Comparative Analysis of Infection by Rickettsia rickettsii Sheila Smith and Taiaçu Strains in a Murine Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Signs and Survival Curve of C3H/HeN after Challenge with R. rickettsii
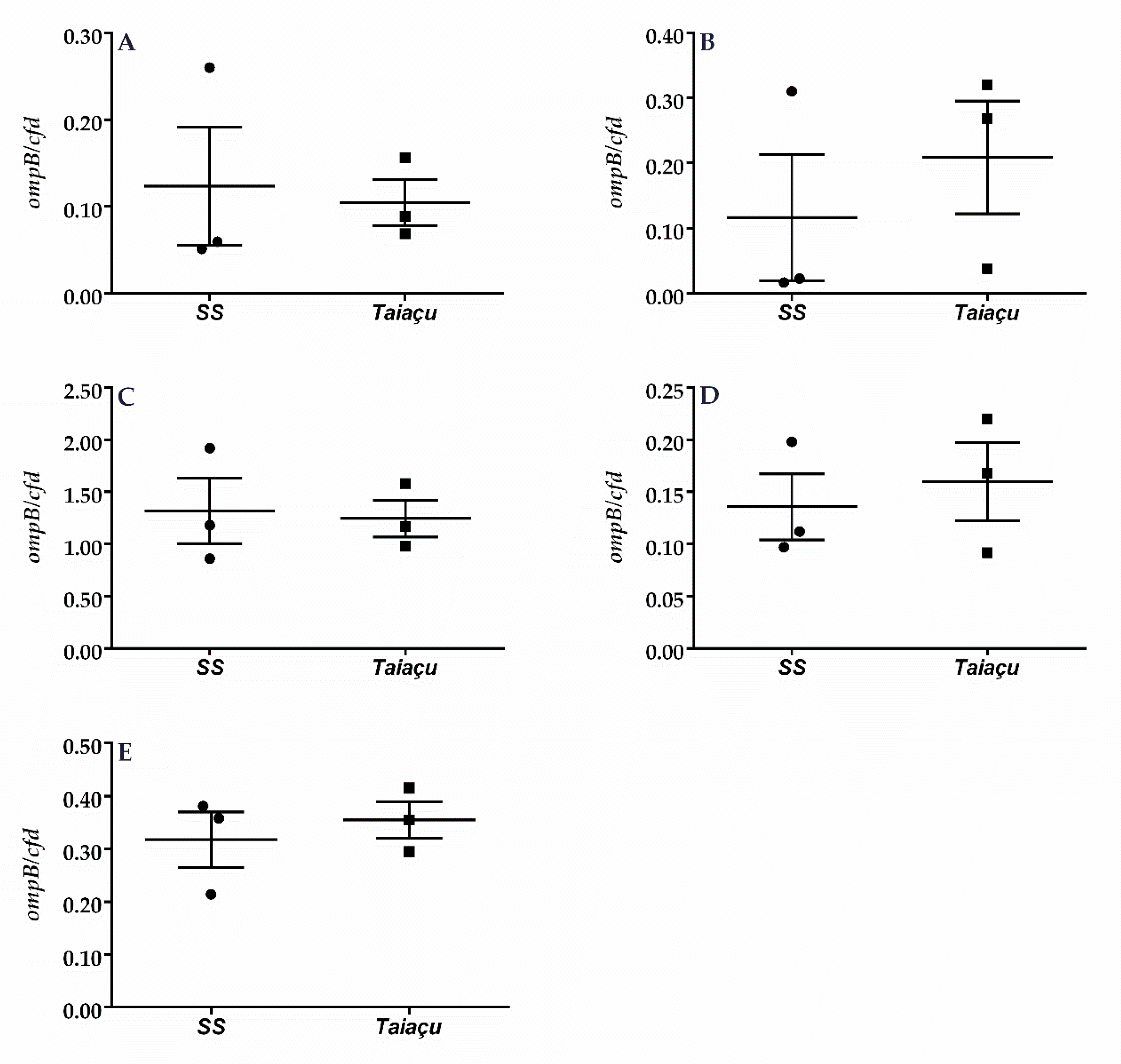
2.2. Dermination of R. rickettsii Load in C3H/HeN
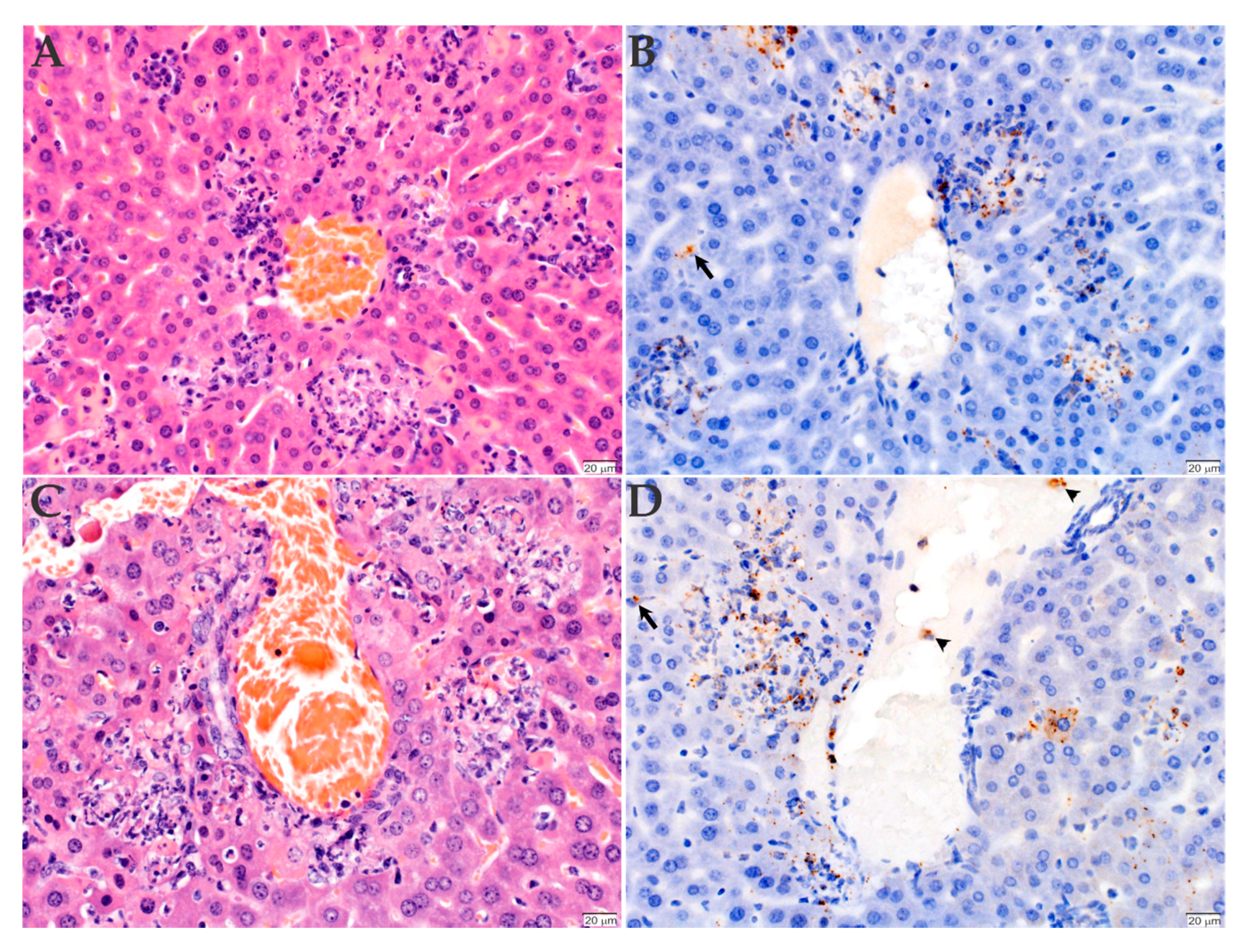
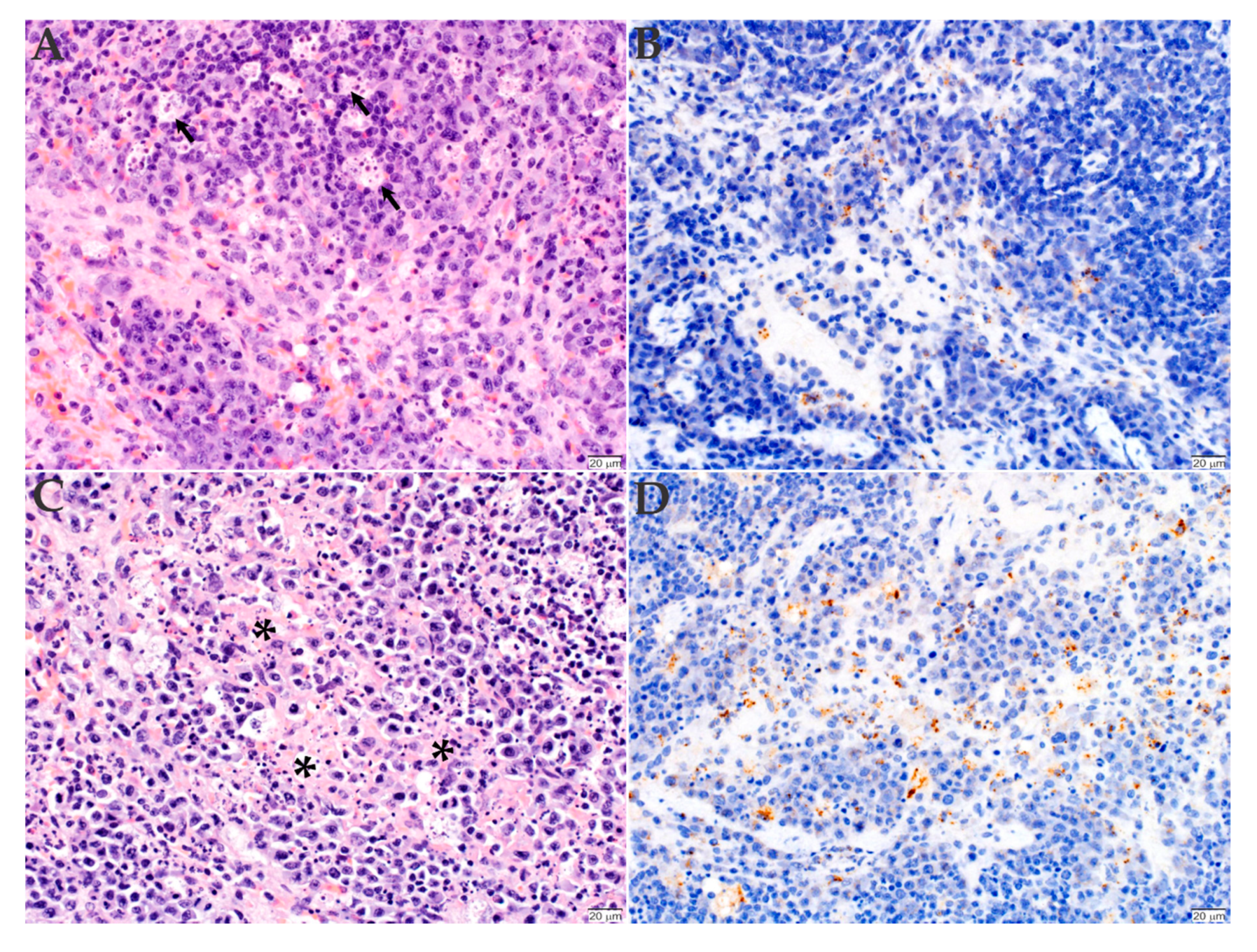
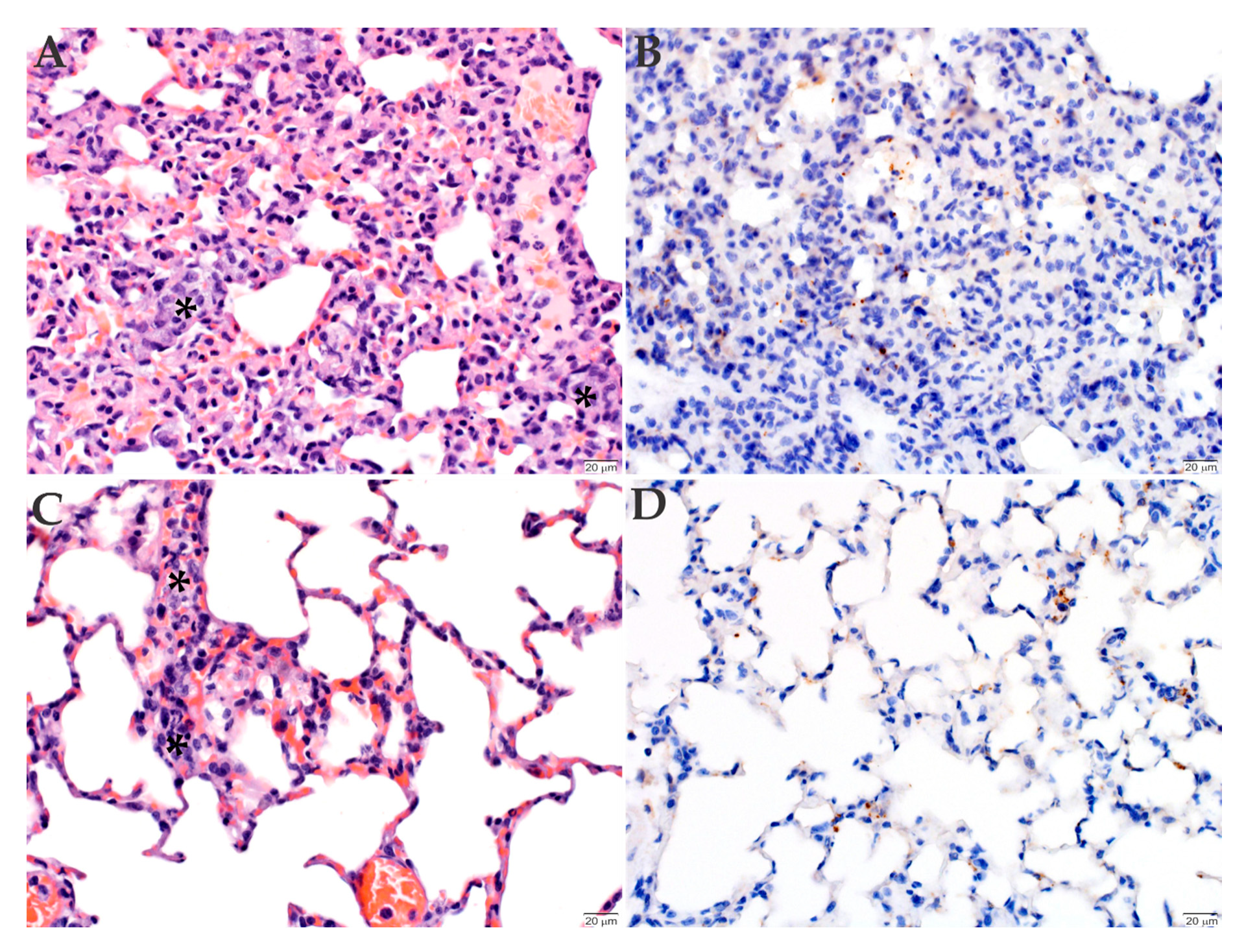
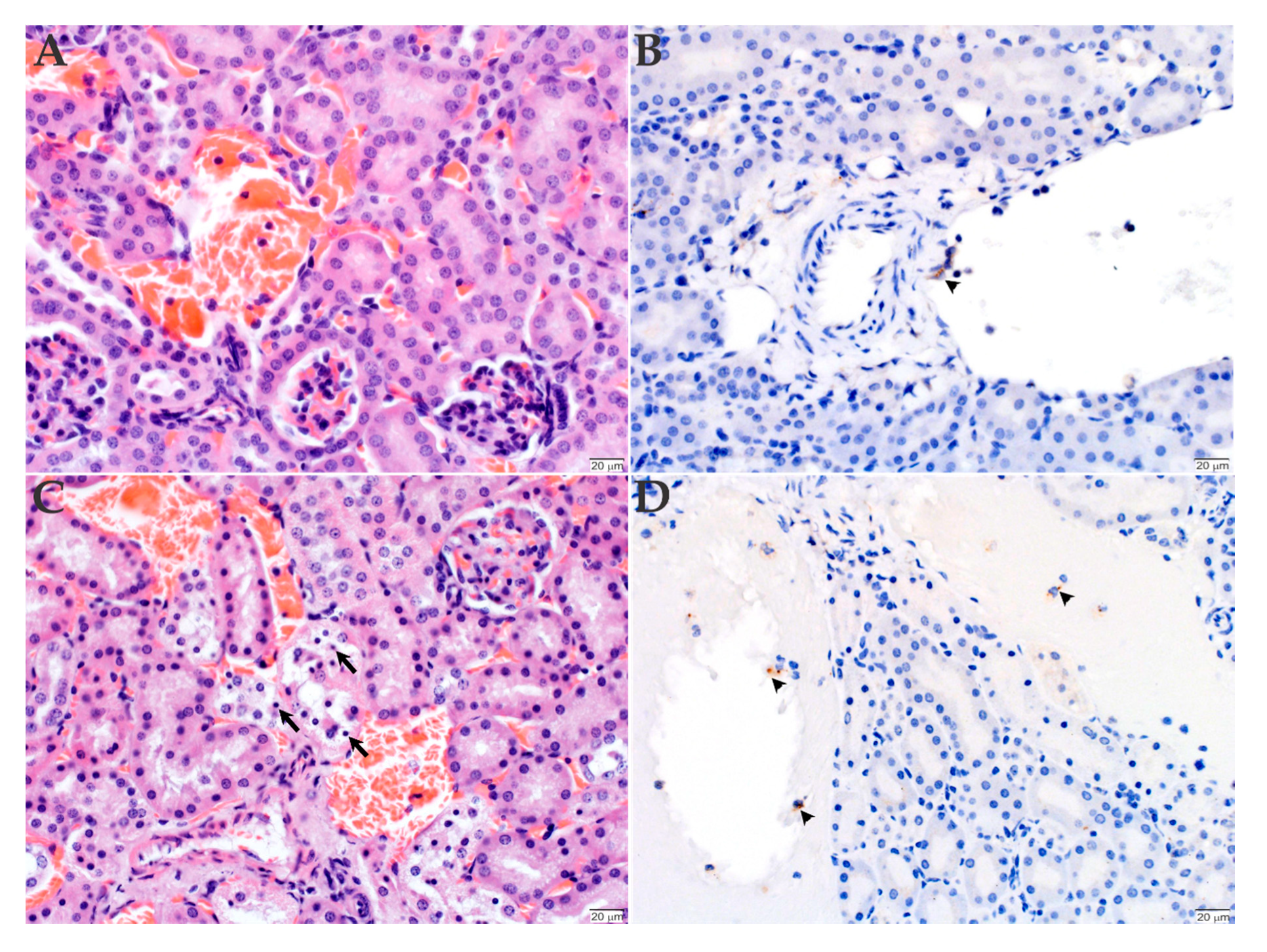
2.3. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry Analyses of the Organs Infected with R. rickettsii
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. R. rickettsii Cultivation and Purification
4.2. Murine Infections
4.3. DNA Extraction and Determination of R. rickettsii Load
