Nonlinear Finite Element Modelling of Thermo-Visco-Plastic Styrene and Polyurethane Shape Memory Polymer Foams
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
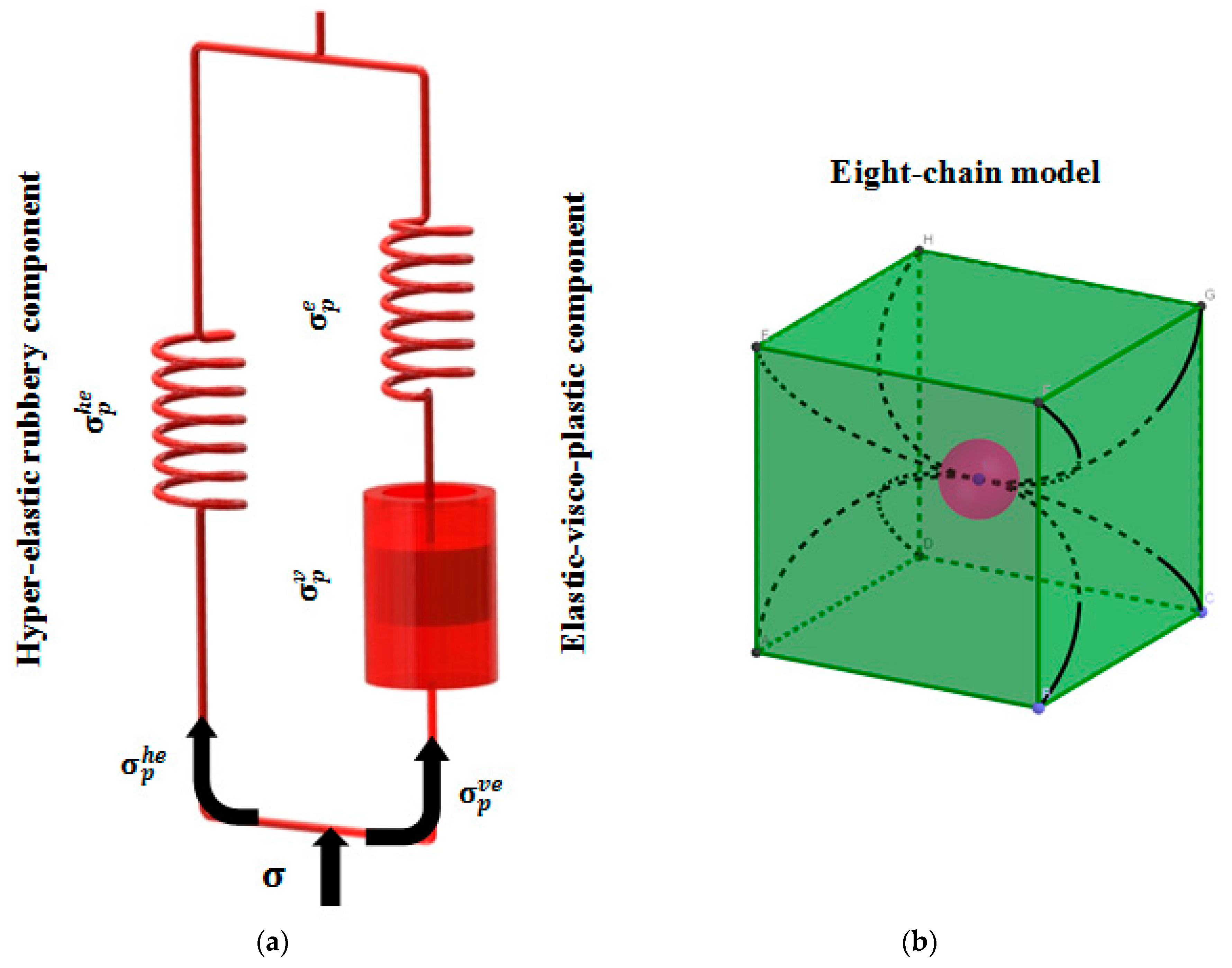
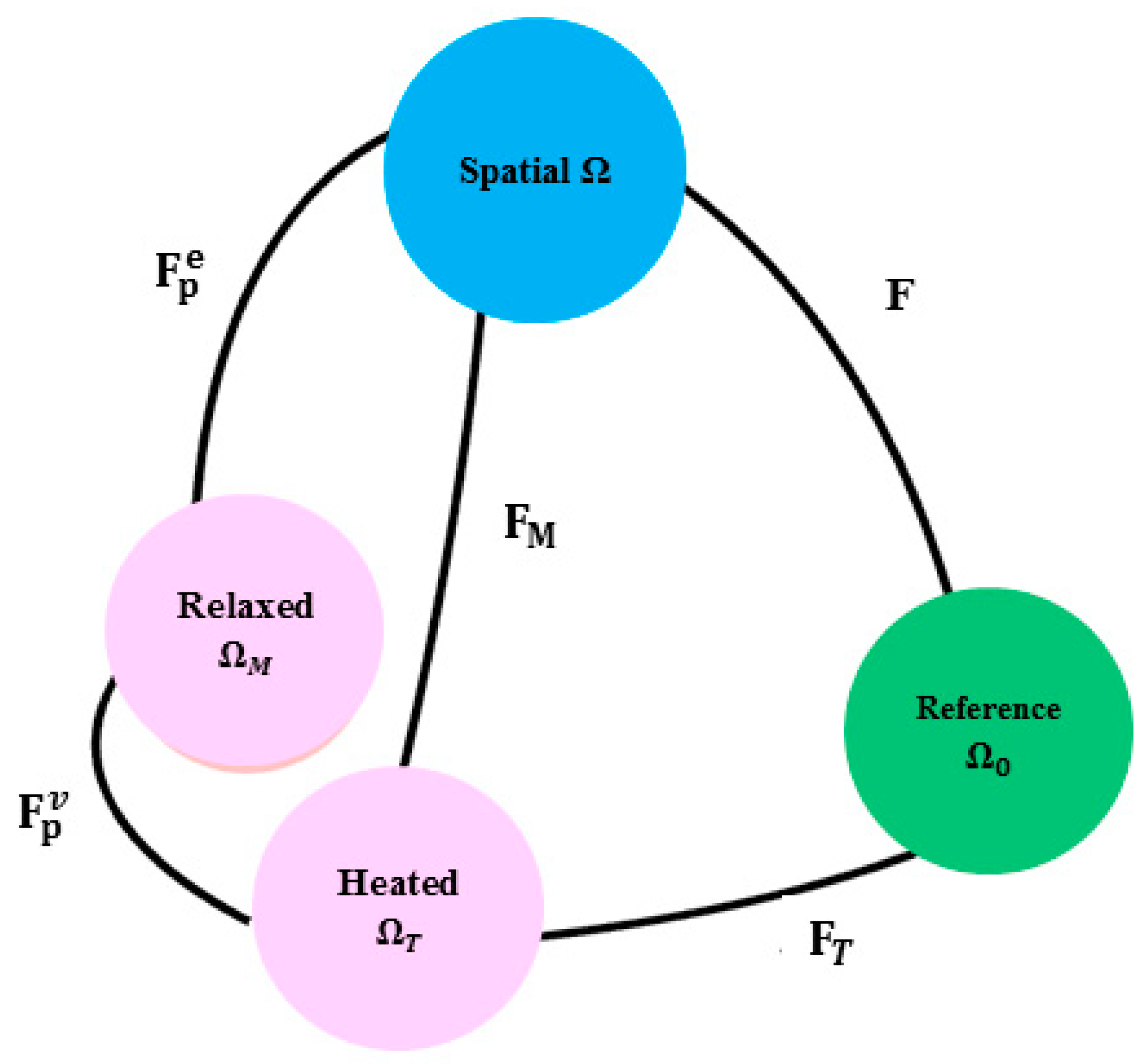
2.1. Constitutive Modelling
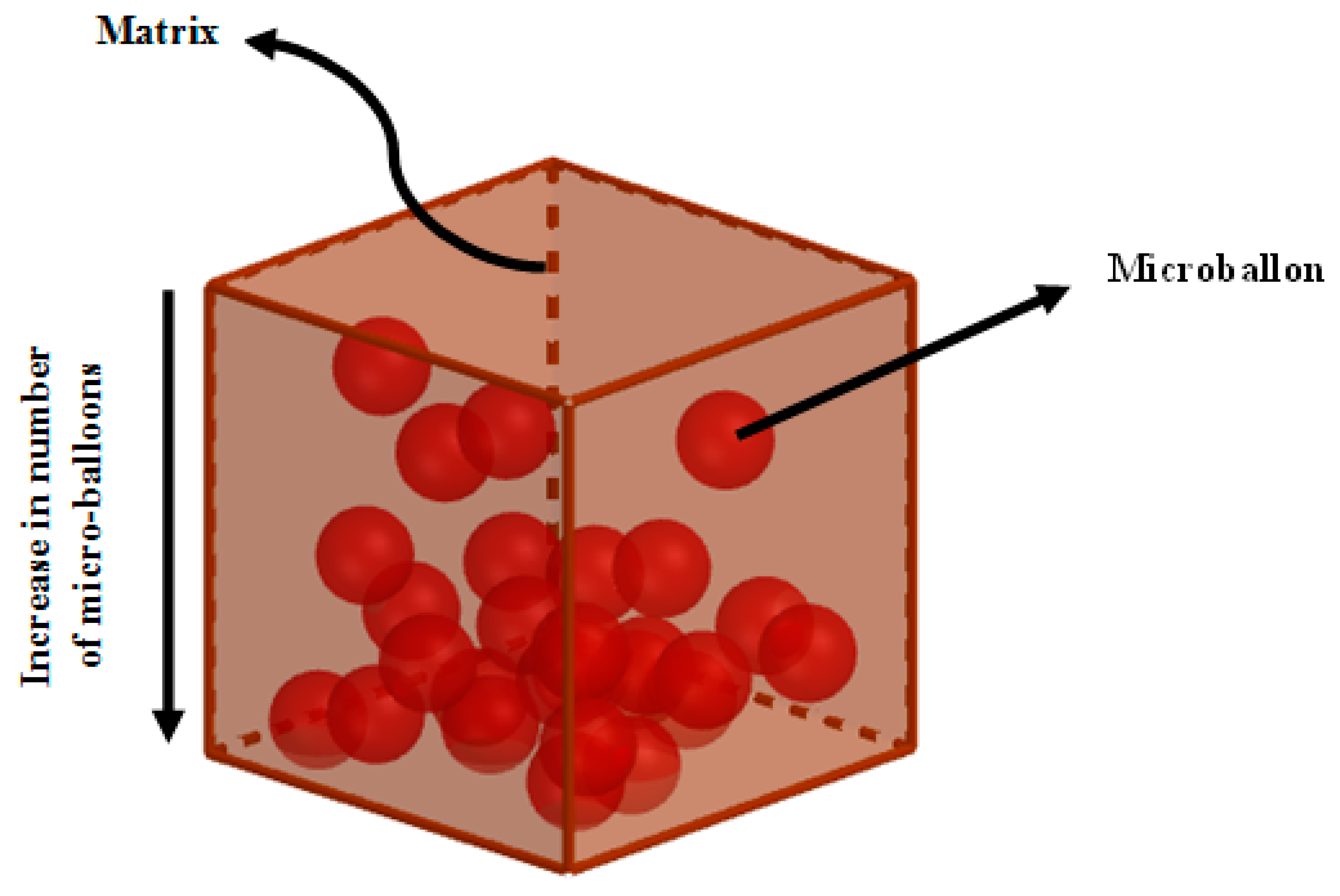
2.2. Materials
2.2.1. PU SMP Foams

| Type | Chemical Characteristic | Average Pore Diameter (μm) | Monomers |
|---|---|---|---|
| PU-I [51] | Stearyl acrylate (A18, Aldrich)-stearyl methacrylate (MA18, Aldrich) | 65 | Polyether polyole series (Diary MF No. 21) |
| PU-II [11] | Polyether polyole (Diary MF No. 21) | 40 | Stearyl acrylate (A18, Aldrich) and stearyl methacrylate (MA18, Aldrich) |
| PU-III [52] | CHEM 5520 | 40 |
2.2.2. Styrene SMP Foam (Veriflex)
2.3. Experimental Setup
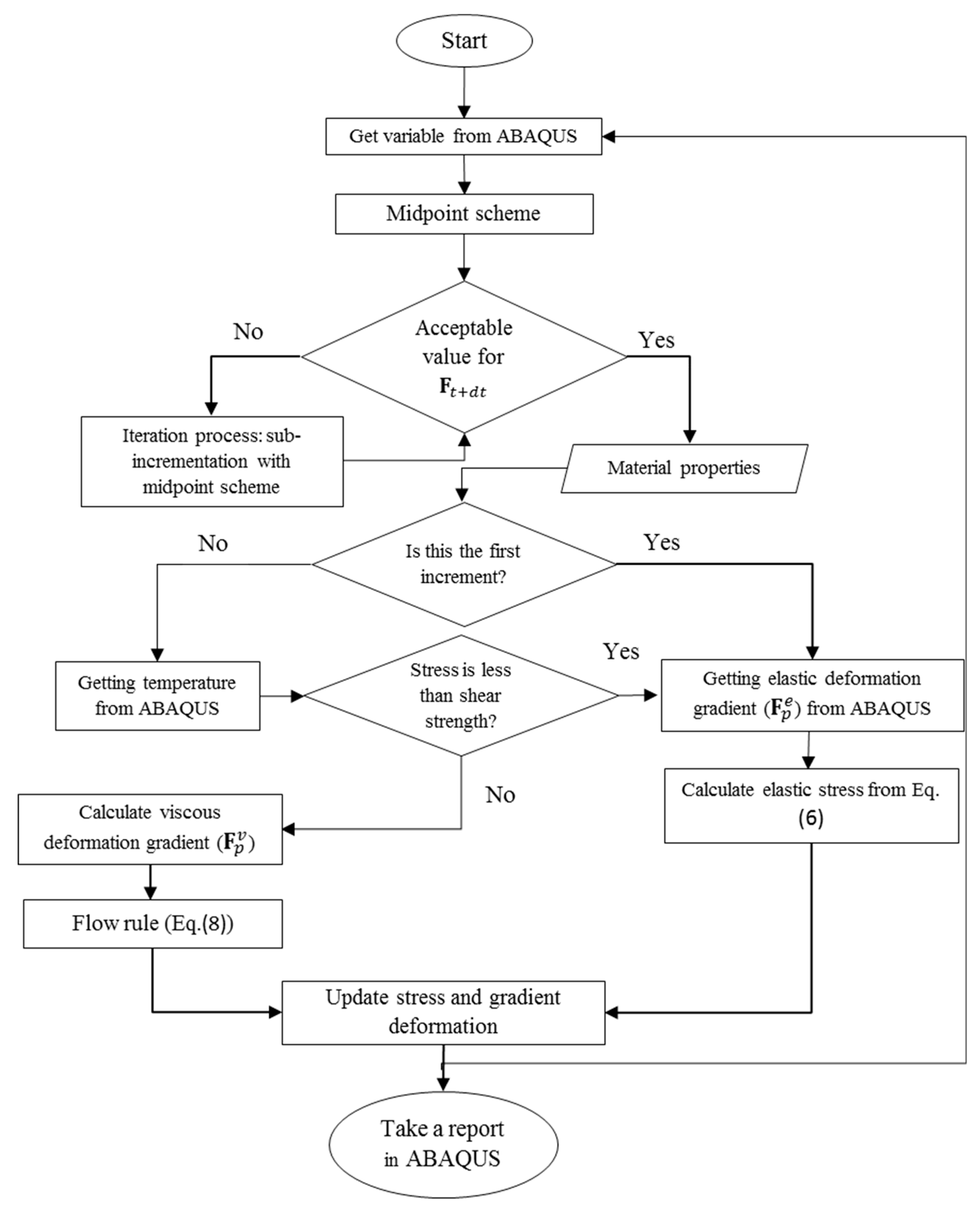
2.4. FE Modelling
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sokolowski, W. Shape Memory Polymer Foams for Biomedical Devices. Open Med. Devices J. 2010, 2, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Atab, N.; Mishra, R.B.; Al-Modaf, F.; Joharji, L.; Alsharif, A.A.; Alamoudi, H.; Diaz, M.; Qaiser, N.; Hussain, M.M. Soft Actuators for Soft Robotic Applications: A Review. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.T.; Wang, P.P.; Liu, S.Q.; Xu, Y.H.; Zheng, R.M.; Deng, Z.F.; Peng, Z.F.; Li, J.Y.; Wu, Y.Y.; Liu, L. A shape-memory soft actuator integrated with reversible electric/moisture actuating and strain sensing. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 193, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Schönfeld, D.; Chalissery, D.; Wenz, F.; Specht, M.; Eberl, C.; Pretsch, T. Actuating Shape Memory Polymer for Thermoresponsive Soft Robotic Gripper and Programmable Materials. Molecules 2021, 26, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalet, G. Two-way and multiple-way shape memory polymers for soft robotics: An overview. Actuators 2020, 9, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodaghi, M.; Noroozi, R.; Zolfagharian, A.; Fotouhi, M.; Norouzi, S. 4D printing self-morphing structures. Materials 2019, 12, 1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodaghi, M.; Damanpack, A.R.; Liao, W.H. Triple shape memory polymers by 4D printing. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.F.; Walters, H.A.; Glesner, C.W. Castable, Sprayable, Low Density Foams and Composites for Furniture, Marble, Marine, Aerospace, Boats and Related Applications. J. Cell. Plast. 1970, 6, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santo, L. Shape memory polymer foams. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 2016, 81, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobushi, H.; Hara, H.; Yamada, E.; Hayashi, S. Thermomechanical properties in a thin film of shape memory polymer of polyurethane series. Smart Mater. Struct. 1996, 5, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobushi, H.; Okumura, K.; Endo, M.; Hayashi, S. Thermomechanical Properties of Polyurethane-Shape Memory Polymer Foam. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2001, 12, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gall, K.; Dunn, M.L.; McCluskey, P. Thermomechanics of shape memory polymer nanocomposites. Mech. Mater. 2004, 36, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadrini, F.; Bellisario, D.; Ciampoli, L.; Costanza, G.; Santo, L. Auxetic epoxy foams produced by solid state foaming. J. Cell. Plast. 2016, 52, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.; Scarpa, F.; Smith, C.W. Shape memory behaviour in auxetic foams: Mechanical properties. Acta Mater. 2010, 58, 858–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, N.; Evans, K.E. The mechanical properties of conventional and auxetic foams. Part I: Compression and tension. J. Cell. Plast. 1999, 35, 130–165. [Google Scholar]
