Ideonella sakaiensis Can Metabolize Bisphenol A as a Carbon Source
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
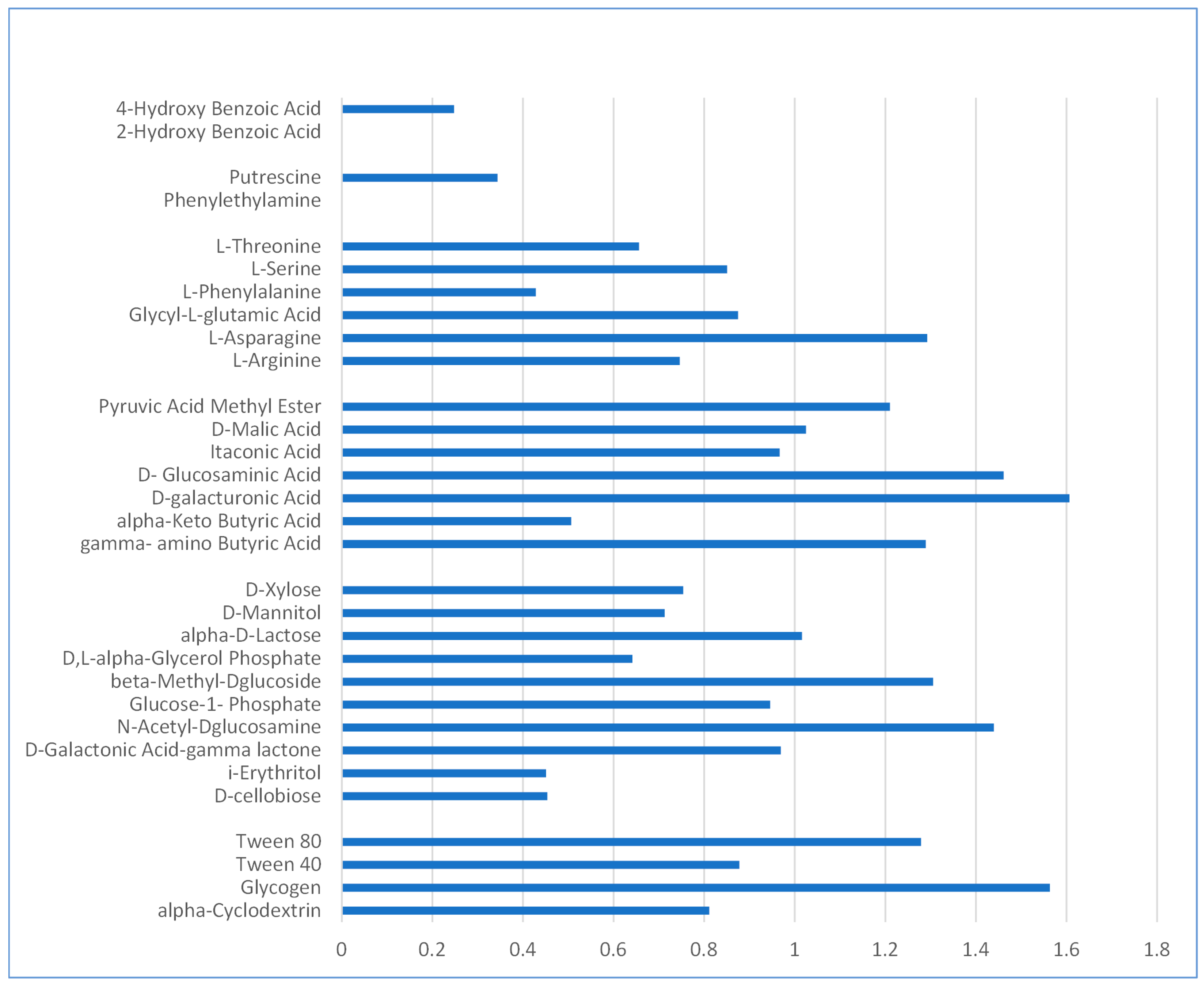
2.1. Microbial Community Analysis
2.2. Primary and Final Taxonomic Identification
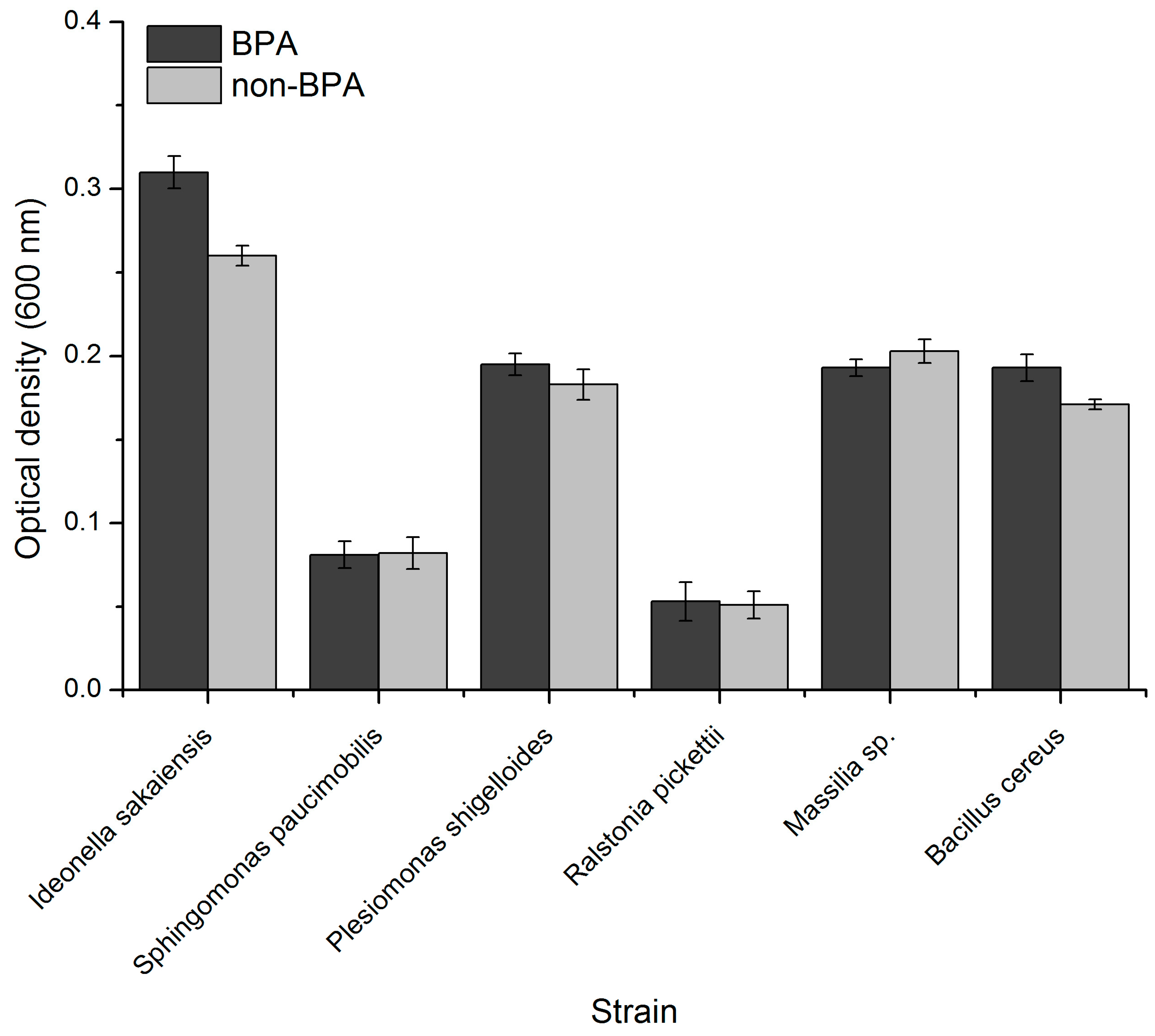
