1. Introduction
In recent decades, distributed cooperation in MASs has received considerable interest due to its intriguing and promising applications in diverse fields, involving multiple unmanned surface vessels formation [
1,
2,
3,
4], drone/satellite formation flight [
5,
6], and multirobot systems [
7,
8] among others. Its main advantages include greater flexibility, adaptability, and higher performance compared with a single agent. Since the consensus problem is an elementary precondition for cooperative control of MASs, it concerns designing an appropriate control protocol to drive the states or outputs of all agents to facilitate agreement between them. Different kinds of consensus problems have elicited the widespread theoretical interest of researchers to carry on the relevant work in this field, including leaderless/leader-following consensus [
9,
10,
11,
12], formation [
13], and flocking behavior [
14].
A key limitation of the aforementioned works is their reliance on continuous-time communication among agents, which demands substantial bandwidth and reliable communication infrastructure to prevent network congestion. However, in practical scenarios, agents are typically equipped with limited communication resources, making such continuous interaction computationally and energetically expensive. In this regard, a commonly used strategy called periodic sampled-data control [
15,
16,
17] is used to decrease the amount of data transfer. Although the cyclical sampling strategy enables intermittent communication, it requires a conservative sampling period to keep all agents synchronized. This means the controller continues to update even after the task is completed. For large-scale systems, such unnecessary communication can lead to high energy consumption, making practical implementation difficult.
To achieve consensus in MASs under resource constraints, several pioneering studies have proposed event-triggered control schemes. Specifically, an event is triggered when the measurement error exceeds or equals the detection threshold. This mechanism leads to asynchronous event-triggered time sequences across agents, effectively reducing controller updates and conserving communication bandwidth. For instance, researchers have investigated event-triggered consensus strategies for MASs with single-integrator/double-integrator in [
18,
19]. In the design rendered in [
19,
20,
21], the event-triggered control mechanism was extended to the general linear MASs over directed and undirected networks. However, a key limitation of many existing approaches is that they still require continuous access to neighbors’ state information, which contradicts the fundamental goal of reducing communication load. To address this issue, an iterative event-triggered algorithm based on combined measurements was introduced in [
22], eliminating the need for continuous state acquisition. Moreover, a decentralized consensus control system based on an event-triggered model was developed in [
23,
24] to avoid continuous monitoring of neighbors’ states.
Nevertheless, it is worth noting that, in most of the aforementioned works, these state-dependent threshold-based approaches are typically considered static. As such, static event-triggered mechanisms can initially help reduce communication costs to some extent. However, as time progresses, the decreasing measurement error leads to a shrinking threshold, which increases the likelihood of triggering and may cause redundant communication events. For the sake of devising flexible event-triggering criteria to attain further and more significant execution interval times and less communication energy cost among agents, a series of dynamic event-triggered methods for MAS consensus has been proposed by researchers, which involves two main types of approaches, i.e., time-dependent/external dynamic variable methods [
25,
26] and state-dependent/internal dynamic variable methods [
27,
28]. Compared to static triggering, both types introduce dynamic variables into the triggering function to adaptively widen the detection range. Notably, the method in [
28] incorporates adaptive mechanisms, allowing dynamic parameters to evolve with the measurement error and the agent’s state. Despite the reliability of the existing event-triggered methods in dealing with the consensus problem of MASs, several components of the global communication graph, e.g., the eigenvalues of the Laplacian matrix and the total number of agents, are highly interrelated. Therefore, some effective strategies known as fully distributed event-triggered control methods [
29,
30,
31] were further proposed to cope with this limitation, but it is limited to the static event triggered control. According to the author’s knowledge, few methods exist focusing on the fully distributed control protocol under the framework of dynamic event-triggered for general linear MASs, which motivates us to study it.
In the consensus achieved for MASs, the previous works have focused on cooperative topologies. Recently, related works have also addressed resilient consensus of heterogeneous or nonlinear MASs subject to disturbances, uncertainties, and actuator faults [
32,
33]. An unsigned graph can denote the agent’s interaction with its neighbors with non-negative weighted edges. Nevertheless, there is cooperation and competition between two individuals in real scenarios. For instance, in multiple autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV) systems [
34], it is necessary to allocate tasks and resources reasonably for AUVs when measuring data in different ocean areas and competing for limited waterway resources. Moreover, the communication topology network used in the above case is constructed by a structurally balanced signed graph with negative and positive weights. From a theoretical perspective, this framework corresponds to bipartite consensus in MASs [
35], where agents converge to values with equal magnitude but opposite signs. With ongoing advances in this area, several results have been achieved, including bipartite containment consensus [
36,
37] and static event-triggered bipartite consensus strategies [
38,
39]. However, no matter the unsigned or signed topology network, most existing works restrict their scope to standard-weight topology networks. In contrast, from both scientific and engineering viewpoints, it is often more accurate to represent the logical interdependence of agents’ states using coupling-weighted topologies. To this end, how to devise dynamic event-triggered bipartite consensus for general linear MASs with coupling-weighted signed topologies needs further investigation.
To address the above issues, this paper proposes a fully distributed dynamic event-triggered control strategy to provide bipartite consensus for general linear MASs under coupling-weighted signed topology in response to the above discussion. As far as the author knows, little attention has been paid to this issue. Note that the design and analysis of bipartite consensus stability become challenging as coupling-weighted topology and dynamic event-triggered control are considered simultaneously. Additionally, taking advantage of the fully distributed adaptive control protocol, global information about the network topology is not required. Relative to the results reported in the current literature [
28,
29,
30,
31,
38,
39], this work makes the following principal contributions:
- (i)
Compared with the static event-triggered methods, the proposed dynamic event-triggering control algorithm includes coupling strength and time-dependent and state-dependent dynamic variables. It not only avoids continuous controller update and trigger detection but also dramatically reduces the number of triggering instants on the premise of ensuring system performance. Thus, this compositional dynamic event-triggering mechanism possesses distinct advantages.
- (ii)
It is well-known that most existing works miss the fully distributed adaptive control problem for general linear MASs. However, this study addresses it. Due to its distributed nature, MASs can achieve a bipartite consensus without relying on global information contained in the communication graph, suppressing the influence of coupling-weighted topology. In addition, this topic can also be regarded as an extension of bipartite consensus problems under single-integrator-type, coupling-weighted, and linearly connected topologies.
