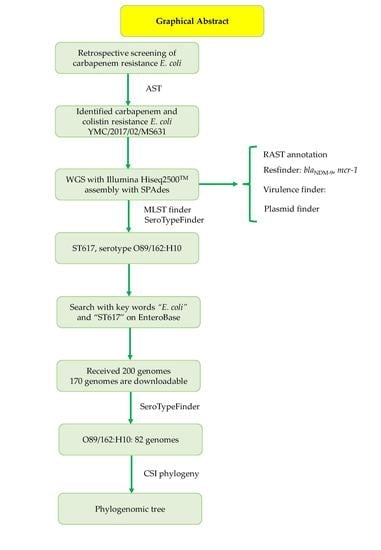
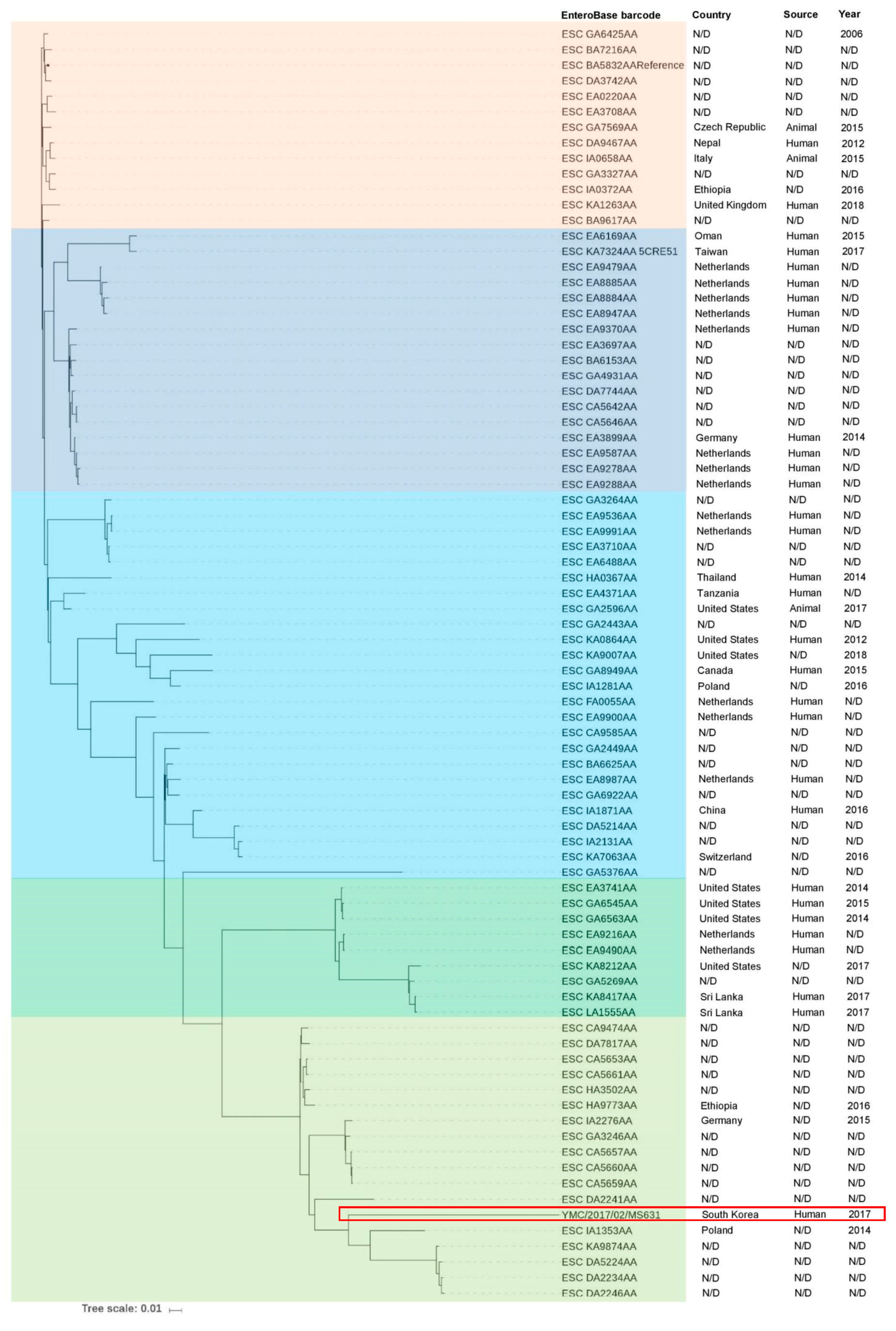
Resistome Profiles, Plasmid Typing, and Whole-Genome Phylogenetic Tree Analyses of BlaNDM-9 and Mcr-1 Co-Harboring Escherichia coli ST617 from a Patient without a History of Farm Exposure in Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Case Report
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Data Availability
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Abbreviations
References
- Yong, D.; Toleman, M.A.; Giske, C.G.; Cho, H.S.; Sundman, K.; Lee, K.; Walsh, T.R. Characterization of a new metallo-beta-lactamase gene, bla(NDM-1), and a novel erythromycin esterase gene carried on a unique genetic structure in Klebsiella pneumoniae sequence type 14 from India. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2009, 53, 5046–5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, H.; Zhao, C.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; He, W.; Zhang, F.; et al. Novel NDM-9 metallo-β-lactamase identified from a ST107 Klebsiella pneumoniae strain isolated in China. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2014, 44, 90–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Doi, Y.; Zeng, L.; Lv, L.; Liu, J.-H. Carbapenem-resistant and colistin-resistant Escherichia coli co-producing NDM-9 and MCR-1. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 288–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Song, F.; Zou, M.; Zhang, Q.; Shan, H. High Incidence of Escherichia coli Strains Coharboring mcr-1 and blaNDM from Chickens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e02347-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.-C.; Chuang, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-C.; Tang, H.-J. Coexistence of MCR-1 and NDM-9 in a clinical carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli isolate. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 517–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Kuroda, M.; Suzuki, S.; Mu, J.-J. Emergence of an Escherichia coli strain co-harbouring mcr-1 and blaNDM-9 from a urinary tract infection in Taiwan. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 16, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wayne, P. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Twenty-Eighth Informational Supplement M100-S28, 28th ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, NY, USA, 2018; ISBN 1-562388-39-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, R.K.; Bartels, D.; Best, A.A.; DeJongh, M.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Formsma, K.; Gerdes, S.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; et al. The RAST Server: Rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joensen, K.G.; Tetzschner, A.M.M.; Iguchi, A.