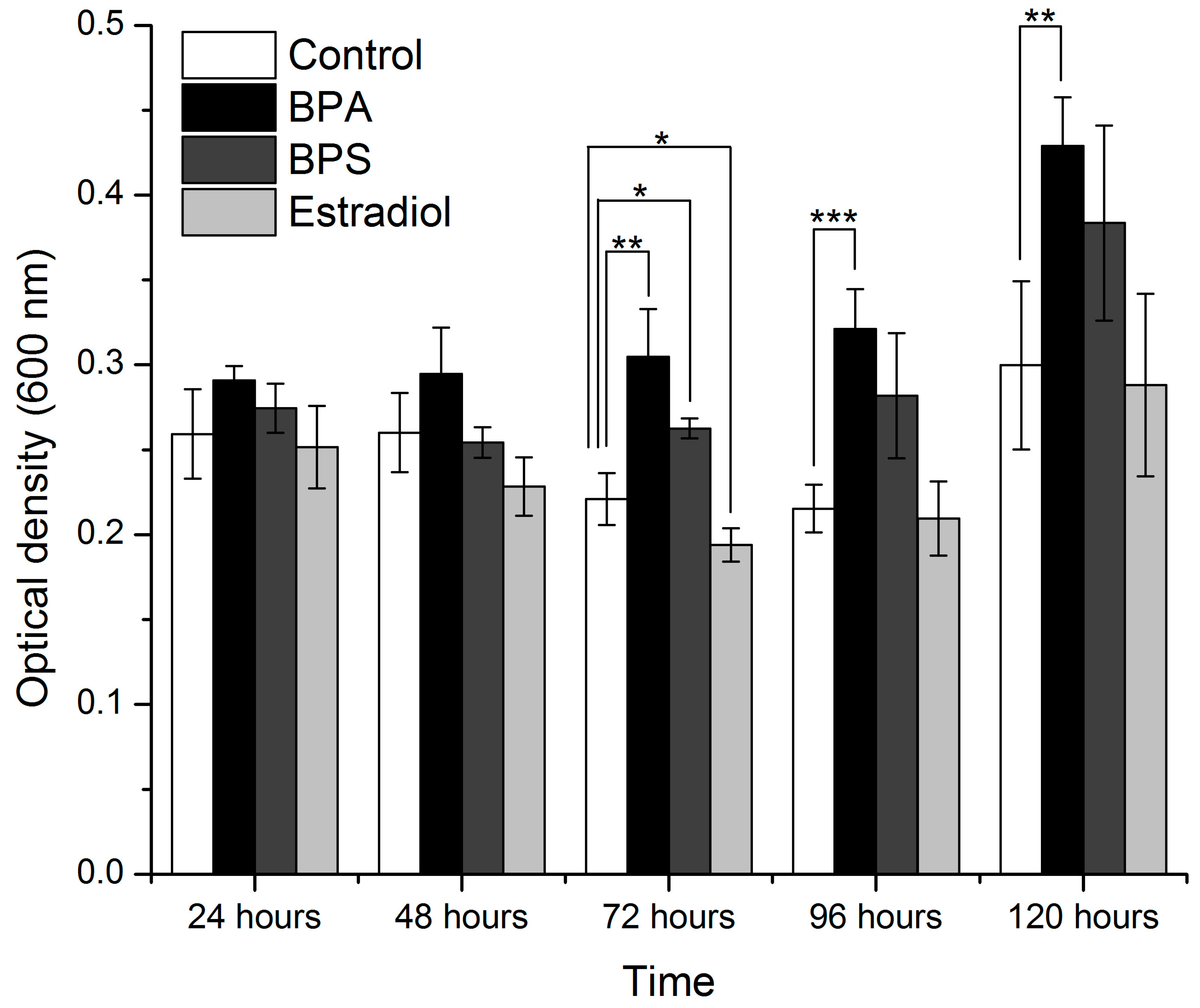
2.3. Species Exposure to Bisphenol A, Bisphenol S, and 17-ß Estradiol
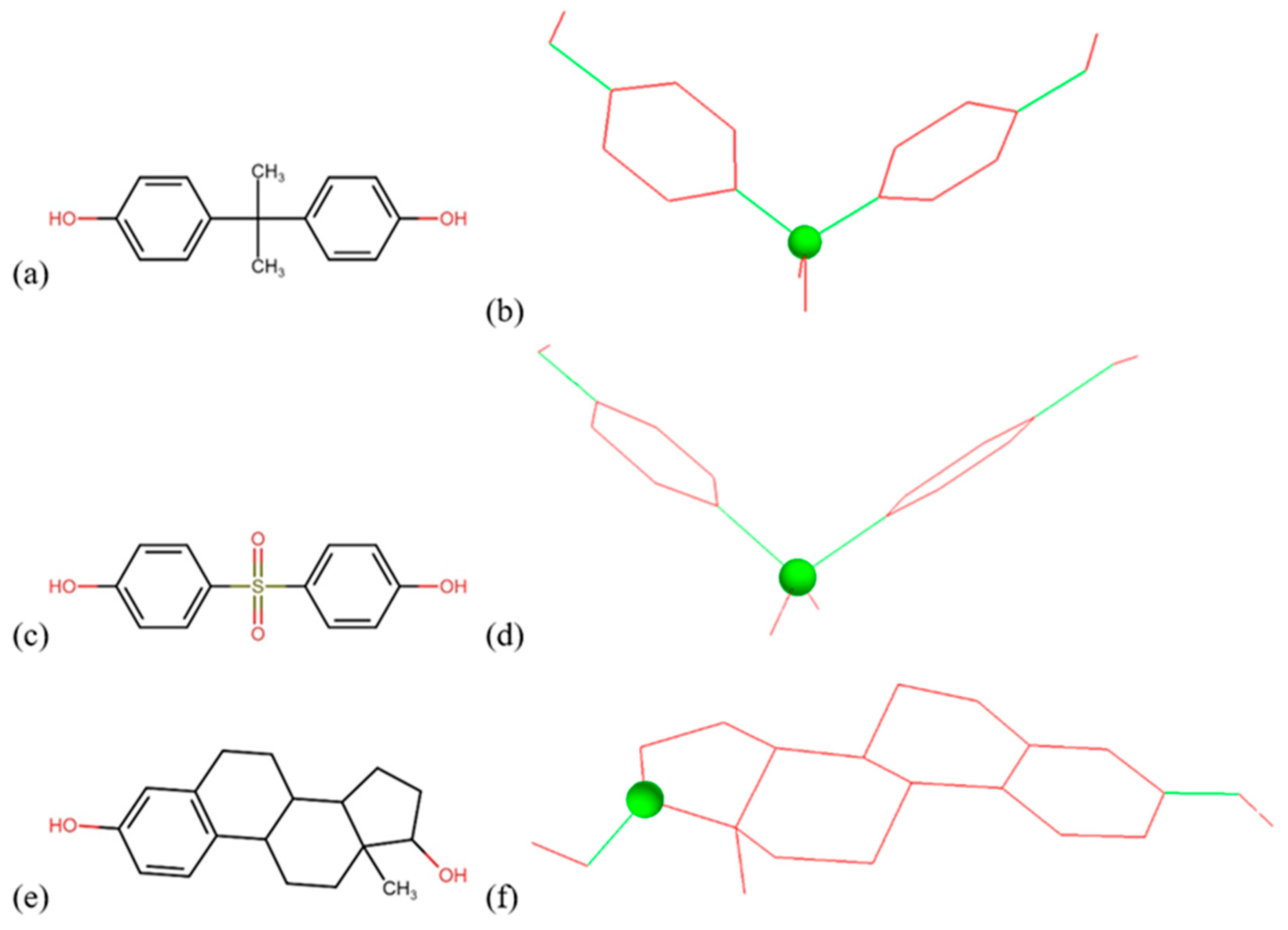
2.4. Computational Simulation of BPA, BPS, and Estradiol as Substrate for I. sakaiensis PETase and MHETase
2.5. Growth Curve Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Community-Level