Model-Independent Observer-Based Current Sensorless Speed Servo Systems with Adaptive Feedback Gain
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- For the entire loop, the observer gain is obtained by allowing each control loop, without addressing the matrix algebra using a model-independent observer, to estimate speed and acceleration as the pivotal subsystems;
- For the inner loop, the robust acceleration error stabilization loop is driven by the active damping, according to the first-order dynamics, which leads to the pole-zero cancellation;
- For the inner loop, the adaptive acceleration feedback gain is governed by the analytic law with the nonlinear excitation term of the acceleration error, thereby boosting and reducing its value according to the transient and steady-state operations.
2. Servo Machine Dynamics
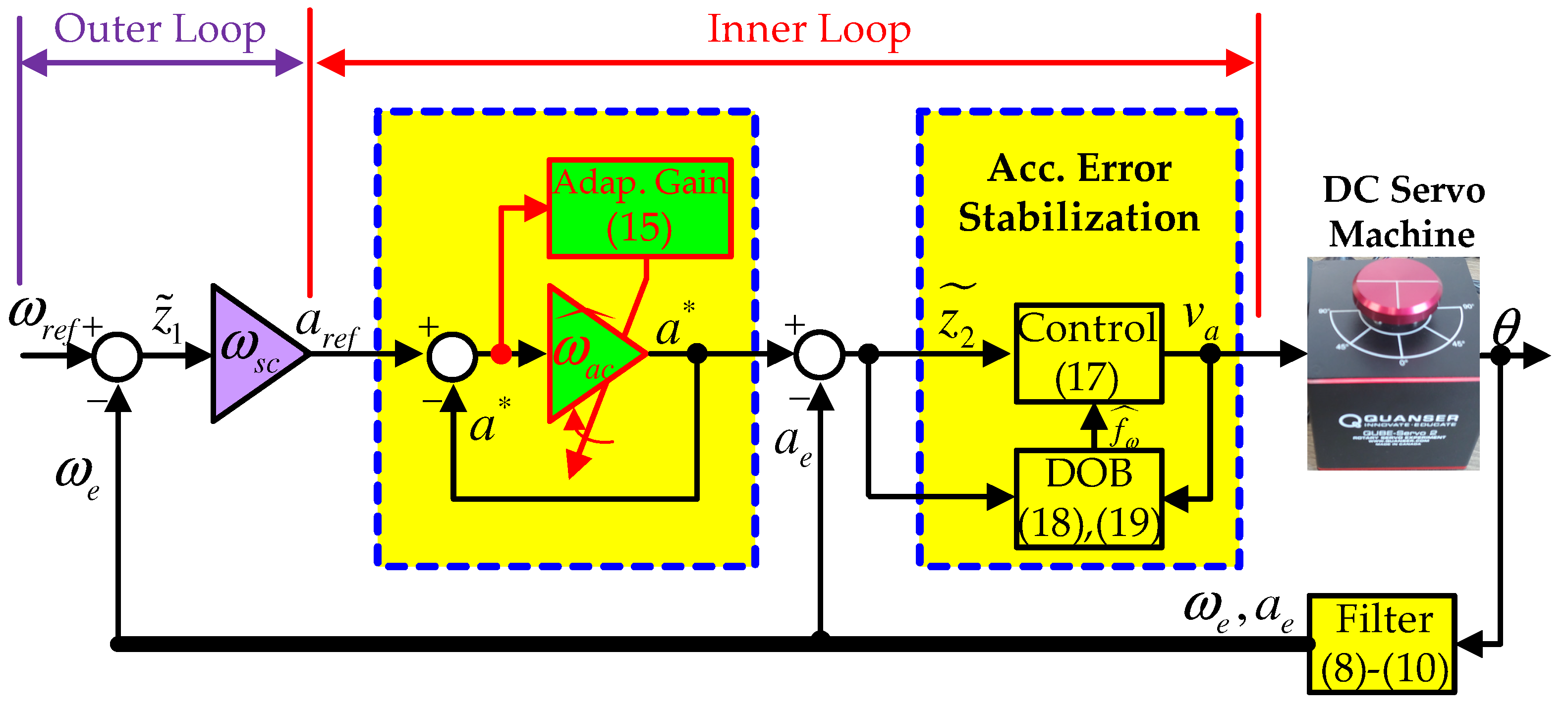
3. Proposed Solution
3.1. Model-Independent Observer
3.2. Outer Loop: Speed Control
3.3. Inner Loop: Acceleration Error Stabilizer
3.3.1. Desired Acceleration Trajectory Generator
3.3.2. Acceleration Error Stabilizing Control
4. Analysis
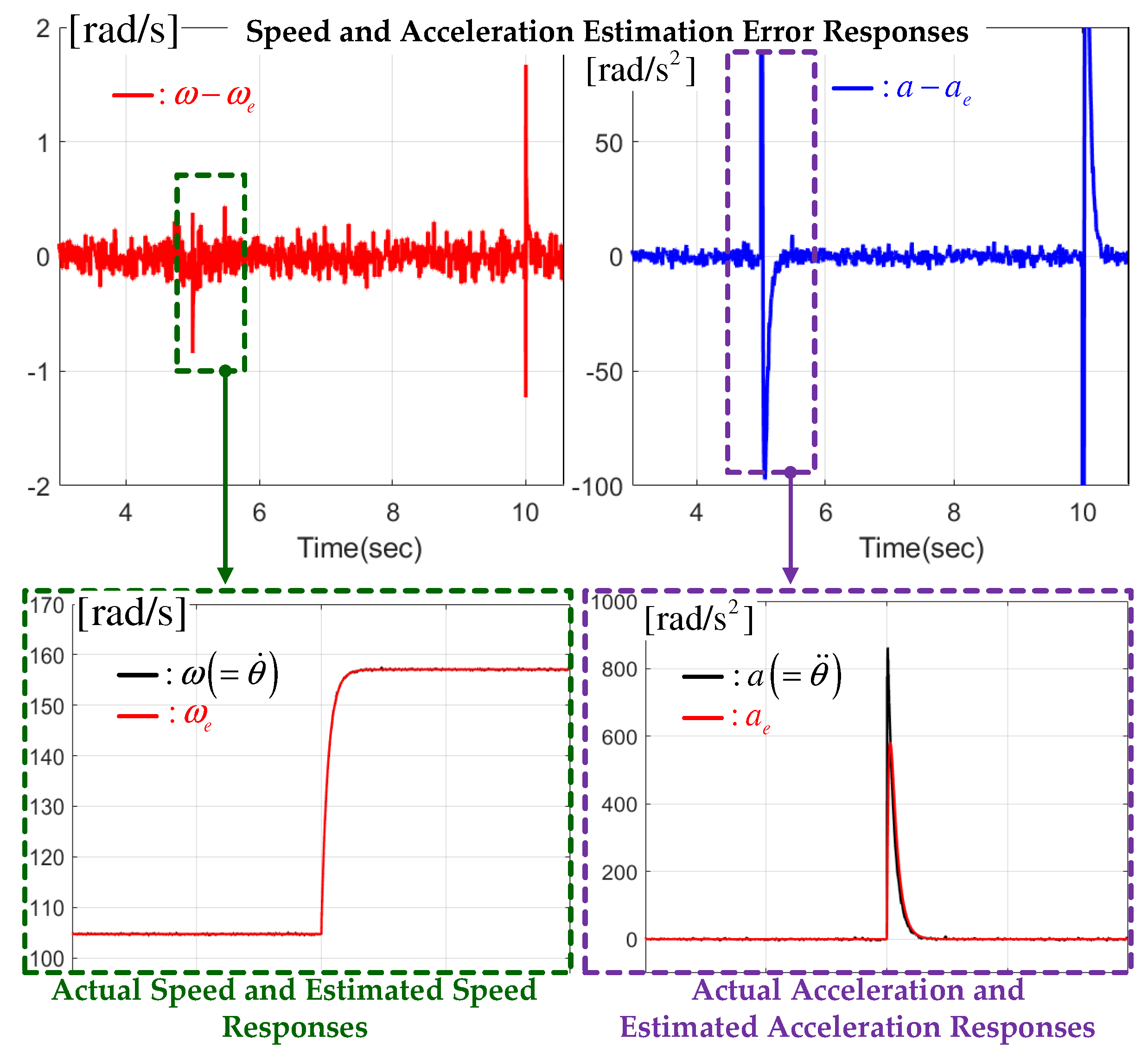
4.1. Observer
4.2. Outer Loop
4.3. Inner Loop
4.4. Entire Loop
5. Experimental Results
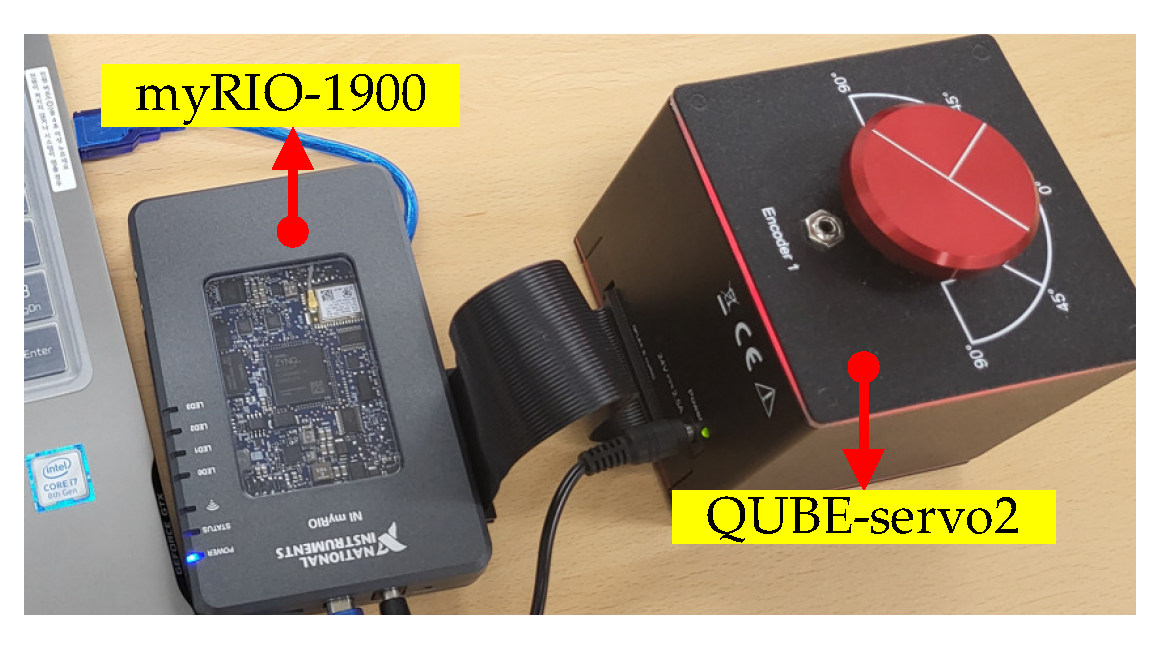
5.1. Set-Up
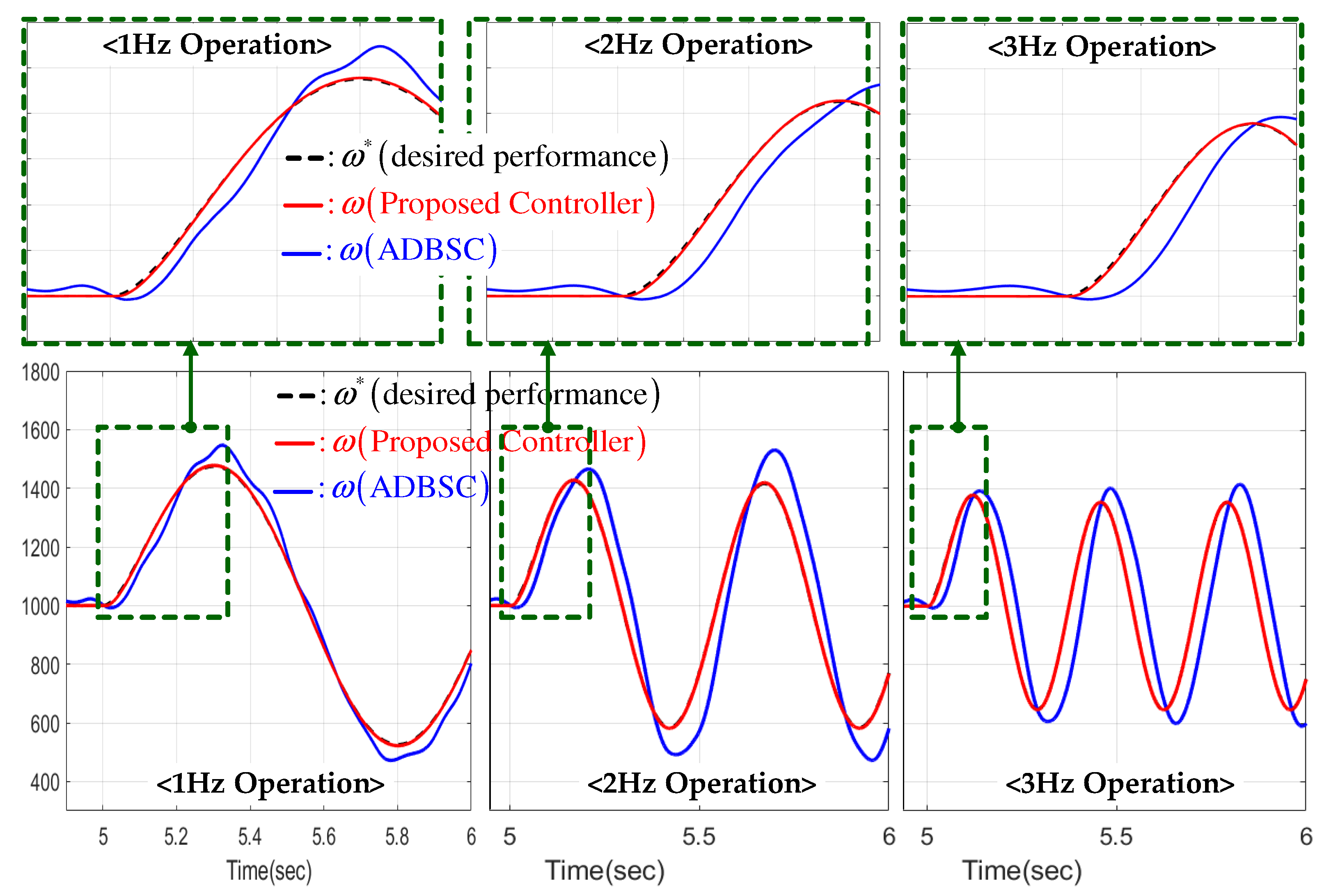
5.2. Tracking Comparison for Stair Speed Reference
5.3. Frequency Response Comparison
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| Plant variable | |
| DC voltage and current | |
| Position, speed and acceleration of rotor | |
| Inertia, viscous friction, inductance and resistance of rotor | |
| Electric torque and load torque | |
| Back electromotive force coefficient and torque coefficient | |
| Controller variable | |
| Desired closed-loop speed trajectory and reference signal | |
