Detection Algorithm of Thrombolytic Solution Concentration with an Optimized Conical Thrombolytic Actuator for Interventional Therapy
Abstract
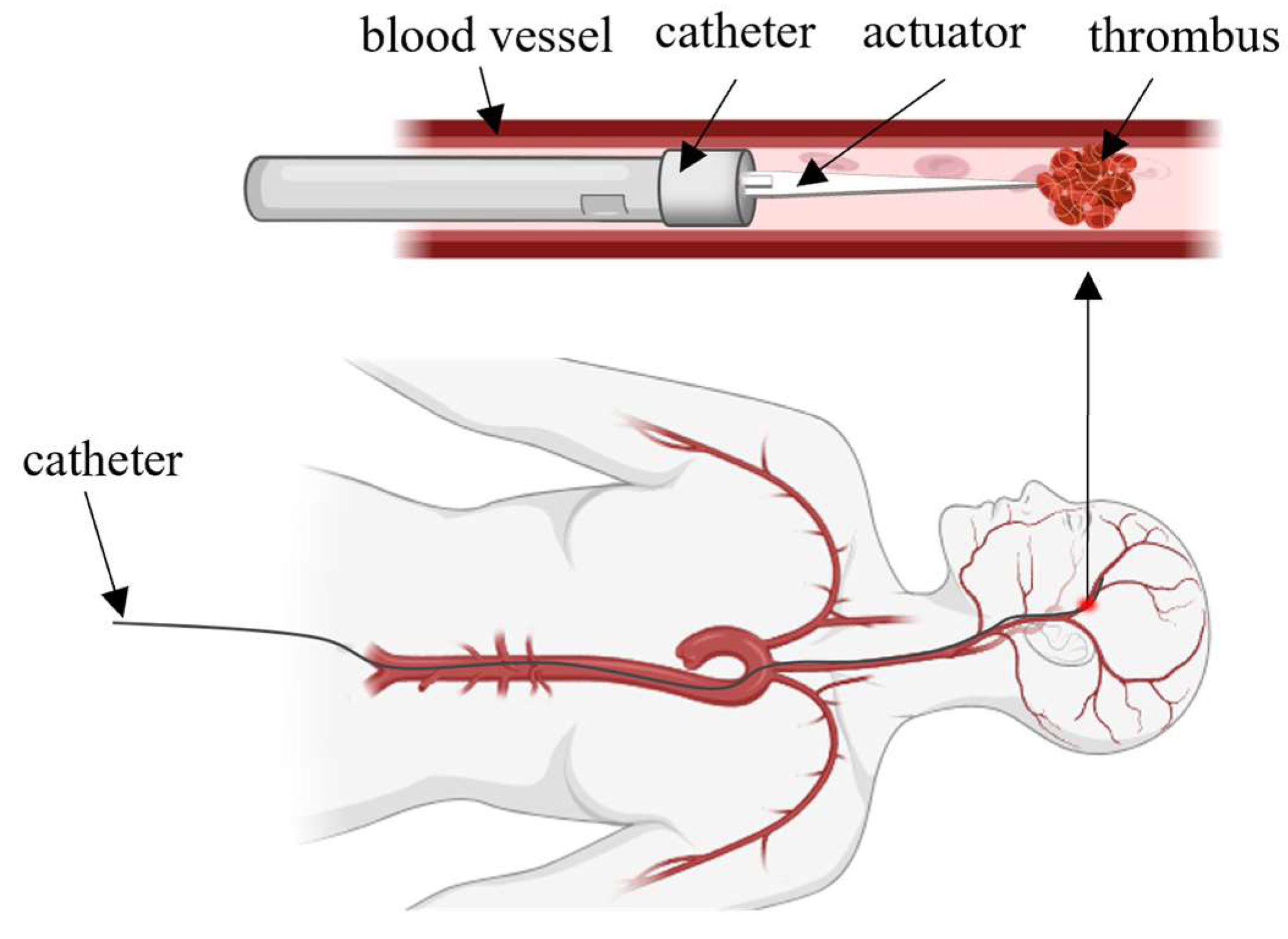
1. Introduction
2. Modelling and Structural Parameter Optimization
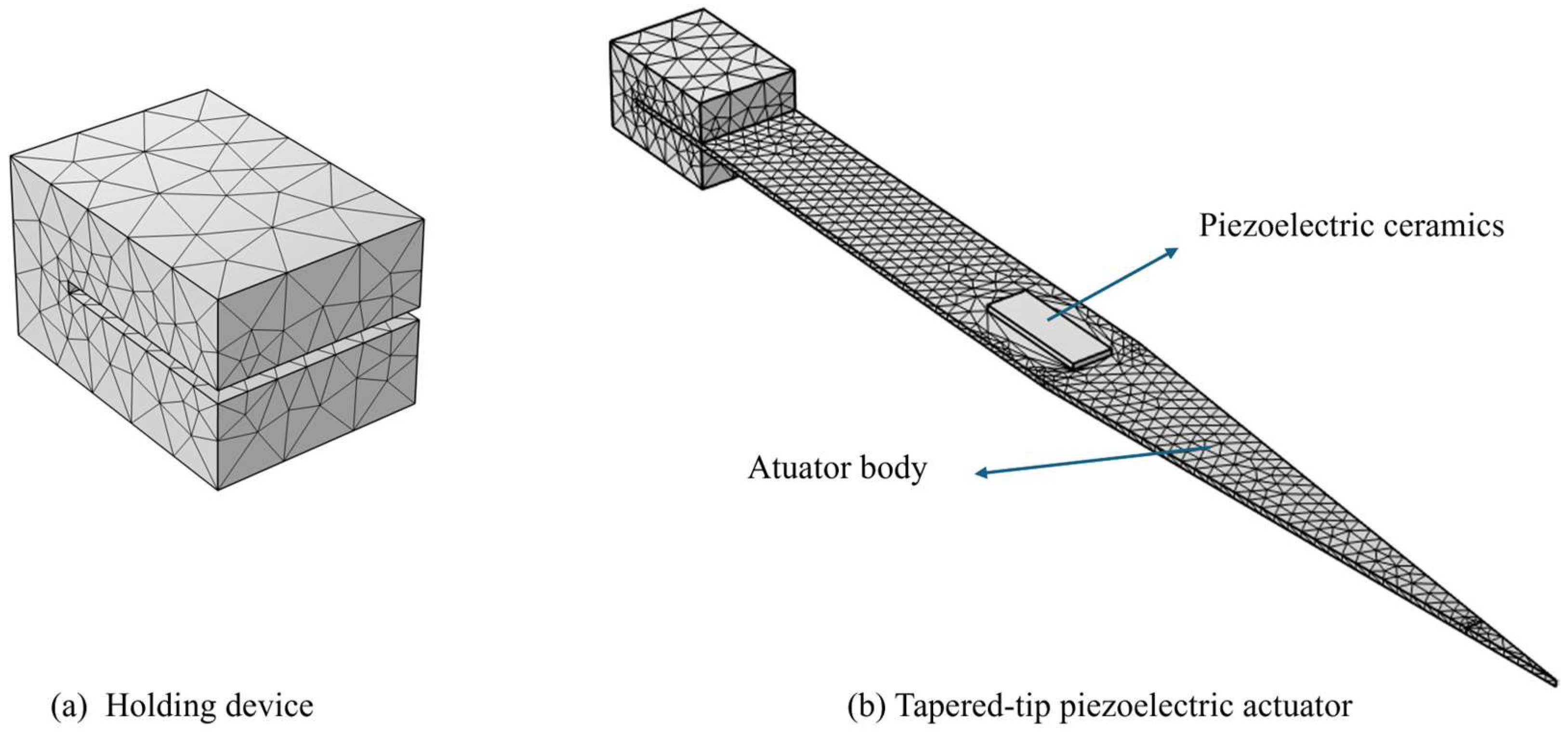
2.1. Actuator Modelling
2.2. Actuator Structural Parameter Optimization
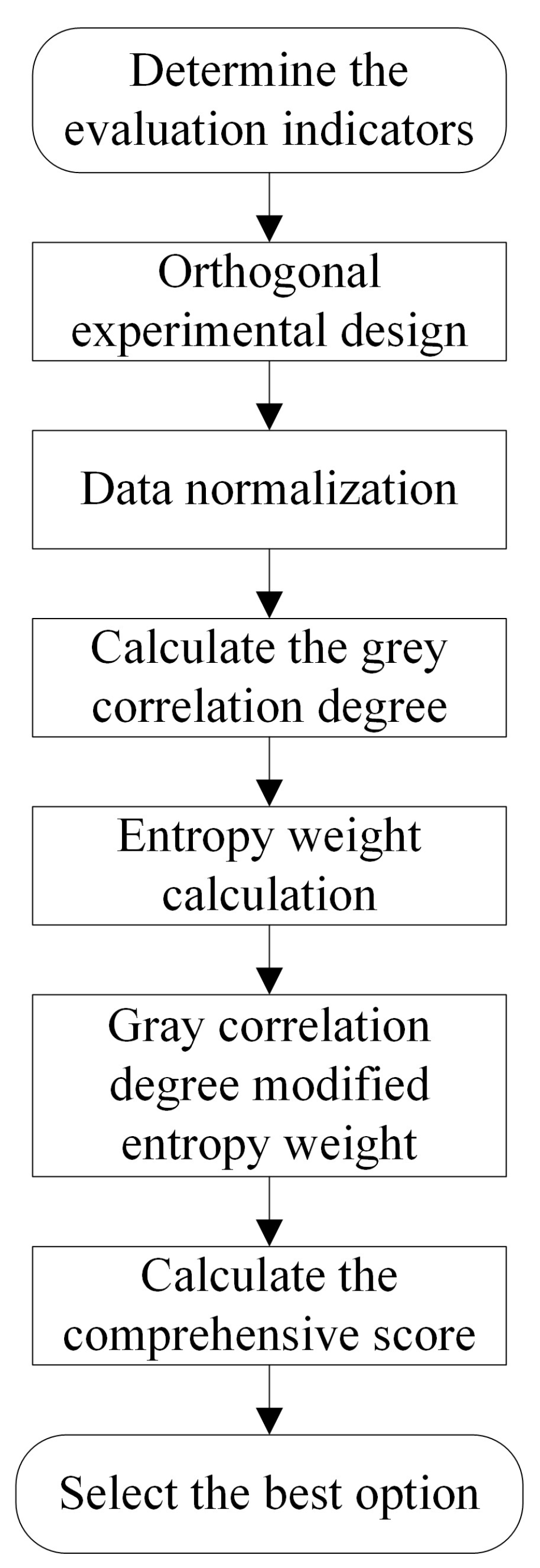
2.2.1. Orthogonal Experimental Design
2.2.2. Grey Relational Analysis with Improved Entropy Weights
- (1)
- Compute the information entropy for the j-th indicator. Its mathematical form is the following:where is a constant ensuring that the entropy lies within [0, 1].
- (2)
- The weights using the improved entropy–weighting formula:where , is the mean of all entropies not equal to 1, and is a default prior weight set to 0.5.
