First Records of Possibly Human Pathogenic Rickettsia Species in Bat Ticks, Carios vespertilionis, in Sweden
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling, Analyses, and Processing of Ticks
2.2. Detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum
2.3. Detection of Babesia Species
2.4. Detection of Neoehrlichia mikurensis
2.5. Detection of TBEV
2.6. Detection of Rickettsia and Determination of Species
2.7. Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Number of Ticks Collected
3.2. Prevalence of Rickettsia
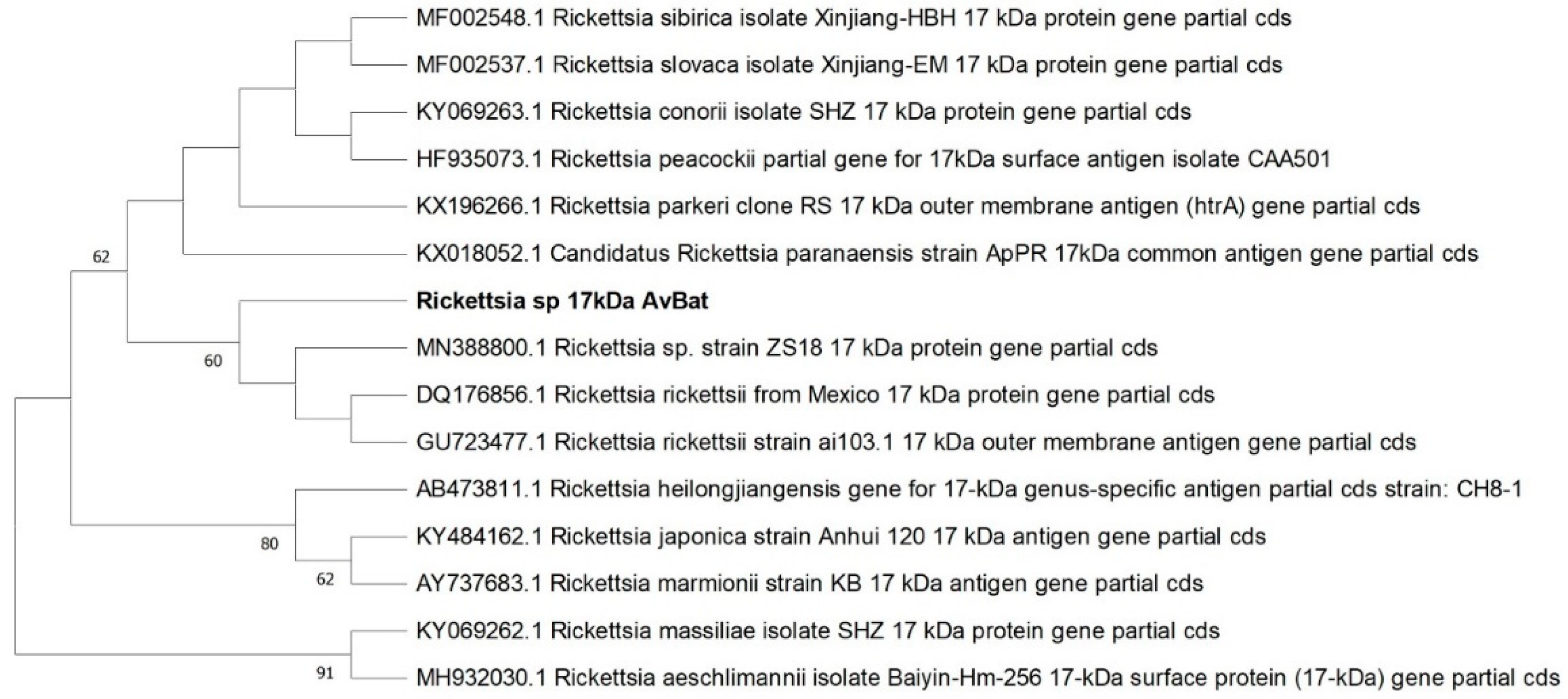
3.3. Sequencing of PCR Products and Phylogenetic Sequence Analysis
3.4. Prevalence of Other Tick-Borne Microorganisms
3.5. Co-Infections
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brook, C.E.; Dobson, A.P. Bats as ‘special’ reservoirs for emerging zoonotic pathogens. Trends Microbiol. 2015, 23, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahlén, I. Agreement on the Conservation of Bats in Europe—National Implementation Report from Sweden 2006; Swedish Enviromental Protection Agency: Stockholm, Sweden, 2006; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Naturvårdsverket. Fladdermusarter i Sverige. Available online: https://www.naturvardsverket.se/amnesomraden/arter-och-artskydd/fladdermossen-i-sverige/fladdermusarter-i-sverige/ (accessed on 2 May 2022).