Physiological Profile and Strains Identification
3.2. Evaluation of Species Growth during BPA Exposure
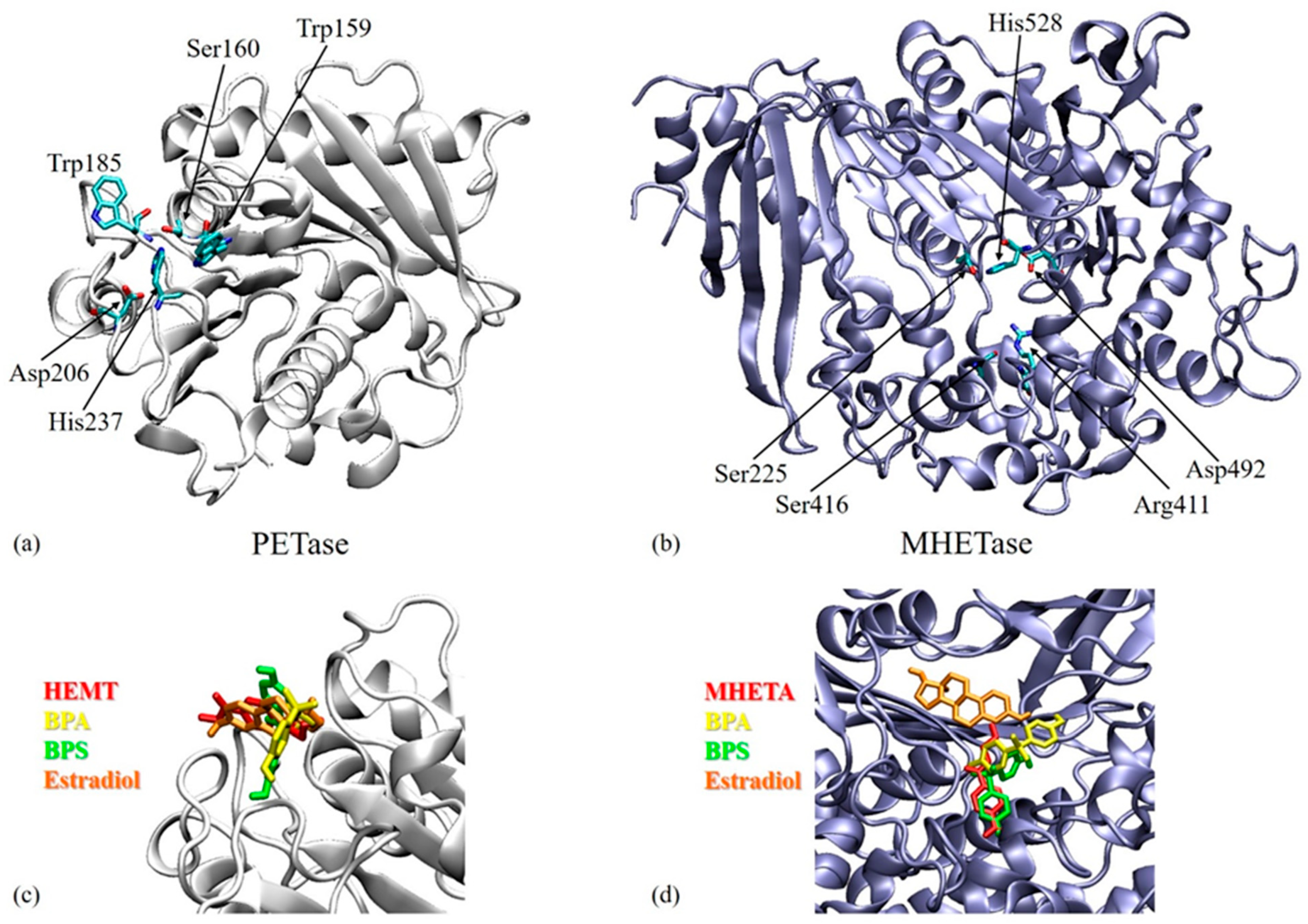
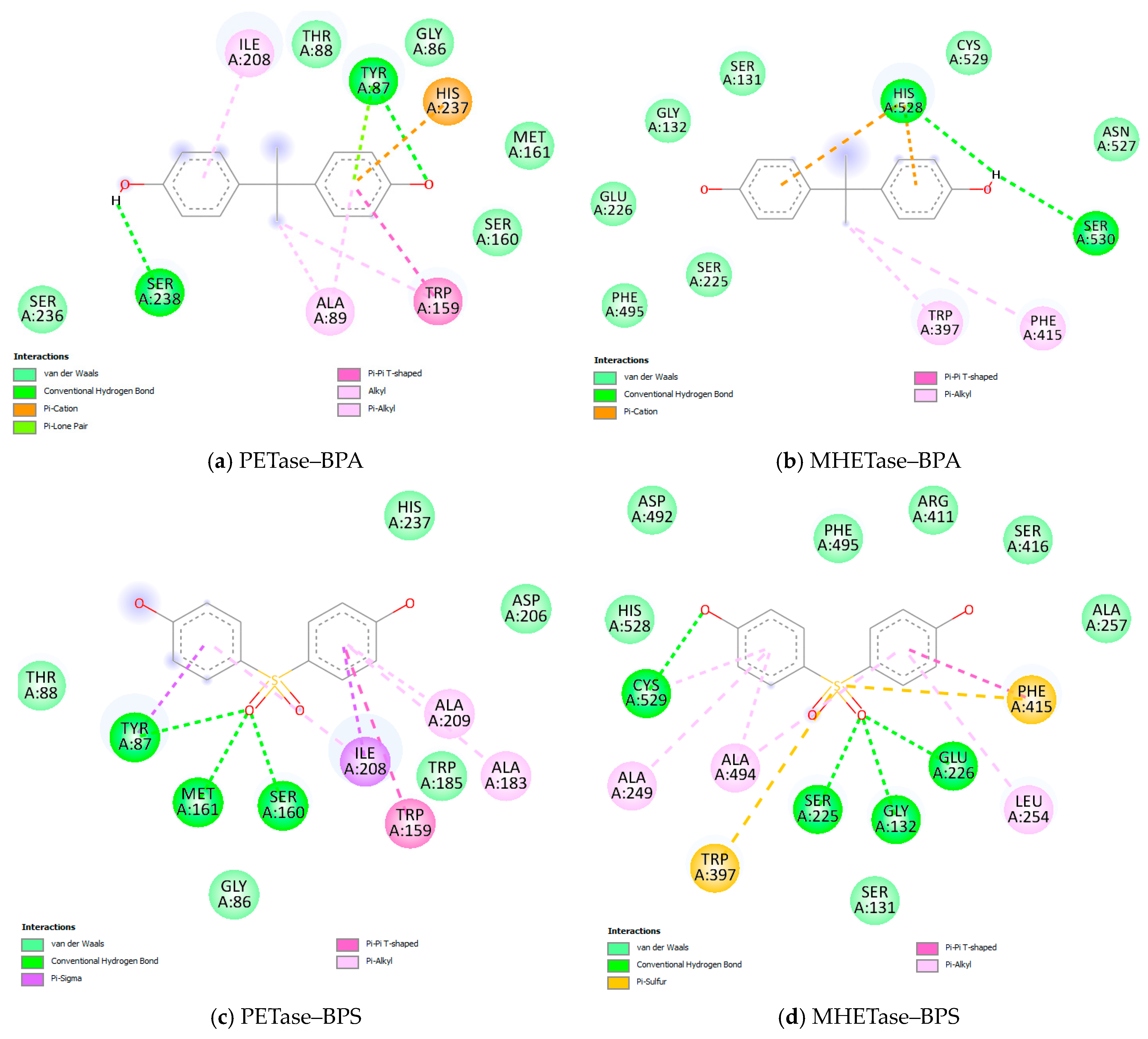
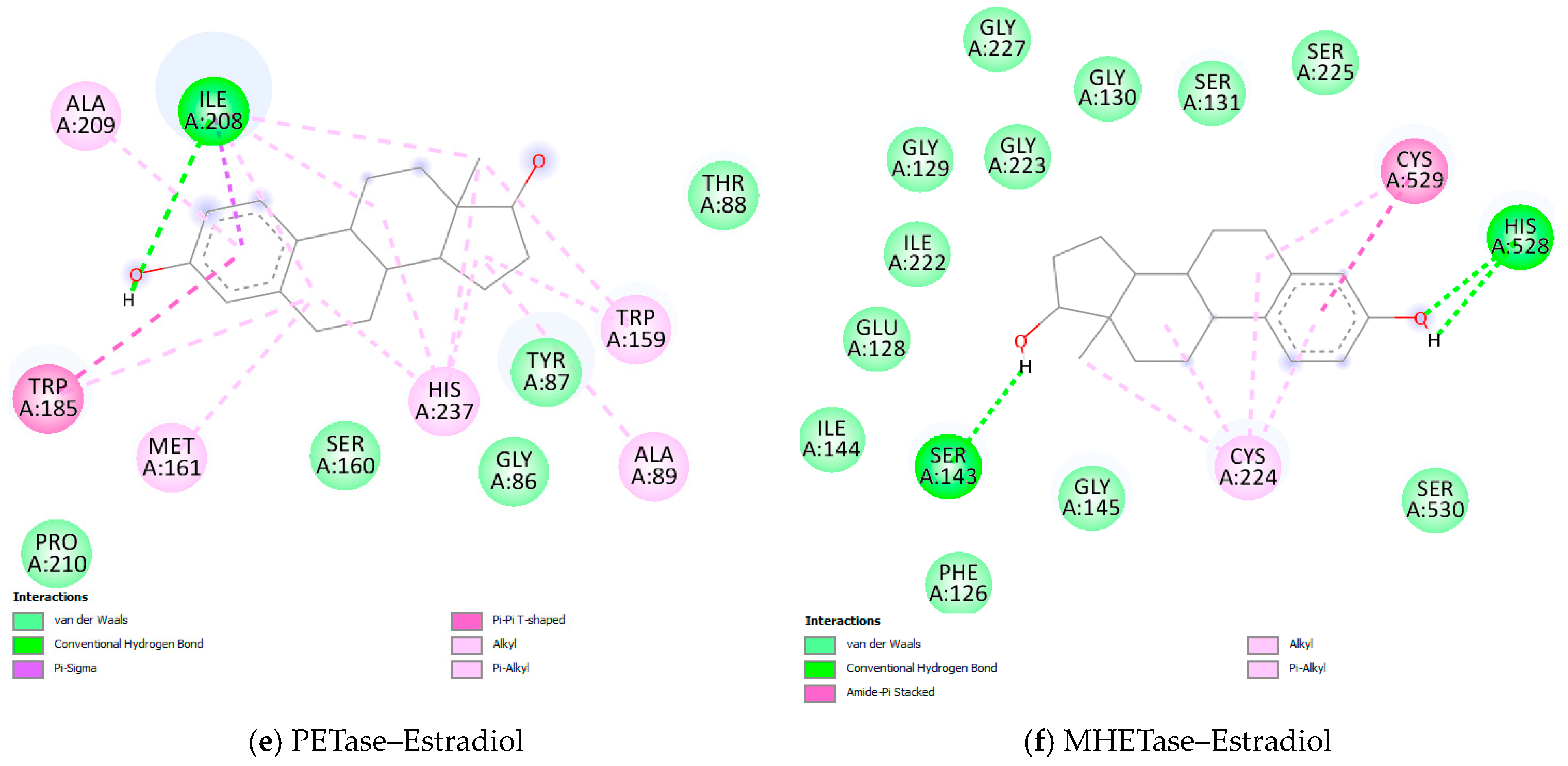
3.3. Molecular Docking Results
3.4. Growth Curve Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Welshons, K.L.H.; Paul, H.P.; Barbara, M.J.; Julia, A.T.; Carl, E.O.; Rachel, L.R.; Frederick, S.V.S.; Wade, V. Bisphenol A is released from used polycarbonate animal cages into water at room temperature. Environ. Health Perspect. 2003, 111, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar]
- A Closer Look at the Global Bisphenol A Market: Demand, Regulations & Sustainability. Available online: https://mcgroup.co.uk/news/20230711/a-closer-look-at-the-global-bisphenol-a-market-demand-regulations-sustainability.html (accessed on 2 October 2023).