4.4. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fang, R.; Blanton, L.S.; Walker, D.H. Rickettsiae as Emerging Infectious Agents. Clin. Lab. Med. 2017, 37, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas-Torres, F.; Chomel, B.B.; Otranto, D. Ticks and tick-borne diseases: A One Health perspective. Trends Parasitol. 2012, 28, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitschwerdt, E.B.; Hegarty, B.C.; Maggi, R.G.; Lantos, P.M.; Aslett, D.M.; Bradley, J.M. Rickettsia rickettsii transmission by a lone star tick, North Carolina. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 873–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demma, L.J.; Traeger, M.S.; Nicholson, W.L.; Paddock, C.D.; Blau, D.M.; Eremeeva, M.E.; Dasch, G.A.; Levin, M.L.; Singleton, J., Jr.; Zaki, S.R.; et al. Rocky Mountain spotted fever from an unexpected tick vector in Arizona. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, S.; Beati, L.; Labruna, M.B.; Caceres, A.G.; Mangold, A.J.; Guglielmone, A.A. Reassessment of the taxonomic status of Amblyomma cajennense with the description of three new species, Amblyomma tonelliae n. sp., Amblyomma interandinum n. sp. and Amblyomma patinoi n. sp., and reinstatement of Amblyomma mixtum, and Amblyomma sculptum (Ixodida: Ixodidae). Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2014, 5, 252–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labruna, M.B. Ecology of rickettsia in South America. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1166, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs, J.E.; Paddock, C.D. Section II: Tick-Borne Rickettsioses–Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. In Rickettsial Diseases; Raoult, D., Parola, P., Eds.; Informa Health Care: New York, NY, USA, 2007; p. 379. [Google Scholar]