- (iii)
Due to the coexistence of cooperative and competitive interactions in the communication topology considered in this paper, the proposed approach is more general and applicable. Furthermore, this work simultaneously addresses several key challenges—fully distributed control, bipartite consensus, dynamic event-triggered mechanisms, and coupling-weighted signed topologies—making it more comprehensive than previous studies that typically focus on only one or a subset of these aspects.
The rest of the paper is described below. A description of the preparatory work is presented in
Section 2.
Section 3 describes the fully distributed bipartite dynamic event-triggered controller. Several numerical simulations are performed in
Section 4 to validate the effectiveness of the approach presented in this paper. Finally, the conclusions are drawn in
Section 5.
2. Preliminaries and Problem Formulation
In this section, the dynamics of the multiple agents, the definitions in algebraic graph theory, as well as mathematical preliminary knowledge and related lemmas are presented briefly. The interaction diagram will be used to simulate the transfer of information between multiple agents, while the proposed controller’s stability is verified by preliminary knowledge of mathematics and lemmas.
Notations: The
dimensional real space is represented by
,
, which stand for the set of
real matrices. Let
(
) be the set of (non-negative) real numbers; an absolute value
is assigned to a scale
. In the case of a vector
,
is its Euclidian norm. The transpose of a matrix
and its Euclidian induced matrix norm are represented by
and
. Moreover,
(or
) means that it is positive definite (or positive semidefinite). The minimum and maximum eigenvalues are labelled
and
. The notation
stands for the Kronecker product. There is a
column vector
with all entries equal to one;
represents the
identity matrix. In addition, the sign function
is defined as
2.1. Graph Theory and Lemmas
Consider a group of MASs with cooperative–competitive interactions among
agents, whose communication topology can be modeled by a signed graph, described as
.
is a nonempty finite node with each agent as a node set;
is an edge set;
is a weighted adjacency matrix. The edge
indicates that the node
can broadcast information to the node
. The adjacency elements
when
. Each adjacency element
is also given a positive or negative sign, indicating whether the agents
and
are in a collaborative or antagonistic relationship. Furthermore, differing from the common graph, the Laplacian matrix
associated with
is redefined as follows.
The neighbor set of agents is denoted by . It is worth noting that the signed graph has no self-loops, i.e., . The signed graph is defined as undirected if and as long as , and meanwhile, holds. Paths from node to node are composed of edges in the form of with distinct nodes. An undirected graph is regarded as connected if there is at least one path connecting two nodes in .
Before giving some lemmas describing the important properties of signed graphs, the necessary definitions are given below.
Definition 1 ([40]). A graph is considered structurally balanced if it has nodes and that are bipartitioned, where and , such that , and , .
Definition 2 ([41]). Gauge transformation changes the quadrant order in through orthogonal matrix . Despite a change in the sign, the modulus value of the entries of a matrix remains the same. The set of gauge transformations in can be written as follows: According to the relevant definitions above, the lemmas are given as below:
Lemma 1 ([42]). The solution to a structurally balanced connected signed graph is easily derived by finding a matrix with all elements of ( is a positive semi-definite matrix) off-diagonals being negative and all elements of being non-negative. It is evident that and are isospectral. The dichotomy of nodes and nodes is bound up with , which can be expressed as follows. Lemma 2 ([43]). In the definition of a Laplacian matrix , zero is one of the eigenvalues of with the right eigenvector , which satisfies . Meanwhile, the eigenvalues of the rest of are positive, which is represented as . Moreover, once a vector satisfying , there is an equality holds.
2.2. Problem Statement
Consider an MAS consisting of
agents over an undirected signed graph
, indexed by
. The
agent dynamics is modeled by
where
and
stand for the state and the control law of agent
;
and
are constant matrices. Note that this state–space formulation may introduce a real zero in the transfer function, which reflects the structural property of the representation rather than an additional physical mode.
Assumption 1. In MAS (5), the signed is undirected, connected, and structurally balanced.
Control objective: Under the framework of a coupling-weighted signed graph , the goal is to achieve bipartite consensus. That is, according to the definition of in (4), the states of all agents satisfy , meaning that agents in the same cluster converge to identical states, while agents in different clusters converge to opposite states. This definition of the objective is consistent with standard bipartite consensus results in signed networks. Simultaneously, the Zeno behavior is guaranteed to be excluded.
Simultaneously, the Zeno behavior is guaranteed to exclude.
3. Fully Distributed Dynamic Bipartite Event-Triggered Control Protocol
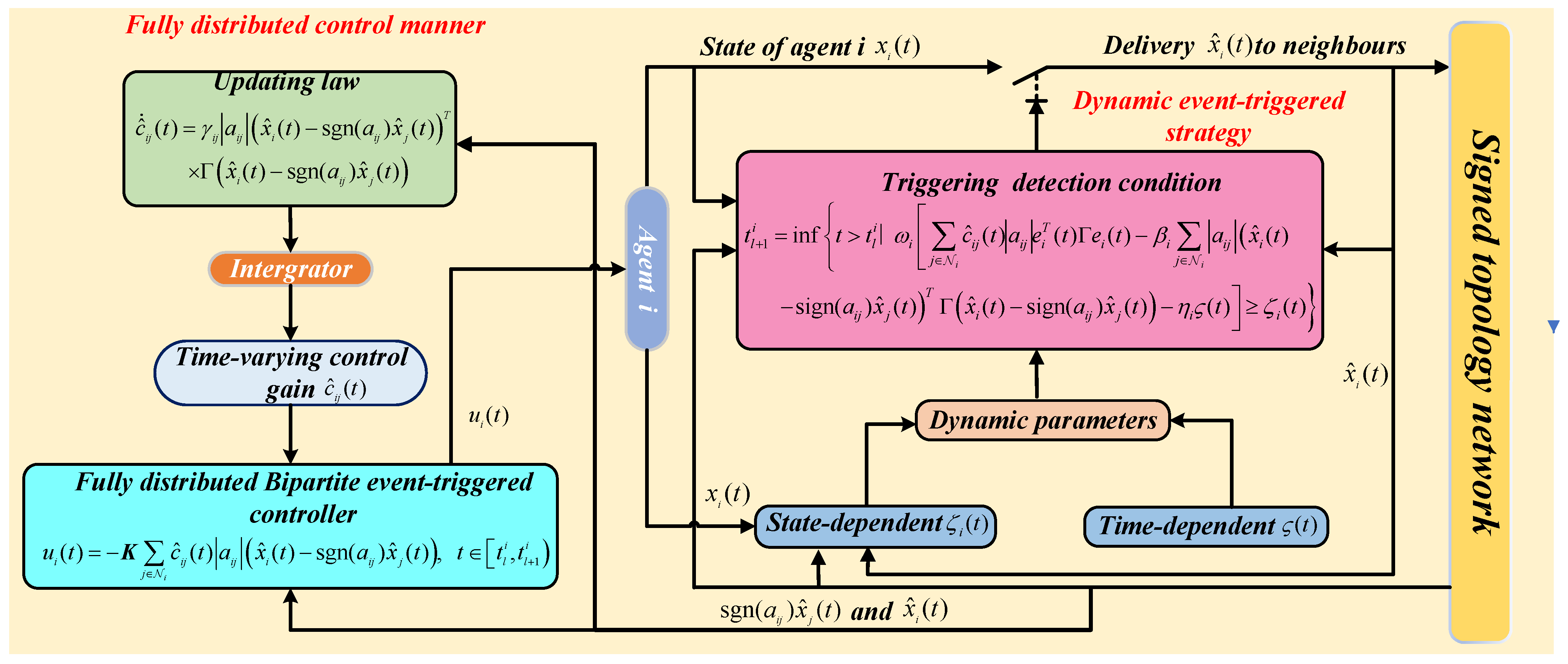
In this section, the communication topology throughout this section is represented as in Assumption 1. Moreover, a fully distributed design and implementation is used for both the triggering detection condition and bipartite consensus protocol. The structure of the proposed controller is depicted in
Figure 1.