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Scheutz, F. Rapid and Easy In Silico Serotyping of Escherichia coli Isolates by Use of Whole-Genome Sequencing Data. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2410–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsen, M.V.; Cosentino, S.; Rasmussen, S.; Friis, C.; Hasman, H.; Marvig, R.L.; Jelsbak, L.; Sicheritz-Pontén, T.; Ussery, D.W.; Aarestrup, F.M.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing of total-genome-sequenced bacteria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Møller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joensen, K.G.; Scheutz, F.; Lund, O.; Hasman, H.; Kaas, R.S.; Nielsen, E.M.; Aarestrup, F.M. Real-time whole-genome sequencing for routine typing, surveillance, and outbreak detection of verotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.; Cho, Y.J.; Yong, D.; Chun, J. Genome sequence of Escherichia coli J53, a reference strain for genetic studies. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 3742–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, T.R.; Weeks, J.; Livermore, D.M.; Toleman, M.A. Dissemination of NDM-1 positive bacteria in the New Delhi environment and its implications for human health: An environmental point prevalence study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaas, R.S.; Leekitcharoenphon, P.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Lund, O. Solving the problem of comparing whole bacterial genomes across different sequencing platforms. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacconelli, E.; Mazzaferri, F.; de Smet, A.M.; Bragantini, D.; Eggimann, P.; Huttner, B.D.; Kuijper, E.J.; Lucet, J.-C.; Mutters, N.T.; Sanguinetti, M.; et al. ESCMID-EUCIC clinical guidelines on decolonization of multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria carriers. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karkman, A.; Pärnänen, K.; Larsson, D.G.J. Fecal pollution can explain antibiotic resistance gene abundances in anthropogenically impacted environments. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameters | E. coli YMC/2017/ 02/MS631 | Transconjugants | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selected by Colistin | Selected by Imipenem | E. coli J53 | ||
| E. coli EJ533 | E. coli EJ5331 | |||
| Source | Asymptomatic carrier | - | - | - |
| Isolation site | Rectal swab | - | - | - |
| Resistance genes | blaNDM-9, blaCTX-M-55, blaTEM-1B, aph(3’)IIa, aph(3’)Ib, rmtB, aph(6)-Id, aadA2, oqxA, oqxB, fosA3, mph(A), mdf(A),floR, sul2, tet(A), dfrA12, mcr-1 | mcr-1 | blaNDM-9, aadA2, fosA3, mph(A), dfrA12 | - |
| MLST | 617 | - | - | - |
| Serotype | O89/162:H10 | - | - | - |
| Plasmid replicon type(s) | IncB, IncFII, IncI2, IncN, IncY, IncR, IncX1 | IncI2 | IncB | - |
| Virulence factors | gad, iss | |||
| ompC, ompF | Intact | |||