- Dantas-Torres, F. Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greca, H.; Langoni, H.; Souza, L.C. Brazilian spotted fever: A reemergent zoonosis. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2008, 14, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Walker, D.H.; Crawford, C.G.; Cain, B.G. Rickettsial infection of the pulmonary microcirculation: The basis for interstitial pneumonitis in Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Hum. Pathol. 1980, 11, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.S.; Walker, D.H. The liver in Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1981, 75, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.L.; Patrick, J.D.; Miller, L.R. Evaluation of immunoperoxidase techniques to detect Rickettsia rickettsii in fixed tissue sections. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1994, 101, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.H.; Yu, X.-J. Rickettsia and Rickettsial Diseases. In Bioterrorism; Morse, S., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.H. Rickettsiae and rickettsial infections: The current state of knowledge. Clin. Infect. Dis 2007, 45, S39–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenberg, R.; Lindsey, N.P.; Fischer, M.; Gregory, C.J.; Hinckley, A.F.; Mead, P.S.; Paz-Bailey, G.; Waterman, S.H.; Drexler, N.A.; Kersh, G.J.; et al. Vital Signs: Trends in Reported Vectorborne Disease Cases —United States and Territories, 2004–2016. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2018, 67, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- saude.gov.br. Available online: https://www.saude.gov.br/images/pdf/2019/junho/14/Casos-de-Febre-Maculosa.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2020).