| Laplace transforms of | |
| Observer output, speed and acceleration estimation | |
| Observer error | |
| Observer tuning parameters | |
| Steady-state gain, tuning parameter and remainder | |
| Lumped disturbance | |
| Adaptive feedback gain | |
| Active damping and stabilization rate tuning parameters |
References
- You, S.; Kim, S.K.; Choi, H. Output-Feedback Position Tracking Servo System with Feedback Gain Learning Mechanism via Order-Reduction Speed-Error-Stabilization Approach. Actuators 2021, 10, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhu, D.; Li, L. Design and Analysis of an Active Disturbance Rejection Robust Adaptive Control System for Electromechanical Actuator. Actuators 2021, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, J.; You, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, W. Back Electro Motive Force Estimation Method for Cascade Proportional Integral Control in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. Actuators 2021, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharov, V.; Minav, T. Influence of Hydraulics on Electric Drive Operational Characteristics in Pump-Controlled Actuators. Actuators 2021, 10, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Ahn, C.K. Active-damping Speed Tracking Technique for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors with Transient Performance Boosting Mechanism. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2021, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.K.; Ahn, C.K. Output-Feedback Speed-Tracking Control Without Current Feedback for BLDCMs Based on Active-Damping and Invariant Surface Approach. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 68, 2528–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.; Wasynczuk, O.; Sudhoff, S. Analysis of Electric Machinery and Drive Systems; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Andeescu, G.D.; Pitic, C.; Blaabjerg, F.; Boldea, I. Combined flux observer with signal injection enhancement for wide speed range sensorless direct torque control of IPMSM drives. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2008, 23, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Zhong, L.; Rahman, M.; Hu, Y. A novel direct torque control for interior permanent-magnet synchronous machine drive with low ripple in torque and flux - a speed-senseroless approach. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2003, 39, 1748–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olalla, C.; Leyva, R.; Queinnec, I.; Maksimovic, D. Robust Gain-Scheduled Control of Switched-Mode DC-DC Converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 3006–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, T.; Zhu, Z.; Lei, G.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, J. Speed Sensorless Model Predictive Current Control Based on Finite Position Set for PMSHM Drives. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2021, 7, 2743–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sul, S.K. Control of Electric Machine Drive Systems; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; Volume 88. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, B.; Kim, S.I. Recursive Optimal Finite Impulse Response Filter and Its Application to Adaptive Estimation. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Jia, Y.; Li, M. Adaptive Square-Root Unscented Kalman Filter Phase Unwrapping with Modified Phase Gradient Estimation. