Abstract
A high-end permanent magnet (PM) synchronous motor’s cogging torque is a significant performance measure (PMSM). During the running of the motor, excessive cogging torque will amplify noise and vibration. Therefore, the cogging torque must be taken into account while optimizing the design of motors with precise motion control. In this research, we proposed a local optimization-seeking approach (RSM+NSGA-II-LR) based on Response Surface Methodology (RSM) and Non-Dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm-II (NSGA-II), which reduced the cogging torque of a permanent magnet synchronous motor (SPMSM). To reduce the complexity of optimization and increase its efficiency, the sensitivity analysis method was utilized to identify the structural parameters that had a significant impact on the torque performance. Second, RSM was utilized to fit the functional relationship between the structural parameters and each optimization objective, and NSGA-II was integrated to provide the Pareto solution for each optimization objective. The solution with a greater average torque than the initial motor and the lowest cogging torque was chosen, and a new finite element model (FEM) was created. On the basis of the sensitivity analysis, the structural factors that had the highest influence on the cogging torque were selected, and the RSM is utilized for local optimization to lower the cogging torque as much as feasible. The numerical results demonstrated that the optimization strategy presented in this study effectively reduced the cogging torque of the motor without diminishing the motor’s average torque or increasing its torque ripple.
1. Introduction
Due to their high power density, low loss, and small size, PMSMs are widely employed in transportation, aircraft, and industrial robots [1,2,3,4]. In order for the windings to fit into the stator slots, PMSMs are frequently designed with slotted magnetic circuit structures. However, the slotting can lead to interaction between the stator core and the magnets, which can have a significant impact on the stable operation of a PMSM. It is crucial to lower the cogging torque of the PMSM [5,6] because this influence is more pronounced in low-speed settings.
The cogging torque is an inherent property of slotted motors and cannot be abolished entirely. In prior research, the cogging torque was weakened primarily by motor control and construction. Regarding control, [7] proposed a solution based on harmonic torque to counteract the cogging torque. A speed- and position-adaptive controller was created to reduce the cogging torque in [8]. Although the aforementioned optimized controller methods could greatly reduce cogging torque, they failed to account for the effect on other motor performance characteristics.
A significant amount of research has centered on the structural design and optimization of electrical machines in an effort to enhance their output performance. In the field of structural design, researchers have altered the topology of electrical machines to enhance their electromagnetic performance [9,10]. In [11], a scheme of skew-toothed stator teeth was proposed to reduce the cogging torque, however the impact of the proposed improvement on other motor performance characteristics was not explored. In [12], a stator-tooth-notching method was used to reduce the cogging torque, but it also reduced the average torque. In [13], the method of offset poles was utilized to lower the cogging torque of the motor; however, the average torque also decreased, and the installation perfection for this approach required high precision. In [14], a PM radially unequal width layering technique was presented to reduce the cogging torque and torque pulsation as well as the average torque. However, the technique was too structurally changed and difficult to install. The preceding research has demonstrated that the weakening of cogging torque is frequently followed by a reduction in electromagnetic torque, and that altering a motor’s construction may make the machining and installation of components more challenging.
In the field of optimization technology for electrical machines, the objective function, constraints, and boundaries are defined based on the electrical machine’s optimization problem, and the design space is searched for the optimal combination of parameters to achieve a significant improvement in the electrical machine’s performance [9,10,15]. With the advancement of optimization techniques, the study of the robustness of electrical machines design is gradually increasing [10,15]. Traditional approaches always optimize each structural parameter sequentially, neglecting structural parameter interactions. The Taguchi approach was proposed in [16,17,18] to optimize the major structural parameters of the motor. This method takes into account the interaction of the structural parameters based on an orthogonal test designed to successfully reduce the cogging torque of the motor. However, for a broad range of structural parameter values, the Taguchi method’s optimization is limited by insufficient precision. In [19,20], a genetic algorithm was employed to optimize the cogging torque of the motor. However, while the cogging torque was effectively lessened, the average torque was also decreased.
In this paper, RSM and NSGA-II were applied to the structural parameter optimization design of a motor in order to optimize the torque performance of SPMSM to ensure that the average torque of the motor was not less than the average torque of the initial motor and minimize the cogging torque. This paper’s outline is as follows: The second section describes the generation causes and analytical formulae for the SPMSM cogging torque. In the third section, a parameterization model for the SPMSM was created in order to examine the structural parameters’ sensitivity. Using RSM and NSGA-II, the torque performance of the motor was optimized in the fourth section. The torque performance of the initial motor was compared to the torque performance of the optimized motor in the fifth section. Conclusions were drawn in the sixth section.