- Jaenson, T.G.T.; Tälleklint, L.; Lundqvist, L.; Olsen, B.; Chirico, J.; Mejlon, H. Geographical distribution, host associations, and vector roles of ticks (Acari: Ixodidae, Argasidae) in Sweden. J. Med. Entomol. 1994, 31, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Péter, Á.; Barti, L.; Corduneanu, A.; Hornok, S.; Mihalca, A.D.; Sándor, A.D. First record of Ixodes Simplex found on a human host, with a review of cases of human infestation by bat tick species occurring in Europe. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2021, 12, 101722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Mihalca, A.D.; Petney, T.N. (Eds.) Ticks of Europe and North Africa; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-63759-4. [Google Scholar]
- Jaenson, T.G.T.; Wilhelmsson, P. First record of a suspected human-pathogenic Borrelia species in populations of the bat tick Carios vespertilionis in Sweden. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socolovschi, C.; Kernif, T.; Raoult, D.; Parola, P. Borrelia, Rickettsia, and Ehrlichia species in bat ticks, France, 2010. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1966–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornok, S.; Szőke, K.; Meli, M.L.; Sándor, A.D.; Görföl, T.; Estók, P.; Wang, Y.; Tu, V.T.; Kováts, D.; Boldogh, S.A.; et al. Molecular detection of vector-borne bacteria in bat ticks (Acari: Ixodidae, Argasidae) from eight countries of the Old and New Worlds. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornok, S.; Szőke, K.; Görföl, T.; Földvári, G.; Tu, V.T.; Takács, N.; Kontschán, J.; Sándor, A.D.; Estók, P.; Epis, S.; et al. Molecular investigations of the bat tick Argas vespertilionis (Ixodida: Argasidae) and Babesia vesperuginis (Apicomplexa: Piroplasmida) reflect “bat connection” between Central Europe and Central Asia. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2017, 72, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Fernández de Marco, M.d.M.; Goharriz, H.; Phipps, L.P.; McElhinney, L.M.; Hernández-Triana, L.M.; Wu, S.; Lin, X.; Fooks, A.R.; Johnson, N. Detection of tick-borne bacteria and Babesia with zoonotic potential in Argas (Carios) vespertilionis (Latreille, 1802) ticks from british bats. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yang, M.; Liu, G.; Hornok, S.; Zhao, S.; Sang, C.; Tan, W.; Wang, Y. Rickettsiae in the common pipistrelle Pipistrellus pipistrellus (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae) and the bat soft tick Argas vespertilionis (Ixodida: Argasidae). Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henningsson, A.J.; Hvidsten, D.; Kristiansen, B.-E.; Matussek, A.; Stuen, S.; Jenkins, A. Detection of Anaplasma phagocytophilum in Ixodes ricinus ticks from Norway using a realtime PCR assay targeting the Anaplasma citrate synthase gene gltA. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casati, S.; Sager, H.; Gern, L.; Piffaretti, J.-C. Presence of potentially pathogenic Babesia sp. for human in Ixodes ricinus in Switzerland. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2006, 13, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Labbé Sandelin, L.; Tolf, C.; Larsson, S.; Wilhelmsson, P.; Salaneck, E.; Jaenson, T.G.T.; Lindgren, P.-E.; Olsen, B.; Waldenström, J. Candidatus Neoehrlichia mikurensis in ticks from migrating birds in Sweden. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwaiger, M.; Cassinotti, P. Development of a quantitative real-time RT-PCR Assay with internal control for the laboratory detection of tick borne encephalitis virus (TBEV) RNA. J. Clin. Virol. 