- Bisphenol A Industry Installed Capacity and Capital Expenditure (CapEx) Forecast by Region and Countries Including Details of All Active Plants, Planned and Announced Projects, 2021–2025. 2023. Available online: https://www.globaldata.com/store/report/bisphenol-a-market-analysis/ (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Czarny-Krzymińska, K.; Krawczyk, B.; Szczukocki, D. Bisphenol A and its substitutes in the aquatic environment: Occurrence and toxicity assessment. Chemosphere 2023, 315, 137763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aalto-Korte, K.; Alanko, K.; Henriks-Eckerman, M.L.; Estlander, T.; Jolanki, R. Allergic contact dermatitis from bisphenol A in PVC gloves. Contact Dermat. 2003, 49, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geethamani, P.; Divya, P. Pathological Conditons Related to Bisphenols and It’s Compounds. In Bisphenols; Pınar, E., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2022; Chapter 4. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, A.V.; Stathis, P.; Permuth, S.F.; Tokes, L.; Feldman, D. Bisphenol-A: An estrogenic substance is released from polycarbonate flasks during autoclaving. Endocrinology 1993, 132, 2279–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erler, C.; Novak, J. Bisphenol A Exposure: Human Risk and Health Policy. J. Pediatr. Nurs. 2010, 25, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahladakis, J.N.; Iacovidou, E.; Gerassimidou, S. An overview of the occurrence, fate, and human risks of the bisphenol-A present in plastic materials, components, and products. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2023, 19, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, N.; Surendranath, A.R.; Pathak, J.L.; Yu, S.; Chung, C.Y. Bisphenol A (BPA) the mighty and the mutagenic. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canesi, L.; Fabbri, E. Environmental Effects of BPA: Focus on Aquatic Species. Dose Response 2015, 13, 1559325815598304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Chakraborty, P. A review on sources and health impacts of bisphenol A. Rev. Environ. Health 2020, 35, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Takehana, T.; Taniguchi, I.; Yamaji, H.; Maeda, Y.; Toyohara, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Kimura, Y.; Oda, K. A bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly(ethylene terephthalate). Science 2016, 351, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennison, A.; Winther, J.R.; Varrone, C. Rational Protein Engineering to Increase the Activity and Stability of IsPETase Using the PROSS Algorithm. Polymers 2021, 13, 3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalathil, S.; Miller, M.; Reisner, E. Microbial Fermentation of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Plastic Waste for the Production of Chemicals or Electricity**. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202211057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khunjar, W.O.; Sahin, A.; West, A.C.; Chandran, K.; Banta, S. Biomass Production from Electricity Using Ammonia as an Electron Carrier in a Reverse Microbial Fuel Cell. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cf, S.F.; Rebello, S.; Mathachan Aneesh, E.; Sindhu, R.; Binod, P.; Singh, S.; Pandey, A. Bioprospecting of gut microflora for plastic biodegradation. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 1040–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galarza-Verkovitch, D.; Turak, O.; Wiese, J.; Rahn, T.; Hentschel, U.; Borchert, E. Bioprospecting for polyesterase activity relevant for PET degradation in marine Enterobacterales isolates. AIMS Microbiol. 2023, 9, 518–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pop, C.-E.; Draga, S.; Măciucă, R.; Niță, R.; Crăciun, N.; Wolff, R. Bisphenol A Effects in Aqueous Environment on Lemna minor. Processes 2021, 9, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, H.C.; Dill, D.C.; Smith, L.W.; Guiney, P.D.; Dorn, P. Bisphenol a: Acute aquatic toxicity. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 1988, 7, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garland, J.L. Analysis and interpretation of community-level physiological profiles in microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 1997, 24, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanowicz, A. The Biolog Plates Technique as a Tool in Ecological Studies of Microbial Communities. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15, 669–676. [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe, B.; Hose, G.C.; Harford, A.J.; Midgley, D.J.; Greenfield, P.; Paulsen, I.T.; Chariton, A.A. Microbial communities are sensitive indicators for freshwater sediment copper contamination. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lladó, S.; Baldrian, P. Community-level physiological profiling analyses show potential to identify the copiotrophic bacteria present in soil environments. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, Ó.; Aquilino, M.; Sánchez-Argüello, P.; Planelló, R. The BPA-substitute bisphenol S alters the transcription of genes related to endocrine, stress response and biotransformation pathways in the aquatic midge Chironomus riparius (Diptera, Chironomidae). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwa, M.; Plottel, C.S.; Blaser, M.J.; Adams, S. The Intestinal Microbiome and Estrogen Receptor-Positive Female Breast Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108, djw029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, K.; Meng, F.; Meng, Q.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Huo, H. The Analysis of Estrogen-Degrading and Functional Metabolism Genes in Rhodococcus equi DSSKP-R-001. Int. J. Genom. 2020, 2020, 9369182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godby, N.; Conklin, A. Comparing adsorption of bisphenol A and similar compounds in aqueous solution by syringe filters. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2017, 35, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, P.A.; Pronk, W.; Schäfer, A.I. Influence of pH on Losses of Analyte Estradiol in Sample Prefiltration. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2009, 26, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, H.P.; Allen, M.D.; Donohoe, B.S.; Rorrer, N.A.; Kearns, F.L.; Silveira, R.L.; Pollard, B.C.; Dominick, G.; Duman, R.; El Omari, K.; et al. Characterization and engineering of a plastic-degrading aromatic polyesterase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E4350–E4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, G.J.; Reisky, L.; Böttcher, D.; Müller, H.; Michels, E.A.P.; Walczak, M.C.; Berndt, L.; Weiss, M.S.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Weber, G. Structure of the plastic-degrading Ideonella sakaiensis MHETase bound to a substrate. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem in 2021: New data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 49, D1388–D1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI. ChatGPT. Available online: https://chat.openai.com (accessed on 10 October 2023).
- Introducing ChatGPT Enterprise. Available online: https://openai.com/blog/introducing-chatgpt-enterprise (accessed on 6 November 2023).
