Comparative Pathology of Domestic Pigs and Wild Boar Infected with the Moderately Virulent African Swine Fever Virus Strain “Estonia 2014”
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
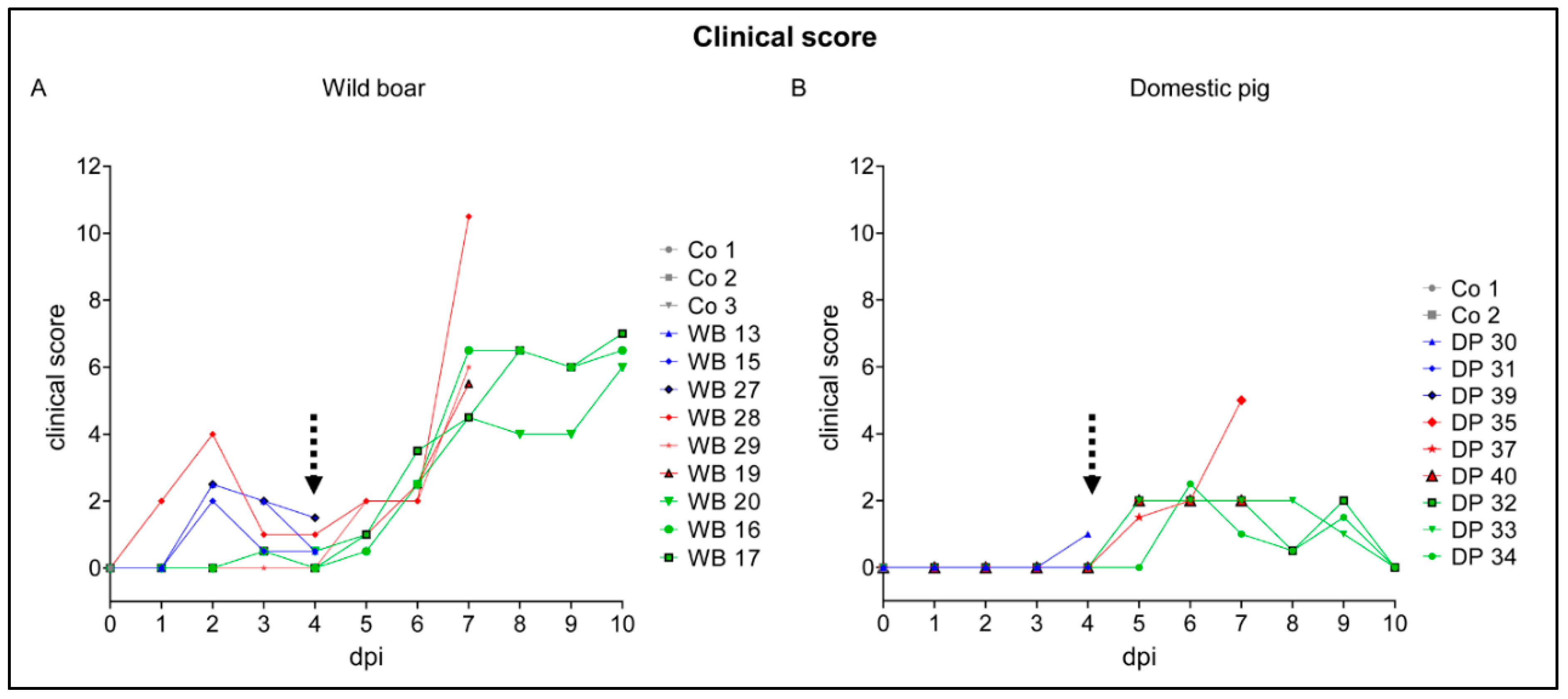
2.1. Clinical Disease
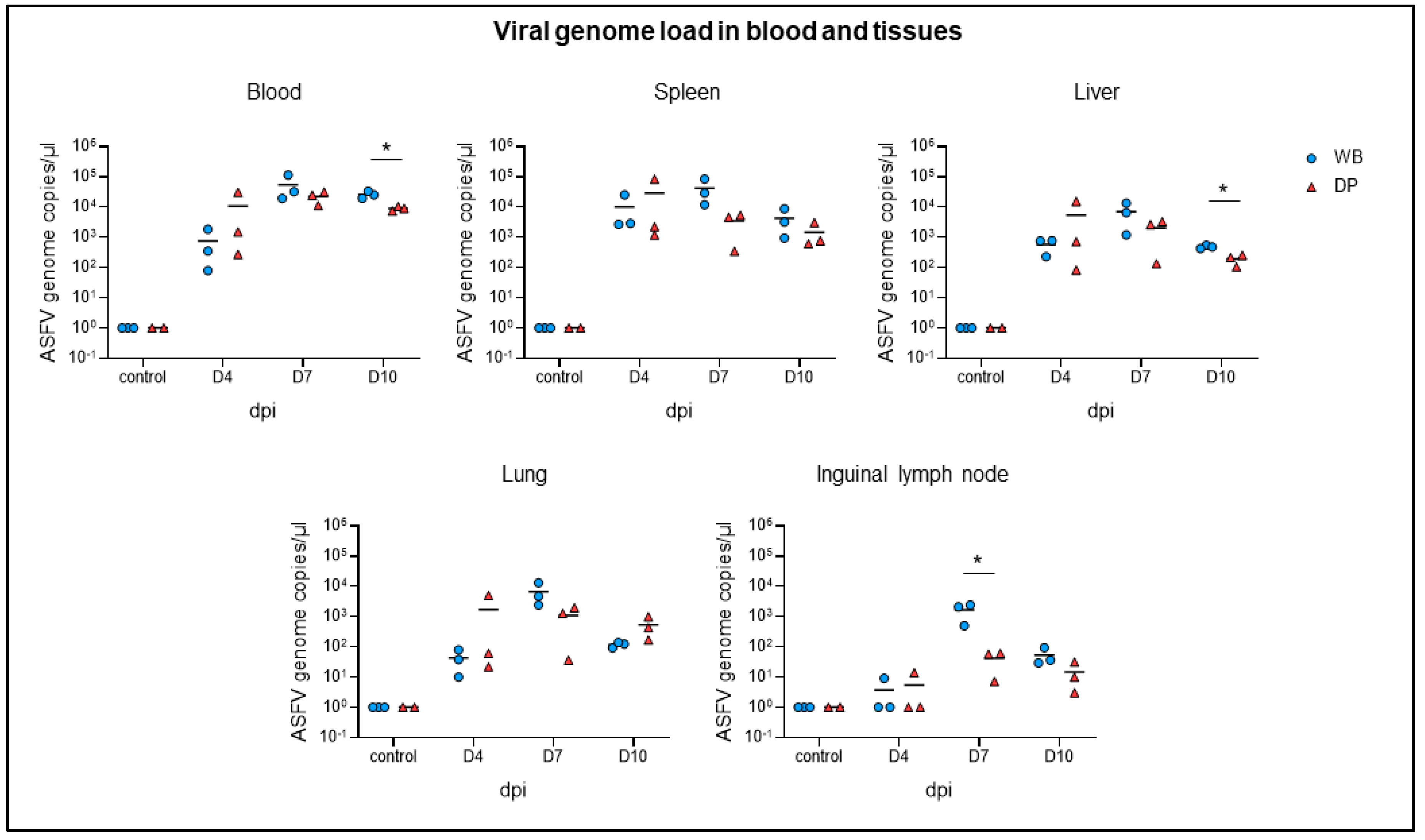
2.2. Viral Genome Load in Blood and Tissues
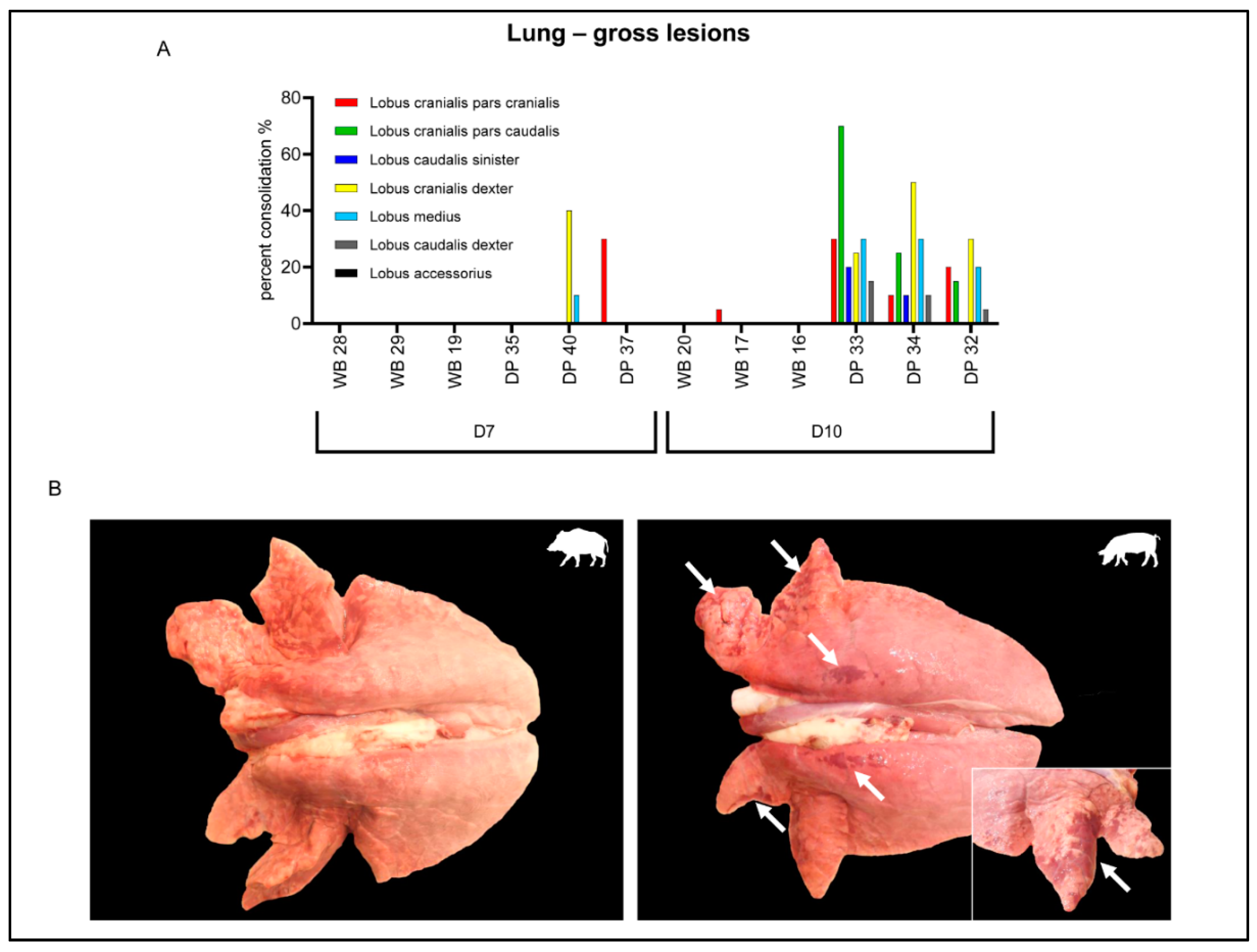
2.3. Gross Pathology
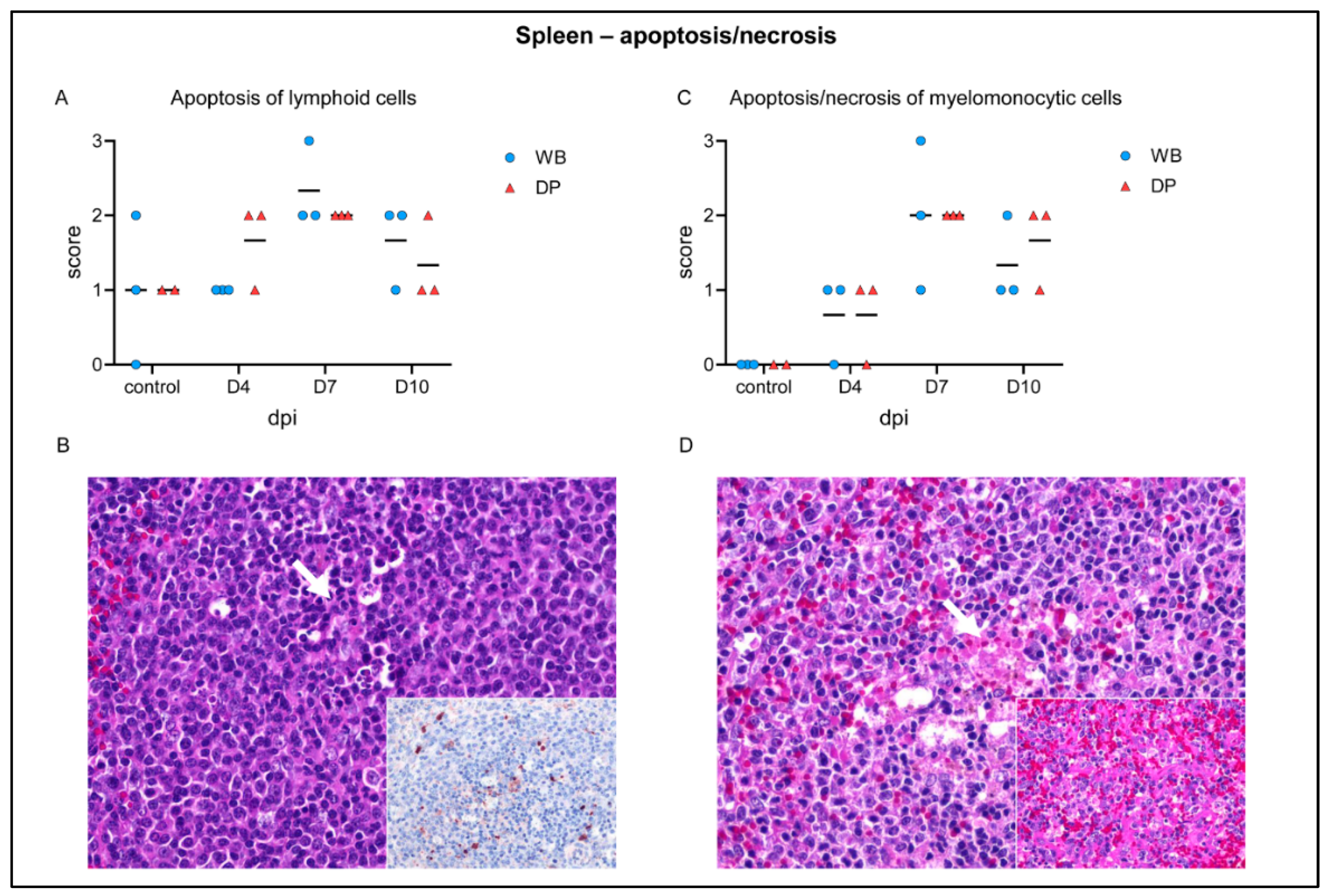
2.4. Histopathological, Immunological, and Electron Microscopical Analysis
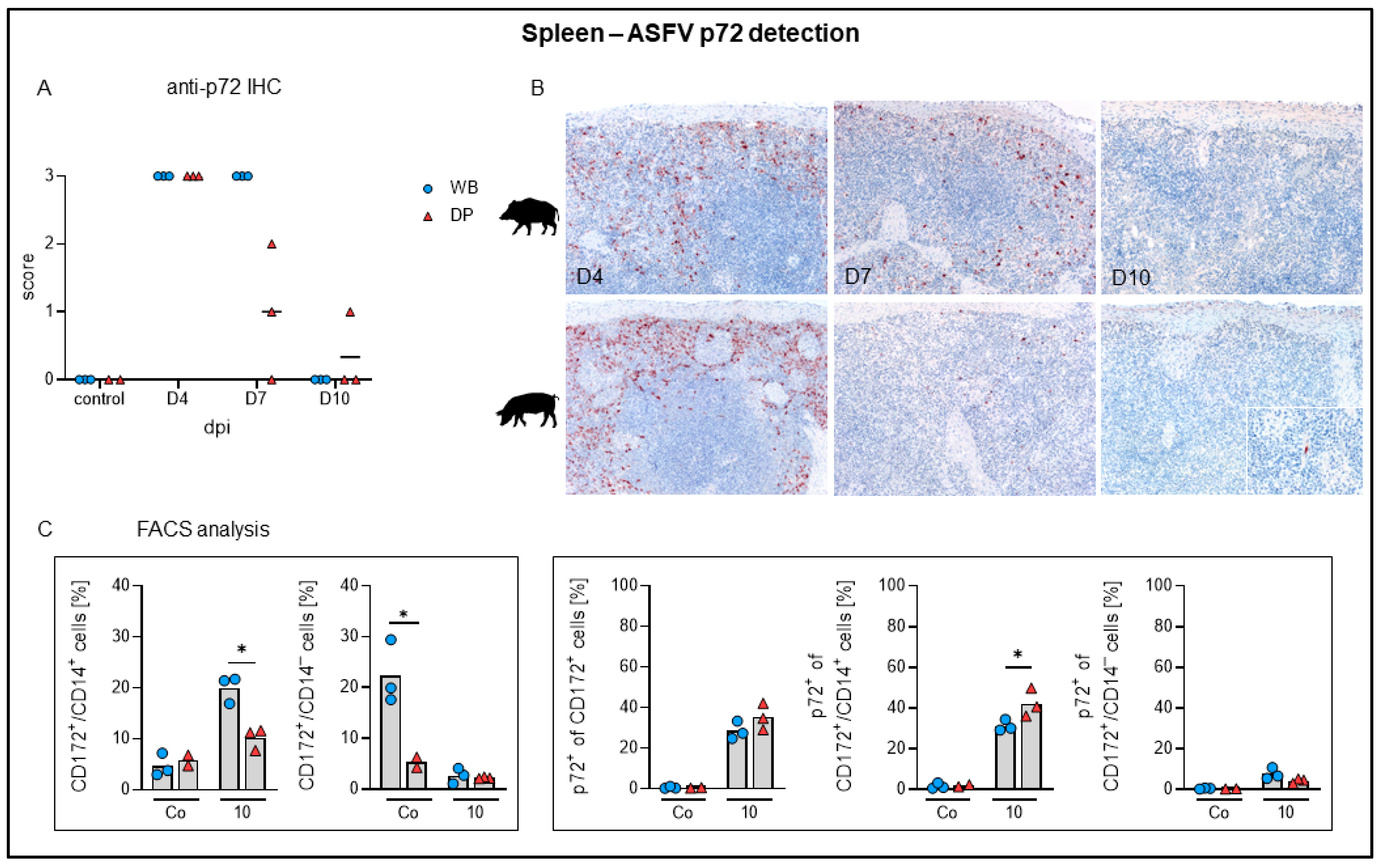
2.4.1. Spleen
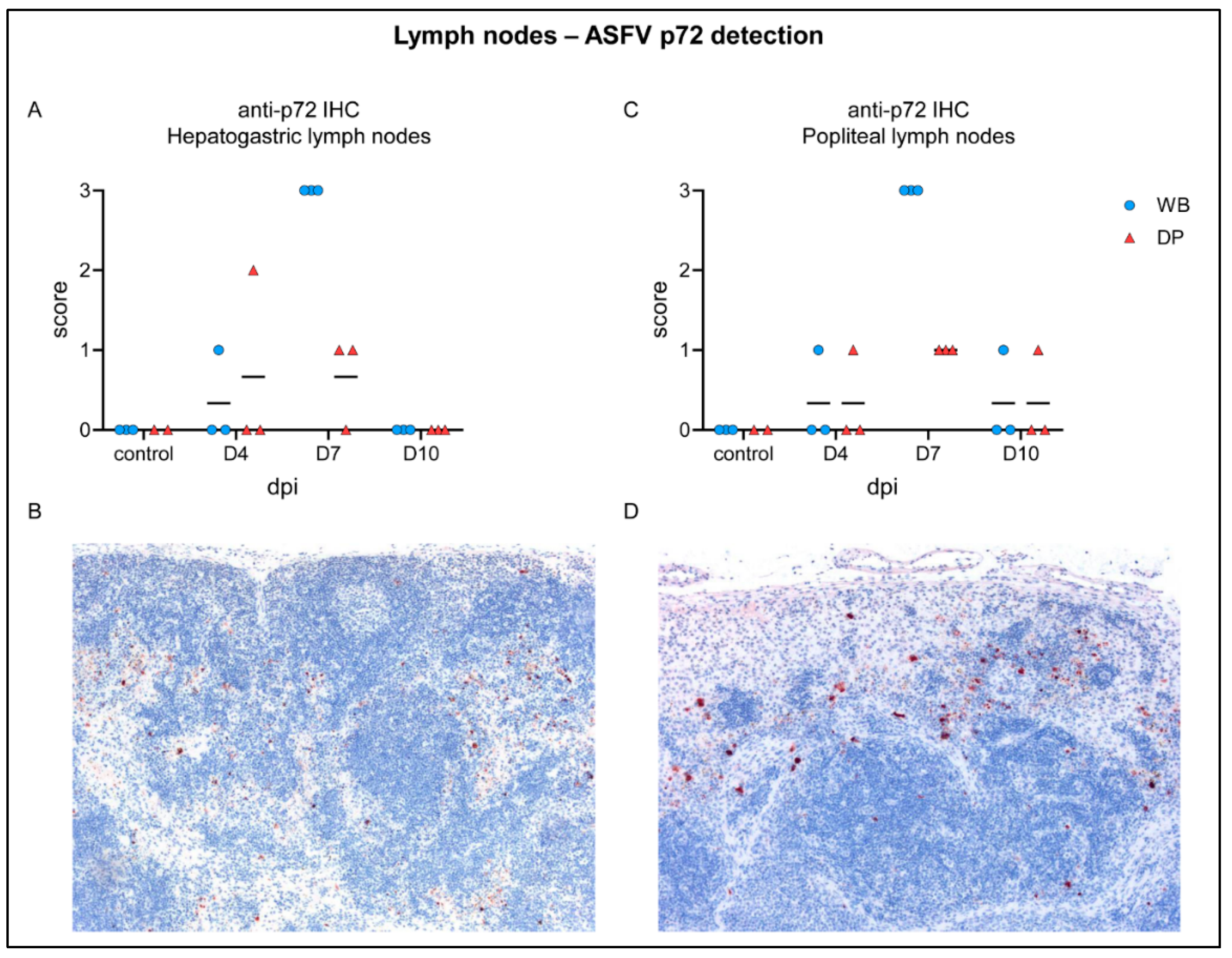
2.4.2. Lymph Nodes
2.4.3. Palatine Tonsil
2.4.4. Bone Marrow
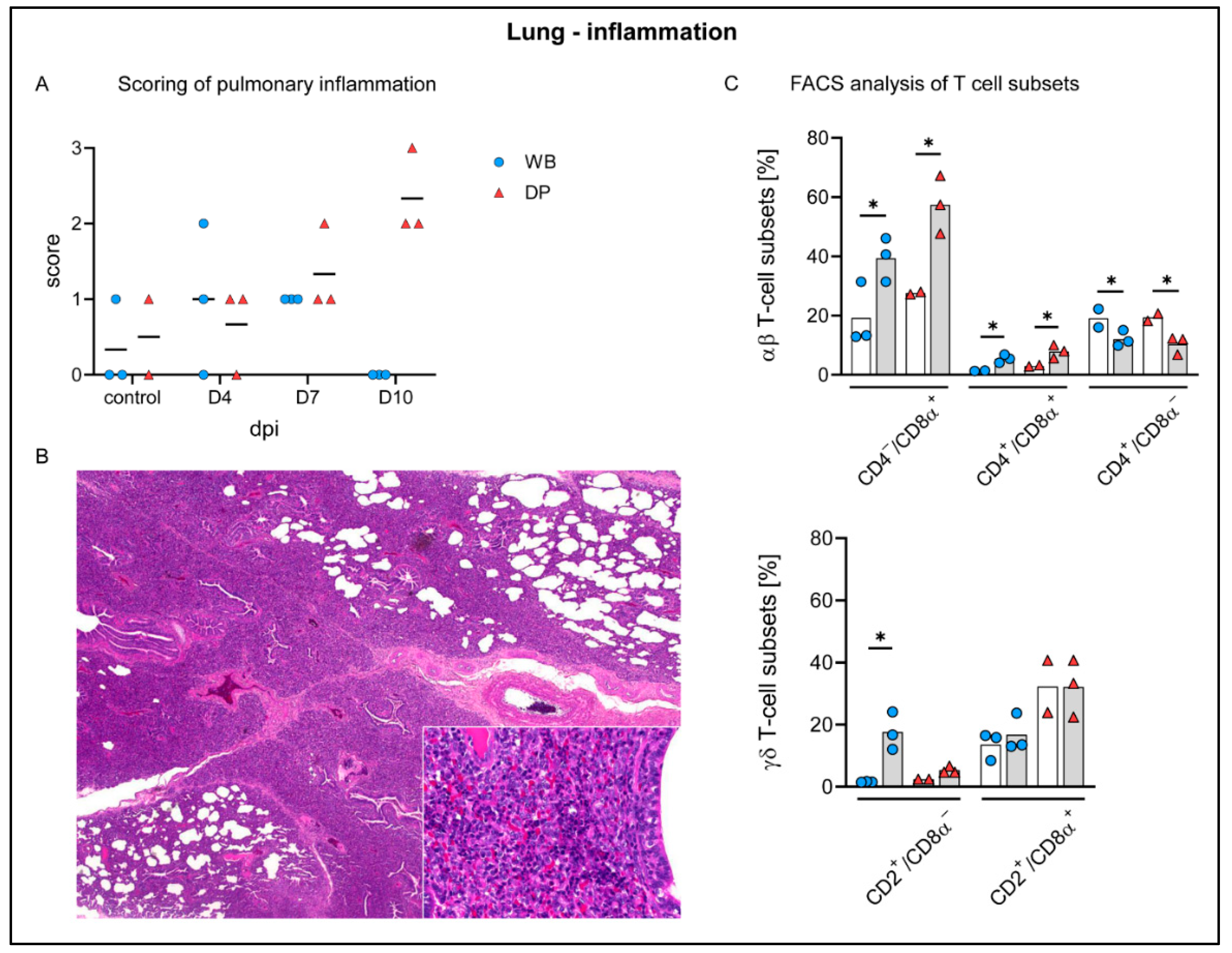
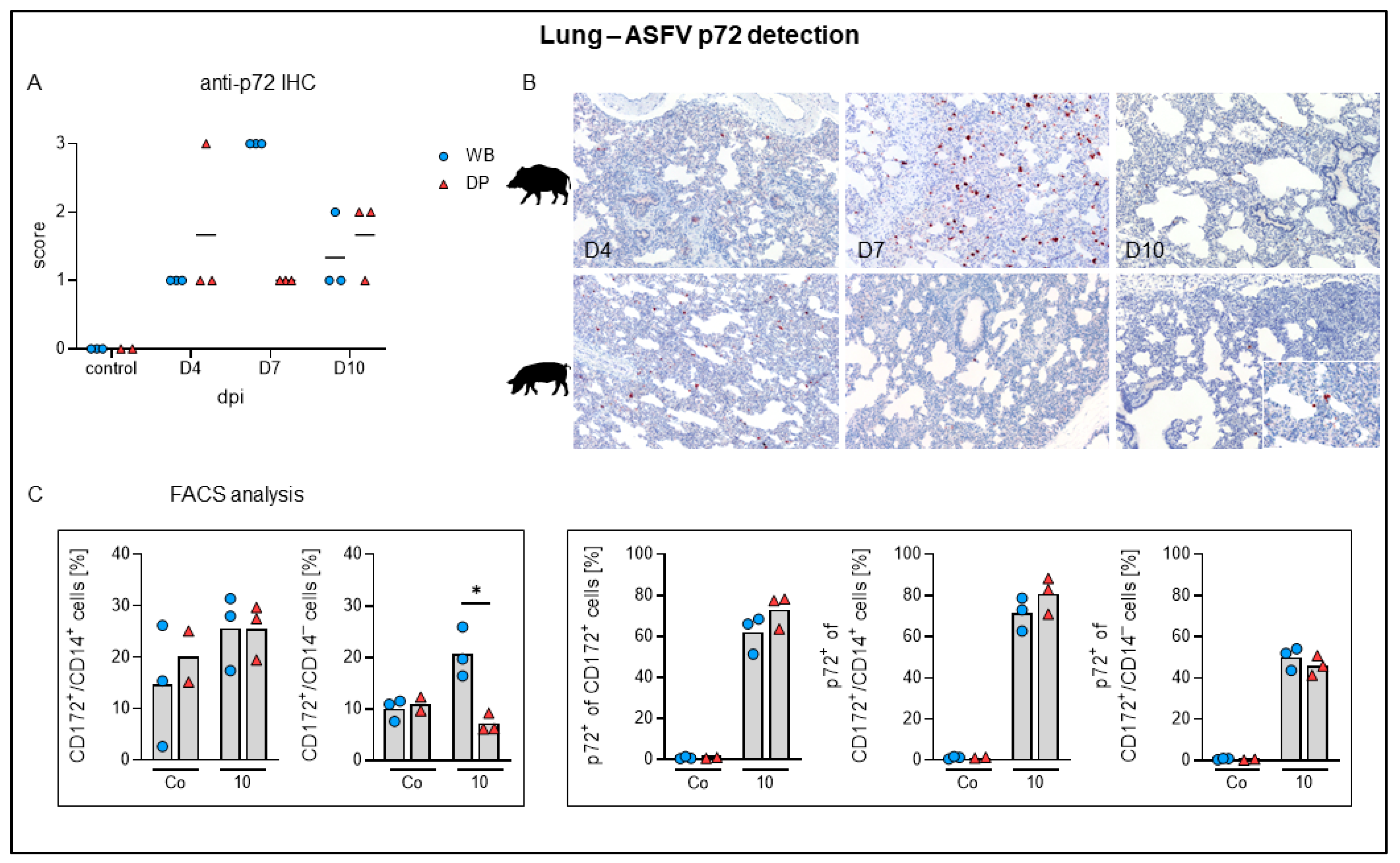
2.4.5. Lung
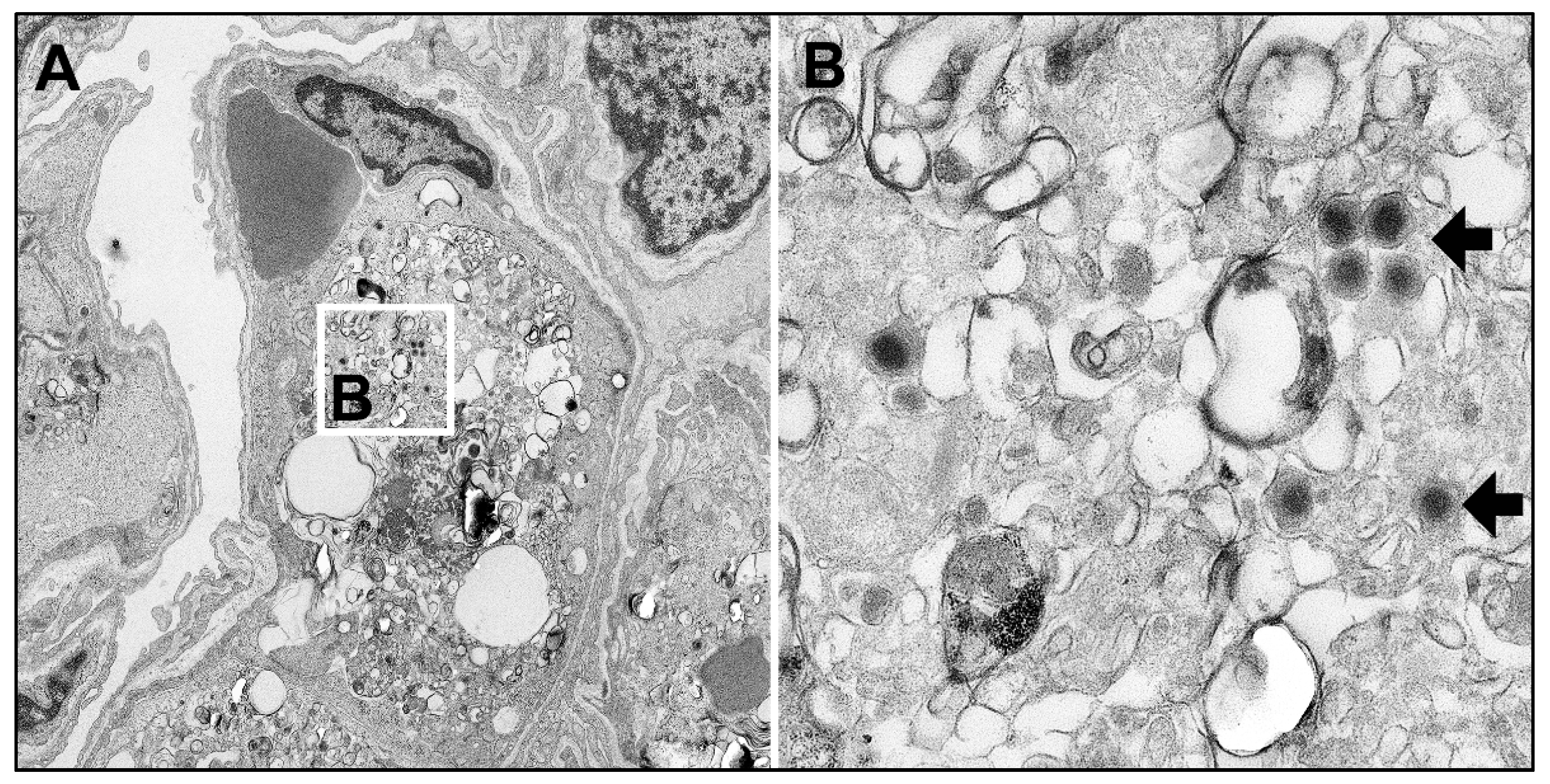
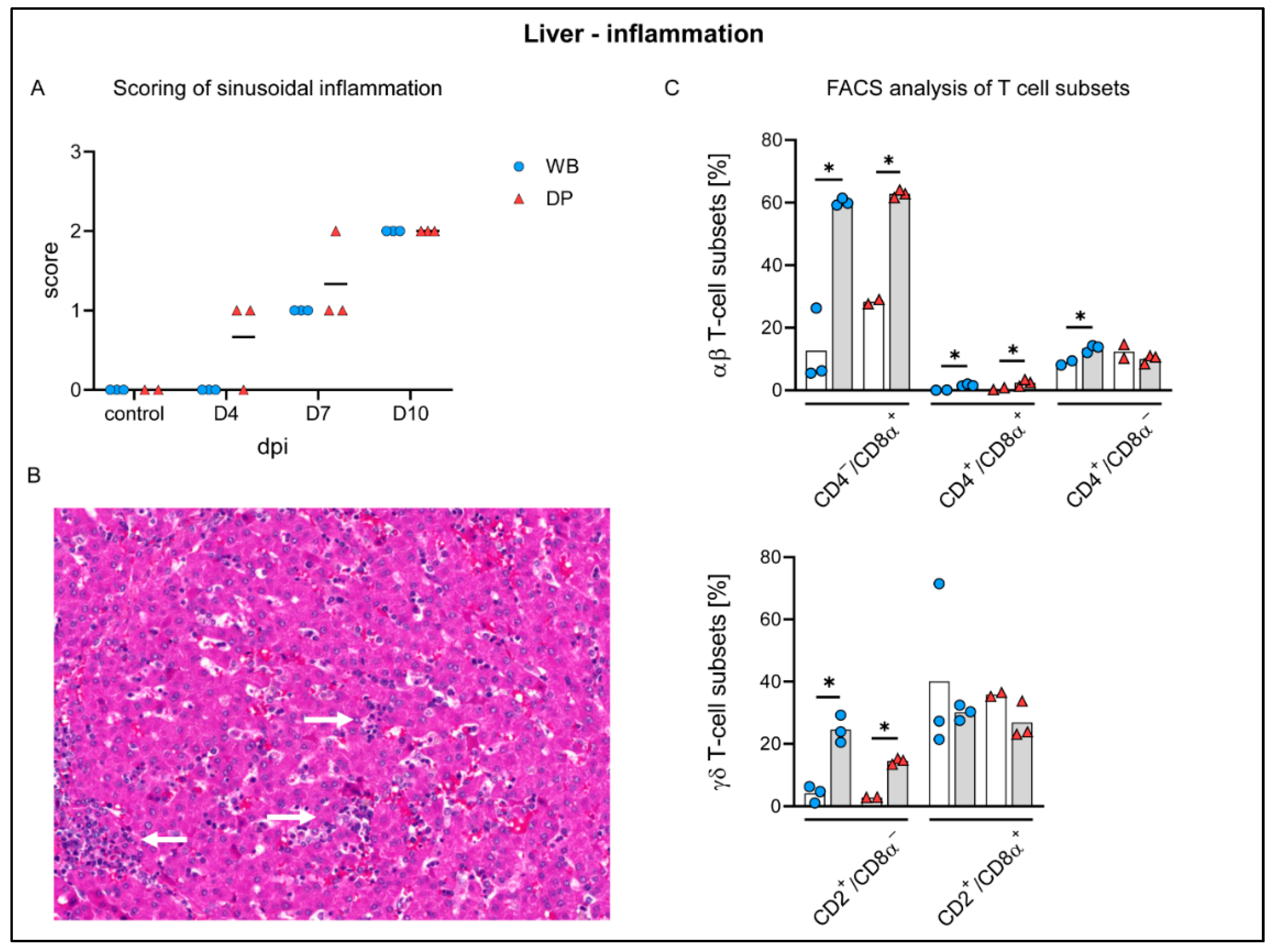
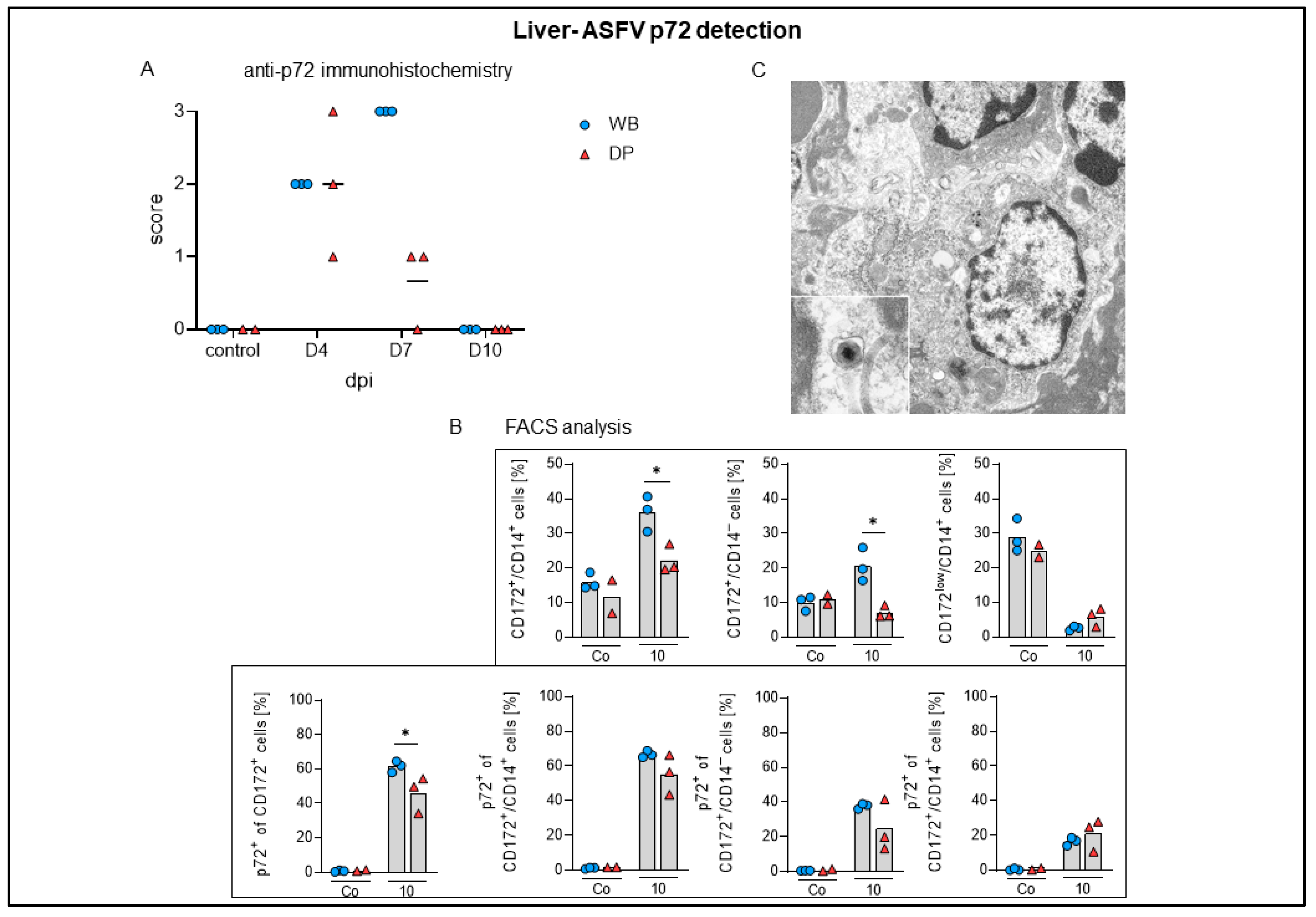
2.4.6. Liver
2.4.7. Kidney
2.4.8. Brain
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Cells
4.3. Virus
4.4. Animal Experiment
4.4.1. Clinical Scoring
4.4.2. Tissue Sample Collection
4.4.3. Pathomorphological and Electron Microscopical Analysis
Gross Pathology and Macroscopic Scoring
Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
Semi-Quantitative Scoring
4.4.4. Electron Microscopy
4.4.5. Flow Cytometry
4.4.6. Processing of Blood Samples
ASFV Antigen and Genome Detection
4.4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mason-D’Croz, D.; Bogard, J.R.; Herrero, M.; Robinson, S.; Sulser, T.B.; Wiebe, K.; Willenbockel, D.; Godfray, H.C.J. Modelling the global economic consequences of a major African swine fever outbreak in China. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrage, T.G. African swine fever virus infection in Ornithodoros ticks. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogin, A.; Gerasimov, V.; Malogolovkin, A.; Kolbasov, D. African swine fever in the North Caucasus region and the Russian Federation in years 2007–2012. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ren, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ge, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, F.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Bao, J.; et al. Infection of African swine fever in wild boar, China, 2018. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 1395–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, R.; Zhang, X.; Li, F.