The Gut Microbiota at Different Developmental Stages of Apis cerana Reveals Potential Probiotic Bacteria for Improving Honeybee Health
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
2.4. 16S rRNA Gut Community Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Summary of NGS-Sequencing
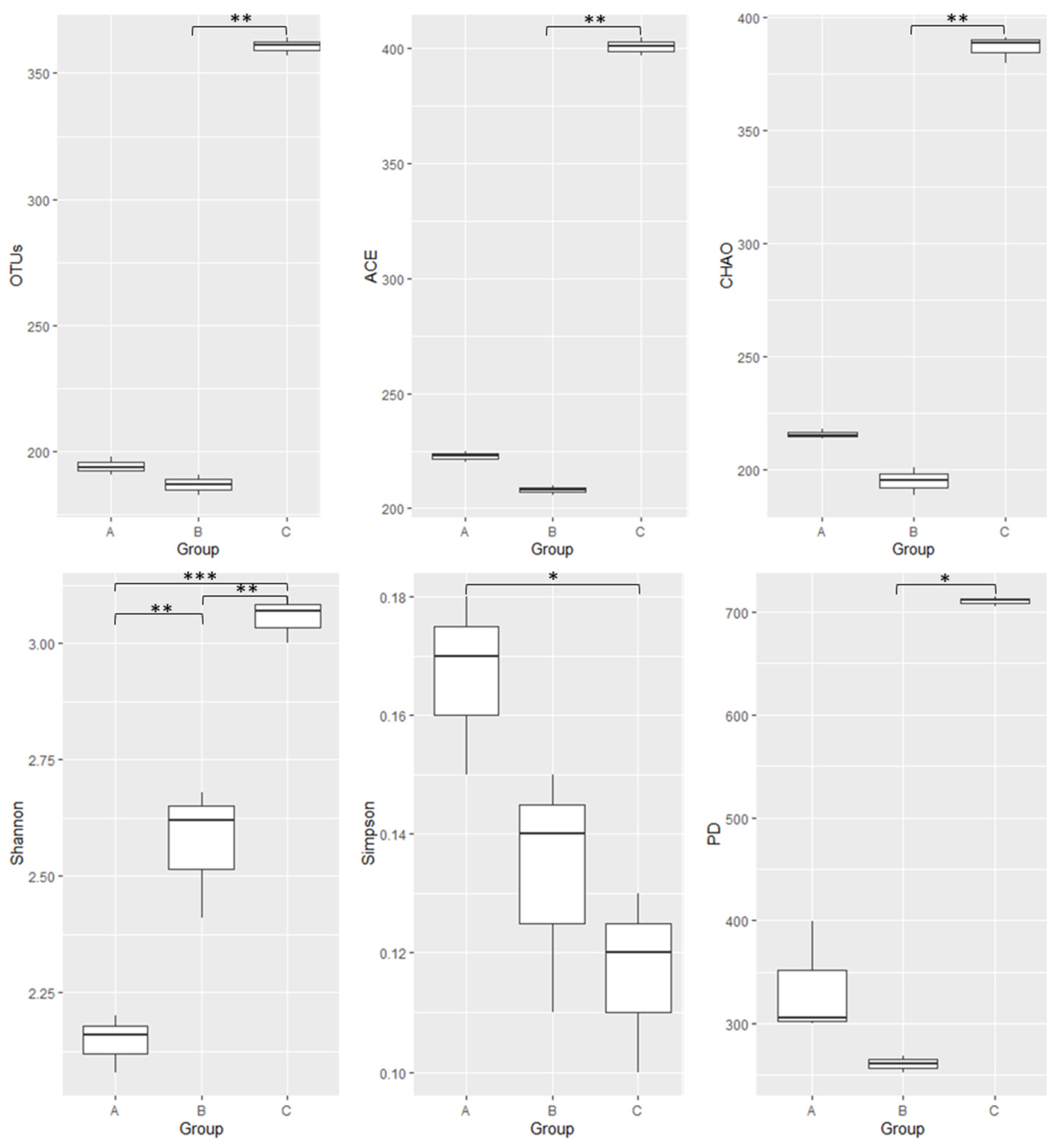
3.2. Gut Bacterial Community Diversity Indices
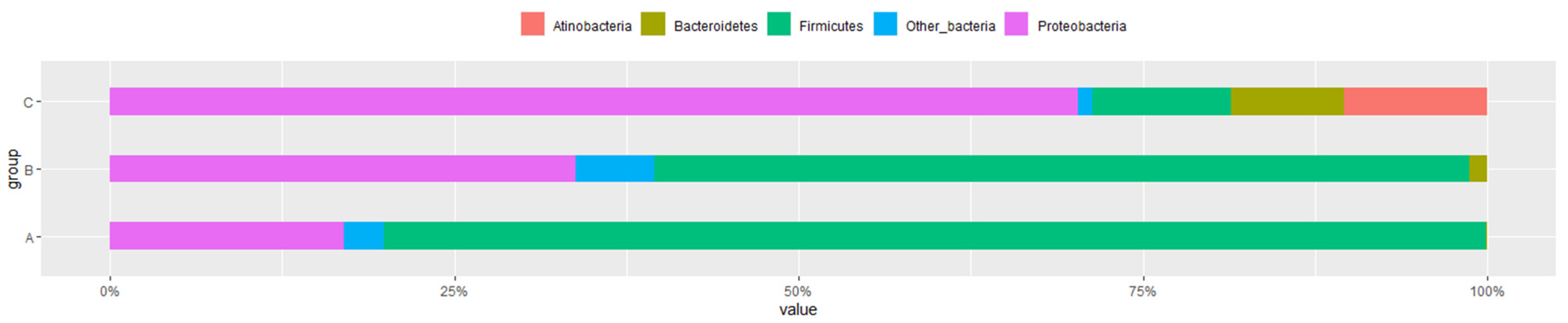
3.3. Microbial Flora at Different Developmental Stages
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| EDTA | ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| rRNA | ribosomal ribonucleic acid |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
References
- Kwong, W.K.; Moran, N.A. Gut microbial communities of social bees. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Steele, M.I.; Leonard, S.P.; Motta, E.V.; Moran, N.A. Honey bees as models for gut microbiota research. Lab. Anim. 2018, 47, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellegaard, K.M.; Tamarit, D.; Javelind, E.; Olofsson, T.C.; Andersson, S.G.; Vásquez, A. Extensive intra-phylotype diversity in lactobacilli and bifidobacteria from the honeybee gut. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossar, D.; Kilchenmann, V.; Forsgren, E.; Charrière, J.-D.; Gauthier, L.; Chapuisat, M.; Dieteman, V. Putative determinants of virulence in Melissococcus plutonius, the bacterial agent causing European foulbrood in honey bees. Virulence 2020, 11, 554–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callegari, M.; Crotti, E.; Fusi, M.; Marasco, R.; Gonella, E.; De Noni, I.; Romano, D.; Borin, S.; Tsiamis, G.; Cherif, A. Compartmentalization of bacterial and fungal microbiomes in the gut of adult honeybees. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymann, K.; Moran, N.A. The role of the gut microbiome in health and disease of adult honey bee workers. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2018, 26, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinson, V.G.; Moy, J.; Moran, N.A. Establishment of characteristic gut bacteria during development of the honeybee worker. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, P.; Moran, N.A. The gut microbiota of insects–diversity in structure and function. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2013, 37, 699–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hroncova, Z.; Killer, J.; Hakl, J.; Titera, D.; Havlik, J. In-hive variation of the gut microbial composition of honey bee larvae and pupae from the same oviposition time. BMC Microbiol. 2019, 19, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, J.E.; Martinson, V.G.; Urban-Mead, K.; Moran, N.A. Routes of acquisition of the gut microbiota of the honey bee Apis mellifera. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7378–7387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genersch, E. Honey bee pathology: Current threats to honey bees and beekeeping. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, A.; Szczuka, D.; Górczyńska, A.; Motyl, I.; Kręgiel, D. Characterization of Apis mellifera Gastrointestinal Microbiota and Lactic Acid Bacteria for Honeybee Protection—A Review. Cells 2021, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzeini, H.M.; Abdel-atti Ali, A.