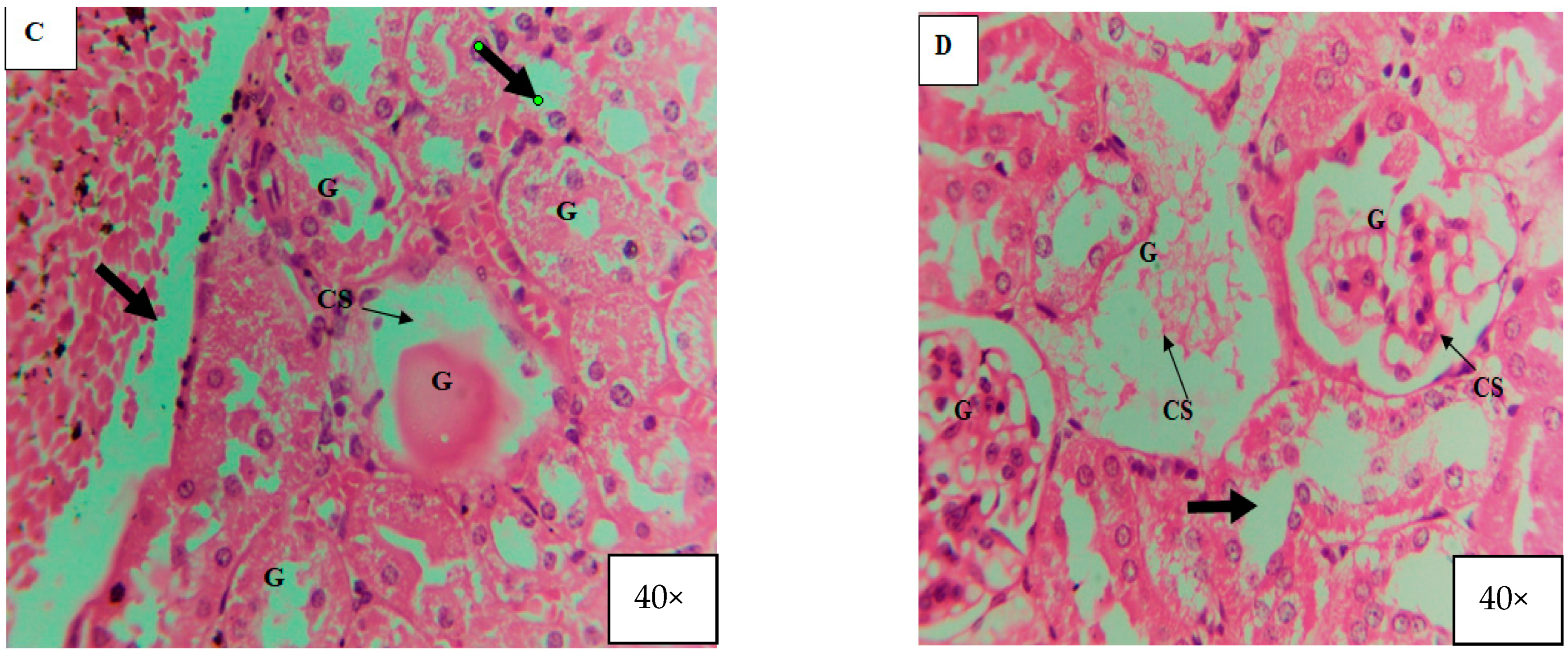
3.4. Effects of ZnO and TiO2 NPs on the Kidney
Histological Examination
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, S.; Ahmad, M.; Swami, B.L.; Ikram, S. A review on plants extract mediated synthesis of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial applications: A green expertise. J. Adv. Res. 2016, 7, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqi, K.S.; Husen, A. Fabrication of metal nanoparticles from fungi and metal salts: Scope and application. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2016, 11, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, I.H.; Ashraf, M.; Sabir, I.A.; Manzoor, M.A.; Malik, M.S.; Gulzar, S.; Zhang, Y. Green synthesis and Characterization of Copper oxide nanoparticles using Calotropis procera leaf extract and their different biological potentials. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1259, 132696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Serrano, A.; Olivas, R.M.; Landaluze, J.S.; Cámara, C. Nanoparticles: A global vision. Characterization, separation, and quantification methods. Potential environmental and health impact. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundschuh, M.; Filser, J.; Luderwald, S.; Mckee, M.S.; Metreveli, G.; Schaumann, G.E.; Wagner, S. Nanoparticles in the environment: Where do we come from, where do we go to. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hu, C.; Shao, L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles: Present situation and prospects for the future. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdiyev, A.M.; Abamor, E.S.; Bagirova, M.; Rafailovich, M. Antimicrobial effects of TiO2 and Ag2O nanoparticles against drug-resistant bacteria and leishmania parasites. Future Microbiol. 2011, 6, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.M.; Shelar, A.; Kasabe, U.; Nikam, L.K.; Pawar, R.A.; Sangshetti, J.; Kale, B.B.; Singh, A.V.; Patil, R.; Chaskar, M.G. Biofilm inhibition in Candida albicans with biogenic hierarchical zinc-oxide nanoparticles. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 134, 112592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singhal, G.; Bhavesh, R.; Kasariya, K.; Sharma, A.R.; Singh, R.P. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using Ocimum sanctum (Tulsi) leaf extract and screening its antimicrobial activity. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2011, 13, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, M.S.; Liaqat, I. Silver nanoparticles and their applications-A comprehensive review. Pure Appl. Biol. (PAB) 2021, 11, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, M.S.; Liaqat, I.; Andleeb, S.; Naseem, S.; Zafar, U.; Sadiqa, A.; Liaqat, I.; Ali, N.M.; Bibi, A.; Arshad, N.; et al. Biogenic synthesis, characterization and antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles against human pathogens. J. Oleo Sci. 2022, 71, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufail, S.; Liaqat, I.; Ali, S.; Ulfat, M.; Shafi, A.; Sadiqa, A.; Iqbal, R.; Ahsan, F. Bacillus licheniformis (MN900686) mediated synthesis, characterization and antimicrobial potential of silver nanoparticles. J. Oleo Sci. 2022, 71, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, Y.H.; Xu, X.; Ma, A.P.; Liu, F.; Ng, A.M.; Shen, Z.; Leung, F.C. Toxicity of ZnO and TiO2 to Escherichia coli cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatasubbu, G.D.; Baskar, R.; Anusuya, T.; Seshan, C.A.; Chelliah, R. Toxicity mechanism of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide nanoparticles against food pathogens. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 148, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Singh, N.B.; Hussain, I.; Singh, H.; Singh, S.C. Plant-nanoparticle interaction: An approach to improve agricultural practices and plant productivity. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Invent. 2015, 4, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Alagumuthu, G.; Kirubha, R. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Cissus quadrangularis plant extract and their antibacterial activity University. Int. J. Nanomater. Biostructures 2012, 2, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, N.H.; Ismail, M.A.; Abdel-Mageed, W.M.; Shoreit, A.A.M. Antimicrobial activity of latex silver nanoparticles using Calotropis procera. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2014, 4, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aati, H.; El-Gamal, A.; Shaheen, H.; Kayser, O. Traditional use of ethnomedicinal native plants in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2019, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.C.C.; da Silva, A.B.; Teixeira, F.M.; de Sousa, P.C.P.; Rondon, R.M.M.; Júnior, J.E.R.H.; de Vasconcelos, S.M.M. Therapeutic and biological activities of Calotropis procera (Ait.) R. Br. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2010, 3, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willander, M.; Nur, O.; Zhao, Q.X.; Yang, L.L.; Lorenz, M.; Cao, B.Q.; Perez, J.Z.; Czekalla, C.; Zimmermann, G.; Grundmann, M.; et al. Zinc Oxide nanorod based photonic devices: Recent progress in growth, light emitting diodes and lasers. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 332001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishwar, S.; Hasan, K.U.; Tzamalis, G.; Nur, O.; Willander, M.; Kwack, H.S.; Dang, D.L.S. Electro-optical and cathodoluminescence properties of low temperature grown ZnO nanorods/p-GaN white light emitting diodes. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 2010, 207, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Shohag, S.; Uddin, M.J.; Islam, M.R.; Nafady, M.H.; Akter, A.; Cavalu, S. Exploring the journey of zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO-NPs) toward biomedical applications. Materials 2022, 15, 2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, S.; Faheem, M.; Hanif, U.; Bahadur, S.; Taj, S.; Liaqat, F.; Pereira, L.; Liaqat, I.; Shaheen, S.; Shuaib, M.; et al. Toxicological effects of the chemical and green ZnO NPs on Cyprinus carpio L. observed under light and scanning electron microscopy. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2022, 85, 848–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irshad, M.A.; Nawaz, R.; ur Rehman, M.Z.; Imran, M.; Ahmad, J.; Ahmad, S.; Inam, A.; Razzaq, A.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, S. Synthesis and characterization of titanium dioxide nanoparticles by chemical and green methods and their antifungal activities against wheat rust. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidya, C.; Hiremath, S.; Chandraprabha, M.N.; Antonyraj, M.L.; Gopal, I.V.; Jain, A.; Bansal, K. Green synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles by Calotropis gigantea. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2013, 1, 118–120. [Google Scholar]
- Prashanth, V.; Priyanka, K.; Remya, N. Solar photocatalytic degradation of metformin by TiO2 synthesized using Calotropis gigantea leaf extract. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 83, 1072–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, I.; Liaqat, M.; Tahir, H.M.; Ali, N.M.; Arshad, M.; Arshad, N. Motility effects biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter cloacae. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 32, 927–932. [Google Scholar]