Before proceeding, define the estimated state as
, where
is the latest event-triggered instant in the trigger time sequence of agent
, and
is the latest broadcast state of agent
. Furthermore, the state measurement error of the
agent is defined as
where
is the difference between the latest broadcast state and the current one of agent
.
Then, a fully distributed dynamic bipartite event-triggered controller is designed as
where
is the feedback gain matrix to be determined in the subsequent;
is the adaptive coupling strength to edge
, which satisfies the following update law
where the initial values
and
are given positive constant.
,
is a positive-definite symmetric matrix to be decided.
Combining Equations (5) and (7), the closed-loop system is presented as
where
and
are stack vectors defined as
and
respectively. Moreover,
Remark 1. Inspired by [39], the time-varying coupling strength is introduced in the controller design to provide a more flexible parameter adjustment pattern than the constant gain parameter. One of the notable caveats is that can restrain the influence of coupling weights by limiting the coupling strength to a reasonable range, and another caveat is that it can avoid designing sufficient large value in advance to satisfy the mission requirement. Remark 2. From Equation (8), since the relative error between agents is large, will increase rapidly at the beginning. As time goes by, the relative error will gradually approach zero under the effect of the controller . Then, will tend to be a constant; the variation trend of will also become stable.
Remark 3. The use of the sign function may cause chattering in practical systems. This issue can be alleviated by replacing it with a smooth approximation such as a saturation function. In practice, the proposed event-triggered mechanism can be implemented using a zero-order hold, where each agent holds the last transmitted value until the next triggering instant.
3.1. Dynamic Event-Triggered Strategy
To highlight the distinct features of the dynamic event-triggered strategy used in this paper, several counterpart event-triggered strategies are introduced, which have been widely adopted in [
22,
24] and related references. Defining the first triggering time
, three types of common triggering conditions for agent
are introduced as follows:
- A.
static event-triggered condition: .
- B.
a kind of “DET condition”: .
- C.
“DET” condition: .
where and ; is a positive constant; the definition of is shown as with ; is an internal dynamic variable, satisfying with , , and .
Observed from the
A,
B, and
C, firstly, it can be seen that
A involves a fixed constant threshold parameter
, specified by designer; this form of design has an adverse effect (the detect condition of Equation (7) will be over-triggered) which may result in unnecessary measurement information transmission even after the control task has been accomplished. Subsequently,
B exhibits a kind of time-dependent/external dynamic variable method, and though it is effective in reducing the triggering instants, it loses flexibility due to the given trajectory over time with function
. Furthermore, the dynamic event-triggered condition
C in [
44] provided an adaptively adjusted strategy in accordance with state errors variation, whereas the global information is utilized in the control method.
In view of these questions, a novel dynamic adaptive bipartite event-triggered scheme developed in this paper is proposed as
where
,
,
,
and
are defined in the three common triggering conditions, and
is a positive constant.
The following is a mathematical solution to the algebraic Riccati equation (ARE):
where the solution of
can be obtained. Then the matrix of
and
introduced in Equations (7) and (8) can also be obtained.
Remark 4. In the common triggering condition A, a fully distributed event-triggered strategy is developed by combining time-dependent and state-dependent conditions. Under this mechanism, continuous communication is no longer required, neither for controller updates nor for triggering detection. Both and play a crucial role in regulating the threshold dynamically. According to Figure 1, agent only transmits its information to all of its neighbors at time instant instead of continuous communication. Unlike the event-triggered schemes presented in [17,45], which rely on continuous, real-time neighbor data, there is no doubt about the significant effect of the proposed strategy in reducing the communication burden. Up to now, the fully distributed dynamic bipartite event-triggered control protocol for general linear MASs has been constructed as shown in Equations (7) and (8) and Equations (10) and (11). To simplify the bipartite consensus analysis in the follow-up, a model transformation is required first.
3.2. Model Transformation
To facilitate the following analysis, some intermediate variables are introduced here. In light of Definition 2 and Lemma 1, for
, define
and
,
. In accordance with Equation (6), it has
. Moreover, denote vector
,
and
. Thus,
and
are valid. Meanwhile, similar to Equation (9), the dynamics of
can be given as follows:
where
,
and
are isospectral, which is by virtue of Lemma 2.
Subsequently, define an average state of
as
. Set
, representing the error signal between the states of agent
and the average state, such that
,
. Define
, it also yields that
with
. In addition, by resorting to the fact that
, the expression of
can be deduced as
with
,
and
. Moreover, Equation (8) can be rewritten as
Using these variables, the bipartite consensus of system Equation has been converted to the traditional consensus of system Equation (13), which implies that the bipartite consensus of can be achieved as long as the stability of is guaranteed. Two theorems will be presented in the next section.
3.3. Consensus Analysis
In this section, bipartite consensus criteria of the general linear MAS under the fully distributed dynamic event-triggered strategy are proven first. Then, it is verified that the Zeno behavior can be ruled out.
Theorem 1. For a general linear MAS described by Equation (5) with communication graph under Assumption 1. Suppose that in Equations (10) and (11) with , , and are defined in Equation (12). Then, for any initial condition, the bipartite consensus dynamic event-triggered issue is resolved by the fully distributed control protocol Equations (7) and (8) and the dynamic adaptive triggering mechanism Equations (10) and (11).