-r.; Nasr, N.F.; Elenany, Y.E.; Hassan, A.A.M. Isolation and identification of lactic acid bacteria from the intestinal tracts of honey bees, Apis mellifera L.; in Egypt. J. Apic. Res. 2020, 60, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Powell, J.E.; Steele, M.I.; Dietrich, C.; Moran, N.A. Honeybee gut microbiota promotes host weight gain via bacterial metabolism and hormonal signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4775–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hroncova, Z.; Havlik, J.; Killer, J.; Doskocil, I.; Tyl, J.; Kamler, M.; Titera, D.; Hakl, J.; Mrazek, J.; Bunesova, V. Variation in honey bee gut microbial diversity affected by ontogenetic stage, age and geographic location. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, B.T.T.; Lien, N.T.K.; Thu, H.T.; Hoa, N.T.; Lanh, P.T.; Yun, B.-R.; Yoo, M.-S.; Cho, Y.S.; Van Quyen, D. Investigation of the gut microbiome of Apis cerana honeybees from Vietnam. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 2309–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kešnerová, L.; Mars, R.A.; Ellegaard, K.M.; Troilo, M.; Sauer, U.; Engel, P. Disentangling metabolic functions of bacteria in the honey bee gut. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2003467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wu, J.; Chen, Y.; Evans, J.D.; Dai, R.; Luo, W.; Li, J. Characterization of gut bacteria at different developmental stages of Asian honey bees, Apis cerana. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 127, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masella, A.P.; Bartram, A.K.; Truszkowski, J.M.; Brown, D.G.; Neufeld, J.D. PANDAseq: Paired-end assembler for illumina sequences. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eddy, S.R. Accelerated profile HMM searches. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2011, 7, e1002195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Moon, T.; Yoon, S.; Weissman, T. DUDE-Seq: Fast, flexible, and robust denoising for targeted amplicon sequencing. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181463. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, R.C. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2460–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, E.W.; Miller, W. Optimal alignments in linear space. Bioinformatics 1988, 4, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Niu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, W. CD-HIT: Accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 3150–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Dong, Z.-X.; Li, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-F.; Tang, Q.-H.; Guo, J. The succession of the gut microbiota in insects: A dynamic alteration of the gut microbiota during the whole life cycle of honey bees (Apis cerana). Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, B.-R.; Truong, A.-T.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, M.Y.; Kim, B.Y.; Seo, M.; Yoon, S.-S.; Yoo, M.-S.; Van Quyen, D.; Cho, Y.S. Comparison of the gut microbiome of sacbrood virus-resistant and-susceptible Apis cerana from South Korea. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 10010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arredondo, D.; Castelli, L.; Porrini, M.P.; Garrido, P.M.; Eguaras, M.J.; Zunino, P.; Antúnez, K. Lactobacillus kunkeei strains decreased the infection by honey bee pathogens Paenibacillus larvae and Nosema ceranae. Benef. Microbes 2018, 9, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.-X.; Li, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.-F.; Wang, F.; Deng, X.-Y.; Lin, L.-B.; Zhang, Q.-L.; Li, J.-L.; Guo, J. Colonization of the gut microbiota of honey bee (Apis mellifera) workers at different developmental stages. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 231, 126370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangberg, A.; Mathiesen, G.; Amdam, G.; Diep, D. The paratransgenic potential of Lactobacillus kunkeei in the honey bee Apis mellifera. Benef. Microbes 2015, 6, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.C.; Sutton, S.D.; Ringelberg, D.B. The genus Sphingomonas: Physiology and ecology. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 1996, 7, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachla, A.; Wicha, M.; Ptaszyńska, A.A.; Borsuk, G.; Trokenheim, Ł.Ł.; Małek, W. The molecular and phenotypic characterization of fructophilic lactic acid bacteria isolated from the guts of Apis mellifera L. derived from a Polish apiary. J. Appl. Genet. 2018, 59, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulkhairi Amin, F.A.; Sabri, S.; Ismail, M.; Chan, K.W.; Ismail, N.; Mohd Esa, N.; Mohd Lila, M.A.; Zawawi, N. Probiotic properties of Bacillus strains isolated from stingless bee (Heterotrigona itama) honey collected across Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustar, S.; Ibrahim, N. A Sweeter Pill to Swallow: A Review of Honey Bees and Honey as a Source of Probiotic and Prebiotic Products. Foods 2022, 11, 2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, M.; Celano, G.; Calabrese, F.M.; Portincasa, P.; Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M. The controversial role of human gut lachnospiraceae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, J.-H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Hyun, D.-W.; Jung, M.-J.; Bae, J.-W. Bombella apis sp. nov., an acetic acid bacterium isolated from the midgut of a honey bee. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 2184–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, K.; Yamazaki, Y.; Shiraishi, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Harada, M.; Yoshiyama, M.; Osaki, M.; Okura, M.; Takamatsu, D. Virulence differences among Melissococcus plutonius strains with different genetic backgrounds in Apis mellifera larvae under an improved experimental condition. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.-W.; Dong, Z.-X.; Chen, Y.-F.; Li, H.-Y.; Tang, Q.-H.; Li, J.-L.; Guo, J. Comparative analysis of the gut microbiota of Apis cerana in Yunnan using high-throughput sequencing. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 2557–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Mu, X.; Cao, Q.; Shi, Y.; Hu, X.; Zheng, H. Honeybee gut Lactobacillus modulates host learning and memory behaviors via regulating tryptophan metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.E.; Rodrigues, P.A.; Mott, B.M.; Maes, P.; Corby-Harris, V. Ecological succession in the honey bee gut: Shift in Lactobacillus strain dominance during early adult development. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 71, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, O.Y.; Basualdo, M.; Libonatti, C.; Vega, M.F. Current status and application of lactic acid bacteria in animal production systems with a focus on bacteria from honey bee colonies. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 128, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruščáková, I.C.; Schusterová, P.; Bielik, B.; Toporčák, J.; Bíliková, K.; Mudroňová, D. Effect of Application of Probiotic Pollen Suspension on Immune Response and Gut Microbiota of Honey Bees (Apis mellifera). Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2020, 12, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daisley, B.A.; Pitek, A.P.; Chmiel, J.A.; Al, K.F.; Chernyshova, A.M.; Faragalla, K.M.; Burton, J.P.; Thompson, G.J.; Reid, G. Novel probiotic approach to counter Paenibacillus larvae infection in honey bees. ISME J. 2020, 14, 476–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erban, T.; Ledvinka, O.; Kamler, M.; Hortova, B.; Nesvorna, M.; Tyl, J.; Titera, D.; Markovic, M.; Hubert, J. Bacterial community associated with worker honeybees (Apis mellifera) affected by European foulbrood. Peer J. 2017, 5, e3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaté, D.; Cruz, M.; Benítez-Ahrendts, M.; Audisio, M. Beneficial effects of Bacillus subtilis subsp. subtilis Mori2, a honey-associated strain, on honeybee colony performance. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2012, 4, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lanh, P.T.; Duong, B.T.T.; Thu, H.T.; Hoa, N.T.; Yoo, M.S.; Cho, Y.S.; Quyen, D.V. The Gut Microbiota at Different Developmental Stages of Apis cerana Reveals Potential Probiotic Bacteria for Improving Honeybee Health. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101938
Lanh PT, Duong BTT, Thu HT, Hoa NT, Yoo MS, Cho YS, Quyen DV. The Gut Microbiota at Different Developmental Stages of Apis cerana Reveals Potential Probiotic Bacteria for Improving Honeybee Health. Microorganisms. 2022; 10(10):1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101938
Chicago/Turabian StyleLanh, Pham Thi, Bui Thi Thuy Duong, Ha Thi Thu, Nguyen Thi Hoa, Mi Sun Yoo, Yun Sang Cho, and Dong Van Quyen. 2022. "The Gut Microbiota at Different Developmental Stages of Apis cerana Reveals Potential Probiotic Bacteria for Improving Honeybee Health" Microorganisms 10, no. 10: 1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101938
APA StyleLanh, P. T., Duong, B. T. T., Thu, H. T., Hoa, N. T., Yoo, M. S., Cho, Y. S., & Quyen, D. V. (2022). The Gut Microbiota at Different Developmental Stages of Apis cerana Reveals Potential Probiotic Bacteria for Improving Honeybee Health. Microorganisms, 10(10), 1938. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10101938