2. Mechanism and Analysis of Cogging Torque Generation in SPMSMs
Cogging torque is produced by the contact between the PM and the stator core, which is damaging to a motor’s performance. During the rotation of the rotor, the magnetic field between the PM and the stator slot is nearly constant, and the PM’s forces are balanced. However, the magnitude of magnetic conductivity along the margins of both sides of the PM is constantly changing, resulting in differential magnitudes of magnetic field strengths on the left and right sides in this region and imbalanced forces on the PM, which generate the cogging torque. The formula for calculating the cogging torque is [21]:
where W is the energy of the magnetic field in the motor when no current is applied to the winding and α is the relative position of the stator and rotor. Assuming that the magnetic conductivity of the armature core is infinite, the energy of the magnetic field inside the motor can be expressed as:
where μ0 is the air magnetic conductivity, B is the air gap magnetic density, WPM is the magnetic field energy of the PM and Wairgap is the magnetic field energy of the air gap.
The distribution, B (θ,α), of the airgap magnetic density along the armature surface of the motor in (2) can be expressed as:
From Equations (2) and (3), it can be seen that:
where hm(θ) is the length of the PM in the magnetization direction, also known as the thickness of the PM, hg(θ,α) is the effective airgap length and Br(θ) is the residual magnetic induction of the PM. To further calculate the magnetic field energy in the motor, a Fourier expansion of and (θ) is required and can be expressed as:
where, Br0 = αp,, αp is the pole arc coefficient, p is the number of pole pairs, Brn is the Fourier decomposition coefficient of the square of the air-gap magnetic density generated by PM, Gn is the Fourier decomposition coefficient of the square of the relative air gap permeability and Br0 and G0 are the constant terms of (θ) and after the Fourier decomposition.
G0 and Gn in Equation (6) can be expressed as:
where, θso is the width of the slot opening of the stator expressed in radians and s is the number of slots.
Substituting Equations (5) and (6) into (4), which is then juggled with (1), the cogging torque, Tc, can be expressed as:
where La is the axial length of the stator core, D2 and Di2 are the inner radius of the armature and the outer radius of the rotor, respectively, and n is the integer that makes ns/2p an integer.
The following equation can be used to calculate the electromagnetic torque of the SPMSM:
where Tem is the electromagnetic torque, Pout is the output power of the motor, wr is the angular speed of the rotor and TL is the load torque, where the output torque power can be expressed as:
where m is the number of phases of the motor, Iph is the effective value of the phase current and E1 is the effective value of a counter electromotive force. E1 can be expressed as [22]:
where Kw1 is the fundamental winding factor, f is the current frequency of the stator, Nph is the number of turns in series per winding, B1 is the magnetic induction, Ns is the number of conductors per slot and ns is the total number of slots. As Ns is related to the area of the stator slot and the wire gauge of the winding, it can be expressed as [23]:
where As and Ai can be expressed as:
where Ci is the insulation thickness of the slot, Aef is the effective area of the slot, ACu is the wire gauge of the estimated winding, As and Ai are the area of the slot and the insulation occupied area of the slot, respectively, Bs1 is the width of the slot, Bs2 is the radius of the slot and Hs2 is the depth of the slot.
Substituting (12) and (13) into (11), the expression for Pout is obtained as:
Letting , (15) and (16) are thus substituted into (14), which is then juggled with (10), (11) and (12) to derive the expression for the electromagnetic torque Tem:
The average torque magnitude (Ta) of the SPMSM can be defined as the peak-to-peak average of the electromagnetic torque (Tem) during steady operation of the motor as follows:
The torque ripple, Tr, can be defined as the ratio of the peak-to-peak difference in the electromagnetic torque to the average torque, as shown below:
where avg means the calculated average, Tmax is the maximum peak of the electromagnetic torque and Tmin is the minimum peak of the electromagnetic torque.