Proof. The proof is organized into two main steps. Step 1 establishes the boundedness and stability of the closed-loop system via a Lyapunov function. Step 2 further shows, by employing Cauchy’s convergence criterion and the analysis of triggering instants, that the agents’ states converge to achieve bipartite consensus.
Step 1: The Lyapunov candidate function (LCF) is selected as
where the matrix
is defined in Equation (12),
and
are given in Equation (15),
is a positive scalar to be determined later. Recalling the definitions of
,
and
, Equation (11) can be rewritten as
Then, the time derivative of
along Equation (14) is presented as
Consider the Lyapunov candidate in (18). Substituting the closed-loop dynamics yields its derivative, which after suitable bounding operations (detailed in
Appendix A) leads to:
In light of the definition of
and
, it can be seen from the triggering condition Equation (10) that
Consequently, from Equation (20), it follows that
where
,
.
Starting from (21), by employing Cauchy–Schwarz and Young inequalities together with the triggering condition, the inequality can be progressively simplified and reduced, which ultimately yields ensuring the negative definiteness of LCF:
where
since condition
exists. Furthermore,
, by choosing
, one can find that
. In accordance with algebraic Riccati equation in Equation (12), Lemmas 1 and 2, Equation (22) can be reduced to
Recalling the definition of
, define
, one has
Attributing to and , is bounded, which indicates that , and are uniformly ultimately bounded. To further illustrate that the proposed control objective can be achieved, i.e., , detailed proof is given as follows.
Step 2: In view of Cauchy’s convergence criterion, for any
, there exists a positive constant
such that
for any
. By defining the increasing time sequence of the triggering instants
for
. Seeing from Equation (24), it can obtain that
Observing Equation (25), it can conclude that
exists. Also,
is twice differentiable due to
meet the condition in Equation (14). Moreover, considering that
is bounded,
is bounded too. Thus,
where
is a positive constant. Consequently, it can draw a conclusion that
and
, which means the MAS can achieve bipartite consensus eventually. □
Thus, Theorem 1 has been proven completely, and the complete derivation steps are provided in
Appendix A for clarity. Next, the Zeno behavior is examined in depth. The exclusion of Zeno behavior is exhibited in Theorem 2.
Theorem 2. The Zeno behavior of MAS can also be excluded under the same condition as in Theorem 1.
Proof. For agent
,
, in view of the event-triggered function in Equation (20) and dynamic variable in Equation (17), one has
where
. By calculating the right-hand Dini derivative of
over interval
, it is not hard to obtain
where
; it follows from Equation (8) that
,
is the upper bound of
. Define a non-negative function
with
Obviously, the solution of Equation (28) is
. Combining with Equations (28) and (29), one can get that
Then, in comparison with the triggering condition Equation (27), the next triggering instant
satisfies
with
. In light of the discussion in Theorem 1 and the definition in the common triggering condition B, it is easy to verify that
,
and continuous function
are both bounded. Thus, the terms of
and
are also bounded. Then, by utilizing Equations (30) and (31), the following inequality exists:
Consequently, there is a trigger interval between two sequential instants
and
, which can be deduced as
Therefore, the Zeno behavior is excluded for each agent at any finite time.
Thus, Theorem 2 is accomplished. □
4. Numerical Simulation Results
In this section, two sets of numerical experiments are provided to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed theoretical results. To be specific, the first experiment indicates that the established control strategy ensures the bipartite consensus performance with dynamic event-triggered mechanism. Furthermore, in order to verify that the developed event-triggered method can remarkably decrease the triggering instants, the second experiment is conducted by comparison with the conventional static one.
The constant matrices are given below as in Equation (5) for a group of six agents.
Since the output is the full state, the corresponding matrices are and , which are implicitly adopted in this system model.
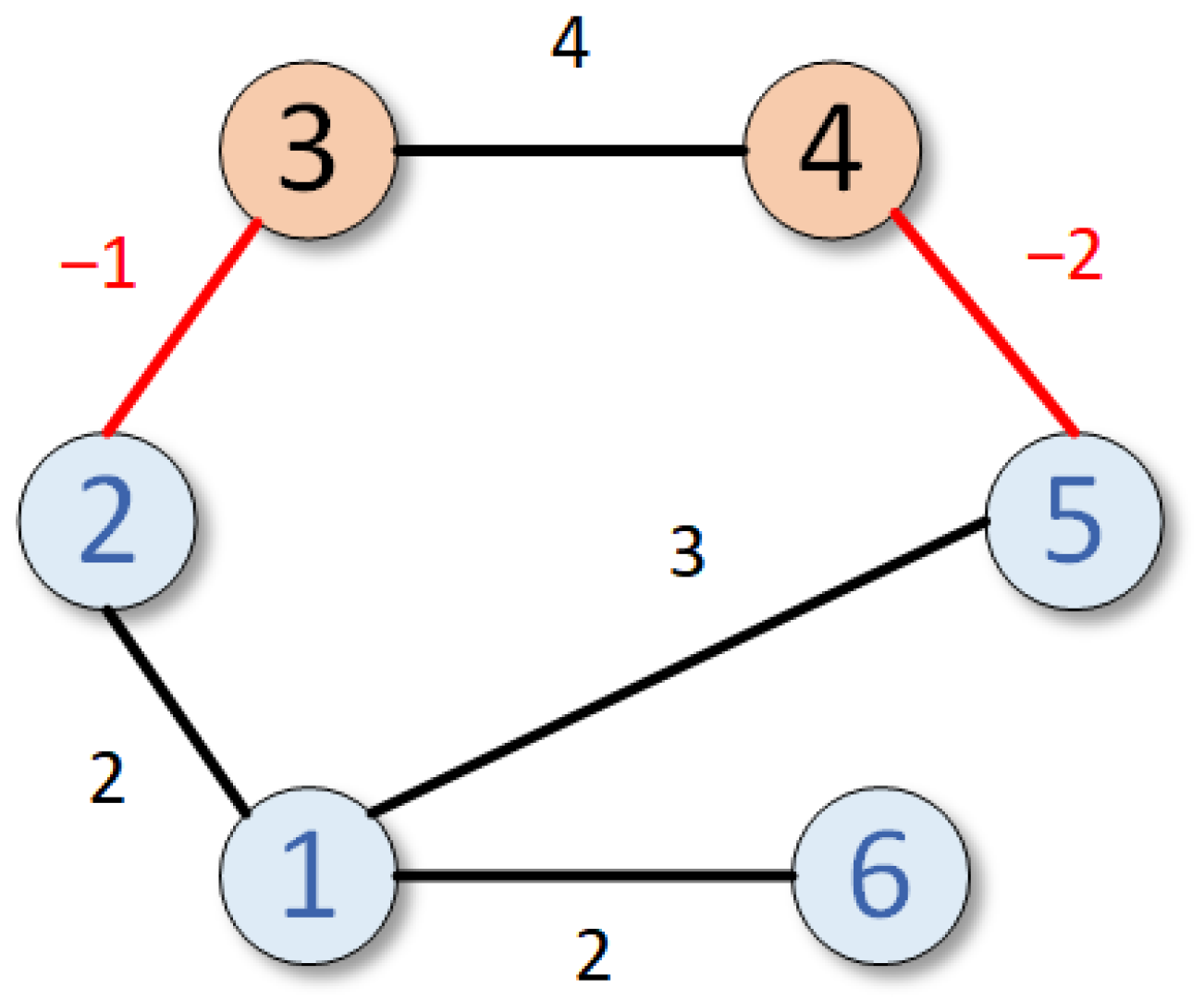
Figure 2 illustrates the weighted signed communication graph
among the six agents. Together with
Figure 1, which indicates the controller and set points, it clarifies how neighbor information is exchanged through cooperative edges in black and antagonistic edges in red, with coupling gains defining the interaction strength.