- Zwietering, M.H.; Jongenburger, I.; Rombouts, F.M.; van’t Riet, K. Modeling of the bacterial growth curve. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An Analysis of Variance Test for Normality (Complete Samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyes, T.K.; Levy, M.S. Analysis of Levene’s Test under Design Imbalance. J. Educ. Behav. Stat. 1997, 22, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keselman, H.J.; Rogan, J.C. The Tukey multiple comparison test: 1953–1976. Psychol. Bull. 1977, 84, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suyamud, B.; Thiravetyan, P.; Gadd, G.M.; Panyapinyopol, B.; Inthorn, D. Bisphenol A removal from a plastic industry wastewater by Dracaena sanderiana endophytic bacteria and Bacillus cereus NI. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2020, 22, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.-W.; Ma, J.; Zheng, Y.; Ko, T.-P.; Xu, L.; Cheng, Y.-S.; Chen, C.-C.; Guo, R.-T. Structural insight into catalytic mechanism of PET hydrolase. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecker, T.; Galaz-Davison, P.; Engelberger, F.; Narui, Y.; Sotomayor, M.; Parra, L.P.; Ramírez-Sarmiento, C.A. Active Site Flexibility as a Hallmark for Efficient PET Degradation by I. sakaiensis PETase. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 1302–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winsor, C.P. The Gompertz curve as a growth curve. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1932, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
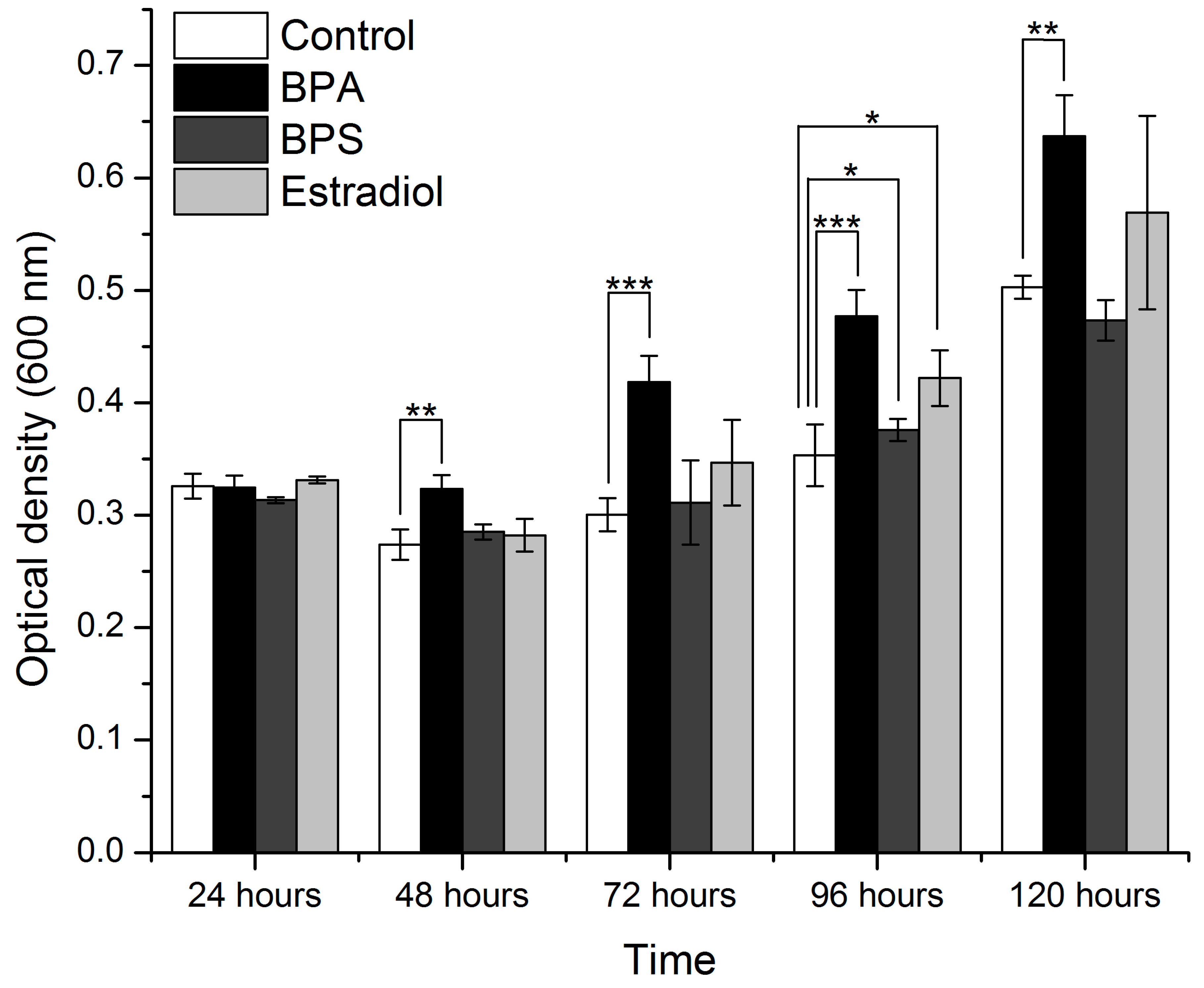
| Incubation Time (Hours) | Medium with 70% Nutrient | Medium with 100% Nutrient | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | |
| 24 | 3.06815 | 0.06898 | 3.589544688 | 0.046460931 (significant) |
| 48 | 7.19515 | 0.00508 | 13.13801863 | 0.000423948 (significant) |
| 72 | 32.6886 | 4.68937 × 10−6 (significant) | 12.55425 | 0.00052 (significant) |
| 96 | 18.0501 | 9.60318 × 10−5 (significant) | 23.77882 | 2.45 × 10−5 (significant) |