According to Equation (9), the cogging torque is dominated by the magnitudes of Gn and Brn. It can be shown from Equation (5) that the pole arc coefficient has a direct effect on Brn. The width of the slot opening of the stator and the thickness of the PM have a direct effect on Gn, as shown by Equation (8). The structural parameters to be optimized are, therefore, the pole arc coefficient, the width of the slot aperture and the thickness of the PM. Changes in the other structural parameters of the stator slot in the SPMSM will likewise impact the magnetic field distribution in the stator’s teeth and yoke as well as the motor’s electromagnetic torque. Therefore, the stator-slot-related structural characteristics were chosen as the structural parameters to be optimized. It can be shown from Equation (18) that variations in the depth, width and radius of the slot will affect the electromagnetic torque capabilities. Changes in the thickness of the PM will also impact the distribution of the flux density in the airgap, thus affecting the electromagnetic torque capability. Consequently, the electromagnetic torque performance must be taken into account when reducing the cogging torque so that the electromagnetic torque performance is not severely diminished.
3. Numerical Simulation Analysis and Optimal Design of SPMSM
3.1. Parameterization Model of a SPMSM
In this study, an SPMSM with eight poles and thirty-six slots served as the object of analysis. Figure 1a illustrates the motor topology. Figure 1b depicts the mesh split for the numerical simulation study. The fundamental motor characteristics are provided in Table 1.
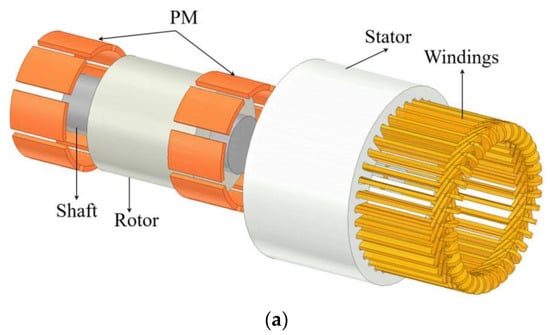
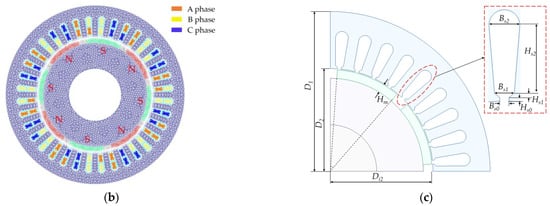
Figure 1.
Model of SPMSM: (a) geometric model; (b) FEM; (c) parameterization model.

Table 1.
Basic parameters of SPMSM.
Figure 1c shows the parameterization model of the motor. Table 2 displays the initial values and variation range for each structural parameter. This research focused on optimizing the stator slot and PM structure of the motor in order to reduce the cogging torque of the motor. Therefore, the pole arc coefficient (αp) of the PM, the thickness (Hm) of the PM, the height (Hs0) of the slot opening, the height (Hs1) of the slot shoulder, the depth (Hs2) of the slot, the width (Bs0) of the slot opening, the width (Bs1) of the slot and the radius (Bs2) of the slot were selected for optimization. αp is the ratio of the arc length spanned by each pole of PM to the pole pitch. The above structural parameters were taken within a reasonable range of variation.

Table 2.
Initial values and range of values of structure parameters.
3.2. Optimized Design of SPMSM
Figure 2 depicts the optimization process of this paper. It focused mostly on the sensitivity analysis of the structural parameters. RSM- and NSGA-II-based structural parameter optimizations were conducted.
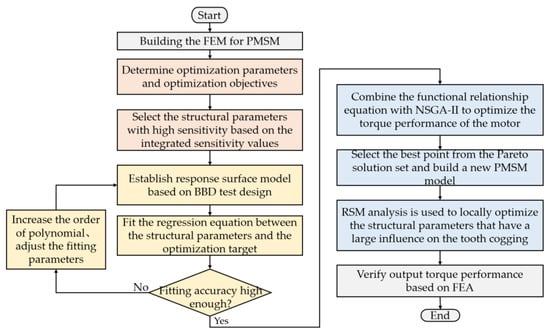
Figure 2.
Optimized flow chart of SPMSM.
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis of Parameters
The sensitivity analysis method refers to an analysis technique in which the structural parameters are altered continually within a predetermined range during numerical simulation in order to observe the change rule and degree of the optimal objectives. A sensitivity analysis identifies the most significant factors among numerous others, thus minimizing the complexity and computational effort required for further optimization [24]. In this research, the Pearson correlation coefficient was utilized to calculate the influence index of each structural parameter on the optimal objective using the following equation:
where X and Y are the structural parameter and the optimized objective, respectively. COV(X,Y) is the covariance of X and Y, and σX and σY are the standard deviations of X and Y, respectively.