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Yao, W.S. Analysis and Design Multiple Layer Adaptive Kalman Filter Applied to Electro-Optical Infrared Payload Vision System. Electronics 2022, 11, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, K.B. Self-Tuning Adaptive Speed Controller for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K. Robust adaptive speed regulator with self-tuning law for surfaced-mounted permanent magnet synchronous motor. Control Eng. Pract. 2017, 61, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sousy, F.F.M.; Abuhasel, K.A. Nonlinear Robust Optimal Control via Adaptive Dynamic Programming of Permanent-Magnet Linear Synchronous Motor Drive for Uncertain Two-Axis Motion Control System. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 1940–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Kim, Y.; Ahn, C.K. Energy-Shaping Speed Controller With Time-Varying Damping Injection for Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2021, 68, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Ahn, C.K. Position Regulator With Variable Cut-Off Frequency Mechanism for Hybrid-Type Stepper Motors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2020, 67, 3533–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errouissi, R.; Ouhrouche, M.; Chen, W.H.; Trzynadlowski, A.M. Robust Cascaded Nonlinear Predictive Control of a Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor With Antiwindup Compensator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 3078–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.I.; Kim, I.H.; Choi, D.S.; Shim, H. Robust Cascade Control of Electric Motor Drives Using Dual Reduced-Order PI Observer. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 3672–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, M.L.; Ippoliti, G.; Longhi, S.; Orlando, G. A Quasi-Sliding Mode Approach for Robust Control and Speed Estimation of PM Synchronous Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Koh, B.K.; Lee, Y.I. A Comparison of Finite Control Set and Continuous Control Set Model Predictive Control Schemes for Speed Control of Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2018, 14, 1334–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, T.; Zhao, W.; Du, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, J. Simplified Fault-Tolerant Model Predictive Control for a Five-Phase Permanent-Magnet Motor With Reduced Computation Burden. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 3850–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, R.H. Two-Reaction Theory of Synchronous Machines Generalized Method of Analysis. AIEE Trans. 1929, 48, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.K. Nonlinear Systems; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, S.; Kim, S.-K.; Kim, K.-C. Model-Independent Observer-Based Current Sensorless Speed Servo Systems with Adaptive Feedback Gain. Actuators 2022, 11, 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11050126
Lim S, Kim S-K, Kim K-C. Model-Independent Observer-Based Current Sensorless Speed Servo Systems with Adaptive Feedback Gain. Actuators. 2022; 11(5):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11050126
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Sun, Seok-Kyoon Kim, and Ki-Chan Kim. 2022. "Model-Independent Observer-Based Current Sensorless Speed Servo Systems with Adaptive Feedback Gain" Actuators 11, no. 5: 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11050126
APA StyleLim, S., Kim, S.-K., & Kim, K.-C. (2022). Model-Independent Observer-Based Current Sensorless Speed Servo Systems with Adaptive Feedback Gain. Actuators, 11(5), 126. https://doi.org/10.3390/act11050126