In this figure, the cooperative and competitive interactions between neighbors are depicted by black and red lines, respectively. Recalling Definition 1 and Lemma 1, it is clear that
has been divided into two parts, i.e.,
and
. In this way, the Laplacian matrix
and adjacency matrix
can be represented as
All simulations were implemented in MATLAB R2021a with a fixed-step 4th-order Runge–Kutta scheme (ode4, step size 0.1 s, horizon 15 s), where the event-triggering condition was evaluated online and the adjacency matrix in Equation (35) was used; each run finished within a few seconds on a standard laptop.
Observing from
Figure 2 and Equations (34) and (35), the existence of Assumption 1 is reasonable. By solving the ARE in Equation (12), one can calculate that
. Then, the feedback gain
can be obtained. The other parameters are summarized in
Table 1.
In addition to the different event-triggered mechanisms embodied in
Section 4.1 (dynamic) and
Section 4.2 (static), the associated parameters used in both experiments remain consistent with those listed in
Table 1. Further details of the simulation results and corresponding discussions are provided in the following subsections.
4.1. Simulation of the DET Scheme
To numerically illustrate that the bipartite consensus of general linear system can be achieved with a dynamic event-triggered strategy under a fully distributed framework. Simulation results are portrayed in
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5. The state trajectories of each agent under the dynamic triggering schemes (10) and (11) are shown in
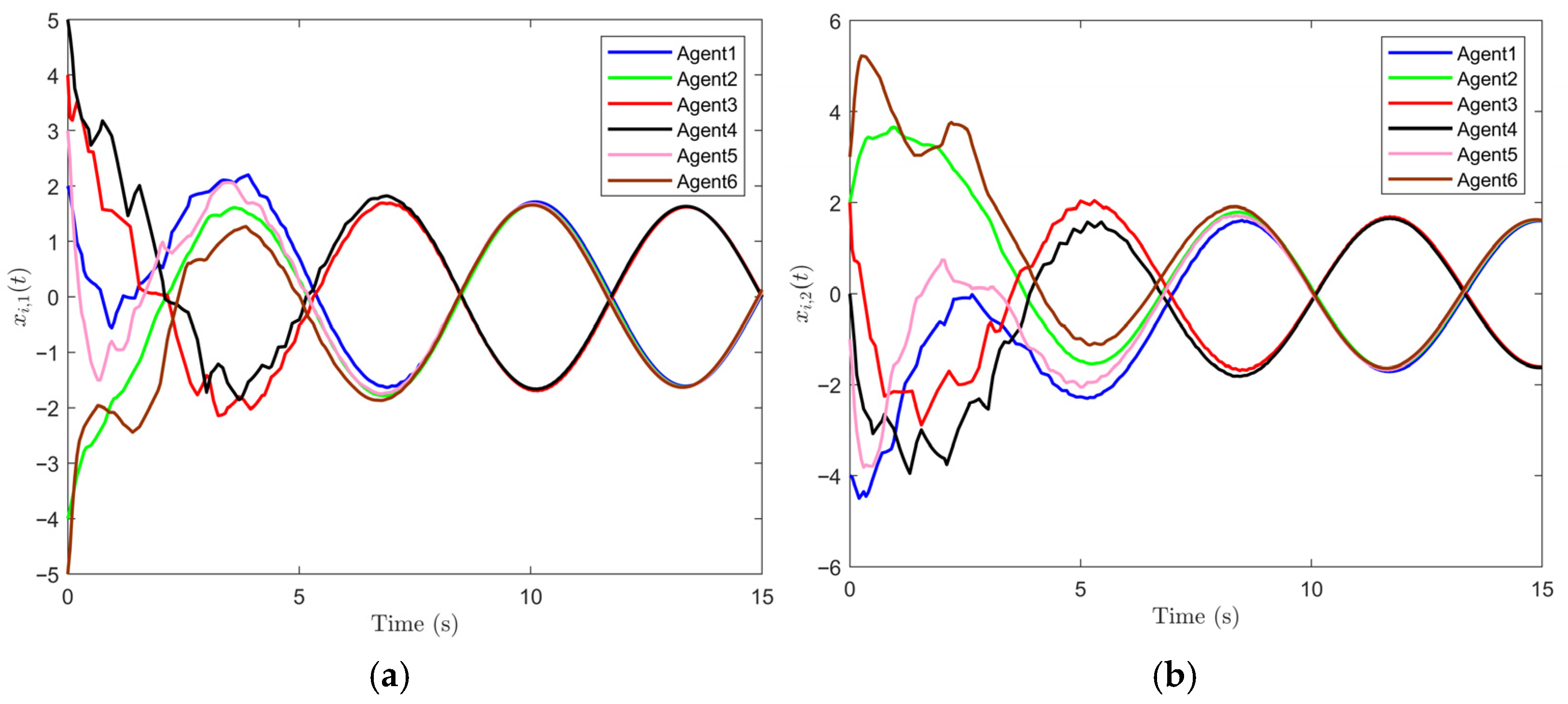
Figure 3a,b, which clearly demonstrate that bipartite consensus of MAS can be achieved. It is observed that the agents within the same cluster converge to identical trajectories, while those in different clusters converge to trajectories with opposite phases. The oscillatory behavior is mainly attributed to the inherent harmonic dynamics of each agent and the antagonistic interactions in the signed topology, rather than to any deficiency of the control effect.