| MIC (μg/mL, interpretation) | ||||
| Amoxicillin-clavulanic acid | 128, R † | 4, S ‡ | 8, R ‡ | 4, S ‡ |
| Piperacillin | ≥256, R † | N/D | N/D | N/D |
| Piperacillin-tazobactam | ≥256, R † | ≤4, S ‡ | ≥128, R‡ | ≤4, S ‡ |
| Cefotaxime | ≥256, R † | ≤1, S ‡ | ≥64, R ‡ | ≤1, S ‡ |
| Ceftazidime | ≥256, R † | ≤1, S ‡ | ≥64, R ‡ | ≤1, S ‡ |
| Cefepime | ≥256, R † | ≤1, S ‡ | ≥64, R ‡ | ≤1, S ‡ |
| Cefoxitin | ≥256, R † | 8, S ‡ | 32, R § | ≤1, S ‡ |
| Aztreonam | ≥128, R † | ≤1, S ‡ | ≤1, S ‡ | ≤1, S ‡ |
| Ertapenem | 64, R † | ≤0.5, S ‡ | 4, R ‡ | ≤0.5, S ‡ |
| Meropenem | 16, R † | N/D | N/D | N/D |
| Imipenem | 32, R † | ≤0.25, S ‡ | 8, R ‡ | ≤0.25, S ‡ |
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | ≥256, R † | N/D | N/D | N/D |
| Colistin | 4, R ‡ | 4, R ‡ | ≤0.125, S ‡ | <0.125, S ‡ |
| Amikacin | ≥16, R ‡ | ≤2, S ‡ | ≤2, S ‡ | ≤2, S ‡ |
| Gentamicin | ≥16, R ‡ | ≤1, S ‡ | ≤1, S ‡ | ≤1, S ‡ |
| Ciprofloxacin | ≥4, R ‡ | ≤0.25, S ‡ | ≤0.25, S ‡ | ≤0.25, S ‡ |
| Tigecycline | 0.5, S ‡ | ≤0.5, S ‡ | ≤0.5, S ‡ | ≤0.5, S ‡ |
| Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole | 320, R ‡ | ≤20, S ‡ | ≤20, S ‡ | ≤20, S ‡ |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, L.P.; Pinto, N.A.; Vu, T.N.; Mai, H.; Pham, A.H.; Lee, H.; Cho, Y.L.; Byun, J.-H.; D’Souza, R.; Yong, D. Resistome Profiles, Plasmid Typing, and Whole-Genome Phylogenetic Tree Analyses of BlaNDM-9 and Mcr-1 Co-Harboring Escherichia coli ST617 from a Patient without a History of Farm Exposure in Korea. Pathogens 2019, 8, 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040212
Nguyen LP, Pinto NA, Vu TN, Mai H, Pham AH, Lee H, Cho YL, Byun J-H, D’Souza R, Yong D. Resistome Profiles, Plasmid Typing, and Whole-Genome Phylogenetic Tree Analyses of BlaNDM-9 and Mcr-1 Co-Harboring Escherichia coli ST617 from a Patient without a History of Farm Exposure in Korea. Pathogens. 2019; 8(4):212. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040212
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Le Phuong, Naina Adren Pinto, Thao Nguyen Vu, Hung Mai, An HT Pham, Hyunsook Lee, Young Lag Cho, Jung-Hyun Byun, Roshan D’Souza, and Dongeun Yong. 2019. "Resistome Profiles, Plasmid Typing, and Whole-Genome Phylogenetic Tree Analyses of BlaNDM-9 and Mcr-1 Co-Harboring Escherichia coli ST617 from a Patient without a History of Farm Exposure in Korea" Pathogens 8, no. 4: 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040212
APA StyleNguyen, L. P., Pinto, N. A., Vu, T. N., Mai, H., Pham, A. H., Lee, H., Cho, Y. L., Byun, J.-H., D’Souza, R., & Yong, D. (2019). Resistome Profiles, Plasmid Typing, and Whole-Genome Phylogenetic Tree Analyses of BlaNDM-9 and Mcr-1 Co-Harboring Escherichia coli ST617 from a Patient without a History of Farm Exposure in Korea. Pathogens, 8(4), 212. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens8040212