| 120 | 7.72841 | 0.00388 (significant) | 9.304546 | 0.001865 (significant) |
| Target | Ligand | Estimated Free Energy of Binding (kcal/mol) | Estimated Inhibition Constant, Ki |
|---|---|---|---|
| PETase | BPA | −6.51 | 17.03 µM |
| BPS | −7.68 | 2.33 µM | |
| Estradiol | −6.89 | 8.87 µM | |
| MHETase | BPA | −5.87 | 49.53 µM |
| BPS | −8.83 | 335.38 nM | |
| Estradiol | −6.64 | 13.61 µM |
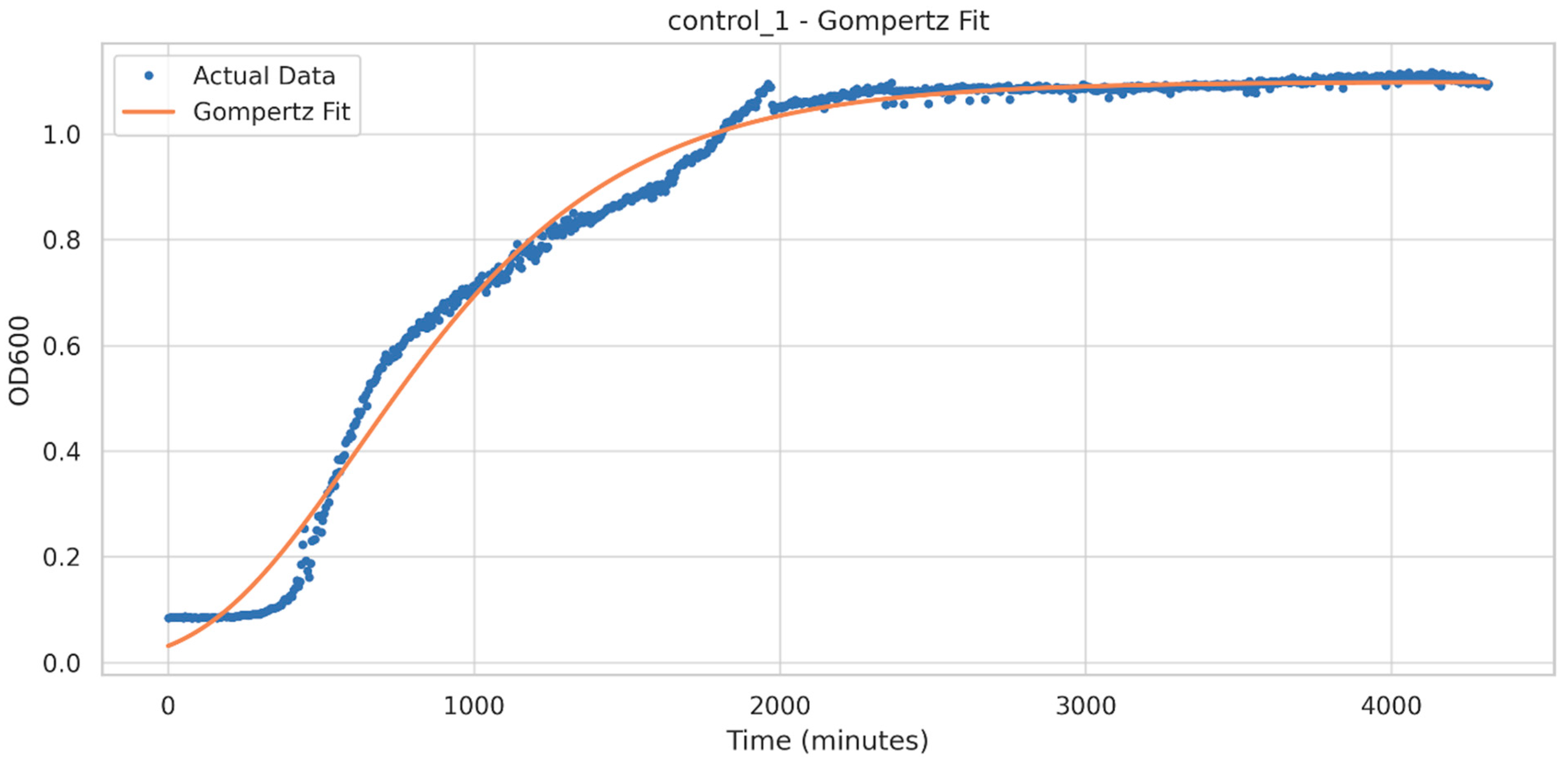
| Upper Asymptote (A) | Maximum Growth Rate (um) | Lag Time (L) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 1.0125 | 0.0008 | 120.3 min |
| Standard deviation | 0.0971 | 0.0001 | 32.7 min |
| Minimum | 0.8027 | 0.0006 | 1.4 min |
| 25th percentile | 0.9515 | 0.0008 | 110.6 min |
| Median | 1.0356 | 0.0008 | 120.6 min |
| 75th percentile | 1.0808 | 0.0008 | 136.8 min |
| Maximum | 1.1689 | 0.0010 | 176.6 min |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pop, C.-E.; Deák, G.; Maria, C.; Ghiță, G.; Ivanov, A.A.; Fendrihan, S.; Mihăilescu, D.F.; Mernea, M. Ideonella sakaiensis Can Metabolize Bisphenol A as a Carbon Source. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122891
Pop C-E, Deák G, Maria C, Ghiță G, Ivanov AA, Fendrihan S, Mihăilescu DF, Mernea M. Ideonella sakaiensis Can Metabolize Bisphenol A as a Carbon Source. Microorganisms. 2023; 11(12):2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122891
Chicago/Turabian StylePop, Cristian-Emilian, György Deák, Cristina Maria, Gina Ghiță, Alexandru Anton Ivanov, Sergiu Fendrihan, Dan Florin Mihăilescu, and Maria Mernea. 2023. "Ideonella sakaiensis Can Metabolize Bisphenol A as a Carbon Source" Microorganisms 11, no. 12: 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122891
APA StylePop, C.-E., Deák, G., Maria, C., Ghiță, G., Ivanov, A. A., Fendrihan, S., Mihăilescu, D. F., & Mernea, M. (2023). Ideonella sakaiensis Can Metabolize Bisphenol A as a Carbon Source. Microorganisms, 11(12), 2891. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms11122891