- Liaqat, I.; Gulab, B.; Hanif, U.; Sultan, A.; Sadiqa, A.; Zafar, U.; Afzaal, M.; Naseem, S.; Akram, S.; Saleem, G. Honey Potential as Antibiofilm, Antiquorum Sensing and Dispersal Agent against Multispecies Bacterial Biofilm. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 71, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dridi, R.; Essghaier, B.; Hannachi, H.; Khedher, G.B.; Chaffei, C.; Zid, M.F. Biosynthesized silver nanoparticles using Anagallis monelli: Evaluation of antioxidant activity, antibacterial and antifungal effects. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1251, 132076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, A.; Karimi, F.; Fatahian, S.; Yazdani, F. Effects of Zinc Oxide nanoparticles on renal function in mice. J. Kashan Univ. Med. Sci. 2013, 16, 603–604. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, P.; Tzeng, T.; Shah, R.; Stutzenberger, F. Nanomaterials for antimicrobial applications and pathogen detection. Curr. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 3, 111–128. [Google Scholar]
- Dhage, S.; Pasricha, R.; Ravi, V. Synthesis of fine particles of ZnO at 100 °C. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falana, M.B.; Nurudeen, Q.O. Evaluation of phytochemical constituents and in vitro antimicrobial activities of leaves extracts of Calotropis procera against certain human pathogens. Not. Sci. Biol. 2020, 12, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, H.; Kumar, S.V.; Rajeshkumar, S. A review on green synthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles–An eco-friendly approach. Resour.-Effic. Technol. 2017, 3, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, I. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy of dental unit water line biofilm bacteria. Spectroscopy 2009, 23, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ye, Z.; Xu, Z. Effect of the morphology on the optical properties of ZnO nanostructures. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostructures 2009, 42, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.C.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, J. Synthesis and characterization of phosphated mesoporous titanium dioxide with high photocatalytic activity. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 2280–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, I.; Shaanzeh, Z.; Bibi, A.; Zafar, U.; Naseem, S.; Ali, R.; Andleeb, S.; Saleem, G.; Liaqat, I.; Afzaal, M. In vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Biogenically Synthesized Nickel and Zinc Nanoparticles against Selected Pathogenic Bacterial Strains. J. Oleo Sci. 2022, 71, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Pervaiz, I.; Malik, H.; Kanwal, Z.; Rafique, M.; Gillani, S.S.A. Investigations on Synergistic and Antioxidant Actions of Medicinal Plant-Based Biosynthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Against E. coli and K. pneumonia Bacteria. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2022, 25, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Rajashekara, S.; Shrivastava, A.; Sumhitha, S.; Kumari, S. Biomedical Applications of Biogenic Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Manufactured from Leaf Extracts of Calotropis gigantea (L.) Dryand. BioNanoScience 2020, 10, 654–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Enazi, N.M.; Alsamhary, K.; Kha, M.; Ameen, F. In vitro anticancer and antibacterial performance of biosynthesized Ag and Ce co-doped ZnO NPs. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 46, 89–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelover, S.; Gómez, L.A.; Reyes, K.; Leal, M.T. A practical demonstration of water disinfection using TiO2 films and sunlight. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3274–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, A.; Marjan, Z.M.; Foong, C.W. Total antioxidant activity and phenolic content in selected vegetables. Food Chem. 2004, 87, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Kumar, S.V.; Ramaiah, A.; Agarwal, H.; Lakshmi, T.; Roopan, S.M. Biosynthesis of zinc oxide nanoparticles using Mangifera indica leaves and evaluation of their antioxidant and cytotoxic properties in lung cancer (A549) cells. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2018, 117, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassan, A.; Alves, V.M.; Amberg, A.; Anger, L.T.; Beilke, L.; Bender, A.; Bernal, A.; Cronin, M.T.; Hsieh, J.H.; Johnson, C.; et al. In silico approaches in organ toxicity hazard assessment: Current status and future needs for predicting heart, kidney and lung toxicities. Comput. Toxicol. 2021, 20, 100188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, R.A.; Toledo, R.P.; Joshi, N.; Berengue, O.M. Green synthesis and applications of ZnO and TiO2 nanostructures. Molecules 2021, 26, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, M.; Jabeen, F.; Shabbir, S.; Asghar, M.S.; Khan, M.S.; Chaudhry, A.S. Toxicity of nano-titanium dioxide (TiO2-NP) through various routes of exposure: A review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 172, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Strains | Zone of Inhibition (mm) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration of C. procera Synthesized ZnO NPs (mg/mL) | ZnO NPs (20 mg/mL) + Antibiotics | |||||||||
| Plant Extract | Chemically Synthesized ZnO NPs | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | IMP | ZnO + IMP | CIP | ZnO + CIP | |
| S. aureus | 6 ± 0.5 | 7 ± 0.4 | 8 ± 0.5 | 12 ± 0.5 | 15 ± 0.2 | 17 ± 0.2 | 25 ± 0.5 | 31 ± 0.1 | R | 13 ± 0.1 |
| S. pyrogenes | 7 ± 0.3 | 5 ± 0.3 | 7 ± 0.3 | 10 ± 0.5 | 13 ± 0.5 | 16 ± 0.5 | 27 ± 0.1 | 30 ± 0.5 | R | 12 ± 0.5 |
| E. coli | 6.5 ± 0.5 | 6 ± 0.4 | 7 ± 0.5 | 10 ± 0.3 | 10 ± 0.1 | 12 ± 0.1 | 18 ± 0.5 | 24 ± 0.3 | R | 11 ± 0.1 |
| P. aeruginosa | 6 ± 0.2 | 7 ± 0.3 | 9 ± 0.2 | 10 ± 0.2 | 11 ± 0.5 | 13 ± 0.5 | 21 ± 0.2 | 27 ± 0.2 | R | 12 ± 0.2 |
| Strains | Zone of Inhibition in mm | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration of C. procera Synthesized TiO2 NPs (mg/mL) | TiO2 NPs (20 mg/mL) + Antibiotics | |||||||||
| Plant Extract | Chemically Synthesized TiO2 NPs | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | IMP | TIO2 + IMP | CIP | TiO2 + CIP | |
| S. aureus | 7 ± 0.3 | 5 ± 0.3 | 10 ± 0.3 | 11 ± 0.2 | 12 ± 0.5 | 14 ± 0.5 | 25 ± 0.5 | 31 ± 0.3 | R | 13 ± 0.1 |
| S. pyrogenes | 6 ± 0.3 | 7 ± 0.3 | 9 ± 0.3 | 10 ± 0.5 | 11 ± 0.5 | 13 ± 0.5 | 27 ± 0.3 | 30 ± 0.5 | R | 12 ± 0.2 |
| E. coli | 6.5 ± 0.2 | 7 ± 0.4 | 6 ± 0.2 | 9 ± 0.2 | 10 ± 0.1 | 10 ± 0.1 | 18 ± 0.5 | 24 ± 0.5 | R | 11 ± 0.5 |
| P. aeruginosa | 7 ± 0.5 | 6 ± 0.4 | 8 ± 0.5 | 9 ± 0.2 | 9 ± 0.3 | 11 ± 0.2 | 21 ± 0.5 | 27 ± 0.2 | R | 12 ± 0.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Habib, S.; Rashid, F.; Tahir, H.; Liaqat, I.; Latif, A.A.; Naseem, S.; Khalid, A.; Haider, N.; Hani, U.; Dawoud, R.A.; et al. Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Effects of Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061363
Habib S, Rashid F, Tahir H, Liaqat I, Latif AA, Naseem S, Khalid A, Haider N, Hani U, Dawoud RA, et al. Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Effects of Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(6):1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061363
Chicago/Turabian StyleHabib, Samrin, Farzana Rashid, Hunaiza Tahir, Iram Liaqat, Asma Abdul Latif, Sajida Naseem, Awais Khalid, Nazima Haider, Umme Hani, Rehab A. Dawoud, and et al. 2023. "Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Effects of Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles" Microorganisms 11, no. 6: 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061363
APA StyleHabib, S., Rashid, F., Tahir, H., Liaqat, I., Latif, A. A., Naseem, S., Khalid, A., Haider, N., Hani, U., Dawoud, R. A., Modafer, Y., Bibi, A., & Jefri, O. A. (2023). Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Effects of Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide and Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles. Microorganisms, 11(6), 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11061363