2003, 27, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gäumann, R.; Mühlemann, K.; Strasser, M.; Beuret, C.M. High-throughput procedure for tick surveys of tick-borne encephalitis virus and its application in a national surveillance study in Switzerland. AEM 2010, 76, 4241–4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenos, J.; Unsworth, N.B.; Graves, S.R. A highly sensitive and specific real-time PCR assay for the detection of spotted fever and typhus group Rickettsiae. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 73, 1083–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carl, M.; Tibbs, C.W.; Dobson, M.E.; Paparello, S.F.; Dasch, G.A. Diagnosis of acute typhus infection using the polymerase chain reaction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1990, 590, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, K.-H.; Koh, Y.-S.; Lee, K.-H.; Baik, H.-S.; Choi, M.-S.; Kim, I.-S.; Jang, W.-J. Evaluation of PCR-based assay for diagnosis of spotted fever group Rickettsiosis in human serum samples. CVI 2005, 12, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallménius, K.; Pettersson, J.H.-O.; Jaenson, T.G.T.; Nilsson, K. Prevalence of Rickettsia spp., Anaplasma phagocytophilum, and Coxiella burnetii in adult Ixodes ricinus ticks from 29 study areas in central and southern Sweden. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, J.N.; Lu, C.R.; Bender, W.G.; Smoak, R.M.; Zhong, J. Molecular detection and identification of Rickettsia species in Ixodes pacificus in California. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2011, 11, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindblom, A.; Severinson, K.; Nilsson, K. Rickettsia felis infection in Sweden: Report of two cases with subacute meningitis and review of the literature. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 42, 906–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandi, G.; Chitimia-Dobler, L.; Choklikitumnuey, P.; Strube, C.; Springer, A.; Albihn, A.; Jaenson, T.G.T.; Omazic, A. First records of adult Hyalomma marginatum and H. rufipes ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in Sweden. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2020, 11, 101403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Epidemiological Situation of Rickettsioses in EU/EFTA Countries; Publications Office: Luxembourg, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Portillo, A.; Santibáñez, S.; García-Álvarez, L.; Palomar, A.M.; Oteo, J.A. Rickettsioses in Europe. Microbes Infect. 2015, 17, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteo, J.A.; Portillo, A. Tick-borne Rickettsioses in Europe. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2012, 3, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parola, P.; Paddock, C.D.; Socolovschi, C.; Labruna, M.B.; Mediannikov, O.; Kernif, T.; Abdad, M.Y.; Stenos, J.; Bitam, I.; Fournier, P.-E.; et al. Update on tick-Borne rickettsioses around the world: A geographic approach. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 26, 657–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.M.; Jado, I.; Padilla, S.; Masiá, M.; Anda, P.; Gutiérrez, F. Human infection with Rickettsia sibirica mongolitimonae, Spain, 2007–2011. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 267–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier, P.-E.; Raoult, D. Chapter 69—Tick-borne Rickettsioses. In Hunter´s Tropical Medicine and Emerging Infectious Diseases; Elsevier: Edinburgh, UK, 2020; Volume 587–593, p. 1236. ISBN 978-0-323-62551-7. [Google Scholar]
- Sjukdomsinformation om Fläckfeber—Folkhälsomyndigheten. Available online: https://www.folkhalsomyndigheten.se/smittskydd-beredskap/smittsamma-sjukdomar/flackfeber-/ (accessed on 22 June 2022).
