Abstract
In this paper, the finite time speed regulation problem is investigated for a dual three-phase hybrid excitation synchronous machine (DTP-HESM) without a torque meter. The electromagnetic torque estimation required in the current coordinative strategy is obtained through the disturbance estimation technology. This method increases fault tolerance and reduces the cost as well as complexity of the DTP-HESM system. In contrast to the existing controllers in the speed loop, the non-singular terminal sliding mode control method is adopted to ensure the finite-time convergence of speed tracking in the whole speed region. To achieve better dynamic performance in the presence of lumped disturbances, including unknown load torque and unmodeled dynamics, the disturbance estimations are introduced into the sliding mode variable to establish a composite speed regulating controller. Simulations and experiments are carried out to validate the feasibility and effectiveness of the proposed control scheme.
1. Introduction
Considering energy reduction and environmental protection, electric vehicles driven by a permanent magnet synchronous machine (PMSM) have been developed with rapid speed [1,2]. To guarantee robust performance in facing the changing conditions of electric vehicles, such as starting, climbing, heavy loading, high-speed overtaking and cruising, the hybrid excitation synchronous machine (HESM) has received much research attention from both mechtronic and control communities [3]. Compared with the traditional PMSM, HESM with organic combinations of permanent magnetic potential and excitation magnetic potential is characterized by a larger loading capacity and wider speed regulation region [4,5].
Dual three-phase PMSM (DTP-PMSM) exhibits several advantages, e.g., strong control flexibility, a small burden on the inverter and great fault tolerance, and can be treated as a machine with two independent three-phase machines [6,7,8,9]. In this way, one of the dual three-phase windings is used as an armature winding, while the other is used as excitation winding. As a result, dual three-phase PMSM can alternatively be referred to as the dual three-phase hybrid excitation synchronous machine (DTP-HESM) and is suitable for the HESM control technique.
A reasonable current coordinative strategy (CCS) is fundamental to ensure the seamless switching operation of HESM [10,11]. The operating states of HESM are generally divided into a low-speed region (LSR) and high-speed region (HSR) for the coordination of the armature and excitation current. In [12], maximum torque control with d-axis current and flux-weakening control are adopted in LSR and HSR, respectively. The study shows a wide speed range under this CCS. In [13], minimum-copper-loss control, combining the copper loss equation with torque and voltage constraints, is established based on the Lagrange multiplier method for both LSR and HSR. Compared with the CCS in [12], the total copper loss significantly decreases. In addition, many CCSs are also investigated, such as maximum torque per ampere control [14], efficiency optimal control [15] and different types of flux-weakening control [16,17,18,19], etc. These algorithms have improved the control performance of HESM from different aspects.
Although HESM was originally designed to provide greater load capacity in LSR and higher speed in HSR, the speed tracking performance also needs to be guaranteed in practical applications. Due to the imperfections in machine design and manufacture, the nonlinearities of the inverter, magnetic circuit saturation, unmodeled dynamics, etc., the DTP-HESM system suffers from strong nonlinearities and multiple disturbances [20,21,22], which increases the difficulty of control design. The above works all utilize a PI regulator in the speed loop. It is reported that this method cannot achieve satisfactory disturbance rejection performance in dealing with fast time-varying disturbances. Moreover, it can only realize the regulation through a feedback measure [23]. Thus, the PI controller cannot guarantee satisfactory capability in the whole speed region.
Among many advanced control methods, sliding mode control (SMC) is a nonlinear control strategy with strong robustness against disturbances and uncertainties [24,25]. However, this superior method is rarely applied in the HESM system. In [26], the sliding mode controllers are adopted in the two independent -axis current loops, where the desired values are generated by the conventional speed-loop PI regulator. It is well known that multiple disturbances exist not only in the current loop but also in the speed loop, including the unknown load torque in the speed loop and the inverter nonlinearity in the current loop. Thus, the above control strategy cannot achieve satisfactory speed regulation performance. To obtain better disturbance rejection performance, a non-singular terminal SMC (NTSMC) method is proposed in [27], which can ensure the finite-time convergence of the system in the presence of lumped disturbances.