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; et al. Replication and virulence in pigs of the first African swine fever virus isolated in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, D.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Yoo, H.S. African swine fever: Etiology, epidemiological status in Korea, and perspective on control. J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 21, e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frant, M.; Wozniakowski, G.; Pejsak, Z. African Swine Fever (ASF) and Ticks. No Risk of Tick-mediated ASF Spread in Poland and Baltic States. J. Vet. Res. 2017, 61, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, C.; Fernandez-Pinero, J.; Pelayo, V.; Gazaev, I.; Markowska-Daniel, I.; Pridotkas, G.; Nieto, R.; Fernandez-Pacheco, P.; Bokhan, S.; Nevolko, O.; et al. Genetic variation among African swine fever genotype II viruses, eastern and central Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 1544–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, D.A.; Darby, A.C.; Da Silva, M.; Upton, C.; Radford, A.D.; Dixon, L.K. Genomic analysis of highly virulent Georgia 2007/1 isolate of African swine fever virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 599–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinat, C.; Reis, A.L.; Netherton, C.L.; Goatley, L.; Pfeiffer, D.U.; Dixon, L. Dynamics of African swine fever virus shedding and excretion in domestic pigs infected by intramuscular inoculation and contact transmission. Vet. Res. 2014, 45, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howey, E.B.; O’Donnell, V.; de Carvalho Ferreira, H.C.; Borca, M.V.; Arzt, J. Pathogenesis of highly virulent African swine fever virus in domestic pigs exposed via intraoropharyngeal, intranasopharyngeal, and intramuscular inoculation, and by direct contact with infected pigs. Virus Res. 2013, 178, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, C.; Blome, S.; Malogolovkin, A.; Parilov, S.; Kolbasov, D.; Teifke, J.P.; Beer, M. Characterization of African swine fever virus Caucasus isolate in European wild boars. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 2342–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikalo, J.; Zani, L.; Hühr, J.; Beer, M.; Blome, S. Pathogenesis of African swine fever in domestic pigs and European wild boar-Lessons learned from recent animal trials. Virus Res. 2019, 271, 197614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, M.C.; Reoyo, A.T.; Fernandez-Pinero, J.; Iglesias, I.; Munoz, M.J.; Arias, M.L. African swine fever: A global view of the current challenge. Porcine Health Manag. 2015, 1, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmoja, I.; Motus, K.; Kristian, M.; Niine, T.; Schulz, K.; Depner, K.; Viltrop, A. Epidemiological analysis of the 2015-2017 African swine fever outbreaks in Estonia. Prev. Vet. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmoja, I.; Petrov, A.; Breidenstein, C.; Zani, L.; Forth, J.H.; Beer, M.; Kristian, M.; Viltrop, A.; Blome, S. Biological characterization of African swine fever virus genotype II strains from north-eastern Estonia in European wild boar. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 2034–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zani, L.; Forth, J.H.; Forth, L.; Nurmoja, I.; Leidenberger, S.; Henke, J.; Carlson, J.; Breidenstein, C.; Viltrop, A.; Höper, D.; et al. Deletion at the 5’-end of Estonian ASFV strains associated with an attenuated phenotype. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Cordon, P.J.; Nunez, A.; Neimanis, A.; Wikstrom-Lassa, E.; Montoya, M.; Crooke, H.; Gavier-Widen, D. African Swine Fever: Disease Dynamics in Wild Boar Experimentally Infected with ASFV Isolates Belonging to Genotype I and II. Viruses 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kärber, G. Beitrag zur kollektiven Behandlung pharmakologischer Reihenversuche. Naunyn-Schmiedeb. Arch. Exp. Pathol. Pharmakol. 1931, 162, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spearman, C. The method of ‘right and wrong cases’ (‘Constant stimuli’) without Gauss’s formulae. Br. J. Psychol. 1904–1920 1908, 2, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Cardiel, I.; Ballester, M.; Solanes, D.; Nofrarias, M.; Lopez-Soria, S.; Argilaguet, J.M.; Lacasta, A.; Accensi, F.; Rodriguez, F.; Segales, J. Standardization of pathological investigations in the framework of experimental ASFV infections. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, K.; Staubach, C.; Blome, S. African and classical swine fever: Similarities, differences and epidemiological consequences. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, L.; Gomez-Villamandos, J.C.; Bautista, M.J.; Martin de las Mulas, J.; Villeda, C.J.; Wilkinson, P.J.; Sierra, M.A. In vivo replication of African swine fever virus (Malawi ’83) in neutrophils. Vet. Res. 1996, 27, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Genovesi, E.V.; Knudsen, R.C.; Whyard, T.C.; Mebus, C.A. Moderately virulent African swine fever virus infection: Blood cell changes and infective virus distribution among blood components. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1988, 49, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Franzoni, G.; Graham, S.P.; Sanna, G.; Angioi, P.; Fiori, M.S.; Anfossi, A.; Amadori, M.; Dei Giudici, S.; Oggiano, A. Interaction of porcine monocyte-derived dendritic cells with African swine fever viruses of diverse virulence. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 216, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golding, J.P.; Goatley, L.; Goodbourn, S.; Dixon, L.K.; Taylor, G.; Netherton, C.L. Sensitivity of African swine fever virus to type I interferon is linked to genes within multigene families 360 and 505. Virology 2016, 493, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, D.A.; Schlafer, D.H.; Mebus, C.A. African swine fever virus infection of skin-derived dendritic cells in vitro causes interference with subsequent foot-and-mouth disease virus infection. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1995, 7, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, D.A.; Mebus, C.A.; Schlafer, D.H. Early infection of interdigitating dendritic cells in the pig lymph node with African swine fever viruses of high and low virulence: Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 1995, 7, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzoni, G.; Graham, S.P.; Dei Giudici, S.; Oggiano, A. Porcine Dendritic Cells and Viruses: An Update. Viruses 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escribano, J.M.; Galindo, I.; Alonso, C. Antibody-mediated neutralization of African swine fever virus: Myths and facts. Virus Res. 2013, 173, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Netherton, C.L.; Connell, S.; Benfield, C.T.O.; Dixon, L.K. The Genetics of Life and Death: Virus-Host Interactions Underpinning Resistance to African Swine Fever, a Viral Hemorrhagic Disease. Front. Genet. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, T.D.; Park, C.; Choi, K.; Jeong, J.; Vo, M.K.; Nguyen, T.T.; Chae, C. Comparison of pathogenicity of highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus between wild and domestic pigs. Vet. Res. Commun. 2015, 39, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzini, R.; Fanelli, R.; Tancredi, F.; Siclari, A.; Garofalo, L. Matching STR and SNP genotyping to discriminate between wild boar, domestic pigs and their recent hybrids for forensic purposes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Gomes, R.; Costa, V.; Santos, P.; Charneca, R.; Zhang, Y.P.; Liu, X.H.; Wang, S.; Bento, P.; Nunes, J.L.; et al. How immunogenetically different are domestic pigs from wild boars: A perspective from single-nucleotide polymorphisms of 19 immunity-related candidate genes. Immunogenetics 2013, 65, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, M.T.; Choi, H.; Lee, H.; Le, V.C.Q.; Ahn, B.; Ho, C.-S.; Hong, K.; Song, H.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, C. SLA-1 Genetic Diversity in Pigs: Extensive Analysis of Copy Number Variation, Heterozygosity, Expression, and Breed Specificity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salguero, F.J. Comparative Pathology and Pathogenesis of African Swine Fever Infection in Swine. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakaryan, H.; Cholakyans, V.; Simonyan, L.; Misakyan, A.; Karalova, E.; Chavushyan, A.; Karalyan, Z. A study of lymphoid organs and serum proinflammatory cytokines in pigs infected with African swine fever virus genotype II. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1407–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oura, C.A.; Powell, P.P.; Parkhouse, R.M. African swine fever: A disease characterized by apoptosis. J. Gen. Virol. 1998, 79, 1427–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Villamandos, J.C.; Hervas, J.; Mendez, A.; Carrasco, L.; Martin de las Mulas, J.; Villeda, C.J.; Wilkinson, P.J.; Sierra, A. Experimental African swine fever: Apoptosis of lymphocytes and virus replication in other cells. J. Gen. Virol. 1995, 76, 2399–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, L.; de Lara, F.C.; Martin de las Mulas, J.; Gomez-Villamandos, J.C.; Perez, J.; Wilkinson, P.J.; Sierra, M.A. Apoptosis in lymph nodes in acute African swine fever. J. Comp. Pathol. 1996, 115, 415–428. [Google Scholar]