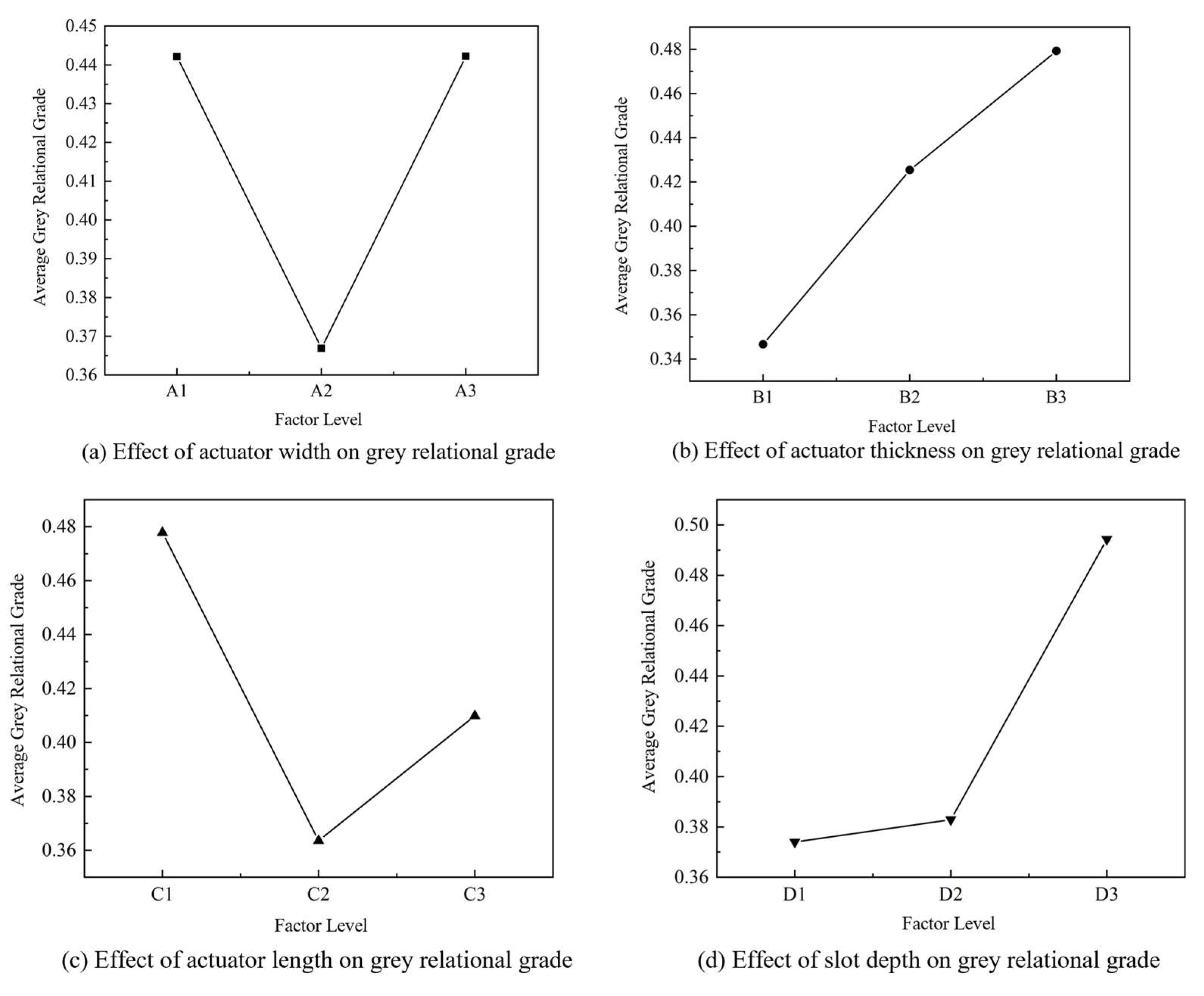
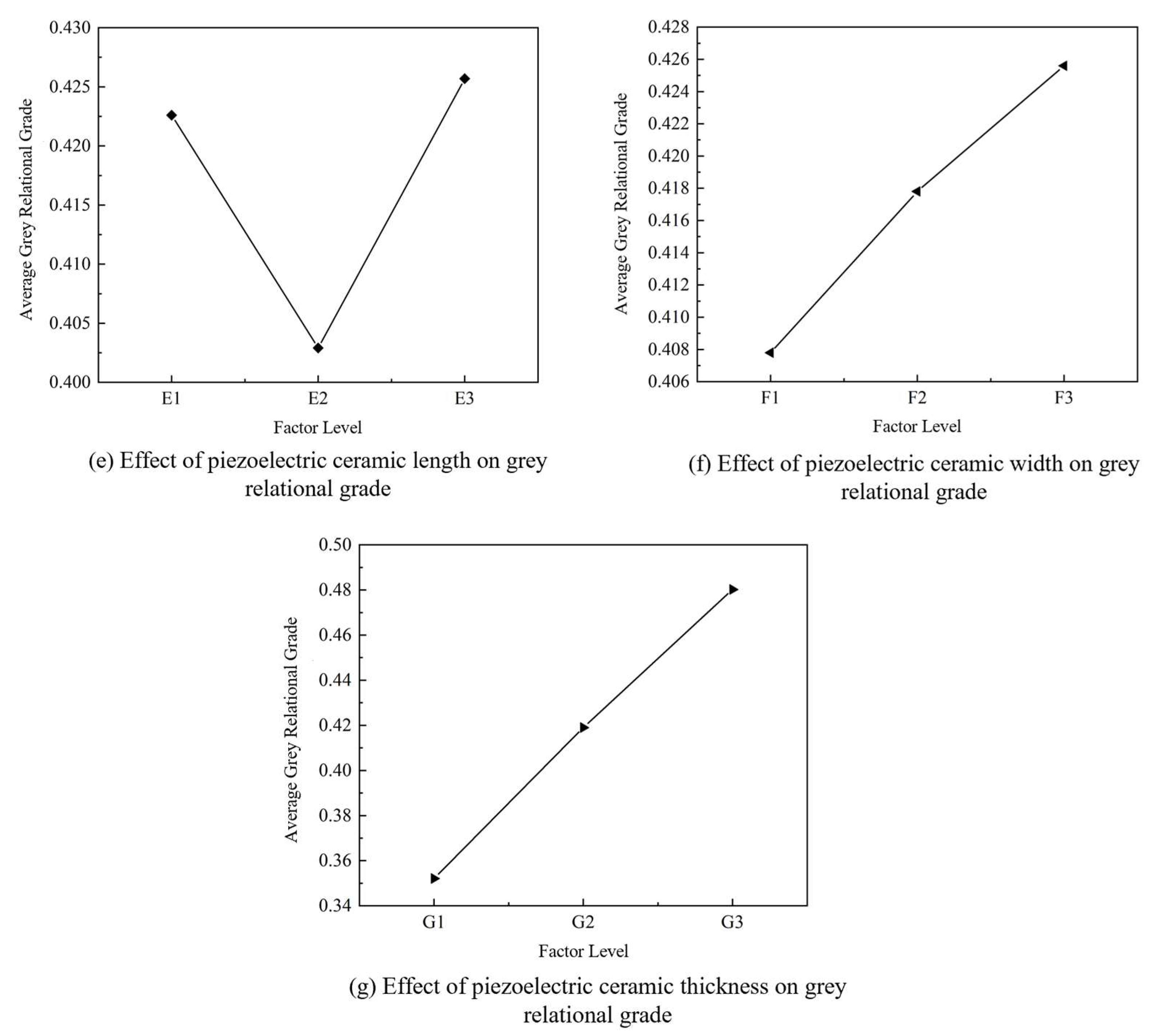
2.2.3. Mean–Range Analysis Based on Grey Relational Grades
3. Detection Algorithm of Thrombolytic-Solution Concentration
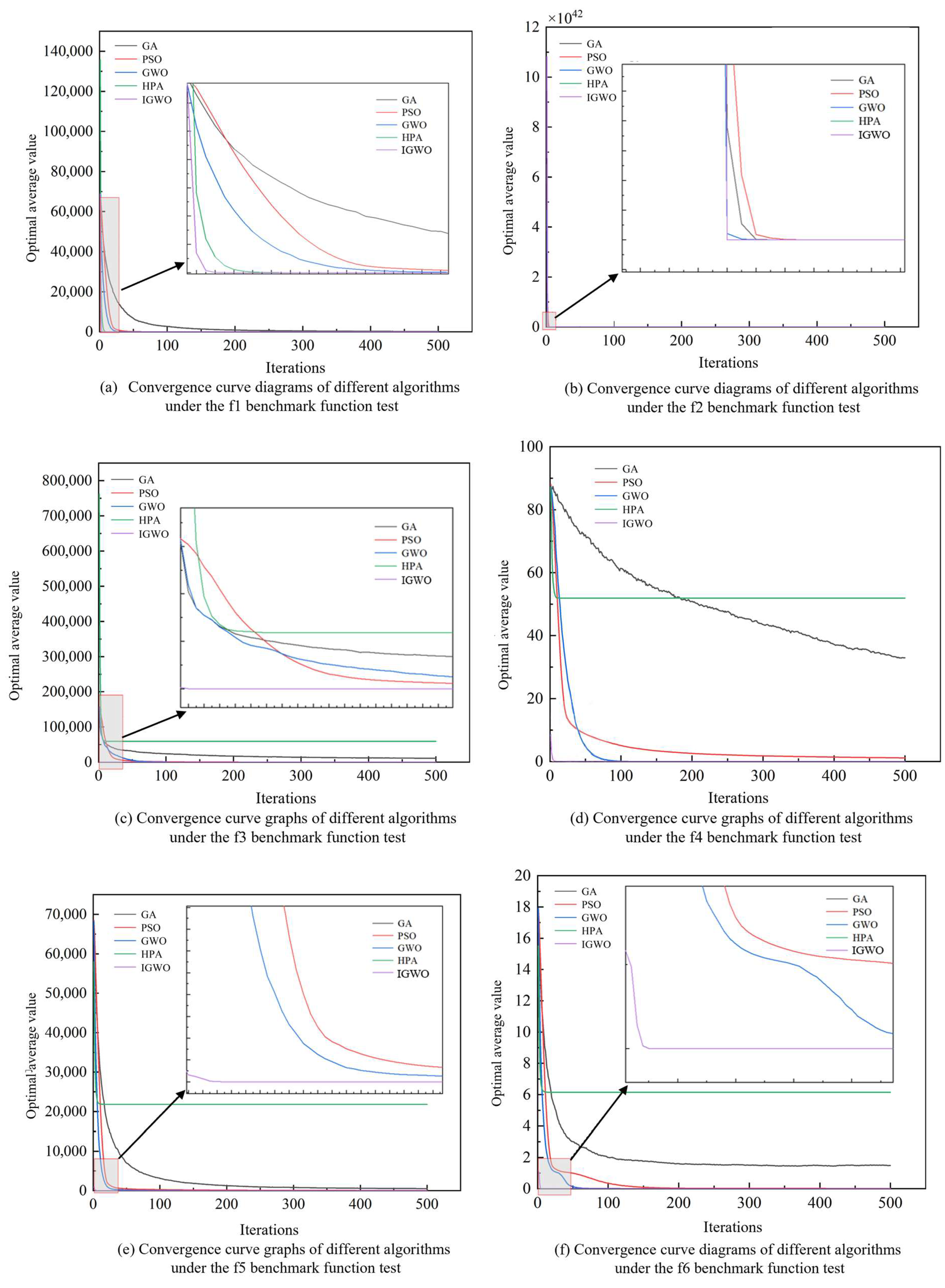
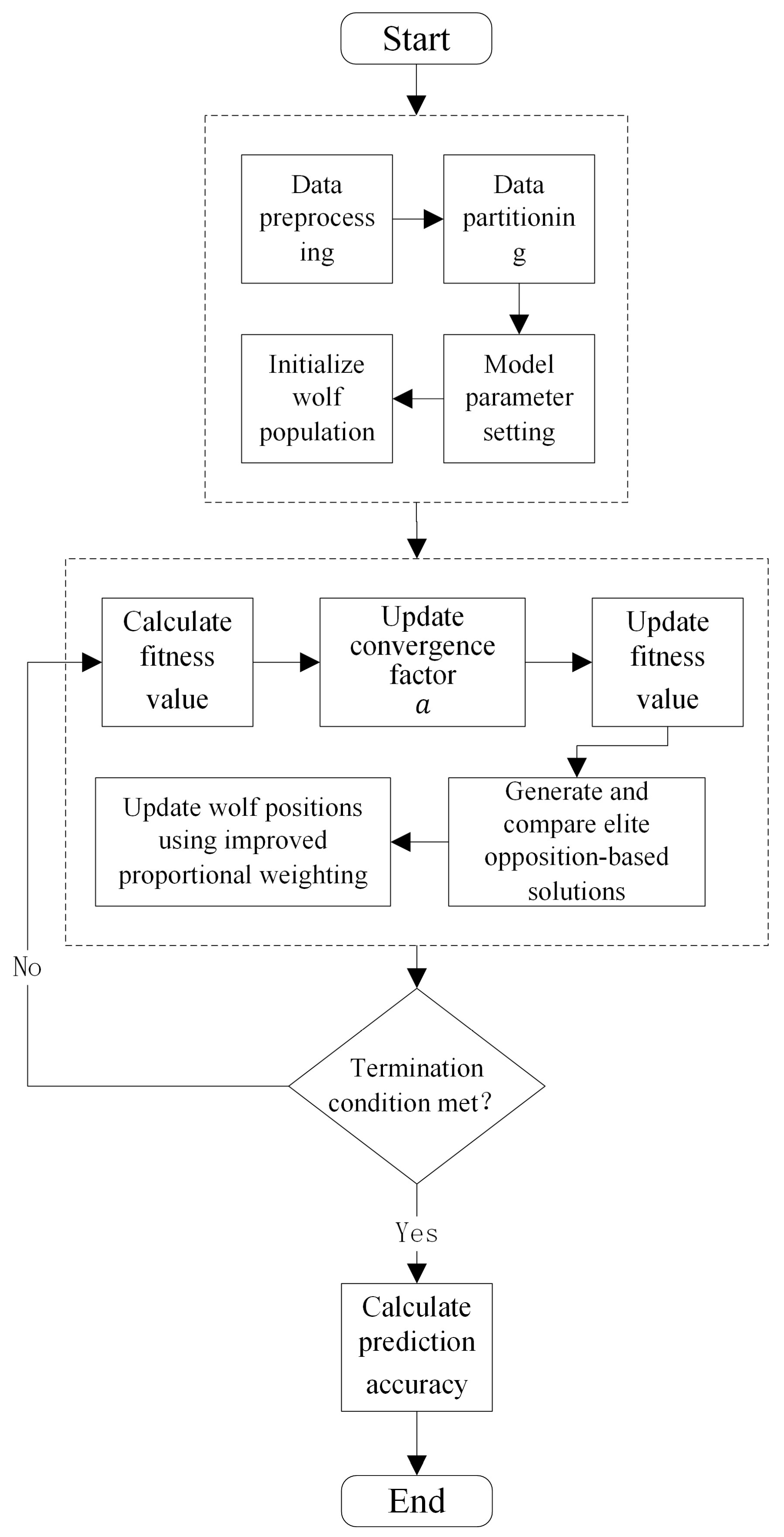
3.1. Improved Grey Wolf Optimizer (IGWO)
3.2. Support Vector Regression for Concentration Detection Based on IGWO
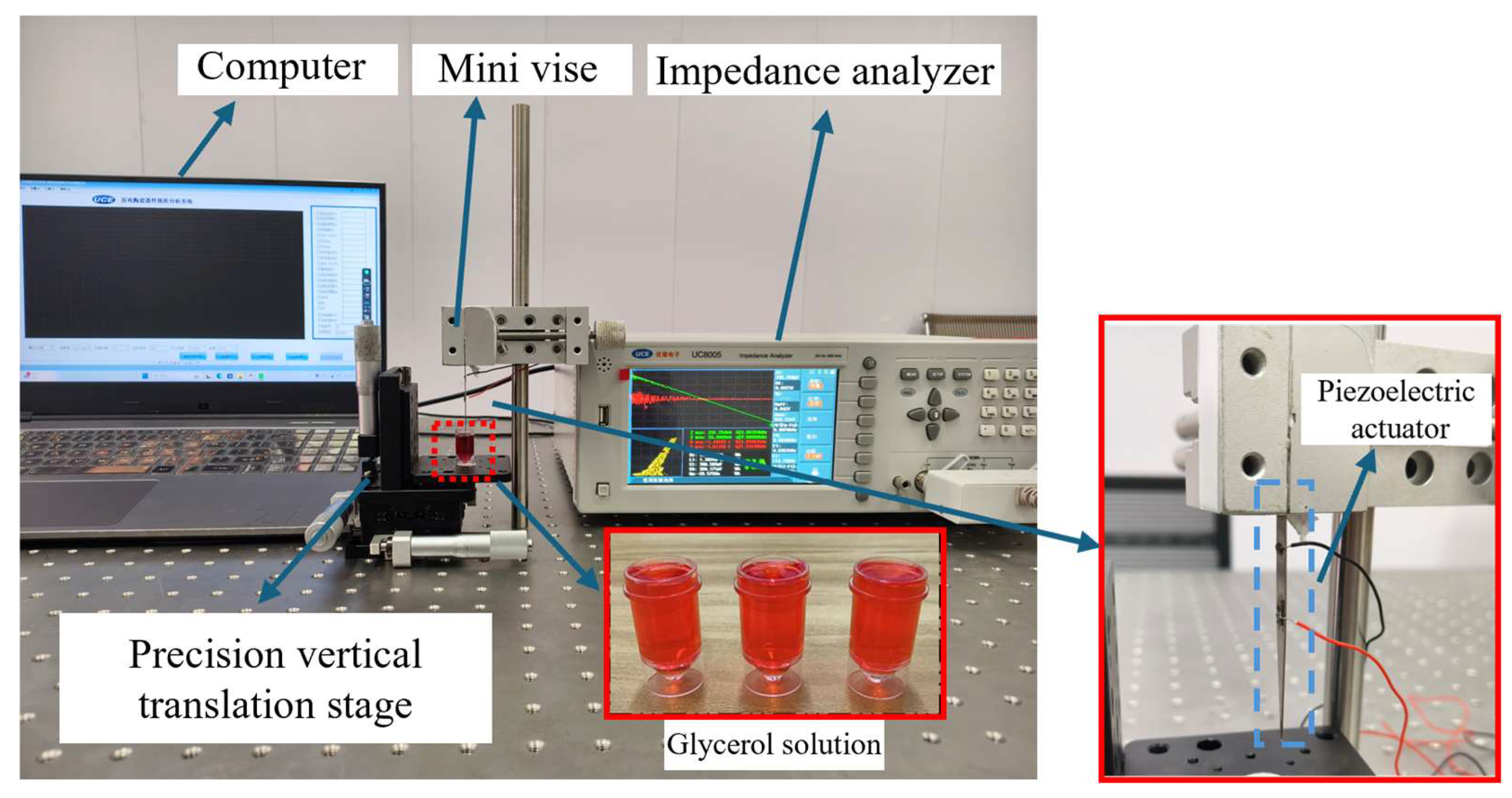
4. Test and Discussion
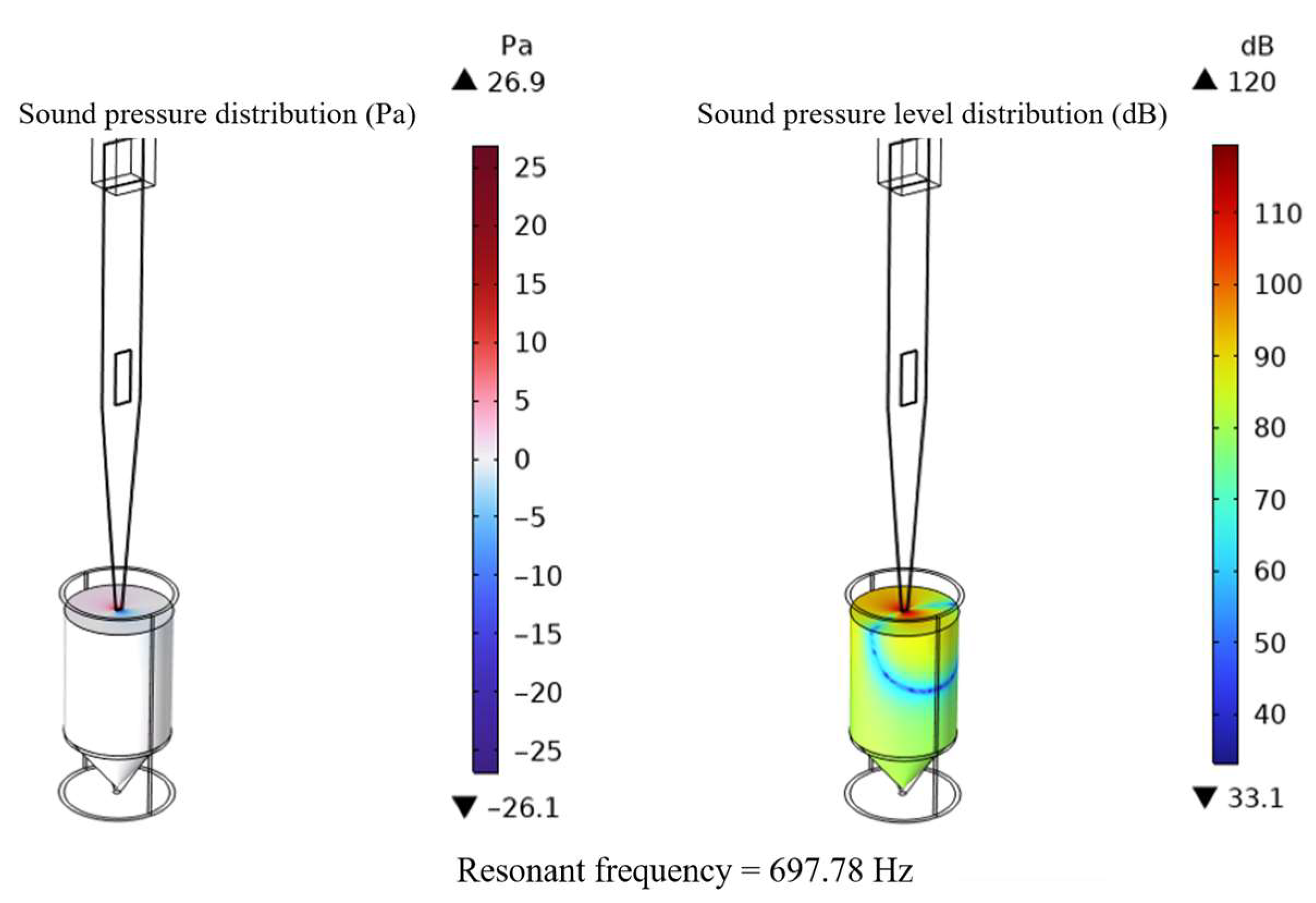
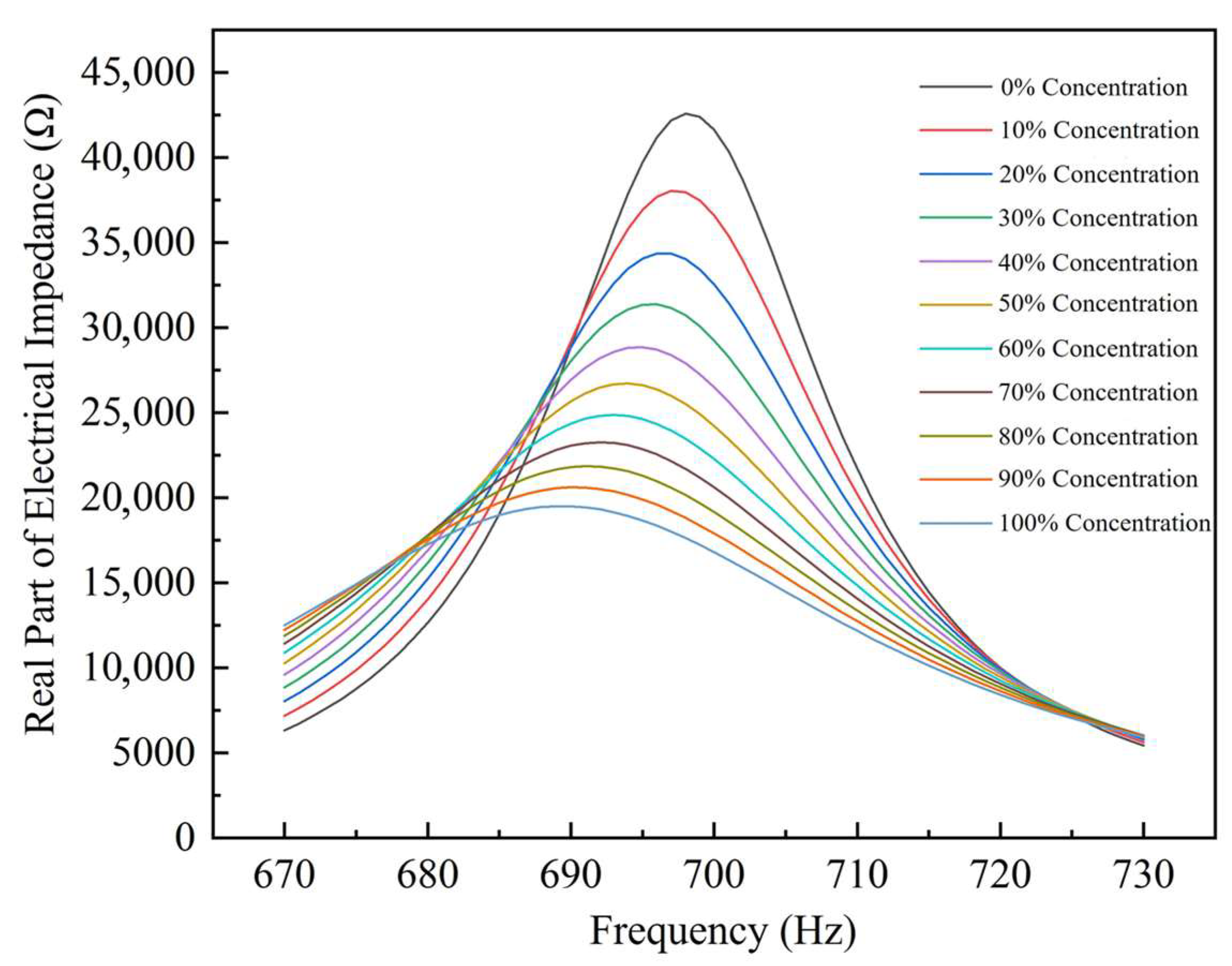
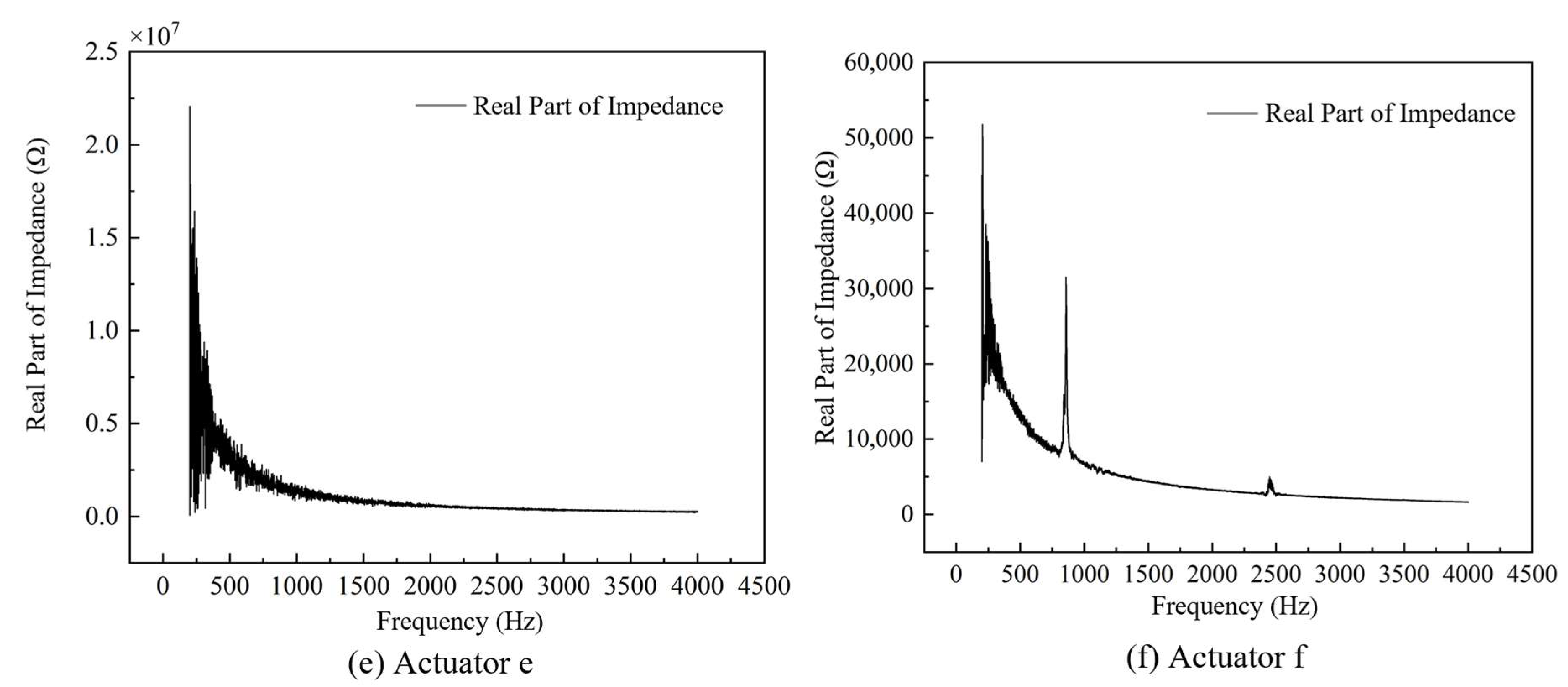
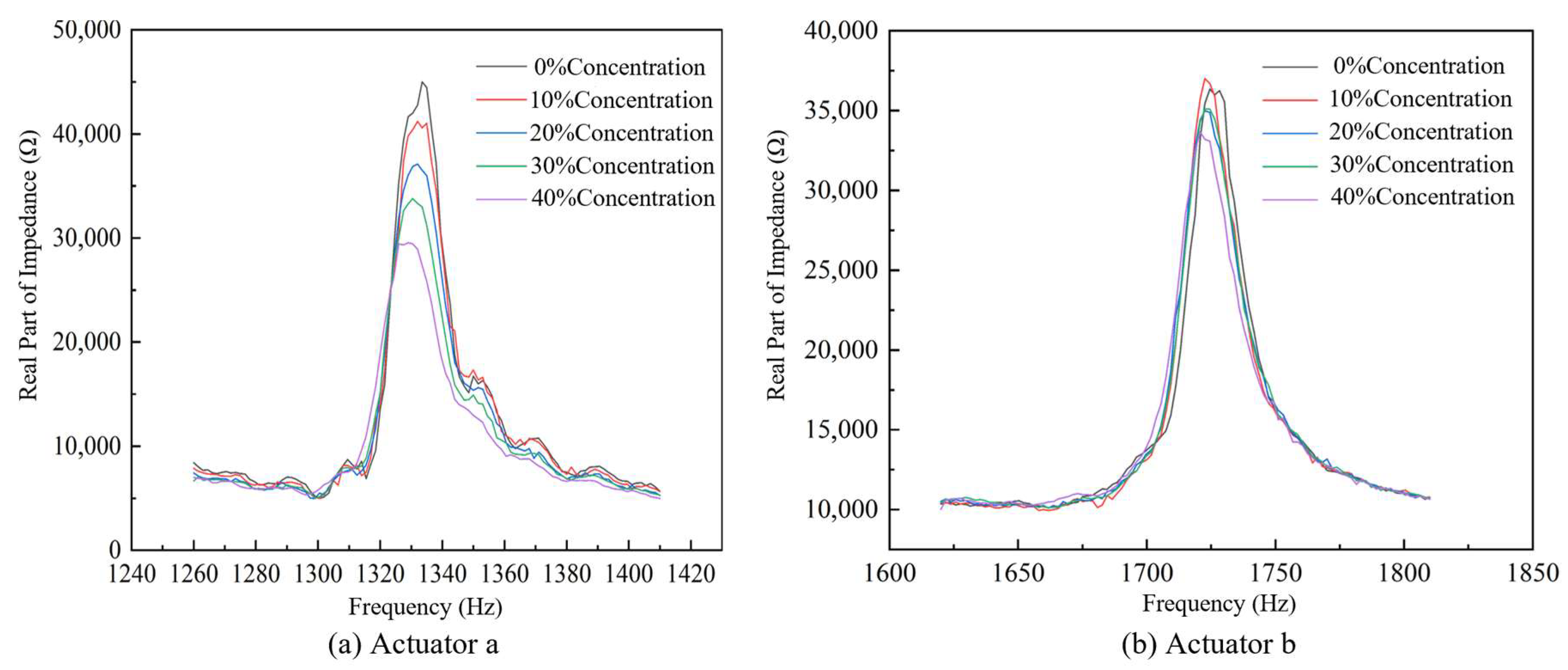
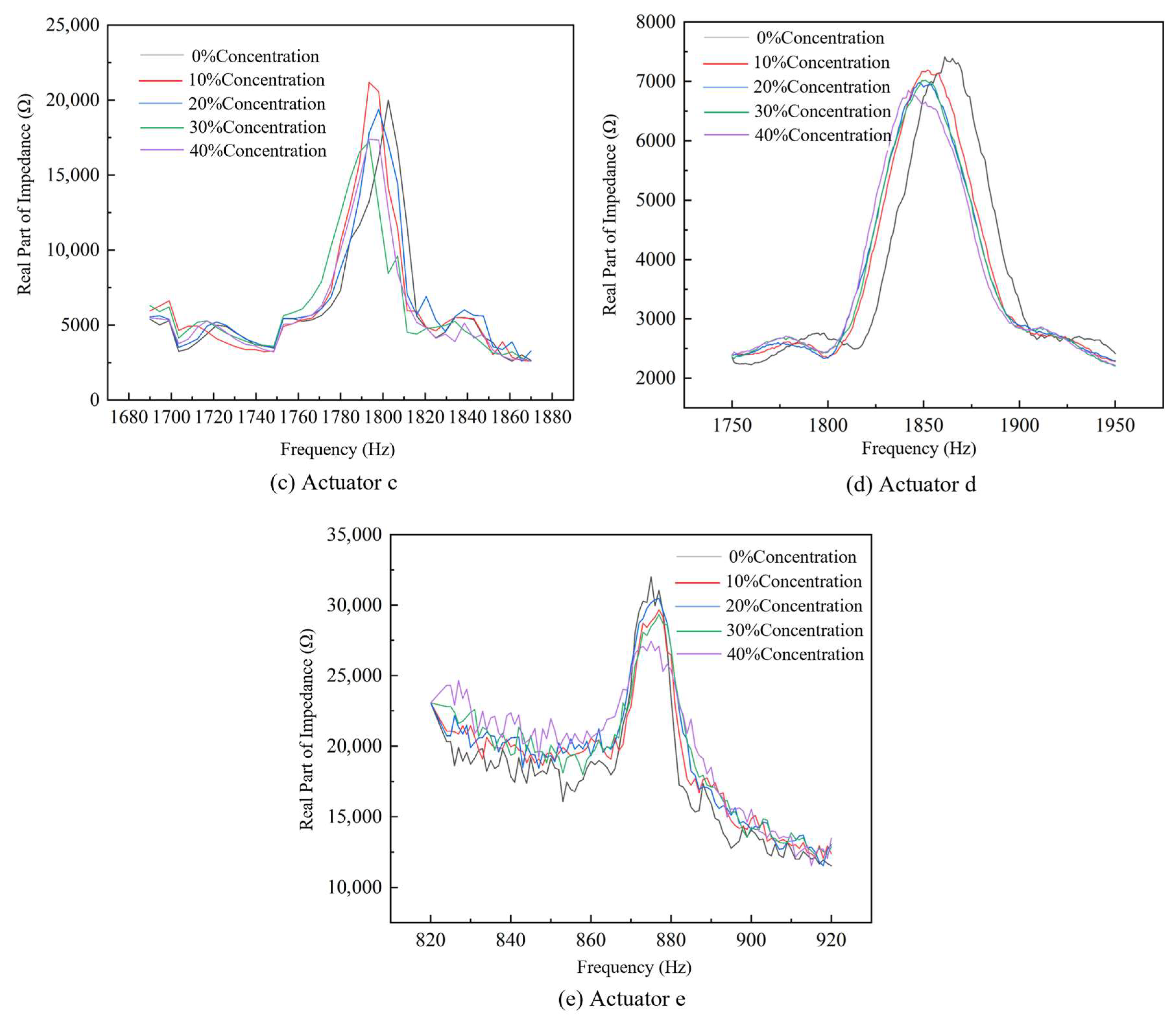
4.1. Impedance Performance Test with the Optimal Structural Parameters
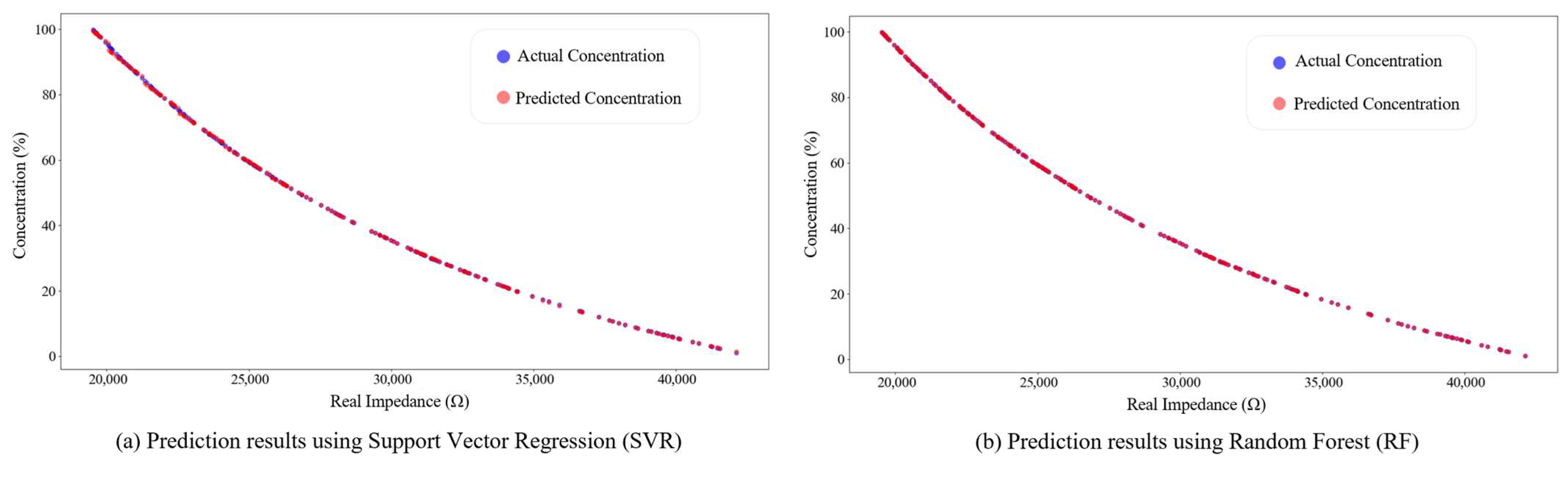
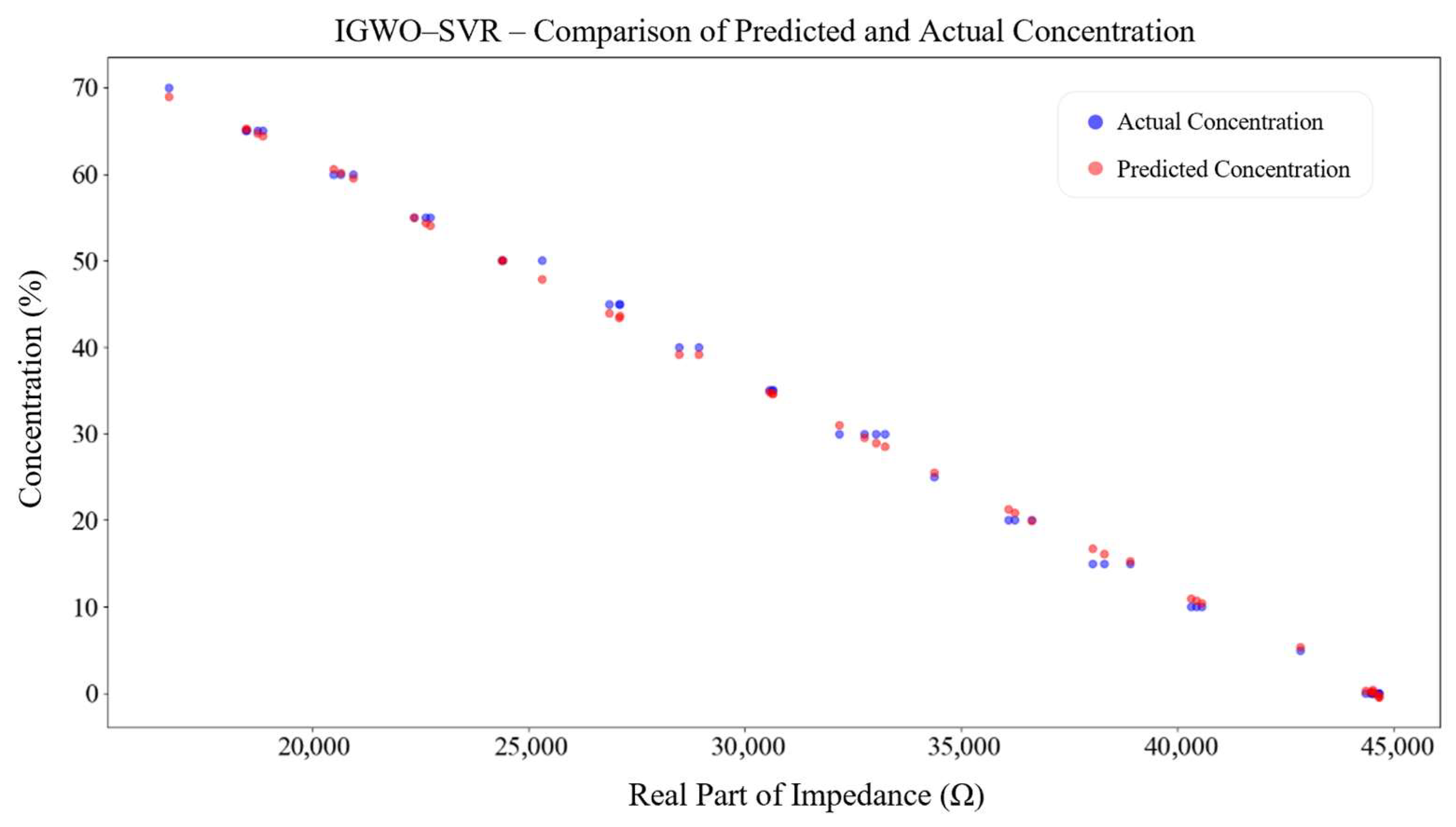
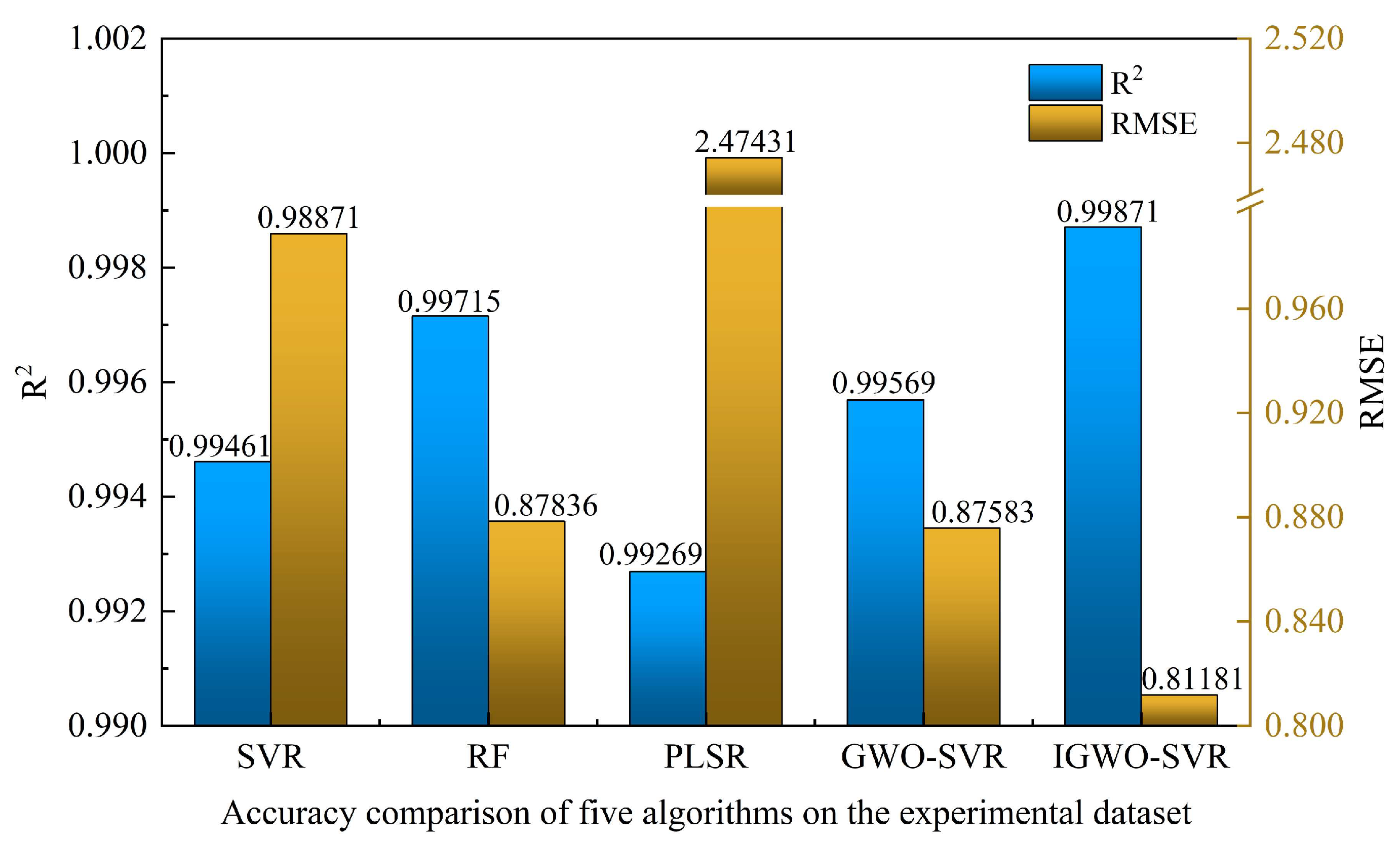
4.2. Performance Validation of the IGWO–SVR Detection Algorithm
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The optimal geometry of the conical actuator is as follows: width 5 mm, thickness 1 mm, length 70 mm, and aperture 2 mm; piezoelectric patch length 8 mm, width 2 mm, and thickness 0.5 mm. The optimized actuator first exhibits a natural frequency of 697.78 Hz, a 42% increase in tip amplitude (2.7322 × 10−5 mm), and an output energy density of 3.3726 × 10−2 W/mm3. The coupled acoustic–solid model further verifies strong tip–fluid interaction, with a sound pressure level of 120 dB.
- (2)
- An IGWO–SVR detection model was proposed. On 1001 simulated samples, the model achieved an R2 of 0.99999, with RMSE values of 0.06213 for training and 0.04183 for testing, outperforming conventional SVR and RF models. Experimental validation on 15 glycerol solutions reported an R2 of 0.99871 and an RMSE of 0.81181, with an average relative error of 0.12815%. The measured real-impedance peak values decreased from 42,587.36 Ω to 19,507.48 Ω. Therefore, the IGWO–SVR algorithm can accurately and in real time track the thrombolysis process, providing reliable technical support for dynamic clinical monitoring and decision-making.
- (3)
- In future studies, incorporating the viscoelastic variations in blood and thrombus under non-Newtonian flow conditions will enable a more realistic simulation of the mechanical behaviour during thrombus dissolution. In addition, the optimized actuator can be miniaturized through MEMS or laser micromachining technologies while maintaining resonance frequencies suitable for vascular thrombolysis. By integrating impedance sensing with microfluidic channels, real-time monitoring under physiological flow conditions can be achieved. Moreover, the Ti–6Al–4V substrate and parylene-coated PZT ensure excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, enabling safe operation in blood-contact environments.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SVR | Support Vector Machine Regression |
| GWO | Grey Wolf Optimization |
| IGWO | Improved Grey Wolf Optimization |
| RF | Random Forest |
| PLSR | Partial Least Squares Regression |
References
- Ferrari, A.J.; Santomauro, D.F.; Aali, A.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd ElHafeez, S.; Abdelmasseh, M.; Abd-Elsalam, S.; Abdollahi, A.; et al. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2133–2161. [Google Scholar]