However, NTSMC suffers from a chattering problem due to a discontinuous control law with overlarge switching gain. An alternatively effective solution is to minimize switching gain while ensuring control performance. In [28], the system disturbances, which include friction and load torque, are estimated by a disturbance observer. The switching gain of the composite controller can be selected to be smaller when the disturbance estimation is compensated into NTSMC. Moreover, in many real applications of HESM, a high-precision torque meter is required to measure the accurate load torque, which greatly increases the cost and design difficulty of the system. The above unknown variable load torque can be considered as a slow time-varying disturbance, which could be estimated by the disturbance estimation technique.
Motivated by the above research works, in this paper, we focus on improving the dynamic performance of DTP-HESM under multiple disturbances based on torque sensorless CCS in the whole speed region. Firstly, a generalized proportional integral observer (GPIO) is developed to estimate the lumped disturbances, which is utilized in the CCS. Then, the NTSMC method is adopted as the speed loop controller. To improve the performance and robustness of the DTP-HESM system, the disturbance estimation is introduced into both the sliding model variable and sliding mode controller. Compared with the PI and NTSMC method, the proposed GPIO-based NTSMC control scheme (NTSMC+GPIO) on the DTP-HESM system achieves a better speed tracking performance. The main contributions of this paper are listed as follows.
- GPIO is designed to estimate the load torque online, avoiding the use of a traditional hardware sensor. This approach not only increases the fault tolerance but also reduces the cost and complexity of the DTP-HESM system.
- The speed regulation based on NTSMC+GPIO is proposed in the whole speed region, which improves the rapidity, accuracy and robustness to multiple disturbances.
- The general idea can also be applied for other CCSs of HESM, such as the minimum copper consumption distribution and the optimal efficiency distribution, etc.
The other parts of this paper are organized as follows. In Section 2, the mathematical model and current coordinative strategy of DTP-HESM are introduced. The main contribution of this paper, i.e., the design of a composite controller based on torque sensorless CCS, is proposed in Section 3. The comparative simulation and experimental results between PI and NTSMC+GPIO are presented in Section 4 and Section 5, respectively. Finally, a conclusion is presented in Section 6.
2. Dynamic Model and Current Coordinative Strategy
2.1. Mathematical Model
The diagram of the whole DTP-HESM control system is shown in Figure 1. As shown in Figure 1, one speed loop and four current loops are involved under the two-individual current control frame. The reference values of the -axis current loop are obtained through the designed CCS. Armature and excitation winding transform and inverter systems contain an inverse park transform, park transform, Clarke transform and SVPWM-driven inverters.
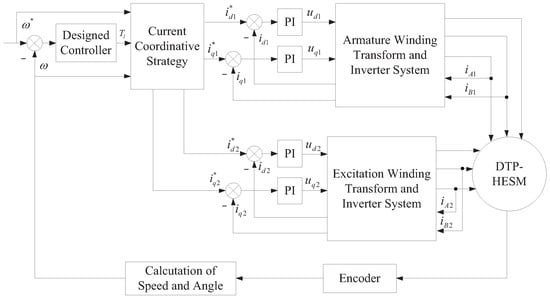
Figure 1.
The control diagram of the DTP-HESM system.
The ideal mathematical model of DTP-HESM in the rotating coordinate system under the two-individual current control frame is expressed as [8,9]
where is the mechanical angular velocity, is the electrical angular velocity and ; , , J, , and are the stator resistance, the number of motor pairs, inertia, load torque, rotor flux linkage and electromagnetic torque, respectively; The subscripts “1” and “2” represent the rotating dq coordinate systems of the two-individual current framework. and are -axis currents and voltages, respectively. and are the phase leakage inductance and mutual inductance, respectively. The electromagnetic torque is presented as with .
2.2. Current Coordinative Strategy
Generally, the low and high speed regions are divided according to the rated speed in the CCS of the DTP-HESM system. The operating region block diagram is presented in Figure 2. As shown in Figure 2, the areas I and II, which are below the rated speed , are the LSRs, and the areas III and IV are the HSRs [13,14,15,16,17,18].