After establishing the range of structural parameters and the optimum objectives, the Latin hypercube sampling approach in [25] was utilized to scan the design space for the sensitivity analysis. Then, a numerical simulation was used to determine the cogging torque, torque ripple and average torque values corresponding to each model. The minimum cogging torque, minimum torque ripple and highest average torque were the objectives of the parameter sensitivity analysis. Accordingly, the sensitivity of the selected structural parameters to the optimized objectives was then computed, as per Equation (21). The results are shown in Figure 3, where TC is the cogging torque, Tr is the torque ripple and Ta is the average torque.
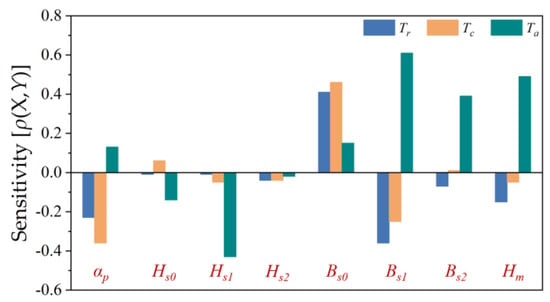
Figure 3.
Analysis of sensitivity of structural parameters to three optimized objectives.
Figure 3 depicts the direction and magnitude of the association between each structural parameter and the optimization aim. Bs0 correlated positively with the cogging torque, torque ripple and average torque. If Bs0 changed in a way that promoted an increase in the average torque, the cogging torque and torque ripple likewise rose. This suggested that three optimized objectives did not always alter in a positive direction when Bs0 was modified. Consequently, it was essential to implement the approach of trade-off optimization. As the number of optimization variables increases, so does the difficulty of optimization. Several structural characteristics that had a higher impact on the torque performance of the motor were selected for the optimization, according to Figure 3, in order to reduce the complexity of the optimization. Overall, the four structural parameters αp, Bs0, Bs1 and Hm had a greater impact on the torque performance of the motor. Therefore, the structural parameters for this optimization were αp, Bs0, Bs1 and Hm.
3.4. Torque Performance Optimization of SPMSM
3.4.1. Constructing RSM Models of Structural Parameters and Optimization Objectives
RSM is a technique for examining the relationship between numerous input factors and output targets. Suitable for studying multivariate problems, RSM can be used to identify optimal combinations by generating the response surfaces of input and output variables. Additionally, RSM can be utilized to develop polynomial equations for input and output variables. The Central Composite Design (CCD) and Box–Behnken Design (BBD) methods are two extensively utilized methods of test designing for response surfaces [26]. With the same number of selected parameters, the BBD design requires fewer trials. This research evaluated the nonlinear relationship between the three optimal objectives and the structural parameters using the BBD design approach. First, based on the number of structural parameters and the range of values, an appropriate test design method was established. Then, a numerical simulation was used to calculate the cogging torque, torque ripple and average torque for each combination of structural parameters. For the ensuing NSGA-II optimization, the polynomial regression equation between the structural parameters and the optimization objective was fitted using RSM. Due to the intricate interaction between the structural factors and the motor’s optimal goals, In order to match their functional relationship, a second-order polynomial was used as the fitting function. The model of its response surface can be described by the following [27]:
where ε is the fitting error, β is the coefficient to be determined, y is the predicted value of the optimized objective and xi denotes the i-th structural parameter.
The number of test points was determined in accordance with the BBD design. There were twenty-five test locations and four specified structural parameters. By building a numerical simulation model for each test point in order to establish a polynomial regression model, the values of the relevant objective were calculated. Table 3 displays the BBD test design table and the numerical analysis findings. The table’s results are kept to two decimal places.

Table 3.
BBD test design table and numerical analysis results.
To ensure the applicability of the regression equation corresponding to the three optimal objectives, the coefficient of determination, R2 (ranging from 0 to 1), was utilized to assess the precision of the regression model fit. The closer to 1 the polynomial regression model fits, the better. R2 can be calculated using Equation (23):
where ya is the actual value of the objective function and y is the mean of the actual values of the objective function. The four parameters αp, Bs0, Bs1 and Hm were fitted as a function of the cogging torque, average torque and torque ripple, respectively, according to Table 4. The R2 values of all three functions obtained by fitting were greater than 0.95, indicating that the fitted functional equation had good applicability.