- Tobushi, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Hayashi, S.; Yamada, E. Thermomechanical constitutive modeling in shape memory polymer of polyurethane series. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1997, 8, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Tobushi, H. Analysis of the isothermal mechanical response of a shape memory polymer rheological model. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2000, 40, 2498–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafka, V.; Hutter, K. Mesomechanical Constitutive Modeling. Advances in Mathematics for Applied Sciences Series. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2002, 55, 83–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kafka, V. Shape memory polymers: A mesoscale model of the internal mechanism leading to the SM phenomena. Int. J. Plast. 2008, 24, 1533–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diani, J.; Gall, K. Molecular dynamics simulations of the shape-memory behaviour of polyisoprene. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, R.; Hosseini-Toudeshky, H.; Sadighi, M.; Mohammadi-Aghdam, M.; Zadpoor, A.A. Multiscale modeling of fatigue crack propagation in additively manufactured porous biomaterials. Int. J. Fatigue 2018, 113, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshedian, J.; Khonakdar, H.A.; Rasouli, S. Modeling of shape memory induction and recovery in heat-shrinkable polymers. Macromol. Theory Simul. 2005, 14, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gall, K.; Yakacki, C.M.; Liu, Y.; Shandas, R.; Willett, N.; Anseth, K.S. Thermomechanics of the shape memory effect in polymers for biomedical applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2005, 73A, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gall, K.; Dunn, M.L.; Greenberg, A.R.; Diani, J. Thermomechanics of shape memory polymers: Uniaxial experiments and constitutive modeling. Int. J. Plast. 2006, 22, 279–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakacki, C.M.; Shandas, R.; Lanning, C.; Rech, B.; Eckstein, A.; Gall, K. Unconstrained recovery characterization of shape-memory polymer networks for cardiovascular applications. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 2255–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.J.; Nguyen, T.D.; Castro, F.; Yakacki, C.M.; Shandas, R. Finite deformation thermo-mechanical behavior of thermally induced shape memory polymers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2008, 56, 1730–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Lagoudas, D.C. A constitutive theory for shape memory polymers. Part I. Large deformations. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2008, 56, 1752–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Jerry Qi, H.; Castro, F.; Long, K.N. A thermoviscoelastic model for amorphous shape memory polymers: Incorporating structural and stress relaxation. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2008, 56, 2792–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boatti, E.; Scalet, G.; Auricchio, F. A three-dimensional finite-strain phenomenological model for shape-memory polymers: Formulation, numerical simulations, and comparison with experimental data. Int. J. Plast. 2016, 83, 153–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, G. Constitutive modeling of shape memory polymer based self-healing syntactic foam. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2010, 47, 1306–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xu, W. Thermomechanical behavior of thermoset shape memory polymer programmed by cold-compression: Testing and constitutive modeling. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2011, 59, 1231–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyce, M.C.; Weber, G.G.; Parks, D.M. On the kinematics of finite strain plasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1989, 37, 647–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Li, G. Thermoviscoplastic modeling and testing of shape memory polymer based self-healing syntactic foam programmed at glassy temperature. J. Appl. Mech. Trans. ASME 2011, 78, 061017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, M.; Friess, F.; Krus, M.; Zolanvari, S.M.H.; Grün, G.; Kröber, H.; Pretsch, T. Shape memory polymer foam with programmable apertures. Polymers 2020, 12, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstrom, J.S. Mechanics of Solid Polymers: Theory and Computational Modeling; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 393–409. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; John, M. A self-healing smart syntactic foam under multiple impacts. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 3337–3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Nettles, D. Thermomechanical characterization of a shape memory polymer based self-repairing syntactic foam. Polymer 2010, 51, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascon, J.P.; Coda, H.B. Finite deformation analysis of visco-hyperelastic materials via solid tetrahedral finite elements. Finite Elem. Anal. Des. 2017, 133, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swetha, C.; Kumar, R. Quasi-static uni-axial compression behaviour of hollow glass microspheres/epoxy based syntactic foams. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 4152–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, E.M.; Boyce, M.C. A three-dimensional constitutive model for the large stretch behavior of rubber elastic materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 1993, 41, 389–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simo, J.C.; Taylor, R.L.; Pister, K.S. Variational and projection methods for the volume constraint in finite deformation elasto-plasticity. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1985, 51, 177–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, H. Viscosity, plasticity, and diffusion as examples of absolute reaction rates. J. Chem. Phys. 1936, 4, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tool, A.Q. Relation between inelastic deformation and thermal expansion of glass in its annealing range. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1946, 29, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, J.; Maitland, D.; Wilson, T.; Tsai, W.; Savaş, Ö.; Saloner, D. Vascular dynamics of a shape memory polymer foam aneurysm treatment technique. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 52, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Du, H.Y.; Liu, L.W.; Leng, J. Shape memory polymers and their composites in aerospace applications: A review. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 023001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.M.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, B.K. Shape memory polyurethane foams. Express Polym. Lett. 2012, 6, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Jang, M.K.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, B.K. Shape memory effects of molded flexible polyurethane foam. Smart Mater. Struct. 2007, 16, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domeier, L.; Nissen, A.; Goods, S.; Whinnery, L.; McElhanon, J. Thermomechanical characterization of thermoset urethane shape-memory polymer foams. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 3217–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neilsen, M.; Lu, W.Y.; Olsson, B.; Hinnerichs, T. A viscoplastic constitutive model for polyurethane foams. In Proceedings of the ASME 2006 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Chicago, IL, USA, 5–10 November 2006; Volume 14551, pp. 301–307. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Ricci, W. Comparison of compressive properties of layered syntactic foams having gradient in microballoon volume fraction and wall thickness. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2006, 427, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matter, S.; Gurevitch, I.; Silverstein, M.S. Shape memory polymer foams from emulsion templating. Soft Matter 2012, 40, 10378–10387. [Google Scholar]
- De Nardo, L.; Alberti, R.; Cigada, A.; Yahia, L.H.; Cristina, M.; Fare, S. Shape memory polymer foams for cerebral aneurysm reparation: Effects of plasma sterilization on physical properties and cytocompatibility. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1508–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hearon, K.; Singhal, P.; Horn, J.; Small, W.; Olsovsky, C.; Maitland, K.C.; Wilson, T.S.; Maitland, D.J. Porous shape-memory polymers. Polym. Rev. 2013, 53, 41–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andresen, T.; Bahr, C.; Ciranna-Raab, C. Efficacy of osteopathy and other manual treatment approaches for malocclusion–A systematic review of evidence. Int. J. Osteopath. Med. 2013, 16, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, P.; Abdelal, G.; Goel, S. FE Simulation of Viscoplastic Consistency Model. In Proceedings of the RAS 4th Aircraft Structural Design Conference, Belfast, UK, 7–9 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Z.H.; Yuan, M.W.; Gao, C.Y. FE Realization of a Thermo-Visco-Plastic Constitutive Model using VUMAT in ABAQUS/Explicit Program. In Computational Mechanics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; p. 301. [Google Scholar]
- Hibbitte, K. ABAQUS User Subroutines Reference Manual; Hks Inc.: Dallas, TX, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Nano/microstructures of shape memory polymers: From materials to applications. Nanoscale Horiz. 2020, 5, 1155–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedayati, R.; Ziaei-Rad, S. Effect of bird geometry and orientation on bird-target impact analysis using SPH method. Int. J. Crashworthiness 2012, 17, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

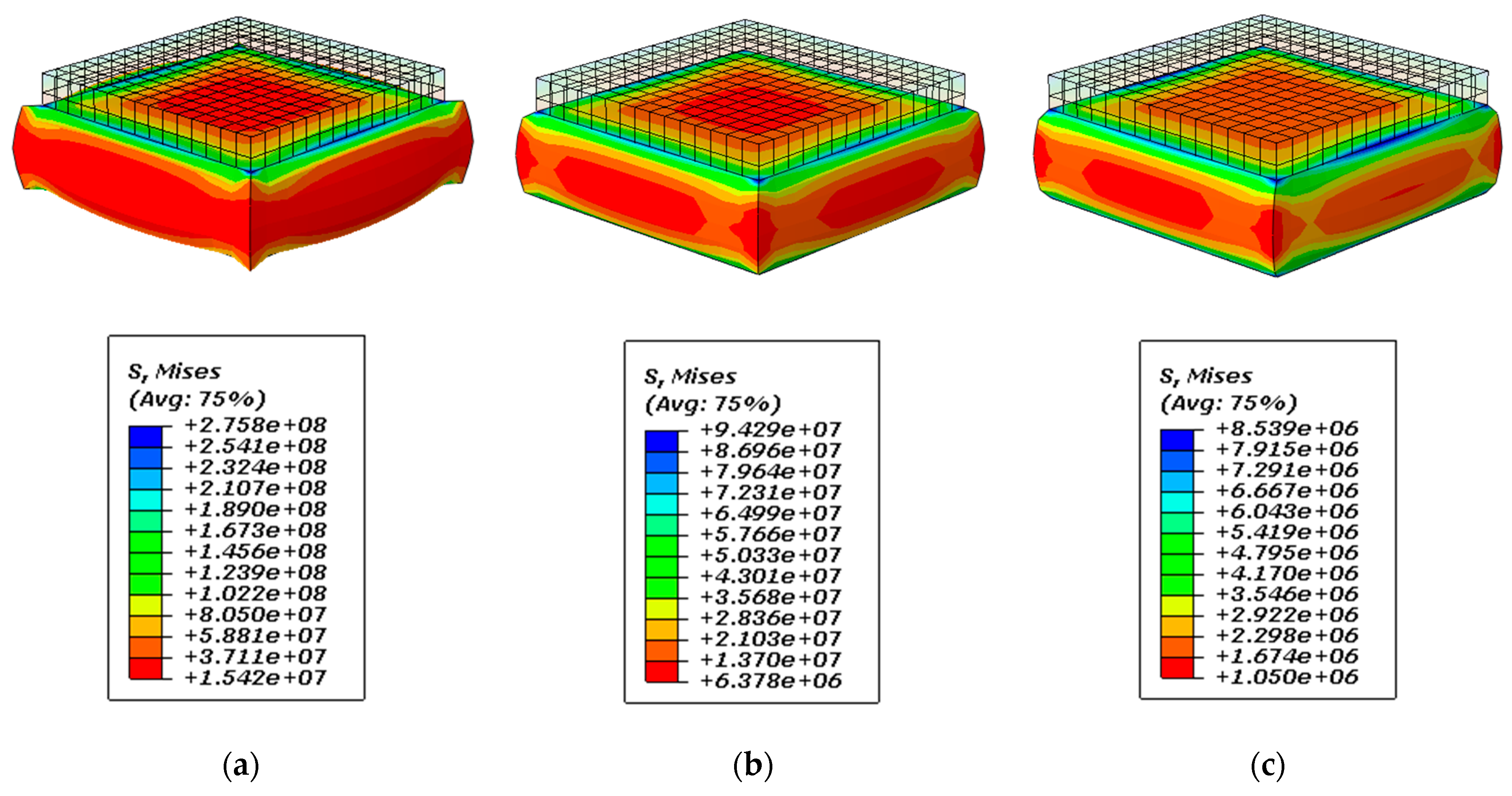
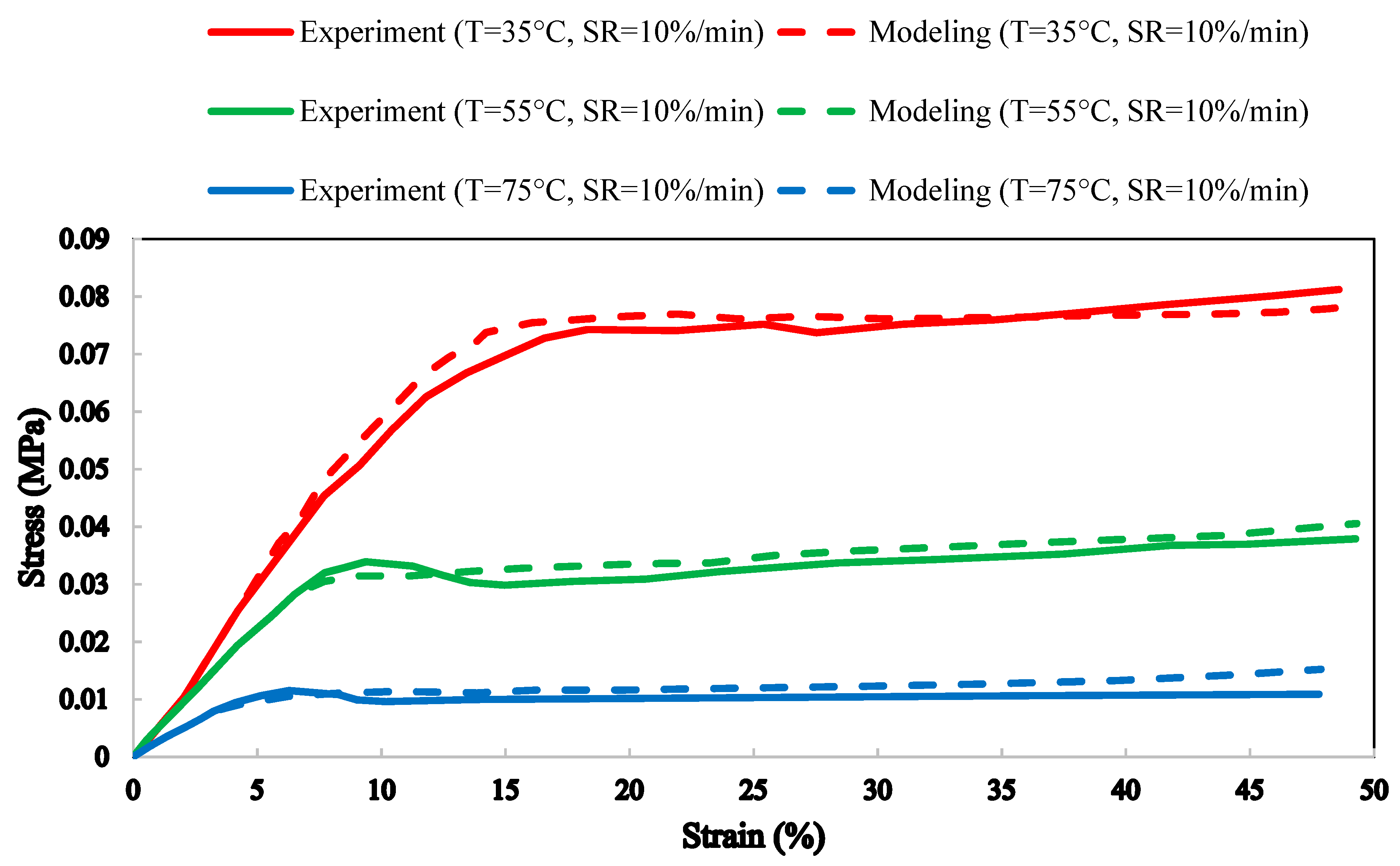

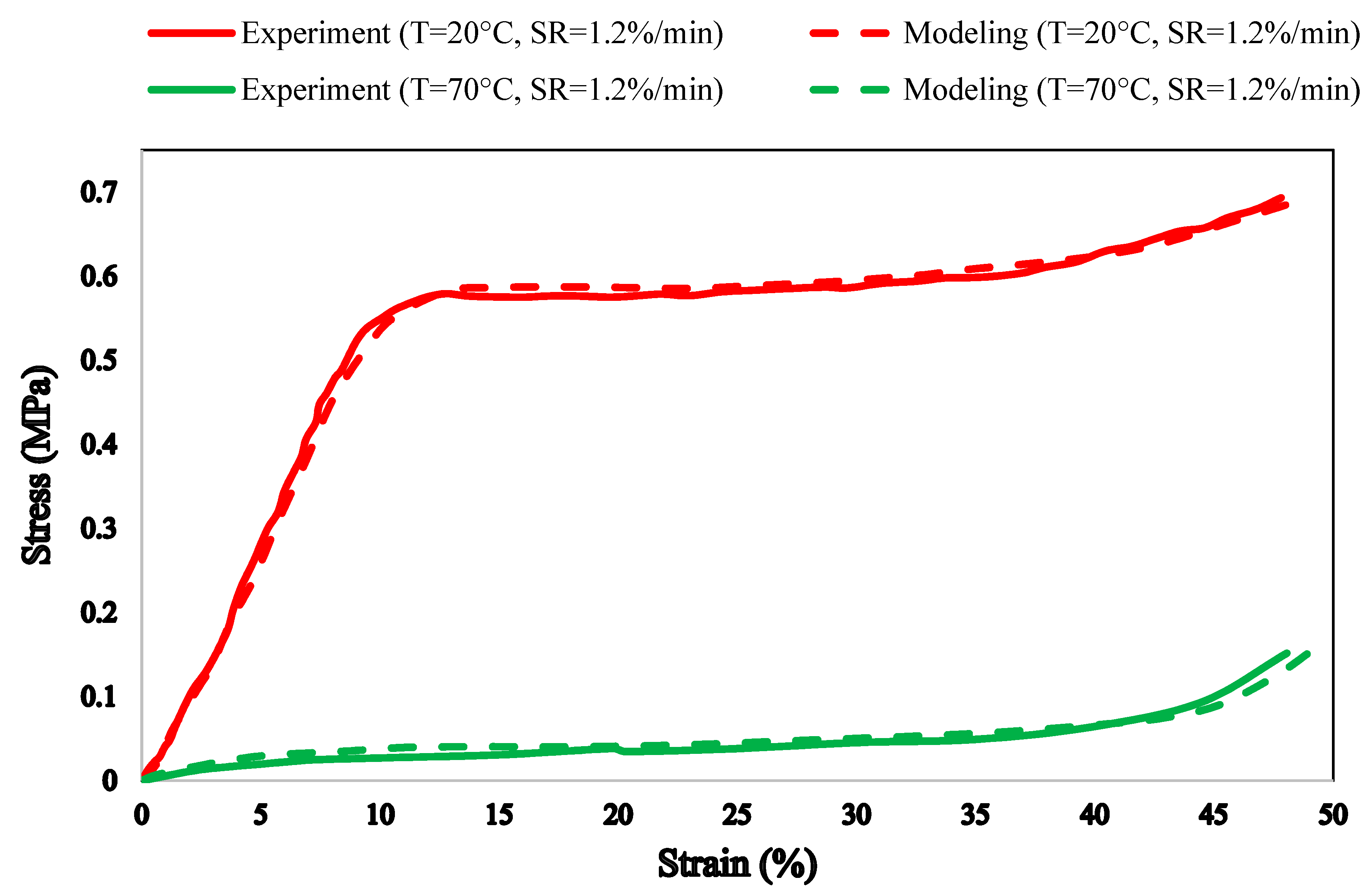
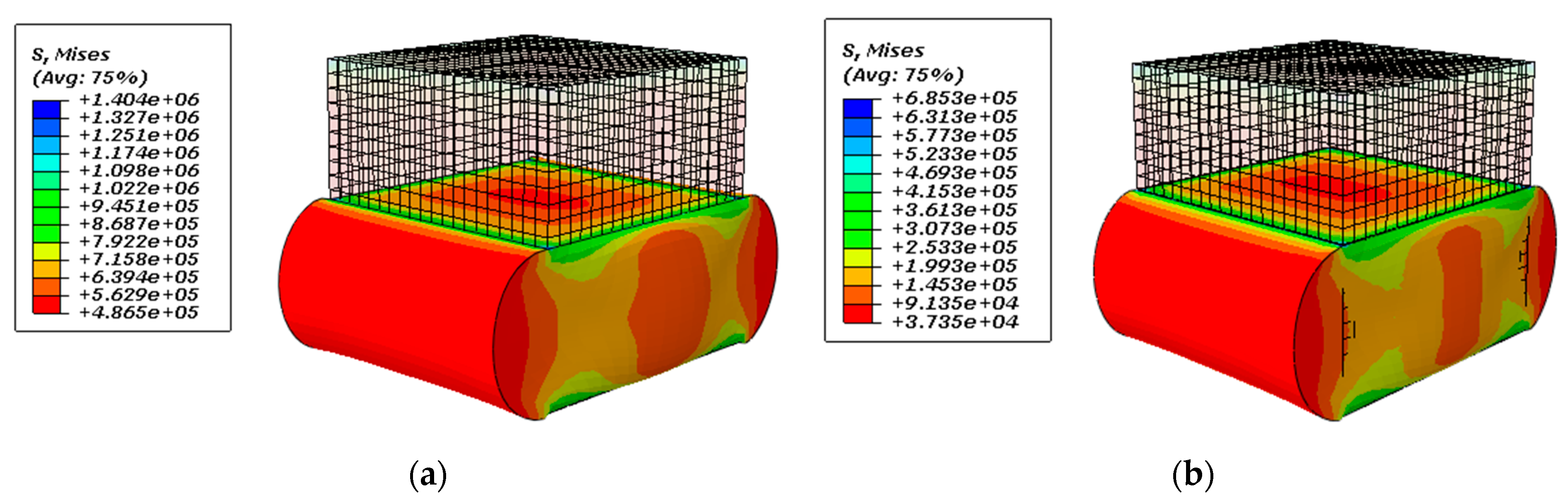
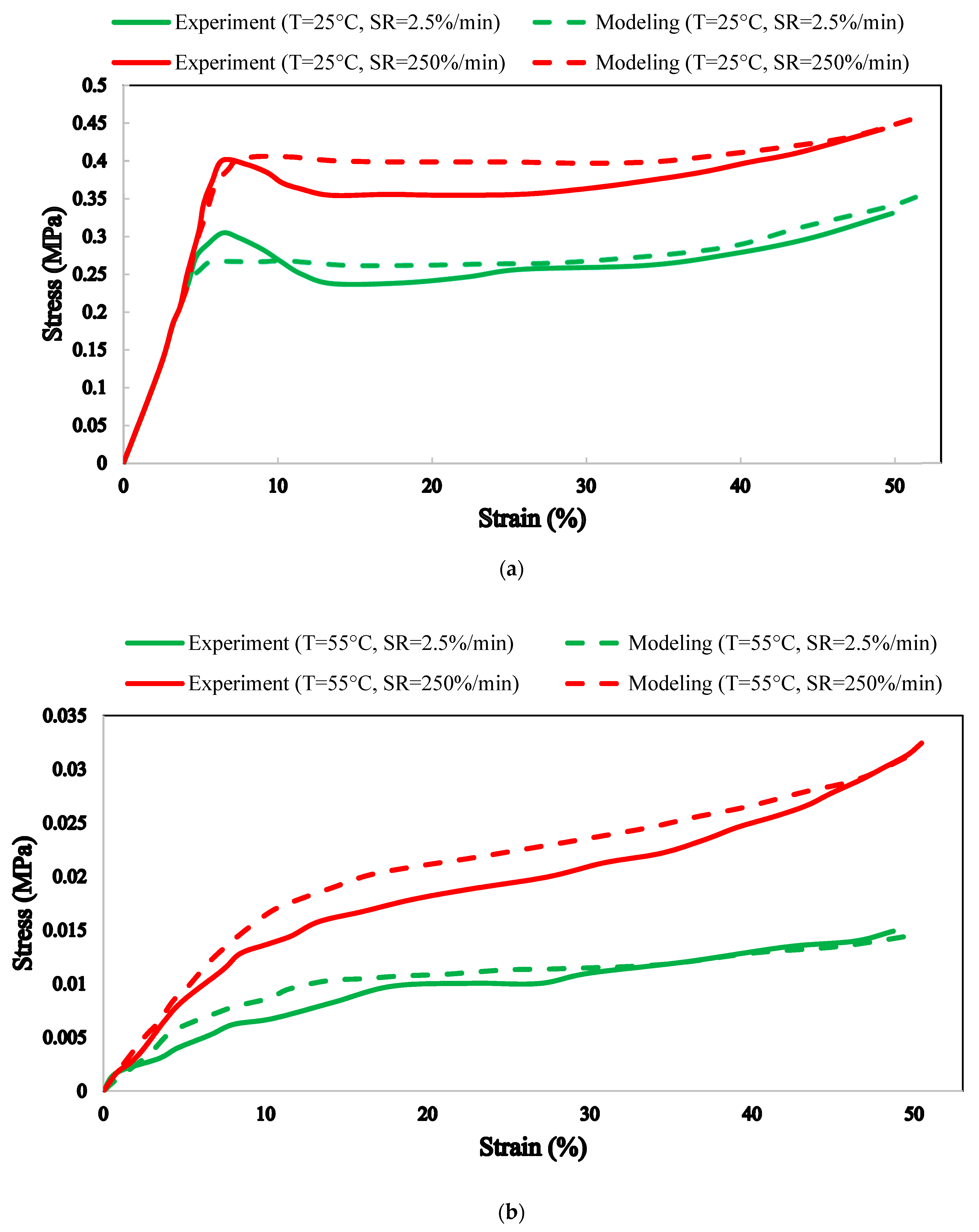

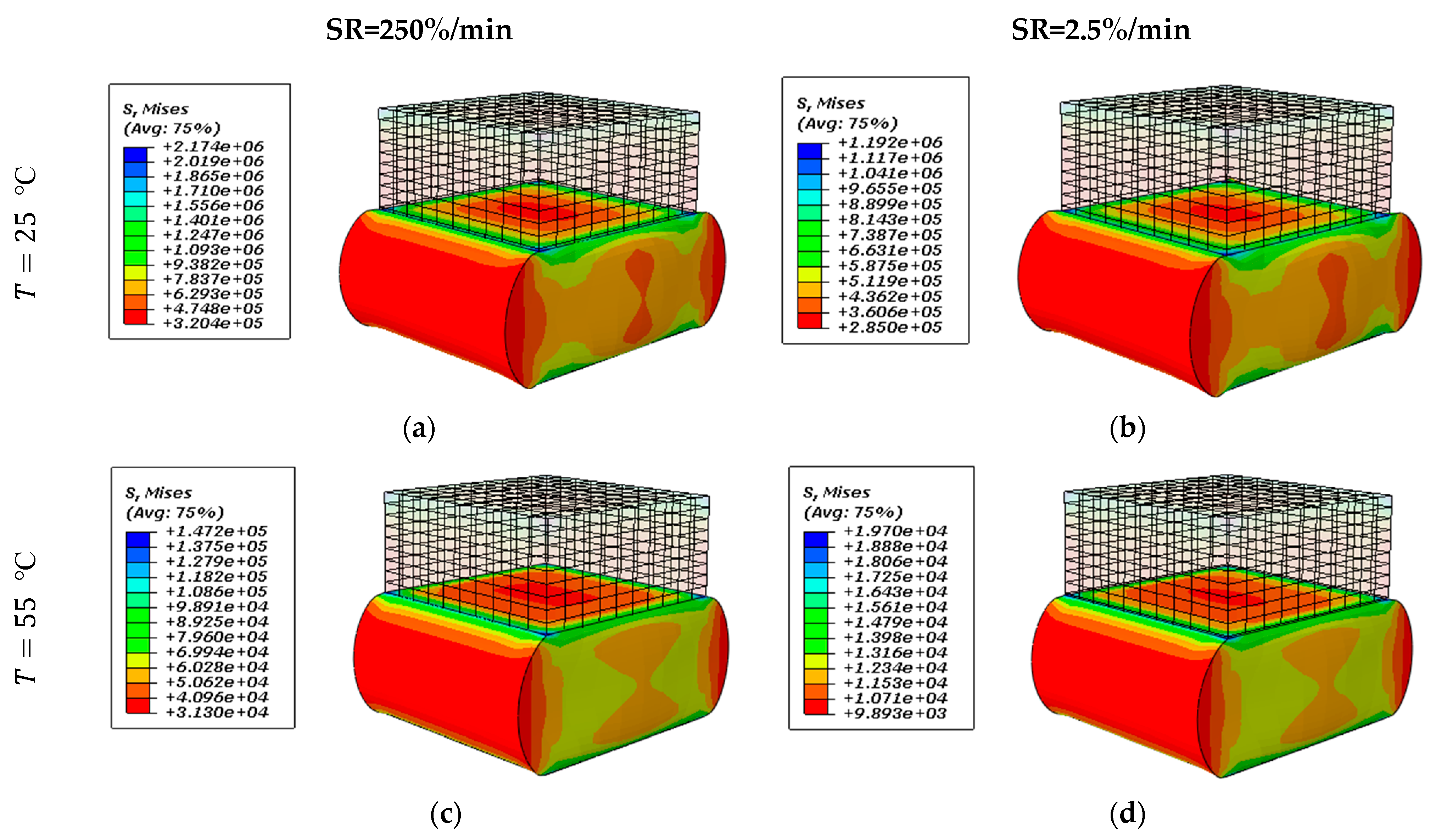
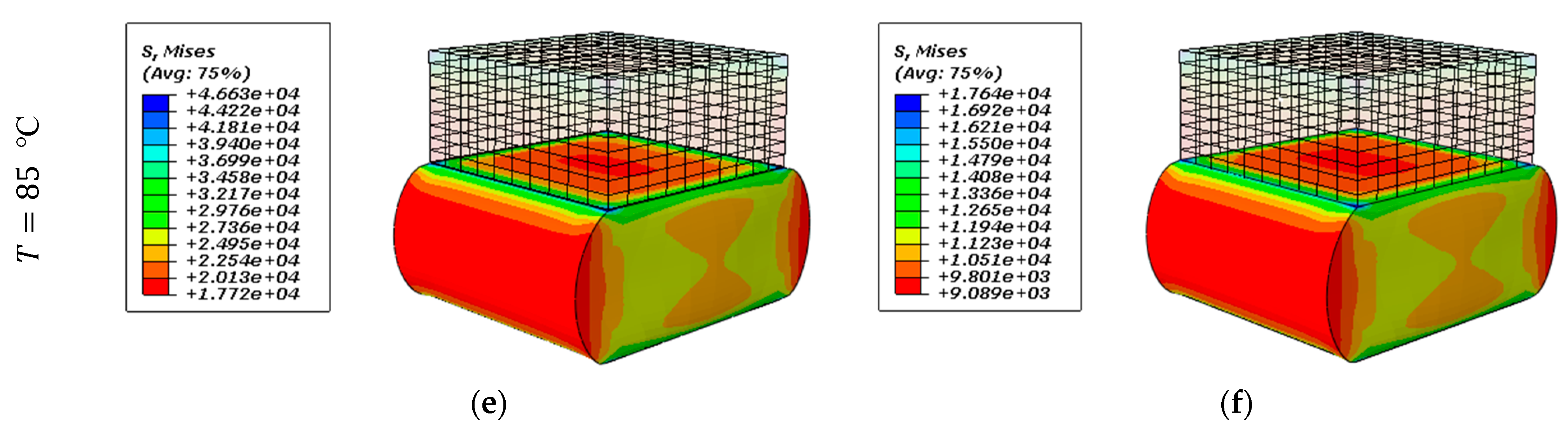
| Parameter | Veriflex [33] | PU-I | PU-II | PU-III | Parameter | Veriflex [33] | PU-I | PU-II | PU-III |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 62 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 | ||
| 25 | 25 | 25 | 25 | h (MPa) | 200 | 200 | 126 | 126 | |
| 80 | 75 | 85 | 85 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 | ||
| 63 | 59 | 57 | 57 | 23 | 0.58 | 0.42 | 0.08 | ||