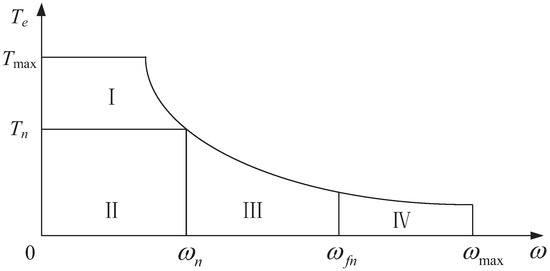
Figure 2.
Operating region block diagram.
The design of CCS in the LSR and HSR is inspired by [13]. -axis current references and are set to zero in the LSR. When the load torque (the rated load torque), DTP-HESM works in area II. The reference values of the armature and excitation current are given by
where is the electromagnetic torque estimation and . In practical application, the load torque is acquired by a high-precision torque meter.
When , DTP-HESM works in area I. In this case, reaches the rated current value , and continues to provide excess torque. The reference values of the armature and excitation current are presented as
If DTP-HESM runs in area III, which is above the rated speed, the speed cannot continue to rise due to the limits of the bus voltage and current. The flux weakening control strategy is adopted to enlarge the range of motor speed, which reverses or . Firstly, and is used for field weakening. According to [13], it yields
When the motor speed continues to increase and reaches area IV, reaches the negative rated current value . is used to weaken the field. It yields
3. Controller Design
In this section, a GPIO is firstly designed to estimate the lumped disturbance in DTP-HESM. Secondly, the composite NTSMC method, which is combined with disturbance estimation, is proposed. Then, a rigorous closed-loop stability analysis is presented.
3.1. Design of GPIO
The multiple disturbances existing in the DTP-HESM system are finally reflected in the speed loop, which can depicted as
where d is the lumped disturbance, including the nonlinearity of the inverter, magnetic circuit saturation, variable load torque and unmodeled dynamics. According to (6), a GPIO can be designed as [29]
where are the observer gains to be designed. is the estimation of the speed . are the estimation of the lumped disturbance and its derivatives.
3.2. Design of the Composite Controller
The Laplace transformation expression of the speed loop (6) and the -axis voltage PI regulator equation are expressed as
where and are the PI regulator parameters. Combining (8) and (9), one obtains
and it can be further obtained that
where
The inverse Laplace transform of (11) is presented as follows:
The derivative of speed can be realized by a differential in practice, but it can amplify the noise of the DTP-HESM system undoubtedly. Equation (13) can be further expressed as
The control-oriented model after simplification is written as
and according to (12), the actual control law is given by
Define the speed tracking error , where is the reference speed. With for in mind, the sliding surface is shown as follows:
where and . Combining with (6), . Differentiating the sliding surface , the composite NTSMC-based GPIO can be designed as follows:
where can be found in (1).
The designed controller is shown in Figure 3.
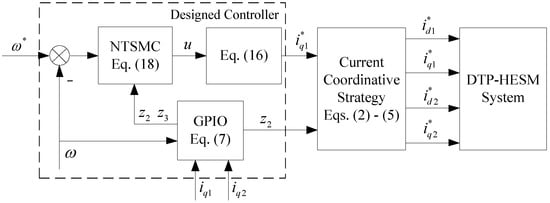
Figure 3.
Block diagram of the designed controller.
3.3. Stability Analysis
Assumption 1.
In the DTP-HESM system (6), the first n-order derivatives of the lumped disturbance d exist, and the n-order derivative satisfies .
Assumption 2.
There exists a positive constant such that , where and are the upper bounds of and , respectively.
Theorem 1.
Suppose that Assumptions 1 and 2 are satisfied for the DTP-HESM system. The speed tracking error e converges to zero in finite-time under the NTSMC+GPIO composite controller, on condition that the observer gains are properly selected and , respectively.
Proof of Theorem 1.
Firstly, the convergence of the disturbance estimation error by GPIO is proven. Here, the disturbance estimation error is defined as
The estimation error is defined as . Then, the estimation error system is obtained as
where and .