- Fournier, P.-E.; Dumler, J.S.; Greub, G.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.; Raoult, D. Gene sequence-based criteria for identification of new Rickettsia isolates and description of Rickettsia heilongjiangensis sp. Nov. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 5456–5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellman, B.P.; Baghdassarian, H.M.; Pramparo, T.; Shamie, I.; Gazestani, V.; Begzati, A.; Li, S.; Nalabolu, S.; Murray, S.; Lopez, L.; et al. Multiple Freeze-Thaw cycles lead to a loss of consistency in poly(A)-enriched RNA sequencing. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, E.H.R.; de Andrade Franco, L.; Pereira, R.G.; Carvalho Mota, L.D.; Campos, A.H.J.F.M.; Carraro, D.M. Biobanking practice: RNA storage at low concentration affects integrity. Biopreservation Biobanking 2014, 12, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artdatabanken. Dvärgpipistrell Pipistrellus pygmaeus. Available online: https://artfakta.se/ (accessed on 22 May 2022).

| Pathogen | Species | Country | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Borrelia | Borrelia sp. CPB1 | France, Sweden | [7,8] |
| Bartonella | Hungary | [9] | |
| Babesia | Hungary, Romania, Italy, Kenya, Vietnam, China Finland, UK | [10] [11] | |
| Ehrlichia | Ehrlichia sp. AvBat Ehrlichia spp. | France United Kingdom | [8] [11] |
| Rickettsia | Rickettsia sp. AvBat | France | [8] |
| SFG Rickettsia | United Kingdom | [11] | |
| Rickettsia helvetica | China | [9] | |
| Rickettsia africae-like | Hungary | [9] | |
| Rickettsia raoultii, Rickettsia rickettsii | China | [12] |
| Organism | Target | Primer/Probe Name | Sequence (5′-3′) | Amplicon Length (bp) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. phagocytophilum | gltA | ApF | TTTTGGGCGCTGAATACGAT | 64 | [13] |
| ApR | TCTCGAGGGAATGATCTAATAACGT | ||||
| ApM | FAM-TGCCTGAACAAGTTATG-BHQ1 | ||||
| Babesia spp. | 18S rRNA | BJ1 | GTCTTGTAATTGGAATGATGG | 411–452 | [14] |
| BN2 | TAGTTTATGGTTAGGACTACG | ||||
| N. mikurensis | 16S rRNA | Neo_16S_F | GTAAAGGGCATGTAGGCGGTTTAA | 107 | [15] |
| Neo_16S_R | TCCACTATCCTCTCTCGATCTCTAGTT TAA | ||||
| 11,054–1112 a | F-TBE 1 | GGGCGGTTCTTGTTCTCC | 68 | [16] | |
| TBEV | R-TBE 1 | ACACATCACCTCCTTGTCAGACT | |||
| TBE-probe-WT | FAM-TGAGCCACCATCACCCAG ACACA-BHQ1 | ||||
| 1329–1416 a | TBEE-F6 | GGCTTGTGAGGCAAAAAAGAA | 88 | [17] | |
| TBEE-R2 | TCCCGTGTGTGGTTCGACTT | ||||
| TBEE-P4 | HEX-AAGCCACAGGACATGTGTACG ACGCC-BHQ1 | ||||
| Rickettsia spp. | gltA | CS-F | TCGCAAATGTTCACGGTACTTT | 74 | [18] |
| CS-R | TCGTGCATTTCTTTCCATTGTG | ||||
| CS-P | FAM-TGCAATAGCAAGAACCGTAGG CTGGATG-BHQ1 | ||||
| 17 kDa | Rr17kDa.61p | GCTCTTGCAACTTCTATGTT | 434 | [19] | |
| Rr17kDa.492n | CATTGTTCGTCAGGTTGGCG | ||||
| ompB | Rc.rompB.4362p | GTCAGCGTTACTTCTTCGATGC | 475 | [20] | |
| Rc.rompB.4836n | CCGTACTCCATCTTAGCATCAG | ||||
| Rc.rompB.4496p | CCAATGGCAGGACTTAGCTACT | 267 | |||
| Rc.rompB.4762n | AGGCTGGCTGATACACGGAGTAA | ||||
| gltA (I) | RH314 | AAACAGGTTGCTCATCATTC | 832 | [21] | |