- Naghavi, M.; Ong, K.L.; Aali, A.; Ababneh, H.S.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasgholizadeh, R.; Abbasian, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbastabar, H.; et al. Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2100–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Fang, B.; Yu, X.; Li, Z. Interpretation of 2018 guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke. Zhong Hua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 2018, 30, 289–295. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.S.; Zhao, X.Q. Interpretation of “Chinese Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke 2023”. Chin. J. Stroke 2024, 19, 956–961. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, G.Z. Interpretation of the Guidelines for Endovascular Interventional Treatment of Ischemic Cerebrovascular Diseases in Chin. In Proceedings of the 2011 Zhejiang Provincial Neurology Academic Conference, Lishui, China, 27 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Evans, C.E. The stimulation of thrombosis by hypoxia. Thromb. Res. 2019, 181, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskam, J.; Hugues, J. The mechanism of arterial thrombus formation. Arch. Des Mal. Du Coeur Et Des Vaiss. 1954, 47, 545–556. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.H.; Lee, J.S.; Park, S.; Ko, Y.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, K.B.; Lee, J.; Kang, K.; Park, J.; Choi, J.C.; et al. Safety and efficacy of intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator administered in the 3- to 4.5-hour window in korea. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2014, 23, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dachs, R.J.; Burton, J.H.; Joslin, J. A user’s guide to the NINDS rt-PA stroke trial database. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.Q.; Shan, W.Y.; Liu, L.; Fu, X.C.; Liu, P.; Hu, Y.Z. Predictors of functional outcome and hemorrhagic complications in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis-a retrospective analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 55, 893–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Luo, G.Q.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Z.Y. Hemorrhagic risk factors after rt-PA thrombolysis in acute cerebral infarction. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 5542–5551. [Google Scholar]
- Son, S.; Choi, D.S.; Oh, M.K.; Hong, J.; Kim, S.; Kang, H.; Park, K.; Choi, N.; Kwon, O.; Lim, B.H. Comparison of solitaire thrombectomy and penumbra suction thrombectomy in patients with acute ischemic stroke caused by basilar artery occlusion. J. Neurointerventional Surg. 2016, 8, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, S.; Furudate, R.; Kumagai, I.; Aoyagi, C.; Hirota, N.; Yamamoto, T. Use of a stent-retriever for treatment of iatrogenic vasospasm secondary to mechanical thrombectomy. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2024, 236, 108107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Rueda, A.; Vargas, A.; Pinana, C.; Chirife, O.; Werner, M.; Aja, L.; Remollo, S.; Tomasello, Y.A. Angioplasty with a stent retriever to treat vasospasm secondary to subarachnoid hemorrhage due to an aneurysm: A multicenter study of safety and efficacy. Radiologia 2022, 64, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, D.; Ishii, A.; Chihara, H.; Ikeda, H.; Miyamoto, S. Histological examination of vascular damage caused by stent retriever thrombectomy devices. J. Neurointerventional Surg. 2016, 8, 992–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehmer, G.J.; Grines, C.L.; Bakaeen, F.G.; Beasley, D.L.; Beckie, T.M.; Boyd, J.