- Salguero, F.J.; Sanchez-Cordon, P.J.; Nunez, A.; Fernandez de Marco, M.; Gomez-Villamandos, J.C. Proinflammatory cytokines induce lymphocyte apoptosis in acute African swine fever infection. J. Comp. Pathol. 2005, 132, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikalo, J.; Schoder, M.E.; Sehl, J.; Breithaupt, A.; Tignon, M.; Cay, A.B.; Gager, A.M.; Fischer, M.; Beer, M.; Blome, S. The African swine fever virus isolate Belgium 2018/1 shows high virulence in European wild boar. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 1654–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samkange, A.; Mushonga, B.; Mudimba, D.; Chiwome, B.A.; Jago, M.; Kandiwa, E.; Bishi, A.S.; Molini, U. African Swine Fever Outbreak at a Farm in Central Namibia. Case Rep. Vet. Med. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moulton, J.E.; Pan, I.C.; Hess, W.R.; DeBoer, C.J.; Tessler, J. Pathologic features of chronic pneumonia in pigs with experimentally induced African swine fever. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1975, 36, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, V.R.; Bevins, S.N. A Review of African Swine Fever and the Potential for Introduction into the United States and the Possibility of Subsequent Establishment in Feral Swine and Native Ticks. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oura, C.A.L.; Denyer, M.S.; Takamatsu, H.; Parkhouse, R.M.E. In vivo depletion of CD8+ T lymphocytes abrogates protective immunity to African swine fever virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2445–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hühr, J.; Schäfer, A.; Schwaiger, T.; Zani, L.; Sehl, J.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Blome, S.; Blohm, U. Impaired T-cell responses in domestic pigs and wild boar upon infection with a highly virulent African swine fever virus strain. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, L.; Fernandez, A.; Gomez Villamandos, J.C.; Mozos, E.; Mendez, A.; Jover, A. Kupffer cells and PIMs in acute experimental African swine fever. Histol. Histopathol. 1992, 7, 421–425. [Google Scholar]