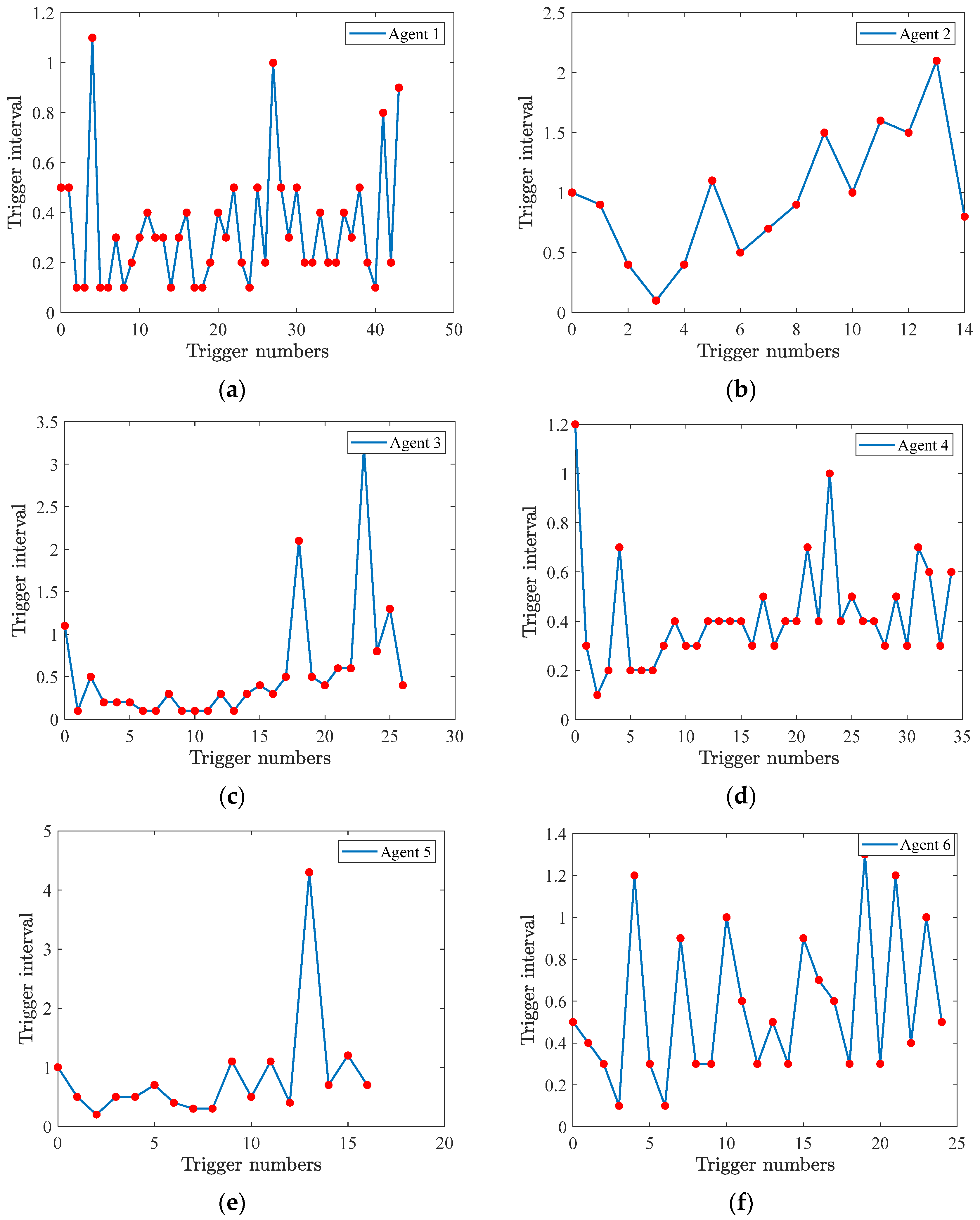
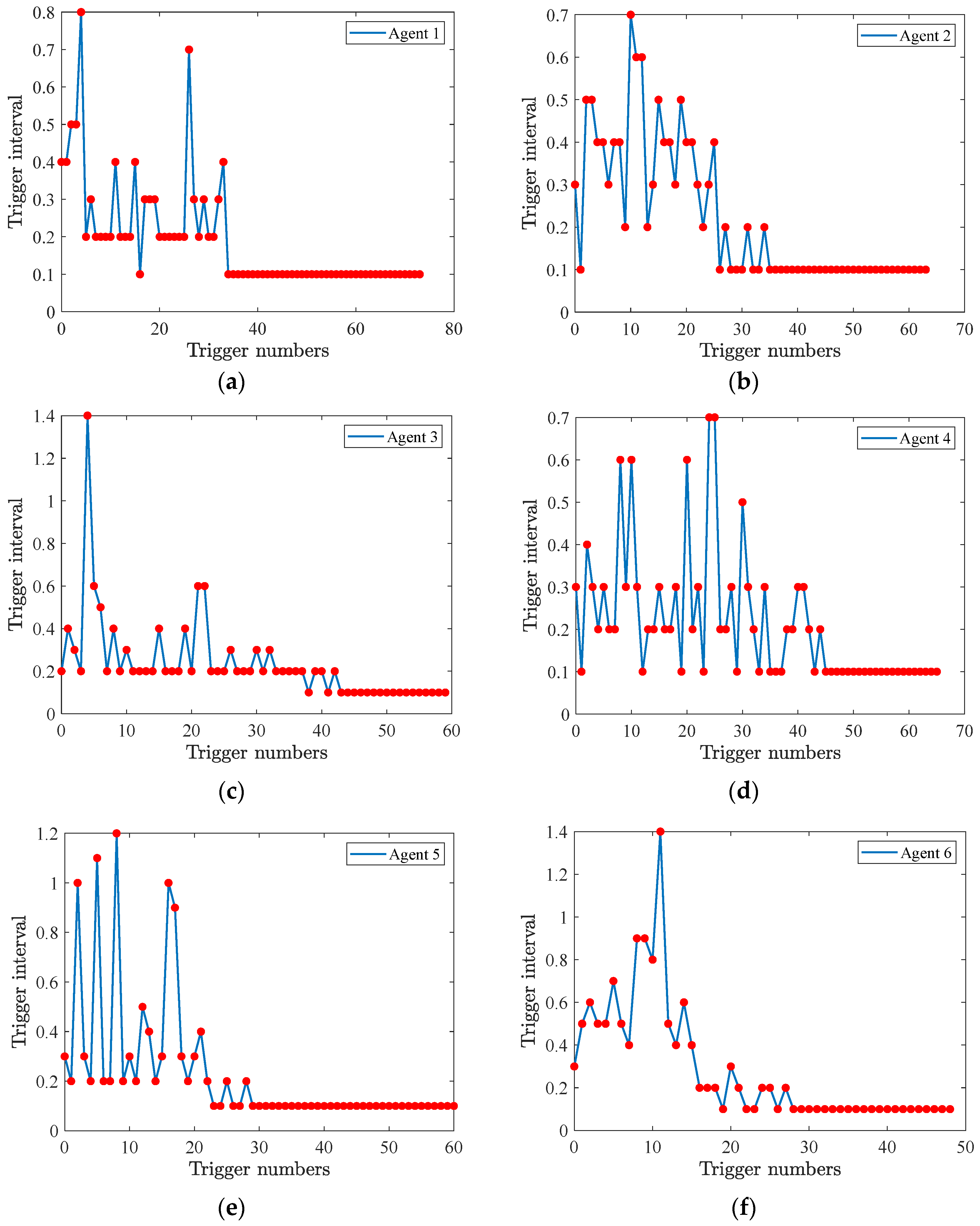
Figure 4a–f displays the number of triggering instants and intervals for all six agents. It can be seen that different agents exhibit distinct triggering patterns, showing that the proposed strategy adaptively balances the communication load without enforcing uniform update frequencies.