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Das, S.R.; Diekemper, R.L.; Frampton, J.; et al. 2023 AHA/ACC clinical performance and quality measures for coronary. J Am Coll Cardiol 2023, 82, 1131–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshekhlee, A.; Pandya, D.J.; English, J.; Zaidat, O.O.; Mueller, N.; Gupta, R.; Nogueira, R.G. Merci mechanical thrombectomy retriever for acute ischemic stroke therapy: Literature review. Neurology 2012, 79, S126–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Morita, M.; Watanabe, T.; Kato, S.; Suzuki, M. Study on in-vivo measurement of solubility for cerebral thrombus dissolution. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2007, 24, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Rong, B.; Wang, L.; Morita, M.; Deng, G.; Jiang, Y.; Qian, J. Analysis and structure optimization of scissor-type micro-stirrer with the most effective output performance for thrombus dissolution in interventional therapy. Actuators 2023, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, G.; Guo, Y.G.; Zhu, J.G.; Chen, X.M.; Xu, W.; Shao, K.R. Sequential subspace optimization method for electromagnetic devices design with orthogonal design technique. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 479–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, Y.M.; Hsieh, H.H. The use of the taguchi method with grey relational analysis to optimize the thin-film sputtering process with multiple quality characteristic in color filter manufacturing. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2009, 56, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.H.; Wang, L.G.; Wang, W.S. Multi-objective optimization in manufacturing engineering for slender pen rod injection molding quality based on grey correlation. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Mechanical Engineering, Industry and Manufacturing Engineering (MEIME 2013), Wuhan, China, 22–23 June 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Priyadarshini, M.; Pal, K. Grey-taguchi based optimizationof EDM process for titanium alloy. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Materials Processing and Characterzation (ICMPC), Hyderabad, India, 14–15 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ajoudanian, M.; Jiang, Z.; Morita, M.; Asme. Analysis and modeling of vibratable end-effector angle of catheter for thrombus dissolution. In Proceedings of the ASME Conference on Smart Materials Adaptive Structures and Intelligent Systems, Philadelphia, America, 28 September–1 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Morita, M.; Jiang, Z. Design of a novel scissoring micro-stirrer for blood clot dissolution. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2016, 248, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babatunde, H.A.; Collins, J.; Lukman, R.; Saxton, R.; Andersen, T.; Mcdougal, O.M. SVR chemometrics to quantify β-lactoglobulin and α-lactalbumin in milk using MIR. Foods 2024, 13, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.Q.; Tang, X.M.; Hu, J.Y.; Ma, Y.; Yang, J.B.; Liu, F.Q.; Yi, X.F.; Liu, Z.Q.; Song, L.J.; Zheng, A.M.; et al. Synergy of pore size and silanols in an -SVR-type zeolite for efficient dynamic benzene/cyclohexane separation. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Fu, X.; Li, H.; Hu, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, L. A method based on improved ant colony algorithm feature selection combined with GWO-SVR model for predicting chlorophyll-a concentration in wuliangsu lake. Water Sci. Technol. A J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2024, 89, 20–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saraoglu, H.M.; Koçan, M. A study on non-invasive detection of blood glucose concentration from human palm perspiration by using artificial neural networks. Expert Syst. 2010, 27, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Cui, J.H.; Luo, D.; Murray, J.; Chen, X.Y.; Hulck, S.; Tripp, R.A.; Zhao, Y.P. Rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 variants using an angiotensin-converting enzyme 2-based surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy sensor enhanced by CoVari deep learning algorithms. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 3158–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, Z.K.; Guo, B.Y.; Zu, J.X.; Zheng, W.Q.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.T. Construction of an ECL-DPV dual model biosensor for dopamine detection based on PSO-ANN algorithm. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 7463–7472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.G.; Jiao, T.H.; Adade, S.; Wang, Z.; Wu, X.X.; Li, H.H.; Chen, Q.S. Based on vis-NIR combined with ANN for on-line detection of bacterial concentration during kombucha fermentation. Food Biosci. 2024, 60, 104346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ren, H.H.; Huang, G.Y.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Hu, C.Z. Predicting blood pressure from physiological index data using the SVR algorithm. BMC Bioinform. 2019, 20, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yan, Z.X.; Zhang, L.T. A comparative study of 11 non-linear regression models highlighting autoencoder, DBN, and SVR, enhanced by SHAP importance analysis in soybean branching prediction. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Liu, D.; Zheng, J.; Tong, J.; Ye, X. Optimization on main steam pressure of a steam turbine under low loads based on IGWO-SVM. J. Chin. Soc. Power Eng. 2024, 44, 1042–1050. [Google Scholar]
- Pao, Y.; Wu, Y.; He, Y.; Ge, X. A new AHP integrated with orthogonal design. Syst. Eng.-Theory Pract. 2005, 25, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Li, W.; Chen, G.; Huang, R. A method of nearly orthogonal experimental design. J. Air Force Eng. University. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2010, 11, 84–88. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Fu, Q.; Sun, Y.; Feng, Y. Grey relational analysis model based on weighted entropy and its application. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2006, 17, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.L.; Fan, R.H.; Chen, X.Y.; Chen, H. Differential evolution with grey wolf adapting optimizer for multi-pid control optimizer. In Proceedings of the 2023 35th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Yichang, China, 20–22 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, L. Mimicking blood rheology for more accurate modeling in benchtop research. Pegasus Rev. UCF Undergrad. Res. J. 2020, 12, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Sadek, S.H.; Rubio, M.; Lima, R.; Vega, E.J. Blood particulate analogue fluids: A review. Materials 2021, 14, 2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Materials | Density (×103 kg/m3) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Elastic Coefficient (×1010 Pa) | Piezoelectric Stress Coefficient (C/m2) | Relative Dielectric Constant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 304 stainless steel | 7.93 | 194,020 | 0.3 | / | / | / |
| PZT-5H | 7.5 | / | / | |||
| Mode | Frequency (Hz) | Amplitude (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1st | 699.8 | 1.8 × 10−5 |
| 2nd | 1698.9 | 1.5 × 10−5 |
| 3rd | 2085.1 | 2.5 × 10−6 |
| Factor | Actuator Width /mm | Actuator Thickness /mm | Actuator Length /mm | Aperture Size /mm | Ceramic Length /mm | Ceramic Width /mm | Ceramic Thickness /mm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | ||||||||
| 1 | 5.00 | 0.50 | 60 | 0 | 6 | 1.50 | 0.10 | |
| 2 | 6.50 | 0.75 | 65 | 1 | 7 | 1.75 | 0.30 | |
| 3 | 8.00 | 1.00 | 70 | 2 | 8 | 2.00 | 0.50 | |
| Sequence | /mm | /mm | /mm | /mm | /mm | /mm | /mm | /mm | /W·mm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5 | 0.5 | 60 | 0 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.1 | 2.4 × 10−5 | 7.3 × 10−5 |
| 2 | 5 | 0.75 | 65 | 1 | 7 | 1.75 | 0.3 | 8.4 × 10−5 | 3.8 × 10−3 |
| 3 | 5 | 1 | 70 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 0.5 | 2.7 × 10−5 | 3.3 × 10−2 |
| 4 | 6.5 | 0.5 | 60 | 1 | 7 | 2 | 0.5 | 1.5 × 10−4 | 8.3 × 10−4 |
| 5 | 6.5 | 0.75 | 65 | 2 | 8 | 1.5 | 0.1 | 9.8 × 10−6 | 7.5 × 10−5 |
| 6 | 6.5 | 1 | 70 | 0 | 6 | 1.75 | 0.3 | 1.6 × 10−4 | 1.5 × 10−3 |
| 7 | 8 | 0.5 | 65 | 0 | 8 | 1.75 | 0.5 | 1.1 × 10−5 | 1.6 × 10−4 |
| 8 | 8 | 0.75 | 70 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 0.1 | 5.3 × 10−5 | 1.9 × 10−5 |
| 9 | 8 | 1 | 60 | 2 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 4.2 × 10−4 | 7.8 × 10−4 |
| 10 | 5 | 0.5 | 70 | 2 | 7 | 1.75 | 0.1 | 4.3 × 10−5 | 0.5 × 10−4 |
| 11 | 5 | 0.75 | 60 | 0 | 8 | 2 | 0.3 | 2.5 × 10−4 | 9.4 × 10−3 |
| 12 | 5 | 1 | 65 | 1 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 5.2 × 10−5 | 2.0 × 10−2 |
| 13 | 6.5 | 0.5 | 65 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 0.3 | 8.4 × 10−7 | 1.5 × 10−4 |
| 14 | 6.5 | 0.75 | 70 | 0 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 9.0 × 10−5 | 1.2 × 10−3 |
| 15 | 6.5 | 1 | 60 | 1 | 8 | 1.75 | 0.1 | 1.9 × 10−4 | 5.2 × 10−4 |
| 16 | 8 | 0.5 | 70 | 1 | 8 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 3.7 × 10−5 | 2.9 × 10−5 |
| 17 | 8 | 0.75 | 60 | 2 | 6 | 1.75 | 0.5 | 4.6 × 10−4 | 7.2 × 10−4 |
| 18 | 8 | 1 | 65 | 0 | 7 | 2 | 0.1 | 5.7 × 10−5 | 1.2 × 10−4 |
| Sequence | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6.24 | 6.03 |
| 2 | 6.78 | 6.51 |
| 3 | 6.27 | 9.54 |
| 4 | 7.35 | 6.12 |
| 5 | 6.11 | 6.03 |
| 6 | 7.43 | 6.21 |
| 7 | 6.11 | 6.04 |
| 8 | 6.50 | 6.02 |
| 9 | 9.34 | 6.12 |
| 10 | 6.41 | 6.02 |
| 11 | 8.14 | 7.16 |
| 12 | 6.49 | 8.29 |
| 13 | 6.02 | 6.04 |
| 14 | 6.83 | 6.17 |
| 15 | 7.64 | 6.09 |
| 16 | 6.36 | 6.02 |
| 17 | 9.54 | 6.11 |
| 18 | 6.54 | 6.03 |
| Evaluation Indicator | Comentropy | Entropy Weight |
|---|---|---|