- Oura, C.A.; Powell, P.P.; Parkhouse, R.M. Detection of African swine fever virus in infected pig tissues by immunocytochemistry and in sity hybridisation. J. Virol. Methods 1998, 72, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, L.; de Lara, F.C.; Gomez-Villamandos, J.C.; Bautista, M.J.; Villeda, C.J.; Wilkinson, P.J.; Sierra, M.A. The pathogenic role of pulmonary intravascular macrophages in acute African swine fever. Res. Vet. Sci. 1996, 61, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietschmann, J.; Guinat, C.; Beer, M.; Pronin, V.; Tauscher, K.; Petrov, A.; Keil, G.; Blome, S. Course and transmission characteristics of oral low-dose infection of domestic pigs and European wild boar with a Caucasian African swine fever virus isolate. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 1657–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyerholz, D.K.; Beck, A.P. Fundamental Concepts for Semiquantitative Tissue Scoring in Translational Research. ILAR Journal 2019, 59, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eguchi-Ogawa, T.; Matsubara, T.; Toki, D.; Okumura, N.; Ando, A.; Kitagawa, H.; Uenishi, H. Distribution of the CD4 Alleles in Sus scrofa Demonstrates the Genetic Profiles of Western Breeds and Miniature Pigs. Anim. Biotechnol. 2018, 29, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, D.P.; Reid, S.M.; Hutchings, G.H.; Grierson, S.S.; Wilkinson, P.J.; Dixon, L.K.; Bastos, A.D.; Drew, T.W. Development of a TaqMan PCR assay with internal amplification control for the detection of African swine fever virus. J. Virol. Methods 2003, 107, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tignon, M.; Gallardo, C.; Iscaro, C.; Hutet, E.; Van der Stede, Y.; Kolbasov, D.; De Mia, G.M.; Le Potier, M.F.; Bishop, R.P.; Arias, M.; et al. Development and inter-laboratory validation study of an improved new real-time PCR assay with internal control for detection and laboratory diagnosis of African swine fever virus. J. Virol. Methods 2011, 178, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrascosa, A.L.; Bustos, M.J.; de Leon, P. Methods for growing and titrating African swine fever virus: Field and laboratory samples. Curr. Protoc. Cell Biol. 2011, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Organ | Lesion (Scored with Normal (0), Mild (1), Moderate (2), Severe (3) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spleen | Apoptosis of Lymphoid Cells (Syn. Lymphocytolysis) | Apoptosis/Necrosis in the Red Pulp | Hyperplasia/Hypertrophy of Myelomonocytic Cells (i.e., Dendritic Cells, Monocytes, Macrophages) | ||||