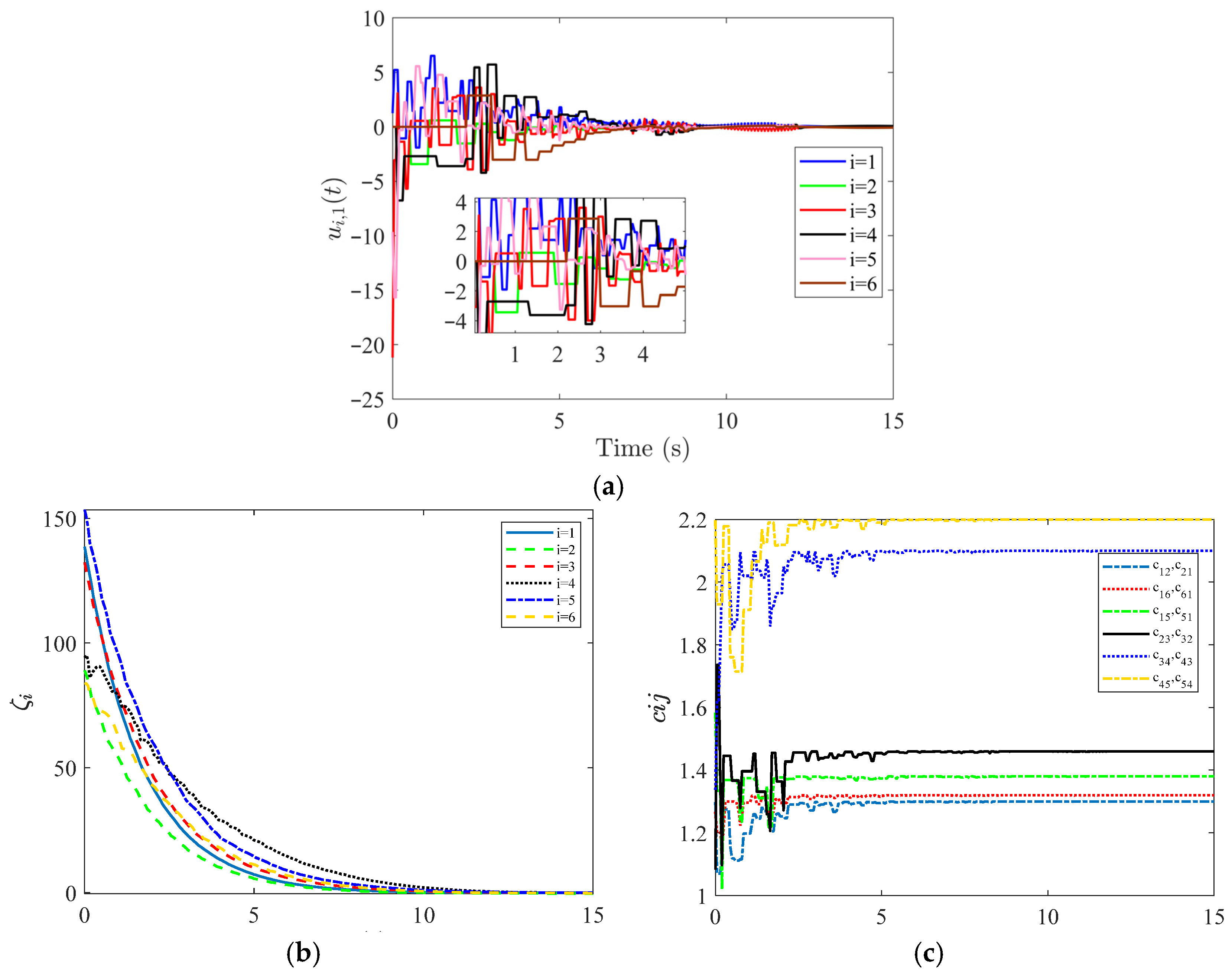
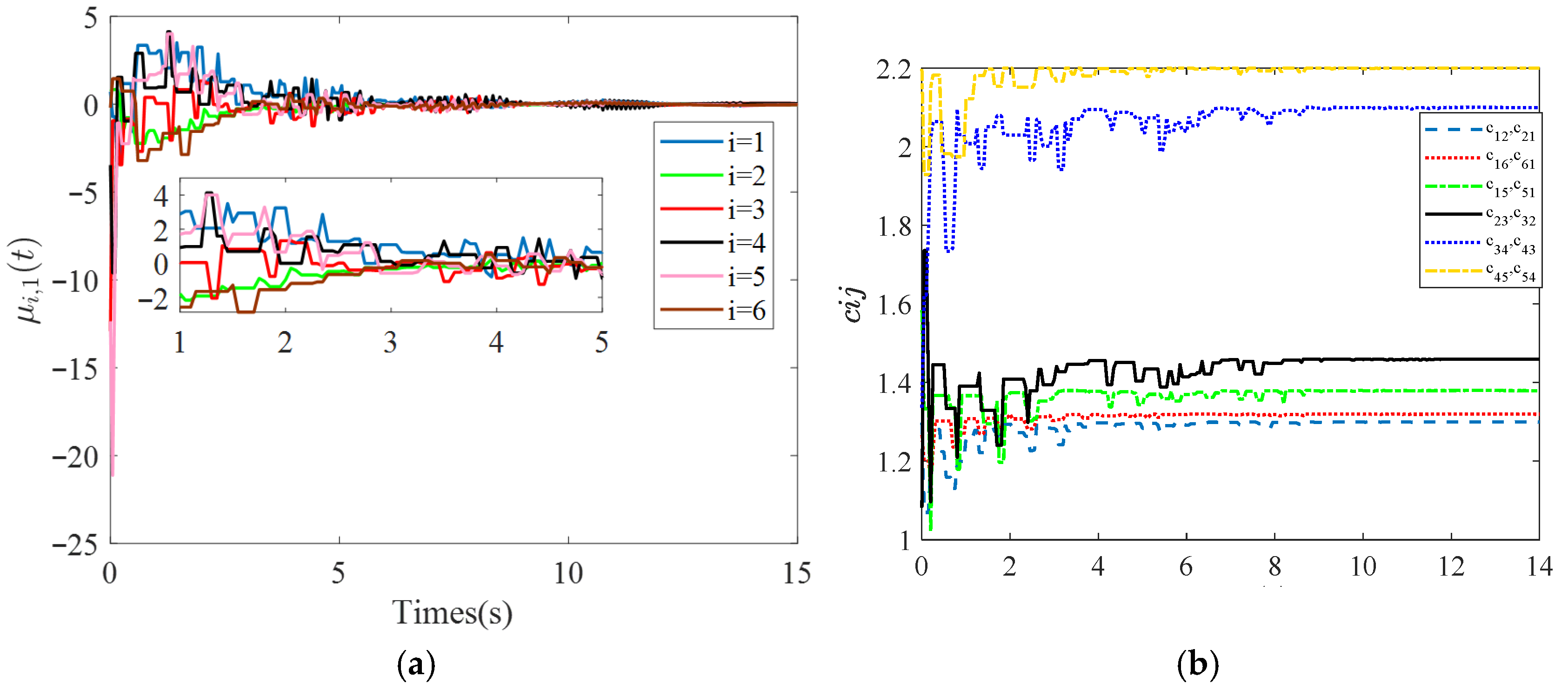
Meanwhile, it is observed from
Figure 5a–c that the time response curves of control inputs
, dynamic threshold parameters
, and adaptive parameters
exhibit a piecewise-constant variation trend. Thus, this demonstrates that the continuous communication of controller updating and event detection mode among agents can be resolved. Furthermore, it can be seen from
Figure 5c that the adaptive coupling strength tends to stabilize constants. In the evolution of
, it not only enables the control output automatically according to the edge weight but also avoids preselecting a large gain in advance (which calls for eigenvalues of the Laplacian matrix) to meet the control requirements.
4.2. Comparison with the SET Scheme
In order to demonstrate the superior performance of the dynamic-based event-triggered control scheme (denoted as “DET”) proposed in this paper, which can greatly reduce the triggering numbers, another static-based event-triggered control scheme (denoted as “SET”) is introduced here as a comparative object. Additionally, for the purpose of providing a fair comparison, the relative parameter, which has been applied in the first experiment except for the “DET”, is utilized. The static event-triggered condition is similar to the triggering conditions A, which can be presented as
The simulation results are shown as
Figure 6,
Figure 7 and
Figure 8. From
Figure 6a,b, it can be found that the bipartite consensus of the MAS can still be achieved under the “SET” scheme with the state trajectories change.
Nonetheless, compared to the “DET” strategy, both the time response curves of control inputs in
in
Figure 7a and the variation of adaptive parameters
in
Figure 7b reveal a significant increase in the number of triggering instants, indicating a higher triggering frequency.
To enhance the clarity of the analysis,
Figure 8a–f illustrates the triggering instants and intervals of all six agents under the “SET” scheme. The results clearly demonstrate that the detection condition in Equation (36) leads to excessive triggering events. Such over-triggering not only imposes unnecessary communication and computational burdens on the networked system but also suggests a potential risk of Zeno behavior, which may undermine the long-term stability and practical applicability of the control strategy.