| Tip Displacement Amplitude | 0.9761 | 0.5003 |
| Tip Output Energy | 0.9794 | 0.4997 |
| Test Number | Tip Lateral Displacement | Tip Output Energy | Grey Relational Grade | Rank | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.0514 | 6.241 | 0.3452 | 2.0016 | 6.0275 | 0.3336 | 0.3394 | 15 |
| 2 | 2.1821 | 6.7775 | 0.3794 | 2.1149 | 6.5058 | 0.3610 | 0.3702 | 9 |
| 3 | 2.0577 | 6.2676 | 0.3467 | 3.0000 | 9.5424 | 1.0000 | 0.6734 | 1 |
| 4 | 2.3297 | 7.346 | 0.4272 | 2.0241 | 6.1246 | 0.3388 | 0.383 | 8 |
| 5 | 2.0197 | 6.1057 | 0.3378 | 2.0017 | 6.028 | 0.3337 | 0.3358 | 17 |
| 6 | 2.3523 | 7.4299 | 0.4357 | 2.0431 | 6.2058 | 0.3432 | 0.3893 | 7 |
| 7 | 2.0217 | 6.1143 | 0.3382 | 20,043 | 60,393 | 0.3343 | 0.3362 | 16 |
| 8 | 2.1138 | 6.5013 | 0.3607 | 2.0000 | 6.0206 | 0.3333 | 0.3470 | 12 |
| 9 | 2.9322 | 9 3439 | 0.8806 | 2.0228 | 6.1191 | 0.3385 | 0.6096 | 3 |
| 10 | 2.0925 | 6.4133 | 0.3552 | 2.001 | 6.0249 | 0.3336 | 0.3444 | 13 |
| 11 | 2.5522 | 8.1383 | 0.5275 | 2.2795 | 71,568 | 0.4097 | 0.4684 | 4 |
| 12 | 2.1108 | 6.4889 | 0.3599 | 2.5985 | 8.2945 | 0.5546 | 0.4571 | 5 |
| 13 | 2.0000 | 6.0206 | 0.3333 | 2.0037 | 6.0367 | 0.3342 | 0.3337 | 18 |
| 14 | 2.1946 | 6.8271 | 0.383 | 2.0346 | 6.1696 | 0.3412 | 0.3621 | 10 |
| 15 | 2.4093 | 7.6378 | 0.4584 | 2.015 | 6.0855 | 0.3367 | 0.3976 | 6 |
| 16 | 2.0798 | 6.3604 | 0.3521 | 2.0003 | 6.0219 | 0.3334 | 0.3428 | 14 |
| 17 | 3.0000 | 9.5424 | 1.0000 | 2.0207 | 6.1100 | 0.3380 | 0.6691 | 2 |
| 18 | 2.1230 | 6.5390 | 0.3631 | 2.0029 | 6.0331 | 0.3340 | 0.3484 | 11 |
| Item | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.4421 | 0.3466 | 0.4778 | 0.3740 | 0.4226 | 0.4078 | 0.3521 | |
| 0.3669 | 0.4254 | 0.3636 | 0.3829 | 0.4029 | 0.4178 | 0.4190 | |
| 0.4422 | 0.4792 | 0.4098 | 0.4943 | 0.4257 | 0.4256 | 0.4802 | |
| Range | 0.0753 | 0.1326 | 0.1142 | 0.1203 | 0.0228 | 0.0178 | 0.1281 |
| Function | Function Expression | Dimension | Hunting Zone | Least Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| f1 | 30 | [−100,100] | 0 | |
| f2 | 30 | [−10,10] | 0 | |
| f3 | 30 | [−100,100] | 0 | |
| f4 | 30 | [−100,100] | 0 | |
| f5 | 30 | [−5.12,5.12] | 0 | |
| f6 | 30 | [−50,50] | 0 |
| Statistical Magnitude | Algorithm | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average value | GA | 1.61 × 102 | 3.52 × 10 | 1.11 × 104 | 3.30 × 10 | 5.27 × 102 | 1.48 |
| PSO | 3.29 × 10−5 | 4.82 × 10−2 | 6.88 × 10 | 1.15 | 6.39 × 10 | 1.98 × 10−2 | |
| GWO | 2.02 × 10−27 | 1.40 × 10−15 | 2.55 × 10−4 | 7.12 × 10−7 | 7.36 | 2.63 × 10−3 | |
| HPA | 0 | 1.14 × 10−222 | 5.91 × 104 | 5.19 × 10 | 2.18 × 104 | 6.15 | |
| IGWO | 0 | 1.06 × 10−251 | 0 | 2.25 × 10−243 | 0 | 0 | |
| Standard deviation | GA | 5.46 × 10 | 7.79 | 2.73 × 103 | 5.65 | 1.10 × 102 | 1.24 × 10−1 |
| PSO | 5.37 × 10−5 | 4.79 × 102 | 3.21 × 10 | 2.70 × 10−1 | 1.90 × 10 | 2.13 × 10−2 | |
| GWO | 3.25 × 10−27 | 1.29 × 10−15 | 1.12 × 10−3 | 7.50 × 10−7 | 4.52 | 6.99 × 10−3 | |
| HPA | 0 | 0 | 5.74 × 104 | 4.78 | 3.55 × 103 | 1.10 | |
| IGWO | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Region | Boundary Name | Physical Type | Boundary Condition Expression | Physical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bottom of actuator | Fixed constraint | Structural mechanics | u = v = w = 0 | Simulated fixed support |
| Piezoelectric crystal surface | Electrode excitation | Electric field | Drive voltage excitation | |