| Liver with gall bladder | Congestion/hemorrhage | Sinusoidal inflammatory infiltrates | Degeneration/necrosis and loss of Kupffer cells | Hyperplasia of bile duct epithelium | |||
| Lymph nodes | Congestion/hemorrhage | Apoptosis of lymphoid cells | Apoptosis/necrosis, perifollicular cortex and paracortex | Presence of tingible body macrophages | Hyperplasia of lymphocytes | ||
| Palatine tonsil | Congestion/hemorrhage | Apoptosis of lymphoid cells | Apoptosis/necrosis, perifollicular cells | Crypt abscessation | |||
| Lung | Congestion/hemorrhage | Edema | Inflammation | Hyperplasia/hypertrophy of alveolar and interstitial monocytes/macrophages | |||
| Kidney | Congestion/hemorrhage | Inflammatory infiltrates | |||||
| Brain | Inflammatory infiltrates | Neuronal degeneration | Gliosis | ||||
| Bone marrow | Necrosis | ||||||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sehl, J.; Pikalo, J.; Schäfer, A.; Franzke, K.; Pannhorst, K.; Elnagar, A.; Blohm, U.; Blome, S.; Breithaupt, A. Comparative Pathology of Domestic Pigs and Wild Boar Infected with the Moderately Virulent African Swine Fever Virus Strain “Estonia 2014”. Pathogens 2020, 9, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9080662
Sehl J, Pikalo J, Schäfer A, Franzke K, Pannhorst K, Elnagar A, Blohm U, Blome S, Breithaupt A. Comparative Pathology of Domestic Pigs and Wild Boar Infected with the Moderately Virulent African Swine Fever Virus Strain “Estonia 2014”. Pathogens. 2020; 9(8):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9080662
Chicago/Turabian StyleSehl, Julia, Jutta Pikalo, Alexander Schäfer, Kati Franzke, Katrin Pannhorst, Ahmed Elnagar, Ulrike Blohm, Sandra Blome, and Angele Breithaupt. 2020. "Comparative Pathology of Domestic Pigs and Wild Boar Infected with the Moderately Virulent African Swine Fever Virus Strain “Estonia 2014”" Pathogens 9, no. 8: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9080662
APA StyleSehl, J., Pikalo, J., Schäfer, A., Franzke, K., Pannhorst, K., Elnagar, A., Blohm, U., Blome, S., & Breithaupt, A. (2020). Comparative Pathology of Domestic Pigs and Wild Boar Infected with the Moderately Virulent African Swine Fever Virus Strain “Estonia 2014”. Pathogens, 9(8), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9080662