By choosing the appropriate parameter , is a Hurwitz matrix. The system (20) naturally satisfies the input-to-state stability. According to the input-to-state stability theorem [30], when Assumption 1 is satisfied, the estimation error of GPIO asymptotically converges to zero.
Then, the stability analysis of the composite controller is given. Choose the energy function as
Taking the derivative of V, one obtains
From (22), it can be proven that if , the speed tracking error reaches the sliding mode surface in finite time. After reaching the sliding mode surface, the dynamic is governed by
Remark 1.
Since the disturbance estimation error converges to zero asymptotically, the upper bound of is usually much smaller than the upper bound of . The chattering problem is effectively alleviated.
4. Number Tests Results
In this part, the speed regulation performance and CCS of the proposed NTSMC and NTSMC+GPIO method are verified by simulations. The PI method that exists in most results [13,14,15,16,17,18] is employed for comparison in the speed loop. In the comparative simulation, the four current loops adopt PI controllers with the same control parameters. The parameters of the DTP-HESM system are listed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Parameters of DTP-HESM system.
In the simulations, the disturbance observer gain is set as , and . = 2.8 and = 166 in four current loops. The control parameters in the speed loop are given as = 0.15 and = 0.3 for PI; = 1.5, = 1000, k = 14,000 for NTSMC; = 1.5, = 1000 and k = 12,000 for NTSMC+GPIO. As in the four areas shown in Figure 2, the speed reference and load torque change in step form are considered, which can be expressed as
Figure 4a–d are the system responses of , , , and , respectively. The performance index includes overshoot (OS), settling time (ST), speed drop (SD) and recovery time (RT) as the comparisons. The results are shown in Table 2. According to Figure 4a and Table 2, the PI method has a greater speed overshoot at each startup, more speed drops and longer recovery times at each loading when compared to the NTSMC and NTSMC+GPIO methods. This indicates that the speed chatting under NTSMC+GPIO is superior to NTSMC in areas I–IV. As shown in Figure 4c, the coordinative values of and in the LSR and HSR satisfy (2)–(5). The estimation of load torque and estimation error under DOB are shown in Figure 4d.
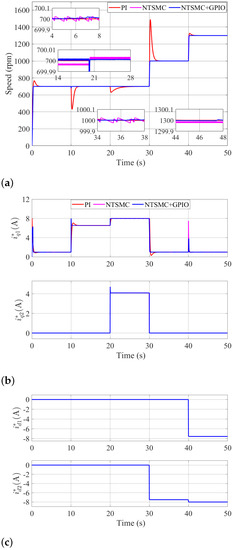
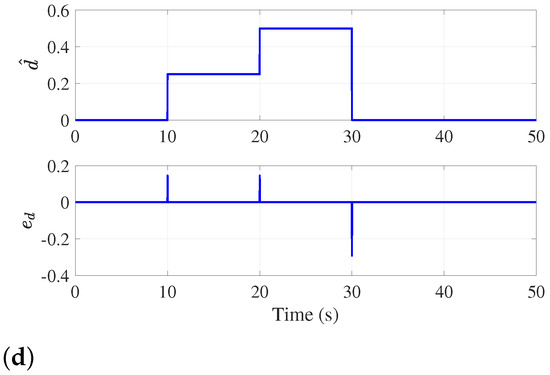
Figure 4.
System responses in the simulations: (a) speed, (b) q-axis current reference, (c) q-axis current reference, (d) disturbance estimation and estimation error.

Table 2.
Performance comparisons in the simulations.
5. Experiment Results and Discussion
In this part, the speed regulation performance and CCS of the proposed NTSMC+GPIO method are verified by experiments. The PI method is employed for comparison in the speed loop. As shown in Figure 5, the experimental system includes the real-time digital controller RTU-BOX 201, two sets of three-phase inverters with hall sensors and a drive circuit and switching power supply. Among them, a complete set of three-phase inverter drives, three-phase inverter bridges and acquisition circuits are integrated in RTI-INV 6030. The load of the DTP-HESM system is a magnetic power brake. An incremental encoder with 2048 lines is used to obtain the position and speed information of the motor.