Moreover, to facilitate a clearer comparison, the number of triggering events for each agent with “SET” and “DET” schemes are summarized in
Table 2.
To emphasize the core contribution, the simulation focuses on the SET as a baseline, rather than incorporating broader comparisons with other strategies. As shown in
Table 2, although both “SET” and “DET” schemes achieve bipartite consensus, the “DET” strategy significantly reduces the number of triggering events across all agents. Consequently, on the premise of ensuring the completion of the bipartite consensus task for MAS, the proposed “DET” method owns the satisfactory control performance in decreasing communication frequency and computational burden.
5. Conclusions
This paper has addressed the fully distributed bipartite consensus control problem for general linear MASs under a structurally balanced and connected signed topology by developing a dynamic event-triggered mechanism. To alleviate the communication burden, the proposed strategy incorporates both state-dependent and time-dependent variables, such that each agent only exchanges information intermittently with its neighbors. The control law and triggering condition are implemented in a fully distributed manner without requiring any global information, thereby avoiding the reliance on Laplacian eigenvalues or the number of agents. Rigorous analysis establishes that bipartite consensus can be achieved under the proposed framework, and the triggering mechanism is proven to exclude Zeno behavior. Numerical simulations further confirm the effectiveness of the method, showing that the proposed scheme significantly reduces triggering frequency while preserving control performance compared with the static event-triggered baseline.
Nevertheless, some limitations remain. The present study is restricted to numerical simulations, and future work will emphasize experimental validation on physical platforms. Moreover, the analysis is confined to structurally balanced signed topologies, and extensions to heterogeneous or nonlinear networks, particularly under disturbances, uncertainties, and actuator faults, represent an important direction. In addition, while the dynamic event-triggered strategy decreases communication load, further refinement is required to enhance transient performance and robustness under model uncertainties. Future research will also focus on edge-based dynamic event-triggered schemes to accommodate more general MAS settings and broader application scenarios.