- Labruna, M.B.; Santos, F.C.; Ogrzewalska, M.; Nascimento, E.M.; Colombo, S.; Marcili, A.; Angerami, R.N. Genetic identification of rickettsial isolates from fatal cases of Brazilian spotted fever and comparison with Rickettsia rickettsii isolates from the American continents. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 3788–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paddock, C.D.; Denison, A.M.; Lash, R.R.; Liu, L.; Bollweg, B.C.; Dahlgren, F.S.; Kanamura, C.T.; Angerami, R.N.; Pereira dos Santos, F.C.; Brasil Martines, R.; et al. Phylogeography of Rickettsia rickettsii genotypes associated with fatal Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 91, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- saude.sp.gov.br. Available online: http://www.saude.sp.gov.br/resources/cve-centro-de-vigilancia-epidemiologica/areas-de-vigilancia/doencas-de-transmissao-por-vetores-e-zoonoses/dados/fmaculosa/fmb0720_cautoctone_ano_evol.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2020).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/rmsf/doxycycline/index.html (accessed on 14 August 2020).
- Riley, S.P.; Cardwell, M.M.; Chan, Y.G.; Pruneau, L.; Del Piero, F.; Martinez, J.J. Failure of a heterologous recombinant Sca5/OmpB protein-based vaccine to elicit effective protective immunity against Rickettsia rickettsii infections in C3H/HeN mice. Pathog. Dis. 2015, 73, ftv101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xiong, X.; Jiao, J.; Yang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Wen, B.; Gong, W. Th1 epitope peptides induce protective immunity against Rickettsia rickettsii infection in C3H/HeN mice. Vaccine 2017, 35, 7204–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Qi, Y.; Xiong, X.; Jiao, J.; Duan, C.; Wen, B. Rickettsia rickettsii outer membrane protein YbgF induces protective immunity in C3H/HeN mice. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2015, 11, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Wang, P.; Xiong, X.; Jiao, J.; Yang, X.; Wen, B. Enhanced protection against Rickettsia rickettsii infection in C3H/HeN mice by immunization with a combination of a recombinant adhesin rAdr2 and a protein fragment rOmpB-4 derived from outer membrane protein B. Vaccine 2015, 33, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Xiong, X.; Qi, Y.; Jiao, J.; Duan, C.; Wen, B. Surface protein Adr2 of Rickettsia rickettsii induced protective immunity against Rocky Mountain spotted fever in C3H/HeN mice. Vaccine 2014, 32, 2027–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, E.; Bizzarro, B.; Costa, F.B.; Ramirez-Hernandez, A.; Peti, A.P.F.; Cataneo, A.H.D.; Wowk, P.F.; Timoteo, R.P.; Labruna, M.B.; Silva Junior, P.I.; et al. Amblyomma sculptum Salivary PGE2 Modulates the Dendritic Cell-Rickettsia rickettsii Interactions in vitro and in vivo. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, E.J.; Pickens, E.G. A toxic substance associated with the rickettsias of the spotted fever group. J. Immunol. 1953, 70, 461–472. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, J.V.; Walker, D.H. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Rickettsia rickettsii. Infect. Immun. 1984, 46, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anacker, R.L.; Philip, R.N.; Williams, J.C.; List, R.H.; Mann, R.E. Biochemical and immunochemical analysis of Rickettsia rickettsii strains of various degrees of virulence. Infect. Immun. 1984, 44, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, T.R.; Noriea, N.F.; Bublitz, D.C.; Ellison, D.W.; Martens, C.; Lutter, E.I.; Hackstadt, T. Comparative genome sequencing of Rickettsia rickettsii strains that differ in virulence. Infect. Immun. 2015, 83, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, W.H. The epidemiology of Rocky Mountain spotted fever. I. The characterization of strain virulence of Rickettsia rickettsii. Am. J. Hyg. 1953, 58, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahni, A.; Fang, R.; Sahni, S.K.; Walker, D.H. Pathogenesis of Rickettsial Diseases: Pathogenic and Immune Mechanisms of an Endotheliotropic Infection. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2019, 14, 127–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpathy, S.E.; Dasch, G.A.; Eremeeva, M.E. Molecular typing of isolates of Rickettsia rickettsii by use of DNA sequencing of variable intergenic regions. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 2545–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremeeva, M.E.; Dasch, G.A. Closing the gaps between genotype and phenotype in Rickettsia rickettsii. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1166, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremeeva, M.E.; Klemt, R.M.; Santucci-Domotor, L.A.; Silverman, D.J.; Dasch, G.A. Genetic analysis of isolates of Rickettsia rickettsii that differ in virulence. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 990, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, H.R. Cultivation of Rickettsiae of the Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever, Typhus and Q Fever Groups in the Embryonic Tissues of Developing Chicks. Science 1941, 94, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellison, D.W.; Clark, T.R.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Virtaneva, K.; Porcella, S.F.; Hackstadt, T. Genomic comparison of virulent Rickettsia rickettsii Sheila Smith and avirulent Rickettsia rickettsii Iowa. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Walker, D.H. rOmpA is a critical protein for the adhesion of Rickettsia rickettsii to host cells. Microb. Pathog. 1998, 24, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noriea, N.F.; Clark, T.R.; Hackstadt, T. Targeted knockout of the Rickettsia rickettsii OmpA surface antigen does not diminish virulence in a mammalian model system. mBio 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackstadt, T.; Messer, R.; Cieplak, W.; Peacock, M.G. Evidence for proteolytic cleavage of the 120-kilodalton outer membrane protein of rickettsiae: Identification of an avirulent mutant deficient in processing. Infect. Immun. 1992, 60, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstrom, P.; Burke, T.P.; Mitchell, G.; Ingabire, N.; Mark, K.G.; Golovkine, G.; Iavarone, A.T.; Rape, M.; Cox, J.S.; Welch, M.D. Evasion of autophagy mediated by Rickettsia surface protein OmpB is critical for virulence. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 2538–2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdad, M.Y.; Abou Abdallah, R.; Fournier, P.E.; Stenos, J.; Vasoo, S. A Concise Review of the Epidemiology and Diagnostics of Rickettsioses: Rickettsia and Orientia spp. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, R.R.; Parker, R.R. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever: Infectivity of fasting and recently fed ticks. Public Health Rep. 1923, 38, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Policastro, P.F.; Munderloh, U.G.; Fischer, E.R.; Hackstadt, T. Rickettsia rickettsii growth and temperature-inducible protein expression in embryonic tick cell lines. J. Med. Microbiol. 1997, 46, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilford, J.H.; Price, W.H. VIRULENT-AVIRULENT CONVERSIONS OF Rickettsia rickettsii IN VITRO. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1955, 41, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, S.F.; Burgdorfer, W. Reactivation of Rickettsia rickettsii in Dermacentor andersoni ticks: An ultrastructural analysis. Infect. Immun. 1982, 37, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galletti, M.F.; Fujita, A.; Nishiyama, M.Y., Jr.; Malossi, C.D.; Pinter, A.; Soares, J.F.; Daffre, S.; Labruna, M.B.; Fogaca, A.C. Natural blood feeding and temperature shift modulate the global transcriptional profile of Rickettsia rickettsii infecting its tick vector. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galletti, M.F.; Fujita, A.; Rosa, R.D.; Martins, L.A.; Soares, H.S.; Labruna, M.B.; Daffre, S.; Fogaca, A.C. Virulence genes of Rickettsia rickettsii are differentially modulated by either temperature upshift or blood-feeding in tick midgut and salivary glands. Parasit. Vectors 2016, 9, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, D.W.; Clark, T.R.; Sturdevant, D.E.; Virtaneva, K.; Hackstadt, T. Limited transcriptional responses of Rickettsia rickettsii exposed to environmental stimuli. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sela, U.; Euler, C.W.; Correa da Rosa, J.; Fischetti, V.A. Strains of bacterial species induce a greatly varied acute adaptive immune response: The contribution of the accessory genome. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labruna, M.B.; Ogrzewalska, M.; Martins, T.F.; Pinter, A.; Horta, M.C. Comparative susceptibility of larval stages of Amblyomma aureolatum, Amblyomma cajennense, and Rhipicephalus sanguineus to infection by Rickettsia rickettsii. J. Med. Entomol. 2008, 45, 1156–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.A.; Galletti, M.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Fujita, A.; Costa, F.B.; Labruna, M.B.; Daffre, S.; Fogaca, A.C. The Distinct Transcriptional Response of the Midgut of Amblyomma sculptum and Amblyomma aureolatum Ticks to Rickettsia rickettsii Correlates to Their Differences in Susceptibility to Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavanelo, D.B.; Schroder, N.C.H.; Pin Viso, N.D.; Martins, L.A.; Malossi, C.D.; Galletti, M.; Labruna, M.B.; Daffre, S.; Farber, M.; Fogaca, A.C. Comparative analysis of the midgut microbiota of two natural tick vectors of Rickettsia rickettsii. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2020, 106, 103606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerardi, M.; Ramirez-Hernandez, A.; Binder, L.C.; Krawczak, F.S.; Gregori, F.; Labruna, M.B. Comparative Susceptibility of Different Populations of Amblyomma sculptum to Rickettsia rickettsii. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, J.F.; Soares, H.S.; Barbieri, A.M.; Labruna, M.B. Experimental infection of the tick Amblyomma cajennense, Cayenne tick, with Rickettsia rickettsii, the agent of Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Med. Vet. Entomol. 2012, 26, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, A.; Labruna, M.B. Isolation of Rickettsia rickettsii and Rickettsia bellii in cell culture from the tick Amblyomma aureolatum in Brazil. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1078, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, S.P.; Pruneau, L.; Martinez, J.J. Evaluation of changes to the Rickettsia rickettsii transcriptome during mammalian infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.G.; Riley, S.P.; Chen, E.; Martinez, J.J. Molecular basis of immunity to rickettsial infection conferred through outer membrane protein B. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 2303–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A Simple Method of Estimating Fifty per Cent Endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasperge, B.J.; Reif, K.E.; Morgan, T.D.; Sunyakumthorn, P.; Bynog, J.; Paddock, C.D.; Macaluso, K.R. Susceptibility of inbred mice to Rickettsia parkeri. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 1846–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, E.K.; Verhoeve, V.I.; Banajee, K.H.; Macaluso, J.A.; Azad, A.F.; Macaluso, K.R. Comparative vertical transmission of Rickettsia by Dermacentor variabilis and Amblyomma maculatum. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2017, 8, 598–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Esteves, E.; Fongsaran, C.; Langohr, I.M.; Riley, S.P.; Labruna, M.B.; Daffre, S.; Fogaça, A.C.; Macaluso, K.R. Comparative Analysis of Infection by Rickettsia rickettsii Sheila Smith and Taiaçu Strains in a Murine Model. Pathogens 2020, 9, 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090744
Esteves E, Fongsaran C, Langohr IM, Riley SP, Labruna MB, Daffre S, Fogaça AC, Macaluso KR. Comparative Analysis of Infection by Rickettsia rickettsii Sheila Smith and Taiaçu Strains in a Murine Model. Pathogens. 2020; 9(9):744. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090744
Chicago/Turabian StyleEsteves, Eliane, Chanida Fongsaran, Ingeborg M. Langohr, Sean P. Riley, Marcelo B. Labruna, Sirlei Daffre, Andréa C. Fogaça, and Kevin R. Macaluso. 2020. "Comparative Analysis of Infection by Rickettsia rickettsii Sheila Smith and Taiaçu Strains in a Murine Model" Pathogens 9, no. 9: 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090744
APA StyleEsteves, E., Fongsaran, C., Langohr, I. M., Riley, S. P., Labruna, M. B., Daffre, S., Fogaça, A. C., & Macaluso, K. R. (2020). Comparative Analysis of Infection by Rickettsia rickettsii Sheila Smith and Taiaçu Strains in a Murine Model. Pathogens, 9(9), 744. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9090744