Table 4.
The range of values for local optimization of structural parameters.
3.4.2. Multi-Objective Optimized Design Based on NSGA-II
For SPMSM multi-objective optimization issues, optimizing the performance of one objective frequently degrades the performance of the other objectives. They are constrained by one another. It is not possible to find a solution that maximizes the performance across all objectives. However, the optimized method can achieve equilibrium so that each aim can be optimized to the greatest extent possible. NSGA-II is suitable for optimizing complicated structures such as SPMSM due to its enhanced global search capabilities and increased resilience. In this research, NSGA-II was used for the thorough optimization of the cogging torque, torque ripple and average torque of the motor, with the objective function specified as follows:
where min means to minimize the target. In order to minimize the cogging torque, only one constraint was added to the NSGA-II optimization search process: f1(x) is less than the initial motor cogging torque (Tc < 4.77Nm).
The RSM-based polynomial equations were integrated with the NSGA-II multi-objective optimization technique to obtain the optimal structural parameter design space. The NSGA-II flowchart is depicted in Figure 4a. Figure 4b depicts the Pareto solution of three optimized objectives obtained after 50 NSGA-II iterations. Each solution presented in the diagram had a greater average torque than the initial motor. As a result, the option with the lowest cogging torque was chosen as the optimal solution. This is represented by the green dot in Figure 4b.
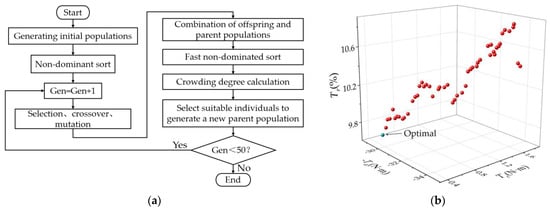
Figure 4.
NSGA-II: (a) flow chart of NSGA-II; (b) Pareto solution set.
To significantly reduce the SPMSM’s cogging torque and enhance its torque performance, in this research, we offered RSM+NSGA-II-LR, a method that employs RSM analysis for local optimization after an NSGA-II search for optimal solutions. The procedure for implementation was as follows: After first optimizing SPMSM using NSGA-II, a new FEM was developed. The structural characteristics with the greatest impact on the cogging torque were then chosen. Figure 3 shows that αp, Bs0 and Bs1 had a significant impact on the cogging torque. However, the connection between Bs1 and the average torque and cogging torque was inverse, and Bs1’s effect on the average torque was substantially bigger than its effect on the cogging torque, hence Bs1 was not considered. The local optimization range of the structural parameters αp and Bs0 was redefined, with the new value being 20% of the initial range of the structural parameters. RSM was also utilized to maximize the cogging torque of the motor. Assuming that the initial value range of structural parameters is [a, c] with a value of b, the optimization range of the local optimization can be described as follows:
The local search ranges of αp and Bs0 were computed in accordance with Equation (25) and Table 4, with the results being displayed in Table 4. Figure 5 depicts the construction of the response surface model using the BBD design following the determination of the local search range.
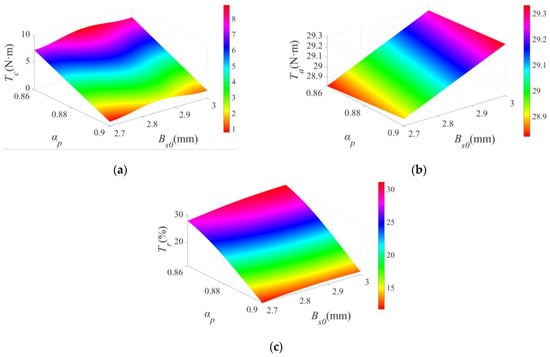
Figure 5.
Response surface diagram: (a) the response surfaces of αp, Bs0 and Tc; (b) the response surfaces of αp, Bs0 and Ta; (c) the response surfaces of αp, Bs0 and Tr.
The cogging torque increased and then dropped with the increase in Bs0 and decreased with the increase in αp, as shown in Figure 5a. Figure 5b demonstrates that when αp increased, the average torque likewise increased slightly. The average torque increased as Bs0 increases, although the increase was not evident, and the average torque varied by less than 1 Nm. Figure 5c demonstrates that the torque ripple increased significantly with increasing Bs0 and diminished with increasing αp.