| CSF-R | AAGTACCGTGAACATTTGCGA | ||||
| CS-Ric-R | CAGTGAACATTTGCGACGGTA | ||||
| CS535d | GCAATGTCTTATAAATATTC | SP | |||
| gltA (II) | Forward | GGCTAATGAAGCGGTAATAA ATATGCTT | 341 | [22] | |
| Reverse | TTTGCGACGGTATACCCATAGC | ||||
| ompA | Forward | CACYACCTCAACCGCAGC | 438–444 | [22] | |
| Reverse | AAAGTTA TATTTCCTAAACCYGTATAAKTATCRGC | ||||
| 16S rRNA | Forward | TAAGGAGGTAATCCAGCC | 1482–1483 | [22] | |
| Reverse | CCTG GCTCAGAACGAA |
| Developmental Stage | No. of Examined Ticks | Rickettsia spp. | A. phagocytophilum | N. mikurensis | Babesia spp. | TBEV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Larva | 31 | 17 (56.7) | ||||
| Nymph | 48 | 27 (56.3) | ||||
| Adult a | 13 | 10 (77.0) | ||||
| Total | 92 | 54 (58.7) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Gene | No. of Successfully Sequenced Samples | Sample | Species | Identity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 kDa | 32/54 | Rickettsia sp. AvBat 17 kDa | R. rickettsii | 100% (434/434) |
| gltA (I) | 43/54 | Rickettsia sp. AvBat gltA | R. parkeri | 100% (795/795) |
| ompA | 9/47 * | Rickettsia sp. AvBat ompA | R. parkeri | 100% (305/305) |
| ompB | 49/54 | Rickettsia sp. AvBat ompB | R. parkeri, R. slovaca, R. conorii, R. sibirica subsp. mongolotimonae | 100% (250/250) |
| Rickettsia sp. AvBat ompB nymph 229 Uppland 2018 | R. parkeri, R. slovaca, R. conorii, R. sibirica subsp. mongolotimonae | 99.6% (251/252) | ||
| Rickettsia sp. AvBat ompB nymph 191 Uppland 2018 | R. parkeri, R. slovaca, R. conorii, R. sibirica subsp. mongolotimonae | 98.8% (249/252) | ||
| gltA (II) | 1/47 * | Rickettsia sp. AvBat gltA adult 179 Uppland 2018 | R. parkeri | 100% (333/333) |
| rrs | 4/47 * | Rickettsia sp. AvBat rrs | uncultured Rickettsia species | 100% (1256/1356) |
| Rickettsia sp. AvBat rrs nymph 159 Uppland 2018 | uncultured Rickettsia species | 99.4% (1248/1256) | ||
| Rickettsia sp. AvBat rrs nymph 161 Uppland 2018 | R. conorii | 94.7% (1325/1399) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tompa, E.; Jaenson, T.G.T.; Wilhelmsson, P. First Records of Possibly Human Pathogenic Rickettsia Species in Bat Ticks, Carios vespertilionis, in Sweden. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020357
Tompa E, Jaenson TGT, Wilhelmsson P. First Records of Possibly Human Pathogenic Rickettsia Species in Bat Ticks, Carios vespertilionis, in Sweden. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(2):357. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020357
Chicago/Turabian StyleTompa, Eszter, Thomas G. T. Jaenson, and Peter Wilhelmsson. 2023. "First Records of Possibly Human Pathogenic Rickettsia Species in Bat Ticks, Carios vespertilionis, in Sweden" Microorganisms 11, no. 2: 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020357
APA StyleTompa, E., Jaenson, T. G. T., & Wilhelmsson, P. (2023). First Records of Possibly Human Pathogenic Rickettsia Species in Bat Ticks, Carios vespertilionis, in Sweden. Microorganisms, 11(2), 357. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11020357