| (Poisson’s ratio) | 0.33 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 20 | 0.55 | 0.38 | 0.071 | |
| (%) | 60 | 91 | 88 | 92 | (°K/MPa) | 800 | 800 | 650 | 650 |
| 96.4 | 22.4 | 7.5 | 7.3 | 5.062 | 5.062 | 5.062 | 5.062 | ||
| 17.3 | 29 | 20 | 20 | 6.841 | 6.841 | 6.841 | 6.841 | ||
| 70 | 44 | 31 | 31 | 140 | 135 | 130 | 130 | ||
| 4050 | 1973 | 1684 | 1851 | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| (s) | 20 | 76 | 90 | 93 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.02 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.95 | 0.019 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 1000 | 8.4 | 4.25 | 4.25 | Dimensions | Cube | Cylinder | |||
| Length (mm) | Diameter (mm) | ||||||||
| 30 | 50 | 20 | 15 | ||||||
| 385.7 | 6.6 | 3.98 | 3.98 | Width (mm) | Length (mm) | ||||
| 30 | 50 | 20 | 10 | ||||||
| Height (mm) | |||||||||
| 12.5 | 50 | 20 | |||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jarrah, H.R.; Zolfagharian, A.; Hedayati, R.; Serjouei, A.; Bodaghi, M. Nonlinear Finite Element Modelling of Thermo-Visco-Plastic Styrene and Polyurethane Shape Memory Polymer Foams. Actuators 2021, 10, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10030046
Jarrah HR, Zolfagharian A, Hedayati R, Serjouei A, Bodaghi M. Nonlinear Finite Element Modelling of Thermo-Visco-Plastic Styrene and Polyurethane Shape Memory Polymer Foams. Actuators. 2021; 10(3):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10030046
Chicago/Turabian StyleJarrah, Hamid Reza, Ali Zolfagharian, Reza Hedayati, Ahmad Serjouei, and Mahdi Bodaghi. 2021. "Nonlinear Finite Element Modelling of Thermo-Visco-Plastic Styrene and Polyurethane Shape Memory Polymer Foams" Actuators 10, no. 3: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10030046
APA StyleJarrah, H. R., Zolfagharian, A., Hedayati, R., Serjouei, A., & Bodaghi, M. (2021). Nonlinear Finite Element Modelling of Thermo-Visco-Plastic Styrene and Polyurethane Shape Memory Polymer Foams. Actuators, 10(3), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/act10030046