In conclusion, the increase in αp was advantageous for the reduction in the cogging torque and torque ripple as well as the enhancement of the average torque, so αp was equal to 0.9. The decrease in Bs0 was advantageous for the reduction in the cogging torque and torque ripple but not for the rise in the average torque. However, the effect of Bs0 on the average torque was diminished, and the objective of this optimization was to lower the motor’s cogging torque; therefore, Bs0 was set as 2.7 mm.
4. Optimized Result Analysis
The improved motor’s structural parameters were produced from the aforementioned study, and a numerical simulation model was created to compare optimization objectives before and after optimization, as depicted in Figure 6. Table 5 displays the particular values. After the NSGA-II parameter search, the torque performance of the motor was significantly enhanced compared to the initial motor. In particular, the cogging torque and torque ripple were decreased by 71% and 33%, respectively, while the average torque was raised by 3%. This significantly increased the motor’s driving performance. Using the RSM+NSGA-II-LR optimization, the torque performance of the motor was enhanced further. Compared to the RSM+NSGA-II-optimized motor torque performance, the cogging torque and torque ripple were reduced by 43% and 9%, respectively, and the average torque was reduced by 2% but was still higher than the initial motor’s average torque, which was consistent with the objectives of this optimization. After optimizing the motor, this solution was chosen as the optimal combination of structural parameters. The motor’s optimal structural parameters were obtained, as given in Table 6.
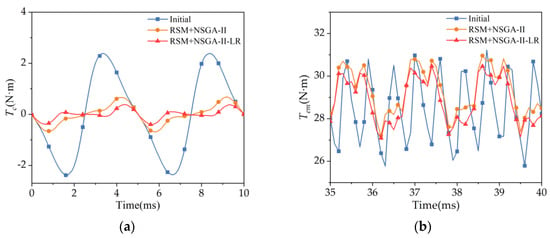
Figure 6.
Results of numerical analysis before and after optimization: (a) curve diagram of cogging torque; (b) curve diagram of electromagnetic torque.

Table 5.
Torque performance of the motor before and after optimization.

Table 6.
Parameters before and after SPMSM optimization.
The results of optimizing the same four structural parameters using the Taguchi technique and RSM analysis are shown in Table 5. After comparison, it was evident that the RSM+NSGA-II-LR approach described in this study lowered the cogging torque while satisfying the assumption that the average torque must be greater than the original motor’s torque.
5. Conclusions
This study combined the sensitivity analysis approach, RSM and NSGA-II and offered a method based on RSM+NSGA-II-LR to optimize the torque performance of a PMSM in order to address the issue of excessive cogging torque. The findings indicated that the method ensured that the average torque of the motor was not less than the average torque before optimization and efficiently minimized the cogging torque and torque ripple of the motor. Consequently, this study presented an efficient method for building an efficient, low-vibration and low-noise SPMSM, which may also be applied to enhance the performance of other motors. In future work, we will study more effective optimization techniques and robust design optimization methods to improve the stability and reliability of motor design and make experimental prototypes.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Y. and Y.P.; methodology, Y.Y.; software, Y.P.; writing—original draft, Y.Y. and Y.P. writing—review and editing, Y.Y., Q.C., D.Z., Y.H., H.-H.G., Z.Z. and S.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52067006, U2034211, 52162044), in part by the Foreign Expert Bureau of the Ministry of science and technology of China (Grant No. G2021022002L), in part by long-term project of innovative leading talents in the “Double Thousand Plan” of Jiangxi Province (jxsq2019101027) and by the Key Research Program of Jiangxi Province (Grant No. 20212BBE51014).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions to improve the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhang, J.M.; Su, H.; Ren, Q.; Li, W.; Zhou, H.C. Review on development and key technologies of permanent magnet synchronous traction system for rail transit. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2021, 21, 63–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, L.; Liu, K.; Li, L.; Jing, J. Optimization Analysis of Automotive Asymmetric Magnetic Pole Permanent Magnet Motor by Taguchi Method. Int. J. Rotating Mach. 2021, 2021, 6691574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Zhu, X.Y.; Quan, L.; Han, X.; He, X.J. Parameter Sensitivity Optimization Design and Performance Analysis of Double-Salient Permanent-Magnet Double-Stator Machine. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2017, 32, 160–168. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Lee, C.H.; Gao, D.; Yu, K. Vibration Optimization of FSCW-IPM Motor Based on Iron-Core Modification for Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 14834–14845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, M.-H.; Lee, H.-S.; Yang, S.-H.; Lee, G.-S.; Han, J.-H.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, H.-W.; Cha, H.