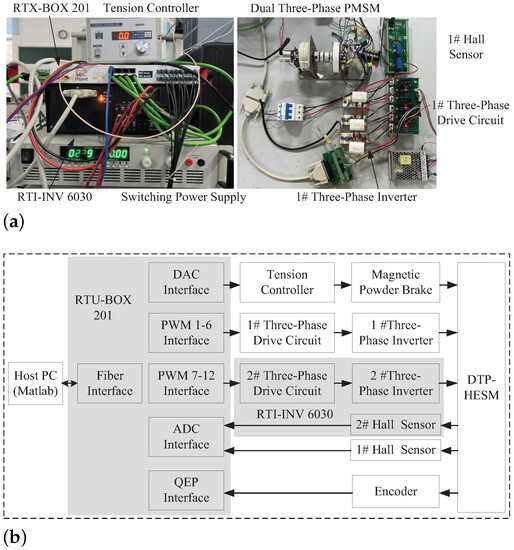
Figure 5.
Experimental system. (a) Setup; (b) configuration.
The control parameters are given as , and for GPIO (7); = 2.8, = 166 are four current loops; = 0.15 and = 3 for PI; = 1.5, = 1200, k = 12,000 for NTSMC+GPIO. For fair comparisons, the steady state errors of the PI and NTSMC+GPIO controllers are made close by tuning the the control parameters. The change of load torque and reference speed in the experiment are consistent with the simulation settings. The experimental results in the LSR and HSR are presented in the two subsections.
5.1. Results in the LSR
Figure 6a–c shows the system responses of , and in the LSR, respectively. In the performance index, OS, ST, SD, RT and root-mean-square error (RMSE) are used for comparisons under startup, first step load torque and second step load torque. The results are shown in Table 3.
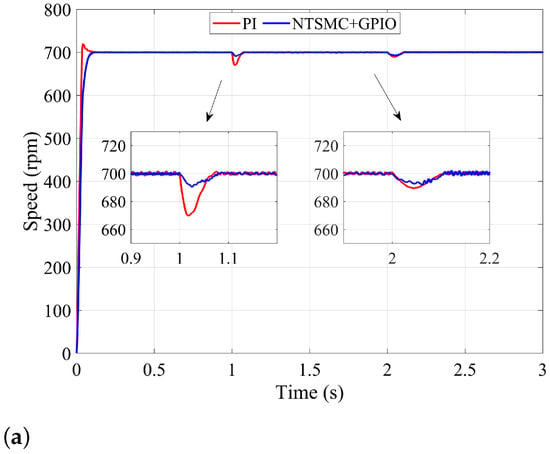
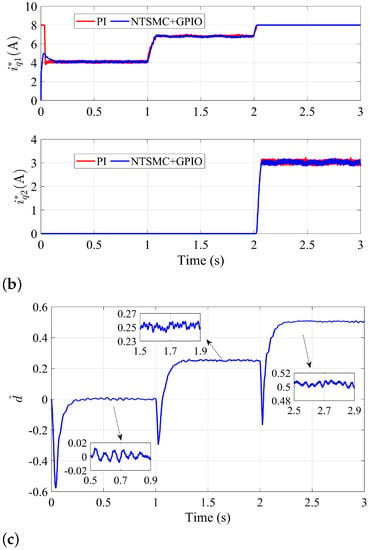
Figure 6.
System responses under NTSMC+GPIO and PI in the LSR: (a) speed, (b) q-axis current reference, (c) disturbance estimation.

Table 3.
Performance comparisons in the LSR.
As shown in Figure 6a and Table 3, the steady-state accuracies for the three cases are close. The speed curve under the NTSMC+GPIO controller has a longer ST, while the OS is almost non-existent at startup. When the load torque increases, the RT is similar, while the SD is less under the NTSMC+GPIO controller.
Figure 6b shows the response curves of and under NTSMC+GPIO and PI. In the LSR, depends on the electromagnetic torque estimation , which requires disturbance estimation information. As shown in Figure 6b, the coordinative values of and with different load torques satisfy (2) and (3). The estimation of load torque under DOB is shown in Figure 6c.