| Contact surface between actuator and liquid | Sound–solid coupling | Coupling | continuous | Pressure and velocity matching |
| Upper surface of liquid | Free surface | Sound field | P = 0 | Simulated liquid surface |
| Side wall/bottom of liquid | Rigid boundary | Sound field | Simulated container wall | |
| Outer boundary of liquid | Absorbing boundary | Sound field | Avoid sound reflection |
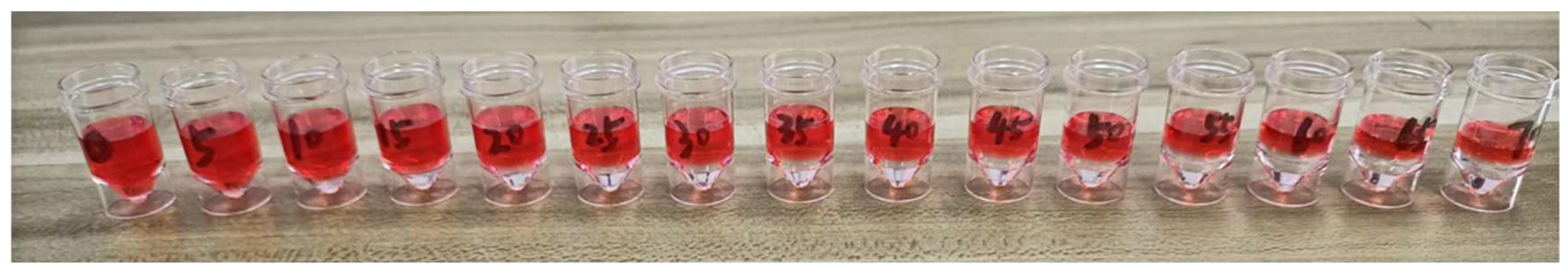
| Concentration of Thrombolytic Solution (%) | Response Frequency (Hz) | ) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 698 | 42,587.3641 |
| 22 | 696 | 42,541.8617 |
| 50 | 694 | 42,496.3593 |
| 70 | 692 | 42,450.8569 |
| … | … | … |
| 100 | 689 | 19,507.4789 |
| Detection Algorithm | Training Set | Testing Set | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | |
| SVR | 0.99989 | 0.29871 | 0.99989 | 0.29709 |
| RF | 0.99999 | 0.07836 | 0.99999 | 0.06083 |
| PLSR | 0.99269 | 2.47431 | 0.99362 | 2.29031 |
| GWO-SVR | 0.99997 | 0.07583 | 0.99998 | 0.18759 |
| IGWO-SVR | 0.99999 | 0.06213 | 0.99999 | 0.04183 |
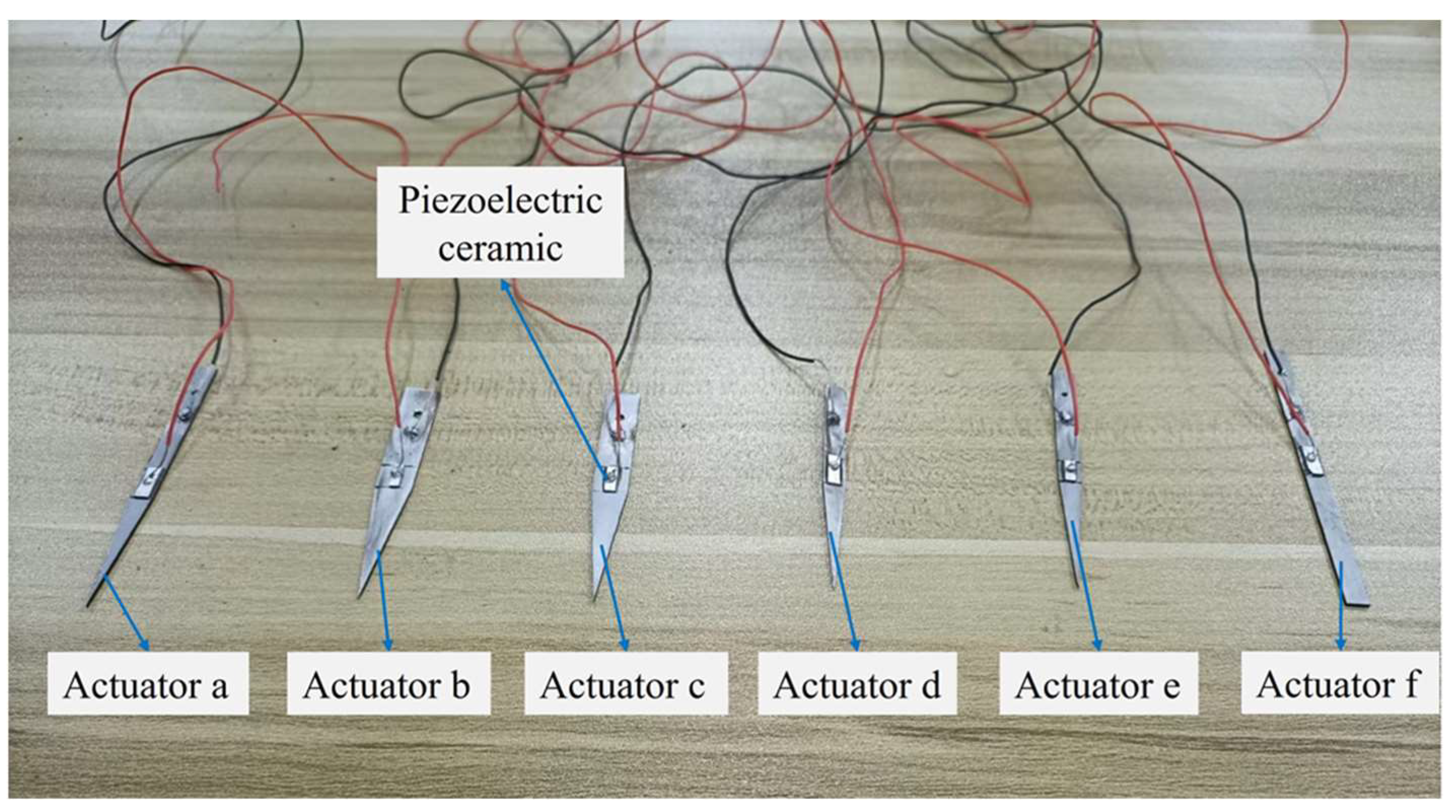
| Actuator | Actuator Body Structure | Piezoelectric Ceramic Structure | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Width (mm) | Thickness (mm) | Length (mm) | Aperture Size (mm) | Length (mm) | Width (mm) | Thickness (mm) | |
| Actuator a | 5 | 1 | 70 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 0.5 |
| Actuator b | 8 | 0.75 | 60 | 2 | 6 | 1.75 | 0.5 |
| Actuator c | 8 | 1 | 60 | 2 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 |
| Actuator d | 5 | 0.75 | 60 | 0 | 8 | 2 | 0.3 |
| Actuator e | 5 | 1 | 65 | 1 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.5 |
| Actuator f | 5 | 1 | 70 | 2 | 8 | 2 | 0.5 |
| Algorithm | Mean Error (%) | Standard Deviation (%) | Min–Max Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SVR | 1.45 | 0.12 | 1.21–1.67 |
| RF | 1.18 | 0.10 | 0.95–1.33 |
| PLSR | 0.98 | 0.08 | 0.82–1.15 |
| GWO-SVR | 0.87 | 0.06 | 0.74–0.96 |
| IGWO-SVR | 0.72 | 0.04 | 0.68–0.80 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Rui, B.; Yang, P.; Deng, G.; Qin, H.; Lei, J. Detection Algorithm of Thrombolytic Solution Concentration with an Optimized Conical Thrombolytic Actuator for Interventional Therapy. Actuators 2025, 14, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14110549
Yang J, Shen Y, Jiang Y, Rui B, Yang P, Deng G, Qin H, Lei J. Detection Algorithm of Thrombolytic Solution Concentration with an Optimized Conical Thrombolytic Actuator for Interventional Therapy. Actuators. 2025; 14(11):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14110549
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jingjing, Yingken Shen, Yifan Jiang, Biyuan Rui, Pengqi Yang, Guifang Deng, Hao Qin, and Junjie Lei. 2025. "Detection Algorithm of Thrombolytic Solution Concentration with an Optimized Conical Thrombolytic Actuator for Interventional Therapy" Actuators 14, no. 11: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14110549
APA StyleYang, J., Shen, Y., Jiang, Y., Rui, B., Yang, P., Deng, G., Qin, H., & Lei, J. (2025). Detection Algorithm of Thrombolytic Solution Concentration with an Optimized Conical Thrombolytic Actuator for Interventional Therapy. Actuators, 14(11), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/act14110549