-R. Cogging Torque Reduction and Offset of Dual-Rotor Interior Permanent Magnet Motor in Electric Vehicle Traction Platforms. Energies 2019, 12, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuja, T.; Doss, M. Reduction of Cogging Torque in Surface Mounted Permanent Magnet Brushless DC Motor by Adapting Rotor Magnetic Displacement. Energies 2021, 14, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Xiang, Z.; Dai, L.; Huang, S.; Ni, D.; Yao, C. Cogging Torque Dynamic Reduction Based on Harmonic Torque Counteract. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 58, 8103405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, A.; Caum, J.; Ibarra, E.; Grino, R. Reducing the Cogging Torque Effects in Hybrid Stepper Machines by Means of Resonant Controllers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 66, 2603–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, G.; Zhu, J.; Guo, Y.; Liu, C.; Ma, B. A Review of Design Optimization Methods for Electrical Machines. Energies 2017, 10, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramerdorfer, G.; Tapia, J.A.; Pyrhonen, J.J.; Cavagnino, A. Modern Electrical Machine Design Optimization: Techniques, Trends, and Best Practices. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 7672–7684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, Y.; Takahashi, H. Cogging Torque Reduction on Transverse-Flux Motor with Multilevel Skew Configuration of Toothed Cores. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2019, 55, 8203005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, J.-H.; Kang, D.-W. Torque Ripple and Cogging Torque Reduction Method of IPMSM Using Asymmetric Shoe of Stator and Notch in Stator. J. Electr. Eng. Technol. 2022, 17, 3465–3471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, I.-H.; Lee, H.-W.; Jeong, G.; Ji, W.-Y.; Park, C.-B. A Study on the Reduction of Cogging Torque for the Skew of a Magnetic Geared Synchronous Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2018, 55, 8100505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahim Ladghem, C.; Kamel, B.; Rachid, I. Permanent magnet shaping for cogging torque and torque ripple reduction of PMSM. COMPEL-Int. J. Comput. Math. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2018, 37, 2232–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosz, T.; Rassõlkin, A.; Kallaste, A.; Arsénio, P.; Pánek, D.; Kaska, J.; Karban, P. Robust Design Optimization and Emerging Technologies for Electrical Machines: Challenges and Open Problems. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Wang, F.Y.; Zheng, C.D. Application for Optimal Designing of Sinusoidal Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors by Using the Taguchi Method. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2011, 26, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, W.G. Multi-objective Optimal Design for Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Taguchi Method. Micromotors 2016, 49, 1780–1783. [Google Scholar]
- Si, J.K.; Zhang, L.F.; Feng, H.C.; Xu, X.Z.; Zhang, X.L. Multi-objective optimal design of a surface-mounted and interior permanent magnet synchronous motor. J. China Coal Soc. 2016, 41, 3167–3173. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, J.J.; Zhao, S.W.; Yang, X.Y. Optimization of Cogging Torque of External Rotor PMSM Based on Genetic Algorithm. Small Spec. Electr. Mach. 2020, 48, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ilka, R.; Alinejad-Beromi, Y.; Yaghobi, H. Cogging torque reduction of permanent magnet synchronous motor using multi-objective optimization. Math. Comput. Simul. 2018, 153, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.Q. Design and Characteristic Research of Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor for New Energy Vehicle; Chongqing Jiaotong University: Chongqing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, R. Permanent Magnet Synchronous and Brushless DC Motor Drives; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.Y. Modern Permanent Magnet Machines: Theory and Design; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, G.; Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Guo, Y. Techniques for Multilevel Design Optimization of Permanent Magnet Motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2015, 30, 1574–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, M.D.; Zhang, J. The generalization of Latin hypercube sampling. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2016, 148, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.J.; Feng, L.L.; Mao, R.; Yu, L.; Jia, H.Y.; Jia, Z. Multi-objective Stratified Optimization Design of Axial-flux Permanent Magnet Memory Motor. Proc. CSEE 2021, 41, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.Y.; Gao, J.N.; Li, M.M.; Yao, P.; Song, Z.X.; Yang, K.W.; Gao, X.Y. Optimization Design of Halbach Interior Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Based on Parameter Sensitivity Stratification. J. Xi’an Jiaotong Univ. 2022, 56, 180–190. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).