5.2. Results in the HSR
In this case, the parameters of NTSMC+GPIO and PI controllers in the HSR are selected to be the same as LSR. Figure 7a–c shows the system responses of , control law and in the HSR, respectively. The performance comparison under the first step speed-up and second step speed-up is shown in Table 4.
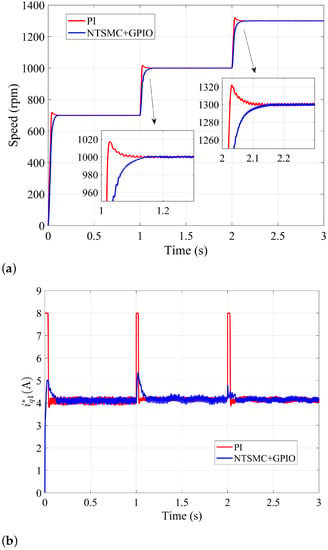
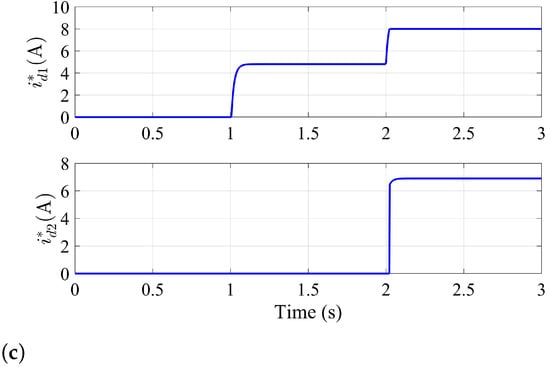
Figure 7.
System responses under NTSMC+GPIO and PI in the HSR: (a) speed, (b) control law, (c) d-axis current reference.

Table 4.
Performance comparisons in the HSR.
As shown in Figure 7a and Table 4, the speed curves under the PI controller have a short ST at each speed-up, while the OS of the NTSMC+GPIO method is smaller.
In the HSR, is used for field weakening firstly. is used to continue to weaken the magnetic field until reaches the limit value. The response curves of and are shown in Figure 7c.
Hence, the experimental results verify the effectiveness of the proposed NTSMC+GPIO method. The speed regulation based on torque sensorless CSS is realized, while maintaining satisfying speed tracking performance in the whole speed region.
6. Conclusions
The composite controller NTSMC+GPIO has been proposed in this study to handle the finite-time speed regulation problem of the DTP-HESM system based on torque sensorless CCS. Firstly, a generalized proportional integral observer (GPIO) has been developed to estimate the lumped disturbances, which is utilized in the CCS. Then, the NTSMC method has been adopted as the speed loop controller. To improve the performance and robustness of the DTP-HESM system, the disturbance estimation is introduced into both the sliding model variable and sliding mode controller. Compared with the conventional PI controller, NTSMC+GPIO has largely improved the performance of speed tracking and robustness against multiple sources of disturbances in the whole speed region. Moreover, the idea of obtaining load torque through disturbance observers instead of the precision torque meter equipment can also be used for other current coordinative strategies in the HESM systems, which is extended as a promising future research direction.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.D.; methodology, B.D.; formal analysis, B.D.; data curation, B.D. and Z.W.; writing—original draft preparation, B.D.; writing—review and editing, B.D. and Z.W.; supervision, B.D. and Z.W.; project administration, Z.W.; and funding acquisition, Z.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (22KJB110012).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yao, G.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, Y. Permanent magnet synchronous motor control based on phase current reconstruction. Electronics 2023, 12, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshandel, E.; Mahmoudi, A.; Kahourzade, S.; Soong, W. Efficiency maps of electrical machines: A tutorial review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Cai, S. Hybrid excited permanent magnet machines for electric and hybrid electric vehicles. CES Trans. Electr. Mach. Syst. 2019, 64, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Gao, Y.; Nakamura, T. High fault-tolerance dual-rotor synchronous machine with hybrid excitation field generated by halbach permanent magnets and high temperature superconducting magnets. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2023, 33, 5202105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Niu, S. Overview of flux-controllable machines: Electrically excited machines, hybrid excited machines and memory machines. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Z. A hybrid direct torque control scheme for dual three-phase PMSM drives with improved operation performance. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 1622–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Stone, D.; Foster, M. A simple sensorless position error correction method for dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karttunen, J.; Kallio, S.; Peltoniemi, P.; Silventoinen, P.; Pyrhonen, O. Dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous machine supplied by two independent voltage source inverters. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Power Electronics Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion, Sorrento, Italy, 20–22 June 2012; pp. 741–747. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Odavic, M. Comparison of two-individual current control and vector space decomposition control for dual three-phase PMSM. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 4483–4492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; El-Refaie, A.; Demerdash, N. Flux-switching permanent magnet machines: A review of opportunities and challenges-part II: Design aspects, control and emerging trends. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Fan, Y.; Chen, J.; Lei, Y. Flux control of consequent-pole hybrid excitation motors in constant power region to achieve both high efficiency and fast convergence speed. J. Power Electron. 2022, 2, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tian, B.; Wang, W. Investigation and implementation of a new hybrid excitation synchronous machine drive system. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, M.; Xu, D. Minimum-copper-loss control of hybrid excited axial field flux-switching machine. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2016, 10, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, C.; Gao, H. Optimization and performance improvement of a hybrid excitation synchronous machine with modular magnetic-shunting rotor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 4381–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druant, J.; Vansompel, H.; Belie, F.; Sergeant, P. Optimal control for a hybrid excited dual mechanical port electric machine. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothi, N.; Zhu, Z.; Ren, Y. Comparison of flux-weakening control strategies of novel hybrid-excited doubly salient synchronous machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 55, 3589–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Guo, X.; Qing, Y. Hybrid excitation synchronous machine adaptive speed region control and experimental verification. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2018, 58, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Li, S. Maximum ratio of torque to copper loss control for hybrid excited flux-switching machine in whole speed range. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 66, 932–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothi, N.; Zhu, Z. Control strategy for hybrid-excited switched-flux permanent magnet machines. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2015, 9, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Han, P.; Chen, X.; Chen, R.; Le, Z.; Lai, Z. Online dead-time compensation method for dual three phase PMSM based on adaptive notch filter. IET Power Electron. 2021, 14, 2452–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zheng, B.; Wang, G.; Yan, H.; Zou, J. Current harmonic suppression in dual three-phase permanent magnet synchronous machine with extended state observer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 12166–12180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karttunen, J.; Kallio, S.; Peltoniemi, P.; Silventoinen, P. Current harmonic compensation in dual three-phase PMSMs using a disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zuo, Y.; Sun, J.; Lee, C.; Wang, Y.; Ding, S. Modified nonlinear active disturbance rejection control for PMSM speed regulation with frequency domain analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 8126–8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Ding, S.; Yu, X. Composite super-twisting sliding mode control design for PMSM speed regulation problem based on a novel disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 2591–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, J.; Varquez, S.; Mazumder, S. Sliding mode control in power converters and drives: A review. IEEE CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2022, 9, 392–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fnaiech, M.; Betin, F.; Fnaiech, F.; Capolino, G. Sliding mode control for dual three-phase induction motor drives. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Power Electronics Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion, Montreal, QC, Canada, 9–13 July 2006; pp. 2281–2285. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, E.; Li, W.; Yang, X.; Liu, Y. Anti-disturbance speed control of low-speed high-torque PMSM based on second-order non-singular terminal sliding mode load observer. ISA Trans. 2019, 88, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhou, M.; Yu, X. Design and implementation of terminal sliding mode control method for PMSM speed regulation system. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2013, 9, 1879–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, C.; Yin, Z.; Luo, J.; Luo, P.; Liu, J. Robust composite finite-time convergent speed control of induction machine based on multiple sources disturbance estimation technology generalized proportional integral observer. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2022, 10, 6160–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, S.; Yu, X. Sliding-mode control for systems with mismatched uncertainties via a disturbance observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2013, 60, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).